Multi-Level Driving Mechanisms: Cascading Relationships Among Physical Factors, Nutrient Cycling, and Biological Responses in the Yangtze River–Lake Ecosystems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Environmental Variables and Biological Community
2.3. Statistical Analyses
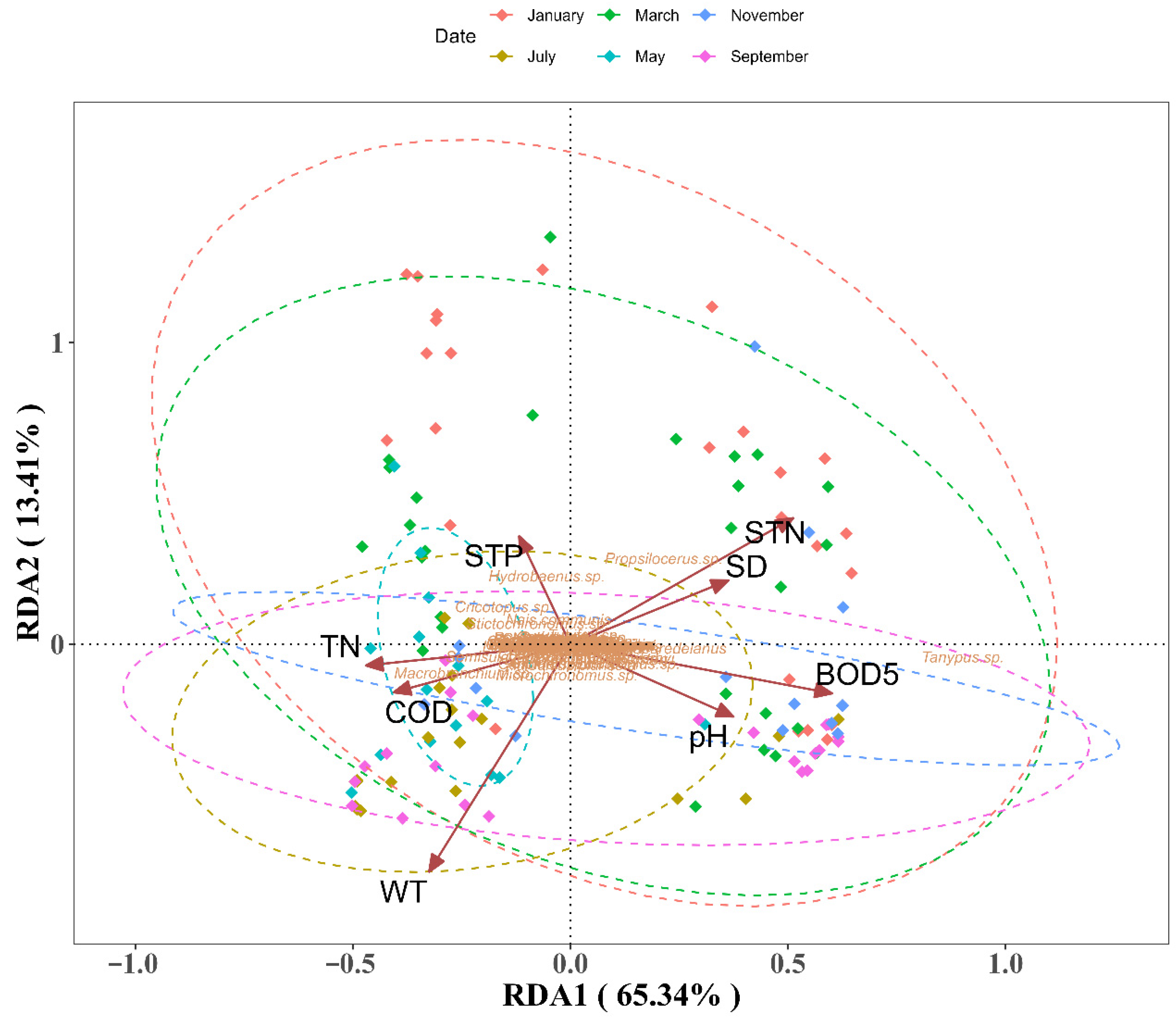
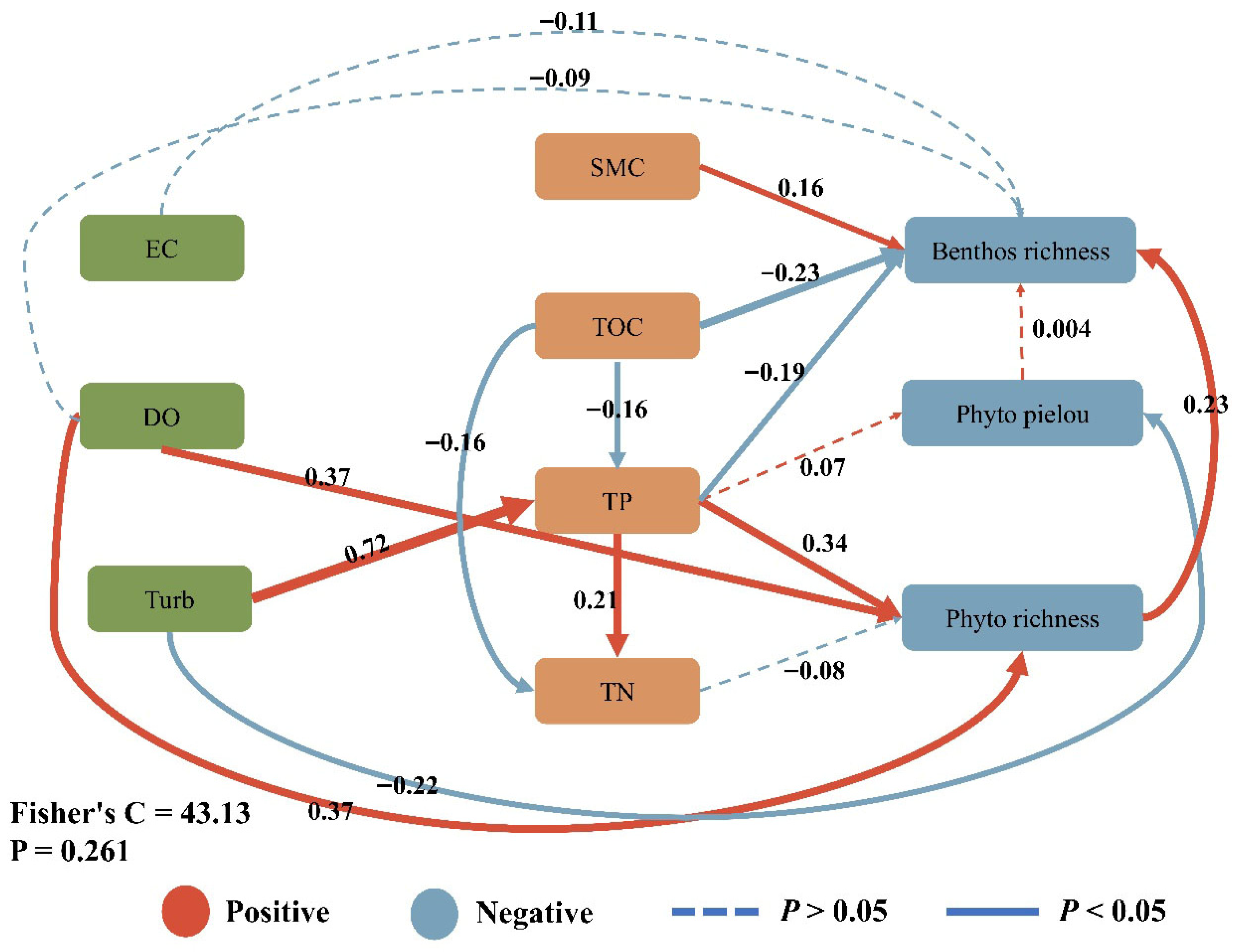
3. Results
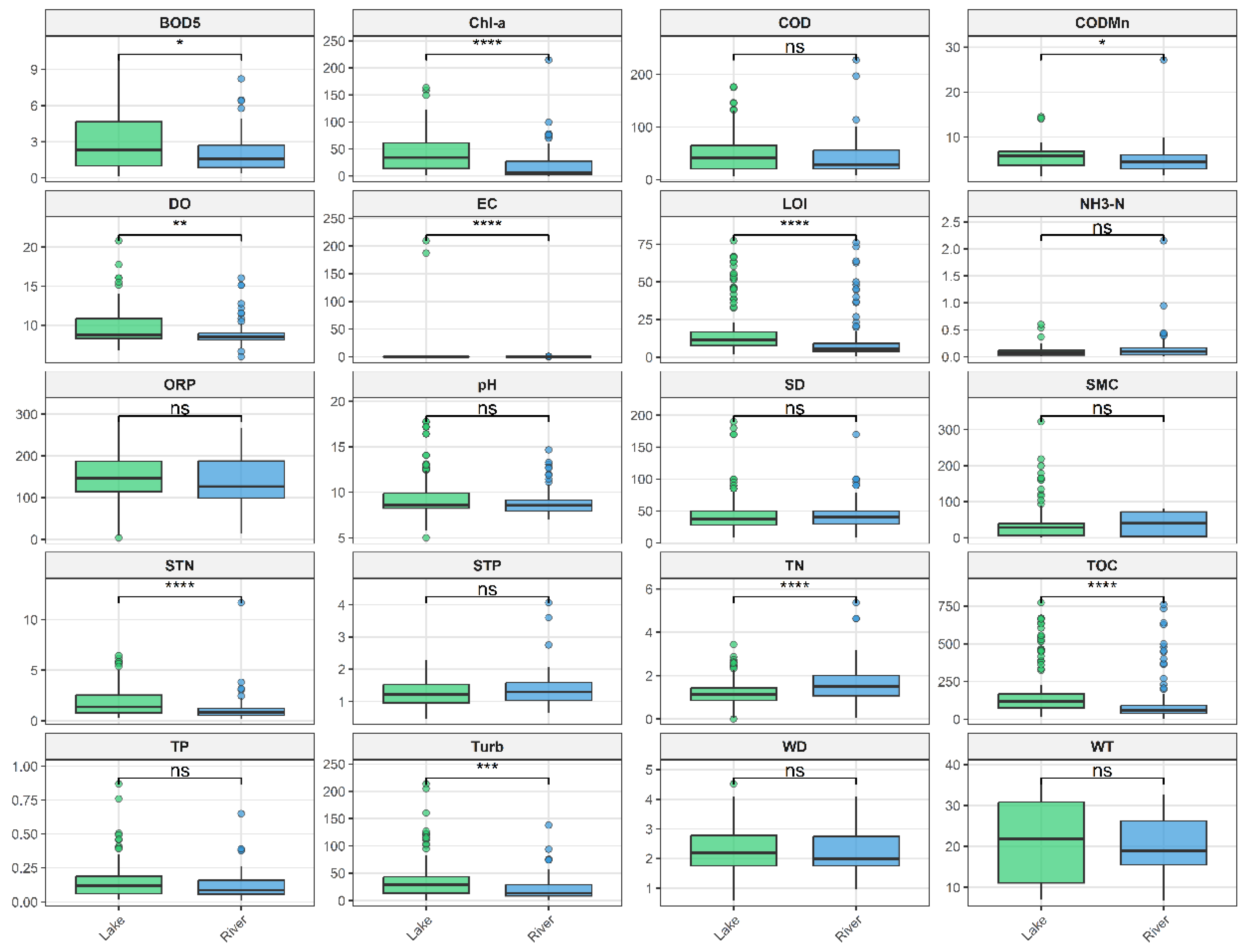
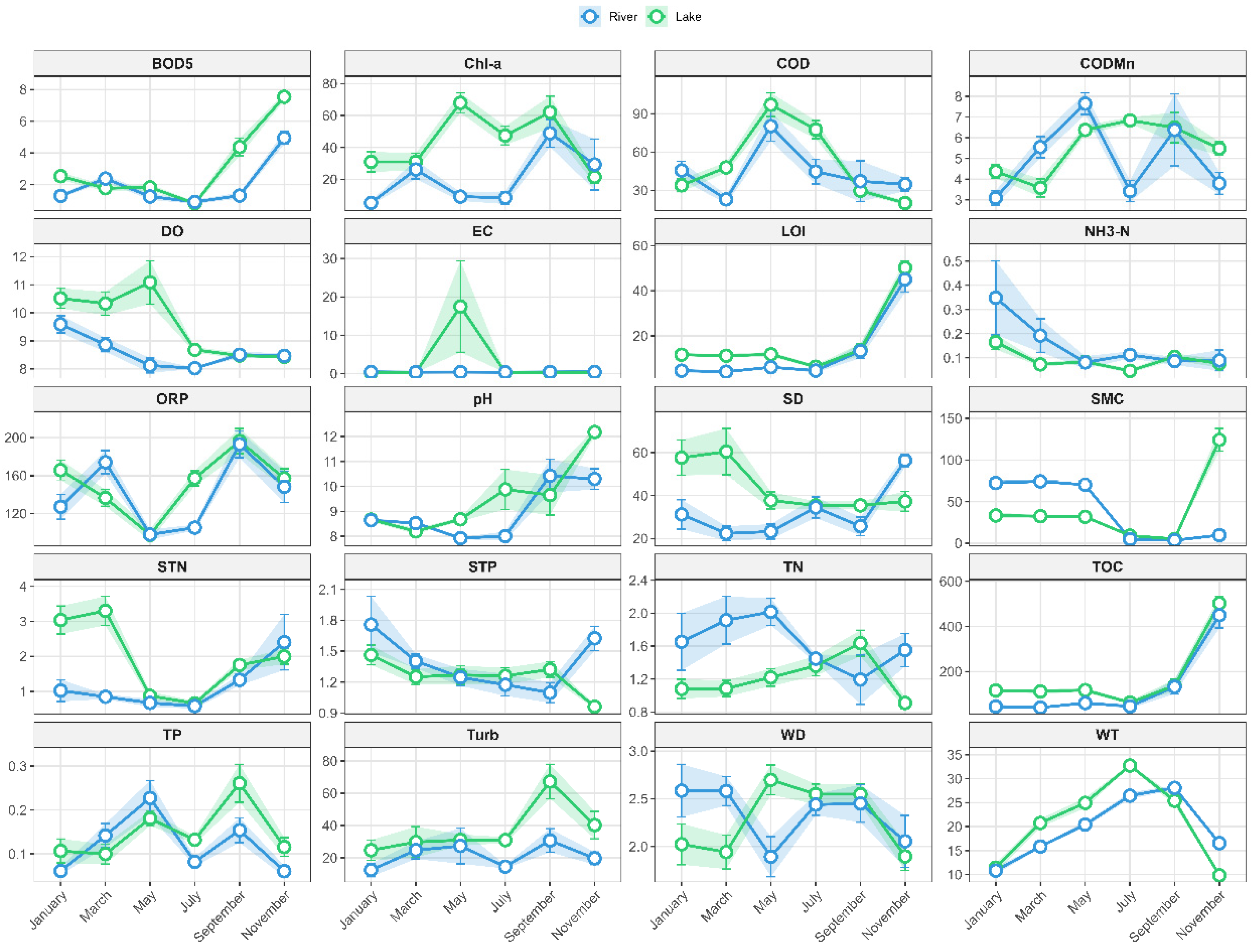
3.1. Spatiotemporal Heterogeneity Patterns
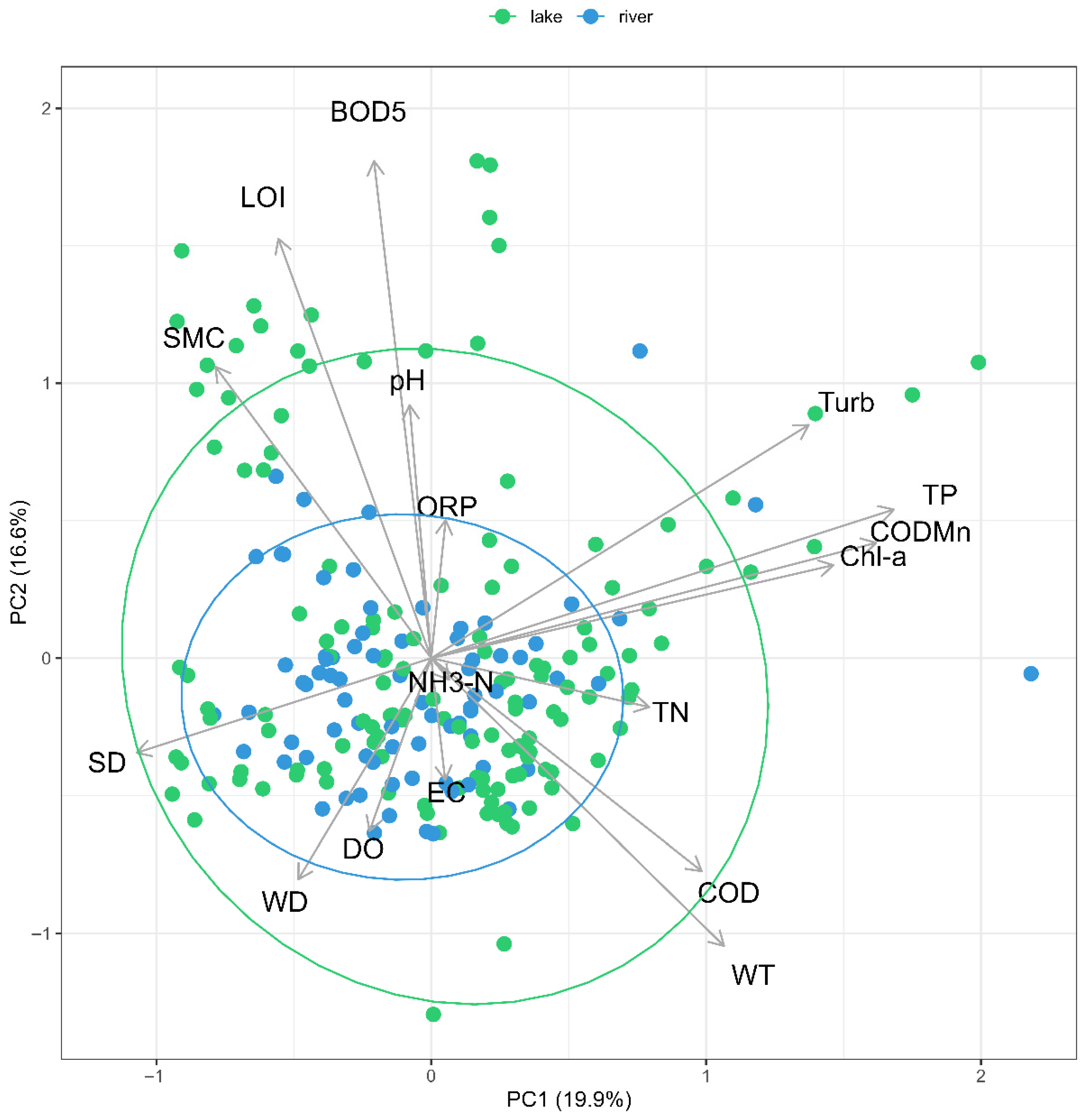
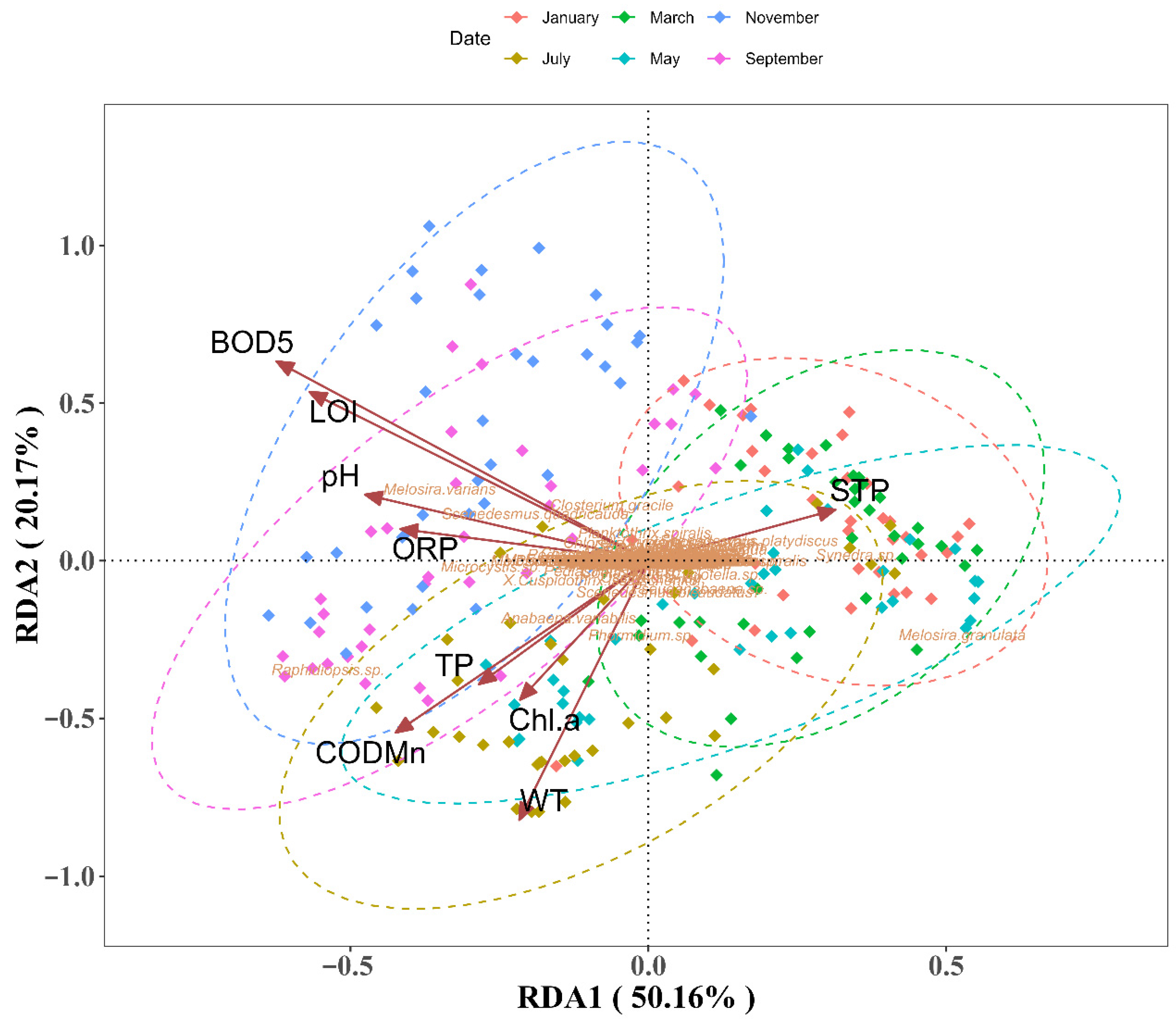
3.2. Biotic-Environment Linkages
3.3. Cascade Mechanism Quantification
4. Discussion
4.1. Heterogeneity in the River–Lake Systems
4.2. Environmental Factors Shaping Aquatic Biotic Communities
4.3. Benthic–Pelagic Cascade Mechanisms and Coupling
4.4. Implications for Sustainable Management
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qiu, J.; Yuan, S.; Tang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wolter, C.; Nikora, V. Ecological Connectivity of River-Lake Ecosystem: Evidence from Fish Population Dynamics in a Connecting Channel. Water Resour. Res. 2024, 60, e2024WR037495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Meng, D.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Yang, Z.; Yin, H.; Liang, Y.; Xiao, N. Biotic and Abiotic Properties Mediating Sediment Microbial Diversity and Function in a River–Lake Continuum. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1479670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cid, N.; Erős, T.; Heino, J.; Singer, G.; Jähnig, S.C.; Cañedo-Argüelles, M.; Bonada, N.; Sarremejane, R.; Mykrä, H.; Sandin, L.; et al. From Meta-System Theory to the Sustainable Management of Rivers in the Anthropocene. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2022, 20, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuriata-Potasznik, A.; Szymczyk, S.; Skwierawski, A. Influence of Cascading River–Lake Systems on the Dynamics of Nutrient Circulation in Catchment Areas. Water 2020, 12, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Xiong, L.; Xing, J.; Deng, Y.; Qihui, S.; Sun, J.; Qin, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, L. Implications on Freshwater Lake-River Ecosystem Protection Suggested by Organic Micropollutant (OMP) Priority List. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 461, 132580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamberti, G.A.; Chaloner, D.T.; Hershey, A.E. Linkages among Aquatic Ecosystems. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2010, 29, 245–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Wang, L.; Lin, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Niu, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L. Pelagic-Benthic Coupling of the Microbial Food Web Modifies Nutrient Cycles along a Cascade-Dammed River. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2021, 16, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, X.; Yin, H.; Jeppesen, E.; Liu, Z. Editorial: The Effects of Benthic-Pelagic Coupling on Shallow Lake Ecosystems: Implications for Lake Management. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 1084861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morata, N.; Renaud, P.E.; Brugel, S.; Hobson, K.A.; Johnson, B.J. Spatial and Seasonal Variations in the Pelagic–Benthic Coupling of the Southeastern Beaufort Sea Revealed by Sedimentary Biomarkers. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 371, 47–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welker, M.; Walz, N. Plankton Dynamics in a River-Lake System—On Continuity and Discontinuity. Hydrobiologia 1999, 408, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baustian, M.; Hansen, G.; De Kluijver, A.; Robinson, K.; Henry, E.; Knoll, L.; Rose, K.; Carey, C. Linking the Bottom to the Top in Aquatic Ecosystems: Mechanisms and Stressors of Benthic-Pelagic Coupling. In Eco-DAS X Symposium Proceedings; Association for the Sciences of Limnology and Oceanography: Waco, TX, USA, 2014; pp. 25–47. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, Y.; Ye, Q.; Liu, Q.; Yu, H.; Tao, Y.; Wang, H.; Niu, Y.; Luo, M. Effect of River–Lake Connectivity on Ecological Stoichiometry of Lake and Carbon Storage Status in Eastern Plain, China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2023, 45, 1905–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Xie, Z.; Ding, M.; Zhang, H.; Huang, G.; Cao, Y.; Yin, G. Sediment Nitrate Dissimilatory Reduction Processes in the River-Lake Ecotone of Poyang Lake, China: Mechanisms and Environmental Implications. J. Soils Sediments 2024, 24, 3515–3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.C.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H. Disentangling Effects of Multiple Stressors on Matter Flow in a Lake Food Web. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 11, 9652–9664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Fu, X.; Li, X.; Yang, Y. Temporal Changes of the Food Web Structure and Function Driven by Changes in Hydrological Regimes and Water Quality in a Large Shallow Lake. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 987600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solé, R.V.; Levin, S.A.; Dent, C.L.; Cumming, G.S.; Carpenter, S.R. Multiple States in River and Lake Ecosystems. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2002, 357, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Dong, Y.; Stoeck, T.; Wang, S.; Fan, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhuang, X. Geographic Characteristics and Environmental Variables Determine the Diversities and Assembly of the Algal Communities in Interconnected River-Lake System. Water Res. 2023, 233, 119792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, P.; Metz, S.; Unrein, F.; Mayora, G.; Sarmento, H.; Devercelli, M. Environmental Heterogeneity Determines the Ecological Processes That Govern Bacterial Metacommunity Assembly in a Floodplain River System. ISME J. 2020, 14, 2951–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Xie, G.; Shao, K.; Hu, Y.; Cai, J.; Bai, C.; Gong, Y.; Gao, G. Contrast Diversity Patterns and Processes of Microbial Community Assembly in a River-Lake Continuum across a Catchment Scale in Northwestern China. Environ. Microbiome 2020, 15, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Wang, Y.; Tan, W.; Saintilan, N.; Lei, G.; Wen, L. Land Cover Alteration Shifts Ecological Assembly Processes in Floodplain Lakes: Consequences for Fish Community Dynamics. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 782, 146724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Laender, F. Community- and Ecosystem-Level Effects of Multiple Environmental Change Drivers: Beyond Null Model Testing. Glob. Change Biol. 2018, 24, 5021–5030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahlai, C.A.; Hart, C.; Kavanaugh, M.T.; White, J.D.; Ruess, R.W.; Brinkman, T.J.; Ducklow, H.W.; Foster, D.R.; Fraser, W.R.; Genet, H.; et al. Cascading Effects: Insights from the U.S. Long Term Ecological Research Network. Ecosphere 2021, 12, e03430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thingstad, T.F. How Trophic Cascades and Photic Zone Nutrient Content Interact to Generate Basin-Scale Differences in the Microbial Food Web. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2020, 77, 1639–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefcheck, J.S. piecewiseSEM: Piecewise Structural Equation Modelling in r for Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2016, 7, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bizzi, S.; Surridge, B.W.J.; Lerner, D.N. Structural Equation Modelling: A Novel Statistical Framework for Exploring the Spatial Distribution of Benthic Macroinvertebrates in Riverine Ecosystems. River Res. Appl. 2013, 29, 743–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Liu, C.; Peng, C.; Zhou, X.; Xie, B.; Li, T.; Li, P.; Zou, Z.; Tang, J.; Liu, Z. Applications of Structural Equation Modeling in Plant Functional Trait Research. Environ. Rev. 2024, 32, 525–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Zheng, H.; Xiao, Y.; Ouyang, Z.; Li, C.; Zhang, J.; Huang, B. Mapping Ecosystem Service Bundles to Detect Distinct Types of Multifunctionality within the Diverse Landscape of the Yangtze River Basin, China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xu, W.; Ouyang, Z.; Zhu, C. Determination of Priority Nature Conservation Areas and Human Disturbances in the Yangtze River Basin, China. J. Nat. Conserv. 2014, 22, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.; Jiang, J.; Liang, Q.; Huang, Q. Large-Scale Hydrodynamic Modeling of the Middle Yangtze River Basin with Complex River–Lake Interactions. J. Hydrol. 2013, 492, 228–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Wan, R.; Li, B.; Tan, Z.; Yang, S.; Zhang, T. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Lake Wetland in the Wanjiang Plain of the Yangtze River Basin, China during the Recent Century. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 142, 109295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Fu, J.; Qin, J.; Su, B.; Hong, Y. Effects of Climate Variability and Urbanization on Spatiotemporal Patterns of Vegetation in the Middle and Lower Yangtze River Basin, China. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1459058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Chen, W.; Xiao, A.; Zhang, R. The Susceptibility of Wetland Areas in the Yangtze River Basin to Temperature and Vegetation Changes. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Li, Z.; Zeng, S.; Zou, L.; She, D.; Cheng, D. Perspectives on Eco-Water Security and Sustainable Development in the Yangtze River Basin. Geosci. Lett. 2021, 8, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, J.; Zhu, G.; Liu, J.; Hamilton, D.P.; Paerl, H.W.; Brookes, J.D.; Wu, T.; Peng, K.; et al. Polluted Lake Restoration to Promote Sustainability in the Yangtze River Basin, China. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2021, 9, nwab207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, A.; Li, X.; Cai, J.; Deng, Y. Evaluation of Water Ecological Security and Diagnosis of Obstacles in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 30981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, M.; Qin, Y.; Ji, M. Analysis of Policy Changes for Yangtze River Basin Governance from 1980 to 2022—Based on Semantic Analysis Method and Punctuated Equilibrium Theory. Front. Urban Rural Plan. 2024, 2, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Janssen, A.B.G.; Bazin, J.; Strokal, M.; Ma, L.; Kroeze, C. Accounting for Interactions between Sustainable Development Goals Is Essential for Water Pollution Control in China. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, A.; Zhu, H.; Wang, L.; Gong, W.; Zou, L. Characteristics of Long-Term Climate Change and the Ecological Responses in Central China. Earth Interact 2016, 20, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 21010-2017; Current Land Use Classification. Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Hou, J.; Li, F.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Cao, R.; Yang, W. Seasonal Dynamics of Sediment Organic Carbon Storage for the Upper Streams of the Yangtze River. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 11, 1093448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Hu, D.; Zhang, C.; Ding, Z. Temporal and Spatial Changes of Macrobenthos Community in the Regions Frequently Occurring Black Water Aggregation in Lake Taihu. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Gong, Z.; Qin, B. Benthic Macroinvertebrate Community Structure in Lake Taihu, China: Effects of Trophic Status, Wind-Induced Disturbance and Habitat Complexity. J. Great Lakes Res. 2012, 38, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becerra-Rueda, O.F.; Rodríguez-Figueroa, G.M.; Marmolejo-Rodríguez, A.J.; Aguíñiga-García, S.; Durán-Álvarez, J.C. Pharmaceutical Residues in Sediments of a Coastal Lagoon in Northwest Mexico—Occurrence and Environmental Risk Assessment. J. Xenobiot. 2024, 14, 1757–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, E.W.; Baird, R.B.; Eaton, A.D.; Clesceri, L.S. (Eds.) Standard Methods for Examination of Water and Wastewater, 22nd ed.; Amer Public Health Assn: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; ISBN 978-0-87553-013-0. [Google Scholar]
- Legendre, P.; Legendre, L. Numerical Ecology; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Deng, C.; Dong, L.; Liu, L.; Li, H.; Wu, J.; Ye, C. Microplastic Pollution in the Yangtze River Basin: Heterogeneity of Abundances and Characteristics in Different Environments. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 287, 117580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhivert, E.; Phuong, N.N.; Mourier, B.; Grosbois, C.; Gasperi, J. Microplastic Trapping in Dam Reservoirs Driven by Complex Hydrosedimentary Processes (Villerest Reservoir, Loire River, France). Water Res. 2022, 225, 119187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, M.C.S.; Marinho, M.M.; Huszar, V.L.M.; Branco, C.W.C.; Azevedo, S.M.F.O. The Effects of Water Retention Time and Watershed Features on the Limnology of Two Tropical Reservoirs in Brazil. Lakes Reserv. Sci. Policy Manag. Sustain. Use 2008, 13, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.-C. Analysis of Water Exchange between River and Lakes in the Middle and Lower Yangtze River in Low Flow Years. J. Nat. Resour. 2011, 26, 1613–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Lek, S.; Loot, G.; Lek-Ang, S.; Li, Z. Variations of Fish Composition and Diversity Related to Environmental Variables in Shallow Lakes in the Yangtze River Basin. Aquat. Living Resour. 2010, 23, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hautier, Y.; Tilman, D.; Isbell, F.; Seabloom, E.W.; Borer, E.T.; Reich, P.B. Anthropogenic Environmental Changes Affect Ecosystem Stability via Biodiversity. Science 2015, 348, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, X.; Tan, Z.; Yao, J. The Role of a Seasonal Lake Groups in the Complex Poyang Lake-Floodplain System (China): Insights into Hydrological Behaviors. J. Hydrol. 2019, 578, 124055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, D.B.; Freedman, S.M. Temporal Heterogeneity and Ecological Community Structure. Int. J. Environ. Stud. 1994, 46, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Yong, J.; Xu, G. Sampling Frequency of Ciliated Protozoan Microfauna for Seasonal Distribution Research in Marine Ecosystems. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 101, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, R.; Turner, J. Ecology of Plankton Ciliates in Marine Food Webs. Rev. Aquat. Sci. 1992, 6, 139–181. [Google Scholar]
- Baek, S.-S.; Kim, Y.O.; Choi, J.; Cho, H.Y.; Jang, M.-C. Determination of Sampling Time Interval for Investigating Ecological Trends of Tintinnids. J. Plankton Res. 2022, 44, 584–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramondenc, S.; Eveillard, D.; Metfies, K.; Iversen, M.H.; Nöthig, E.-M.; Piepenburg, D.; Hasemann, C.; Soltwedel, T. Unveiling Pelagic-Benthic Coupling Associated with the Biological Carbon Pump in the Fram Strait (Arctic Ocean). Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Q.; Tian, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, X.; Tian, Y.; Xue, J. Effect of Land Use and Environmental Variables on Phytoplankton Community Structure in High-Elevation River, Upper Yangtze River, China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1084461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhou, F.; Shi, K.; Johnes, P.J.; Dungait, J.A.J.; Ma, M.; Lu, Y. Identifying the Main Drivers of Change of Phytoplankton Community Structure and Gross Primary Productivity in a River-Lake System. J. Hydrol. 2020, 583, 124633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Xiong, F.; Lu, Y.; Xin, W.; Wang, H.; Feng, G.; Kong, C.; Fang, L.; Gao, X.; Chen, Y. Water Quality and Habitat Drive Phytoplankton Taxonomic and Functional Group Patterns in the Yangtze River. Ecol. Process. 2024, 13, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Nan, J.; Li, J. Driving Factors and Dynamics of Phytoplankton Community and Functional Groups in an Estuary Reservoir in the Yangtze River, China. Water 2019, 11, 1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, I.M.; Williamson, T.J.; González, M.J.; Vanni, M.J. Nitrate, Ammonium, and Phosphorus Drive Seasonal Nutrient Limitation of Chlorophytes, Cyanobacteria, and Diatoms in a Hyper-Eutrophic Reservoir. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2020, 65, 962–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessen, D.O.; Hafslund, O.T.; Andersen, T.; Broch, C.; Shala, N.K.; Wojewodzic, M.W. Changes in Stoichiometry, Cellular RNA, and Alkaline Phosphatase Activity of Chlamydomonas in Response to Temperature and Nutrients. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Li, Q.; Liu, W.; Zhang, S.; Xu, H.; Pei, H. Changes of Phytoplankton and Water Environment in a Highly Urbanized Subtropical Lake during the Past Ten Years. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 879, 162985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simião-Ferreira, J.; DeMarco, P., Jr.; Mazão, G.R.; Carvalho, A.R. Chironomidae Assemblage Structure in Relation to Organic Enrichment of an Aquatic Environment. Neotrop. Entomol. 2009, 38, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, M.-H.; Choi, J. Effects of Environmental Contaminants on Hemoglobin of Larvae of Aquatic Midge, Chironomus riparius (Diptera: Chironomidae): A Potential Biomarker for Ecotoxicity Monitoring. Chemosphere 2008, 71, 1928–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Roche, H.; Caquet, T. Effects of Physical (Hypoxia, Hyperoxia) and Chemical (Potassium Dichromate, Fenitrothion) Stress on Antioxidant Enzyme Activities in Chironomus riparius Mg. (Diptera, Chironomidae) Larvae: Potential Biomarkers. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2000, 19, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auladell, A.; Barberán, A.; Logares, R.; Garcés, E.; Gasol, J.M.; Ferrera, I. Seasonal Niche Differentiation among Closely Related Marine Bacteria. ISME J. 2022, 16, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, H.; Jin, X.; Li, W.; Cai, K.; Yang, G.; Chen, K.; Xu, J.; Johnson, A.C. Identifying Critical Land Use Thresholds for Biodiversity Conservation in China’s Lake Ecosystems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 59, 5431–5442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheifhacken, N.; Fiek, C.; Rothhaupt, K.-O. Complex Spatial and Temporal Patterns of Littoral Benthic Communities Interacting with Water Level Fluctuations and Wind Exposure in the Littoral Zone of a Large Lake. Fundam. Appl. Limnol. 2007, 169, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yang, G.; Ma, J.; Wei, Y.; Kang, L.; He, Y.; He, Q. The Role of Turbulence in Internal Phosphorus Release: Turbulence Intensity Matters. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenken, T.; Brandenburg, K.M.; Van de Waal, D.B. Long-Term Nutrient Load Reductions and Increasing Lake TN: TP Stoichiometry Decrease Phytoplankton Biomass and Diversity in a Large Shallow Lake. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2023, 68, 2389–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, D.W.; Hecky, R.E.; Findlay, D.L.; Stainton, M.P.; Parker, B.R.; Paterson, M.J.; Beaty, K.G.; Lyng, M.; Kasian, S.E.M. Eutrophication of Lakes Cannot Be Controlled by Reducing Nitrogen Input: Results of a 37-Year Whole-Ecosystem Experiment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 11254–11258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, S.; Hu, J.; Li, M.; Zheng, J.; Wang, H.; Hu, J. Benthic Assemblages in Relation to Planktonic Assemblages in a Eutrophic, Thermally Stratified Reservoir. Aquat. Biol. 2024, 33, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedberg, P.; Albert, S.; Nascimento, F.J.A.; Winder, M. Effects of Changing Phytoplankton Species Composition on Carbon and Nitrogen Uptake in Benthic Invertebrates. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2021, 66, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, J.R.; Kadin, M.; Nascimento, F.J.A.; Tamelander, T.; Törnroos, A.; Bonaglia, S.; Bonsdorff, E.; Brüchert, V.; Gårdmark, A.; Järnström, M.; et al. The Importance of Benthic–Pelagic Coupling for Marine Ecosystem Functioning in a Changing World. Glob. Change Biol. 2017, 23, 2179–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Tan, Y.; Yang, G. Environmental Impact Assessments of the Three Gorges Project in China: Issues and Interventions. Earth Sci. Rev. 2013, 124, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Cheng, R.; Xiao, W.; Zeng, L.; Wang, L.; Sun, P.; Chen, T. Temporal Dynamics of Soil Nutrients in the Riparian Zone: Effects of Water Fluctuations after Construction of the Three Gorges Dam. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 139, 108865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xue, C.; Yao, J.; You, H. The Impact of Three Gorges Dam on the Hydrological Connectivity of “off-Stream” Floodplains. J. Hydrol. 2024, 629, 130619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Yang, G.; Tan, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, S.; Bryan, B. Unravelling the Effects of Large-Scale Ecological Programs on Ecological Rehabilitation of China’s Three Gorges Dam. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 256, 120446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Strokal, M.; Van Vliet, M.T.H.; Stuiver, J.; Wang, M.; Bai, Z.; Ma, L.; Kroeze, C. Multi-Scale Modeling of Nutrient Pollution in the Rivers of China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 9614–9625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Chang, Y.; Dong, X.; Wang, S.; Che, F.; Huang, W. The Coupled Effect of Sediment Resuspension and Microbiota on Phosphorus Release and Transformation in a Simulated Aquatic Ecosystem. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 57, 104653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.; He, J.; Lü, C.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, F.; Otgonbayar, K. Effects of Environmental Factors on Nutrients Release at Sediment-Water Interface and Assessment of Trophic Status for a Typical Shallow Lake, Northwest China. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 716342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audet, J.; Hoffmann, C.C.; Andersen, P.M.; Baattrup-Pedersen, A.; Johansen, J.R.; Larsen, S.E.; Kjaergaard, C.; Elsgaard, L. Nitrous Oxide Fluxes in Undisturbed Riparian Wetlands Located in Agricultural Catchments: Emission, Uptake and Controlling Factors. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 68, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miao, T.; Shen, L.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, H.; Ji, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, N.; Zhou, C. Multi-Level Driving Mechanisms: Cascading Relationships Among Physical Factors, Nutrient Cycling, and Biological Responses in the Yangtze River–Lake Ecosystems. Sustainability 2025, 17, 9928. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17229928
Miao T, Shen L, Zhao H, Zhang H, Ji Y, Hu Y, Zhou N, Zhou C. Multi-Level Driving Mechanisms: Cascading Relationships Among Physical Factors, Nutrient Cycling, and Biological Responses in the Yangtze River–Lake Ecosystems. Sustainability. 2025; 17(22):9928. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17229928
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiao, Teng, Laiyin Shen, Hanmei Zhao, Hang Zhang, Yachan Ji, Yanxin Hu, Nianlai Zhou, and Chi Zhou. 2025. "Multi-Level Driving Mechanisms: Cascading Relationships Among Physical Factors, Nutrient Cycling, and Biological Responses in the Yangtze River–Lake Ecosystems" Sustainability 17, no. 22: 9928. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17229928
APA StyleMiao, T., Shen, L., Zhao, H., Zhang, H., Ji, Y., Hu, Y., Zhou, N., & Zhou, C. (2025). Multi-Level Driving Mechanisms: Cascading Relationships Among Physical Factors, Nutrient Cycling, and Biological Responses in the Yangtze River–Lake Ecosystems. Sustainability, 17(22), 9928. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17229928









