The Relationship Between Plant Community Functional Traits and Soil Physical and Chemical Properties Under Different Levels of Human Disturbance: A Case Study of the East Coast of Pingtan Island, Fujian Province
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
2.2. Classification
2.3. Plot Setup
2.4. Sample Collection
2.4.1. Soil Sample Collection
2.4.2. Sampling of Plant Specimens
2.5. Indicator Measurement
2.5.1. Soil Indicator Measurement
2.5.2. Plant Trait Measurement
2.6. Data Calculation and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Differential Soil Physicochemical Properties Among Plant Communities Under Different Disturbance Types
3.2. Differences in Functional Traits of Plant Communities Under Different Disturbance Types
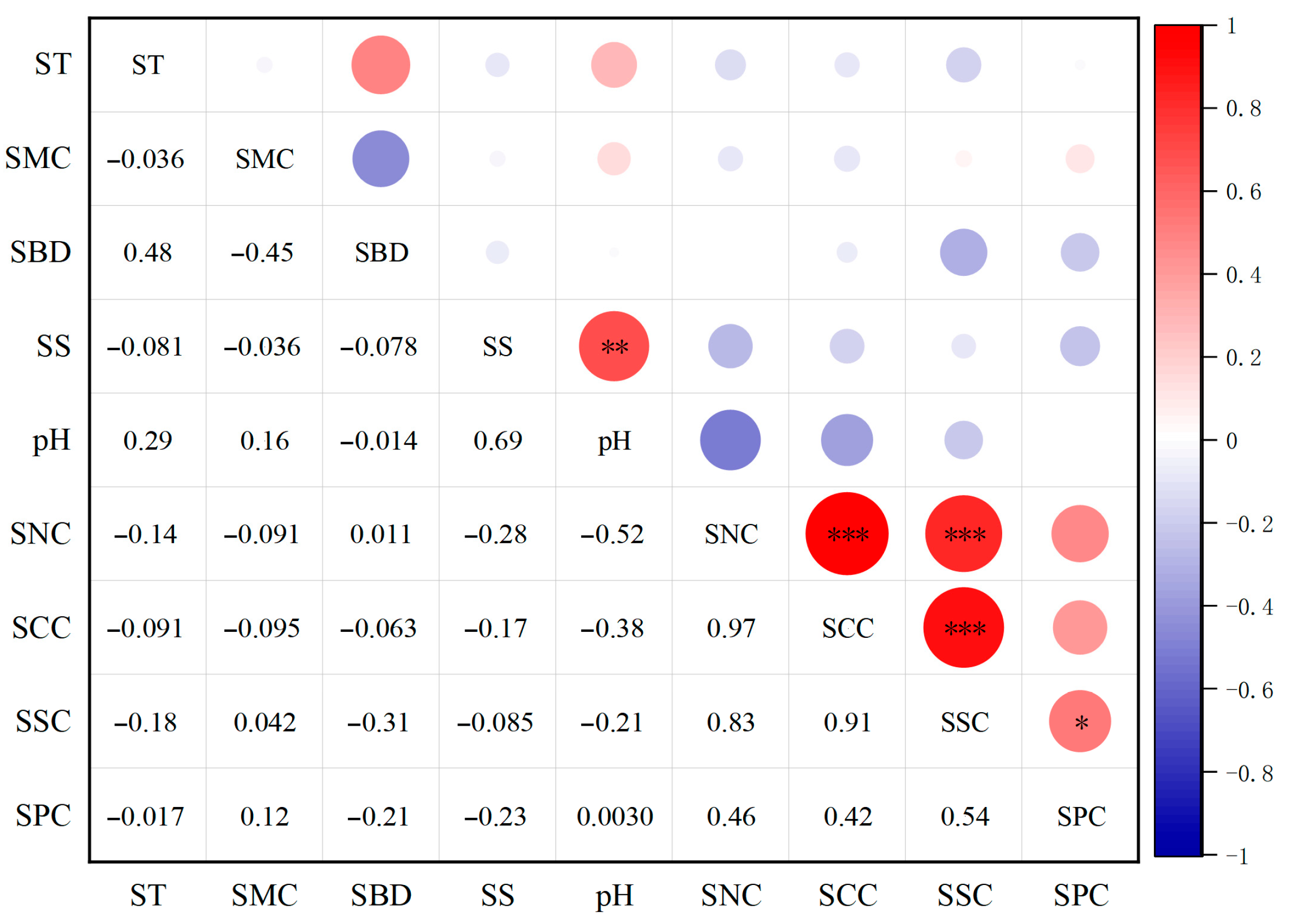
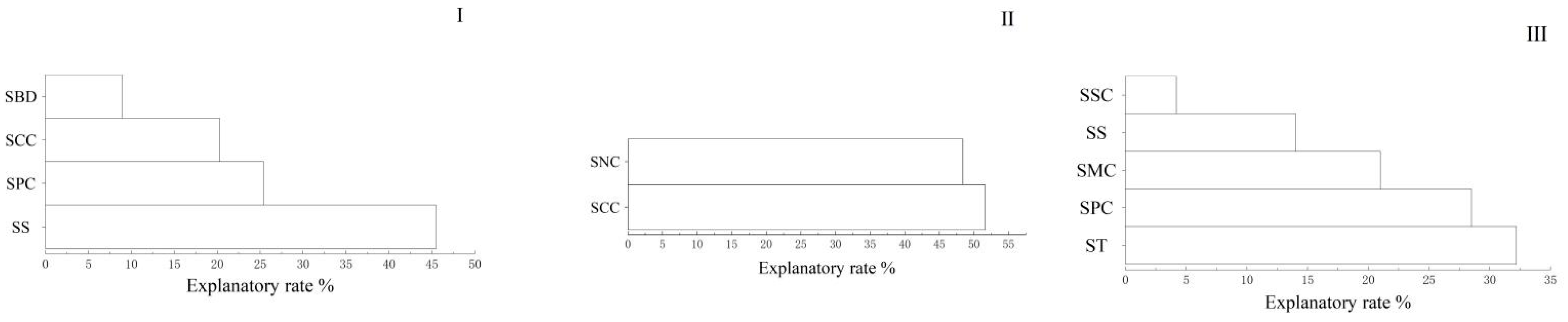
3.3. Relationship Between Functional Traits of Plant Communities and Soil Physical and Chemical Properties Under Different Disturbance Types
4. Discussion
4.1. Soil Physical and Chemical Properties of Plant Communities with Different Types of Disturbance
4.2. Functional Trait Characteristics of Plant Communities Under Different Disturbance Types
4.3. Response of Plant Community Functional Traits to Soil Physical and Chemical Properties
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, X.; Liu, J.K.; Luo, S.X.; Zhao, K.K.; Li, X.J. Divergence of leaf functional traits of coastal sand plants and their relationship with soil physicochemical properties in Hainan Island. J. Trop. Subtrop. Bot. 2022, 30, 708–717. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.S.; Yao, X.Y.; Liu, Y.H. Functional traits of forest plants and their relationships with topographic factors at different successional stages in Changbai Mountain. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2014, 34, 5915–5924. [Google Scholar]
- Song, D.H.; Zhang, X.N.; Yang, J.F.; Tian, J.Y. Functional trait characteristics of different desert plant functional groups and their relationships with soil environment. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 7403–7411. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, L.K.; Zhang, W.; Yuan, M.; Cheng, Y.; Yang, Y.F.; Zhao, K.; Wu, J.H.; Xiao, J.J. Functional traits of dominant plants in the tidal wetlands of the lower Yangtze River and their relationships with soil physicochemical properties. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2025, 45, 13–24. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Chen, D.Q.; Liu, H.K.; Zhao, C.Z.; Zhao, W.T.; Dong, Z.; Zhang, Y.T.; Wang, Y.P. Responses of fine root anatomical traits of 11 afforestation tree species to soil conditions in the coastal saline-alkali land of the Yellow River Delta. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 4150–4159. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.L.; Chen, Y.Z.; Qian, A.G.; Li, J.; Xu, J.; Fu, J.; Cai, L.; Sun, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhang, F.; et al. Salt tolerance of four typical coastal plant species. J. Appl. Oceanogr. 2022, 41, 15–24. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.Y.; Tang, K.X.; Sun, Y.M.; Cai, L.C.; Song, H.; Tu, W.-L. Screening of drought-resistant plants and research on drought-resistant techniques in island vegetation restoration. J. Appl. Oceanogr. 2016, 35, 223–228. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, R.L.; Pang, J.Q.; Song, Y. Physiological responses of the coastal wind-resistant plant Pinus thunbergii to clean wind and aeolian sand flow. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 2033–2044. [Google Scholar]
- You, Y.J.; Wang, Y.X.; Zhang, H.F.; Qiu, W.T.; Wu, M.J. Effects of different human disturbance measures on soil fertility and water retention capacity of natural secondary shrublands. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Z.Y. Floristic Geography of Seed Plants on Pingtan Island, Fujian and the Impact of Alien Plants. Guihaia 2017, 37, 280–293. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, X.P. The State Council’s approval of the construction plan for Pingtan International Tourism Island. Fujian Light Ind. 2016, 8, 32–33. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.J.; Zhang, Z.K.; Zheng, J.M.; Huang, S.J.; Lin, L.L.; Wang, Q.; Deng, C.Y.; Liu, X.Z. Functional trait characteristics and evolutionary trends of wild plants on continental islands: A case study of Pingtan Island. J. Trop. Subtrop. Bot. 2017, 25, 429–437. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, F.J.; Chen, H.X.; Huang, F.M.; Chen, Q.M.; Yang, S.Z. Identification and optimization of land-sea connected ecological corridors based on coastal zone ecological function assessment. J. Appl. Oceanogr. 2025, 44, 84–98. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, S.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, B.S.; Yan, D.L. Research progress on plant leaf morphological characteristics, functional traits and their interactions in environmental adaptation. Anhui For. Sci. Technol. 2024, 50, 11–18+51. [Google Scholar]
- Bakerbrosh, K.F.; Peet, R.K. The ecological significance of lobed and toothed leaves in temperate forest trees. Ecology 1997, 78, 1250–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.J.; Zong, N.; Li, Z.W. Research progress on the trade-off strategies of functional traits in alpine plants. Chin. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. 2025, 31, 1157–1172. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Zheng, L.; Qi, D. Variation in leaf traits at different altitudes reflects the adaptive strategy of plants to environmental changes. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 10, 8166–8175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.J.; Li, Z.J.; Yang, Z.P.; Bai, G.Z. Structural traits and their interrelationships of Populus euphratica heteromorphic leaves. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2010, 30, 4636–4642. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, F.; Wu, C.; Zhang, Y.H.; Yu, H.; Wei, Z.H.; Zheng, W.; Liu, X.F.; Chen, S.D.; Yang, Z.J.; Xiong, D.C. Effects of warming on the growth, morphology, and physiological metabolism of fine roots in a mature Masson pine plantation across different seasons. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2023, 47, 856–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Arif, M.; Zhang, S.; Yuan, Z.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Ding, D.; Li, C. Dam inundation simplifies the plant community composition. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 801, 149827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.; Chen, Y.L.; Wang, F.; Xiong, K.H.; Ma, X.D.; Deng, C.Y. Survey of wild liana resources and analysis of their landscape applications in Pingtan. For. Resour. Manag. 2021, 28, 121–129. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.D.; Fu, B.J. Types, characteristics, and ecological significance of disturbances. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2000, 20, 581–586. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Harguindeguy, N.; Díaz, S.; Garnier, E.; Lavorel, S.; Poorter, H.; Jaureguiberry, P.; Bret-Harte, M.S.; Cornwell, W.K.; Craine, J.M.; Gurvich, D.E.; et al. Corrigendum to: New handbook for standardised measurement of plant functional traits worldwide. Aust. J. Bot. 2016, 64, 715–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matziris, E.; Stefanou, S.; Papazafeiriou, A.; Seilopoulos, D.; Papaioannou, A. Impacts of human activities on soil physical properties of urban green areas: A case study in Thessaloniki city, Greece. Carpathian J. Earth. Environ. Sci. 2016, 11, 381–394. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.B.; Shen, Z.P. Impact of human disturbance on soil physical properties of Pinus tabuliformis artificial forests in Ziwuling, Loess Plateau. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2006, 26, 3685–3695. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, F.; Bai, Z.L. Effects of tourism disturbance on vegetation and soil properties in Poyang Lake National Wetland Park. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2015, 22, 33–39. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, Z.L.; Song, C.L.; Wang, L.; Qi, T.; Chen, M.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, L.; Xu, L.; Liu, J. Spatial variability characteristics of soil salinization in the northern plain irrigation district of Yinchuan, Ningxia. J. Resour. Ecol. 2025, 16, 148–158. (In English) [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Liu, L.; Lu, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Shu, L.; Yang, Q.; Song, Q.; et al. When microclimates meet soil microbes: Temperature controls soil microbial diversity along an elevational gradient in subtropical forests. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 166, 108566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.J.; Zhang, X.M.; Wang, X.J.; Cheng, Z.Y.; Shan, Y.Y. Effects of different soil moisture treatments on soil temperature of spring wheat under film irrigation. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2008, 24, 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Kuang, Y.W.; Wen, D.Z.; Zhong, C.W.; Zhou, G.Y. Root exudates and their roles in phytoremediation. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2003, 27, 709–717. [Google Scholar]
- He, W.Q.; Chen, L.; Pang, D.B.; Cao, M.H.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Li, X.B. Effects of litter input changes on soil physicochemical properties in forest ecosystems. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2024, 44, 1755–1763. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Mu, X.M.; Gao, P. Accumulation and Water-Holding Characteristics of Litter under Different Site Conditions on the Loess Plateau. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2021, 28, 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Shi, R.K.; Li, D.H.; Xu, R.Q.; Wu, D.F.; Miao, R.H. Effects of litter input on the chemical stoichiometric characteristics of forest soil. J. Shandong Agric. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2024, 55, 70–75. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Ma, L.; Sun, X.; Zhang, J.G. Water retention characteristics of litter and soil and their influencing factors under single rainfall conditions. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2023, 34, 3169–3176. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, T.T.; Ni, J.; Wang, G.H. Plant functional traits and environment and ecosystem functions. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2007, 31, 150–165. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.D.; Zhou, X.L.; Tian, J.J.; Yang, L.; Wang, Y.H.; Shen, S.K. Mechanism of Terrestrial Plant Community Assembly under Different Intensities of Anthropogenic Disturbance in Dianchi Lakeside. Forests 2023, 14, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.J.; Li, Z.J.; Yang, Z.P.; Liang, J.Y.; Bai, G.Z. Heteromorphic leaf structural characteristics and their correlations with diameter at breast height of Populus euphratica. Chin. J. Ecol. 2010, 29, 2347–2352. [Google Scholar]
- Grime, J.P. Evidence for the existence of three primary strategies in plants and its relevance to ecological and evolutionary theory. Am. Nat. 1977, 111, 1169–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korablev, A.P.; Sandalova, E.V.; Arapov, K.A.; Zaripova, K.M. Biomorphological traits and leaf dry matter content are important to plant persistence in a highly unstable volcanic ground. Nat. Conserv. Res. 2024, 9, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.Q.; Li, J.X.; Gong, J.W.; Zhao, L.J.; Xiang, W.H.; Cheng, X.; Wang, W.J.; Zhang, Y.L. Leaf trait variation and adaptive strategies of dominant tree species in evergreen broad-leaved forests of Castanopsis sclerophylla. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 7256–7265. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Zhao, C.Z.; Zhao, L.C.; Wang, J.W.; Wen, J. Correlation analysis between specific leaf area and photosynthetic efficiency of Phragmites australis in the Qiwangchuan salt marsh wetland. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 7124–7133. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.Q.; Zha, T.S.; Jia, X.; Wu, Y.J.; Zhang, M.Y.; Mu, J.W. Seasonal dynamics of photosynthetic parameters of Artemisia ordosica and their relationships with leaf nitrogen content and specific leaf area. Chin. J. Ecol. 2017, 36, 916–924. [Google Scholar]
- Poorter, H.; Niinemets, Ü.; Poorter, L.; Wright, I.J.; Villar, R. Causes and consequences of variation in leaf mass per area (LMA): A meta-analysis. New Phytol. 2009, 182, 565–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.W.; Zhao, C.Z.; Zhao, L.C.; Wang, X.P.; Li, Q. Response of root morphology and biomass allocation of Phragmites australis in inland salt marshes to soil salinity factors. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 4843–4851. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, J.X.; Ren, L.; Pan, Y.P.; Zhao, J.; Xiang, X.; Yu, C.; Meng, D.H.; Wang, Y.Y.; Lu, R.J.; Huang, Y.M. Functional traits of desert plants in the Qaidam Basin and their responses to environmental factors. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 4494–4503. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, B. Intraspecific interactions shift from competitive to facilitative across a low to high disturbance gradient in a salt marsh. Plant Ecol. 2016, 217, 959–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.L.; Liu, C.M.; Wang, L. Regulatory effects of soil moisture on crop root growth and distribution. Res. Eco-Agric. 1996, 4, 7–11. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, R.L.; Wen, Z.M.; Liu, Y.Y.; Cui, M.Y.; Yang, Y.T.; Lu, J.X.; Zheng, C.; Lin, Z.Q.; Yuan, L.H. Variations in plant functional traits and their responses to environmental factors across different vegetation zones in the Yan River Basin. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 6045–6057. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.C.; Xuan, J.; Wang, Q.X.; Peng, S.T.; Sun, G.M.; Huang, L.Q. Differences in leaf functional traits of plants in different habitats on the Minjiang River island and their responses to soil properties. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2024, 44, 6301–6316. [Google Scholar]





| No. | (Elevation) /m | (Temperature) /°C | (Humidity) /(%) | (Wind Speed) /m/s | (Levels of Disturbance) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4.15 | 15.29 | 46.07 | 0.57 | I |
| 2 | 2.83 | 14.88 | 48.82 | 0.49 | I |
| 3 | 2.85 | 16.93 | 42.91 | 0.95 | I |
| 4 | 5.57 | 17.95 | 46.00 | 0.46 | I |
| 5 | 5.42 | 17.78 | 44.20 | 0.77 | I |
| 6 | 4.18 | 16.93 | 44.27 | 1.12 | II |
| 7 | 3.02 | 14.11 | 55.59 | 0.64 | II |
| 8 | 5.72 | 16.03 | 50.63 | 0.87 | II |
| 9 | 5.04 | 16.90 | 47.13 | 0.44 | II |
| 10 | 6.00 | 14.23 | 53.47 | 1.77 | II |
| 11 | 2.97 | 19.19 | 48.31 | 0.89 | III |
| 12 | 4.89 | 15.70 | 58.33 | 1.89 | III |
| 13 | 1.54 | 21.09 | 41.49 | 1.95 | III |
| 14 | 8.77 | 16.70 | 58.68 | 2.05 | III |
| 15 | 5.96 | 17.14 | 57.15 | 0.19 | III |
| Trait Index | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SRL | 0.850 | 0.076 | −0.335 | 0.026 |
| SRA | 0.863 | 0.091 | −0.315 | 0.009 |
| SLA | 0.875 | 0.221 | −0.183 | 0.060 |
| RPC | 0.879 | 0.161 | −0.010 | −0.183 |
| RTD | −0.693 | 0.360 | −0.103 | −0.335 |
| RNC | 0.089 | 0.955 | −0.134 | 0.210 |
| RCC | 0.095 | 0.953 | −0.129 | 0.182 |
| RSC | 0.136 | 0.940 | −0.076 | 0.251 |
| H | −0.022 | −0.598 | 0.286 | 0.200 |
| LNC | −0.165 | −0.247 | 0.824 | −0.237 |
| LCC | −0.381 | −0.325 | 0.645 | −0.395 |
| LPC | −0.152 | −0.110 | 0.902 | 0.198 |
| LSC | 0.152 | 0.111 | −0.902 | −0.198 |
| LT | 0.001 | 0.156 | 0.243 | 0.803 |
| LTD | 0.377 | 0.222 | 0.075 | 0.804 |
| LDMC | −0.314 | 0.040 | −0.298 | 0.808 |
| (Eigenvalue) | 3.981 | 3.548 | 3.253 | 2.563 |
| (Contribution rate) | 24.884% | 22.173% | 20.334% | 16.020% |
| (Cumulative contribution rate) | 24.884% | 47.057% | 67.391% | 83.411% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.; Yu, H.; Luo, P.; Cai, K.; Chen, Y. The Relationship Between Plant Community Functional Traits and Soil Physical and Chemical Properties Under Different Levels of Human Disturbance: A Case Study of the East Coast of Pingtan Island, Fujian Province. Sustainability 2025, 17, 10337. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172210337
Yang Y, Yu H, Luo P, Cai K, Chen Y. The Relationship Between Plant Community Functional Traits and Soil Physical and Chemical Properties Under Different Levels of Human Disturbance: A Case Study of the East Coast of Pingtan Island, Fujian Province. Sustainability. 2025; 17(22):10337. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172210337
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Yanling, Hongli Yu, Panlan Luo, Kongzhen Cai, and Ying Chen. 2025. "The Relationship Between Plant Community Functional Traits and Soil Physical and Chemical Properties Under Different Levels of Human Disturbance: A Case Study of the East Coast of Pingtan Island, Fujian Province" Sustainability 17, no. 22: 10337. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172210337
APA StyleYang, Y., Yu, H., Luo, P., Cai, K., & Chen, Y. (2025). The Relationship Between Plant Community Functional Traits and Soil Physical and Chemical Properties Under Different Levels of Human Disturbance: A Case Study of the East Coast of Pingtan Island, Fujian Province. Sustainability, 17(22), 10337. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172210337






