Abstract
Capsicum residue generated from industrial capsaicin extraction is rich in nutrients and represents a significant fraction of solid waste in the food processing industry. Despite its potential value, limited efforts have been devoted to its resource recovery, leading to considerable resource loss and environmental burdens. This study systematically evaluates the applicability of existing food waste recycling technologies for capsicum residue and assesses its valorization potential through comprehensive characterization. The results indicate that capsicum residue holds promise as a feedstock for pectin extraction and as a component in animal feed. Regarding anaerobic fermentation for acid production, the maximum volatile fatty acids (VFAs) yield and VFAs/SCOD ratio reached 462.09 mg·L−1 and 3.16%, respectively, suggesting moderate potential for acidogenic conversion but limited suitability for methanogenesis. Fluorescence spectroscopy of dissolved organic matter revealed that microbial humic-like substances (C1) were the dominant fluorophore, accounting for 42.64% of the total fluorescence, followed by terrestrial humic-like (C2, 19.28%), fulvic-like (C3, 19.12%), and tryptophan-like (C4, 18.95%) components. The favorable C/N ratio of amino acids and humic substances supports the feasibility of composting. Additionally, trace levels of residual capsaicin may confer antibacterial benefits and enhance soil fertility, further supporting the potential of capsicum residue as a value-added resource.
1. Introduction
The rapid growth of global population and shifting consumption patterns have led to a significant increase in food waste (FW) generation. Food waste, which includes vegetable residues, fruit peels, and by-products from meat processing, represents a complex and heterogeneous biomass stream with high organic content and moisture levels [1]. Improper management of FW not only occupies vast land resources but also poses serious environmental risks, including leachate infiltration and greenhouse gas emissions. It is projected that FW generation in Asia will reach 4.16 billion tons by 2025 (China National Bureau of Statistics, 2020). The high moisture content, variable composition, and organic richness of FW complicate its treatment and resource recovery [2]. Currently, landfilling and incineration remain the predominant disposal methods [3]; however, these approaches fail to recover valuable organic matter and may lead to soil and groundwater contamination [4]. Therefore, developing tailored and sustainable treatment strategies based on the specific characteristics of FW is urgently needed.
Capsicum frutescens L., commonly known as chili pepper, is a widely cultivated and consumed crop, particularly in China [5]. In addition to its culinary uses, chili pepper is extensively utilized in industrial applications, especially for the extraction of capsanthin, a natural red pigment. Capsanthin exhibits excellent color stability, non-toxicity, and strong coloring capacity, making it highly desirable in food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries. For instance, it is commonly used in artificial food coloring, sugar coatings, and enteric capsules, and has been shown to disperse uniformly in medicinal syrups, making it suitable for pediatric formulations [6]. Thus, capsanthin holds significant commercial potential across multiple sectors.
However, the extraction of capsanthin generates a considerable amount of solid residue, the quantity of which varies depending on the extraction method. For example, solvent-based extraction yields 30–50% residue by dry weight [7], while supercritical CO2 extraction produces 15–25% residue [8]. The accumulation of this residue places increasing pressure on waste management systems. Traditional disposal methods such as landfilling and composting are limited by land requirements, leachate generation, and potential groundwater pollution. Therefore, developing innovative and sustainable strategies for the valorization of capsicum residue is essential.
Previous studies have explored limited applications of capsicum residue. For instance, it has been evaluated as a low-value animal feed [9], a source of pectin [10], and a substrate for protein extraction [11]. Akinci et al. [12] incorporated chili pulp protein and oil into corn starch films, enhancing their mechanical strength and antibacterial properties. Anaerobic digestion of chili residues for biogas production has also been investigated, with untreated chili pulp yielding 464 ± 25 NL CH4/kg VS [13]. However, challenges such as VFA accumulation, process instability, and foaming remain unresolved [1]. Other studies have explored the conversion of chili residues into biofuels [14], but high processing costs and technical complexity hinder large-scale application [15]. While composting is a mature and environmentally friendly option, issues such as gas leakage and inefficient carbon sequestration persist [16,17,18].
In China, chili pigment extraction is concentrated in five major regions, Xinjiang, Inner Mongolia, Gansu, Hebei, and Yunnan, with Xinjiang being the most prominent [19]. In 2023, the chili cultivation area in Xinjiang reached approximately 500,000–600,000 mu (33,333–40,000 hectares), with a total fresh chili output of 1.5–2 million metric tons [20,21]. Consequently, large volumes of capsicum residue are generated, containing valuable components such as pectin, vitamins, and bioactive compounds. This underscores the industrial significance and environmental urgency of developing high-value utilization pathways for capsicum residue.
Despite its potential, the high-value resource utilization of capsicum residue remains underexplored. This study aims to address this gap by investigating the physicochemical properties of capsicum residue and evaluating its potential for valorization through various bioconversion and extraction technologies. The findings are expected to contribute to (i) the development of sustainable waste management strategies for the chili processing industry and (ii) the promotion of circular economy practices in agricultural waste utilization.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Source and Physical Properties of Capsicum Residue
Figure 1 illustrates the industrial extraction process used to obtain capsaicin from chili peppers via solvent extraction and leaching. The production process begins with harvested capsicum, which is industrially ground into particles to facilitate extraction. These particles are then loaded into extraction equipment where a solvent is used to dissolve the target compounds, primarily capsaicinoids. Following this extraction, the process splits into two streams: the solid leftover, now depleted of most solubles, is discharged as the capsicum residue, while the liquid extract is concentrated through evaporation to remove the solvent. This concentrate is subsequently purified by passing it through decolorizing particles to remove impurities and pigments, resulting in the semi-finished capsaicin product. After capsaicin is separated and packaged, the by-product—capsicum residue—is generated. The residue used in this study was supplied by a biotechnology company. It contains trace amounts of capsaicin, carotenoids, vitamin C, and other organic compounds. Physically, the residue is a deep-red, semi-solid material with high viscosity and fluidity at room temperature. It has a moisture content of 65.25%, a pH of 4.53 (indicating weak acidity), an oxidation–reduction potential (ORP) of 218.8 mV, and an ash content of 11.86%. It also emits a pungent odor.
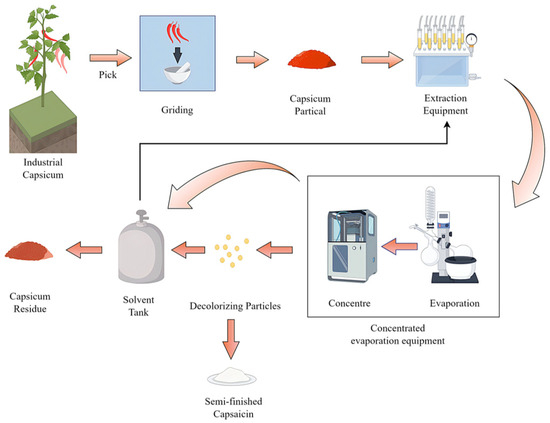
Figure 1.
Production process of capsicum residue.
2.2. Chemical Properties of Capsicum Residue
The pectin content in capsicum residue was analyzed using the carbazole-sulfuric acid spectrophotometric method. Briefly, the dried residue was subjected to acidic hydrolysis to solubilize pectic polysaccharides. An aliquot of the hydrolysate was then reacted with a carbazole solution in concentrated sulfuric acid. The resulting pink chromogen was measured at a wavelength of 530 nm using a UV-Vis spectrophotometer (TU-1800, Beijing Purkinje General Instrument Co., Ltd., Beijing, China). A standard calibration curve was prepared using galacturionic acid, and the pectin content was expressed as galacturonic acid equivalents. The pectin yield was subsequently calculated using Formula (1).
The Vitamin C content in capsicum residue was quantified using high-performance liquid chromatograph (HPLC). The analysis was performed on an HPLC system (Agilent 1260 Infinity II, Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) equipped with a UV detector and a reversed-phase C18 column (ZORBAX Eclipse Plus, Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA, 4.6 × 150 mm, 5 μm). The capsicum residue was extracted with a meta-phosphoric acid solution to stabilize vitamin C prior to analysis. The mobile phase consisted of a potassium dihydrogen phosphate buffer (pH 2.5) and was run under isocratic conditions at a flow rate of 1.0 mL/min. Detection was carried out at a wavelength of 245 nm. Quantification was achieved by comparing the peak areas of the samples to a Vitamin C standard calibration curve.
Fluorescent organic components in the residue were identified via three-dimensional excitation–emission matrix (EEM) fluorescence spectroscopy using a Shimadzu RF-6000 spectrofluorometer (Shimadzu Corporation, Kyoto, Japan).
2.3. Anaerobic Sludge Co-Fermentation
The anaerobic sludge inoculum, characterized by 16S rRNA gene sequencing, was dominated by bacterial phyla essential for hydrolysis and acidogenesis, including Bacteroidetes (~28%) and Firmicutes (~22%). The archaeal community, responsible for methanogenesis, was primarily composed of the acetolactic genus Methanosaeta (~61%) and the hydrogenotrophic genus Methanobacterium (~17%), indicating a robust methanogenic potential. The anaerobic sludge collected from the mesophilic digester of Beijing Jingcheng Huitong Environmental Protection Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China). (pH 7.3, ORP −120 mV, vs. 24.8%) was blended with the residue to give a VS-based ratio of 6:1, and the mixture was adjusted to the desired starting pH. The initial total solids (TS) concentration of the fermentation system was 6.4%. Two series of 250 mL serum bottles were prepared, each sealed with butyl rubber stoppers, flushed with N2 and connected to gas-sampling bags to ensure strict anaerobiosis. One series was incubated at 25 °C and the other at 35 °C, both shaken at 120 rpm. Over 20 days, aliquots were withdrawn every 48 h, centrifuged and filtered through 0.22 µm membranes for subsequent analyses. Volatile fatty acids (VFAs) were quantified using a Gas Chromatograph (Agilent 7890B, Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) equipped with a flame ionization detector (FID) and a DB-FFAP capillary column (30 m × 0.32 mm × 0.25 μm). High-purity nitrogen was used as the carrier gas at a constant flow rate of 2.0 mL/min. The injector and detector temperatures were set at 250 °C and 300 °C, respectively. The oven temperature program was as follows: initial temperature held at 70 °C for 1 min, then increased to 140 °C at a rate of 10 °C/min, and finally ramped to 240 °C at 20 °C/min and held for 2 min. VFAs converted to COD equivalents using standard stoichiometric factors of 0.35, 1.07, 1.51 and 1.81 g COD g−1 for formic, acetic, propionic and n-butyric acids, respectively.
3. Results
3.1. Nutrient and Water-Soluble Organic Components in Capsicum Residue
Table 1 presents the pectin and vitamin C contents in capsicum residue compared with other common fruit and vegetable wastes reported in previous studies. The pectin was extracted from the residue using a hydrochloric acid solution (pH 2.0) at a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:25 (w/v), 85 °C, for 90 min, yielding 8.09%. The extracted pectin was characterized as a high-methoxyl pectin with a degree of methylation of 65% and a galacturonic acid content of 75%, meeting the key quality criteria outlined in the Chinese industry standard QB 2484-2000 [22]. Meanwhile, the vitamin C content in fresh chili peppers is approximately 110 mg/100 g, whereas the residue contained significantly less vitamin C (27.65 mg/100 g).

Table 1.
Comparative analysis of Pectin and Vitamin C contents in capsicum residues and other commonly occurring fruit and vegetable waste materials in research studies (Source: Authors’ own data).
The water-soluble organic components in capsicum residue were analyzed using excitation–emission matrix (EEM) fluorescence spectroscopy. After preprocessing to eliminate Rayleigh and Raman scattering, the fluorescence contour plot (Figure 2) revealed the presence of aromatic compounds, particularly fulvic-like and humic-like acids, as well as protein- and peptide-like substances [42,43].
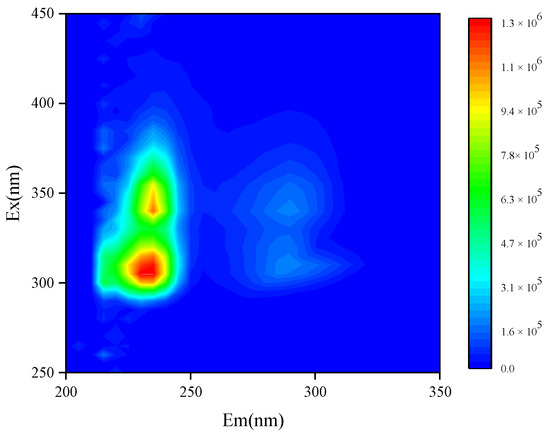
Figure 2.
Three-dimensional fluorescent contour map of capsicum residue (Source: Authors’ own data).
Figure 3 shows the 4 fluorescent components (C1, C2, C3, and C4) in capsicum residue obtained by Parallel factor analysis (PARAFAC) analysis, where colors represent the fluorescence intensity in Raman units (R.U.). The model generated by PARAFAC was uploaded to OpenFluor for querying to match the carrier spectra with the data from other studies. The minimum similarity of the models was above 0.95.
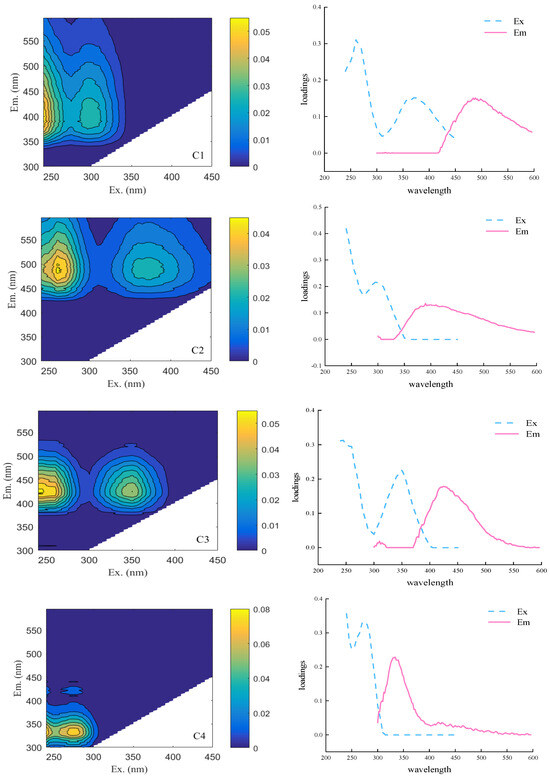
Figure 3.
Fluorescence components and their maximum excitation/emission wavelength distribution (Source: Authors’ own data).
Component C1 exhibits its maximum excitation when the excitation wavelength Ex < 250 nm, with a lower excitation peak at 300 nm and an emission peak at 390 nm. Its spectral characteristic is peak M, which mainly represents low molecular weight microbial humus-like fluorescent groups. In anaerobic systems, these microbial-derived humic substances are not merely metabolic byproducts; they can act as electron shuttles, potentially facilitating direct interspecies electron transfer (DIET) to enhance the efficiency of acidogenesis and methanogenesis [44,45]. The dynamics of C1 may thus reflect the activity of the key microbial consortia and the overall stability of the fermentation process.
C2 shows a major excitation maximum at 260 nm, followed by a lower intensity excitation peak at 350 nm and a maximum emission peak at 490 nm. The C2 spectral characteristics are similar to the traditional humus peaks A and C [46], and are considered to be high molecular weight terrestrial source humus material [47]. The C3 excitation peak is located at Ex < 300 nm, with a slightly lower excitation peak at 350 nm and an emission peak at 425 nm. The C3 component is mainly composed of terrestrial yellow rot compounds [48]. The C4 excitation peak is located at Ex < 250/275 nm, with an emission peak at 335 nm. The component is considered to be protein-like substances [49].
Furthermore, the presence of residual capscaicin in the substrate may have a shaping influence on this fluorescent organic matter profile. Its antimicrobial properties could selectively inhibit certain microbial populations, thereby indirectly affecting the synthesis and degradation pathways of components like C1 (microbial humics) and C4 (protein-like substances). This potential interaction offers a plausible explanation for the unique evolution of the fluorescent components observed in capsicum residue compared to other organic wastes.
Figure 4 illustrates the relative abundance of these components. Microbial humic-like C1 was the dominant fraction, accounting for 42.64% of total fluorescence. Terrestrial humic-like C2, fulvic-like C3, and protein-like C4 contributed 19.28%, 19.12%, and 18.95%, respectively.
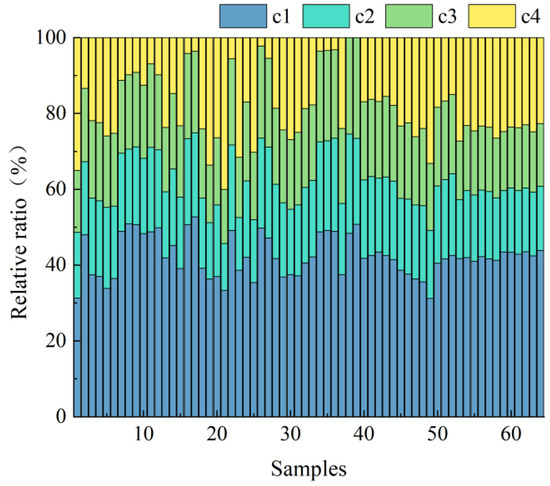
Figure 4.
Relative proportions of different fluorescent components in different capsicum residue samples (Source: Authors’ own data).
3.2. VFAs Production in the Anaerobic Fermentation
Poly-hydroxy-alkanoates (PHAs) are bioploymers derived from bacteria, which can serve as carbon sources for biological culture media and essential nutrients for growth limiting concentrations [50] The microbial synthesis of PHAs mostly uses high-value pure substances such as glucose and pure acid as carbon sources, but the production cost is relatively high [51,52]. VFAs and lactic acid can serve as low-cost carbon source for PHAs synthesis. Many researchers have studied VFAs, anaerobic fermentation products from bagasse, straw, food processing waste, and municipal sludge as the low-cost resources for PHAs synthesis [53,54]. This study aims to determine the potential of capsicum residue as a raw material for synthesizing PHAs by analyzing the yield and composition of VFAs and lactic acid produced by anaerobic fermentation of capsicum residue under different temperature and pH conditions.
The VFAs composition and concentration of capsicum residue after 20 days of anaerobic fermentation under initial pH values of 4, 5, 6, and 7 at 25 °C and 35 °C are shown in Figure 5. In general, the VFAs concentration reached a maximum of 462.09 mg/L after 14 days of fermentation at a temperature of 35 °C and initial pH of 6, with the concentrations of Formic Acid, Lactic Acid, Acetic Acid, Propionic Acid, N-butyric Acid of 108.78 mg/L, 45.42 mg/L, 172.33 mg/L, 68.06 mg/L, 67.50 mg/L, respectively.
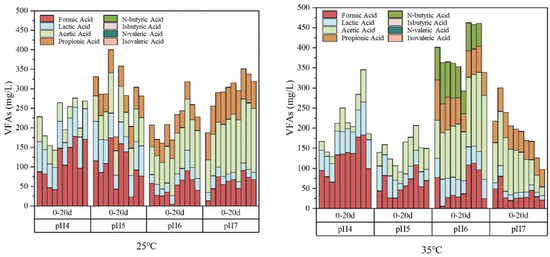
Figure 5.
The VFAs composition and concentration of capsicum residue after 20 days of anaerobic fermentation under different initial pH at 25 °C and 35 °C (Source: Authors’ own data).
The composition of VFAs formed by anaerobic fermentation of capsicum residue for 20 days was analyzed, and it was found that isobutyric acid, n-valeric acid, and isovaleric acid were not detected in several samples. Butyric acid was only detected at a temperature of 35 °C and an initial pH of 5. When the pH is 4 and 5, formic acid is the main component of VFAs, and when the pH is 6 and 7, acetic acid is the main component of VFAs. Under the conditions of producing the highest concentration of VFAs (temperature of 35 °C pH of 6), acetic acid is the main component, accounting for 37.39%.
3.3. Lactic Acid Production in the Anaerobic Fermentation
Jiang et al. [55] found that lactic acid as a carbon source has more advantages in synthesizing PHAs, and the higher the content of lactic acid, the higher the content of synthesized PHAs. In addition, lactic acid has high stability and its properties are not easily changed during storage and transportation [56]. Therefore, the lactic acid content in anaerobic fermentation broth is also an important factor to consider when using capsicum residue as a raw material for PHA synthesis.
The proportion of lactic acid after 20 days of anaerobic fermentation under initial pH of 4, 5, 6, and 7 at temperatures of 25 °C and 35 °C is shown in Figure 6. The proportion of lactic acid in pH of 4 and 5 is higher than that at pH of 6 and 7, indicating that acidic conditions are more conducive to lactic acid production. When the temperature is 35 °C and the pH is 5, the proportion of lactic acid is highest at 44.35% after 2 days of fermentation.
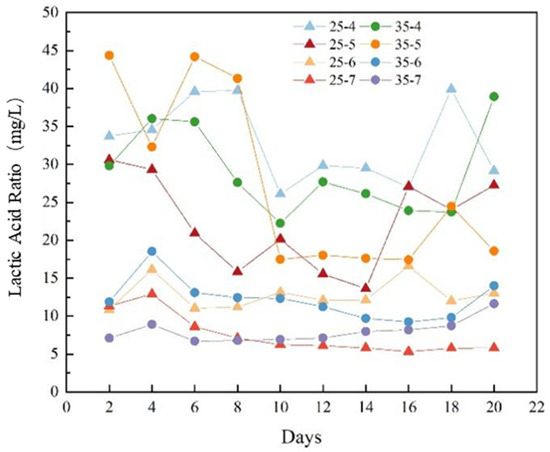
Figure 6.
The proportion of lactic acid after 20 days of anaerobic fermentation under different initial pH at temperatures of 25 °C and 35 °C (Source: Authors’ own data).
3.4. VFAs/SCOD Ratio as an Indicator of Acidification Efficiency
Soluble COD (SCOD) characterizes the hydrolysis efficiency of anaerobic fermentation, including the content of VFAs, soluble carbohydrates, and proteins [57,58]. The ratio of VFAs/SCOD is the ratio of the sum of COD concentrations corresponding to VFAs to SCOD, indicating how much dissolved organic matter in the fermentation broth is converted into VFAs, reflecting the anaerobic acid production effect. The larger the ratio, the better the acid production effect [55,57].
The results of the VFAs concentration and the ratio of VFAs/SCOD under different temperature and pH were shown in Figure 7. Under the temperature of 35 °C and pH of 6, the VFAs/COD ratio of anaerobic fermentation of capsicum residue was higher than that of other conditions, indicating that the acid production effect was the best under this condition, which was similar to the trend of VFAs production. Under the temperature of 25 °C and pH of 7, VFAs concentration and VFAs/SCOD ratio increased slowly with anaerobic fermentation time, and the increase value of VFAs was higher than other conditions at 25 °C. However, under other conditions, the VFAs concentration and VFAs/SCOD ratio fluctuated with time, which may be due to the inhibition of the fermentation process due to the limitation of the activity of acidogenic bacteria. Under the condition of temperature of 35 °C and pH of 7, VFAs/SCOD ratio showed an upward trend in the first 4 days, and gradually decreased in the last 16 days. Under the condition of temperature of 35 °C and pH of 6, there was a minimum total VFAs/SCOD ratio at 12 days of fermentation. With the increase in fermentation time, the limit was also lifted, and reached the highest VFAs/SCOD ratio of 3.16% after 14 days of fermentation. In addition, it was found that there was no obvious gas production in the anaerobic fermentation process except under the condition of temperature of 35 °C and pH of 7, indicating that the substrate was not converted into methane and other gases in the whole anaerobic fermentation process.
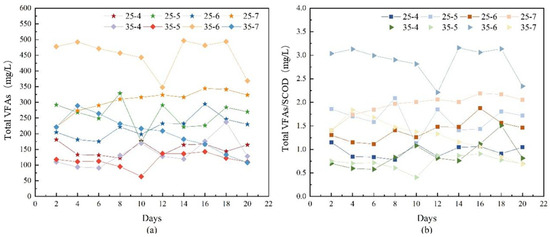
Figure 7.
(a) Total VFA concentrations at different pH at 25 °C and 35 °C; (b) Ratio of total VFAs/SCOD at different pH at 25 °C and 35 °C (Source: Authors’ own data).
4. Discussion
4.1. Feasibility of Recycling Valuable Substances from Capsicum Residue
Pectin extracted from various agro-industrial residues is widely used as a thickening, gelling, and stabilizing agent in the food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries [59]. For optimal performance in food matrices such as confectionery, yogurt, and fruit juices, pectin must meet specific requirements regarding degree of methoxylation and molecular weight [10]. Wang et al. [60] optimized ultrasound-assisted acid extraction of pectin from chili peppers, achieving a yield of 16.85%, which is comparable to that of citrus peel—a conventional pectin source. The extracted pectin also met the quality standards specified in the Chinese National Standard QB 2484-2000.
In this study, the pectin extraction yield from capsicum residue was 8.09%, slightly lower than the 8.72% reported by Xu et al. [10]. This discrepancy may be attributed to differences in chili varieties, capsaicin extraction methods, or pectin degradation during storage and transportation. It is well documented that pectin-rich biomass is sensitive to moisture, temperature, and processing conditions, all of which can affect extractability and functionality [61]. Therefore, while capsicum residue shows potential as an alternative pectin source, further optimization of storage protocols and extraction techniques is necessary for its industrial application.
Vitamin C content in capsicum residue is significantly influenced by processing, storage, and environmental factors, as ascorbic acid is highly susceptible to degradation under light and heat [62]. Although the residue retains a relatively high vitamin C content compared to many other fruit and vegetable wastes, its recovery is less economically attractive due to lower yields and higher sensitivity to handling conditions. Thus, from a valorization perspective, pectin extraction appears to be the more viable route.
As shown in Table 1, apple pomace, mango peel, and grape pomace exhibit the highest pectin contents, while capsicum residue, banana peel, and citrus peel fall within the intermediate range. In contrast, passion fruit peel and coffee pulp show relatively low pectin levels. Regarding vitamin C, capsicum residue, banana peel, and citrus peel contain notably higher concentrations than apple pomace and mango peel. These results highlight the dual-value potential of capsicum residue as a source of both pectin and vitamin C, supporting its candidacy for integrated biorefinery approaches.
The fluorescence characteristics of capsicum residue in this study are consistent with those reported by Pérez-Murcia et al. [43] prior to composting. However, their study showed that protein- and peptide-like substances were largely degraded during aerobic composting, while fulvic- and humic-like compounds accumulated. This suggests that aerobic composting of capsicum residue not only stabilizes organic matter but also enhances the formation of humic substances, offering both economic and environmental benefits. Therefore, depending on the target product—pectin, vitamin C, or humified organic matter—different processing strategies (e.g., extraction vs. composting) can be applied to maximize resource recovery from capsicum residue.
4.2. Evaluation of Anaerobic Fermentation Potential
The production of volatile fatty acids (VFAs) during anaerobic fermentation is strongly influenced by pH and temperature. An initial pH of 6 favors the enrichment of hydrolytic and acidogenic microbial communities, promoting the activity of extracellular hydrolytic enzymes. These enzymes catalyze the breakdown of complex organic macromolecules into soluble monomers, which are subsequently metabolized by acidogenic bacteria to produce VFAs [63].
The optimal temperature range for acidogenic bacteria is 35–55 °C. Elevated temperatures accelerate hydrolysis rates and enhance microbial metabolic activity, leading to increased conversion of soluble carbohydrates and proteins into VFAs [64].
VFAs such as acetic, propionic, n-butyric, and isobutyric acids are primarily derived from the fermentation of soluble proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids, whereas n-valeric and isovaleric acids are typically produced via proteolysis [57]. Notably, branched-chain VFAs (e.g., propionic, butyric, and valeric acids) are readily degraded into acetic acid prior to methanogenesis.
At pH 6, methanogenic activity is inhibited due to suboptimal conditions (optimal pH for methanogens: 6.5–8.5) [65], resulting in acetic acid accumulation and minimal degradation of intermediate VFAs [66,67]. This explains the absence of isobutyric, n-valeric, and isovaleric acids, and the dominance of acetic acid at pH 6–7.
Lactic acid production was favored under acidic conditions (pH 4–5), consistent with Tang et al. [68], who reported that neutral to alkaline pH suppresses lactic acid bacteria (LAB) activity. At pH 6, LAB activity declines prematurely, limiting lactic acid accumulation [69]. Additionally, lactic acid can be further metabolized into propionic acid, which is subsequently converted to acetic acid [70]. The limited dissolution of organic matter in the fermentation broth resulted in the reduction in the content of soluble organic matter, thus affecting the ratio [71].
The higher the pH, the more likely it will produce more soluble chemical oxygen demand, such as soluble proteins and carbohydrates, which will make the substrate easier to acidify [72]. Higher pH values generally enhance the solubilization of proteins and carbohydrates, increasing substrate bioavailability for acidogenesis. However, under these conditions, methanogens may become active, reducing VFA accumulation through methanogenic consumption [71].
4.3. Environmental Implications
As a by-product remaining after capsaicin extraction, capsaicin residue retains various nutrients such as vitamins, pectin, and amino acids. However, due to the influence of the extraction process, the actual measured contents of pectin and vitamins, and other bioactive compounds are considerably lower than those in the original capsicum material. A preliminary techno-economic analysis reveals that the dedicated re-extraction of these components from the residue is currently challenged by high operational costs and limited yield, resulting in a unit cost that is not yet competitive with established pectin sources. Thus, while capsicum residue holds potential as a raw material for future extraction applications, its utilization must be evaluated in terms of technical feasibility, economic viability, and environmental impact to identify more sustainable approaches.
Capsicum residue is rich in organic matter, humus, and protein, making it a suitable feedstock for composting and bioenergy production. However, for large-scale implementation, practical barriers must be addressed. The high moisture content (65.25%) significantly increases transportation and handling costs, suggesting that pre-treatment (e.g., mechanical dewatering) or decentralized processing near source locations is critical for economic feasibility.
Studies on the anaerobic co-fermentation of capsicum residue with sewage sludge have shown that, under conditions of 35 °C and pH at 6, the maximum VFAs/SCOD ratio reached 3.16% after 14 days within a 20-day fermentation period. However, throughout the entire process, the VFA/SCOD ratio remined below 4%, indicating a limited conversion efficiency. This suggests that while capsicum residue has the potential for PHA synthesis, the low VFA yield may be attributed to insufficient organic content, low biodegradability, or suboptimal fermentation conditions. Furthermore, at scale, operational challenges such as foam control would need to be managed. To enhance acidogenic performance, an integrated biorefinery approach is recommended. Further investigation should focus on adjusting parameters such as C/N ratio, N/P ratio, and hydraulic retention time (HRT) within a cascading valorization framework. For instance, the solid fraction after fermentation retains value and can be directed to composting, thereby improving the overall benefit–cost ratio of the waste management chain.
In a related study, Du et al. [73] investigated the effect of capsaicin as an additive on short-chain fatty acid (SCFA) production during food waste recycling. They found that low concentrations of capsaicin (4 mg/g VS) promoted solubilization, hydrolysis and acidification processes, accompanied by a mild accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) that stimulated microbial activity, resulting in a 12.5% increase in SCFA yield. In contrast, high concentrations exerted an inhibitory effect. These findings suggest that determining the residual capsaicin content in the residue and utilizing it as an additive to enhance fermentation of other organic substrates may represent a viable pathway for valorizing capsicum residue. This strategy of using the residue as a low-cost bio-stimulant could offer a higher economic return and simpler implementation pathway than dedicated extraction or standalone fermentation, presenting a promising avenue for industrial application.
Author Contributions
Z.H.: Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing—review and editing; S.L.: Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing—original draft; T.Y.: Supervision; D.L.: Formal analysis, Supervision; X.W.: Methodology, Supervision, Writing—review and editing; Y.C.: Data curation, Formal analysis; Z.Z.: Supervision; Z.Y.: Supervision; D.Y.: Supervision; S.C.: Formal analysis; Y.W.: Formal analysis; J.L.: Formal analysis. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by Beike Sprout Plan of Beijing Academy of Science and Technology (25CE-BGS-02) and the Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52400021).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Zhe Zhang is employed by MCC Eco-Environmental Protection Group Co., Ltd. The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- He, K.; Liu, Y.; Tian, L.; He, W.; Cheng, Q. Review in Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste. Heliyon 2024, 10, e28200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Bano, A.; Singh, S.P.; Srivastava, S.K.; Singh, S.P.; Iqbal, H.M.N.; Varjani, S. Different Stages of Microbial Community during the Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 60, 2079–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, P.; Mohanty, A.K.; Dick, P.; Misra, M. A Review on the Challenges and Choices for Food Waste Valorization: Environmental and Economic Impacts. ACS Environ. Au 2023, 3, 58–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Cheng, K. Enhanced Biogas Production Efficiency of Kitchen Waste by Anaerobic Co-Digestion and Pretreatment. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 2024, 14, 24949–24962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.; Zhang, S.; Xiao, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, T.; Hu, X.; Yi, J. Effect of Pasteurization Processing and Storage Conditions on Softening of Acidified Chili Pepper: Pectin and It Related Enzymes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 126690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijay, A.; Kumar, A.; Islam, K.; Momo, J.; Ramchiary, N. Chapter 11-Functional Genomics to Understand the Tolerance Mechanism against Biotic and Abiotic Stresses in Capsicum Species. In Transcriptome Profiling; Ajmal Ali, M., Lee, J., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 305–332. ISBN 978-0-323-91810-7. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, T. New Process Study on Organic Solvent Extraction of Capsanthin from Red Chillies. Food Drug 2008, 10, 33–36. [Google Scholar]
- Barros, H.D.F.Q.; Coutinho, J.P.; Grimaldi, R.; Godoy, H.T.; Cabral, F.A. Simultaneous Extraction of Edible Oil from Avocado and Capsanthin from Red Bell Pepper Using Supercritical Carbon Dioxide as Solvent. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2016, 107, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georganas, A.; Giamouri, E.; Pappas, A.C.; Papadomichelakis, G.; Galliou, F.; Manios, T.; Tsiplakou, E.; Fegeros, K.; Zervas, G. Bioactive Compounds in Food Waste: A Review on the Transformation of Food Waste to Animal Feed. Foods 2020, 9, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Tai, K.; Wei, T.; Yuan, F.; Gao, Y. Physicochemical and in Vitro Antioxidant Properties of Pectin Extracted from Hot Pepper (Capsicum annuum L. Var. acuminatum (Fingerh.)) Residues with Hydrochloric and Sulfuric Acids. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 4953–4960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Tang, X.; Ouyang, M.; Wang, Y. Analysis and Evaluation of Nutritional Components in Pepper Meal. China Condiment 2017, 42, 131–134. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinci, Z.K.; Karaman, H.; Yildirim-Yalcin, M.; Olcay, H.S.; Inan, M.; Toker, O.S. Effects of Red Pepper Pomace Protein and Oil on the Properties of Starch-Based Edible Films. Waste Biomass Valor. 2024, 15, 3579–3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parralejo Alcobendas, A.I.; Royano Barroso, L.; Cabanillas Patilla, J.; González Cortés, J. Pretreatment and Nanoparticles as Catalysts for Biogas Production Reactions in Pepper Waste and Pig Manure. Catalysts 2023, 13, 1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocer, A.; Yaka, I.F.; Gungor, A. Evaluation of Greenhouse Residues Gasification Performance in Hydrogen Production. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 23244–23249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvi, T.; Asif, Z.; Iqbal Khan, M.K. Clean Label Extraction of Bioactive Compounds from Food Waste through Microwave-Assisted Extraction Technique-A Review. Food Biosci. 2022, 46, 101580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerda, A.; Artola, A.; Font, X.; Barrena, R.; Gea, T.; Sánchez, A. Composting of Food Wastes: Status and Challenges. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 248, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.-T.; Vu, C.-T.; Lin, C.; Bui, X.-T.; Huang, W.-Y.; Vo, T.-D.-H.; Hoang, H.-G.; Liu, W.-Y. Remediation of Highly Fuel Oil-Contaminated Soil by Food Waste Composting and Its Volatile Organic Compound (VOC) Emission. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2018, 4, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Ahmed Mohamed, T.; Zhao, L.; Zhu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, J. Microhabitat Drive Microbial Anabolism to Promote Carbon Sequestration during Composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 346, 126577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Gao, C.; Ye, Q.; Ruan, M.; Liu, C.; Yao, Z.; Wan, H.; Cheng, Y. Comparative Analysis of Fruit Quality Components Between Processed and Fresh-eating Chili Pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) at Different Developmental Stages. China Veg. 2025, 2, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Yao, L. Development Achievements and Countermeasures of High Quality Developmentof Pepper Industry in Xinjiang. Southeast Hortic. 2024, 12, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Q.; Zhao, B.; Wang, Z.; Qiao, L.; Li, W. Trend, Risk and Countermeasures of Chinese Processed Pepper Industry MovingWestward. China Veg. 2025, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- QB 2484-2000; Food Additive—Pectin. National Bureau of Light Industry: Beijing, China, 2000.
- Dranca, F.; Vargas, M.; Oroian, M. Physicochemical Properties of Pectin from Malus domestica ‘Fălticeni’ Apple Pomace as Affected by Non-Conventional Extraction Techniques. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 100, 105383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobczak, P.; Nadulski, R.; Kobus, Z.; Zawiślak, K. Technology for Apple Pomace Utilization within a Sustainable Development Policy Framework. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauser, S.; Murtaza, M.A.; Hussain, A.; Imran, M.; Kabir, K.; Najam, A.; An, Q.U.; Akram, S.; Fatima, H.; Batool, S.A.; et al. Apple Pomace, a Bioresource of Functional and Nutritional Components with Potential of Utilization in Different Food Formulations: A Review. Food Chem. Adv. 2024, 4, 100598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girma, E. Extraction and Characterization of Pectin from Selected Fruit Peel Waste. Int. J. Sci. Res. Publ. 2016, 6, 447–454. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoud, K.F.; Shedeed, N.A.; Hussein, A.M.S. Production and Quality Evaluation of Corn Crackers Fortified with Freeze-Dried Banana Peel and Pulp. Food Humanit. 2023, 1, 1680–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marçal, S.; Sousa, S.; Araújo-Rodrigues, H.; Silva, I.V.; Campos, D.A.; Pintado, M. Impact of Washing and Freezing on Nutritional Composition, Bioactive Compounds, Antioxidant Activity and Microstructure of Mango Peels. Food Chem. 2024, 442, 138368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minjares-Fuentes, R.; Femenia, A.; Garau, M.C.; Meza-Velázquez, J.A.; Simal, S.; Rosselló, C. Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Pectins from Grape Pomace Using Citric Acid: A Response Surface Methodology Approach. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 106, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oloye, M.T.; Arawande, J.O.; Borokini, F.B.; Lawal, T.P.; Oderemi, Y.O. Extraction and Determination of Vitamins from Pectin Obtained from Four Different Citrus Fruit Peels. GSC Biol. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 22, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, P.; Liu, Z.; An, L.; Zhang, X.; Xie, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Gao, W. Evaluation of Citrus Pectin Extraction Methods: Synergistic Enhancement of Pectin’s Antioxidant Capacity and Gel Properties through Combined Use of Organic Acids, Ultrasonication, and Microwaves. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 266, 131164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasirin, S.M.; Puspasari, I.; Sahalan, A.Z.; Mokhtar, M.; Ghani, M.K.A.; Yaakob, Z. Drying of Citrus sinensis Peels in an Inert Fluidized Bed: Kinetics, Microbiological Activity, Vitamin C, and Limonene Determination. Dry. Technol. 2014, 32, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zheng, L.; Zheng, X.; Xiao, D.; Wang, S.; Ai, B.; Sheng, Z. Extraction of Pectin from Passion Fruit Peel: Composition, Structural Characterization and Emulsion Stability. Foods 2022, 11, 3995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manasa, V.; Padmanabhan, A.; Anu Appaiah, K.A. Utilization of Coffee Pulp Waste for Rapid Recovery of Pectin and Polyphenols for Sustainable Material Recycle. Waste Manag. 2021, 120, 762–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Garawani, I.M.; El-Nabi, S.H.; El-Shafey, S.; Elfiky, M.; Nafie, E. Coffea Arabica Bean Extracts and Vitamin C: A Novel Combination Unleashes MCF-7 Cell Death. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2020, 21, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- del Amo-Mateos, E.; Fernández-Delgado, M.; Lucas, S.; López-Linares, J.C.; García-Cubero, M.T.; Coca, M. Valorization of Discarded Red Beetroot through the Recovery of Bioactive Compounds and the Production of Pectin by Surfactant-Assisted Microwave Extraction. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 389, 135995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kujala, T.S.; Loponen, J.M.; Klika, K.D.; Pihlaja, K. Phenolics and Betacyanins in Red Beetroot (Beta vulgaris) Root: Distribution and Effect of Cold Storage on the Content of Total Phenolics and Three Individual Compounds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 5338–5342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarv, V.; Hussain, S.; Rätsep, R.; Kikas, A. The Proximate Composition, Mineral and Pectin Content and Fatty Acid Profile of the Pomace Fraction of 16 Rowanberry Cultivars. Plants 2024, 13, 1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sady, S.; Ligaj, M.; Pachołek, B.; Błaszczyk, A.; Płaczek, Z.; Dłużniewska, N.; Kawałek, P.; Pakuła, K.; Konopelski, A.; Gołaszewski, E. Designing the Quality Characteristics of Berry Processing Byproducts Using Fermentation. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 3110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.-S.; Mu, T.-H.; Ma, M.-M. Extraction, Structure, and Emulsifying Properties of Pectin from Potato Pulp. Food Chem. 2018, 244, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camire, M.E.; Kubow, S.; Donnelly, D.J. Potatoes and Human Health. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2009, 49, 823–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Mata, J.; Marhuenda-Egea, F.C.; Moral, R.; Torres-Climent, A.; Martínez-Sabater, E.; Paredes, C.; Barber, X.; Morales, J. Characterization of Dissolved Organic Matter from Sewage Sludge Using 3D-Fluorescence Spectroscopy and Chemometric Tools. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2015, 46, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Murcia, M.D.; Martínez-Sabater, E.; Domene, M.A.; González-Céspedes, A.; Bustamante, M.A.; Marhuenda-Egea, F.C.; Barber, X.; López-Lluch, D.B.; Moral, R. Role of Proteins and Soluble Peptides as Limiting Components during the Co-Composting of Agro-Industrial Wastes. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 300, 113701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Yu, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Y. Insight into the Role of Intermittent Microaeration in Enhancing Lignocellulose-Containing Anaerobic Digestion and Humic Substances Formation. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 520, 166500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Q.; Ji, J.-L.; Li, Y.; Wang, D.; Pan, J.; Wang, Y.-Z. Effect of Biochar Addition on Biogas Production and Humic Acid Formation during Solid-State Anaerobic Digestion and Subsequent Aerobic Fermentation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 116596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Fallah, R.; Rouillon, R.; Vouvé, F. Spectral Characterization of the Fluorescent Components Present in Humic Substances, Fulvic Acid and Humic Acid Mixed with Pure Benzo(a)Pyrene Solution. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2018, 199, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Yang, L.; Hong, H.; Stedmon, C.A.; Wang, F.; Xu, J.; Xie, Y. Assessing the Dynamics of Chromophoric Dissolved Organic Matter in a Subtropical Estuary Using Parallel Factor Analysis. Mar. Chem. 2011, 124, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retelletti Brogi, S.; Balestra, C.; Casotti, R.; Cossarini, G.; Galletti, Y.; Gonnelli, M.; Vestri, S.; Santinelli, C. Time Resolved Data Unveils the Complex DOM Dynamics in a Mediterranean River. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 733, 139212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmala, E.; Haraguchi, L.; Markager, S.; Massicotte, P.; Riemann, B.; Staehr, P.A.; Carstensen, J. Eutrophication Leads to Accumulation of Recalcitrant Autochthonous Organic Matter in Coastal Environment. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2018, 32, 1673–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, K.; Nayak, R.; Shukla, A.; Parmar, P.; Goswami, D.; Saraf, M. Polyhydroxyalkanoates: An Exotic Gleam in the Gloomy Tale of Plastics. J. Polym. Environ. 2021, 29, 2013–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Battashi, H.; Al-Kindi, S.; Gupta, V.K.; Sivakumar, N. Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) Production Using Volatile Fatty Acids Derived from the Anaerobic Digestion of Waste Paper. J. Polym. Environ. 2021, 29, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szacherska, K.; Oleskowicz-Popiel, P.; Ciesielski, S.; Mozejko-Ciesielska, J. Volatile Fatty Acids as Carbon Sources for Polyhydroxyalkanoates Production. Polymers 2021, 13, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan-Sagastume, F.; Hjort, M.; Cirne, D.; Gérardin, F.; Lacroix, S.; Gaval, G.; Karabegovic, L.; Alexandersson, T.; Johansson, P.; Karlsson, A.; et al. Integrated Production of Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) with Municipal Wastewater and Sludge Treatment at Pilot Scale. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 181, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesh Saratale, R.; Cho, S.-K.; Dattatraya Saratale, G.; Kadam, A.A.; Ghodake, G.S.; Kumar, M.; Naresh Bharagava, R.; Kumar, G.; Su Kim, D.; Mulla, S.I.; et al. A Comprehensive Overview and Recent Advances on Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) Production Using Various Organic Waste Streams. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 325, 124685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, K.; Wang, Q.; Gong, C.; Li, M. Volatile Fatty Acids Production from Food Waste: Effects of pH, Temperature, and Organic Loading Rate. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 143, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Wang, S.; Zhang, W.; Yin, F.; Cao, Q.; Lian, T.; Dong, H. Polyhydroxyalkanoates Production from Lactic Acid Fermentation Broth of Agricultural Waste without Extra Purification: The Effect of Concentrations. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2023, 32, 103311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Yin, J.; Shen, D.; Li, N. Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste for Volatile Fatty Acids (VFAs) Production with Different Types of Inoculum: Effect of pH. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 161, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, X.; Yuan, H.; Wachemo, A.C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Wen, H.; Wang, J.; Li, X. The Relationships among sCOD, VFAs, Microbial Community, and Biogas Production during Anaerobic Digestion of Rice Straw Pretreated with Ammonia. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 28, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Wang, B.; Xi, W.; Liu, X.; Tang, S.; Tan, X.; Li, G.; Huang, L.; Liu, Y.; Bai, J. Modification Methods, Biological Activities and Applications of Pectin: A Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhu, X.; Liu, J.; Tian, R. Optimization on pectin extraction from pepper slag. China Food Addit. 2016, 8, 79–85. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sunanta, P.; Rose Sommano, S.; Luiten, C.A.; Ghofrani, M.; Sims, I.M.; Bell, T.J.; Carnachan, S.M.; Hinkley, S.F.R.; Kontogiorgos, V. Fractionation and Characterisation of Pectin-Rich Extracts from Garlic Biomass. Food Chem. 2024, 436, 137697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitravathi, K.; Chauhan, O.P.; Raju, P.S. Postharvest Shelf-Life Extension of Green Chillies (Capsicum annuum L.) Using Shellac-Based Edible Surface Coatings. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2014, 92, 146–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Lv, L.; Li, W.; Ren, Z.; Wang, P.; Liu, X.; Gao, W.; Sun, L.; Zhang, G. A Comprehensive Review on Food Waste Anaerobic Co-Digestion: Research Progress and Tendencies. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 878, 163155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.S.; Chua, A.S.M.; Yeoh, H.K.; Ngoh, G.C. A Review of the Production and Applications of Waste-Derived Volatile Fatty Acids. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 235, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Fu, Z.; Guan, D.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Xie, J.; Sun, Y.; Guo, L.; Wang, D. A Comprehensive Review on Food Waste Anaerobic Co-Digestion: Current Situation and Research Prospect. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 179, 546–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Q. Effect of Solids Retention Time and Temperature on Waste Activated Sludge Hydrolysis and Short-Chain Fatty Acids Accumulation under Alkaline Conditions in Continuous-Flow Reactors. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengmeng, C.; Hong, C.; Qingliang, Z.; Shirley, S.N.; Jie, R. Optimal Production of Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) in Activated Sludge Fed by Volatile Fatty Acids (VFAs) Generated from Alkaline Excess Sludge Fermentation. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 1399–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Wang, X.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y. Lactic Acid Fermentation from Food Waste with Indigenous Microbiota: Effects of pH, Temperature and High OLR. Waste Manag. 2016, 52, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Wang, X.C.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y. Effect of pH on Lactic Acid Production from Acidogenic Fermentation of Food Waste with Different Types of Inocula. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 224, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Hua, J.; Kang, T.; Meng, B.; Yue, L.; Dong, H.; Li, H.; Zhou, J. Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron Improved Lactic Acid Degradation to Produce Methane through Anaerobic Digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 317, 124013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouallagui, H.; Touhami, Y.; Ben Cheikh, R.; Hamdi, M. Bioreactor Performance in Anaerobic Digestion of Fruit and Vegetable Wastes. Process Biochem. 2005, 40, 989–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, W.; Peng, Y.; Ren, N.; Li, B. Volatile Fatty Acids (VFAs) Accumulation and Microbial Community Structure of Excess Sludge (ES) at Different pHs. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 152, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Liu, X.; Li, C.; Long, S.; Luo, L.; Guo, Y.; Wang, D. Uncovering the Mechanisms of How Capsaicin Affects Short-Chain Fatty Acid Production during Food Waste Valorization. ACS EST Eng. 2023, 3, 1986–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).