Assessment of Glyphosate Runoff Pollution in Water Samples from Agricultural, Touristic and Ecologically Protected Areas
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
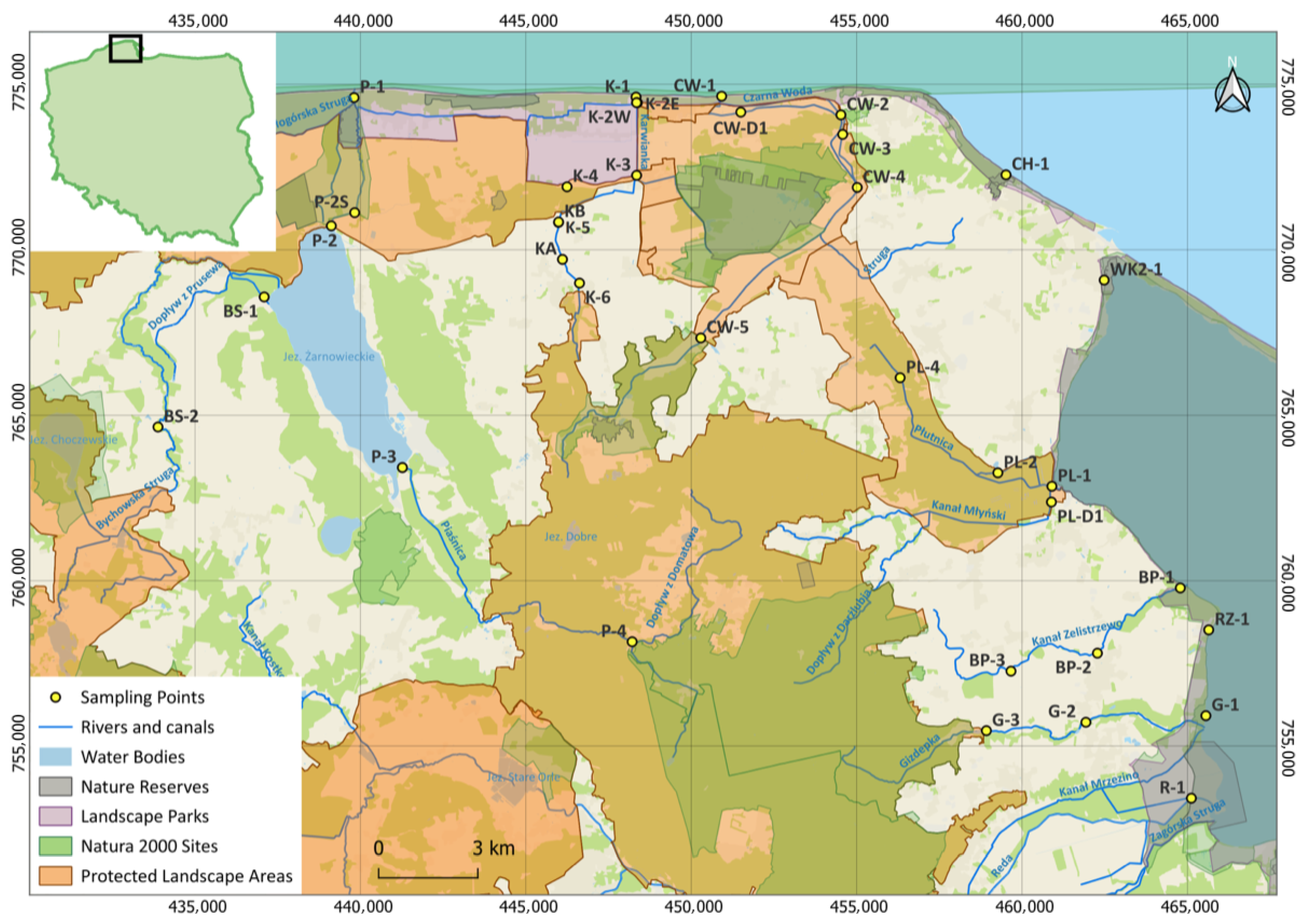
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Analytical Procedure
2.3.1. Sample Preparation
2.3.2. Ultrahigh-Performance Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry
2.4. Quality Assurance/Quality Control (QA/QC)
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Human Risk Assessment
2.7. Evaluation of the Ecotoxicological Risk
3. Results and Discussion
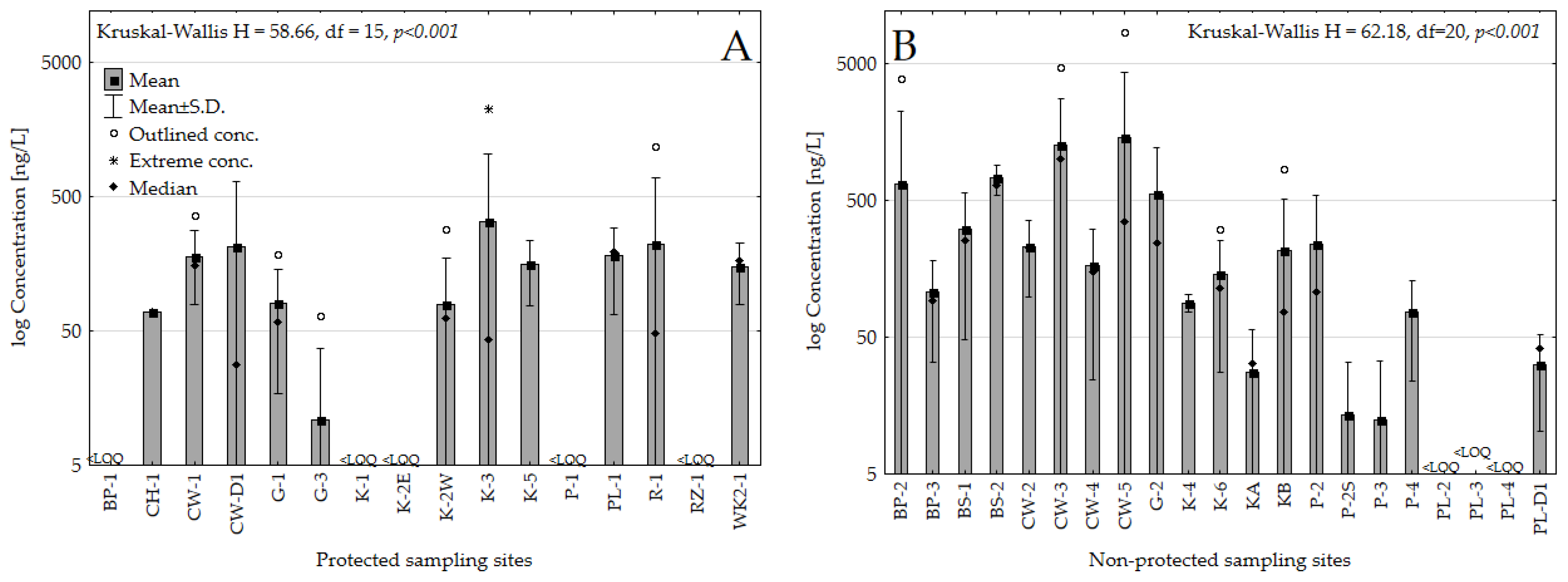
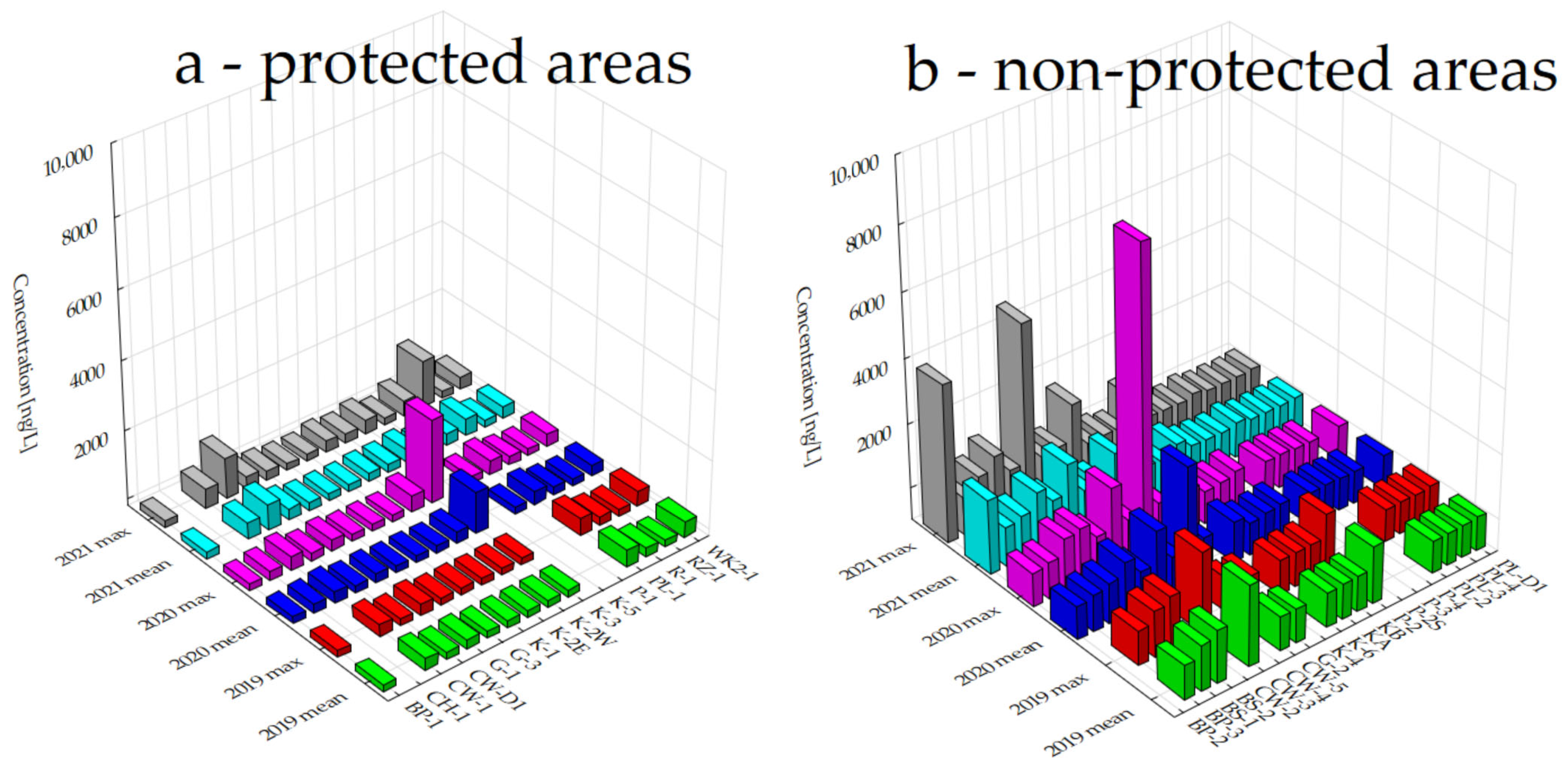
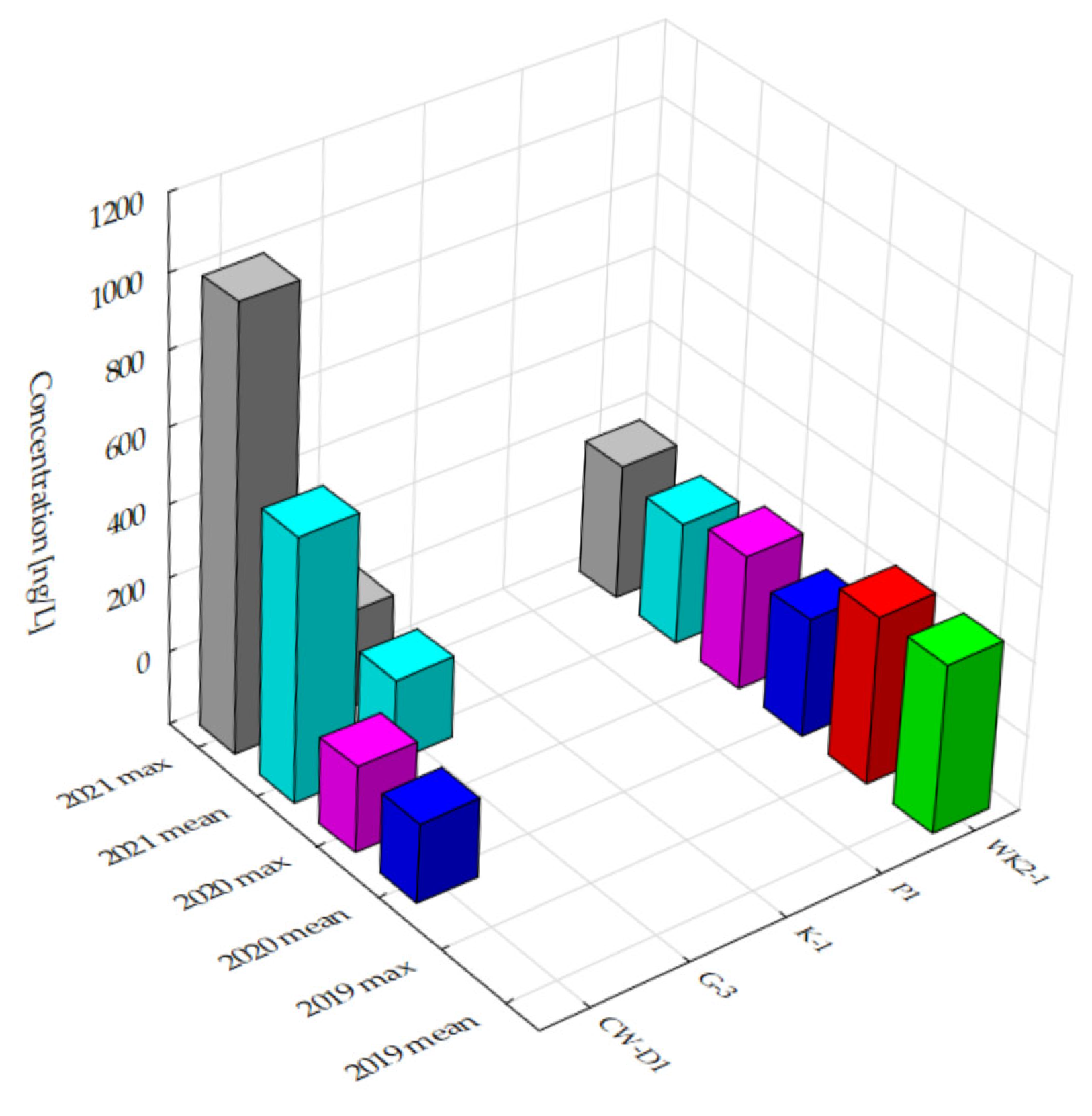
3.1. Assessing Glyphosate Trends in Water: A Comparative Analysis of Protected and Unprotected Areas (2019–2021)
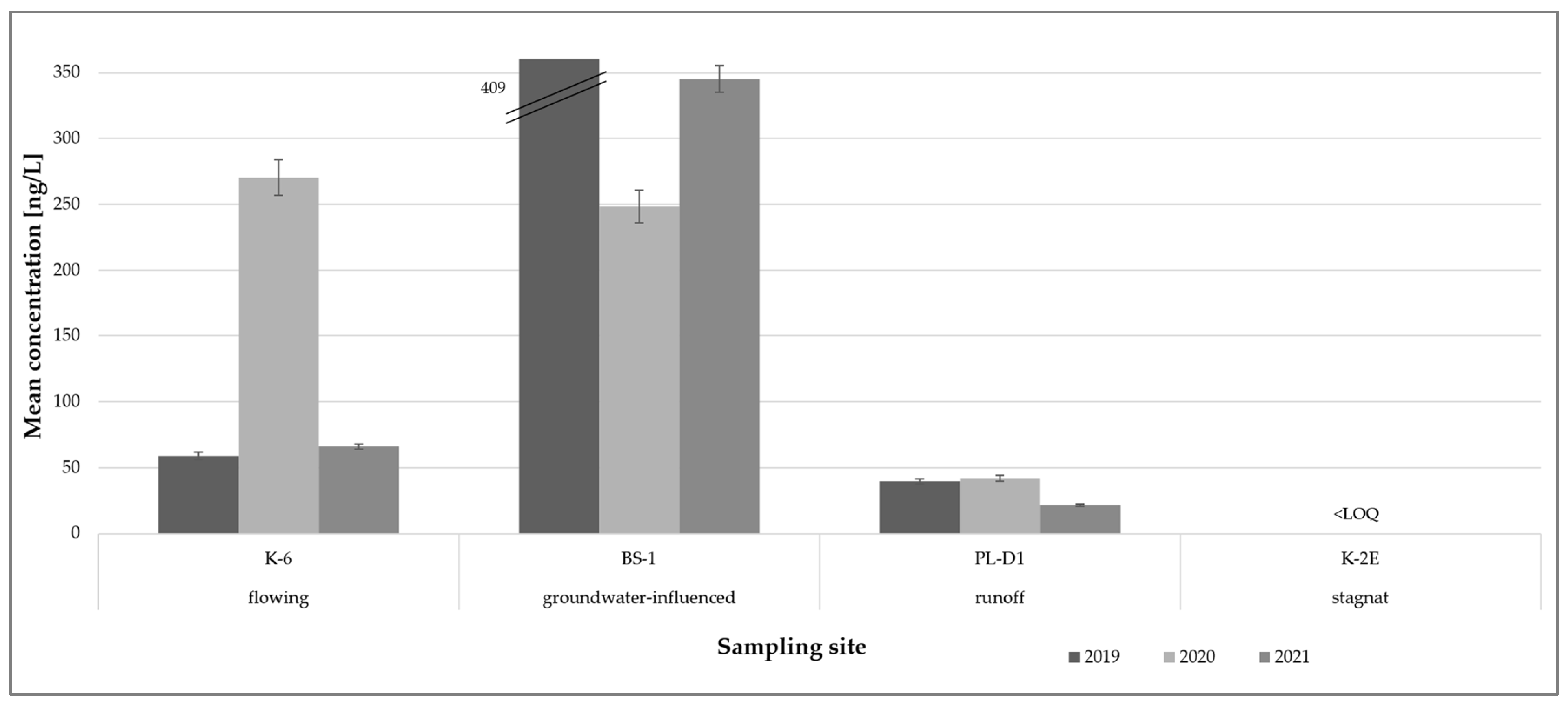
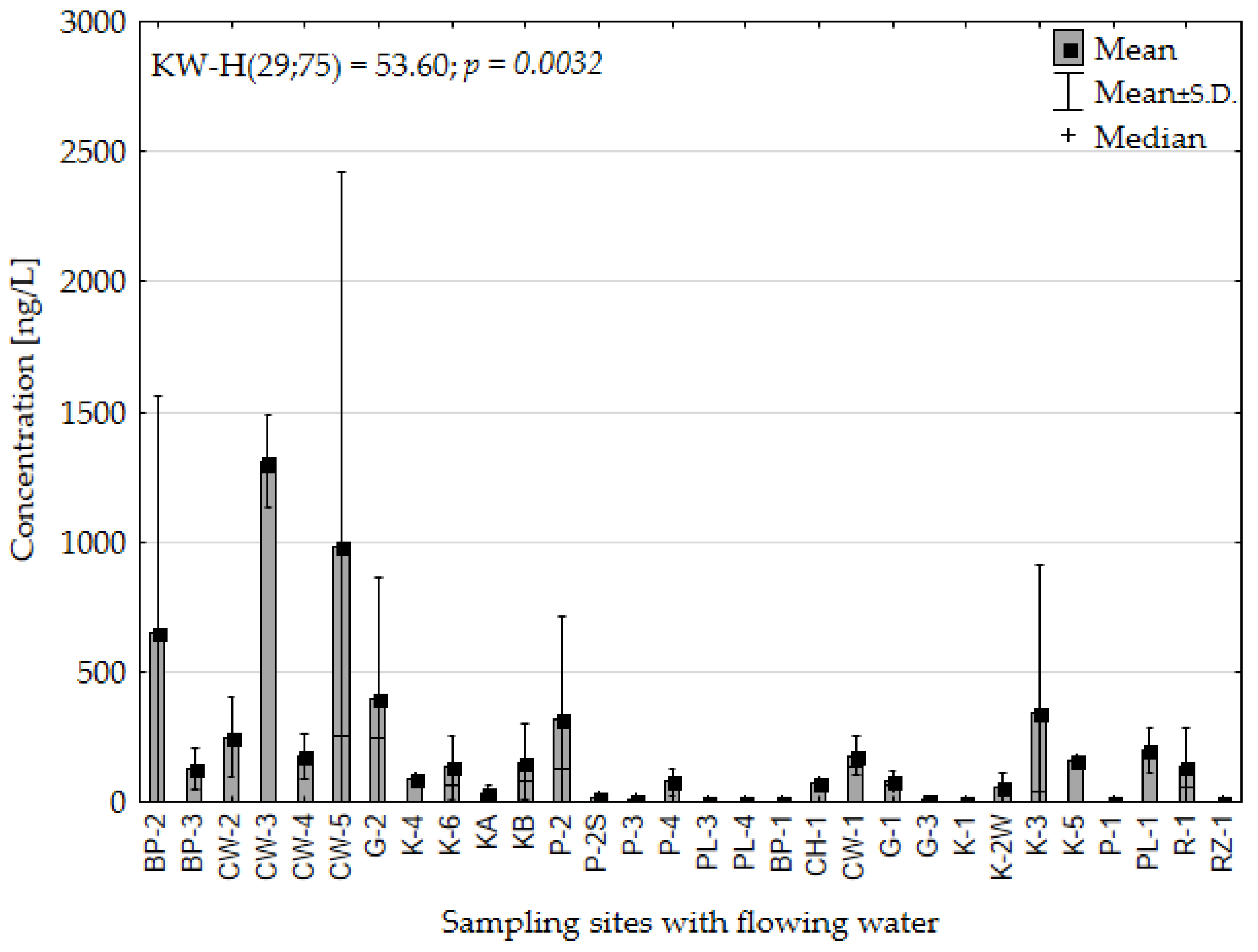
3.2. Impact of Anthropogenic Activities on Glyphosate Levels in Various Types of Water Bodies
3.3. Analysis of Glyphosate Concentrations in Water at High-Tourism Areas
3.4. Risk Assessment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References and Note
- Clapp, J. Explaining Growing Glyphosate Use: The Political Economy of Herbicide-Dependent Agriculture. Glob. Environ. Change 2021, 67, 102239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piovesana, S.; Aita, S.E.; Cavaliere, C.; Cerrato, A.; Laganà, A.; Montone, C.M.; Taglioni, E.; Capriotti, A.L. Validation of a Global Method for the Simultaneous Analysis of Polar and Non-Polar Pesticides by Online Extraction and LC-MS/MS. Anal. Chim. Acta 2024, 1329, 343231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masci, M.; Caproni, R.; Nevigato, T. Chromatographic Methods for the Determination of Glyphosate in Cereals Together with a Discussion of Its Occurrence, Accumulation, Fate, Degradation, and Regulatory Status. Methods Protoc. 2024, 7, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez, F.; Arena, M.; Auteri, D.; Binaglia, M.; Castoldi, A.F.; Chiusolo, A.; Crivellente, F.; Egsmose, M.; Fait, G.; Ferilli, F.; et al. Peer Review of the Pesticide Risk Assessment of the Active Substance Glyphosate. EFSA J. 2023, 21, e08164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, J.P.; Bleak, T.C.; Calaf, G.M. Glyphosate and the Key Characteristics of an Endocrine Disruptor: A Review. Chemosphere 2021, 270, 128619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benbrook, C.M. Trends in Glyphosate Herbicide Use in the United States and Globally. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2016, 28, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baird, D.D. Introduction of a New Broad Spectrum Post Emergence Herbicide Class with Utility for Herbaceous Perennial Weed Control. In Proceedings of the 26th North Central Weed Conference, Kansas City, MO, USA, 7–9 December 1971; North Central Weed Science Society: Westminster, CO, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Peruzzo, P.J.; Porta, A.A.; Ronco, A.E. Levels of Glyphosate in Surface Waters, Sediments and Soils Associated with Direct Sowing Soybean Cultivation in North Pampasic Region of Argentina. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 156, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrante, M.; Rapisarda, P.; Grasso, A.; Favara, C.; Oliveri Conti, G. Glyphosate and Environmental Toxicity with “One Health” Approach, a Review. Environ. Res. 2023, 235, 116678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparicio, V.C.; De Gerónimo, E.; Marino, D.; Primost, J.; Carriquiriborde, P.; Costa, J.L. Environmental Fate of Glyphosate and Aminomethylphosphonic Acid in Surface Waters and Soil of Agricultural Basins. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 1866–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suciu, N.; Russo, E.; Calliera, M.; Luciani, G.P.; Trevisan, M.; Capri, E. Glyphosate, Glufosinate Ammonium, and AMPA Occurrences and Sources in Groundwater of Hilly Vineyards. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 866, 161171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Kumar, V.; Gill, J.P.K.; Datta, S.; Singh, S.; Dhaka, V.; Kapoor, D.; Wani, A.B.; Dhanjal, D.S.; Kumar, M.; et al. Herbicide Glyphosate: Toxicity and Microbial Degradation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daouk, S.; de Alencastro, L.F.; Pfeifer, H.R. The Herbicide Glyphosate and Its Metabolite AMPA in the Lavaux Vineyard Area, Western Switzerland: Proof of Widespread Export to Surface Waters. Part II: The Role of Infiltration and Surface Runoff. J. Environ. Sci. Health-Part B Pestic. Food Contam. Agric. Wastes 2013, 48, 725–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunarathna, S.; Gunawardana, B.; Jayaweera, M.; Manatunge, J.; Zoysa, K. Glyphosate and AMPA of Agricultural Soil, Surface Water, Groundwater and Sediments in Areas Prevalent with Chronic Kidney Disease of Unknown Etiology, Sri Lanka. J. Environ. Sci. Health-Part B Pestic. Food Contam. Agric. Wastes 2018, 53, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, W.; Li, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Song, W.; Yao, T.; Cheng, M.; Wang, W.; Hou, R. Establishment of a HPLC-MS/MS Detection Method for Glyphosate, Glufosinate-Ammonium, and Aminomethyl Phosphoric Acid in Tea and Its Use for Risk Exposure Assessment. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 7969–7978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillezeau, C.; Van Gerwen, M.; Shaffer, R.M.; Rana, I.; Zhang, L.; Sheppard, L.; Taioli, E. The Evidence of Human Exposure to Glyphosate: A Review. Environ. Health A Glob. Access Sci. Source 2019, 18, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peillex, C.; Pelletier, M. The Impact and Toxicity of Glyphosate and Glyphosate-Based Herbicides on Health and Immunity. J. Immunotoxicol. 2020, 17, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanissery, R.; Gairhe, B.; Kadyampakeni, D.; Batuman, O.; Alferez, F. Glyphosate: Its Environmental Persistence and Impact on Crop Health and Nutrition. Plants 2019, 8, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyva-Soto, L.A.; Balderrama-Carmona, A.P.; Moran-Palacio, E.F.; Diaz-Tenorio, L.M.; Gortares-Moroyoqui, P. Glyphosate and Aminomethylphosphonic Acid in Population of Agricultural Fields: Health Risk Assessment Overview. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2018, 16, 5127–5140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dill, G.M.; Sammons, R.D.; Feng, P.C.C.; Kohn, F.; Kretzmer, K.; Mehrsheikh, M.B.; Hohegger, J.L.; Farmer, D.W.; Haupfear, E.A. Glyphosate: Discovery, Development, Applications, and Properties. In Glyphosate Resistance in Crops and Weeds: History, Development, and Management; Nandula, V.K., Ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 1–33. [Google Scholar]
- Sivakumar, M.V.K.; Ndiang’ui, N. Climate and Land Degradation; Springer Nature: London, UK, 2019; Volume 11, ISBN 9788578110796. [Google Scholar]
- Henderson, A.M.; Gervais, J.A.; Luukinen, B.; Buhl, K.; Stone, D.; Cross, A.; Jenkins, J. Glyphosate General Fact Sheet. Available online: http://npic.orst.edu/factsheets/glyphogen.html (accessed on 2 October 2025).
- Maggi, F.; Tang, F.H.; la Cecilia, D.; McBratney, A. PEST-CHEMGRIDS, Global Gridded Maps of the Top 20 Crop-Specific Pesticide Journal Pre-Proof Journal Pre-Proof Application Rates from 2015 to 2025. Sci. Data 2019, 6, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, T.; Ito, A.; Tanimizu, M. Simultaneous and Sensitive Analysis of Glyphosate, Glufosinate, and Their Metabolites in Surface Water by HPLC-ICP-MS/MS. Anal. Sci. 2023, 39, 1047–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Matos, F.S.; de Carvalho, G.S.; Prestes, O.D.; Adaime, M.B.; Zanella, R. Simultaneous Determination of Glyphosate, AMPA and Inorganic Anions in Water Samples by Gradient Capillary Ion Chromatography. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2023, 34, 1691–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Vázquez, J.; Pérez-Mayán, L.; Fernández-Fernández, V.; Cela, R.; Rodríguez, I. Direct, Automated and Sensitive Determination of Glyphosate and Related Anionic Pesticides in Environmental Water Samples Using Solid-Phase Extraction on-Line Combined with Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2023, 1687, 463697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prezilius, A.C.M.; dos Santos, G.F.S.; Silva, L.R.G.; Barbieri, E.M.S.; Brandão, G.P.; de, Q. Ferreira, Rafael. Development of an Electroanalytical Methodology Associated with Screen-Printed Electrodes for the Determination of Glyphosate in River Waters. Ionics 2022, 28, 4035–4043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, A.; Koch, H.M.; Bury, D.; Koslitz, S.; Kolossa-Gehring, M.; Conrad, A.; Murawski, A.; McGrath, J.A.; Leahy, M.; Brüning, T.; et al. A Human Biomonitoring Study Assessing Glyphosate and Aminomethylphosphonic Acid (AMPA) Exposures among Farm and Non-Farm Families. Toxics 2022, 10, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campanale, C.; Triozzi, M.; Massarelli, C.; Uricchio, V.F. Development of a UHPLC-MS/MS Method to Enhance the Detection of Glyphosate, AMPA and Glufosinate at Sub-Microgram/L Levels in Water Samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2022, 1672, 463028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dovidauskas, S.; Okada, I.A.; dos Santos, F.R. Validation of a Simple Ion Chromatography Method for Simultaneous Determination of Glyphosate, Aminomethylphosphonic Acid and Ions of Public Health Concern in Water Intended for Human Consumption. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1632, 461603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojelade, B.S.; Durowoju, O.S.; Adesoye, P.O.; Gibb, S.W.; Ekosse, G.I. Review of Glyphosate-Based Herbicide and Aminomethylphosphonic Acid (AMPA): Environmental and Health Impacts. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimani, M.; Pérez-Padilla, V.; Valderrey, V.; Gawlitza, K.; Rurack, K. Red-Emitting Polymerizable Guanidinium Dyes as Fluorescent Probes in Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Glyphosate Detection. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarazona, J.V.; Court-Marques, D.; Tiramani, M.; Reich, H.; Pfeil, R.; Istace, F.; Crivellente, F. Glyphosate Toxicity and Carcinogenicity: A Review of the Scientific Basis of the European Union Assessment and Its Differences with IARC. Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 91, 2723–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IARC; WHO. IARC Monographs Volume 112: Evaluation of Five Organophosphate Insecticides and Herbicides; IARC Press: Lyon, France, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ulrich, J.C.; Ferguson, P.L. Development of a Sensitive Direct Injection LC-MS/MS Method for the Detection of Glyphosate and Aminomethylphosphonic Acid (AMPA) in Hard Waters. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 3763–3774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasnier, C.; Dumont, C.; Benachour, N.; Clair, E.; Chagnon, M.-C.; Séralini, G.-E. Glyphosate-Based Herbicides Are Toxic and Endocrine Disruptors in Human Cell Lines. Toxicology 2009, 262, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaufan, G.; Coalova, I.; del Carmen Ríos de Molina, M. Glyphosate Commercial Formulation Causes Cytotoxicity, Oxidative Effects, and Apoptosis on Human Cells: Differences with Its Active Ingredient. Int. J. Toxicol. 2014, 33, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattani, D.; de Liz Oliveira Cavalli, V.L.; Heinz Rieg, C.E.; Domingues, J.T.; Dal-Cim, T.; Tasca, C.I.; Mena Barreto Silva, F.R.; Zamoner, A. Mechanisms Underlying the Neurotoxicity Induced by Glyphosate-Based Herbicide in Immature Rat Hippocampus: Involvement of Glutamate Excitotoxicity. Toxicology 2014, 320, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Li, X. Alteration in the Cytokine Levels and Histopathological Damage in Common Carp Induced by Glyphosate. Chemosphere 2015, 128, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samsel, A.; Seneff, S. Glyphosate, Pathways to Modern Diseases III: Manganese, Neurological Diseases, and Associated Pathologies. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2015, 6, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayasumana, C.; Gunatilake, S.; Senanayake, P. Glyphosate, Hard Water and Nephrotoxic Metals: Are They the Culprits behind the Epidemic of Chronic Kidney Disease of Unknown Etiology in Sri Lanka? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 2125–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbera, M.; Hidalgo, M.; Salvadó, V.; Wieczorek, P.P. Determination of Glyphosate and Aminomethylphosphonic Acid in Natural Water Using the Capillary Electrophoresis Combined with Enrichment Step. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 540, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qiao, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, Y. Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Soils and Vegetables from Wastewater Irrigated Area, Beijing-Tianjin City Cluster, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 24, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, F.; Al-Sisi, M.; Ghanem, K. Occurrence, Human Health, and Ecotoxicological Risk Assessment of Pesticides in Surface Waters of the River Nile’s Rosetta Branch, Egypt. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 55511–55525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.S.; Winston, R.J.; Tirpak, R.A.; Wituszynski, D.M.; Boening, K.M.; Martin, J.F. The Seasonality of Nutrients and Sediment in Residential Stormwater Runoff: Implications for Nutrient-Sensitive Waters. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 276, 111248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliko, V.; Multisanti, C.R.; Turani, B.; Faggio, C. Get Rid of Marine Pollution: Bioremediation an Innovative, Attractive, and Successful Cleaning Strategy. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupi, L.; Bedmar, F.; Puricelli, M.; Marino, D.; Aparicio, V.C.; Wunderlin, D.; Miglioranza, K.S.B. Glyphosate Runoff and Its Occurrence in Rainwater and Subsurface Soil in the Nearby Area of Agricultural Fields in Argentina. Chemosphere 2019, 225, 906–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keesstra, S.D.; Rodrigo-Comino, J.; Novara, A.; Giménez-Morera, A.; Pulido, M.; Di Prima, S.; Cerdà, A. Straw Mulch as a Sustainable Solution to Decrease Runoff and Erosion in Glyphosate-Treated Clementine Plantations in Eastern Spain. An Assessment Using Rainfall Simulation Experiments. Catena 2019, 174, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gendy, K.; Mosallam, E.; Ahmed, N.; Aly, N. Determination of Glyphosate Residues in Egyptian Soil Samples. Anal. Biochem. 2018, 557, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, L.; Kumari, R.; Kuma, A.; Tunio, I.A. Claudio Sassanelli Water Quality Assessment and Monitoring in Pakistan: A Comprehensive Review. Sustainability 2023, 15, 38. [Google Scholar]
- Bogalecka, M. An Attempt to Assess Nutrients Emissions from Fertilisers on Eutrophication in the Baltic Sea Coastal Zone. In Maritime Security Yearbook; Polish Naval Academy: Gdynia, Poland, 2024; pp. 343–388. [Google Scholar]
- Nawaz, A.; Razpotnik, A.; Rouimi, P.; De Sousa, G.; Cravedi, J.P.; Rahmani, R. Cellular Impact of Combinations of Endosulfan, Atrazine, and Chlorpyrifos on Human Primary Hepatocytes and HepaRG Cells after Short and Chronic Exposures. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2014, 30, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.P.; Lu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Li, Q. GSH-AuNCs/Cu2+ as Selective Fluorescent Sensing Probe for Sensitive Determination of Glyphosate in the Environment. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2024, 159, 111842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- In, S.; Ana, L.; Em, S. Environmental Risk Assessment of Glyphosate and Aminomethylphosphonic Acid (AMPA) in Portuguese Groundwater Ecosystems. Environments 2024, 11, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, C.; Lopes, I. Glyphosate and Roundup® Ready Effects in Hydra Viridissima: New Data in an Old Issue. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, P.; Köck-Schulmeyer, M.; Alvarenga, P.; Ledo, L.; Barbosa, I.R.; de Alda, M.L.; Barceló, D. Risk Assessment of Pesticides Detected in Surface Water of the Alqueva Reservoir (Guadiana Basin, Southern of Portugal). Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 488–489, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brovini, E.M.; Cardoso, S.J.; Quadra, G.R.; Vilas-boas, J.A.; Paranaíba, J.R.; Pereira, R.D.O.; Mendonça, R.F. Glyphosate Concentrations in Global Freshwaters: Are Aquatic Organisms at Risk? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 60635–60648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2023/2660 of 28 November 2023 Renewing the Approval of the Active Substance Glyphosate in Accordance with Regulation (EC). 2023; pp. 23–29. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg_impl/2023/2660/oj/eng (accessed on 2 October 2025).
- European Commission. Directive (EU) 2020/2184 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 December 2020 on the Quality of Water Intended for Human Consumption (Recast). 2020; pp. 1–62. Available online: https://www.legislation.gov.uk/eudr/2020/2184 (accessed on 2 October 2025).
- European Commission. Directive 2009/128/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 21 October 2009 Establishing a Framework for Community Action to Achieve the Sustainable Use of Pesticides. Off. J. Eur. Union 2009, L 309, 71–86.
- Wolfram, J.; Bub, S.; Petschick, L.L.; Schemmer, A.; Stehle, S.; Schulz, R. Pesticide Occurrence in Protected Surfacewaters in Nature Conservation Areas of Germany. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 160074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission. European Commission Regulation on the Sustainable Use of Plant Protection Products-EC 2021/2115-COM/2022/305 Final. 2021. Available online: https://Bit.Ly/3RpGk7q (accessed on 30 August 2025).
- Bączkowska, E.; Agnieszka, K.; Ronda, O.; Jankowska, K.; Bray, R.; Płóciennik, B.; Polkowska, Z. Microbial and Chemical Quality Assessment of the Small Rivers Entering the South Baltic. Part I: Case Study on the Watercourses in the Puck Bay Catchment Area. Arch. Environ. Prot. 2021, 47, 55–73. [Google Scholar]
- Kramkiel, J.-D. Impact of Tourism on Mediterranean Marine and Coastal Biodiversity; Nimes, France, 2003. Available online: https://www.rac-spa.org/sites/default/files/doc_spabio/feng.pdf (accessed on 2 October 2025).
- Spenceley, A.; Mccool, S.; Newsome, D.; Báez, A.; James, R.; Blye, C.; Bricker, K.; Cahyadi, H.S.; Halpenny, E.; Hvenegaard, G.; et al. Tourism in Protected and Conserved Areas Amid the COVID-19 Pandemic. Parks 2021, 27, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radosław, W.; Rucińska, M.; Rudowski, S.; Sitkiewicz, P. Hel Peninsula—A Distinctive Spit on the Polish Baltic Coast. In Landscapes and Landforms of Poland; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 741–747. [Google Scholar]
- Bay, P. Characteristics of Morphodynamic Conditions in the Shallows of By. Oceanol. Hydrobiol. Stud. 2021, 50, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajewska, Z.; Fac-Beneda, J. Transport of Biogenic Substances in Water–Courses of Coastal Landscape Park. J. Elem. 2016, 21, 413–423. [Google Scholar]
- Bączkowska, E.; Kalinowska, A.; Ronda, O.; Jankowska, K.; Bray, R.; Płóciennik, B.; Polkowska, Ż. Microbial and Chemical Quality Assessment of the Small Rivers Entering the South Baltic. Part II: Case Study on the Watercourses in the Puck Bay Catchment Area. Arch. Environ. Prot. 2022, 48, 58–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Council Directive 92/43/EEC of 21 May 1992 on the Conservation of Natural Habitats and of Wild Fauna and Flora; European Community Environmental Law: EU, 1992. Available online: https://www.legislation.gov.uk/eudr/1992/43/introduction (accessed on 2 October 2025).
- Council of Ministers (1988). Orders of the Minister of Environmental Protection and Natural Resources of 17 November 1988 (Official Gazette No. 32, item 292) and 10 May 1989 (Official Gazette No. 17, item 119). (In Polish, archival source)
- Wojciechowska, E.; Pietrzak, S.; Matej-Łukowicz, K.; Nawrot, N.; Zima, P.; Kalinowska, D.; Wielgat, P.; Obarska-Pempkowiak, H.; Gajewska, M.; Dembska, G.; et al. Nutrient Loss from Three Small-Size Watersheds in the Southern Baltic Sea in Relation to Agricultural Practices and Policy. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 252, 109637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaborska, A.; Siedlewicz, G.; Szymczycha, B.; Lidia Dzierzbicka-Głowacka, K.P. Legacy and Emerging Pollutants in the Gulf of Gdańsk (Southern Baltic Sea)–Loads and Distribution Revisited. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 139, 238–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkowski, R. Bezpiecze Stwo i Ryzyko w Sporcie i Turystyce. Wprowadzenie 2014, 4, 165–175. [Google Scholar]
- Garcı, M.; Berry, P.; Palomo, I.; Go, E.; Carlos, I.I.; David, M.; Martı, B. What Can Conservation Strategies Learn from the Ecosystem Services Approach ? Insights from Ecosystem Assessments in Two Spanish Protected Areas. Biodivers. Conserv. 2018, 27, 1575–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Vega, C.; Schückel, U.; Horn, S.; Kröncke, I.; Asmus, R.; Asmus, H. How to Include Ecological Network Analysis Results in Management? A Case Study of Three Tidal Basins of the Wadden Sea, South-Eastern North Sea. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2018, 163, 401–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baloch, Q.B.; Shah, S.N.; Iqbal, N.; Asadullah, M.S.M.; Mahar, S. Asia Umar Khan Impact of Tourism Development upon Environmental Sustainability: A Suggested Framework for Sustainable Ecotourism. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 5917–5930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trstenjak, A.; Tomas Žiković, I.; Žiković, S. Making Tourism More Sustainable: Empirical Evidence from EU Member Countries; Springer: Dordrecht/Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2025; Volume 27, ISBN 0123456789. [Google Scholar]
- Commission Decision 2002/657/EC of 12 August 2002 implementing Council Directive 96/23/EC concerning the Performance of Analytical Methods and the Interpretation of Results (Notified under Document Number C(2002) 3044). Official Journal of the European Communities, L 221, 17 August 2002, pp. 8–36. Brussels: European Commission. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dec/2002/657/oj (accessed on 2 October 2025).
- Sulej-Suchomska, A.M.; Klupczynska, A.; Dereziński, P.; Matysiak, J.; Przybyłowski, P.; Kokot, Z.J. Urban Wastewater Analysis as an Effective Tool for Monitoring Illegal Drugs, Including New Psychoactive Substances, in the Eastern European Region. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA. Guidance Manual for Assessing Human Health Risks from Chemically Contaminated, Fish and Shellfish, 1989; EPA-503/8-89-002. Available online: https://nepis.epa.gov/Exe/ZyNET.exe/40001CR2.TXT?ZyActionD=ZyDocument&Client=EPA&Index=1986+Thru+1990&Docs=&Query=&Time=&EndTime=&SearchMethod=1&TocRestrict=n&Toc=&TocEntry=&QField=&QFieldYear=&QFieldMonth=&QFieldDay=&IntQFieldOp=0&ExtQFieldOp=0&XmlQuery=&File=D%3A%5Czyfiles%5CIndex%20Data%5C86thru90%5CTxt%5C00000017%5C40001CR2.txt&User=ANONYMOUS&Password=anonymous&SortMethod=h%7C-&MaximumDocuments=1&FuzzyDegree=0&ImageQuality=r75g8/r75g8/x150y150g16/i425&Display=hpfr&DefSeekPage=x&SearchBack=ZyActionL&Back=ZyActionS&BackDesc=Results%20page&MaximumPages=1&ZyEntry=1&SeekPage=x&ZyPURL (accessed on 2 October 2025).
- USEPA. Regional Screening Levels (RSLs)–Generic Tables. 2019. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/risk/regional-screening-levels-rsls-generic-tables (accessed on 2 October 2025).
- European Commission; Joint Research Centre (JRC); European Chemicals Bureau (ECB). Part II: Environmental Risk Assessment. EUR 20418 EN/2. In Technical Guidance Document on Risk Assessment in support of Commission Directive 93/67/EEC on Risk Assessment for New Notified Substances, Commission Regulation (EC) No 1488/94 on Risk Assessment for Existing Substances, and Directive 98/8/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council Concerning the Placing of Biocidal Products on the Market; Office for Official Publications of the European Communities: Luxembourg, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- EPA. ECOTOX Database. Available online: https://cfpub.epa.gov/ecotox/ (accessed on 30 October 2025).
- European Commission; Joint Research Centre (JRC); European Chemicals Bureau (ECB). Part IV: Emission Scenario Documents. EUR 20418 EN/4. In Technical Guidance Document on Risk Assessment in support of Commission Directive 93/67/EEC on Risk Assessment for New Notified Substances, Commission Regulation (EC) No 1488/94 on Risk Assessment for Existing Substances, and Directive 98/8/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council Concerning the Placing of Biocidal Products on the Market; Office for Official Publications of the European Communities: Luxembourg, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Meshkini, S.; Rahimi-Arnaei, M.; Tafi, A.A. The Acute and Chronic Effect of Roundup Herbicide on Histopathology and Enzymatic Antioxidant System of Oncorhynchus Mykiss. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 6847–6856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, M.; Drost, W.; Germer, S.; Juffernholz, T.; Hahn, S. Evaluation of Acute-to-chronic Ratiosof Fish and Daphnia to Predict Acceptable No-effect Levels. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2016, 28, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, H.J.; Chen, C.Y. Toxicity Assessment of Pesticides to Pseudokirchneriella Subcapitata under Air-Tight Test Environment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 131, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrodin, Y.; Boillot, C.; Angerville, R.; Donguy, G.; Emmanuel, E. Ecological Risk Assessment of Urban and Industrial Systems: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 5162–5176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzierzbicka-Glowacka, L.A.; Janecki, M.; Dybowski, D.; Szymczycha, B. A New Approach for Investigating the Impact of Pesticides and Nutrient Flux from Agricultural Holdings and Land-Use Structures on Baltic Sea Coastal Waters. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2019, 28, 2531–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, W.C.; Aggarwal, P.K.; Aureli, A.; Bokuniewicz, H.; Cable, J.E.; Charette, M.A.; Kontar, E.; Krupa, S.; Kulkarni, K.M.; Loveless, A.; et al. Quantifying Submarine Groundwater Discharge in the Coastal Zone via Multiple Methods. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 367, 498–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarah, M.; Elliott, D.D.V. A Regional Assessment of Chemicals of Concern in Surface Waters of Four Midwestern United States National Parks. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 1726–1735. [Google Scholar]
- Feltracco, M.; Barbaro, E.; Morabito, E.; Zangrando, R.; Piazza, R.; Barbante, C.; Gambaro, A. Assessing Glyphosate in Water, Marine Particulate Matter, and Sediments in the Lagoon of Venice. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 16383–16391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montiel-León, J.M.; Munoz, G.; Vo Duy, S.; Do, D.T.; Vaudreuil, M.A.; Goeury, K.; Guillemette, F.; Amyot, M.; Sauvé, S. Widespread Occurrence and Spatial Distribution of Glyphosate, Atrazine, and Neonicotinoids Pesticides in the St. Lawrence and Tributary Rivers. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 250, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Stempvoort, D.R.; Roy, J.W.; Brown, S.J.; Bickerton, G. Residues of the Herbicide Glyphosate in Riparian Groundwater in Urban Catchments. Chemosphere 2014, 95, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masiol, M.; Giannì, B.; Prete, M. Herbicides in River Water across the Northeastern Italy: Occurrence and Spatial Patterns of Glyphosate, Aminomethylphosphonic Acid, and Glufosinate Ammonium. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 24368–24378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medalie, L.; Baker, N.T.; Shoda, M.E.; Stone, W.W.; Meyer, M.T.; Stets, E.G.; Wilson, M. Science of the Total Environment In Fl Uence of Land Use and Region on Glyphosate and Aminomethylphosphonic Acid in Streams in the USA. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 707, 136008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, G.; Háhn, J.; Szoboszlay, S.; Harkai, P.; Farkas, M.; Radó, J.; Göbölös, B. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Multi-Pesticide Residues in the Largest Central European Shallow Lake, Lake Balaton, and Its Sub-Catchment Area. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2022, 34, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro Berman, M.; Marino, D.J.G.; Quiroga, M.V.; Zagarese, H. Occurrence and Levels of Glyphosate and AMPA in Shallow Lakes from the Pampean and Patagonian Regions of Argentina. Chemosphere 2018, 200, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Liu, L.; Liu, X.; Lu, J.; Hao, H.; Yuan, H.; Zhou, H. The Organic Contamination Survey and Health Risk Assessment of 16 Source Water Reservoirs in Haihe River Basin. Water Sci. Technol. 2012, 65, 998–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadakis, E.N.; Vryzas, Z.; Kotopoulou, A.; Kintzikoglou, K.; Makris, K.C.; Papadopoulou-Mourkidou, A. Pesticide Monitoring Survey in Rivers and Lakes of Northern Greece and Its Human and Ecotoxicological Risk Assessment. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 116, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, S.; Chen, B.; Qiu, X.; Chen, M.; Ma, Z.; Yu, X. Distribution and Risk Assessment of 82 Pesticides in Jiulong River and Estuary in South China. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 1177–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, I.B.; Boëchat, I.G.; Fernandes, M.D.; Monteiro, J.A.F.; Rivaroli, L.; Gücker, B. Glyphosate Pollution of Surface Runoff, Stream Water, and Drinking Water Resources in Southeast Brazil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 27030–27040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Materials and Supplies | |
|---|---|
| Reagents and chemicals | Glyphosate-2-13C (part number 606502—100 mg, 99 atom% 13C), Sigma-Aldrich (Seelze, Germany); Glyphosate (part number 45521—250 mg), Sigma-Aldrich (Seelze, Germany); |
| Standard solutions | |
| Solvents | Methanol (part number 1.06035.2500), Sigma-Aldrich (Seelze, Germany); Deionized water Milli-Q (Millipore Corporation, Burlington, MA, USA); |
| Other chemical reagents | Formic acid (part number 33015-1L-M), Sigma-Aldrich (Seelze, Germany); Agilent InfinityLab deactivator additive (part number 5191-4506), Agilent Technologies (Palo Alto, CA, USA); |
| Equipment | Automatic pipettes 10 μL, 100 μL, 1000 μL, 10 mL (Brand, Wertheim, Germany); Glass syringes with a capacity of 5 μL, 100 μL (Hamilton, Reno, NV, USA); 0.2 μm polyethersulfone (PES) filters (part number 5190-5096), Agilent Technologies (Palo Alto, CA, USA); Polypropylene (PP) tubes (15 mL, 1.5 mL), Sigma-Aldrich (Seelze, Germany). |
| No. | Sampling Code | Sampling Site Description | Sampling Site Cordinates | Water Type | Protection Status | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | E | NR 1 | CLP 2 | N2000 3 | ||||
| 1 | BP-1 | Błądzikowski Stream, the mouth | 54.70043 | 18.45344 | FW 4 | no | yes | yes |
| 2 | BP-2 | Błądzikowski Stream, Pucka Street, Żelistrzewo | 54.68251 | 18.41479 | FW | no | no | no |
| 3 | BP-3 | Błądzikowski Stream, Voivodeship Road 216, Celbów | 54.67743 | 18.37433 | FW | no | no | no |
| 4 | BS-1 | Bychowska Struga Stream, Brzyno | 54.77681 | 18.02164 | SGI 5 | no | no | no |
| 5 | BS-2 | Bychowska Struga, Bychowo | 54.74106 | 17.97260 | SGI | no | no | no |
| 6 | CH-1 | Chłapowo, the mouth in Chłapowo Valley (Rudnik) | 54.81232 | 18.3699 | FW | no | yes | yes |
| 7 | CW-1 | Czarna Wda River, the mouth in Ostrowo | 54.83291 | 18.23568 | FW | no | yes | yes |
| 8 | CW-2 | Czarna Wda River, downstream of the WWTP, Jastrzębia Góra | 54.82818 | 18.29193 | FW | no | no | no |
| 9 | CW-3 | Czarna Wda River, upstream of the WWTP in Jastrzębia Góra | 54.82288 | 18.29285 | FW | no | no | no |
| 10 | CW-4 | Czarna Wda River, Czarny Młyn | 54.80850 | 18.29994 | FW | no | no | no |
| 11 | CW-5 | Czarna Wda River, Voivodeship Road 213 (DW213), Kłanino | 54.76714 | 18.22714 | FW | no | no | no |
| 12 | CW-D1 | Czarna Wda, Plażowa Street, Ostrowo (tributary of the old riverbed) | 54.82864 | 18.24479 | RW 6 | no | yes | yes |
| 13 | G-1 | Gizdepka River, mouth in Osłonino | 54.66576 | 18.46589 | FW | no | yes | yes |
| 14 | G-2 | Gizdepka Stream, Pucka Street, Smolno | 54.66371 | 18.40966 | FW | no | no | no |
| 15 | G-3 | Gizdepka Stream, Morska Street, Osłonino | 54.66119 | 18.36304 | FW | no | yes | yes |
| 16 | K-1 | Karwianka, the mouth in Karwia | 54.83242 | 18.19540 | FW | no | yes | yes |
| 17 | K-2E | Karwianka, weir (upstream of the mouth) | 54.83089 | 18.19604 | SW 7 | no | yes | |
| 18 | K-2W | Karwianka, weir (upstream of the mouth) | 54.83091 | 18.19567 | SW | no | yes | yes |
| 19 | K-3 | Karwianka Stream, Plażowa Street, Karwieńskie Błoto Pierwsze | 54.81115 | 18.19608 | FW | no | yes | yes |
| 20 | K-4 | Karwianka Stream, Żwirowa Street, | 54.80781 | 18.16340 | FW | no | no | no |
| 21 | K-5 | Karwianka Stream, Parszczyce | 54.79811 | 18.15959 | FW | no | yes | yes |
| 22 | K-6 | Karwianka River, Krokowa (Voivodeship Road 213, upstream of the Krokowa WWTP) | 54.78168 | 18.16982 | FW | no | no | no |
| 23 | KA | Karwianka River, downstream of the WWTP | 54.78807 | 18.16167 | FW | no | no | no |
| 24 | KB | Karwianka River, bridge upstream of the WWTP, Parszczyce–Łętowice | 54.798214 | 18.159638 | FW | no | no | no |
| 25 | P-1 | Piaśnica River, Dębki, Bałtycka Street, the mouth | 54.83132 | 18.06261 | FW | no | yes | yes |
| 26 | P-2S | Piaśnica River, Dmuchowo | 54.80006 | 18.06367 | FW | no | no | no |
| 27 | P-3 | Piaśnica River, the mouth into Lake Żarnowieckie, Kartoszyno | 54.73095 | 18.08767 | FW | no | no | no |
| 28 | P-4 | Piaśnica River, Wielka Piaśnica | 54.68437 | 18.19650 | FW | no | no | no |
| 29 | PL-1 | Płutnica River, upstream of the mouth, Voivodeship Road 216, Puck | 54.72777 | 18.39276 | FW | no | yes | yes |
| 30 | PL-2 | Płutnica River, Gnieżdżewo | 54.73130 | 18.36733 | SGI | no | no | no |
| 31 | PL-3 | Płutnica River (confluence with Kanał Młyński) | 54.73095 | 18.08767 | FW | no | no | no |
| 32 | PL-4 | Płutnica River (between Werblinia and Łebcz) | 54.75690 | 18.32101 | FW | no | no | no |
| 33 | PL-D1 | Płutnica River, Voivodeship Road 216, Puck (field tributary) | 54.72349 | 18.39261 | RW | no | no | no |
| 34 | R-1 | Reda River, upstream of the mouth | 54.64330 | 18.45938 | FW | yes | yes | yes |
| 35 | RZ-1 | The Rzucewo Stream, the mouth | 54.68910 | 18.46691 | FW | no | yes | yes |
| 36 | WK2-1 | Władysławowo, Channel 2 (outlet to the Bay) | 54.78394 | 18.41651 | RW | no | yes | yes |
| Sample Type | N | Mean | Median | Minimum | Maximum | S.D. 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| all | 197 | 258 | 50.8 | <LOQ | 8406 | 790 |
| BP-1 | 6 | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | - |
| BP-2 | 6 | 653 | <LOQ | <LOQ | 3882 | 1582 |
| BP-3 | 4 | 107 | 91.1 | 41.9 | 203 | 73.9 |
| BS-1 | 6 | 307 | 253 | 66.4 | 605 | 260 |
| BS-2 | 5 | 720 | 636 | 612 | 1028 | 175 |
| CH-1 | 1 | 68.3 | 68.3 | 68.3 | 68.3 | - |
| CW-1 | 6 | 178 | 153 | 94.3 | 364 | 100 |
| CW-2 | 5 | 227 | 224 | 92.6 | 364 | 129 |
| CW-3 | 8 | 1257 | 1001 | 68.6 | 4683 | 1503 |
| CW-4 | 5 | 165 | 150 | <LOQ | 327 | 140 |
| CW-5 | 8 | 1422 | 350 | 46.7 | 8406 | 2856 |
| CW-D1 | 5 | 211 | 27.7 | <LOQ | 996 | 439 |
| G-1 | 7 | 80.0 | 58.6 | <LOQ | 184 | 62.8 |
| G-2 | 6 | 547 | 244 | 34.4 | 1539 | 651 |
| G-3 | 6 | 10.8 | <LOQ | <LOQ | 64.8 | 26.5 |
| K-1 | 10 | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | - |
| K-2E | 8 | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | - |
| K-2W | 8 | 78.1 | 62.4 | <LOQ | 287 | 96.5 |
| K-3 | 10 | 322 | 43.0 | <LOQ | 2234 | 705 |
| K-4 | 2 | 89.0 | 88.9 | 79.6 | 98.4 | 13.3 |
| K-5 | 2 | 156 | 156 | 99.8 | 213 | 79.8 |
| K-6 | 8 | 142 | 114 | <LOQ | 304 | 114 |
| KA | 5 | 27.4 | 32.3 | <LOQ | 71.0 | 29.4 |
| KB | 7 | 215 | 76.0 | 50.8 | 849 | 293 |
| P-1 | 4 | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | - |
| P-2 | 5 | 239 | 107 | 48.4 | 772 | 303 |
| P-2S | 2 | 13.4 | 13.4 | <LOQ | 26.9 | 19.0 |
| P-3 | 3 | 12.3 | <LOQ | <LOQ | 36.8 | 21.3 |
| P-4 | 2 | 76.8 | 76.8 | 39.3 | 114 | 53.1 |
| PL-1 | 5 | 180 | 196 | <LOQ | 292 | 114 |
| PL-2 | 5 | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | - |
| PL-3 | 3 | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | - |
| PL-4 | 3 | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | - |
| PL-D1 | 4 | 31.2 | 40.9 | <LOQ | 43.0 | 20.8 |
| R-1 | 6 | 220 | 47.4 | <LOQ | 1172 | 467 |
| RZ-1 | 6 | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | - |
| WK2-1 | 5 | 151 | 167 | 71.0 | 255 | 72.3 |
| drainage channel | 14 | 138 | 42.5 | <LOQ | 996 | 258 |
| regulated channel | 20 | 161 | <LOQ | <LOQ | 2234 | 513 |
| regulated stream | 28 | 223 | 76.80 | <LOQ | 1539 | 367 |
| river | 114 | 331 | 57.2 | <LOQ | 8406 | 989 |
| weir | 21 | 86.7 | <LOQ | <LOQ | 772 | 175 |
| non-protected | 102 | 401 | 75.7 | <LOQ | 8406 | 1045 |
| protected | 95 | 105 | <LOQ | <LOQ | 2234 | 286 |
| Water Type | N | Mean | Median | Minimum | Maximum | Interquartile Range | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| flowing | 159 | 274 | 56 | <LOQ | 8406 | 169 | 867 |
| runoff | 14 | 138 | 43 | <LOQ | 996 | 140 | 258 |
| stagnant | 8 | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | - | - |
| groundwater-influenced | 16 | 340 | 253 | <LOQ | 1028 | 624 | 343 |
| Sampling Site | Year | N | Mean | Median | Minimum | Maximum | S.D.1 | Percentage of Exceedence Above 100 ng/L |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CW-D1 | 2019 | 1 | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | - | 0% |
| 2020 | 2 | 16.0 | 16.1 | <LOQ | 32.0 | 23.0 | 0% | |
| 2021 | 2 | 512 | 512 | 28.0 | 996 | 685 | 50% | |
| G-3 | 2019 | 1 | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | - | 0% |
| 2020 | 2 | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | - | 0% | |
| 2021 | 3 | 22 | <LOQ | <LOQ | 65 | 37.0 | 0% | |
| K-1 | 2019 | 1 | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | - | 0% |
| 2020 | 3 | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | - | 0% | |
| 2021 | 6 | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | - | 0% | |
| P-1 | 2020 | 3 | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | - | 0% |
| 2021 | 1 | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | - | 0% | |
| WK2-1 | 2019 | 1 | 255 | 255 | 255 | 255 | - | 100% |
| 2020 | 2 | 120 | 120 | 71.0 | 168 | 69.0 | 50% | |
| 2021 | 2 | 131 | 131 | 94.0 | 167 | 52.0 | 50% |
| Sampling Site | Concentration [mg/L] | Ecotoxicological Risk Assessment | Human Risk Assessment | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oncorhynchus mykiss | Daphnia magna | Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata | |||||||
| LC50 (mg/L) | NOEC (mg/L) | LC50 (mg/L) | NOEC (mg/L) | LC50 (mg/L) | NOEC (mg/L) | RQ | THQ | ||
| BP-2 | 0.003882 | 27.3 | 0.5 | 52.6 | 5.0 | 15.8 | 2.6 | 0.0025 | 0.00111 |
| BP-3 | 0.000203 | 0.0001 | 0.00006 | ||||||
| BS-1 | 0.000605 | 0.0004 | 0.00017 | ||||||
| BS-2 | 0.001028 | 0.0007 | 0.00029 | ||||||
| CW-1 | 0.000364 | 0.0002 | 0.00010 | ||||||
| CW-2 | 0.000364 | 0.0002 | 0.00010 | ||||||
| CW-3 | 0.004683 | 0.0030 | 0.00134 | ||||||
| CW-4 | 0.000327 | 0.0002 | 0.00009 | ||||||
| CW-5 | 0.008406 | 0.0053 | 0.00240 | ||||||
| CW-D1 | 0.000996 | 0.0006 | 0.00028 | ||||||
| G-1 | 0.000184 | 0.0001 | 0.00005 | ||||||
| G-2 | 0.001539 | 0.0010 | 0.00044 | ||||||
| K-2W | 0.000287 | 0.0002 | 0.00008 | ||||||
| K-3 | 0.002234 | 0.0014 | 0.00064 | ||||||
| K-5 | 0.000213 | 0.0001 | 0.00006 | ||||||
| K-6 | 0.000304 | 0.0002 | 0.00009 | ||||||
| KB | 0.000849 | 0.0005 | 0.00024 | ||||||
| P-2 | 0.000772 | 0.0005 | 0.00022 | ||||||
| P-2S | 0.0000269 | 0.00001 | 0.01312 | ||||||
| P-4 | 0.000114 | 0.0001 | 0.00003 | ||||||
| PL-1 | 0.000292 | 0.0002 | 0.00008 | ||||||
| R-1 | 0.001172 | 0.0007 | 0.00033 | ||||||
| WK2-1 | 0.000255 | 0.0002 | 0.00007 | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sulej-Suchomska, A.M.; Jóźwik, J.K.; Kozłowska-Tylingo, K.; Ruman, M.; Lehmann-Konera, S.; Przybyłowski, P.; Astel, A.M.; Polkowska, Ż. Assessment of Glyphosate Runoff Pollution in Water Samples from Agricultural, Touristic and Ecologically Protected Areas. Sustainability 2025, 17, 10054. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172210054
Sulej-Suchomska AM, Jóźwik JK, Kozłowska-Tylingo K, Ruman M, Lehmann-Konera S, Przybyłowski P, Astel AM, Polkowska Ż. Assessment of Glyphosate Runoff Pollution in Water Samples from Agricultural, Touristic and Ecologically Protected Areas. Sustainability. 2025; 17(22):10054. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172210054
Chicago/Turabian StyleSulej-Suchomska, Anna Maria, Joanna Katarzyna Jóźwik, Katarzyna Kozłowska-Tylingo, Marek Ruman, Sara Lehmann-Konera, Piotr Przybyłowski, Aleksander Maria Astel, and Żaneta Polkowska. 2025. "Assessment of Glyphosate Runoff Pollution in Water Samples from Agricultural, Touristic and Ecologically Protected Areas" Sustainability 17, no. 22: 10054. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172210054
APA StyleSulej-Suchomska, A. M., Jóźwik, J. K., Kozłowska-Tylingo, K., Ruman, M., Lehmann-Konera, S., Przybyłowski, P., Astel, A. M., & Polkowska, Ż. (2025). Assessment of Glyphosate Runoff Pollution in Water Samples from Agricultural, Touristic and Ecologically Protected Areas. Sustainability, 17(22), 10054. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172210054








