Abstract
This study aims to quantify the spatiotemporal evolution of ecosystem service value (ESV) in the Zhengzhou Metropolitan Area from 2010 to 2022. We employed an improved equivalent factor method to calculate ESV and used Geodetector analysis to identify its key driving factors. Over this 12-year period, the total ESV exhibited a spatial decreasing pattern from west to east, with farmland and forestland contributing the most to total ESV. Geodetector results across four grid scales indicate that vegetation cover (Fractional Vegetation Cover, FVC) and slope Digital Elevation Model (DEM) are the primary natural drivers; notably, the optimal model fit was achieved at finer grid scales. These findings provide a scientific basis for promoting coordinated eco-economic development and formulating conservation strategies during the urbanization process of the Zhengzhou Metropolitan Area.
1. Introduction
Ecosystem services are functions and processes provided by nature that directly or indirectly benefit human well-being and support the material needs and development of human societies [1,2]. In recent years, human activities have exacerbated damage to the surface environment, caused large-scale land use changes, and seriously affected ecosystem services, leaving ecosystems facing serious challenges. More than 60% of the world’s natural resources are being depleted (Millennium Ecosystem Assessment, MA) [3]. Scientific assessment and quantitative description of ESV can provide a key basis for the formulation of rational ecological protection policies [4]. Due to the overexploitation of water resources, coupled with rapid population growth and rapid industrial economic development, the ecosystem of metropolitan area is facing serious challenges [5,6,7,8]. It not only affects the stability of urban development but also brings negative impacts on human socio-economic development. Therefore, exploring the ecosystem services of the metropolitan area and clarifying their drivers are crucial for formulating sustainable development strategies and protecting the ecological environment.
The study of ecosystem services emerged in the 1970s when foundational works by Daily [9] and Costanza [10] established its conceptual framework and pioneered the quantification of ecosystem service value (ESV). This catalyzed global research efforts to systematically evaluate ESV, which reflects the economic benefits humans derive from ecosystems, including goods, regulatory functions, and cultural services [11]. Monetary valuation of ESV [12] enhances decision-making by prioritizing conservation strategies and ecosystem management [13,14]. Crucially, land-use changes profoundly disrupt ecosystem service provision [15,16], threatening long-term human well-being and resource security. Methodologically, current research integrates geography, economics, and data science, with the equivalent factor approach remaining dominant. However, novel models and interdisciplinary frameworks are increasingly explored to address regional ESV variability.
For example, Wang Geng et al. [1] systematically analyzed the evolution of ESV in the delta by using land use data from 1990 to 2020, and Hu Feng et al. [17] predicted the future trend of ESV in the Taihang Mountainous Region by using the revised equivalent factor method and MCCA model. It is crucial to identify the key factors affecting the change in ecosystem service value (ESV), and their spatial and temporal characteristics need to be explored. Numerous scholars have begun to explore the influencing factors contributing to the spatial differentiation of ESV, but most of them have used traditional linear regression [18], geographically weighted regression [19], correlation model [20], principal component analysis and regression analysis [21], etc., which are somewhat limited in revealing the influence of different factors on the spatial differentiation of ESV [22], and these methods do not fully consider the interactions among multiple factors and may face endogeneity problems. To address these limitations, scholars increasingly employ geodetectors—a spatial statistical model—to identify key drivers and quantify factor interactions in ecosystem service value (ESV) studies factors [23]. For instance, Pan et al. [24] applied geodetector analysis to disentangle ESV drivers in the Shule River Basin, while Hu et al. [25] integrated geodetectors with geographically weighted regression (GWR) to assess climate, human activity, and vegetation impacts on ESV in Shanxi Province. Methodologically, administrative divisions and grid scales (e.g., 1–3 km2 grids) remain prevalent spatial units for analyzing ESV heterogeneity, balancing regional specificity with granular insights. For instance, Deng et al. [26] conducted the ecosystem supply-demand balance and the response mechanism of land use types to urbanization based on different spatial scales. Researchers have adopted grid resolutions (e.g., 1 km × 1 km [27], 2 km × 2 km [28], 3 km × 3 km [29]) to reveal ESV-driving factors with higher spatial precision than administrative divisions, capturing their multidimensional interactions. While existing studies have examined ESV spatial heterogeneity and driving mechanisms through diverse approaches, systematic comparisons of factor influences across grid resolutions within identical regions remain scarce.
Metropolitan areas, unlike traditional city administrative planning, break through administrative barriers and are strategic cornerstones for the high-quality development of urban areas, with the advantage of promoting infrastructure integration and strengthening inter-city industrial cooperation [30]. Accelerated urbanization coupled with persistent reliance on polluting industries has intensified metropolitan challenges: ecological degradation, abrupt land-use transitions, urban heat islands [31], and air quality deterioration [32]. The Zhengzhou metropolitan area faces escalating pressures on natural resources, with intensifying conflicts between urban expansion and ecological conservation. Scarcities of forests and water systems directly undermine regional environmental sustainability. Against this backdrop, exploring the spatiotemporal dynamics of ESV and its drivers in the Zhengzhou Metropolitan Area is critical for addressing these region-specific challenges. While prior studies have advanced ESV research, gaps remain for the Zhengzhou context. Basin studies overlook the area’s dual attributes as a “lower Yellow River basin core” and “major grain-producing region,” failing to quantify ESV impacts of farmland conversion to built-up land or wetlands in the Yellow River floodplain. Addressing these challenges requires systematic characterization of spatiotemporal ESV dynamics and context-specific analysis of driver interactions in the Zhengzhou metropolitan area. This study contributes in three key areas: Methodologically, this study refines the “multi-scale, multi-factor” framework for analyzing drivers of ESV via grid-scale geodetector analysis and confirms the synergistic effects of natural and topographic factors.
As the core of China’s primary wheat-producing region, Zhengzhou Metropolitan Area’s practice of advancing urbanization while safeguarding the red line for arable land offers valuable insights for global “urbanization in major grain-producing areas.” Similar regions such as India’s Ganges Plain and the U.S. Central Plains can draw upon its “dual red line management for arable land and ecology” model to balance food security with urbanization demands. Regionally, it optimizes the ecosystem service value accounting system for major grain-producing areas, quantifying changes in ESV resulting from land use transitions. At the practical level, it provides targeted policy recommendations for ecological conservation in the Yellow River Basin and offers reference for similar metropolitan areas. The specific research purposes are: This study analyzes ESV changes from 2010 to 2022 in the Zhengzhou metropolitan area using land use/cover, natural environment, and socioeconomic data. Through geographic detector analysis, we identified key drivers of ESV variation. This study lays the foundation for optimizing regional land use structures and formulating ecosystem management strategies and provides a reference for the sustainable development and conservation of ecosystems.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
The Zhengzhou Metropolitan Area (33°7′–35°50′ N, 111°8′–115°16′ E) occupies a pivotal position within China’s “Two Horizontal and Three Vertical” urbanization framework, intersecting the Land Bridge Corridor and Beijing-Guangzhou Corridor development axes. Located in central China along the lower Yellow River basin, its northern boundary is defined by the Taihang Mountains, while the Funiu Mountains flank its western periphery. The central and eastern sectors consist of the expansive Yellow-Huaihai Alluvial Plain. Encompassing the Yellow, Huaihe, and Haihe River basins, the region exhibits a distinct west-to-east topographical gradient. Designated as China’s 10th national metropolitan area (Figure 1), this zone holds critical strategic significance. According to the Zhengzhou Metropolitan Area Development Plan, the metropolitan area is centered mainly on Zhengzhou. It encompasses the entire areas of eight cities: Kaifeng, Xinxiang, Jiaozuo, Xuchang, Luoyang, Pingdingshan, Luohe, and Jiyuan. The total area is approximately 58,900 km2, accounting for 35.57% of the province’s total land area. The land is mainly composed of arable land, woodland, and grassland. In the study area, the soil types are mainly brown soil and tidal soil. The climate is a north-temperate continental monsoon climate. Summers are hot and rainy, while winters are cold and dry. The average annual temperature is 14 °C, and the average annual rainfall is about 400–1000 mm. Rainfall is mainly concentrated from June to August.
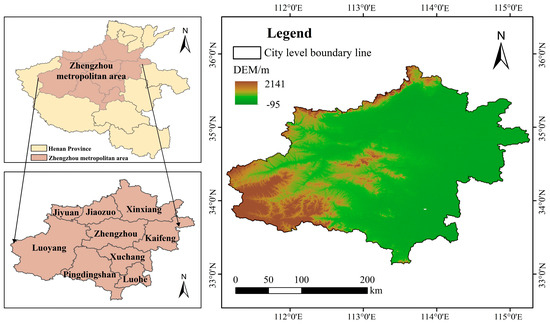
Figure 1.
Location Map of the Zhengzhou Metropolitan Area.
As a major national grain production base, this region’s proportion of arable land in 2010 was significantly higher than comparable areas like the Nanchang metropolitan area. Simultaneously, with the expansion of construction land, the annual reduction in arable land has created a sharp contradiction between “ensuring food security” and “accommodating urbanization.” This characteristic of “highly arable land-dependent urbanization” is typical only in a few areas in central and western metropolitan regions, such as Zhengzhou, and its ESV change patterns cannot be substituted by research from other regions. The region simultaneously implements multiple national and provincial policies, including the “Ecological Protection and High-Quality Development of the Yellow River Basin,” “Development of the Central Plains Urban Cluster,” and “Grain-for-Green Program.” The cumulative impact of these overlapping policies on land use and ESV holds irreplaceable research value, offering a valuable case study for optimizing ESV under multi-policy coordination.
With the advancement of urbanization in the Zhengzhou metropolitan area, the contradiction between urban construction and ecological space has gradually intensified the scarcity of forests and water resources, and the large amount of emissions of gases and sewage, etc., have caused damage to the high-quality development of the ecological environment. In this regard, revealing the characteristics and drivers of ecosystem evolution in the Zhengzhou metropolitan area is crucial for ecological environmental protection and collaborative management. Therefore, we chose the Zhengzhou metropolitan area as the focus area of our study.
2.2. Data Sources and Pre-Processing
The data employed in this study include raster data, LUCC data, and socio-economic data such as grain price data, sown area data, and GDP data. The land-use raster data of the Zhengzhou Metropolitan Area were sourced from the Landsat-derived annual Chinese land-cover dataset, which was developed by scholars from Wuhan University on the Google Earth Engine (GEE) platform. This dataset achieves high accuracy through rigorous preprocessing and validation. Specifically, using Landsat remote sensing images as the basis, the dataset undergoes radiometric calibration, atmospheric correction, and geometric precision adjustment. The selected land—use data were from 2010, 2015, 2020, and 2022, and the spatial resolution was 30 m. The temperature data and Normalized Vegetation Index (NVI) were acquired from the National Center for Ecological Sciences Data (https:/www.nesdc.org.cn/). The Digital Elevation Model (DEM) were the ASTER GDEM 30 M dataset from Geospatial Data Cloud (https://www.gscloud.cn/) with a spatial resolution of 30 m, and the elevation and slope of the study area were obtained by ArcGIS 10.8. Socio-economic data were taken from the China Statistical Yearbook, the Henan Provincial Statistical Yearbook, and the National Compendium of Cost and Benefit Information of Agricultural Products, respectively. The original Land Use and Cover Change (LUCC) data, derived from land resource inventories, were reclassified into six functional categories based on Zhengzhou Metropolitan Area’s actual conditions and research objectives: farmland, forest, grassland, water, built-up land, and unused land. Following the Millennium Ecosystem Assessment framework, we categorized ecosystem services into 11 standardized classes such as food production, material production, water production, gas production, climate production, purifying the environment, hydrological regulation, soil conservation, maintaining nutrient circulation, biodiversity, and aesthetic landscape.
2.3. Research Methodology
2.3.1. Research Approach
A multi-scale analysis of the spatial distribution of land-based ESV clarifies spatiotemporal patterns and identifies dominant drivers of ESV spatial heterogeneity, as well as the intensity of their interactions. This method reveals the variability of influencing factors, providing a scientific basis for differentiated optimization strategies and green development. The research framework is illustrated in Figure 2.
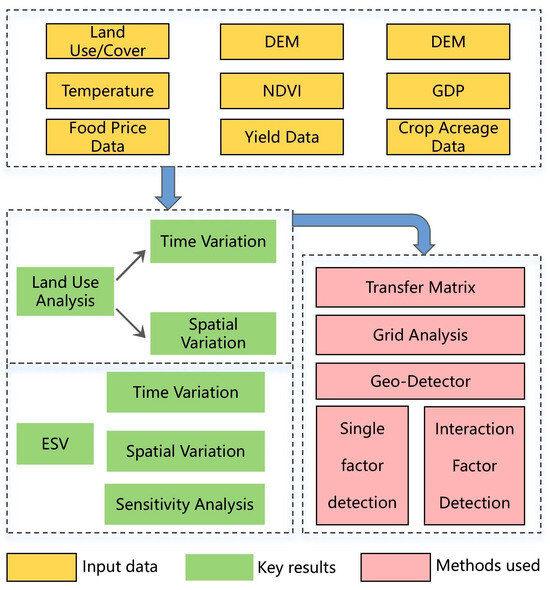
Figure 2.
Theoretical Framework for LUCC Impacts on Ecosystem Services.
2.3.2. Analysis of the Spatial and Temporal Dynamics of Land-Use Change
In this paper, we use ArcGIS to overlay the land use data in 2010, 2015, 2020, and 2022, and calculate the land use transfer matrix so as to analyze the amount and direction of change in land use in the Zhengzhou metropolitan area in the past 12 years, and the specific principles and formulas of the land use dynamic attitude and the land use transfer matrix can be found in the literature [33,34].
2.3.3. Accounting for the Value of Ecosystem Services
A standard unit of ecosystem service value equivalent factor is defined as the economic value of the annual natural food production from 1 hm2 of farmland with the national average yield. This paper calculates the ESV of the Zhengzhou metropolitan area. It is based on the actual condition of the area and refers to the 2015 Xie et al. [2] revised and improved equivalent factor method of assessing the economic value of ecosystems with appropriate revisions. With reference to the economic value of one standard equivalent factor is equal to 1/7 of the economic value of the grain produced by 1 hm2 of farmland in the study area as a way to collect data on the main crops [35] in the Zhengzhou metropolitan area (wheat, corn, and rice), grain production per unit area, sown area, and unit price data, and calculate their mean values. The formula for calculating the economic value created by grain production per unit area in the study area is as follows:
where Ea is the economic value of grain production per unit area (yuan·hm−2), i is the type of grain crop, pi is the national average grain purchase price for food crop i from 2010 to 2022 (yuan·kg−1), qi is the yield of the i-th food crop, mi is the sown area of the i-th food crop, and M is the planted area of all crops (hm2). The economic value of 1 standard equivalent factor in the Zhengzhou metropolitan area was calculated to be 2029.19 yuan/hm2.
Calculate the value of each ecosystem service based on the table of area and value coefficients of various land use types in the Zhengzhou metropolitan area:
where ESV is the total value of ecosystem services (yuan); Ak is the area of land in category k (hm2); VCik is the value of i ecosystem services per unit area provided by land in category k (yuan·hm−2), and k is the land use type.
The modified ESV coefficients per unit area of the study area were calculated as shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
The value coefficient of ecosystem services in the Zhengzhou metropolitan area (yuan·hm−2·a−1).
2.3.4. Sensitivity Analysis of the Value of Ecosystem Services
To validate the accuracy of the revised accounting for the ecosystem service values of different land types in the Zhengzhou metropolitan area, a sensitivity analysis of the ESV results is necessary.
Based on the concept of elasticity coefficient in economics [36], in this study, the equivalent coefficients of the ESV for each unit area are adjusted upwards and downwards by 50%, respectively. This is done to assess the magnitude of the sensitivity indices and to test the reasonableness of the coefficients of each ecosystem service value [37]. The calculation formula is presented as follows:
where CS is the sensitivity index; VCik is the original value coefficient and VCjk is the adjusted coefficient; ESVi and ESVj are the original and adjusted values of the ESV results, respectively, and k is the land use type. If CS > 1, it means that ESV is elastic to VC, the value coefficient is poorly accurate and less credible; if CS < 1, it means that ESV is inelastic to VC and the result is credible.
2.3.5. Geodetector
Geodetectors are spatial analysis tools that identify key drivers of observed patterns through quantifying spatial stratified heterogeneity. This method detects homogeneities within subregions and heterogeneities between subregions to reveal dominant influencing factors [24,38]. In this study, we used the factor detection and interaction detection modules in Geodetector to analyze the influence of factors on ESV of the study area. We first analyzed the explanatory power of single factors on ESV through factor detection. Then, using interaction detection, we determined the explanatory power of ESV when two factors acted jointly. Finally, we identified the strength and type of factor interactions. The specific calculation formula is as follows:
(1) In factor detection, we take ESV as the dependent variable Y and each influencing factor as the independent variable X. The magnitude of the q-value is used to measure the spatial variability of ESV within the area affected by the influencing factors:
where q is an indicator for explaining the spatial heterogeneity of ESV, q ∈ [0, 1], with larger values of q representing greater explanatory power of the dependent variable and vice versa. N and n are the number of samples and the number of strata in the entire study area, respectively, and σ2 is the discrete variance of the entire area.
(2) The interaction detector is used to assess whether the interaction on the changes in ESV is enhanced or weakened when two drivers act jointly. The interaction types are categorized into five types (Table 2).

Table 2.
Probe factor interaction type.
2.3.6. Driver Selection
ESV in the Zhengzhou metropolitan area is affected by a diverse range of natural environmental and socio-economic factors. Specifically, meteorological factors, such as temperature change, and topographical factors, including elevation, slope, Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI), and Fractional Vegetation Cover (FVC), may impact different aspects of the hydrological cycle and the ESV [39,40]. Moreover, socio-economic factors like GDP can serve as good indicators reflecting the level of human activities. In this study, considering the specific circumstances of the study area, we selected DEM, slope, gross domestic product (GDP), normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI), fractional vegetation cover (FVC), and temperature (T) as independent variables to explore the driving forces behind the changes in the ecosystem service value in 2022. To ensure the consistency of the input data for the Geodetector, we employed the natural segment point method to discretize the data. Then, based on the characteristics and distribution of the data, we reclassified the data in a way that minimized the total sum of the differences across all levels.
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Spatio-Temporal Dynamic Analysis of LULC
From 2010 to 2022, the land use in the Zhengzhou metropolitan area was dominated by cropland and forest land, with the combined proportion of these two land types exceeding 82%. Overall, forest land and grassland were mainly located in the mountainous regions of the northwest, southwest, and central parts of the city; Water areas were predominantly distributed in the Yellow River Basin in the northern part and along the Yiluo, Ru, and Sha rivers in the southwestern part.; Cropland was primarily distributed in the central part of the city, while construction land was mainly concentrated in the urban centers of each city within the study area (Figure 3).
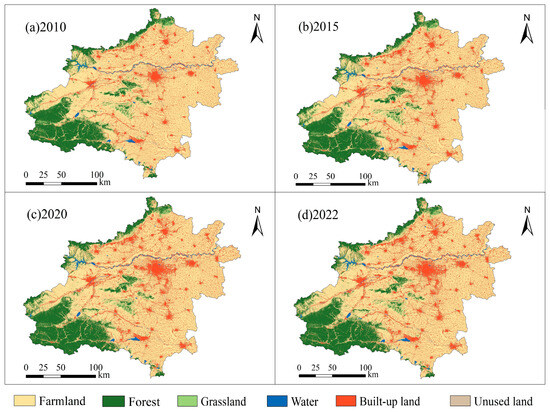
Figure 3.
Land use change in the Zhengzhou Metropolitan Area from 2010 to 2022.
Regarding spatial distribution, the most prominent land transformation pattern is the conversion of arable land into construction land. This transformation is mainly concentrated in the central region, which aligns with the trend of urbanization expansion. When compared to 2010, by 2022, the areas of forest land, construction land, and water areas in the Zhengzhou metropolitan area had generally increased. Conversely, the areas of cultivated land, grassland, and unused land showed a continuous decline over the period. With the construction and development of the Zhengzhou metropolitan area, construction land experienced the greatest growth among all land use types. Its area significantly increased from 8289.07 square kilometers in 2010 to 10,684.34 square kilometers in 2022. Forest cover exhibited sustained expansion (2010–2022), increasing from 10,000.16 km2 to 10,369.36 km2 with a 3.7% net gain. The water area fluctuates slightly yet exhibits an overall increasing trend. The areas of cultivated land, grassland, and unutilized land all show a year-on-year decreasing trend. Among them, the area of arable land decreased most significantly, by 2216.25 km2; the area of grassland decreased by 548.93 km2; and the area of unutilized land decreased the least, by 1.55 km2.
The concept of land use dynamics measures the regional differences in the rate and intensity of human-induced changes in land use patterns. It reflects the extent to which human activities influence land development and utilization. Regarding land use dynamics (Table 3), the unutilized land exhibited the most significant fluctuations in single dynamics, with grassland following closely behind. Between 2010 and 2015 and 2015–2020, the single-motor attitude was negative, the value of the single-dynamic indicator was negative, which indicated a reduction in the area of unutilized land during these two periods. The decrease was particularly significant from 2010 to 2015, with a 11.55% reduction in the area of unutilized land. The increase in the area of unutilized land from 2020 to 2022 may be related to socio-economic factors with a motivation of 5.14%. In addition, the dynamic indicator of arable land has been negative since 2010, suggesting that the area of arable land has been decreasing annually. The decrease was particularly evident from 2010 to 2015, with a reduction of 0.65%, which might be consistent with the implementation direction of the “returning farmland to forests” policy. During the period from 2010 to 2015, the area of construction land increased by 1243.44 km2 with a 3.00% attitude; the area of grassland increased by 28.51 km2 with a 0.49% attitude; the area of forest land increased by 36.55 km2 with a 0.07% attitude; the area of arable land decreased by 1258.45 km2 with a −0.65% attitude; and the area of water and unutilized The motivation of water and unutilized land is −1.46% and −11.55%, respectively. From 2015 to 2022, the area of the six land types in the study area changed at a slower pace. The growth rate of construction land was 1.73%, that of water areas was 1.18%, and that of forest lands was 0.47%. From 2010 to 2022, the area of built-up land changes most significantly, with a growth rate of 2.41%; the unutilized land area decreased the fastest, with a decrease rate of 6.09%.

Table 3.
Proportion of land use area in the Zhengzhou Metropolitan area from 2010 to 2022.
To comprehensively analyze the trend of mutual transformation in land use changes within the Zhengzhou metropolitan area during the period from 2010 to 2022, a land use transfer matrix (Table 4) was constructed. In terms of area, during 2010–2022, the land use types that experienced the most significant transformation were the conversion of cropland into construction land and forest land. Next in line was the conversion of forest land and grassland into cropland. Among all land categories, construction land had the largest transferred area. Cultivated land was transferred to construction land and forest land by 2397 km2 and 660.92 km2 respectively, and forest land and grassland were transferred to cultivated land by 501.86 km2 and 439.62 km2 respectively.

Table 4.
Land use transfer matrix in the Zhengzhou Metropolitan area from 2010 to 2022 (unit: km2).
3.2. ESV Spatiotemporal Evolution Characteristics
3.2.1. ESV Time Variation
From 2010 to 2022, the ESV of the Zhengzhou metropolitan area generally shows a decreasing trend, decreasing from 93.099 billion RMB to 90.635 billion RMB, representing a decrease of 2.65% (Figure 4). Specifically, from 2010 to 2015, the ESV of the study area declined significantly, from 93.099 billion RMB in 2010 to 91.090 billion RMB in 2015, marking a decrease of 2.16%. From 2015 to 2022, the ESV showed a continuous downward trend, from 91.090 billion RMB in 2020 to 90.635 billion RMB in 2022, representing a decrease of 0.50%. The continuous change in LULC in the later period is closely related to the shift in LULC from cropland to forest land in the Zhengzhou metropolitan area. The area of cultivated land decreased significantly, and its ESV coefficient was low, In contrast, the expansion of forested land and water area, along with their higher ESV coefficients, were the main reasons for the increase in the total ESV in 2022.
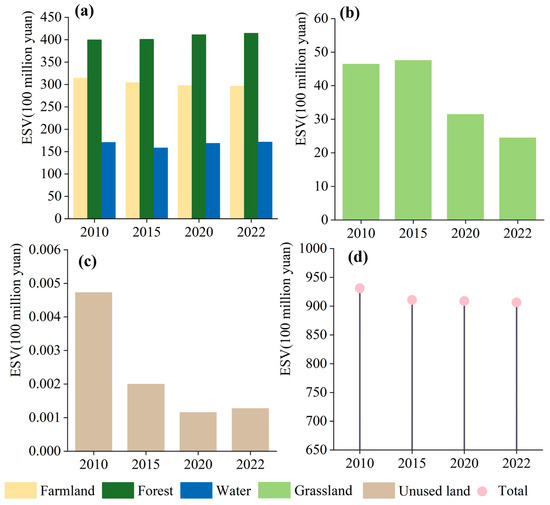
Figure 4.
ESV of each LULC category and total ESV in the Zhengzhou Metropolitan area during 2010–2022. (a): ESV of farmland, forest, and water from 2010 to 2022; (b): ESV of grassland during 2010–2022; (c): ESV of unused land during 2010–2022; (d): total ESV in the Zhengzhou Metropolitan area during 2010–2022.
In addition, changes in LULC from 2010 to 2022 resulted in different trends in ESV for LULC types in the Zhengzhou metropolitan area. Specifically, from 2010 to 2015, the ESV of the study area decreased by 2.009 billion RMB, of which unutilized land and water decreased by 0.0027 billion RMB and 1.244 billion RMB, accounting for 57.76% and 7.29%, respectively, and the ESV of forested land and grassland increased by or 0.37% and 2.45%, respectively. From 2015 to 2022, the ESV showed a slow decreasing trend. Specifically, the ESV of grassland decreased significantly, with a decrease rate of 2.307 billion RMB or 48.50%, compared to the ESV in 2020, which decreased by 207 million RMB and 249 million RMB in 2015 and 2022, respectively. In terms of land use type, the increase in ESV of forest land during the study period was 3.69%, while the ESV of cropland decreased by 5.74%, which is consistent with the land use situation.
From 2010 to 2022, the ESV of primary service types in the Zhengzhou metropolitan area follows the same trend as the total ESV, showing a decreasing trend year by year (Table 5). Regulating services exhibited a fluctuating decline. In contrast, supply services, support services, and cultural services showed a stable and continuous decline. Regulating services accounted for the highest proportion, reaching 60.06%, followed by support services with 22.33%. Supply services and cultural services had the least share with 14.55% and 3.06%, respectively.

Table 5.
Value of individual ecosystem services in the Zhengzhou Metropolitan area from 2010 to 2022 (unit: 108 yuan).
Among different secondary ecosystem services, the values of hydrologic regulation and water supply services increased year by year. However, the values of the other nine services showed a decreasing trend. Among them, climate regulation and hydrological regulation accounted for 26.77% and 17.24% of the total ESV, respectively. Their proportions were significantly higher than those of other ecosystem services. This could be attributed to the increase in the values of these two types of services resulting from the 7·20 rainstorm disaster in Zhengzhou. Due to climate change, the precipitation intensity increased, leading to a stronger hydrological regulation capacity. Meanwhile, aesthetic appreciation, water supply, and the service of maintaining nutrient cycling contributed relatively little to the total ESV. Among them, the service of maintaining nutrient cycling contributed the least, accounting for only 1.43%. Among the individual service values, the value of soil conservation services experienced a dramatic change, decreasing by 556 million RMB over 22 years, and the value of food production services decreased by 405 million RMB.
Thus, regulating services constitute the primary source of total ESV. Specifically, climate regulation and hydrological regulation exert a substantial influence on the overall ESV.
3.2.2. ESV Spatial Variation
Based on the land use data of the Zhengzhou metropolitan area in 2010, 2015, 2020, and 2022, the ecosystem service value of the Zhengzhou metropolitan area was partitioned into 5 km × 5 km grid cells using the grid method in ArcGIS. Then, the distribution of ecosystem service value within this 5 km × 5 km grid of the metropolitan area was calculated. Subsequently, the values were classified into five categories in ascending order: low-value area, lower-value area, medium-value area, higher-value area, and high-value area (Figure 5).
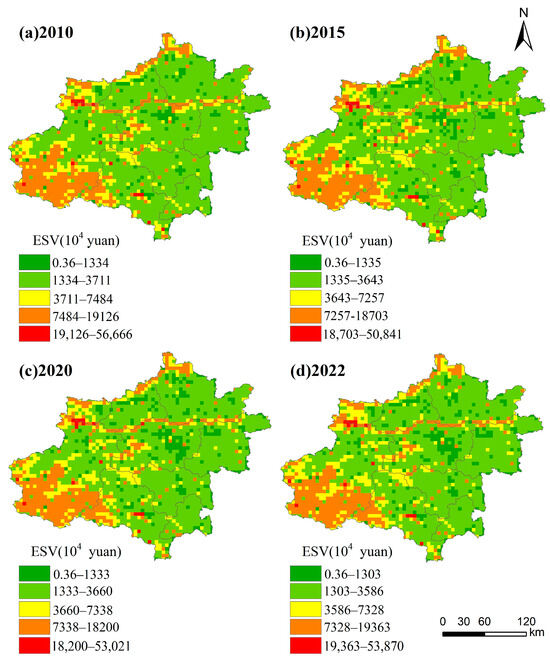
Figure 5.
Zhengzhou Metropolitan area’s ecosystem service value’s spatial distribution from 2010 to 2022 (a–d).
From 2010 to 2022, ESV in the study area generally exhibited a spatial distribution pattern characterized by a gradual decrease from west to east. The high-value area shrank to the western mountains, while the low-value areas were predominantly distributed in the built-up areas of the municipalities and expanded outward along the directions of urban transportation arteries. The vast majority of the eastern plains within the study area are covered with forests. In 2010, ESV of a single 5 km × 5 km grid ranged from 13,340,000–37,110,000 RMB. This value decreased to the range of 13,340,000 to 3,643,000 RMB in 2015, 13,330,000–3,660,000 RMB in 2020, and 13,030,000–35,860,000 RMB in 2022. Forest land primarily performs the regulating function within the ecosystem. It not only conducts gas regulation, climate regulation, and hydrological regulation and purifies the environment but also plays a role in soil retention. Due to the emphasis on the protection of forestry resources, ESV provided by forest land has steadily increased over the past 22 years.
From 2010 to 2015, ESV of the Zhengzhou metropolitan area exhibited a decrease in the area of higher-value zones and a more significant decline in ESV. Specifically, the higher-value areas in the central part of the Yellow River Basin were transformed into lower-value areas. In contrast, the lower-value areas of forest and grassland between the central mountain ranges were converted into medium-value areas and a small number of higher-value areas. This transformation, to a certain extent, mitigated the decline of the ESV. During the period of 2015–2022, the change in the ESV was not significant and presented a slow growth trend. This was mainly attributed to the increase in the area of the lower-value areas in the northeast.
3.3. Sensitivity Testing
The ecosystem service value coefficient of each ecosystem type was adjusted by increasing it by 50%. Then the sensitivity index of the ESV of the Zhengzhou metropolitan area was calculated. The sensitivity results (Table 6) indicated that the sensitivity index of each land use type in the study area from 2010 to 2022 was less than 1, indicating that the ESV was inelastic. The sensitivity index of forest land is the highest, with a mean value of 0.297. The sensitivity indexes of cropland and waters are 0.221 and 0.121, respectively. Those of grassland and unutilized land are all less than 0.1. All the sensitivity indexes are less than 1. This indicates that the ESV coefficient in the study area is inelastic. In other words, adjustments to the value coefficient have little impact on the value of ecosystem services. The accounting results are reliable.

Table 6.
ESV sensitivity test results for the Zhengzhou Metropolitan area.
3.4. Analysis of Factors Influencing the Value of Ecosystem Services
3.4.1. Factor Detection Results
Factor probes of the geodetector were used to conduct a quantitative attribution analysis of the driving factors at different grid scales (1500 m × 1500 m, 2000 m × 2000 m, 2500 m × 2500 m, and 3000 m × 3000 m) in the study area. The explanatory power of these driving factors for the ESVs was then identified (Table 7). The p-value of each driver was lower than 0.05, passing the significance test. This indicates that the selected drivers can explain the spatial differentiation of 2022 ESV in the study area to some extent.

Table 7.
Results of detecting driving factors for spatial differentiation of ecosystem service value in the Zhengzhou metropolitan area (based on 2022 data).
According to the results of the factor detector, both natural and socioeconomic factors affect the spatial heterogeneity of ESV in the study area. As the grid scale changes, the degree of influence of each factor on ESV varies significantly. Notably, natural factors have a more pronounced impact on the spatial heterogeneity of ESV in the metropolitan area. In the four grid scale ranges of 1500–3000 m, the main driver influencing the value of ecosystem services was FVC. It demonstrated the highest explanatory power, with values of 0.635, 0.632, 0.632, 0.632, and 0.632, respectively. Following FVC was the slope factor, which had explanatory power of 0.585, 0.582, 0.581, 0.582, and 0.582. This is because FVC and slope are indicators of natural and topographic factors, respectively. It indicates that natural and topographic factors are the main drivers of the spatial differentiation of ecosystem service values in the study area. Secondly, the explanatory power of human activity indicator (GDP) for ESV was lower than that of topographic factors but higher than that of climatic factors (temperature). This suggests that climatic factors have a relatively weak influence on the ecosystem service value in the study area. Further analysis revealed that the individual drivers had the highest explanatory power at the 1500 m grid scale and the lowest at the 3000 m grid scale. This trend indicates the spatial heterogeneity of ESVs in the study area decreases as the grid scale increases. In summary, both natural factors and socio-economic factors jointly influence the spatial variation in ESV in the Zhengzhou metropolitan area. Among them, natural factors play a significant role in the study area.
3.4.2. Interactive Detection Results
The above content analyzes the degree of influence of individual influencing factors on the spatial distribution of ecosystem service value, but in practice there exists a complex interaction between multiple factors that shape and influence the spatial distribution pattern of ecosystem service value. Therefore, the interaction detector was employed to identify the interactions between different factors, and the two-by-two interactions of the driving factors had a greater effect on the spatial differentiation of ESV in the study area than a single factor, and the interaction detection types of the factors were mainly two-factor-enhanced, followed by nonlinear-enhanced. Based on the results of the driver interaction detections of ESV spatial differentiation, the q-values of the interactions between different drivers at the four grid scales of 1500–3000 m were higher than those of a single influencing factor. Among the 21 sets of interaction factor detections, most of the factors exhibited a two-factor enhancement relationship, while a few showed a nonlinear enhancement relationship.
As shown in Figure 6, among the four grid scales of 1500–3000 m, the interaction q statistic of X5 with X1, X5 with X3, and X5 with X4 has the highest value of 0.926. This highlights the significant impact on the spatial heterogeneity of ESV in the study area. It further confirms that the natural factors are the dominant factor influencing the spatial differentiation of ESV in the study area. This indicates that after the natural influence factor indicator and terrain factor indicators, their influence on ESV has increased significantly. The explanatory power of X1 after interaction with X6 was also more obvious, with a q-value of 0.913, indicating that although there was an increase in ESV after two-by-two interaction between human activity influence factor indicators and natural factor indicators, it was relatively small. For instance, variables X1 and X5 exhibit the highest explanatory power, reaching 0.926. This reflects the precise overlap between high GDP zones and low NDVI zones within the Zhengzhou metropolitan area. From 2010 to 2022, the region expanded its construction land by 2397.00 square kilometers, while the proportion of farmland (high NDVI) decreased from 59.9% to 52.3%. NDVI exhibited a significant negative correlation with GDP growth. This “high GDP—low NDVI” spatial pattern means their interaction with ESV is not a simple summation. Instead, GDP-driven construction land expansion causes NDVI decline, triggering a chain reaction that precipitates sharp ESV drops and amplifies explanatory power. As a major grain-producing region, Zhengzhou’s GDP growth relies far more heavily on arable land (high NDVI) than non-agricultural areas, forming a unique interactive mechanism specific to the metropolitan area. Therefore, it is recommended that Zhengzhou incorporate an NDVI loss threshold per unit of GDP growth into its annual urban expansion planning to offset expansion-induced degradation. Low-GDP areas must strictly control development in high-NDVI zones to ensure regional NDVI stability, establishing a dual-constraint urban expansion system.
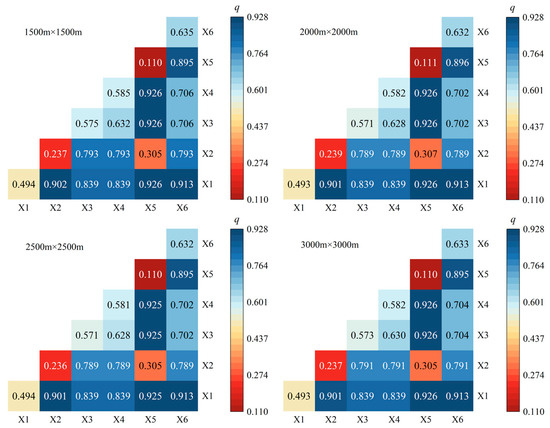
Figure 6.
Map of interaction detection results in the Zhengzhou Metropolitan area.
Overall, the multi-factor interactions were significant in explaining the spatial heterogeneity of ecosystem service values within the grid scale of 1500–3000 m, which jointly affected the changes in ESV in the Zhengzhou metropolitan area, and this result revealed that the spatial heterogeneity of ESV in the study area was largely influenced by natural factors, consistent with the factor detection results mentioned above. At different grid scales, the interactions between natural factors and topographic factors as well as socio-economic factors presented more significant explanatory power compared to the interactions within topographic factors and within socio-economic factors, indicating that when the ecosystem service value in the study area is simultaneously affected by both natural ecology and human activities, the differences in its spatial distribution will become more pronounced. Therefore, when developing and utilizing this area, we must focus on environmental protection and restoration. This ensures the stability of local ecosystems. Moreover, we can fully harness the area’s value to better serve society and nature.
4. Discussion
Land use change is the human activity that most profoundly affects ecosystems. Urban master plans serve as guiding policies for urban development. Their implementation is significant.
4.1. Factors Influencing Land-Use Change
Land use change is the human activity that most profoundly affects ecosystems. Urban master plans serve as guiding policies for urban development. Their implementation significantly alters the structure, functions, and processes of urban ecosystems. As a result, it affects ecosystem services and the ecological well-being of residents [41]. Key factors influencing land use change include land use patterns, land management systems, and land use master plans [42]. Urbanization is one of the main factors affecting land use change, and the rapid expansion of urban areas has triggered changes in land use types [43]. Scholars such as Cao [44], Wang [45], and Yuan [46] have verified the existence of this problem in different scales and cities. Specifically, during this period, the cultivated land area in Zhengzhou metropolitan area continues to decrease and is mainly converted into construction land, which is related to natural factors and human activities. The main reason for this is the loss of arable land in the Zhengzhou metropolitan area as the core of the Central Plains urban agglomeration, the loss of arable land due to the construction of the Zhengdong New Area and the aviation port area, the destruction of 68,000 mu of arable land on the outskirts of Zhengzhou caused by the 7·20 rainstorm in 2021, and the quality of the arable land replenished through the Yellow River beach area is generally deteriorating. According to the Ministry of Natural Resources, there is a disparity between the current situation and the state’s requirement of “double balance of quantity and quality.” From 2010 to 2022, the water area has been continuously increasing. This is because after the “7·20” rainstorm in 2021, the government converted over 1600 hectares of low-lying and flood-vulnerable cultivated land into a wetland park. This conversion directly led to the phased expansion of the water area. The inter-conversion of cultivated land and forest land areas is based on the implementation of the farmland-to-forest project in the Zhengzhou section of the Yellow River Basin Ecological Protection Plan of Henan Province during 2020–2023. There has been an increase in vegetation cover in ecologically fragile areas. During 2021–2022, policy impacts directly drove a 1.01% increase in water areas and a 0.3% growth in forested land. They also contributed 58% to land use transformation in this period, which is far higher than the 22% contribution from economic growth. This contrasts with Wuhan during the same period (where post-pandemic land use transformation remained primarily economically driven, with policies contributing only 30%). Also, through the monitoring of cultivated land quality equivalence, the phenomenon of replanting on slopes steeper than 25° has been discovered. These situations reflect the dynamic interaction between the food security policy and ecological protection measures. From 2010 to 2015, the grassland area shows an increasing trend. This was because of the implementation of the return-to-grass program, which led to an expansion of the grassland area. However, from 2015 to 2022, the grassland area decreased. This was due to the rise in average annual temperature and the occurrence of the “grass destruction and replanting” phenomenon in many regions. The large increase in corn prices was the driving force behind this replanting behavior. The area of unutilized land fluctuates, which is a contradiction between land remediation and ecological degradation. Before 2020, the area of unutilized land decreased as a result of the development of unutilized land to support the construction of industrial parks. After 2020, the Ministry of Natural Resources (MNR) strictly regulated the development of ecologically fragile zones. These ecologically fragile zones coincided with the land areas that had been damaged by rainstorms and disasters. This led to a rebound in the area of unutilized land. In conclusion, land use/land cover changes in the Zhengzhou metropolitan area are closely related to human activities and climate change.
4.2. Impact of Land-Use Change on the Value of Ecosystem Services
Land use change is a major driver of the gains and losses of ESV and significantly influences the spatial changes in ESV [47]. Land use change affects the structure and function of ecosystems to different extents. These impacts then affect the services that ecosystems provide for human social development and well-being. Ultimately, this leads to changes in ESV, and such changes have a more pronounced effect on ESV at the regional scale [41]. By estimating the value of ecosystem services in the Zhengzhou metropolitan area, it can be concluded that from 2010 to 2022, the value of ecosystem services in this area showed a downward trend, dropping from 93.099 billion yuan to 90.635 billion yuan. Regarding each category, forest land has the highest ecosystem service value, while unutilized land has the lowest ecosystem service value. From 2010 to 2015, the ESV of the Zhengzhou metropolitan area showed a decreasing trend. This was mainly because of the significant decline in the ESV of cultivated land and watersheds. The reduction in their area was the primary factor contributing to the decline in the ESV of the study area. The land conversion from high ESV to low ESV resulted in the decline of ESV in CRBCGS. Wang [48] and Han [49] studied the effects of China’s grain for green policy on ESV, while Hu [40] studied the effects of Pearl River Delta urbanization on ESV, and their conclusions are consistent with the present paper. This indicates that there is a certain correlation between land use and ESV change [50]. From 2015 to 2022, the ESV of the Zhengzhou metropolitan area showed a slow decreasing trend, but the ESV of forested land and waters gradually increased over time, which is the same as the planning direction. Governmental departments have set new, higher standards for water resource protection and utilization in the Zhengzhou metropolitan area to further enhance water resource security capabilities.
4.3. Analysis of the Effect of Driving Factors on ESV at Different Grid Scales
In this study, geoprobes were used to explore the response mechanism of the ESV in the Zhengzhou metropolitan area. The results show that the ESV of the Zhengzhou metropolitan area is jointly influenced by multiple factors, including GDP, slope, mean temperature, and FVC. Notably, after interacting with DEM and GDP, the NDVI has the strongest explanatory power. It serves as the main driver affecting spatial analysis. As an aggregate of the city and its surrounding areas, changes in the natural vegetation cover of the Zhengzhou metropolitan area will significantly impact the ESV. This finding is consistent with the results of Yang et al. [47] study on the Greater Nanchang Metropolitan Area, which suggests that the natural factors are the primary factors influencing the fluctuation of ESV. Meanwhile, after the human activity impact index interacts with other influencing factors, its influence is stronger than that of a single factor. This finding is largely consistent with the results of existing studies [51,52]. This might be because human activities lead to more drastic changes in the land use structure, which endows the anthropogenic impact index with a significant effect on ESV. Therefore, in future planning and management strategies, the interactions among different driving factors should be given priority. Control strategies should be adopted based on local conditions, and a sound policy mechanism should be established. This is to ensure that land use and development approaches are in harmony with regional natural conditions and socio-economic development levels, thus reducing the pressure on the ecosystem.
4.4. Limitations and Directions for Future Research
This study integrates quantitative analysis methods, including the equivalent factor method, sensitivity analysis, land use transition matrix, and Geodetector, to develop a multi-scale research framework for ESs. Using this framework, we quantified the spatiotemporal distribution characteristics of ESs in the Zhengzhou Metropolitan Area and conducted an in-depth exploration of the spatiotemporal dynamics of ES interactions and their underlying mechanisms. This study provides guidance for determining appropriate spatial management units and zoning strategies, offering insights for spatial planning and management. It contributes to advancing regional ecological conservation and high-quality development. However, further research is needed to refine these approaches.
First, uncertainties in parameterization and modeling are prevalent in ecosystem services research [53]. Investigating the potential impacts of these uncertainties on ecosystem service performance and interactions across different spatial units is crucial [54]. Second, this study uses the Zhengzhou Metropolitan Area as a case study region, which exhibits relative locality within the broader context of Henan Province. When studying ecosystem services across large-scale regions, it is necessary to integrate broader experimental and survey efforts to further refine methodologies for determining appropriate research units and temporal scales. Moreover, ecosystem services and their interactions are not only influenced by regional factors but also dynamically evolve over time. This phenomenon arises from time-lagged changes and feedback mechanisms inherent to ecological processes—mechanisms that can amplify, mitigate, or reverse the effects of spatial differentiation through dynamic temporal interactions [55]. Identifying these temporal variations is crucial for prioritizing ecosystem management and designing effective policy interventions [56]. Future research should comprehensively investigate the temporal evolution of ES interactions and apply multi-scenario simulations to support comparative analyses of various spatial planning and management strategies, thus laying a more robust scientific foundation for decision-making.
5. Conclusions and Policy Implications
This study, based on Land Use and Land Cover (LULC) data and multi-method analysis in ArcGIS, reveals the spatiotemporal evolution of ecosystem service value (ESV) in the Zhengzhou Metropolitan Area from 2010 to 2022 and its driving mechanisms, providing a scientific basis for ecosystem management in the study area. Key findings are as follows:
The land use transition matrix indicates that farmland and forest land dominate the Zhengzhou metropolitan area’s land use types, with construction land experiencing the fastest growth. This expansion primarily stems from the conversion of farmland in central areas, directly reflecting urbanization’s impact on land use structure.
Spatiotemporal analysis reveals a declining trend in total ESV (2.64% decrease), with a west-to-east diminishing spatial pattern: low-value zones concentrate in central built-up and idle lands, while high-value zones are distributed in western forested areas and northern water bodies. Regulatory and supporting services constitute the primary components of ESV.
Geodetector analysis across four grid scales confirms that natural and topographic factors are the primary drivers of ESV spatial heterogeneity, while socioeconomic factors (GDP) and climatic factors (temperature) play secondary roles.
Western hilly areas, characterized by steep slopes and high ecosystem service values, should establish ecological conservation redlines. Convert steep-slope farmland into soil and water conservation forests to reduce erosion. In eastern plains, construct “field-forest-water-village” ecological networks around farmland to enhance windbreak, sand fixation, and water purification functions. Tailor ecological conservation policies to local conditions to improve their effectiveness.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.W.; methodology, S.W. and J.J.; software, A.W.; validation, C.X., S.W. and J.J.; formal analysis, S.W.; investigation, J.J.; resources, A.W.; data curation, S.W.; writing—original draft preparation, S.W. and J.J.; writing—review and editing, J.J.; visualization, S.W.; supervision, C.X.; project administration, A.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the General Project of the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 52079051, the Key Scientific Research Project of Henan Province Colleges and Universities, Nos. 22A570004 & 23A570006, the Program for Innovative Research Team (in Science and Technology) in University of Henan Province (24IRTSTHN012), and the Science and Technology Program of Zhejiang Province, No. 2021C03019.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Wang, G.; Zhang, F. Spatial and Temporal Evolution and Impact Factors Analysis of Ecosystem Service Value in the Liaohe River Delta over the Past 30 Years. Huanjing Kexue 2024, 45, 228–238. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, G.D.; Zhang, C.X.; Zhang, C.S.; Xiao, Y.; Lu, C.X. The value of ecosystem services in China. Resour. Sci. 2015, 37, 1740–1746. [Google Scholar]
- Millennium Ecosystem Assessment. Ecosystems and Human Well-Being; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, Y.; Zhou, M.; Ou, G.; Dai, D.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Nie, X.; Yang, C. Integrating ecosystem services value for sustainable land-use management in semi-arid region. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 186, 662–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baró, F.; Palomo, I.; Zulian, G.; Vizcaino, P.; Haase, D.; Gómez-Baggethun, E. Mapping ecosystem service capacity, flow and demand for landscape and urban planning: A case study in the Barcelona metropolitan region. Land Use Policy 2016, 57, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Su, Y.; Shahtahmassebi, A.R.; Huang, L.; Zhou, M.; Gan, M.; Deng, J.; Zhao, G.; Wang, K.E. Assessing and mapping cultural ecosystem services supply, demand and flow of farmlands in the Hangzhou metropolitan area, China-ScienceDirect. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 692, 756–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Shi, D.; Zhou, L.; Fang, R. Identification of ecosystem services supply and demand areas and simulation of ecosystem service flows in Shanghai. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 115, 106418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Crittenden, J.C.; Li, F.; Lu, Z.; Dou, X. Urban expansion simulation and the spatio-temporal changes of ecosystem services, a case study in Atlanta Metropolitan area, USA. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 622–623, 974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daily, G.C. Nature’s Services: Societal Dependence on Natural Ecosystems; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Costanza, R.; d’Arge, R.; De Groot, R.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; O’neill, R.V.; Paruelo, J.; et al. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Ren, F.; Xu, W.; Ma, X.; Zhang, H.; He, W. China’s ecosystem service value in 1992–2018: Pattern and anthropogenic driving factors detection using Bayesian spatiotemporal hierarchy model-ScienceDirect. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 302, 114089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Su, H.; Sammonds, P.; Xu, M.; Yan, C.; Zhu, Z. Evaluation and Prediction of Ecosystem Services Value in Urban Agglomerations Using Land Use/Cover Change Analysis: Case Study of Wuhan in China. Land 2024, 13, 1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tribot, A.S.; Deter, J.; Mouquet, N. Integrating the aesthetic value of landscapes and biological diversity. Proc. R. Soc. Biol. Sci. 2018, 285, 20180971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Wu, T.; Fu, B. The value of ecosystem services in China: A systematic review for twenty years. Ecosyst. Serv. 2021, 52, 101365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Li, Z.; Huang, J.; Shi, Q.; Li, Y. A Revisit to the Impacts of Land Use Changes on the Human Wellbeing via Altering the Ecosystem Provisioning Services. Adv. Meteorol. 2013, 2013, 183–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintas-Soriano, C.; Castro, A.J.; Castro, H.; García-Llorente, M. Impacts of land use change on ecosystem services and implications for human well-being in Spanish drylands. Land Use Policy 2016, 54, 534–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, C.C.; Hu, G.H. Spatial and temporal evolution and prediction of ecosystem service value in Taihang Mountains based on MCCA land use scenario modeling. Environ. Sci. 2024, 45, 5912–5923. [Google Scholar]
- An, Y.; Zhao, W.; Li, C.; Ferreira, C.S.S. Temporal changes on soil conservation services in large basins across the world. Catena 2022, 209, 105793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, X. Synergistic relationships of ecosystem service trade-offs and their spatial and temporal heterogeneity in the Yellow River Basin. Environ. Sci. 2025, 46, 972–989. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.Q.; Han, L.; Zhu, H.L.; Zhao, Y.H.; Liu, Z.; Chen, R. Change of ecological service value before and after returning farmland to forest based on land use in Yan’an City. J. Northwest For. Univ. 2020, 35, 203–211. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Huang, Y. Spatiotemporal evolution of ecosystem service value and its driving force in Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2021, 28, 382–389. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.Y.; Li, J.; Zhou, Z.X.; Ma, X.P.; Zhang, C. Expression of ecosystem service tradeoff synergistic relationship based on multi-scale in Qinba Mountain area. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 5465–5477. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Xu, C. Geodetector: Principle and prospective. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 72, 116–134. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, N.; Guan, Q.; Wang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Li, H.; Ma, Y. Spatial Differentiation and Driving Mechanisms in Ecosystem Service Value of Arid Region:A case study in the middle and lower reaches of Shule River Basin, NW China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 319, 128718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Kang, F.; Han, H.; Cheng, X.; Li, Z. Exploring drivers of ecosystem services variation from a geospatial perspective: Insights from China’s Shanxi Province. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 131, 108188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Yang, J.; Yin, X.; Jia, K.; Sun, J.; Shu, S.; Huang, A. Supply and demand of ecosystem services and their responses to urbanization at multiple spatial scales in the Greater Bay Area of Guangdong, Hong Kong and Macao. J. Ecol. 2024, 44, 9094–9107. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, W.; Li, J.; Shen, S.; Ma, L.; Chen, L. Spatial and temporal changes in the value of ecosystem services and their driving forces in Beijing. J. Ecol. 2025, 45, 306–318. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Zhao, M.; Li, Y.; Fan, Y.; Wang, J. Spatial and temporal relationship between ecosystem service value and human activity intensity in Xi’an metropolitan area. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2024, 40, 325–334. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Luo, J.; Shi, P.; Zhou, L. Spatial and temporal evolution of ecosystem service value and topographic gradient differentiation characteristics in Zhangye at grid scale. J. Appl. Ecol. 2020, 31, 543–553. [Google Scholar]
- Kourtit, K.; Nijkamp, P.; Suzuki, S. Are global cities sustainability champions? A double delinking analysis of environmental performance of urban agglomerations. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 709, 134963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Jensen, J.; Weng, Q.; Weaver, R. A Geographically Weighted Regression Analysis of the Underlying Factors Related to the Surface Urban Heat Island Phenomenon. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; She, J.; Long, X.; Zhang, M. Spatio-temporal evolution and driving factors of eco-environmental quality based on RSEI in Chang-Zhu-Tan metropolitan circle, central China. circle, central China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 144, 109436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, X.; Guo, Q.Z.; Pan, Y.Y.; Fu, Y. Research on land use dynamic change and prediction in Lucheng City of Shanxi Province based on the results of a study on the impacts of land use change and prediction in Lucheng City. on TM and OLI. Remote Sens. Land Resour. 2018, 30, 125–131. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.S.; Pan, H.Y.; Liu, Y.H.; Tang, Y.P.; Zhang, Z.F.; Ma, H.J. Evolution and driving force of ecosystem service value based on dynamic equivalent in Leshan City. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 76–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaodi, X.; Caixia, Z.; Lin Zab, L.Z. Dynamic changes in the value of China’s ecosystem services-ScienceDirect. Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 26, 146–154. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.Z.; Guo, A.; Sun, Z.Y. Impacts of land use change on ecological services value in Duolun County of Inner Mongolia based on RS and GIS. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2011, 31, 110–116. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, M.Y.; Fang, B.; Yue, W.Z.; Feng, S.R. Spatial differentiation of ecosystem service values and its geographical detection in Chaohu Basin during 1995–2017. Geogr. Res. 2019, 38, 2790–2803. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Yang, D.; Tang, L.; Qiao, Z.; Ma, L.; Chen, M. Exploring the Impact of Grain-for-Green Program on Trade-Offs and Synergies among Ecosystem Services in West Liao River Basin, China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, L.; Yang, X.; Liang, T.; Zhang, Q.; Liao, X.; White, J.R.; Rinklebe, J. Interactive influences of meteorological and socioeconomic factors on ecosystem service values in a river basin with Interactive influences of meteorological and socioeconomic factors on ecosystem service values in a river basin with different geomorphic features. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 829, 154595. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, M.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Jiao, M.; Li, M.; Xia, B. Spatio-temporal changes in ecosystem service value in response to land-use/cover changes in the Pearl River Delta. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 149, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polasky, S.; Nelson, E.; Pennington, D.; Johnson, K.A. The Impact of Land-Use Change on Ecosystem Services, Biodiversity and Returns to Landowners: A Case Study in the State of Minnesota. Environ. Resour. Econ. 2011, 48, 219–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, E.F.; Meyfroidt, P. Global land use change, economic globalization, and the looming land scarcity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 3465–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, S.; Shi, W.; Zhu, X. Impact of land use land cover changes on ecosystem service value-A case study of Guangdong, Hong Kong, and Macao in South China. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Kong, L.; Zhang, L.; Ouyang, Z. The balance between economic development and ecosystem service value in the process of land urbanization: A case study of China’s land urbanization from 2000 to 2015. Land Use Policy 2021, 108, 105536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, W.; Pickett, S.T.; Yu, W.; Li, W. A multiscale analysis of urbanization effects on ecosystem services supply in an urban megaregion. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 662, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Wu, S.; Yu, Y.; Tong, G.; Mo, L.; Yan, D.; Li, F. Spatiotemporal interaction between ecosystem services and urbanization: Case study of Nanjing City, China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 95, 917–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Chen, B.; Huang, X.; Wei, Y.D. Effect of land-use change and optimization on the ecosystem service values of Jiangsu province, China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 106507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Fang, C. Factors influencing ecosystem services in the Pearl River Delta, China: Spatiotemporal differentiation and varying importance. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 168, 105477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Yu, J.; Shi, L.N.; Zhao, X.; Wang, J. Spatiotemporal evolution of ecosystem service values in an area dominated by vegetation restoration: Quantification and mechanisms. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 131, 108191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Li, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y. Evolution and prediction of ecosystem service values of the Yangtze River Basin. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 6203–6211. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, M.; Yue, W.; Fang, B.; Feng, S. 1970–2015 Characteristics of ecological service value scale response and geodetection mechanism in Dabie mountain area. J. Geogr. 2019, 74, 1904–1920. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Wang, Y. Spatial and temporal evolution of ecosystem service value and spatial differentiation mechanism in Dongjiang Basin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2023, 34, 2498–2506. [Google Scholar]
- Grêt-Regamey, A.; Brunner, S.H.; Altwegg, J.; Bebi, P. Facing uncertainty in ecosystem services-based resource management. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 127, S145–S154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Jin, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Y. Ecosystem services to support sustainable development: The modifiable areal unit problem in the transition between evaluation and management units. Sustain. Dev. 2024, 32, 6253–6273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallimer, M.; Davies, Z.G.; Diaz-Porras, D.F.; Irvine, K.N.; Maltby, L.; Warren, P.H.; Armsworth, P.R.; Gaston, K.J. Historical influences on the current provision of multiple ecosystem services. Glob. Environ. Change 2015, 31, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Liu, C.; Liu, L.; Wang, W. Dynamic Analysis of Supply and Demand Coupling of Ecosystem Services in Loess Hilly Region: A Case Study of Lanzhou, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2021, 31, 276–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).