Research on a Multi-Objective Synergistic Approach to Improve the Performance of Rural Dwellings in Cold Regions of China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Framework and Method
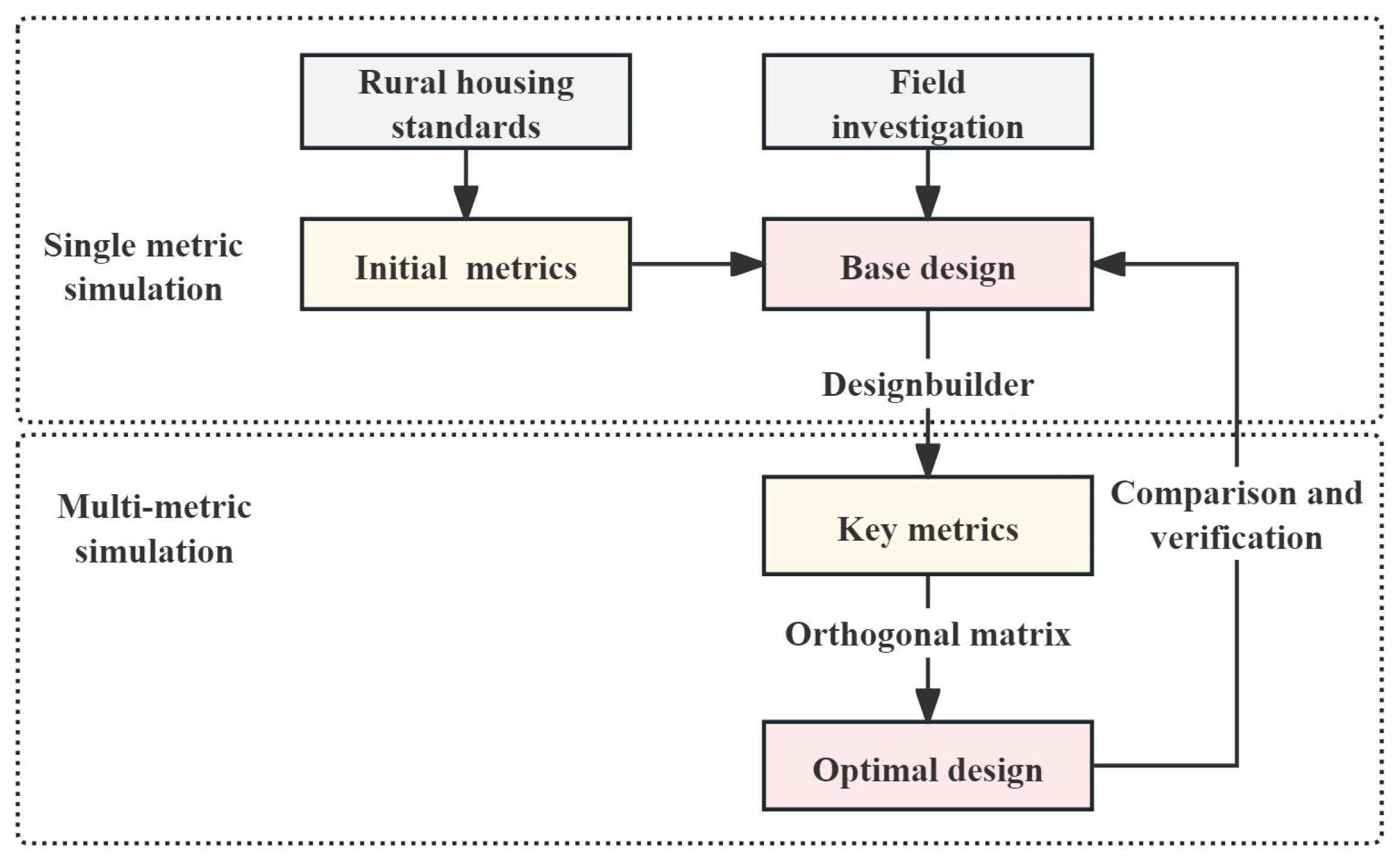
2.1. Research Framework
2.2. Research Methods
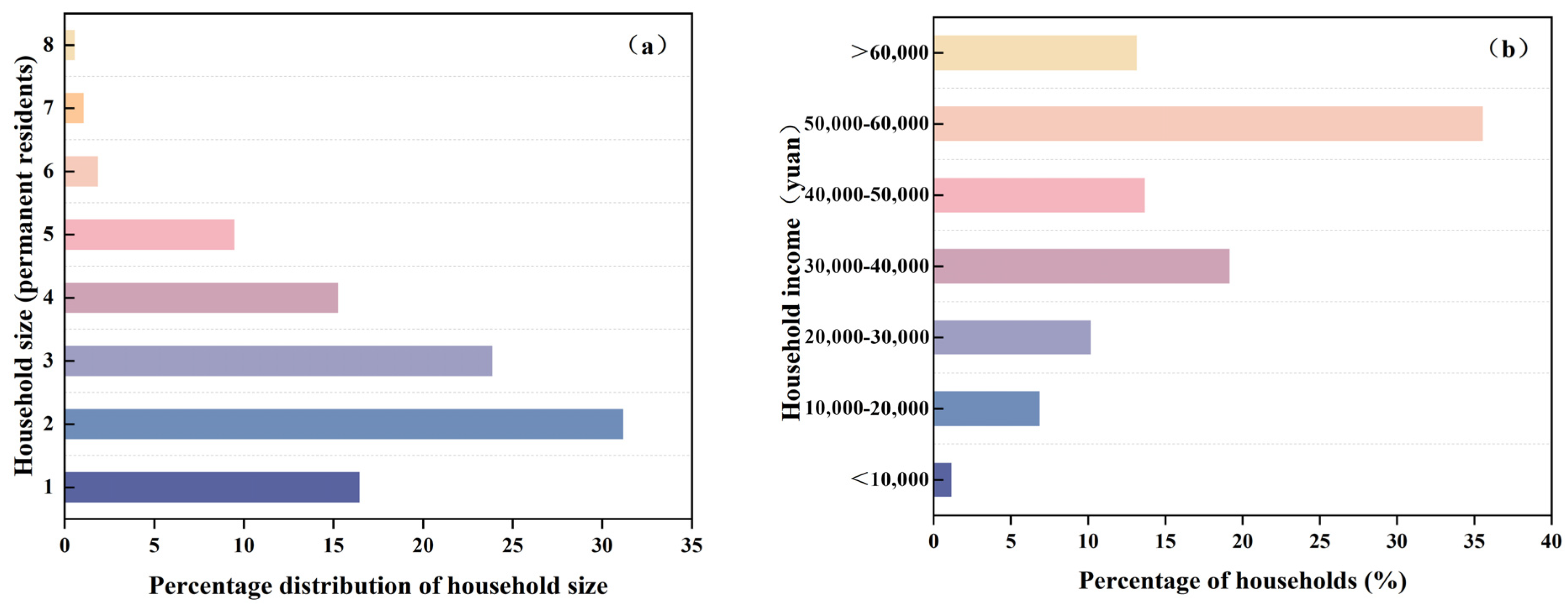
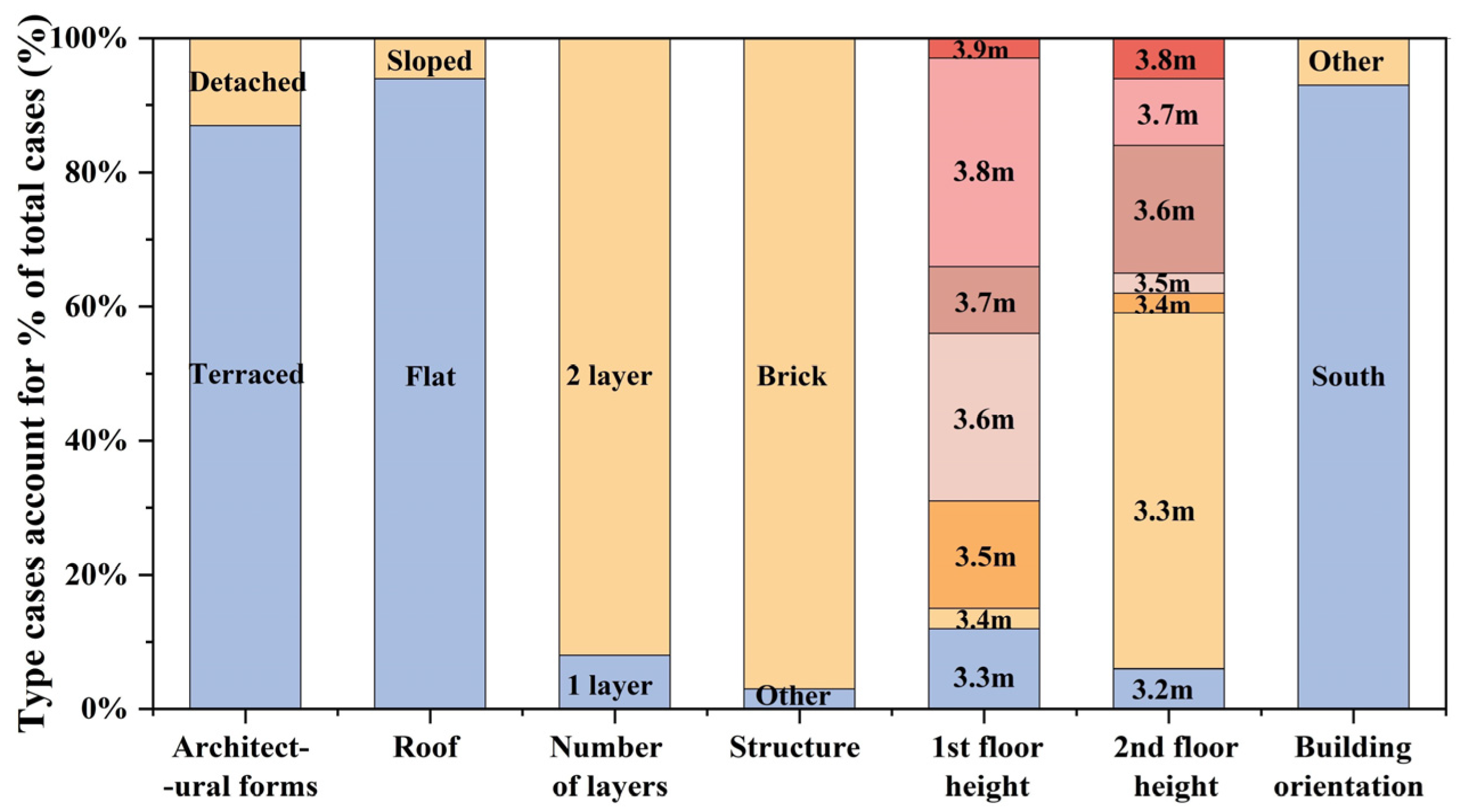
2.2.1. Questionnaire Survey
2.2.2. Establishment of Base Design Model
2.2.3. Research Steps
3. Results
3.1. Single Metrics Simulation
3.1.1. Building Orientation
3.1.2. Interior Clear Height
3.1.3. Body Shape Factor
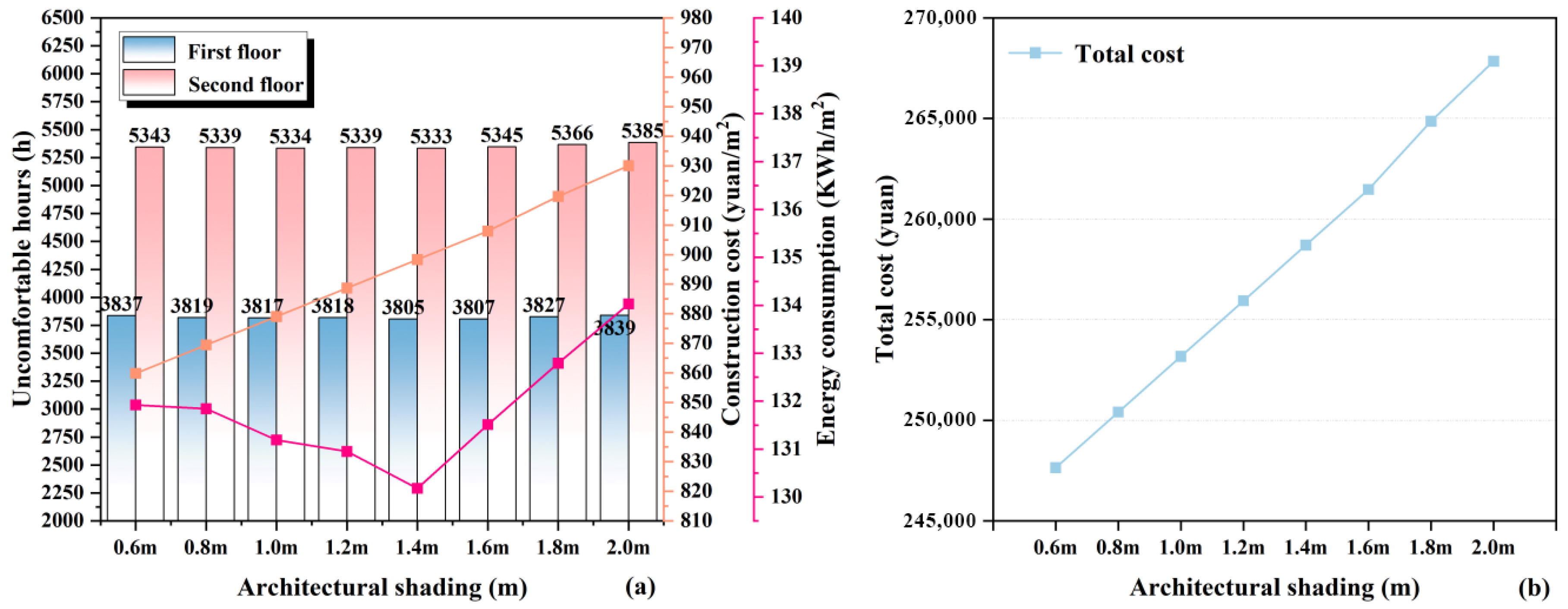
3.1.4. Building Shading
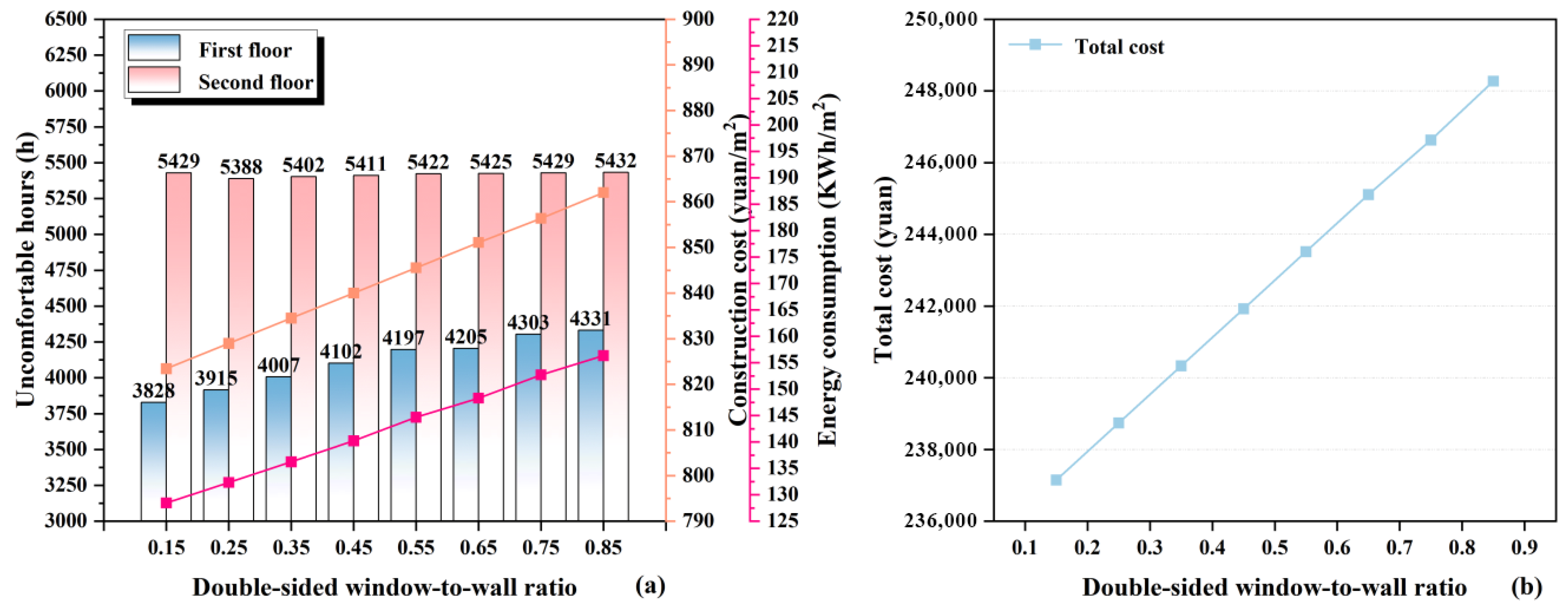
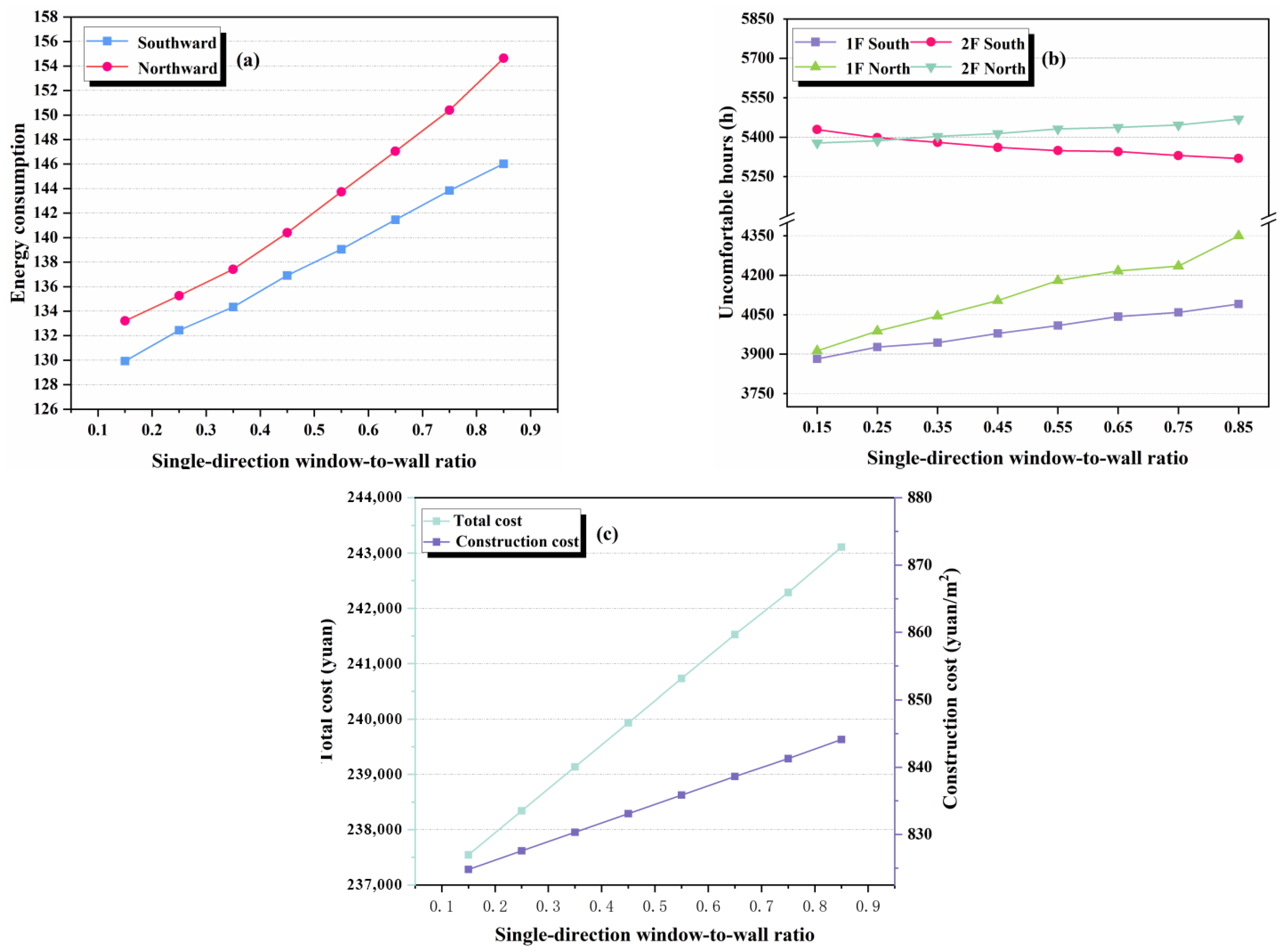
3.1.5. Window-to-Wall Ratio
Double-Sided Window-to-Wall Ratio
Single-Direction Window-to-Wall Ratio
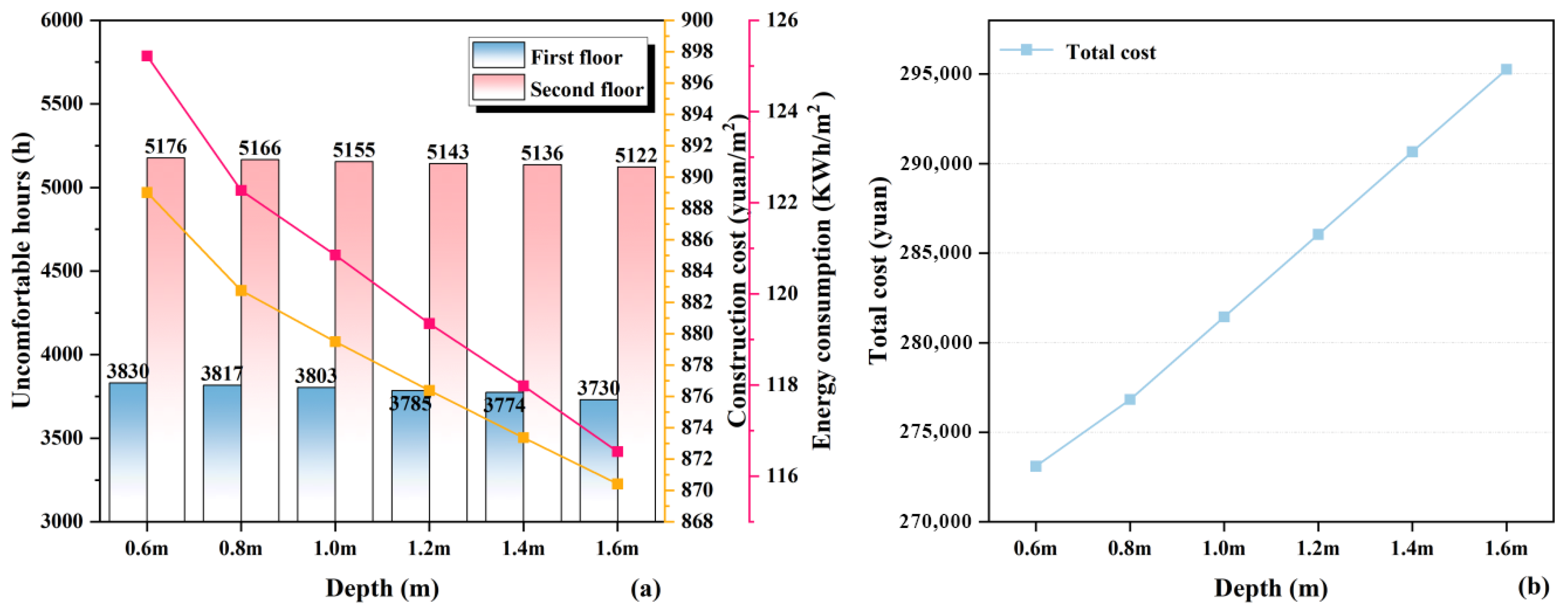
3.1.6. Additional Sunroom
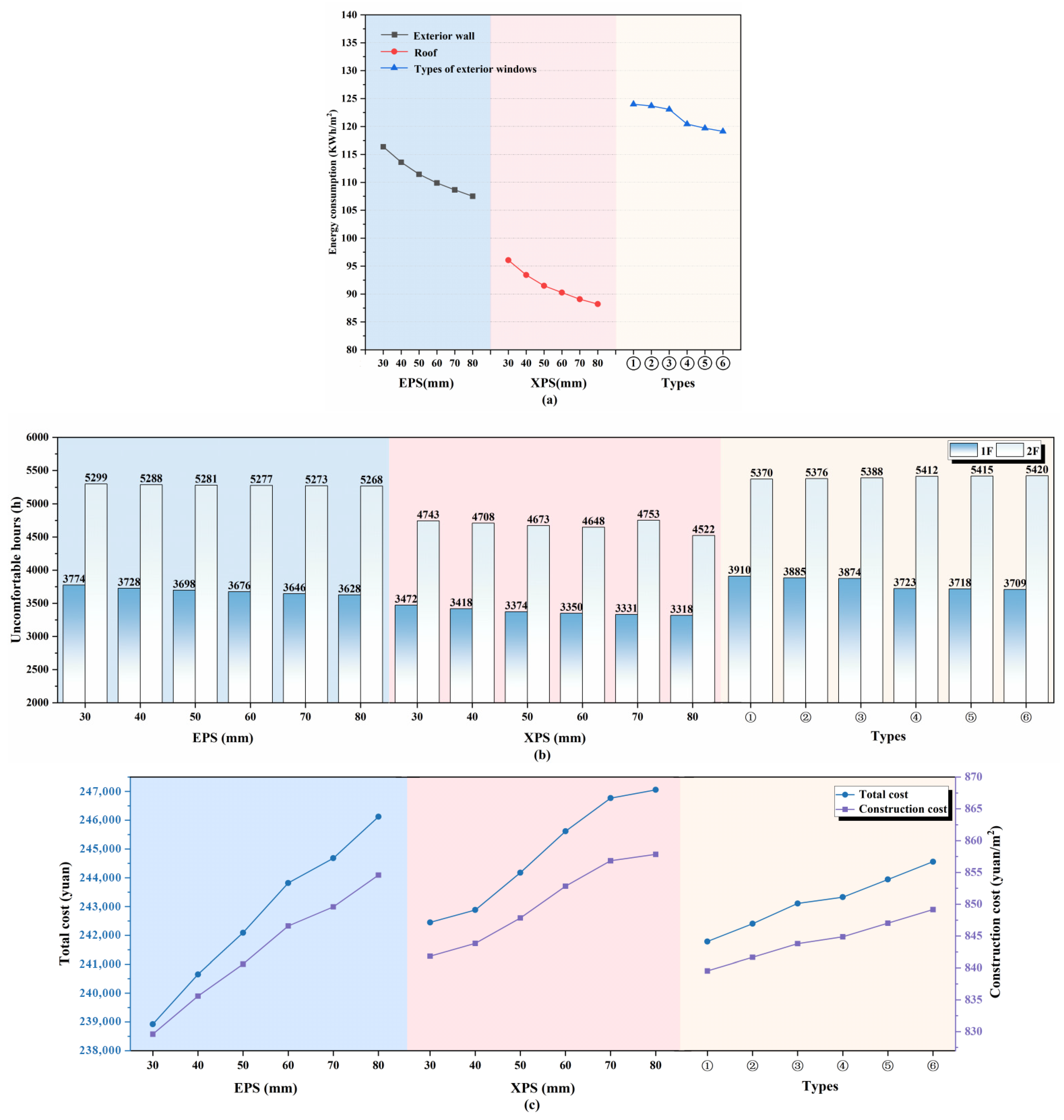
3.1.7. Exterior Envelope
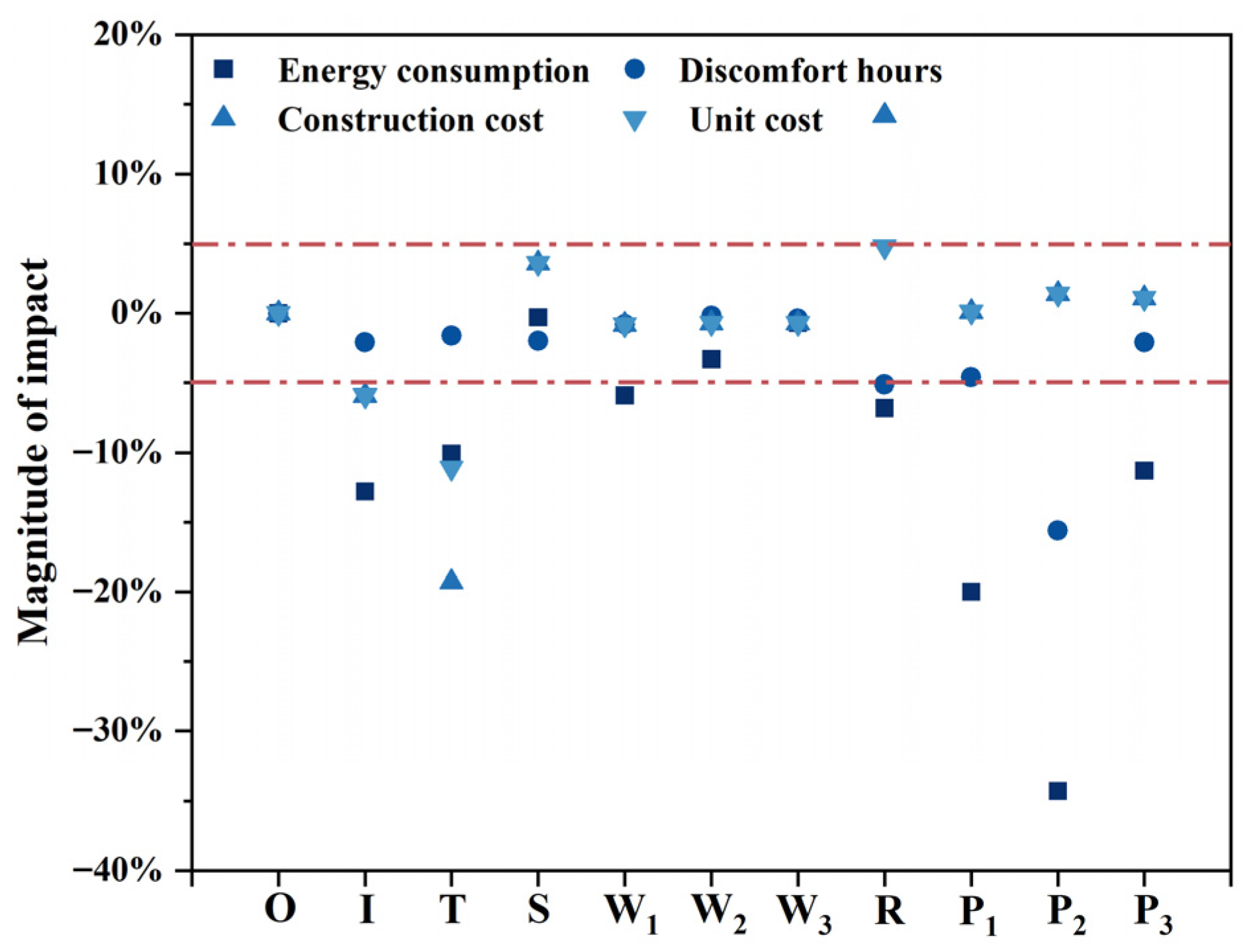
3.1.8. Level of Impact
3.2. Multi-Metric Simulation
3.2.1. Data Analysis
3.2.2. Multi-Metric Calculations and Analyses
4. Discussion
4.1. Characteristics of Rural Dwellings
4.2. Representativeness and Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Convective Heat Transfer Coefficient [W/(m2·K)] | Radiant Heat Transfer Coefficient [W/(m2·K)] | |
|---|---|---|
| Indoor side | 2 | 5 |
| Outdoor side | 20 | 5 |
Appendix B. Matrix Formulae (A1)–(A5)
Appendix C
| Number | Factor | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01 | ||||||
| 02 | ||||||
| 03 | ||||||
| 04 | ||||||
| 05 | ||||||
| 06 | ||||||
| 07 | ||||||
| 08 | ||||||
| 09 | ||||||
| 10 | ||||||
| 11 | ||||||
| 12 | ||||||
| 13 | ||||||
| 14 | ||||||
| 15 | ||||||
| 16 | ||||||
| 17 | ||||||
| 18 | ||||||
| 19 | ||||||
| 20 | ||||||
| 21 | ||||||
| 22 | ||||||
| 23 | ||||||
| 24 | ||||||
| 25 | ||||||
Appendix D
| Average Building Energy Consumption (KWh/m2) | Factor | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | E | F | |
| 42.98 | 47.77 | 47.15 | 48.75 | 50.11 | 47.71 | |
| 43.84 | 46.04 | 46.75 | 45.99 | 46.85 | 45.58 | |
| 45.14 | 45.16 | 45.49 | 45.17 | 44.90 | 45.11 | |
| 46.90 | 44.06 | 44.35 | 43.76 | 42.84 | 43.37 | |
| 47.61 | 43.43 | 42.72 | 42.80 | 41.77 | 44.69 | |
| 4.63 | 4.34 | 4.43 | 5.95 | 8.34 | 3.02 | |
| Order of importance of factors | E > D > A > C > B > F | |||||
| Best option | ||||||
| Worst-case scenario | ||||||
Appendix E
| Total Hours of Thermal Discomfort (h) | Factor | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | E | F | |
| 6195 | 6679 | 6455 | 6539 | 6824 | 6966 | |
| 6266 | 6584 | 6358 | 6397 | 6444 | 6611 | |
| 6324 | 6337 | 6363 | 6368 | 6319 | 6049 | |
| 6440 | 6167 | 6327 | 6241 | 6128 | 6206 | |
| 6591 | 6048 | 6313 | 6270 | 6100 | 5984 | |
| 396 | 631 | 142 | 298 | 724 | 982 | |
| Order of importance of factors | F > E > B > A > D > C | |||||
| Best option | ||||||
| Worst-case scenario | ||||||
Appendix F
| Construction Cost Per Unit Area (yuan/m2) | Factor | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | E | F | |
| 915.25 | 967.18 | 933.57 | 914.47 | 919.86 | 918.88 | |
| 918.67 | 948.74 | 931.42 | 928.41 | 922.93 | 928.32 | |
| 925.06 | 923.17 | 932.73 | 926.76 | 927.53 | 926.05 | |
| 933.81 | 906.51 | 921.34 | 931.52 | 933.65 | 928.76 | |
| 943.24 | 890.45 | 916.98 | 934.88 | 932.07 | 934.03 | |
| 27.99 | 76.73 | 16.59 | 20.41 | 13.79 | 15.15 | |
| Order of importance of factors | B > A > D > C > F > E | |||||
| Best option | ||||||
| Worst-case scenario | ||||||
References
- Jia, C.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, M.; Han, S.; Cao, J.; Rong, Y.; Du, C. Investigation on indoor thermal environment of industrial heritage during the cooling season and its impacts on thermal comfort. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2023, 52, 103769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Ma, S.; Guo, Y.; Yan, Y.; Xu, X. Research on the coupling relationship between energy consumption and architectural form design of university dormitory buildings under the target of low energy consumption. Energy Build. 2025, 337, 115664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, A.; Keane, M.M.; Torrens, J.I.; Corry, E. Building operation and energy performance: Monitoring, analysis and optimisation toolkit. Appl. Energy 2013, 101, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannan, M.; Al-Ghamdi, S.G. Indoor air quality in buildings: A comprehensive review on the factors influencing air pollution in residential and commercial structure. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Hou, M.; Yao, W.; Gao, W.; Jia, F.; Wang, T. Research on indoor thermal environment evaluation and thermal adaptation in winter of Japanese wood-framed detached houses. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2024, 55, 104126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgarm, N.; Sajadi, B.; Delgarm, S. Multi-objective optimization of building energy performance and indoor thermal comfort: A new method using artificial bee colony (ABC). Energy Build. 2016, 131, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Li, Y.; Long, H.; Kang, C. The evolution of China’s rural depopulation pattern and its influencing factors from 2000 to 2020. Appl. Geogr. 2023, 159, 103089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; He, Y.; Zhou, Q. Impact of multi-energy complementary system on carbon emissions: Insights from a rural building in Shangluo City, China. Energy Convers. Manag. 2025, 327, 119595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.-J.; Yang, L.; Ye, M.; Mou, B.; Zhou, Y. Overview of rural building energy efficiency in China. Energy Policy 2014, 69, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Building Energy Research Center of Tsinghua University. Comparison of Energy Consumption and Carbon Emissions from Building Operation Between China and Other Countries. In Decarbonize Urban Heating System: China Building Energy and Emission Yearbook 2023; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 27–40. [Google Scholar]
- Berardi, U. A cross-country comparison of the building energy consumptions and their trends. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 123, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahsildoost, M.; Zomorodian, Z. Energy, carbon, and cost analysis of rural housing retrofit in different climates. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 30, 101277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yetiskul, E.; Aydın, N.; Gökçe, B. Governing the rural: The case of Izmir (Turkey) in the Post-2000 era. J. Rural Stud. 2021, 88, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, D.; Kwon, Y. In-Migration and Housing Choice in Ho Chi Minh City: Toward Sustainable Housing Development in Vietnam. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowaltowski, D.C.C.K. Aesthetics and self-built houses: An analysis of a Brazilian setting. Habitat Int. 1998, 22, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efficiency, C. Research Report of China Building Energy Consumption and Carbon Emissions. Architecture 2022, 2023, 57–69. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, M.; Yu, S.; Song, B.; Deng, Q.; Liu, J.; Delgado, A. Building energy efficiency in rural China. Energy Policy 2014, 64, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Chi, J.; Luo, S.; Ke, H.; Yuan, J.; Yue, X. Multi objective optimization technical framework for passive energy-saving design of rural residential buildings in Tianjin based on Octopus+ Honeybee. J. Xi’an Univ. Technol. 2021, 37, 488–497. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Xiang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Lin, Q.; Wang, W.; Wang, H. Active–passive combined energy-efficient retrofit of rural residence with non-benchmarked construction: A case study in Shandong province, China. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 1360–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Guo, S.; Wu, Z.; Alsaedi, A.; Hayat, T. SWOT analysis for the promotion of energy efficiency in rural buildings: A case study of China. Energies 2018, 11, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Sun, X. Machine learning-based energy consumption models for rural housing envelope retrofits incorporating uncertainty: A case study in Jiaxian, China. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2025, 72, 106253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Liu, B.; Li, Q.; Li, D.; Ma, L. Weight of energy consumption parameters of rural residences in severe cold area. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2021, 26, 101131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Guo, J.; Li, J.; Hou, H.; Meng, Q.; Wang, W. A multi-objective optimization design method in zero energy building study: A case study concerning small mass buildings in cold district of China. Energy Build. 2018, 158, 1613–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, J.; Lv, H.; Yue, C.; Fu, M. Sensitivity analysis and multiobjective optimization for rural house retrofitting considering construction and occupant behavior uncertainty: A case study of Jiaxian, China. Appl. Energy 2024, 360, 122835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Xu, Z.; Shi, Y.; Tang, W.; Liu, C.; Yunusa-Kaltungo, A.; Cui, H. Multi-objective optimization designs of phase change material-enhanced building using the integration of the Stacking model and NSGA-III algorithm. J. Energy Storage 2023, 68, 107807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Yao, S.; Song, J.; Bi, W.; Qin, G.; Ni, P. Multi-performance collaborative optimization of existing residential building retrofitting in extremely arid and hot climate zone: A case study in Turpan, China. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 89, 109304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Wu, Y.; Ni, X.; Zhao, S.; Wu, X.; Li, M. Optimization design of rural residences in severe cold zone of China weighing the dual-control objectives of life cycle carbon emission and economic cost. Energy Build. 2025, 328, 115156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Wang, G.; Deng, Q. Multi-objective optimization of rural residential envelopes in cold regions of China based on performance and economic efficiency. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2024, 61, 104937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 50178-93; Building Climate Zoning Standards. China Architecture and Building Press: Beijing, China, 2025.
- Amani, N. Energy efficiency of residential buildings using thermal insulation of external walls and roof based on simulation analysis. Energy Storage Sav. 2024, 4, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, M.; Xu, Y.; Li, X.; Wu, Y.; Chi, F.A. Evaluation System Creation and Application of “Zero-Pollution Village” Based on Combined FAHP-TOPSIS Method: A Case Study of Zhejiang Province. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L. How to combine catalogue and stratified sampling in construction statistics. Shanghai Stat. 1996, 4, 14–17. Available online: https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SHTJ199604006.htm (accessed on 29 October 2024).
- Zhang, G. The application of stratified random sampling in audit. Audit Mon. 2013, 8, 1. Available online: https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SJYK201308017.htm (accessed on 18 October 2024).
- GB 5015-2021; General Code for Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy Application in Buildings. China Architecture and Building Press: Beijing, China, 2021.
- GB55016-2021; Chinese National Standard, General Code for Building Environment. China Architecture and Building Press: Beijing, China, 2021.
- GB 50176-2016; Code for Thermal Design of Civil Buildings. China Architecture and Building Press: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB/T 50824-2013; Design Standard for Energy Efficiency of Rural Residential Buildings. China Architecture Publishing & Media Co., Ltd.: Beijing, China, 2013.
- GB 50096-2011; Residential Design Code. Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development: Beijing, China, 2011.
- JGJ26—95; Energy Efficiency Design Standards for Civil Buildings. Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People Republic of China: Beijing, China, 1995.
- GB 50495-2019; Technical Standard for Solar Heating System. Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2019.
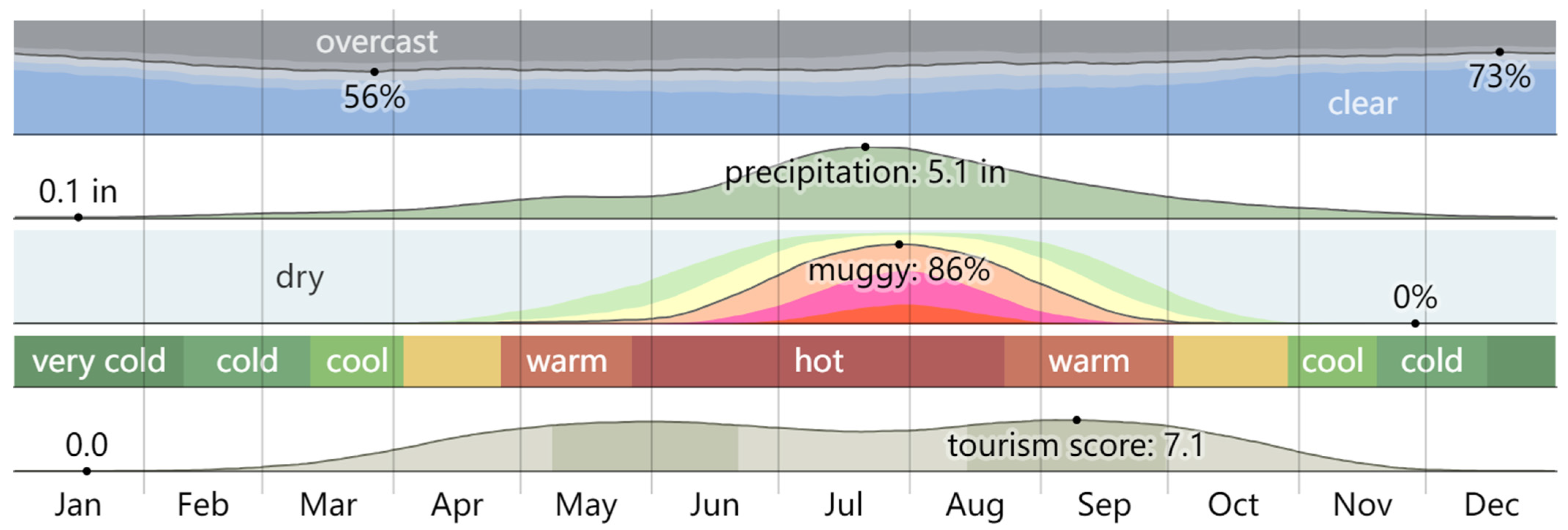
- Spark, W. Climate and Average Weather Year Round in Hebi. Available online: https://zh.weatherspark.com/ (accessed on 18 December 2024).
- Ebert, J.F.; Huibers, L.; Christensen, B.; Christensen, M.B. Paper- or Web-Based Questionnaire Invitations as a Method for Data Collection: Cross-Sectional Comparative Study of Differences in Response Rate, Completeness of Data, and Financial Cost. J. Med. Internet Res. 2018, 20, e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China, NBSO. Households’ Income and Consumption Expenditure in 2024 of the People’s Republic of China. Available online: https://www.stats.gov.cn/english/PressRelease/202501/t20250124_1958443.html (accessed on 12 October 2024).
- Hussainzad, E.A.; Gou, Z. Exploring the impact of demographic, architectural, and well-being factors on health outcomes in informal settlements: The role of daylight, window depth, and building orientation. Wellbeing Space Soc. 2025, 8, 100242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshino, H.; Murakami, S.; Akabayashi, S.; Kurabuchi, T.; Kato, S.; Tanabe, S.; Adachi, M. Survey on minimum ventilation rate of residential buildings in fifteen countries. In Proceedings of the 25th AIVC Conference-Ventilation and retrofitting, Prague, Czech Republic, 15–17 September 2004; pp. 227–238. [Google Scholar]
- Hesaraki, A.; Holmberg, S. Demand-controlled ventilation in new residential buildings: Consequences on indoor air quality and energy savings. Indoor Built Environ. 2015, 24, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Duan, Y.; Jiao, Z.; Ye, X.; Hu, Q.; Fukuda, H.; Gao, W. Towards Improving Rural Living Environment for Chinese Cold Region Based on Investigation of Thermal Environment and Space Usage Status. Buildings 2022, 12, 2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henan Provincial Engineering Cost Information Network. Henan Province Construction Engineering Material Price Information, January–February 2022 [EB/OL]. Available online: http://www.hncost.com/ (accessed on 14 November 2023).
- Chi, F.A.; Wang, Y.; Wang, R.; Li, G.; Peng, C. An investigation of optimal window-to-wall ratio based on changes in building orientations for traditional dwellings. Sol. Energy 2020, 195, 64–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Wang, J.; Bart, D.; Gao, W. The impact of building enclosure type and building orientation on indoor thermal comfort—A case study of Kashgar in China. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2023, 49, 103291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Sun, C.; Sang, M.; Chen, S.; Li, J.; Han, Y.; Xu, S. The synergistic effect of multiple design factors on building energy consumption of office blocks: A case study of Wuhan, China. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 95, 110200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Bande, L.; Ahmed, W.; Young, K.; Jha, M. AI application in architecture in UAE: Application of an advanced optimized shading structure as a retrofit strategy of a midrise residential building façade in downtown Abu Dhabi. Energy Build. 2024, 325, 114995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Xu, B.; Fei, Y.; Chen, X.-N.; Pei, G.; Ji, J. Passive energy-saving design strategy and realization on high window-wall ratio buildings in subtropical regions. Renew. Energy 2024, 229, 120709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Ma, L.; Li, Q.; Li, D.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, X.; Hu, H.; Han, Y. Energy saving retrofit of rural house based on the joint utilization of solar collector and attached sunspace. Energy Build. 2023, 299, 113591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Ding, Y.; Li, M.; Cao, Y.; Xie, W.; Wang, Z. Research and simulation analysis of thermal performance and hygrothermal behavior of timber-framed walls with different external thermal insulation layer: Cork board and anticorrosive pine plate. J. Build. Phys. 2021, 45, 180–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, T.V.; Cruickshank, C.A.; Beausoleil-Morrison, I.; Lacasse, M. Thermal evaluation of a highly insulated steel stud wall with vacuum insulation panels using a guarded hot box apparatus. J. Build. Phys. 2021, 45, 303–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Li, T.; Wang, F. Heat insulation and thermal insulation method of passive low energy consumption residential building exterior envelope structure based on BIM. Results Eng. 2024, 23, 102734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Ran, M.Y.; Yuan, J.J.; Li, J. Discussion on Shading Optimization Design for Residential Buildings. Build. Sci. 2010, 26, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Du, Z.; Xue, T.; Jiang, T. An integrated artificial intelligence-driven approach to multi-criteria optimization of building energy efficiency and occupants’ comfort: A case study. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 103, 111944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Zhang, T.; Yang, Y.; Li, P.; Mo, W.; Jiao, Z.; Gao, W. A multi-objective approach to optimizing the geometry and envelope of rural dwellings for energy demand, thermal comfort, and daylight in cold regions of China: A case study of Shandong province. Energy Convers. Manag. 2024, 322, 119128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Kan, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhong, K.; Hu, J. Optimization of synthesis parameters for C-S-H/PCE nanocomposites: A comprehensive study using orthogonal experiments and multi-analysis approaches. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 417, 135332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, Y.; Hu, Y.; Xu, M.; Wu, T.; Liu, S.; Zhang, H.; Sun, N.; Liu, S. Effects of vacuum hot-pressed sintering parameters on the microstructures and mechanical properties and process optimization of TiB2p/Al7050 composites. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 938, 168580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurnitski, J.; Saari, A.; Kalamees, T.; Vuolle, M.; Niemelä, J.; Tark, T. Cost optimal and nearly zero energy performance requirements for buildings in Estonia. Est. J. Eng. 2013, 19, 183–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, V.T. Low Energy Housing for the Hot Humid Climate of Vietnam: The value of a Passive House Approach. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Huddersfield, Huddersfield, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Guillante, P.; Compton, A.; Gioppo, Z.; Raleigh, Q.; Kiesling, C.; Cooper, J.; Cetin, K.; Poleacovschi, C. Development of residential building archetype models for rural Alaskan communities. J. Build. Perform. Simul. 2025, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
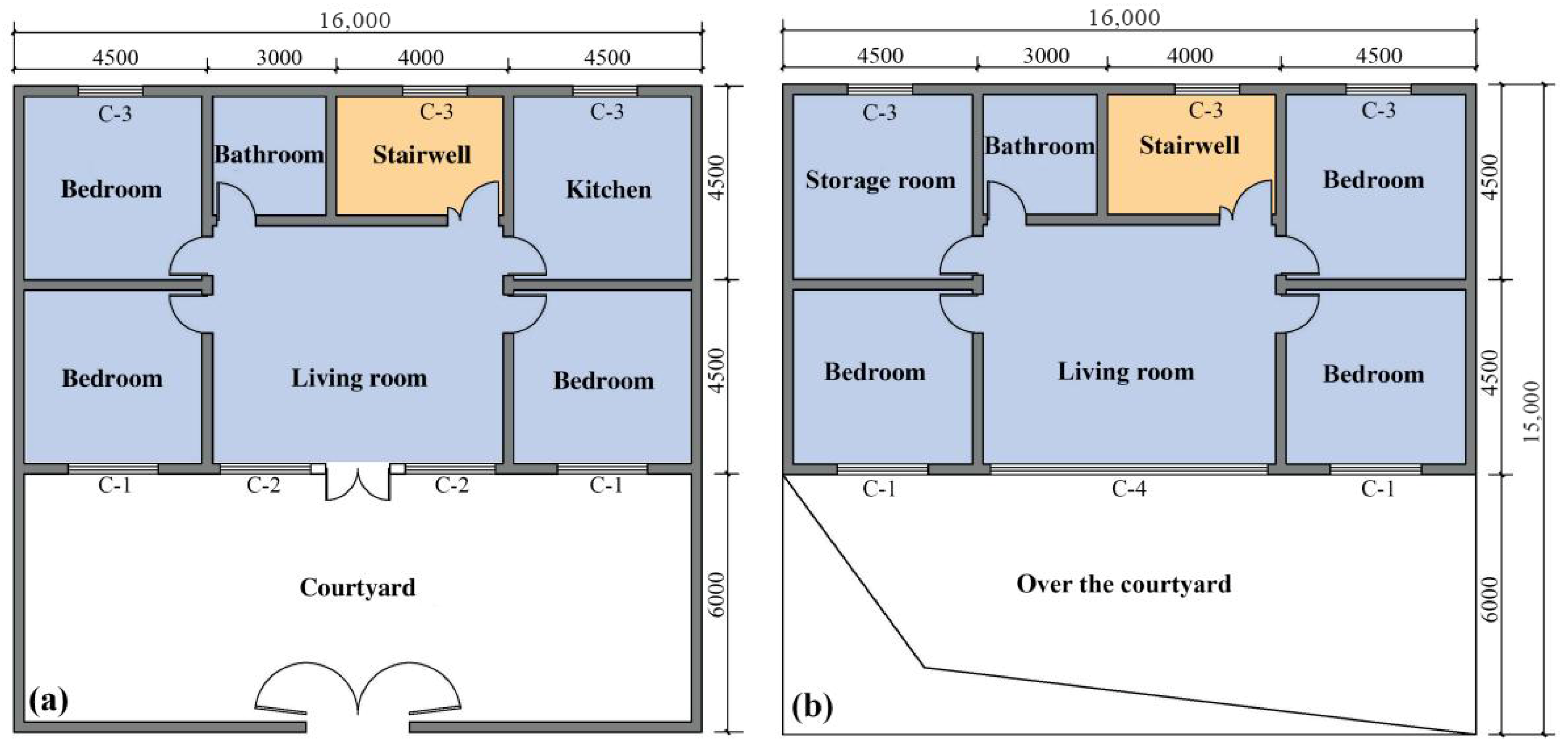
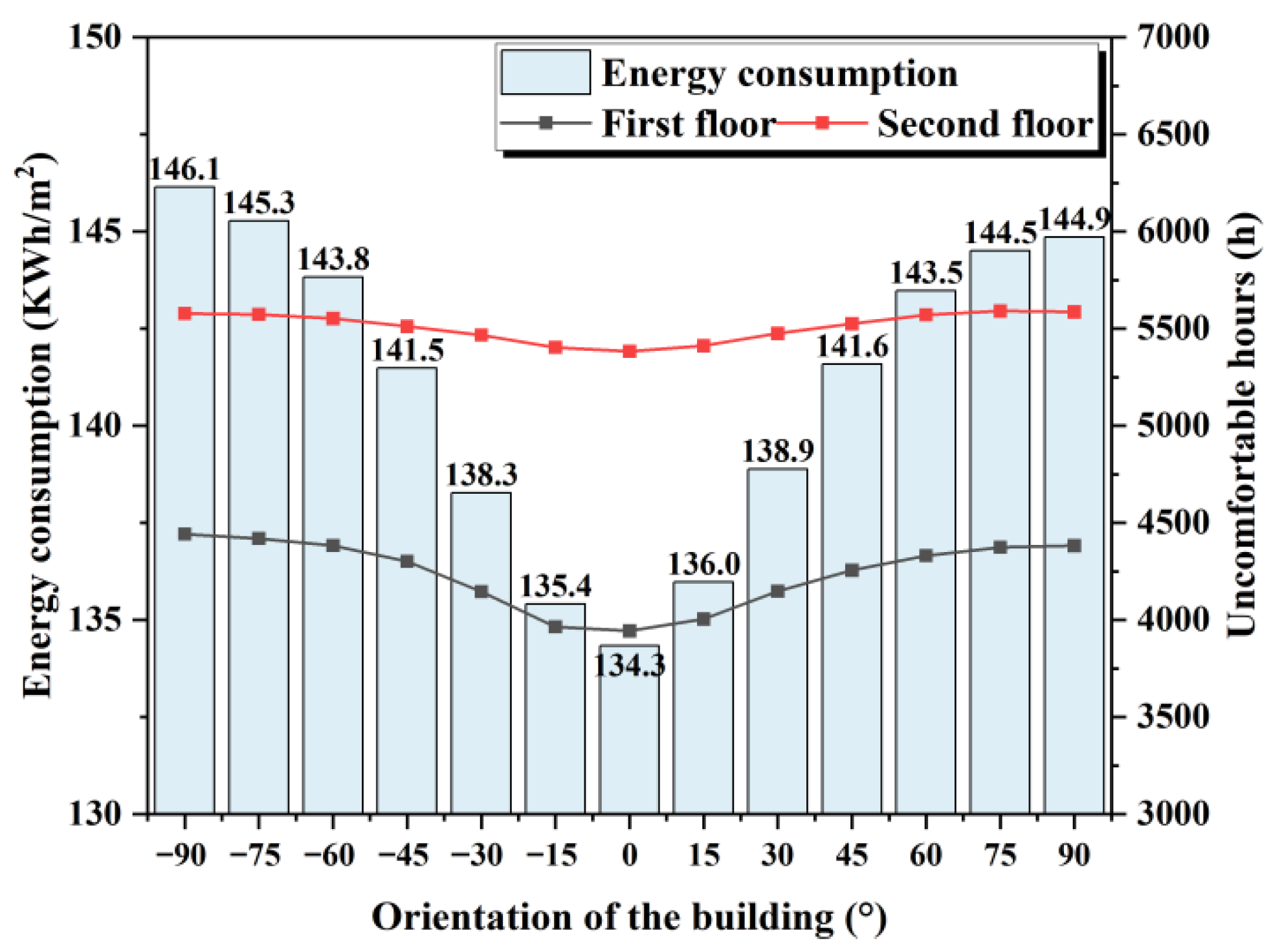
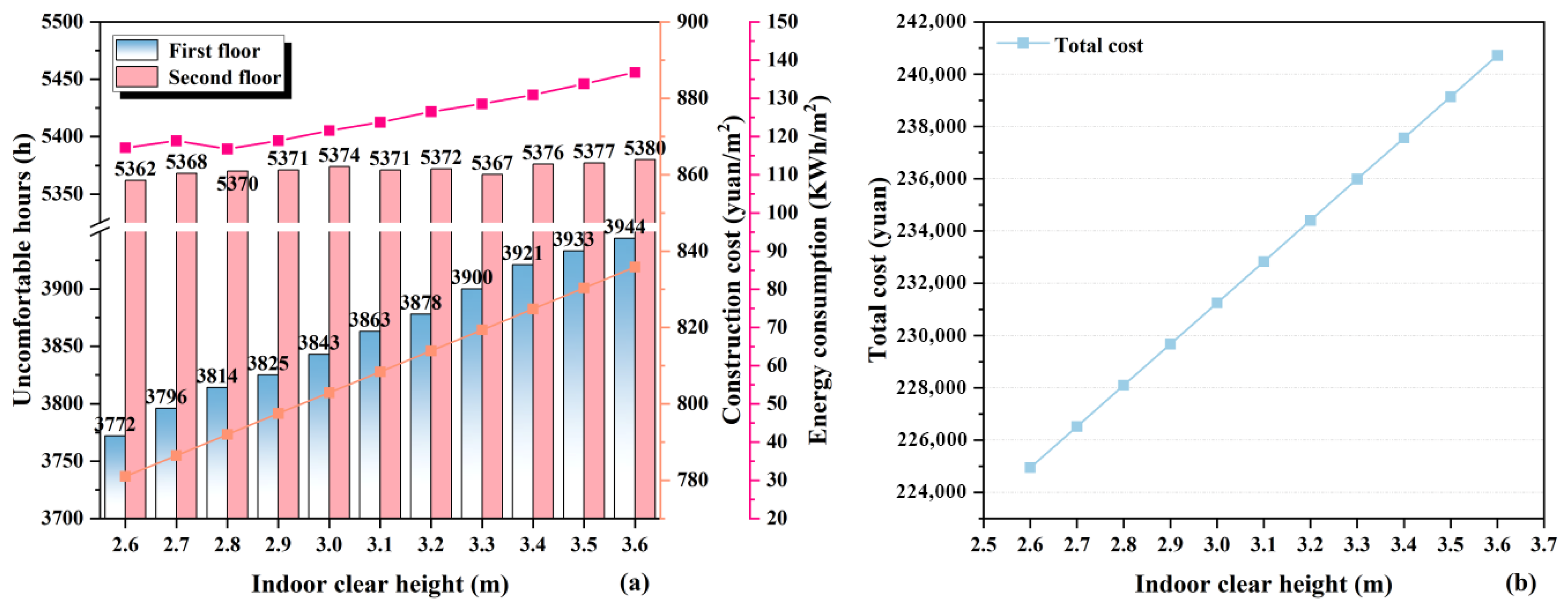
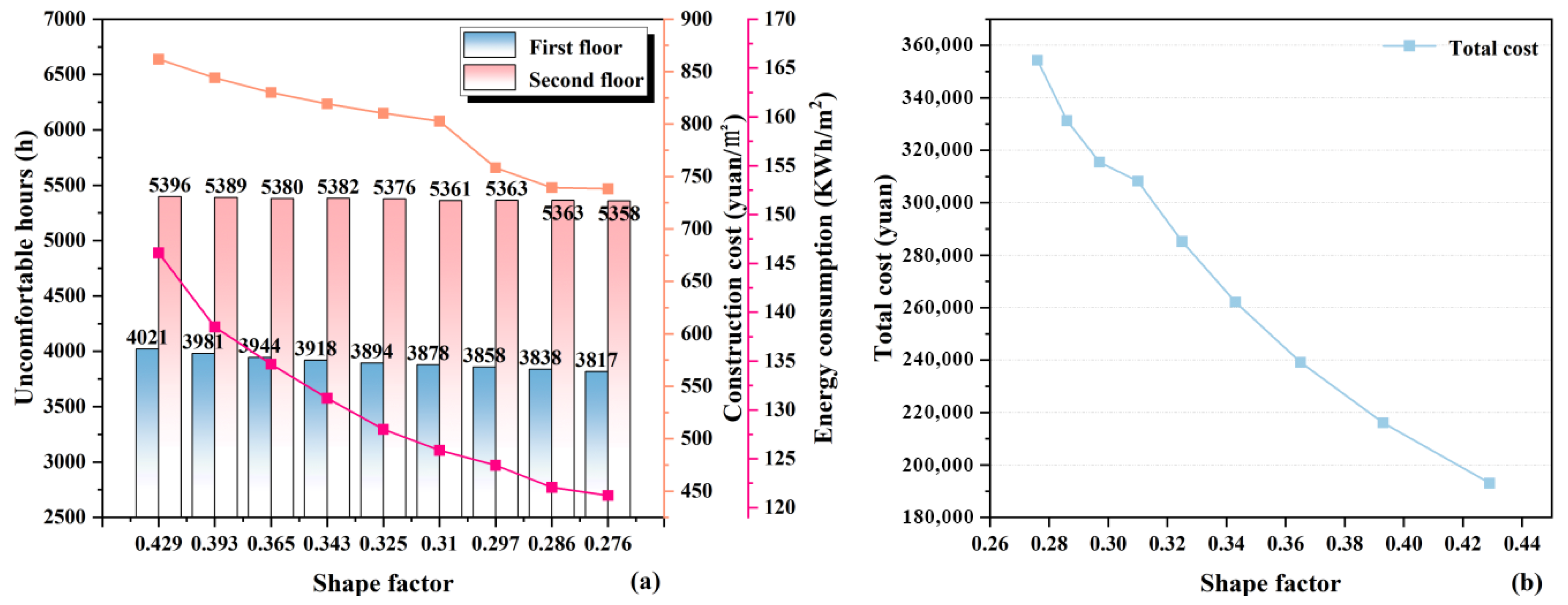
| Building Area (m2) | Span/Depth (m) | First/Second Floor Height (m) | Orientation | Roof | Window (m2) | Window-to-Wall Ratio | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 288 | 16/9 | 3.6 m/3.4 m | South | Flat Roof | C-1 | C-2 | C-3 | C-4 | Southward | Northward |
| 2.1 × 2.0 | 2.45 × 2.0 | 1.5 × 2.0 | 6.4 × 2.0 | 0.35 | 0.2 | |||||
| Metrics | O (°) | I (m) | T (m) | S (m) | W | R (m) | P (mm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W1 | W2 | W3 | P1 | P2 | P3 | ||||||
| 1 | 0 | 3.0 | 11.0 | 0.6 | 0.15 | 0.6 | 30 | 30 | 6 transparent + 6 air + 6 transparent | ||
| 2 | −15/15 | 2.9/3.1 | 10.0/12.0 | 0.8 | 0.25 | 0.8 | 40 | 40 | 6 transparent + 9 air + 6 transparent | ||
| 3 | −30/30 | 2.8/3.2 | 9.0/13.0 | 1.0 | 0.35 | 1.0 | 50 | 50 | 6 transparent + 12 air + 6 transparent | ||
| 4 | −45/45 | 2.7/3.3 | 8.0/14.0 | 1.2 | 0.45 | 1.2 | 60 | 60 | 6 high transmittance Low-E + 6 air + 6 transparent | ||
| 5 | −60/60 | 2.6/3.4 | 7.0/15.0 | 1.4 | 0.55 | 1.4 | 70 | 70 | 6 high transmittance Low-E + 9 air + 6 transparent | ||
| 6 | −75/75 | 3.5 | 1.6 | 0.65 | 1.6 | 80 | 80 | 6 high transmittance Low-E + 12air + 6 transparent | |||
| 7 | −90/90 | 3.6 | 0.75 | ||||||||
| 8 | 0.85 | ||||||||||
| First Layer | Metrics of Experimental Investigations | ||||||||||||
| Second layer | ··· | ||||||||||||
| Third layer | ··· | ··· | |||||||||||
| Factor Change Volume | Factor 1 | Factor 2 | Factor 3 | Factor 4 | Factor 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| : Indoor clear height | : 2.8 m | : 2.9 m | : 3.0 m | : 3.1 m | : 3.2 m |
| : Ratio | : 0.429 | : 0.393 | : 0.365 | : 0.343 | : 0.325 |
| : Additional sunroom | : 0.8 m | : 1.0 m | : 1.2 m | : 1.4 m | : 1.6 m |
| : Thickness of external wall EPS board | : 30 mm | : 40 mm | : 50 mm | : 60 mm | : 70 mm |
| : Roofing XPS sheet thickness | : 30 mm | : 40 mm | : 50 mm | : 60 mm | : 70 mm |
| : Exterior window type | : 6 transparent + 6 air + 6 transparent | : 6 transparent + 9 air + 6 transparent | : 6 transparent + 12 air + 6 transparent | : 6 high transmittance Low-E + 6 air + 6 transparent | : 6 high transmittance Low-E + 9 air + 6 transparent |
| Information | Base Design | Optimal Design |
|---|---|---|
| Building area | 288 m2 | 249.6 m2 |
| Ratio of building footprint to home site area | 0.365 | 0.343 |
| Number of storeys | 2F | 2F |
| First/second floor clear height | 3.4 m/3.6 m | 2.8 m/2.8 m |
| External wall structure | 20 mm cement mortar + 240 mm brick wall + 20 mm cement mortar (inside to outside) (K = 1.735 W/m2·k) | 20 mm cement mortar + 240 mm hollow brick + cement mortar levelling layer + adhesive + 70 mm EPS board + glass fibre mesh cloth + 20 mm cement mortar (from inside to outside) (K = 0.484 W/m2·k) |
| Roof structure | Waterproofing layer + 20 mm cement mortar + levelling layer + slope layer + 120 mm reinforced concrete roof slab + cement plaster (from outside to inside) (K = 3.711 W/m2·k) | Waterproofing layer + 20 mm cement mortar + levelling layer + slope layer + 70 mm XPS board + levelling layer + 120 mm reinforced concrete roof slab + cement plaster (from outside to inside) (K = 0.430 W/m2·k) |
| External window | Single frame single glass plastic steel window (6 mm transparent, K = 4.7 W/m2·k) | 6 high transmittance Low-E + 12 air + 6 transparent (K = 2.4 W/m2·k) |
| Energy consumption for building operation | 134.33 KWh/m2 | 46.66 KWh/m2 |
| Total thermally uncomfortable hours | 9327 h | 6602 h |
| Total construction cost | 239,137.50 yuan | 242,253.53 yuan |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, M.; Feng, Z.; Yuan, L.; Xia, Z.; Song, H.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, K. Research on a Multi-Objective Synergistic Approach to Improve the Performance of Rural Dwellings in Cold Regions of China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 9813. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219813
Lu M, Feng Z, Yuan L, Xia Z, Song H, Lv Y, Zhang K. Research on a Multi-Objective Synergistic Approach to Improve the Performance of Rural Dwellings in Cold Regions of China. Sustainability. 2025; 17(21):9813. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219813
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Meijun, Zhiruo Feng, Lu Yuan, Zongjun Xia, Haijing Song, Yajun Lv, and Kangjie Zhang. 2025. "Research on a Multi-Objective Synergistic Approach to Improve the Performance of Rural Dwellings in Cold Regions of China" Sustainability 17, no. 21: 9813. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219813
APA StyleLu, M., Feng, Z., Yuan, L., Xia, Z., Song, H., Lv, Y., & Zhang, K. (2025). Research on a Multi-Objective Synergistic Approach to Improve the Performance of Rural Dwellings in Cold Regions of China. Sustainability, 17(21), 9813. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219813







