Underground Space Planning Optimization Under the TOD Model Using NSGA-II: A Case Study of Qingdaobei Railway Station and Its Surroundings
Abstract
1. Introduction
- An NSGA-II-based intelligent optimization model is proposed, integrating ABM with TOPSIS for solution selection. The concept of computational planning schemes is introduced to provide heuristic, data-driven support for improving the scientific foundation and adaptability of underground space infrastructure planning.
- A spatial optimization approach tailored to the TOD model is constructed, enabling three-dimensional coordination and optimization of underground and above-ground functions such as commercial areas, parking facilities, and municipal infrastructure, thereby improving spatial efficiency and multimodal transfer convenience.
- The effectiveness of the model is validated through a case study of Qingdaobei Railway Station. Based on multi-source spatial data and GIS-based analyses, optimization analysis is conducted, and the generated planning schemes provide scientific decision support for underground space development under the TOD model, while enhancing overall outcomes through existing condition optimization.
2. Methods
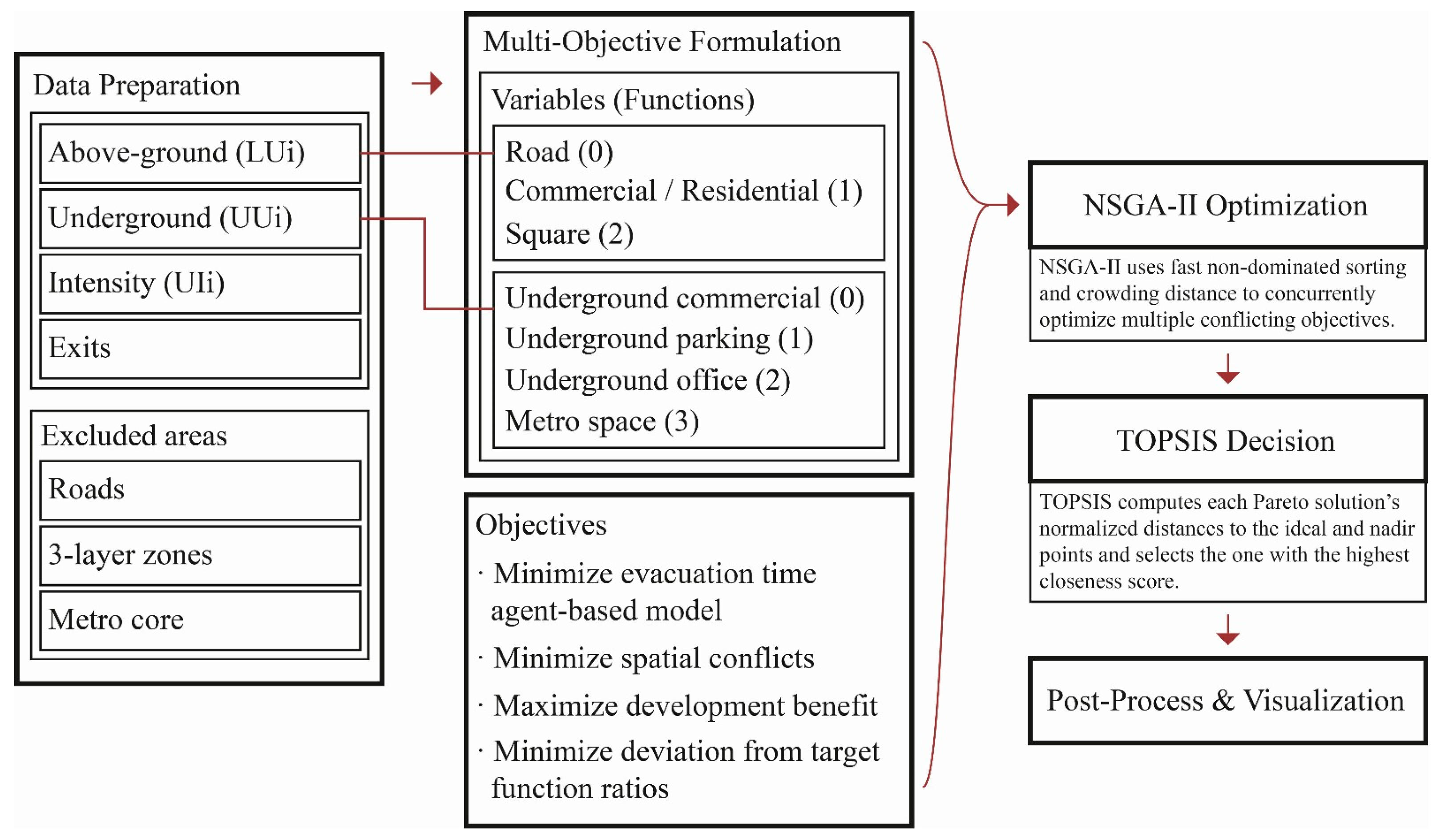
2.1. Research Framework
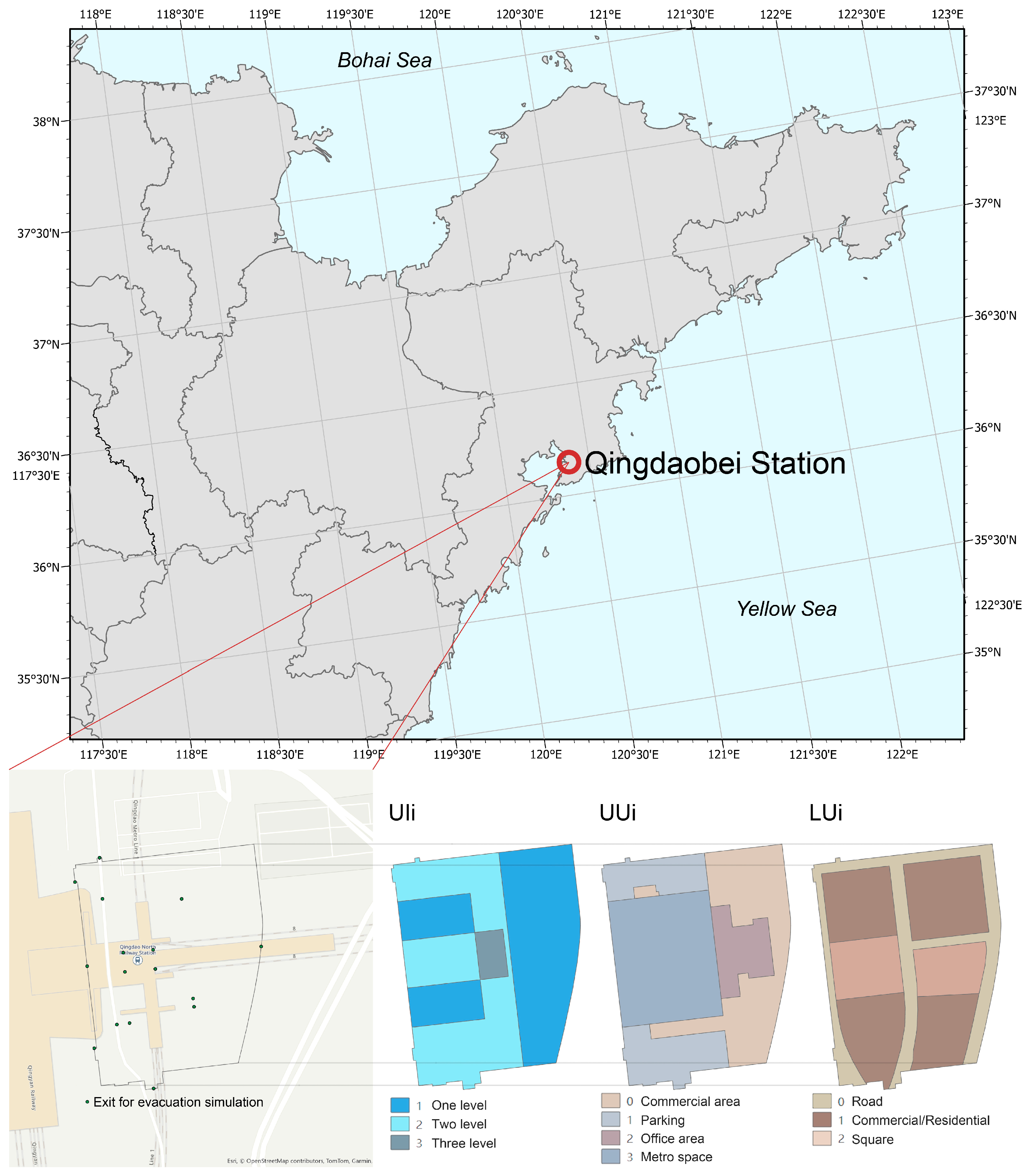
2.2. Data
- Above-ground land use types (LUi): including roads, commercial and residential zones, public plazas, and other surface-level functional areas. These data are extracted from current urban planning documents.
- Underground land use types (UUi): covering underground commercial areas, parking facilities, office spaces, and metro infrastructure. These datasets are derived from field surveys and publicly available urban development plans.
- Underground development intensity (UIi): indicating the depth classification of underground spaces (first-, second-, or third-level), also sourced from field surveys and official planning schemes.
2.3. NSGA-II Optimization Modeling
2.3.1. Variable Definition
2.3.2. Evacuation ABM
2.3.3. Constrains
2.3.4. NSGA-II Computational Process
2.4. TOPSIS-Based Solution Selection
3. Results
3.1. Study Area Analysis
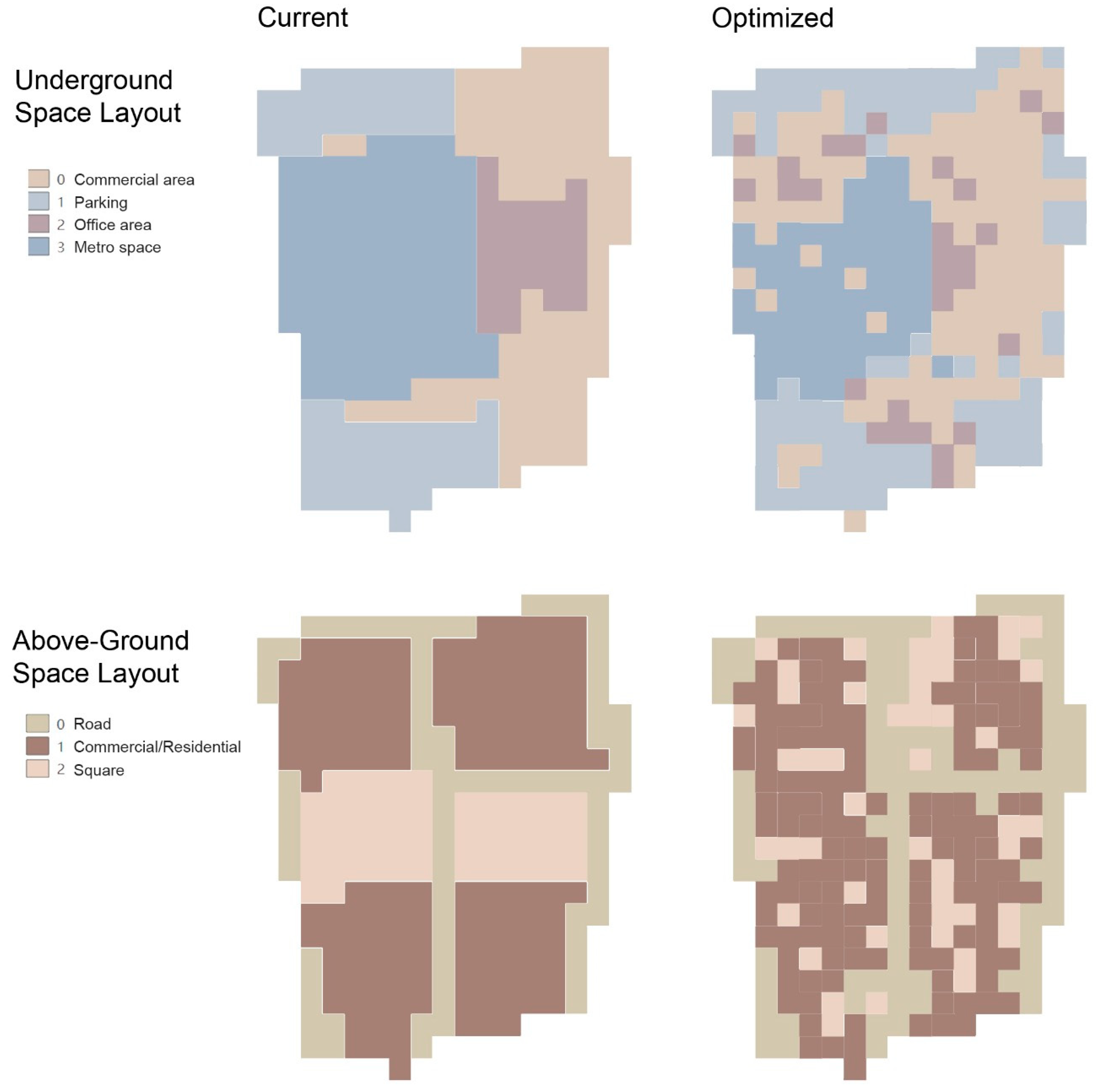
3.2. NSGA-II Optimization Results and TOPSIS Selection
3.3. Implications for Practice
- Evacuation Time (): Through the decentralization of office functions and the rational reconfiguration of entrances and exits, evacuation time is reduced from over 900 s in the current layout to approximately 737 s—an improvement exceeding 15%. This highlights how spatial redistribution can directly enhance pedestrian safety and evacuation efficiency in high-density hubs.
- Development Conflict (): Representing the overall degree of functional incompatibility among adjacent spatial units, this indicator decreased from 68,000 to 60,450. The reduction, achieved through coordinated planning of parking and commercial areas, indicates stronger functional synergy and a more coherent spatial structure—an outcome that underscores the value of integrated land-use strategies in practice.
- Development Benefit (): Increased to −20,050, reflecting a tangible improvement in infrastructure efficiency arising from the coordinated integration of commercial and transport functions. This result demonstrates how multi-objective optimization can help planners identify configurations that simultaneously strengthen operational and economic performance.
- Development Scale Deviation (): Stabilized at 1.29 after appropriately adjusting the proportions of commercial, office, and parking functions. This alignment with the target structure reveals a more balanced and context-responsive functional composition—offering a reference for practitioners seeking to harmonize spatial allocation with planning goals in complex underground systems.
4. Discussion
4.1. Advantages and Limitations of the Method
4.2. Implications for Planning Practice
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TOD | Transit-Oriented Development |
| ABM | Agent-Based Model |
| NSGN-II | Non-dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm II |
| TOPSIS | Technique for Order Preference by Similarity to Ideal Solution |
| USSMS | Underground Space Synchronously with Metro Stations |
| AIGA | Artificially Intervened Genetic Algorithm |
| HUX | Half Uniform Crossover |
| LCA | Life-cycle Assessment |
| SDGs | The United Nations Sustainable Development Goals |
Appendix A. Sensitivity Analysis of Agent Speed Parameters in the ABM
Appendix A.1. Methodology
- Global Scaling: All speed coefficients were uniformly scaled by ±10% and ±20%, simulating the effects of overall faster or slower pedestrian movement.
- One-at-a-Time (OAT): Each coefficient was independently increased and decreased by 10%, while keeping all others fixed, to assess its individual contribution to the output variance.
- Monte Carlo Simulation: 100 simulations were conducted with all four coefficients subjected to independent random perturbations sampled from a normal distribution (mean = 0, standard deviation = 5%), clipped to ensure values remain within a plausible range [0.5, 1.5].
Appendix A.2. Results
| Scenario | Min (%) | Max (%) | Mean (%) | Std Dev (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monte Carlo (MC) | −14.69 | 27.33 | 3.5821 | 8.0805 |
| OAT–Commercial | −4.47 | −3.32 | −3.8950 | 0.8132 |
| OAT–Parking | 1.53 | 10.09 | 5.8100 | 6.0528 |
| OAT–Office | −1.15 | 10.60 | 4.7250 | 8.3085 |
| OAT–Metro | −2.30 | 13.15 | 5.4250 | 10.9248 |
| Global Scaling | −14.69 | 38.95 | 8.3780 | 19.4778 |
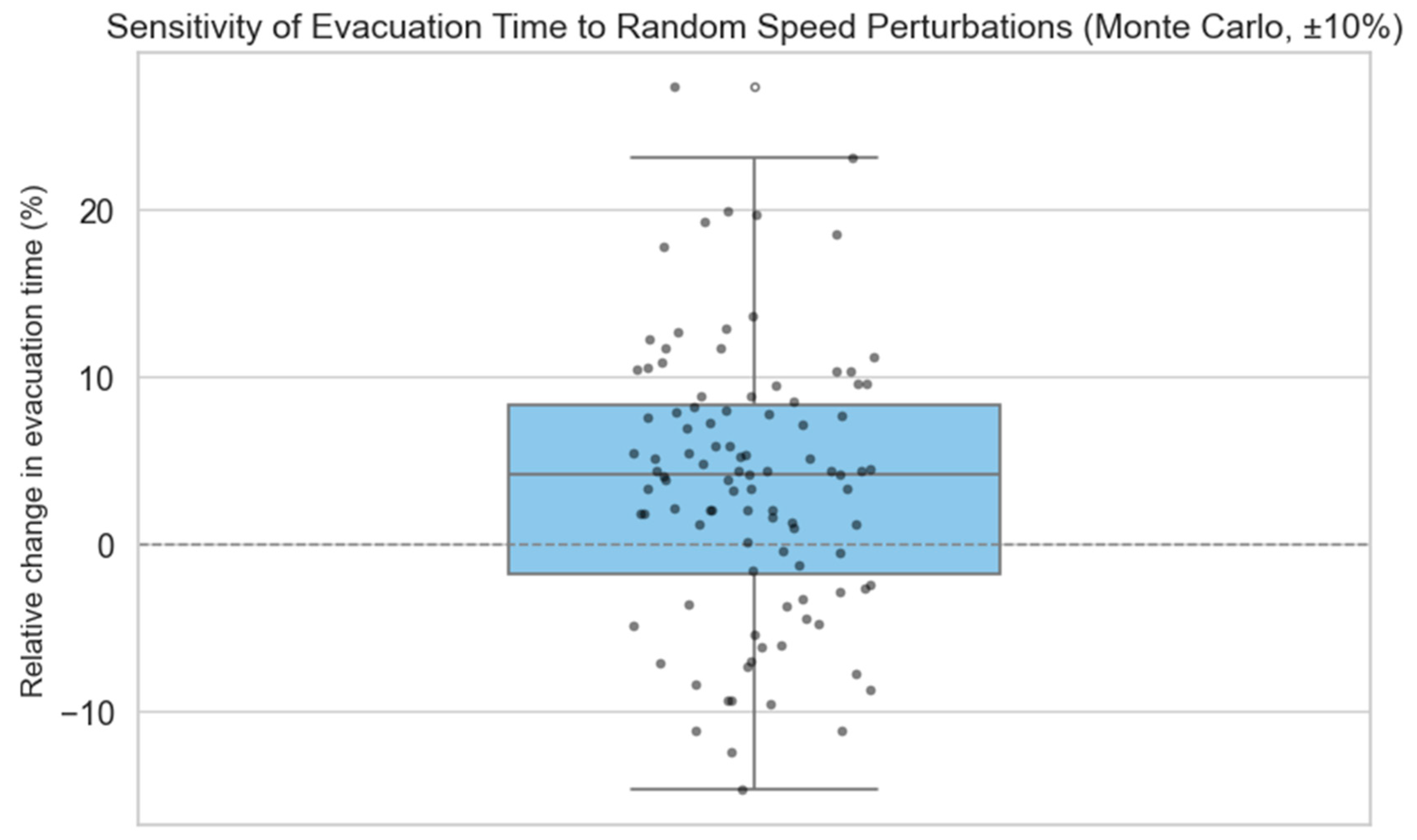
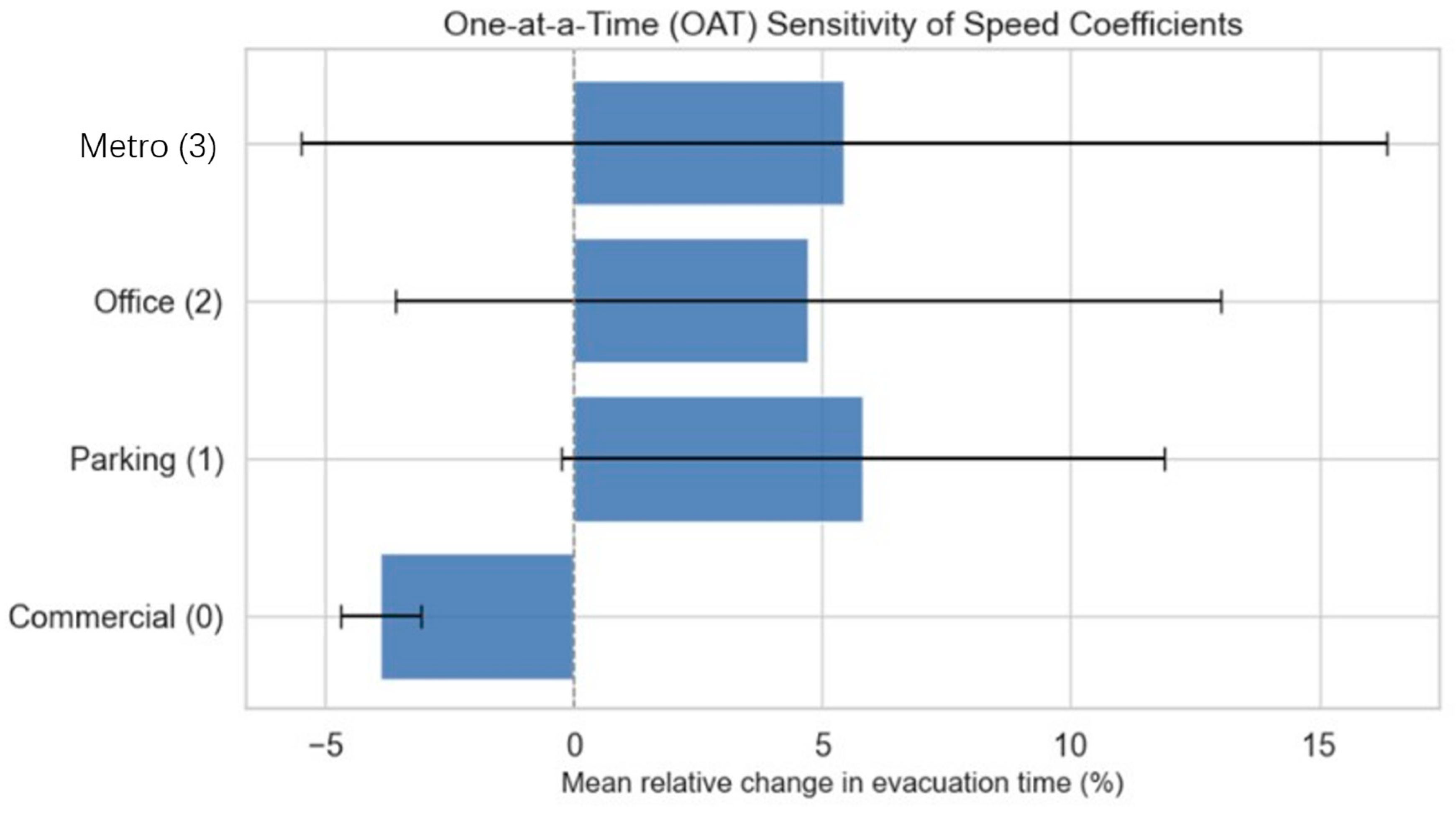
Appendix A.3. Discussion
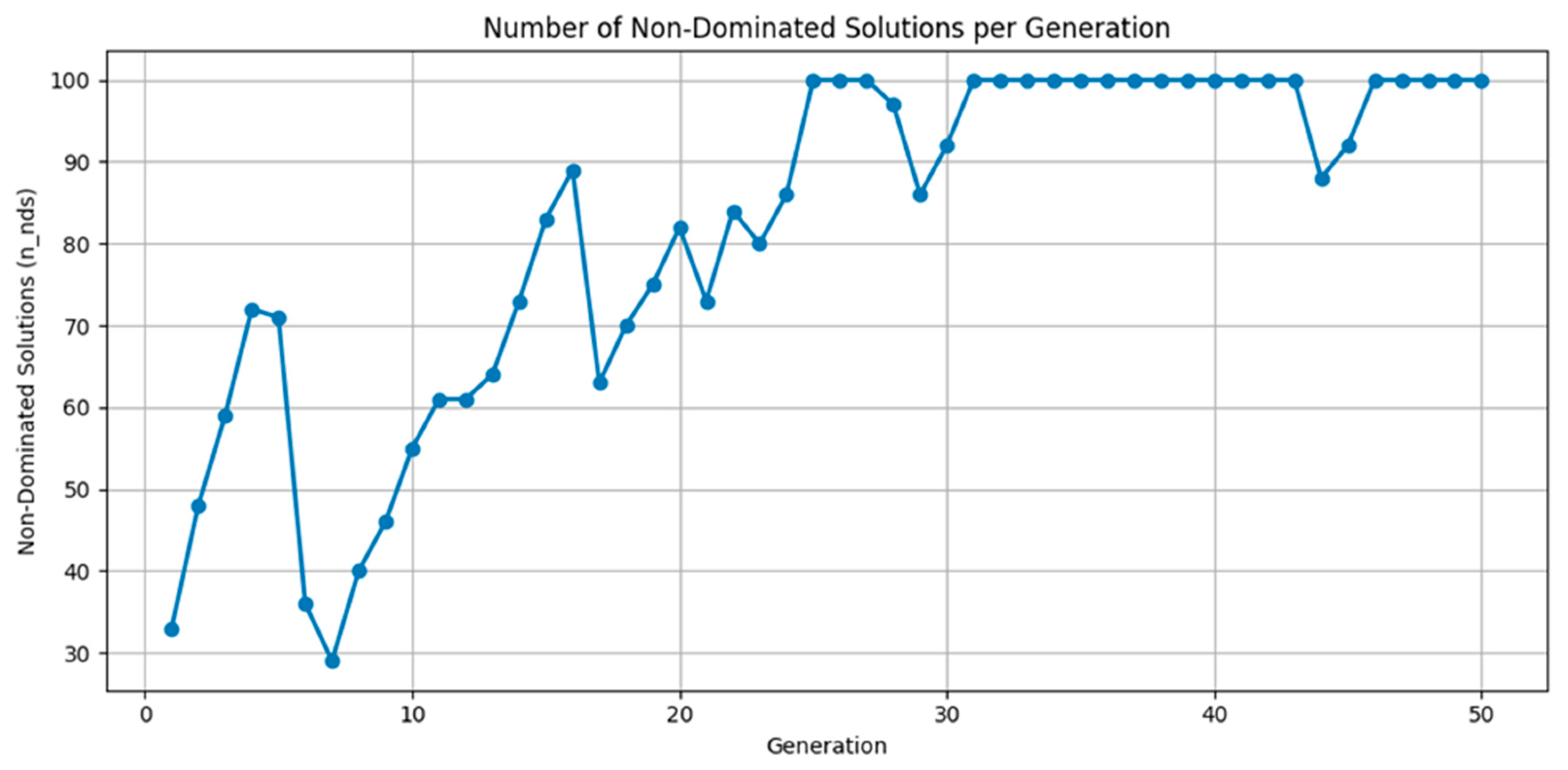
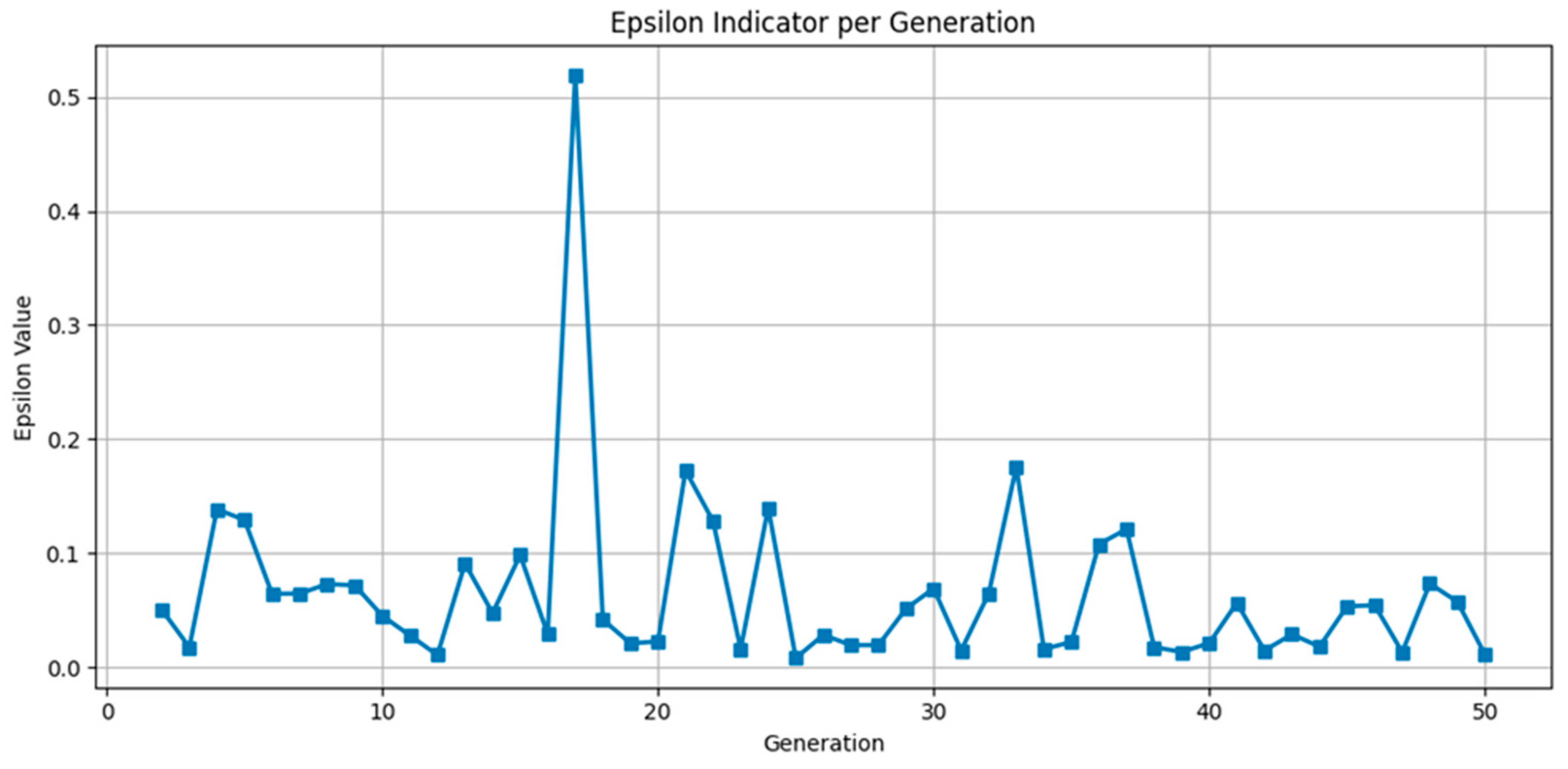
Appendix B. Optimization Process Convergence Analysis
References
- Cervero, R.; Kockelman, K. Travel demand and the 3Ds: Density, diversity, and design. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 1997, 2, 199–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolini, L. Spatial Development Patterns and Public Transport: The Application of an Analytical Model in the Netherlands. Plan. Pract. Res. 1999, 14, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, C.; Renne, J.L.; Bertolini, L. Transit Oriented Development: Making it Happen; Ashgate Publishing, Ltd.: Surrey, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Papa, E.; Bertolini, L. Accessibility and Transit-Oriented Development in European metropolitan areas. J. Transp. Geogr. 2015, 47, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.J.; Gau, C.C. A TOD planning model to review the regulation of allowable development densities around subway stations. Land Use Policy 2006, 23, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J. Design of Underground Space Around Metro Station Based on TOD Theory. 2021. Available online: https://www.politesi.polimi.it/handle/10589/177488 (accessed on 22 June 2025).
- Li, H.; Li, X.; Soh, C.K. An integrated strategy for sustainable development of the urban underground: From strategic, economic and societal aspects. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2016, 55, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.-H.; Peng, F.-L.; Guo, T.-F. Quantitative assessment method on urban vitality of metro-led underground space based on multi-source data: A case study of Shanghai Inner Ring area. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2021, 116, 104108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Nelson, J.D.; Beecroft, M.; Cui, J. An overview of recent developments in China’s metro systems. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2021, 111, 103783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.-L.; Qiao, Y.-K.; Zhao, J.-W.; Liu, K.; Li, J.-C. Planning and implementation of underground space in Chinese central business district (CBD): A case of Shanghai Hongqiao CBD. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2020, 95, 103176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israel, A. Issues for Infrastructure Management in the 1990s; World Bank Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Nuuyandja, H.; Pisa, N.; Masoumi, H.; Chakamera, C. Association of Urban Form, Neighbourhood Characteristics, and Socioeconomic Factors with Travel Behaviour in Windhoek, Namibia. Sustainability 2025, 17, 7800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Bai, Y.; Zheng, N. Simulation and Optimization of Pedestrian Regular Evacuation in Comprehensive Rail Transit Hub—A Case Study in Beijing. Promet-Traffic Transp. 2020, 32, 383–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P. Car use, commuting and urban form in a rapidly growing city: Evidence from Beijing. Transp. Plan. Technol. 2011, 34, 509–527. Available online: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/03081060.2011.600049 (accessed on 27 August 2025). [CrossRef]
- Mees, P. TOD and Multi-modal Public Transport. Plan. Pract. Res. 2014, 29, 461–470. Available online: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/02697459.2014.977633 (accessed on 17 June 2025). [CrossRef]
- Mariette, J.; Blanchard, O.; Berne, O.; Aumont, O.; Carrey, J.; Ligozat, A.; Lellouch, E.; Roche, P.-E.; Guennebaud, G.; Thanwerdas, J.; et al. An open-source tool to assess the carbon footprint of research. Environ. Res. Infrastruct. Sustain. 2022, 2, 035008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durmiševic, S. Perception Aspects in Underground Spaces Using Intelligent Knowledge Modeling; TU Delft: Delft, The Netherlands, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Y.; Wang, H.; Chugh, T.; Guo, D.; Miettinen, K. Data-Driven Evolutionary Optimization: An Overview and Case Studies. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2019, 23, 442–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, F.; Zhang, S.; Qin, X.; Xi, G. From informational empowerment to comprehensive empowerment: Exploring the ideas of smart territorial spatial planning. J. Nat. Resour. 2019, 34, 2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yajie, X.; Chen, X. Current Situation and Prospect of Comprehensive Development of Underground Space in Metro Area. Chin. J. Undergr. Space Eng. 2023, 19, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadi, A.; Amador-Jimenez, L.; Nasiri, F. Reliable, Effective, and Sustainable Urban Railways: A Model for Optimal Planning and Asset Management. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2020, 146, 04020057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, F.; Wang, Y. Intelligent overall planning model of underground space based on digital twin. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2022, 104, 108393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Liao, Z.; Guo, J.; Xie, H.; Peng, Q. An intelligent planning model for the development and utilization of urban underground space with an application to the Luohu District in Shenzhen. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2021, 112, 103933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.-L.; Dong, Y.-H.; Wang, W.-X.; Ma, C.-X. The next frontier: Data-driven urban underground space planning orienting multiple development concepts. Smart Constr. Sustain. Cities 2023, 1, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Liu, P.; Yang, H.; Zhang, K.; Wang, Y.; Pu, Z. Few-shot learning for novel object detection in autonomous driving. Commun. Transp. Res. 2025, 5, 100194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.-H.; Peng, F.-L.; Zha, B.-H.; Qiao, Y.-K.; Li, H. An intelligent layout planning model for underground space surrounding metro stations based on NSGA-II. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2022, 128, 104648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, K.; Pratap, A.; Agarwal, S.; Meyarivan, T. A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2002, 6, 182–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Pant, M.; Snasel, V. A Comprehensive Review on NSGA-II for Multi-Objective Combinatorial Optimization Problems. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 57757–57791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Z.; Wang, B.; Xue, J.; Shan, S. Research on practical application of multi-objective optimization based on NSGA-II algorithm. Adv. Appl. Math. 2023, 12, 4195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-K.; Yeh, C.-T. Multi-objective optimization for stochastic computer networks using NSGA-II and TOPSIS. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2012, 218, 735–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazbei, M.; Rafati, N.; Kharma, N.; Eicker, U. Optimizing architectural multi-dimensional forms; a hybrid approach integrating approximate evolutionary search, clustering and local optimization. Energy Build. 2024, 318, 114460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafati, N.; Hazbei, M.; Eicker, U. Louver configuration comparison in three Canadian cities utilizing NSGA-II. Build. Environ. 2023, 229, 109939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senanayake, G.P.D.P.; Kieu, M.; Zou, Y.; Dirks, K. Agent-based simulation for pedestrian evacuation: A systematic literature review. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2024, 111, 104705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Qiao, Y.; Zhao, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, C.; Huang, R.; Cui, Y. Improving emergency evacuation capacity for subway stations based on agent-based modelling. Constr. Innov. 2024. ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wei, C.; Yang, Y.; Luo, L.; Biancardo, S.A.; Mei, X. Personnel Trajectory Extraction From Port-Like Videos Under Varied Rainy Interferences. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2024, 25, 6567–6579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, H.-Y.; Ip, L.-C.; Mansoor, U.; Chen, A. Pedestrian route choice with respect to new lift-only entrances to underground space: Case study of a metro station area in hilly terrain in Hong Kong. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2022, 129, 104678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidmann, U. Transporttechnik der Fussgänger: Transporttechnische Eigenschaften des Fussgängerverkehrs, Literaturauswertung; ETH Zurich: Zurich, Switzerland, 1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, M.J.; Gottuk, D.T.; Hall, J.R.; Harada, K.; Kuligowski, E.D.; Puchovsky, M.; Torero, L.; Watts, J.M. SFPE Handbook of Fire Protection Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kramer, O. A Review of Constraint-Handling Techniques for Evolution Strategies. Appl. Comput. Intell. Soft Comput. 2010, 2010, 185063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, S.; Liu, T.; Shan, Y. A comprehensive survey on NSGA-II for multi-objective optimization and applications. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2023, 56, 15217–15270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudas, C.; Ng, A.H.C.; Boström, H. Post-analysis of multi-objective optimization solutions using decision trees. Intell. Data Anal. 2015, 19, 259–278. Available online: https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.3233/IDA-150716 (accessed on 19 June 2025). [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, T. Performance evaluation and obstacle factors analysis of urban public transport priority. Transp. Plan. Technol. 2019, 42, 696–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Hu, W.; Xue, X.; Dong, J. Multi-objective optimization model for planning metro-based underground logistics system network: Nanjing case study. J. Ind. Manag. Optim. 2023, 19, 170. Available online: https://openurl.ebsco.com/EPDB%3Agcd%3A8%3A34565128/detailv2?sid=ebsco%3Aplink%3Ascholar&id=ebsco%3Agcd%3A159631038&crl=c&link_origin=scholar.google.com (accessed on 22 June 2025). [CrossRef]
- Helmrich, A.; Markolf, S.; Li, R.; Carvalhaes, T.; Kim, Y.; Bondank, E.; Natarajan, M.; Ahmad, N.; Chester, M. Centralization and decentralization for resilient infrastructure and complexity. Environ. Res. Infrastruct. Sustain. 2021, 1, 021001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, A.M.; Dikshit, A.K.; Soni, A. Environmental life cycle assessment of underground metro rail: A case study in Mumbai Metropolitan Region, India. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2024, 106, 107501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhu, H.; Shen, Y.; Li, T.; Liu, A. Embodied carbon assessment on road tunnels using integrated digital model: Methodology and case-study insights. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2024, 143, 105485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geurs, K.T.; van Wee, B. Accessibility evaluation of land-use and transport strategies: Review and research directions. J. Transp. Geogr. 2004, 12, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Shen, Z.; Huang, Z.; Li, H. Optimization design of anti-seismic engineering measures for intake tower based on non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm-II. Front. Struct. Civ. Eng. 2023, 17, 1428–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, G.; Wang, H. Optimal Lane Change Path Planning Based on the NSGA-II and TOPSIS Algorithms. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krivorotko, M.; Setoguchi, T.; Watanabe, N. Efficient Public Underground Pedestrian Space in a Cold-Climate City: A Case Study of Sapporo, Japan. Sustainability 2024, 16, 9995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spyrou, E.D.; Kappatos, V.; Gkemou, M.; Bekiaris, E. Multimodal Transport Optimization from Doorstep to Airport Using Mixed-Integer Linear Programming and Dynamic Programming. Sustainability 2025, 17, 7937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagarlamudi, L. Examining the Effectiveness of Park-and-Ride Facilities in German Metropolitan Areas: Promoting Modal Shift and Mitigating Traffic Congestion. 2024. Available online: https://libdoc.fh-zwickau.de/opus4/frontdoor/index/index/docId/17356 (accessed on 22 June 2025).
- Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Xia, H. Behavior decision model for park-and-ride facilities utilization. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2017, 9, 1687814017708907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wang, G.; Xu, Q.; He, J.; Yang, M.; Su, C. Dynamic Response Study of Space Large-Span Structure under Stochastic Crowd-Loading Excitation. Buildings 2024, 14, 1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, R.K.; Singh, B.; Zhao, J. Underground Infrastructures: Planning, Design, and Construction; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Furlan, R.; Al-Mohannadi, A.; Major, M.D.; Paquet, T.N.K. A planning method for transit villages in Qatar: Souq Waqif historical district in Doha. Open House Int. 2022, 48, 425–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taboada, H.A.; Baheranwala, F.; Coit, D.W.; Wattanapongsakorn, N. Practical solutions for multi-objective optimization: An application to system reliability design problems. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2007, 92, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, C.; Sun, N. Modeling and Combined Application of Orthogonal Chaotic NSGA-II and Improved TOPSIS to Optimize a Conceptual Hydrological Model. Water Resour. Manag. 2018, 32, 3781–3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Study | Key Factors Considered | Optimization/Planning Methods | Application Area | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dong et al. (2022) [26] | Spatial compatibility, pedestrian accessibility, function matching | NSGA-II + compatibility matrix | Shanghai | Focused on layout design of underground commercial space |
| Xu & Chen (2023) [20] | Morphological types, functional linkage | Typological classification | Japan/China metro | Proposed 6 typologies without optimization |
| Zhang et al. (2021) [23] | Functional distribution, space hierarchy | Artificially Intervened Genetic Algorithm (AIGA) | Shenzhen | Emphasized hierarchical design principles |
| Peng et al. (2023) [24] | Development concepts, spatial co-occurrence | Data-driven keyword network analysis | Multiple cities | Conceptual framework, not layout optimization |
| Mohammadi et al. (2020) [21] | Infrastructure reliability, cost efficiency | Mathematical model for network design | Tehran | Rail network level, not specific to underground layout |
| This study | Evacuation time, conflict minimization, benefit maximization, functional ratio | NSGA-II + ABM + TOPSIS | Qingdao | Integrated model for TOD-based underground optimization |
| Serial Number | Data Types | Variable Name | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Underground land type | UUi | Underground commercial (0), Underground parking (1), Underground office (2), Metro (3) |
| 2 | Underground Development Intensity | UIi | One level, two level, three level (only one level and two level spaces are optimized) |
| 3 | Land use type | Lui | Road (0), Commercial/Residential (1), Office (2), Public Space (3) |
| 4 | Distance to metro | dist_to_metro | The Euclidean distance from the cell center to the nearest metro area center, used for benefit decay calculation |
| 5 | Functional efficiency coefficient | , | Determined by the ground function assignment, each type of function is set with a different profit coefficient |
| 6 | Target function ratio | Target ratio of underground to above-ground functional configuration (e.g., 40%, 30%, 20%, 10%) |
| Ground Function Type | Underground Business (0) | Underground Parking (1) | Underground Office (2) | Metro (3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Commercial/Residential (1) | 1.0 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.2 |
| Office (2) | 0.3 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.2 |
| Public Space (3) | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.2 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Population size | 100 |
| Number of generations | 50 |
| Sampling method | BinaryRandomSampling |
| Crossover operator | HUX (Half Uniform Crossover) |
| Crossover probability | 1.0 |
| Mutation operator | BitflipMutation |
| Mutation probability | 1/974 |
| Selection scheme | Binary tournament |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kong, W.; Feng, W.; Liu, Y. Underground Space Planning Optimization Under the TOD Model Using NSGA-II: A Case Study of Qingdaobei Railway Station and Its Surroundings. Sustainability 2025, 17, 9761. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219761
Kong W, Feng W, Liu Y. Underground Space Planning Optimization Under the TOD Model Using NSGA-II: A Case Study of Qingdaobei Railway Station and Its Surroundings. Sustainability. 2025; 17(21):9761. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219761
Chicago/Turabian StyleKong, Weiyan, Wenhan Feng, and Yimeng Liu. 2025. "Underground Space Planning Optimization Under the TOD Model Using NSGA-II: A Case Study of Qingdaobei Railway Station and Its Surroundings" Sustainability 17, no. 21: 9761. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219761
APA StyleKong, W., Feng, W., & Liu, Y. (2025). Underground Space Planning Optimization Under the TOD Model Using NSGA-II: A Case Study of Qingdaobei Railway Station and Its Surroundings. Sustainability, 17(21), 9761. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219761






