External Costs of Road Traffic Accidents in Türkiye: The Willingness-to-Pay Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Data
3.2. Methods
4. Research Findings and Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| WTP | Willingness-to-Pay |
| GDP | Gross Domestic Product |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| GNP | Gross National Product |
| WB | World Bank |
| GDH | General Directorate of Highways |
| EU | European Union |
| HC | Human Capital |
| VSL | Value of a Statistical Life |
| GO | Gross Output |
| VOT | Value of Time |
| VSSI | Value of a Statistical Serious Injury |
| GDS | General Directorate of Security |
| TSI | Turkish Statistical Institute |
| CBRT | Central Bank of the Republic of Türkiye |
| PPS GDP | Gross Domestic Product at Purchasing Power Standards |
| TPRZ | Traffic Police Responsibility Zone |
| GRZ | Gendarmerie Responsibility Zone |
| € | Euro |
| TL (₺) | Turkish Lira |
References
- Wegman, F. The future of road safety: A worldwide perspective. IATSS Res. 2017, 40, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization, WHO. Brasilia Declaration Second Global High-Level Conference on Road Safety: Time for Results Brasilia, 18–19 November 2015. Available online: https://www.gtkp.com/knowledge/brasilia-declaration-on-road-safety/ (accessed on 18 May 2023).
- World Health Organization, WHO. Global Status Report on Road Safety. 2019. Available online: https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/44122/9789241563840_eng.pdf (accessed on 22 May 2023).
- Wijnen, W. Road Safety and Welfare—5. Economic Valuation of Preventing Non-Fatal Road Injuries: A Literature Review. Ph.D. Thesis, Delft University of Technology, Delft, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 95–111. Available online: https://repository.tudelft.nl/record/uuid:a370c3e3-22d8-4a33-81fe-a8c2a3043565 (accessed on 2 June 2023).
- Stephan, K.L. A Multidisciplinary Investigation of the Influence of the Built Urban Environment on Driver Behaviour and Traffic Crash Risk. Ph.D. Thesis, Monash University, Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 2015. Available online: https://figshare.com/articles/A_multidisciplinary_investigation_of_the_influence_of_the_built_urban_environment_on_driver_behaviour_and_traffic_crash_risk/4712170 (accessed on 7 July 2024).
- Anokhin, A.; Holovko, K.; Mul, S. Road Accidents and The National Economy: Legal Analysis. Balt. J. Econ. Stud. 2023, 9, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coruh, E.; Bilgic, A.; Tortum, A. Accident analysis with aggregated data: The random parameters negative binomial panel count data model. Anal. Methods Accid. Res. 2015, 7, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.C.; Shiu, Y.-M.; Chou, P.-L.; Chen, Y.-M.J. Vehicle insurance and the risk of road traffic accidents. Transp. Res. Ppart A Policy Pract. 2015, 74, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Kuhn, M.; Prettner, K.; E Bloom, D. The global macroeconomic burden of road injuries: Estimates and projections for 166 countries. Lancet Planet. Health 2019, 3, e390–e398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ETSC, European Transport Safety Council. Social and Economic Consequences of Road Traffic Injury in Europe; ETSC: Brussels, Belgium, 2007; Available online: https://etsc.eu/wp-content/uploads/Social-and-economic-consequences-of-road-traffic-injury-in-Europe.pdf (accessed on 6 June 2024).
- Haddak, M.M.; Lefèvre, M.; Havet, N. Willingness-to-pay for road safety improvement. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2016, 87, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Bank. The High Toll of Traffic Injuries: Unacceptable and Preventable; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2007; Available online: https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/entities/publication/8d9b43ee-4ad4-501c-8e49-c58463ce6d52 (accessed on 13 September 2024).
- World Bank. Socioeconomic Impacts of Road Traffic Injuries in Central Asia; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2022; Available online: https://documents1.worldbank.org/curated/en/099655004252264808/pdf/P1747490e067d50a20b0c908773b95f7991.pdf (accessed on 15 September 2024).
- World Health Organization, WHO. Road Traffic Injuries. 2023. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/road-traffic-injuries (accessed on 20 October 2025).
- Macioszek, E.; Wyderka, A.; Jurdana, I. The bicyclist safety analysis based on road incidents maps. Sci. J. Silesian Univ. Technol. Ser. Transp. 2025, 126, 129–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jomnonkwao, S.; Wisutwattanasak, P.; Ratanavaraha, V. Factors influencing willingness to pay for accident risk reduction among personal car drivers in Thailand. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0260666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhalla, K.; Mohan, D.; O’neill, B. How much would low-and middle-income countries benefit from addressing the key risk factors of road traffic injuries? Int. J. Inj. Control Saf. Promot. 2020, 27, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahab, L.; Jiang, H. A comparative study on machine learning based algorithms for prediction of motorcycle crash severity. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijnen, W.; Dahdah, S.; Pkhikidze, N. The value of a statistical life in the context of road safety: A new value transfer approach. Traffic Inj. Prev. 2025. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougna, T.; Hundal, G.; Taniform, P. Quantitative analysis of the social costs of road traffic crashes literature. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2022, 165, 106282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hejazi, R.; Shamsudin, M.N.; Radam, A.; Rahim, K.A.; Ibrahim, Z.Z.; Yazdani, S. Estimation of traffic accident costs: A prompted model. Int. J. Inj. Control Saf. Promot. 2013, 20, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvik, R. How much do road accidents cost the national economy? Accid. Anal. Prev. 2000, 32, 849–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijnen, W.; Stipdonk, H. Social costs of road crashes: An international analysis. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2016, 94, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijnen, W.; Weijermars, W.; Schoeters, A.; Van den Berghe, W.; Bauer, R.; Carnis, L.; Elvik, R.; Martensen, H. An analysis of official road crash cost estimates in European countries. Saf. Sci. 2019, 113, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmas, G.; Yıldızhan, B. Transportation Policies and Economic Analysis of Traffic Accidents in Turkey, II. In Transportation and Traffic Congress and Exhibition Proceedings Book; Union of Chambers of Turkish Engineers and Architects (UCTEA), UCTEA Chamber of Mechanical Engineers: Ankara, Türkiye, 1999; pp. 268–286. Available online: https://www.mmo.org.tr/kitaplar/ii-ulasim-ve-trafik-kongresi-ve-sergisi-bildiriler-kitabi (accessed on 19 June 2024).
- Ayati, E. The Cost of Traffic Accidents in Iran; Ferdowsi University of Mashhad: Mashhad, Iran, 2002; Available online: https://civilica.com/doc/1391209/ (accessed on 21 April 2024).
- Sakhapov, R.; Nikolaeva, R. Economic aspects of traffic safety administration. Transp. Res. Procedia 2017, 20, 578–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijnen, W. Socio-economic costs of road crashes in middle-income countries: Applying a hybrid approach to Kazakhstan. IATSS Res. 2021, 45, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engombe, M. The Economic Costs of Road Traffic Accidents in Namibia; A Research Project Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree. Bachelor’s Thesis, University of Namibia, Windhoek, Namibia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, H.D. The Study on National Road Traffic Safety Master Plan in the Socialist Republic of Vietnam Chapter 9: Examination of Traffic Safety Institutions, 2008. (Draft). Available online: https://www.academia.edu/7106115/Economic_Losses_by_Road_Traffic_Accidents_in_Vietnam (accessed on 8 February 2024).
- Mohamed, H.A. Estimation of socio-economic cost of road accidents in Saudi Arabia: Willingness-to-pay approach (WTP). Adv. Manag. Appl. Econ. 2015, 5, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Turkish Statistical Institute, TSI. Highway Traffic Accident Statistics. 2018. Available online: https://data.tuik.gov.tr/Bulten/Index?p=Karayolu-Trafik-Kaza-Istatistikleri-2018-30640 (accessed on 13 February 2020).
- MTI, Ministry of Transport and Infrastructure. 2018. Available online: https://www.uab.gov.tr/ (accessed on 17 May 2024).
- Topcu, R. The Costs of Occurrıng Traffıc Accıdents and Transportatıon in Turkey. Master’s Thesis, Gümüşhane University, Gümüşhane, Turkey, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Chaturabong, P.; Kanitpong, K.; Jiwattanakulpaisarn, P. Analysis of Motorcycle accident cost in Thailand by Willingness-to-Pay method. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2011, 2239, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles-Zurita, J.A. Valuation of safety under reference-dependent evaluation of income. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2015, 79, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, P.; Xu, X. Estimation of social value of statistical life using willingness-to-pay method in Nanjing, China. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2016, 95, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainy, E.; Soori, H.; Ganjali, M.; Le, H.; Baghfalaki, T. Estimating cost of road traffic injuries in Iran using willingness to pay (WTP) method. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jou, R.C.; Chen, T.Y. The willingness to pay of parties to traffic accidents for loss of productivity and consolation compensation. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2015, 85, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasnatscheew, A.; Felix, H.; Schoenebeck, S.; Markus, L.; Hosta, P. Review of European Accident Cost Calculation Methods—With Regard to Vulnerable Road Users; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2016; Project No. 635895 (InDeV); Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/research/participants/documents/downloadPublic?appId=PPGMS&documentIds=080166e5b2bdebfd (accessed on 8 April 2021).
- De Blaeij, A.; Florax, R.J.; Rietveld, P.; Verhoef, E. The value of statistical life in road safety: A meta-analysis. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2003, 35, 973–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, M.; Johansson, M.V. Willingness to pay for private and public road safety in stated preference studies: Why the difference? Accid. Anal. Prev. 2010, 42, 1205–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, K.J. Improving safety culture through the health and safety organization: A case study. J. Saf. Res. 2014, 48, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wachter, J.K.; Yorio, P.L. A system of safety management practices and worker engagement for reducing and preventing accidents: An empirical and theoretical investigation. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2014, 68, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hojman, P.; De Dios Ortuzar, J.; Rizzi, L.I. On the joint valuation of averting fatal and severe injuries in highway accidents. J. Saf. Res. 2005, 36, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iragüen, P.; De Dios Ortúzar, J. Willingness-to-pay for reducing fatal accident risk in urban areas: An Internet-based Web page stated preference survey. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2004, 36, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzi, L.I.; De Dios Ortúzar, J. Stated preference in the valuation of interurban road safety. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2003, 35, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, H. Willingness to pay for road safety and estimates of the risk of death: Evidence from a Swedish contingent valuation study. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2007, 39, 853–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, L.A.; Hammitt, J.K.; O’keeffe, L. Valuing mortality risk reductions in global benefit-cost analysis. J. Benefit-Cost Anal. 2019, 10, 15–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaździk-Osmólska, A. Willingness to Pay for Road Safety Improvements in Poland. 2021. Available online: https://www.um.edu.mt/library/oar/handle/123456789/106280 (accessed on 22 June 2024).
- Baker, R.; Chilton, S.M.; Jones-Lee, M.W.; Metcalf, H.R.T. Valuing lives equally in a benefit-coast analysis of safety projects: A method to reconcile theory and practice. Saf. Sci. 2009, 47, 813–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, L.A. Estimating the Values of Mortality Risk Reductions in Low-and Middle-Income Countries1. J. Benefit-Cost Anal. 2017, 8, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijnen, W.; Wesemann, P.; De Blaeij, A. Valuation of road safety effects in cost–benefit analysis. Eval. Program Plan. 2009, 32, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishan, E.J. Evaluation of life and limb: A theoretical approach. J. Political Econ. 1971, 79, 687–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, M.C.; Shepard, D.S.; Pliskin, J.S. The economic value of changing mortality probabilities: A decision-theoretic approach. Q. J. Econ. 1980, 94, 373–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maśniak, D. Social and Economic Costs of Road Accidents in Europe. 2008. Available online: https://www.law.muni.cz/sborniky/dp08/files/pdf/financ/masniak.pdf (accessed on 12 August 2025).
- Mcinerney, R.; Smith, G. Saving lives through investment in safer roads: The iRAP partnership. In Proceedings of the REAAA Conference, Incheon, Republic of Korea, 23–26 September 2009; Available online: https://trid.trb.org/View/1149491 (accessed on 26 April 2024).
- Mcmahon, K.; Dahdad, S. The True Cost of Road Casualties: Valuing Life and the Cost of a Serious Injury; iRAP: London, UK, 2008; Available online: https://www.eaprso.org/data-and-knowledge/the-true-cost-of-road-casualties-valuing-life-and-the-cost-of-a-serious-injury (accessed on 4 March 2022).
- Andersson, H. Willingness to pay for car safety: Evidence from Sweden. Environ. Resour. Econ. 2008, 41, 579–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, H. Consistency in preferences for road safety: An analysis of precautionary and stated behavior. Res. Transp. 2013, 43, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindhjem, H.; Navrud, S.; Braathen, N.A.; Biausque, V. Valuing mortality risk reductions from environmental, transport, and health policies: A global meta-analysis of stated preference studies. Risk Anal. Int. J. 2011, 31, 1381–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hultkrantz, L.; Svensson, M. The value of a statistical life in Sweden: A review of the empirical literature. Health Policy 2012, 108, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trawen, A.; Maraste, P.; Persson, U. Methods for estimating road accident costs: A comparison of costs for a fatal casualty in different countries. In Proceedings of the Traffic Safety on Three Continents: International Conference, Moscow, Russia, 19–21 September 2001; Statens Väg-Och Transportforskningsinstitut. pp. 759–768. Available online: https://trid.trb.org/View/721443 (accessed on 11 March 2022).
- Balakrishnan, S.; Karuppanagounder, K. Estimating the cost of two-wheeler road accident injuries in India using the willingness to pay method. Aust. J. Civ. Eng. 2020, 18, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nankunda, C.; Evdorides, H. A systematic review of the application of road safety valuation methods in assessing the economic impact of road traffic injuries. Future Transp. 2023, 3, 1253–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, J.; Barns, S.; Cameron, M.; Lim, S.; Scrimgeour, F.; Tressler, J. The value of statistical life and the economics of landmine clearance in developing countries. World Dev. 2007, 35, 512–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elvik, R. An analysis of official economic valuations of traffic accident fatalities in 20 motorized countries. Accid. Anal. Prev. 1995, 27, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoeters, A.; Wijnen, W.; Carnis, L.; Weijermars, W.; Elvik, R.; Daniels, S.; Johannsen, H. Costs related to serious road injuries: A European perspective. Eur. Transp. Res. Rev. 2020, 12, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silcock, R. Guidelines for Estimating the Cost of Road Crashes in Developing Countries; Department for International Development: London, UK, 2003; Available online: https://trid.trb.org/View/873533 (accessed on 17 April 2022).
- Dionne, G.; Lanoie, P. Public choice about the value of a statistical life for cost benefit analysis. J. Transp. Econ. Policy 2004, 32, 247–274. [Google Scholar]
- Mon, E.E.; Jomnonkwao, S.; Khampirat, B.; Satiennam, T.; Ratanavaraha, V. Willingness to pay for mortality risk reduction for traffic accidents in Myanmar. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2018, 118, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, N.M.; El Hakim, A.S.; Wahdan, A.H.; El Refaeye, M.A. Analysis of accidents cost in Egypt using the willingness-to-pay method. Int. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. 2016, 5, 10–18. Available online: http://article.sapub.org/10.5923.j.ijtte.20160501.02.html (accessed on 2 May 2024).
- Bhattacharya, S.; Alberini, A.; Cropper, M.L. The value of mortality risk reductions in Delhi, India. J. Risk Uncertain. 2007, 34, 21–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BITRE, Bureau of Infrastructure Transport and Regional Economics. Cost of Road Crashes in Australia 2006; BITRE: Canberra, Australia, 2010; Report 118. Available online: https://www.bitre.gov.au/publications/2010/report_118 (accessed on 7 September 2024).
- Le, H.; van Geldermalsen, T.; Lim, W.L.; Murphy, P. Deriving accident costs using willingness-to-pay approaches-A case study for Singapore. In Proceedings of the 34th Australasian Transport Research Forum (ATRF), Adelaide, Australia, 28–30 September 2011; Available online: https://trid.trb.org/View/1138215 (accessed on 11 October 2024).
- Ainy, E.; Soori, H.; Ganjali, M.; Baghfalaki, T. Eliciting road traffic injuries cost among Iranian drivers’ public vehicles using willingness to pay method. Int. J. Crit. Illn. Inj. Sci. 2015, 5, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subhan, F.; Zhao, S.; Diop, E.B.; Ali, Y.; Zhou, H. Public intention to pay for road safety improvement: A case study of Pakistan. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2021, 160, 106315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisutwattanasak, P.; Jomnonkwao, S.; Se, C.; Ratanavaraha, V. Influence of psychological perspectives and demographics on drivers’ valuation of road accidents: A combination of confirmatory factor analysis and preference heterogeneity model. Behav. Sci. 2022, 12, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoeters, A.; Large, M.; Koning, M.; Carnis, L.; Daniels, S.; Mignot, D.; Urmeew, R.; Wijnen, W.; Bijleveld, F.; van der Horst, M. Economic valuation of preventing fatal and serious road injuries. Results of a Willingness-To-Pay study in four European countries. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2022, 173, 106705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawłowska, B. External costs of transport in Poland. Sci. Rev.–Eng. Environ. Sci. 2018, 27, 28–41. [Google Scholar]
- Anokhin, A.; Vaida, T.; Siur, N. Economic and legal means of preventing road accidents in foreign countries. Balt. J. Econ. Stud. 2023, 9, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TSI, Turkish Statistical Institute. Labor Statistics (Database); Turkish Statistical Institute: Ankara, Turkiye, 2018. Available online: https://data.tuik.gov.tr/Bulten/Index?p=Isgucu-Istatistikleri-2018 (accessed on 25 April 2023).
- TSI, Turkish Statistical Institute. Population Statistics (Database); Turkish Statistical Institute: Ankara, Turkiye, 2018. Available online: https://data.tuik.gov.tr/Kategori/GetKategori?p=Nufus-ve-Demografi-109 (accessed on 25 April 2023).
- TSI, Turkish Statistical Institute. Annual Gross Domestic Product (Database); TSI: Ankara, Turkiye, 2018. Available online: https://data.tuik.gov.tr/Bulten/Index?p=Annual-Gross-Domestic-Product-2018-30890 (accessed on 25 April 2023).
- The Central Bank of the Republic of Turkiye, CBRT. Indicative Central Bank Rates. 2018. Available online: https://evds2.tcmb.gov.tr/index.php (accessed on 25 April 2023).
- CE Delft. Handbook on Estimation of External Costs in the Transport Sector; CE Delft: Delft, The Netherlands, 2019; Version 1.1; 332p, Available online: https://cedelft.eu/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/2021/03/CE_Delft_4K83_Handbook_on_the_external_costs_of_transport_Final.pdf (accessed on 11 May 2024).
- TSI, Turkish Statistical Institute. Purchasing Power Parity. 2021. Available online: https://data.tuik.gov.tr/Bulten/Index?p=Satinalma-Gucu-Paritesi-2021-45868 (accessed on 8 April 2023).
- OECD, Organisation for Economic Co-Operation and Development. External Costs of Transport in Central and Eastern Europe; Final Report, ENV/EPOC/WPNEP/T(2002)5/FINAL; OECD: Zurich, Switzerland, 2003; 105p. Available online: https://rosap.ntl.bts.gov/view/dot/34169 (accessed on 22 May 2024).
- INFRAS. External Costs of Transport: Update Study; Final Report; INFRAS: Zurich, Switzerland, 2004; 169p, ISBN 2-7461-0891-7. Available online: https://www.infras.ch/en/projects/external-costs-of-transport/ (accessed on 17 May 2024).
- HEATCO. Developing Harmonised European Approaches for Transport Costing and Project Assesment, Deliverable 5: Proposal for Harmonised Guidelines; Institute of Energy Economics and Rational Energy Use University of Stuttgart: Stuttgart-Vaihingen, Germany, 2006; 193p, Available online: https://elib.uni-stuttgart.de/server/api/core/bitstreams/99416160-e71b-4e00-a4ec-74b22c81da54/content (accessed on 14 May 2024).
- OECD. Mortality Risk Valuation in Environment, Health and Transport Policies; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eurostat. GDP per Capita in PPS. 2021. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/databrowser/product/page/TEC00114 (accessed on 1 May 2024).
- Hammitt, J.K.; Robinson, L.A. The income elasticity of the value per statistical life: Transferring estimates between high- and low-income populations. J. Benefit-Cost Anal. 2011, 2, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viscusi, W.K.; Masterman, C.J. Income elasticities and global values of a statistical life. J. Benefit-Cost Anal. 2017, 8, 226–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD; Eurostat; UNECE. Illustrated Glossary for Transport Statistics, 4th ed.; OECD Publishing: París, France, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TSI, Turkish Statistical Institute. Motor Vehicle Statistics 2020; TSI: Ankara, Turkiye, 2020. Available online: https://data.tuik.gov.tr/Bulten/Index?p=Motorlu-Kara-Tasitlari-Ocak-2020-33649 (accessed on 29 September 2025).
- MTI, Ministry of Transport and Infrastructure. Transport and Infrastructure Annual Report 2022; MTI: Ankara, Turkiye, 2022. Available online: https://www.uab.gov.tr/uploads/announcements/2022-yili-ulastirma-ve-altyapi-bakanligi-faaliyet/2022-yili-uab-faaliyet-raporu.pdf (accessed on 29 September 2025).
- Coruh, E.; Yıldız, M.S.; Urak, F.; Bilgiç, A.; Cengiz, V. Motivating green transition: Analyzing fuel demands in Turkiye amidst the climate crisis and economic impact. Sustainability 2025, 17, 4851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD/ITF. Reporting on Serious Road Traffic Casualties: Combining and Using Different Data Sources to Improve Understanding of Non-Fatal Road Traffic Crashes; International Transport Forum; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2011; Available online: https://www.itf-oecd.org/sites/default/files/docs/road-casualties-web.pdf (accessed on 29 September 2025).
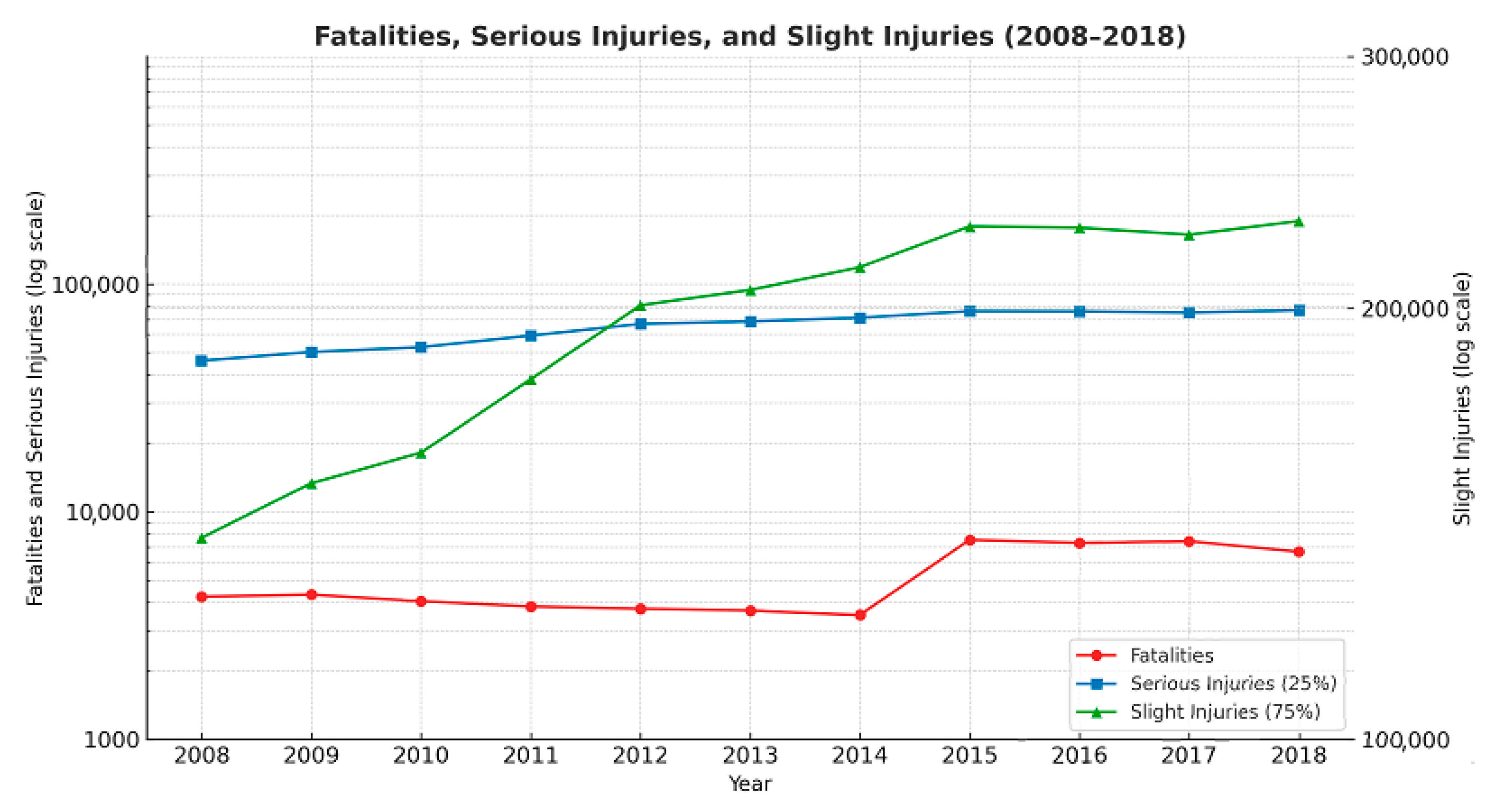
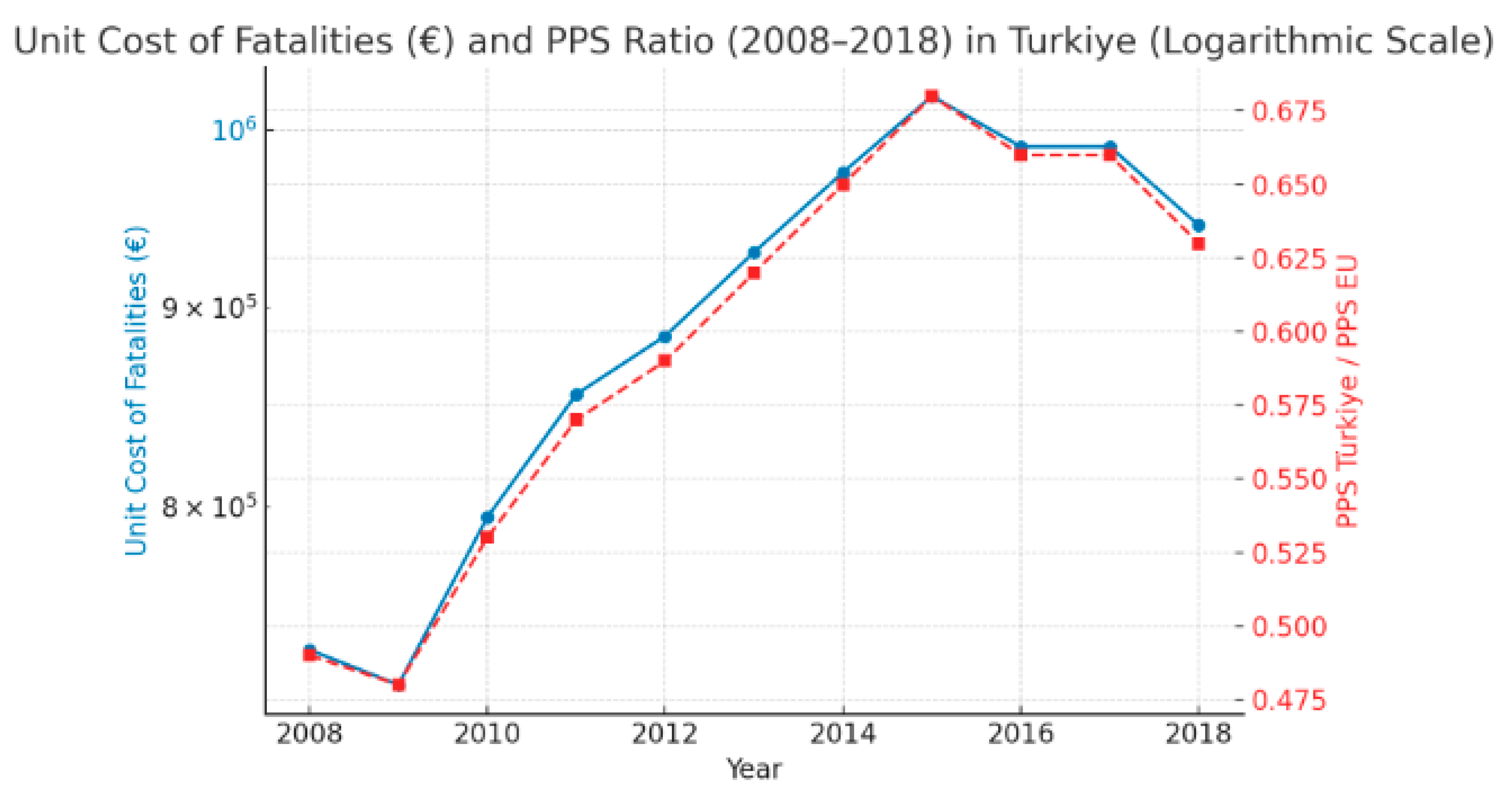
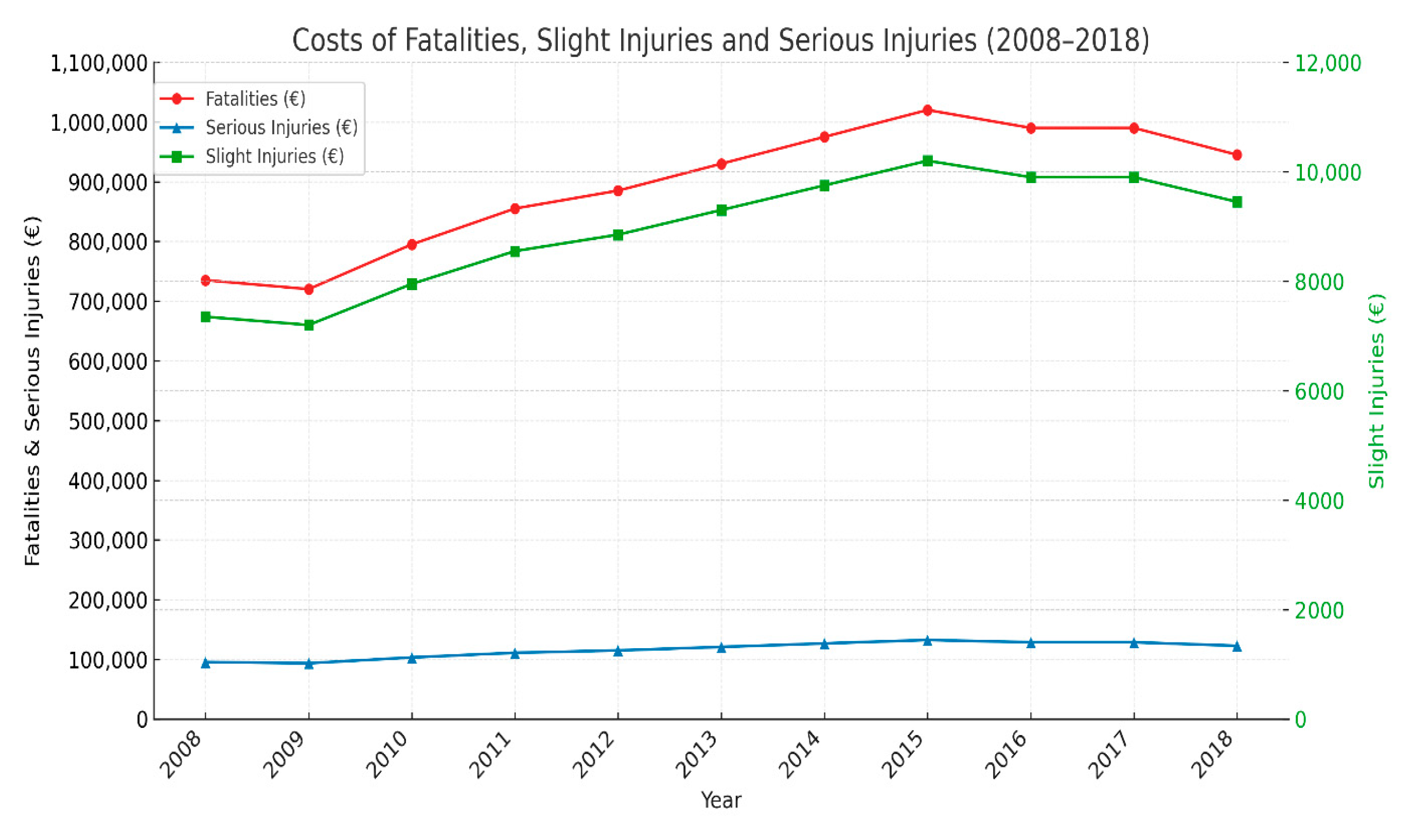
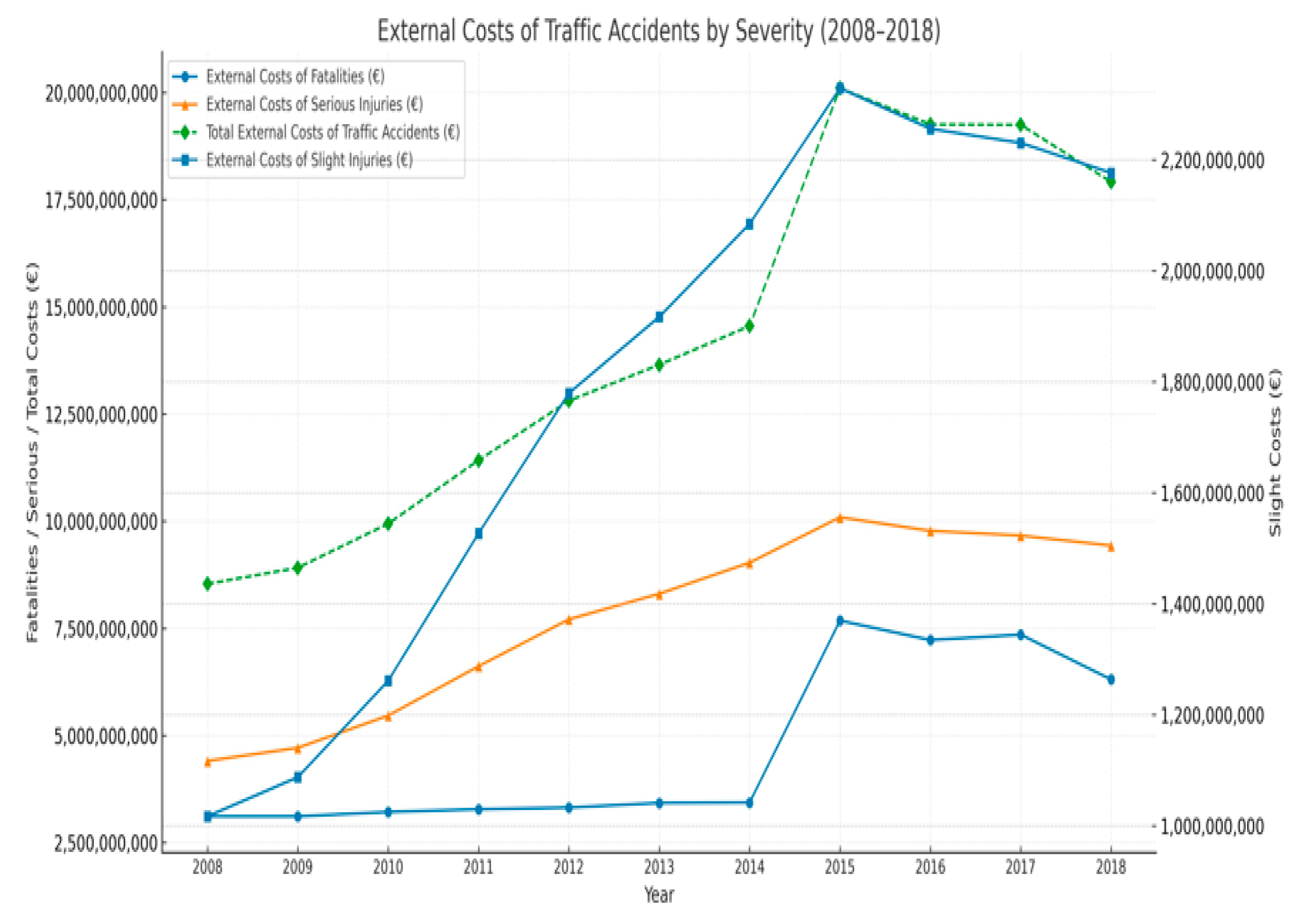
| Year | Responsible Authority | Number of Fatalities | Number of Injuries | Estimated Number of Serious Injuries | Estimated Number of Slight Injuries | Total Estimated Serious Injuries | Total Estimated Slight Injuries |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2008 | TPRZ | 2948 | 145,163 | 36,291 | 108,872 | 46,117 | 138,351 |
| GRZ | 1288 | 39,305 | 9826 | 29,479 | |||
| 2009 | TPRZ | 2993 | 161,719 | 40,430 | 121,289 | 50,345 | 151,035 |
| GRZ | 1331 | 39,661 | 9915 | 29,746 | |||
| 2010 | TPRZ | 2738 | 171,475 | 42,869 | 128,606 | 52,874 | 158,622 |
| GRZ | 1307 | 40,021 | 10,005 | 30,016 | |||
| 2011 | TPRZ | 2582 | 194,149 | 48,537 | 14,612 | 59,519 | 178,556 |
| GRZ | 1253 | 43,925 | 10,981 | 32,944 | |||
| 2012 | TPRZ | 2555 | 221,108 | 55,277 | 165,831 | 67,020 | 201,059 |
| GRZ | 1195 | 46,971 | 11,743 | 35,228 | |||
| 2013 | TPRZ | 2393 | 224,287 | 56,072 | 168,215 | 68,707 | 206,122 |
| GRZ | 1292 | 50,542 | 12,636 | 37,907 | |||
| 2014 | TPRZ | 2296 | 233,336 | 58,334 | 175,002 | 71,265 | 213,794 |
| GRZ | 1228 | 51,723 | 12,931 | 38,792 | |||
| 2015 | TPRZ | 2555 | 250,362 | 62,591 | 187,772 | 76,105 | 228,316 |
| GRZ | 4975 | 54,059 | 13,515 | 40,544 | |||
| 2016 | TPRZ | 2266 | 249,714 | 62,429 | 187,286 | 75,953 | 227,859 |
| GRZ | 5034 | 54,098 | 13,525 | 40,574 | |||
| 2017 | TPRZ | 2299 | 246,264 | 61,566 | 184,698 | 75,096 | 225,287 |
| GRZ | 5034 | 54,119 | 13,530 | 40,589 | |||
| 2018 | TPRZ | 2138 | 249,687 | 62,422 | 187,265 | 76,768 | 230,303 |
| GRZ | 4537 | 57,384 | 14,346 | 43,038 |
| Year | PPS Türkiye/PPS EU Average | Unit Cost of Fatalities (€) |
|---|---|---|
| 2008 | 0.49 | 735,000 |
| 2009 | 0.48 | 720,000 |
| 2010 | 0.53 | 795,000 |
| 2011 | 0.57 | 855,000 |
| 2012 | 0.59 | 885,000 |
| 2013 | 0.62 | 930,000 |
| 2014 | 0.65 | 975,000 |
| 2015 | 0.68 | 1,020,000 |
| 2016 | 0.66 | 990,000 |
| 2017 | 0.66 | 990,000 |
| 2018 | 0.63 | 945,000 |
| Year | Fatalities (€) | Serious Injuries (€) | Slight Injuries (€) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2008 | 735,000 | 95,550 | 7350 |
| 2009 | 720,000 | 93,600 | 7200 |
| 2010 | 795,000 | 103,350 | 7950 |
| 2011 | 855,000 | 111,150 | 8550 |
| 2012 | 885,000 | 115,050 | 8850 |
| 2013 | 930,000 | 120,900 | 9300 |
| 2014 | 975,000 | 126,750 | 9750 |
| 2015 | 1,020,000 | 132,600 | 10,200 |
| 2016 | 990,000 | 128,700 | 9900 |
| 2017 | 990,000 | 128,700 | 9900 |
| 2018 | 945,000 | 122,850 | 9450 |
| Year | Number of Fatalities | Estimated Number of Serious Injuries | Estimated Number of Slight Injuries | External Costs of Fatalities (€) | External Costs of Serious Injuries (€) | External Costs of Slight Injuries (€) | Total External Costs of Traffic Accidents (€) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2008 | 4236 | 46,117 | 138,351 | 3,113,460,000 | 4,406,479,350 | 1,016,879,850 | 8,536,819,200 |
| 2009 | 4324 | 50,345 | 151,035 | 3,113,280,000 | 4,712,292,000 | 1,087,452,000 | 8,913,024,000 |
| 2010 | 4045 | 52,874 | 158,622 | 3,215,775,000 | 5,464,527,900 | 1,261,044,900 | 9,941,347,800 |
| 2011 | 3835 | 59,519 | 178,556 | 3,278,925,000 | 6,615,536,850 | 1,526,653,800 | 11,421,115,650 |
| 2012 | 3750 | 67,020 | 201,059 | 3,318,750,000 | 7,710,651,000 | 1,779,372,150 | 12,808,773,150 |
| 2013 | 3685 | 68,707 | 206,122 | 3,427,050,000 | 8,306,676,300 | 1,916,934,600 | 13,650,660,900 |
| 2014 | 3524 | 71,266 | 213,794 | 3,435,900,000 | 9,032,965,500 | 2,084,491,500 | 14,553,357,000 |
| 2015 | 7530 | 76,105 | 228,316 | 7,680,600,000 | 10,091,523,000 | 2,328,823,200 | 20,100,946,200 |
| 2016 | 7300 | 75,953 | 227,859 | 7,227,000,000 | 9,775,151,100 | 2,255,804,100 | 19,257,955,200 |
| 2017 | 7427 | 75,096 | 225,287 | 7,352,730,000 | 9,664,855,200 | 2,230,341,300 | 19,247,926,500 |
| 2018 | 6675 | 76,768 | 230,303 | 6,307,875,000 | 9,430,948,800 | 2,176,363,350 | 17,915,187,150 |
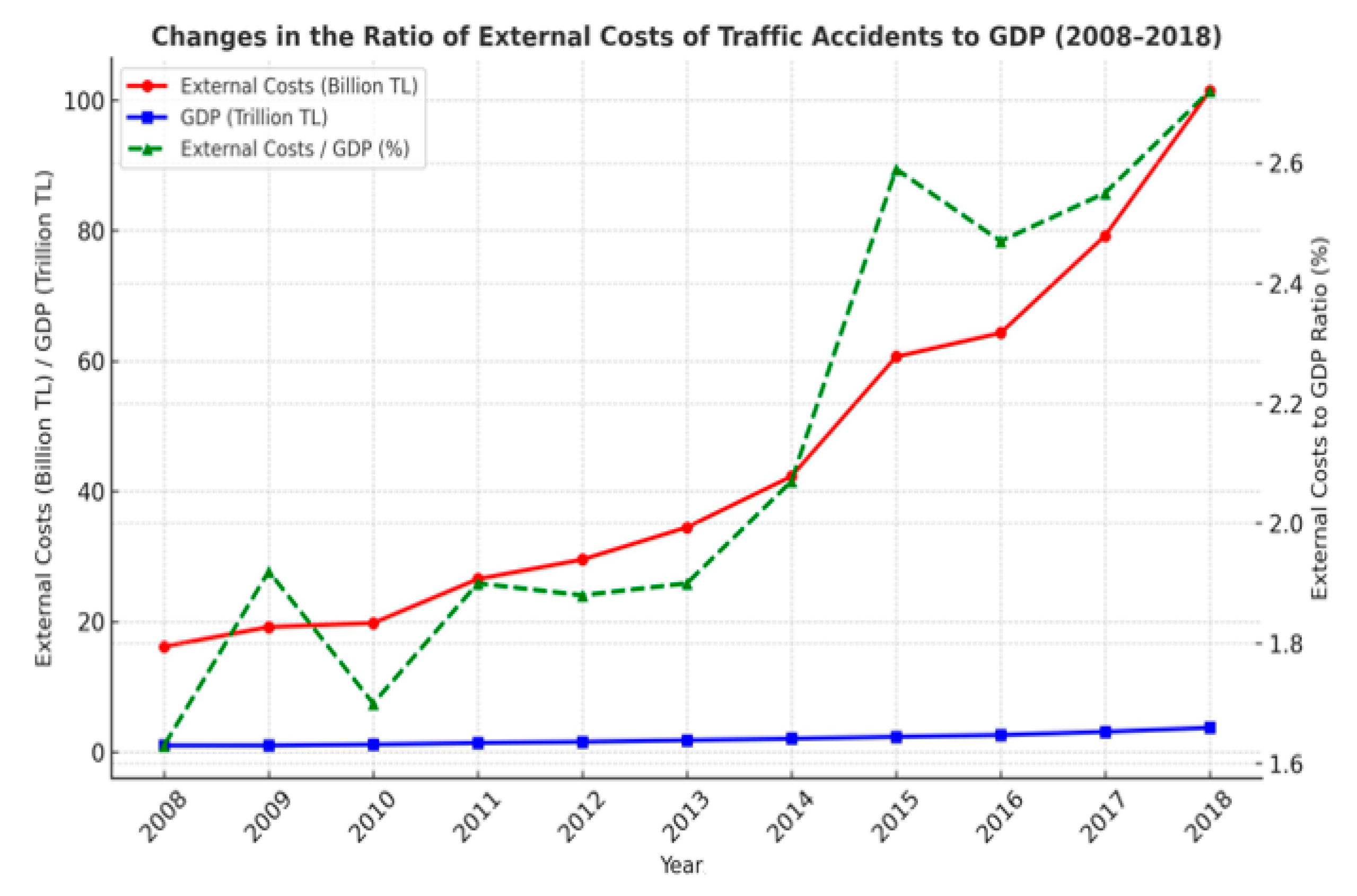
| Years | External Costs (€) | EURO/TRY Exchange Rate | External Costs (₺) | GDP (₺) | External Costs to GDP Ratio (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2008 | 8,536,819,200 | 1.896 | 16,183,845,734 | 994,782,858,000 | 1.63 |
| 2009 | 8,913,024,000 | 2.151 | 19,167,636,372 | 999,191,848,000 | 1.92 |
| 2010 | 9,941,347,800 | 1.989 | 19,776,820,245 | 1,160,013,978,000 | 1.70 |
| 2011 | 11,421,115,650 | 2.322 | 26,524,398,985 | 1,394,477,166,000 | 1.90 |
| 2012 | 12,808,773,150 | 2.304 | 29,517,689,636 | 1,569,672,115,000 | 1.88 |
| 2013 | 13,650,660,900 | 2.525 | 34,472,696,503 | 1,809,713,087,000 | 1.90 |
| 2014 | 14,553,230,250 | 2.906 | 42,291,250,509 | 2,044,465,876,000 | 2.07 |
| 2015 | 20,100,946,200 | 3.018 | 60,669,881,877 | 2,338,647,494,000 | 2.59 |
| 2016 | 19,257,955,200 | 3.340 | 64,317,911,356 | 2,608,525,749,000 | 2.47 |
| 2017 | 19,247,926,500 | 4.116 | 79,232,357,123 | 3,110,650,155,000 | 2.55 |
| 2018 | 17,915,187,150 | 5.663 | 101,447,792,818 | 3,724,387,936,000 | 2.72 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Topcu, R.; Coruh, E. External Costs of Road Traffic Accidents in Türkiye: The Willingness-to-Pay Method. Sustainability 2025, 17, 9514. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219514
Topcu R, Coruh E. External Costs of Road Traffic Accidents in Türkiye: The Willingness-to-Pay Method. Sustainability. 2025; 17(21):9514. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219514
Chicago/Turabian StyleTopcu, Rahmi, and Emine Coruh. 2025. "External Costs of Road Traffic Accidents in Türkiye: The Willingness-to-Pay Method" Sustainability 17, no. 21: 9514. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219514
APA StyleTopcu, R., & Coruh, E. (2025). External Costs of Road Traffic Accidents in Türkiye: The Willingness-to-Pay Method. Sustainability, 17(21), 9514. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219514






