A Combined AHP–TOPSIS-Based Decision Support System for Highway Pavement Type Selection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Study Area
4. Methodology
4.1. Conceptual Framework
4.2. Data and Application
4.3. Analytical Methods
5. Results
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NSC | National Safety Council |
| AHP | Analytic Hierarchy Process |
| TOPSIS | Technique for Order Preference by Similarity to Ideal Solution |
| MEPDG | Mechanistic–Empirical Pavement Design Guide |
| SAMDM | South African Mechanistic Pavement Design Method |
| USA | United States of America |
| MCDM | Multi-Criteria Decision Making |
| Csa | Hot-summer Mediterranean climate type |
| CI | Consistency Index |
| CR | Consistency Ratio |
References
- Çetin, B.; Barış, S.; Saroğlu, S. Türkiye’de karayollarının gelişimine tarihsel bir bakış. Çankırı Karatekin Üniversitesi İktisadi Ve İdari Bilim. Fakültesi Derg. 2011, 1, 123–150. [Google Scholar]
- Mohod, M.V.; Kadam, K.N. A comparative study on rigid and flexible pavement: A review. IOSR J. Mech. Civ. Eng. 2016, 13, 84–88. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.H. Pavement Analysis and Design; Pearson/Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2004; Volume 2, pp. 401–409. [Google Scholar]
- Zakeri, H.; Nejad, F.M.; Fahimifar, A. Image based techniques for crack detection, classification and quantification in asphalt pavement: A review. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2017, 24, 935–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Q.; Lau, D. Real-time detection of cracks in tiled sidewalks using YOLO-based method applied to unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) images. Autom. Constr. 2023, 147, 104745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, R.G.; Moulthrop, J.S.; Daleiden, J. Selecting a preventive maintenance treatment for flexible pavements. Transp. Res. Rec. 1999, 1680, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AASHTO. Mechanistic-Empirical Pavement Design Guide. A Manual of Practice-Interim Edition; American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials: Washington, DC, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, P.; Pais, J. Main flexible pavement and mix design methods in Europe and challenges for the development of an European method. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. (Engl. Ed.) 2017, 4, 316–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theyse, H.L.; De Beer, M.; Rust, F.C. Overview of South African mechanistic pavement design method. Transp. Res. Rec. 1996, 1539, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasha, A.; Mansourian, A.; Ravanshadnia, M. A hybrid fuzzy multi-attribute decision making model to select road pavement type. Soft Comput. 2020, 24, 16135–16148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taher, S.A.; Alyousify, S.; Hassan, H.J.A. Comparative study of using flexible and rigid pavements for roads: A review study. J. Duhok Univ. 2020, 23, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusida, D.; Oetomo, W.; Marleno, R. Cost and Time Comparison Research Between Rigid Pavement and Flexible Pavement on the Temuireng-Jetis Road Section, Mojokerto District. Asian J. Eng. Soc. Health 2025, 4, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yu, S.; Huang, Y.; Liu, L.; Pan, Y. A systematic review of rigid-flexible composite pavement. J. Road Eng. 2024, 4, 203–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, A.; Ansari, M.T.; Cook, A.; Hedden, J.; Ogundipe, T.; Ortlieb, J.; Nunez, T.; Roy, A.; Turben, T.; Braham, A. Comparative life-cycle cost analysis of flexible and rigid pavement: A case study of four Arkansas roadway sections. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2025, 26, 2489044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanyıldızı, M.M.; Geçkil, T. AASHTO Metodunda Rijit ve Esnek Üstyapıların Projelendirilmesinde Kullanılan Parametrelerin İncelenmesi. Fırat Üniversitesi Mühendislik Bilim. Derg. 2019, 31, 187–194. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmood, M.S. Network-Level Maintenance Decisions for Flexible Pavement Using a Soft Computing-Based Framework; Nottingham Trent University: Nottingham, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hafez, M.; Ksaibati, K. Studying the Effectiveness of Changing Parameters in Pavement Management Systems on Optimum Maintenance Strategies of Low-Volume Paved Roads. J. Transp. Eng. Part B Pavements 2021, 147, 04020075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallin, J. Guide for Pavement-Type Selection; Transportation Research Board: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; Volume 703. [Google Scholar]
- Beg, M.A.; Zhang, Z.; Hudson, W.R. A Rational Pavement Type Selection Procedure; Center for Transportation Research, University of Texas at Austin: Austin, TX, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, J.R.; Petts, R.C.; Rolt, J. Low Volume Rural Road Surfacing and Pavements: A Guide to Good Practice; OTB Engineering UK LLP: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Howe, J.; Richards, P.; Howe, J.D.G.F. Rural Roads and Poverty Alleviation; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, Z.; Eng, P.; Maher, M. Context sensitive pavement design for low volume road applications. In Proceedings of the Low-Volume Roads–Beyond the Boundaries: Design and Policy Issues Session of the 2006 Annual Conference of the Transportation Association of Canada, Charlottetown, PE, Canada, 17–20 September 2006; Transportation Association of Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2006; Volume 17. [Google Scholar]
- Plessis-Fraissard, M. Planning roads for rural communities. Transp. Res. Rec. 2007, 1989, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landers, S.; Mason, D.; MacNaughton, J. Development of a Sustainable Pavement Management Strategy for Resurfacing Low Volume Roads in New Brunswick. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Managing Pavement Assets, Alexandria, VA, USA, 18–21 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, K.; Tiwari, R.; Wadhwani, A.K.; Chaturvedi, S. An integrated GIS-MCDM framework for zoning, ranking and sensitivity analysis of municipal landfill sites. Sustain. Resilient Infrastruct. 2025, 10, 313–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topaloğlu, F. Development of a new hybrid method for multi-criteria decision making (MCDM) approach: A case study for facility location selection. Oper. Res. 2024, 24, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.tomtom.com/traffic-index/ranking/ (accessed on 25 August 2025).
- Öztürk, M.Z.; Çetinkaya, G.; Aydın, S. Köppen-Geiger iklim sınıflandırmasına göre Türkiye’nin iklim tipleri. Coğrafya Derg. 2017, 35, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- T.C. Çevre Şehircilik Ve İklim Değişikliği Bakanliği Meteoroloji Genel Müdürlüğü Köppen İklim Siniflandirmasina Göre Türkiye İklimi. Available online: https://www.mgm.gov.tr/files/iklim/iklim_siniflandirmalari/koppen.pdf (accessed on 25 August 2025).
- Adrese Dayalı Nüfus Kayıt Sistemi Sonuçları. 2024. Available online: https://data.tuik.gov.tr/Bulten/Index?p=Adrese-Dayali-Nufus-Kayit-Sistemi-Sonuclari-2024-53783 (accessed on 25 August 2025).
- Liu, Y.; Yu, C.; Guo, F.; Zhao, X.; Shan, J.; Lu, T.; Peng, H.; Yuan, D. Multi-criteria decision-making framework (AHP-TOPSIS): Pavement preventive maintenance case study for ordinary national trunk highways. Buildings 2024, 14, 3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Q.; Huang, J.; Du, S.; Yang, K.; Wang, H. Comprehensive evaluation of very thin asphalt overlays with different aggregate gradations and asphalt materials based on AHP and TOPSIS. Buildings 2022, 12, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavana, M.; Soltanifar, M.; Santos-Arteaga, F.J. Analytical hierarchy process: Revolution and evolution. Ann. Oper. Res. 2023, 326, 879–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillén-Mena, V.; Quesada-Molina, F.; Astudillo-Cordero, S.; Lema, M.; Ortiz-Fernández, J. Lessons learned from a study based on the AHP method for the assessment of sustainability in neighborhoods. MethodsX 2023, 11, 102440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stofkova, J.; Krejnus, M.; Stofkova, K.R.; Malega, P.; Binasova, V. Use of the analytic hierarchy process and selected methods in the managerial decision-making process in the context of sustainable development. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canco, I.; Kruja, D.; Iancu, T. AHP, a reliable method for quality decision making: A case study in business. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madzík, P.; Falát, L. State-of-the-art on analytic hierarchy process in the last 40 years: Literature review based on Latent Dirichlet Allocation topic modelling. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0268777. [Google Scholar]
- Lamrini, L.; Abounaima, M.C.; Talibi Alaoui, M. New distributed-topsis approach for multi-criteria decision-making problems in a big data context. J. Big Data 2023, 10, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taherdoost, H.; Madanchian, M. A comprehensive survey and literature review on TOPSIS. Int. J. Serv. Sci. Manag. Eng. Technol. 2024, 15, 1–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yıldırım, B.F.; Önder, E. Çok Kriterli Karar Verme Yöntemleri, 2nd ed.; Dora Yayınevi: Bursa, Turkey, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, D.R.; Sweeney, D.J.; Williams, T.A.; Camm, J.D.; Cochran, J.J.; Fry, M.J.; Ohlmann, J.W. Quantitative Methods for Business, 12th ed.; South-Western, Cengage Learning: Independence, KY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.L.; Ding, J.H.; Hou, H. Application of a triangular fuzzy AHP approach for flood risk evaluation and response measures analysis. Nat. Hazards 2013, 68, 657–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, T.L. Decision making with the analytic hierarchy process. Int. J. Serv. Sci. 2008, 1, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, J.A.; Lamata, M.T. Consistency in the analytic hierarchy process: A new approach. Int. J. Uncertain. Fuzziness Knowl.-Based Syst. 2006, 14, 445–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koç, K. Development of an Integrated Multi Agent Risk Management Platform for Flood Disaster Management. Master’s Thesis, Yıldız Technical University, İstanbul, Turkey, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Saaty, R.W. The analytic hierarchy process—What it is and how it is used. Math. Model. 1987, 9, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzeng, G.H.; Huang, J.J. Multiple Attribute Decision Making: Methods and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, C.L.; Yoon, K. Methods for multiple attribute decision making. In Multiple Attribute Decision Making: Methods and Applications a State-of-the-Art Survey; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1981; pp. 58–191. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, Y.J.; Liu, T.Y.; Hwang, C.L. Topsis for MODM. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1994, 76, 486–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Benefits of Pavement Markings: A Renewed Perspective Based on Recent and Ongoing Research. Available online: https://www.nsc.org/road/safety-topics/driving-at-night?srsltid=AfmBOoqjWNB2wI3Q9CeiQMguJYQ2oZRnkyXRbrYoZL_GFoEze55hNMSa&utm_source (accessed on 25 August 2025).
- Evren, Ü.; Aslıyüksek, H.; Çevik, F.E. Adli Tıp Kurumu Trafik İhtisas Dairesi Bilirkişi Raporlarında yol, araç mekanik arızaları, iklim koşulları ve işaretleme eksikliği durumlarının trafik kazalarına etkenliğinin değerlendirilmesi. Adli Tıp Derg. 2022, 36, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, P.J.; Park, E.S.; Andersen, C.K. Benefits of pavement markings: A renewed perspective based on recent and ongoing research. Transp. Res. Rec. 2009, 2107, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://highways.dot.gov/safety/other/visibility/benefits-pavement-markings-renewed-perspective-based-recent-and-ongoing (accessed on 25 August 2025).
- Karahacıoğlu, İ.A.; Corum, A. Asfalt yolların yaşam döngüsü maliyet analizi: İstanbul O3 otoyolunda uygulanması. Int. J. Eng. Res. Dev. 2020, 12, 32–39. [Google Scholar]
- Sarıaslan, H. Yatırım Projelerinin Hazırlanması ve Değerlendirilmesi: Planlama, Analiz, Fizibilite; Turhan Kitabevi: Ankara, Turkey, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Canver, S.; Özen, H.; Saraçoğlu, A.; Maltaş, A. Yol geometrik standartlarının karayolu işletme maliyetleri üzerindeki etkisinin incelenmesi. Mehmet Akif Ersoy Üniversitesi Uygulamalı Bilim. Derg. 2020, 4, 209–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güzel, İ. Ülkemizin Devlet Ve İl Yollarının Üst Yapı Bakım Onarım Maliyetinin Parametrik Çoklu Doğrusal Regresyonla Analizi. Bingöl Üniversitesi Tek. Bilim. Derg. 2024, 5, 29–44. [Google Scholar]
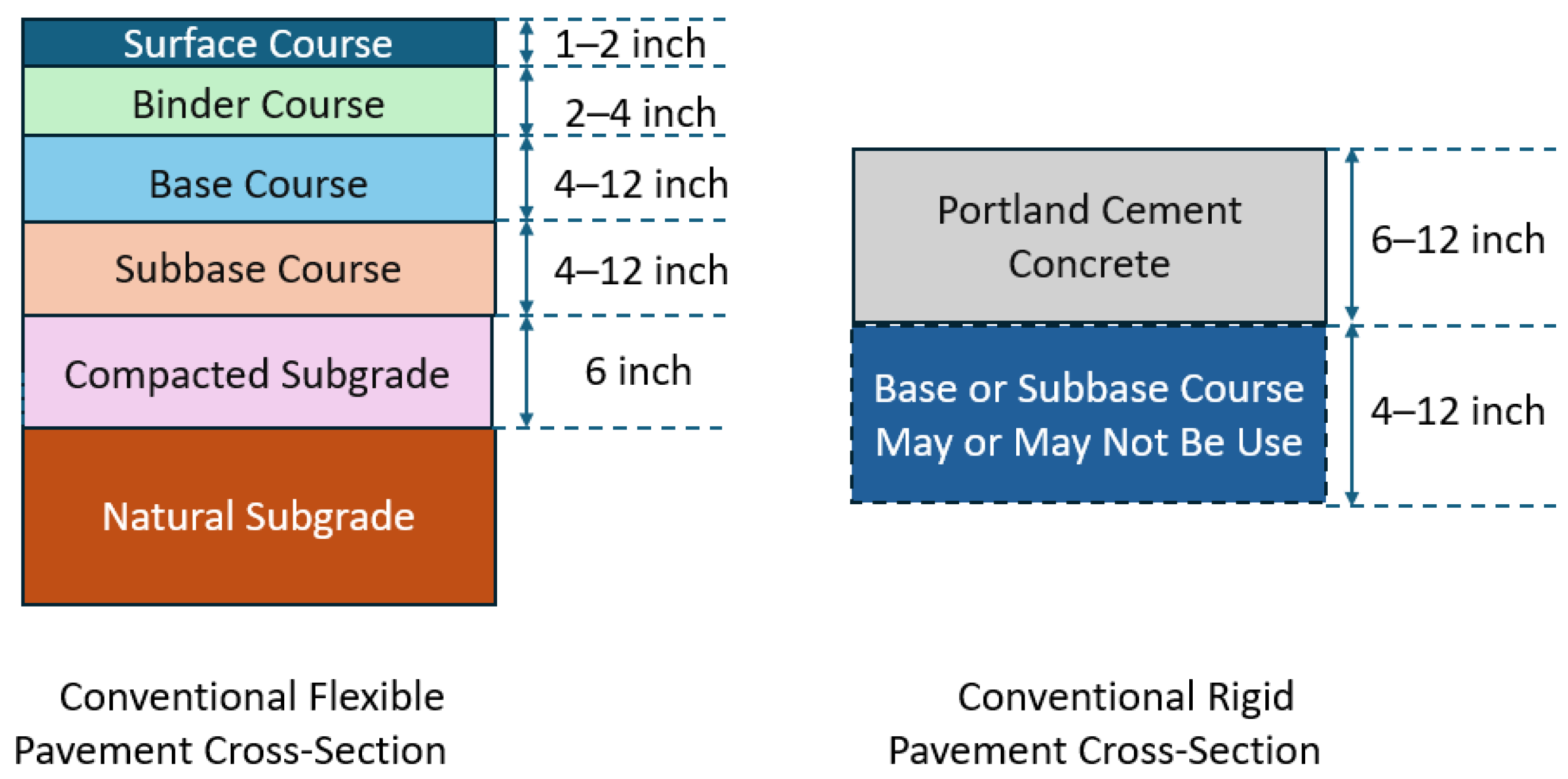
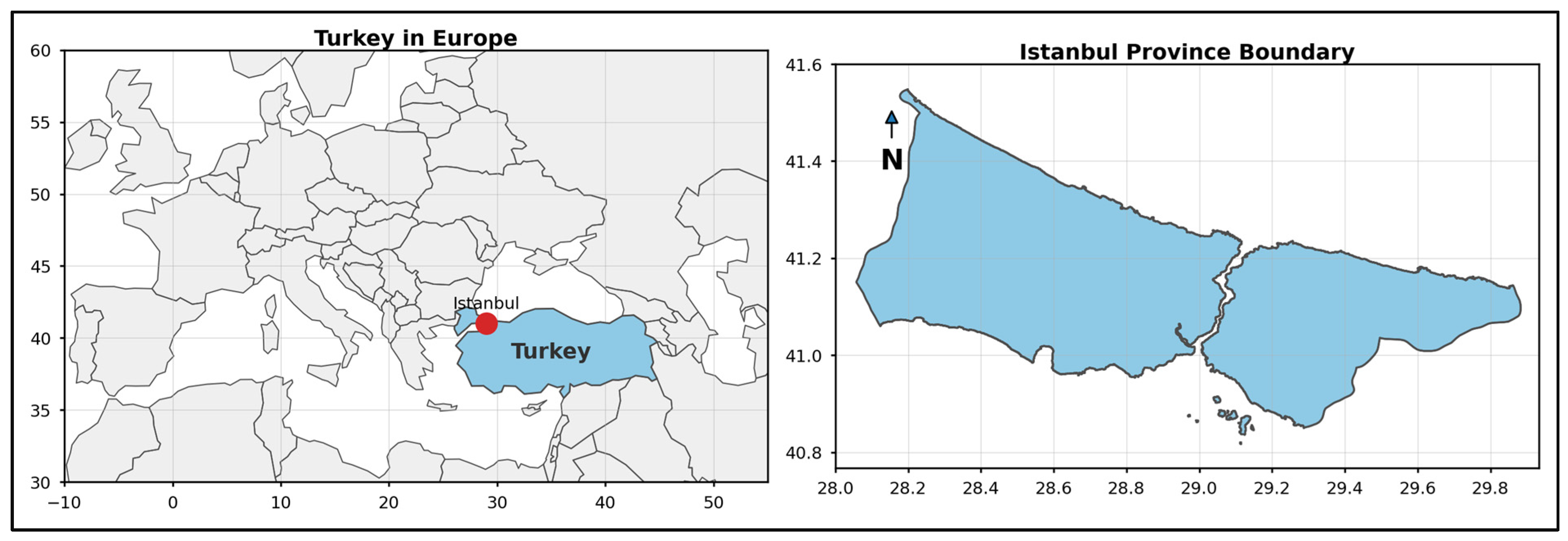

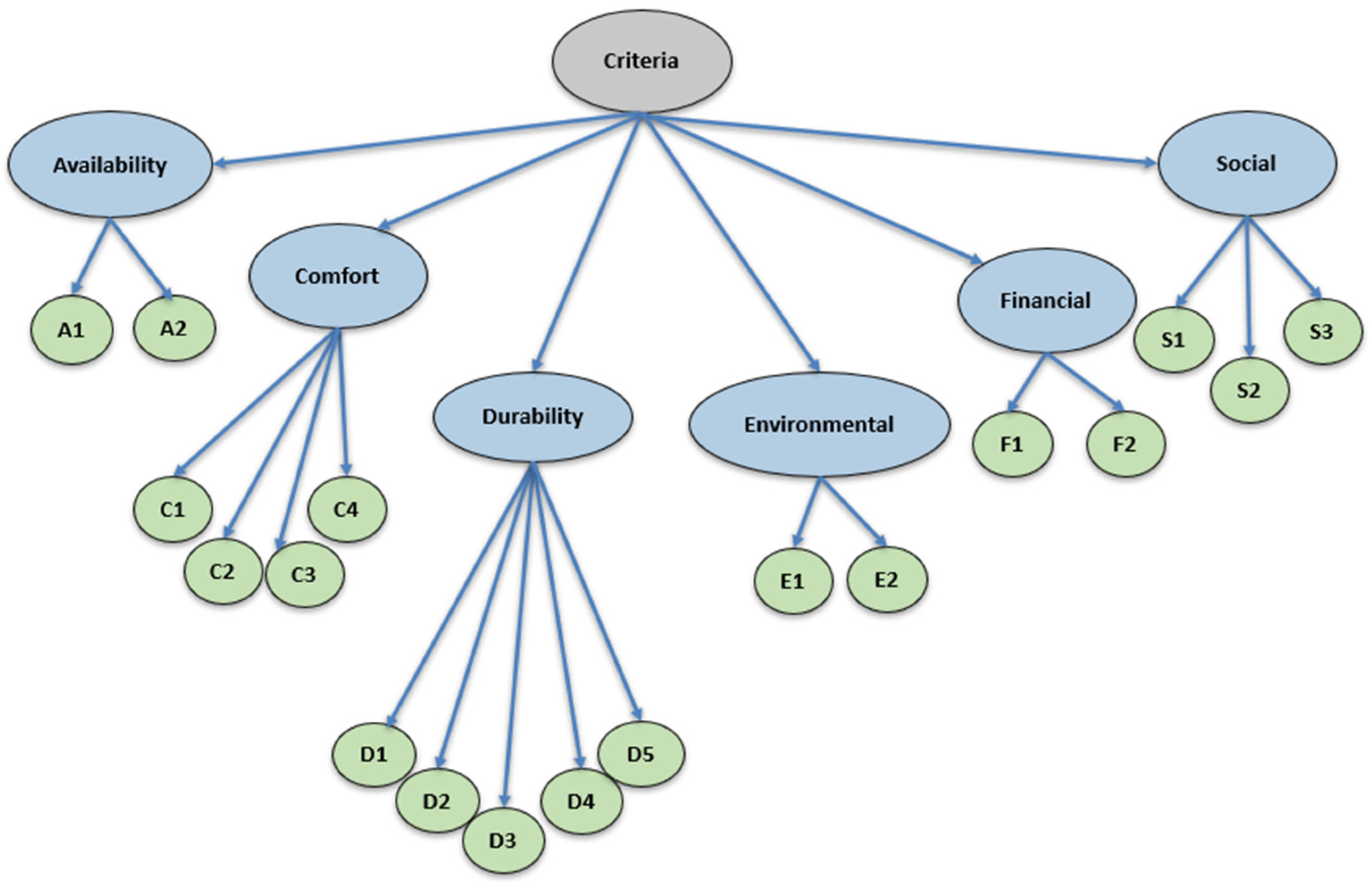
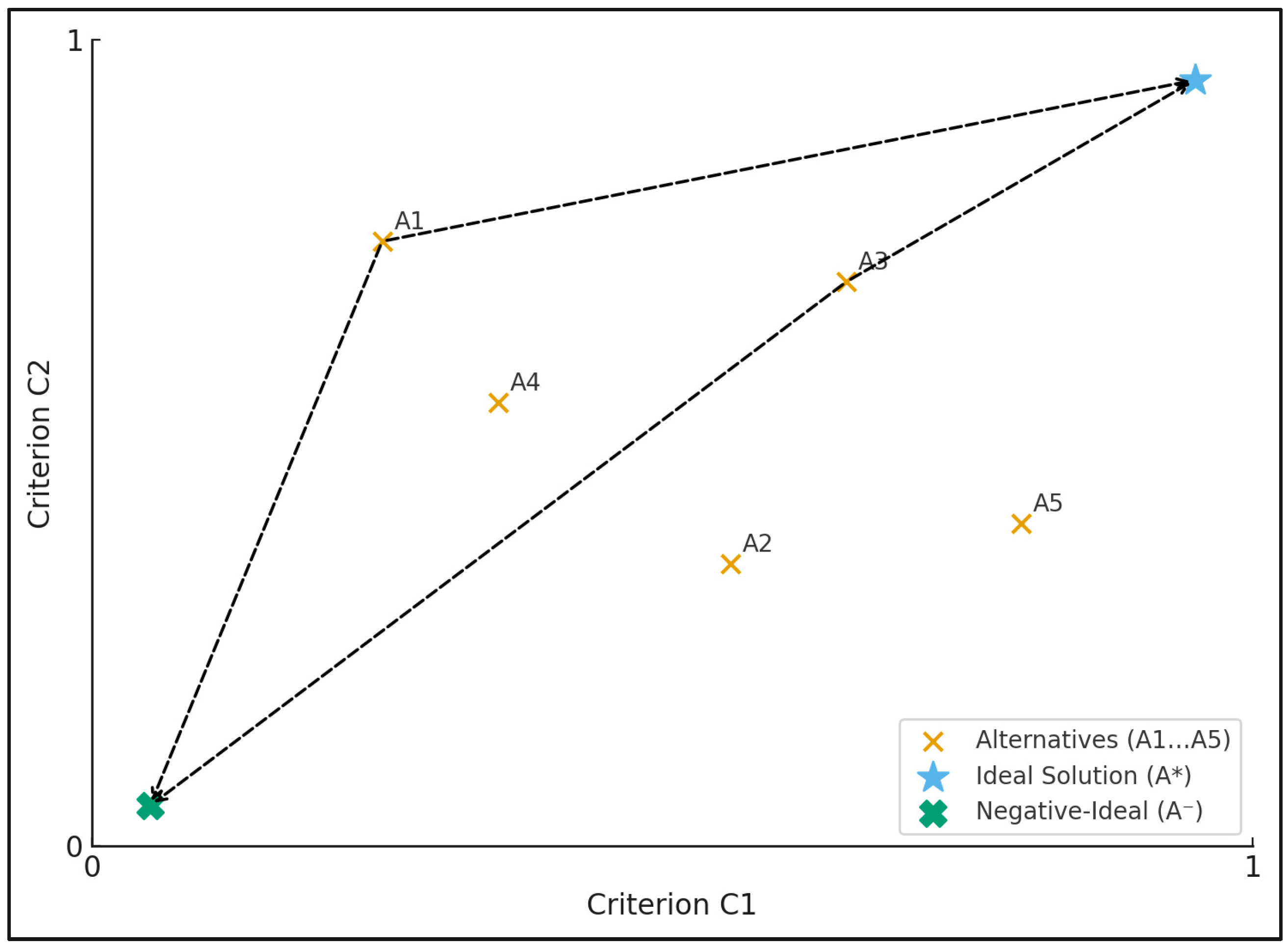
| Code | Explanations |
|---|---|
| A1 | Ease and availability of construction and repair equipment |
| A2 | Ease and availability of construction crew/personnel |
| C1 | Lane visibility |
| C2 | Noise level |
| C3 | Night visibility |
| C4 | Glare from sunlight |
| D1 | Pavement age |
| D2 | Resistance to environmental effects |
| D3 | Resistance to traffic loads |
| D4 | Surface polishing |
| D5 | Shoulder (edge) durability |
| E1 | Recyclability of materials |
| E2 | Eco-friendliness (Environmental Sustainability) |
| F1 | Initial construction cost |
| F2 | Maintenance/Repair cost |
| S1 | Maintenance/Repair frequency |
| S2 | Initial construction time |
| S3 | Service reopening time after maintenance/repair |
| ID | Company/Institution Name | Experience in the Sector (Years) | Experience in Transport/Materials (Years) | Position in the Institution |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ID1 | Istanbul Metropolitan Municipality | 12 | 12 | Deputy Director |
| ID2 | Istanbul Metropolitan Municipality | 25 | 25 | Regional Director |
| ID3 | Istanbul Metropolitan Municipality | 28 | 4 | Engineer |
| ID4 | Istanbul Metropolitan Municipality | 13 | 13 | Regional Chief |
| ID5 | Istanbul Metropolitan Municipality | 8 | 5 | Regional Chief |
| ID6 | Istanbul Metropolitan Municipality | 20 | 20 | Regional Chief |
| ID7 | İston A.Ş. | 20 | 10 | Construction Project Manager |
| ID8 | Istanbul Metropolitan Municipality | 4 | 4 | Transportation Engineer |
| ID9 | Istanbul Metropolitan Municipality | 19 | 18 | Deputy Director |
| ID10 | Istanbul Metropolitan Municipality Road Maintenance Department | 9 | 9 | Supervising Engineer |
| Intensity of Importance | Definition | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Equal importance | Two activities contribute equally to the objective |
| 2 | Weak | |
| 3 | Moderate importance | Experience and judgment slightly favor one activity over another |
| 4 | Moderate plus | |
| 5 | Strong importance | Experience and judgment strongly favor one activity over another |
| 6 | Strong plus | |
| 7 | Very strong or demonstrated importance | An activity is favored very strongly over another; its dominance is demonstrated in practice |
| 8 | Very, very strong | The evidence favoring one activity over another is of the highest possible order of affirmation |
| 9 | Extreme importance | |
| Reciprocals of above | If activity i has one of the above nonzero numbers assigned to it when compared with activity j, then j has the reciprocal value when compared with i | A reasonable assumption |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Random index ( ) | 0 | 0 | 0.58 | 0.9 | 1.12 | 1.24 | 1.32 | 1.41 | 1.45 | 1.49 |
| Experts | Main | Comfort | Durability | Social |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ID1 | 0.097 | 0.023 | 0.095 | 0.033 |
| ID2 | 0.053 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| ID3 | 0.096 | 0.022 | 0.068 | 0.046 |
| ID4 | 0.098 | 0.000 | 0.024 | 0.016 |
| ID5 | 0.087 | 0.069 | 0.026 | 0.000 |
| ID6 | 0.097 | 0.069 | 0.000 | 0.046 |
| ID7 | 0.097 | 0.011 | 0.062 | 0.046 |
| ID8 | 0.059 | 0.044 | 0.006 | 0.000 |
| ID9 | 0.090 | 0.017 | 0.044 | 0.046 |
| ID10 | 0.059 | 0.023 | 0.004 | 0.064 |
| Aggregated | 0.019 | 0.000 | 0.003 | 0.004 |
| Main Criteria | Weights | Rank |
|---|---|---|
| Availability | 0.1340 | 5 |
| Comfort | 0.2160 | 1 |
| Durability | 0.1341 | 4 |
| Environmental | 0.1868 | 3 |
| Financial | 0.2001 | 2 |
| Social | 0.1289 | 6 |
| Sub-Criteria | Sub-Criteria Weights | Overall Weight | Overall Rank |
|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 0.5547 | 0.0743 | 5 |
| A2 | 0.4453 | 0.0597 | 8 |
| C1 | 0.2433 | 0.0526 | 9 |
| C2 | 0.1923 | 0.0415 | 11 |
| C3 | 0.3220 | 0.0696 | 6 |
| C4 | 0.2423 | 0.0523 | 10 |
| D1 | 0.1334 | 0.0179 | 18 |
| D2 | 0.2242 | 0.0301 | 14 |
| D3 | 0.2779 | 0.0373 | 12 |
| D4 | 0.1836 | 0.0246 | 16 |
| D5 | 0.1809 | 0.0243 | 17 |
| E1 | 0.4382 | 0.0819 | 4 |
| E2 | 0.5618 | 0.1050 | 2 |
| F1 | 0.4282 | 0.0857 | 3 |
| F2 | 0.5718 | 0.1144 | 1 |
| S1 | 0.4944 | 0.0637 | 7 |
| S2 | 0.2320 | 0.0299 | 15 |
| S3 | 0.2736 | 0.0353 | 13 |
| Sub-Criteria | Flexible Pavement (Average) | Rigid Pavement (Average) | Ideal Position in TOPSIS |
|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 5.6 | 4.5 | Max |
| A2 | 6.3 | 4.1 | Max |
| C1 | 6.3 | 4.9 | Max |
| C2 | 4.8 | 4.5 | Min |
| C3 | 4.4 | 5.5 | Max |
| C4 | 3.9 | 4.7 | Min |
| D1 | 3.1 | 6.2 | Min |
| D2 | 3.4 | 5.7 | Max |
| D3 | 3.6 | 6.1 | Max |
| D4 | 4.2 | 4.0 | Min |
| D5 | 3.8 | 5.2 | Max |
| E1 | 4.8 | 3.4 | Max |
| E2 | 2.1 | 5.2 | Max |
| F1 | 4.8 | 4.0 | Min |
| F2 | 5.2 | 3.8 | Min |
| S1 | 4.7 | 3.9 | Min |
| S2 | 5.6 | 3.5 | Min |
| S3 | 5.4 | 3.2 | Min |
| Alternatives | Rank | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flexible pavement | 0.004851 | 0.00101 | 0.172379 | 2 |
| Rigid pavement | 0.00101 | 0.004851 | 0.827621 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sahin, O.; Aksoy, B. A Combined AHP–TOPSIS-Based Decision Support System for Highway Pavement Type Selection. Sustainability 2025, 17, 9396. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219396
Sahin O, Aksoy B. A Combined AHP–TOPSIS-Based Decision Support System for Highway Pavement Type Selection. Sustainability. 2025; 17(21):9396. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219396
Chicago/Turabian StyleSahin, Onur, and Berna Aksoy. 2025. "A Combined AHP–TOPSIS-Based Decision Support System for Highway Pavement Type Selection" Sustainability 17, no. 21: 9396. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219396
APA StyleSahin, O., & Aksoy, B. (2025). A Combined AHP–TOPSIS-Based Decision Support System for Highway Pavement Type Selection. Sustainability, 17(21), 9396. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219396






