The Impact of Environmental Regulation on Greenization Level of Manufacturing Industrial Chains: A Dual Perspective of Direct Effects and Spatial Spillovers
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- Methodological: We develop a novel provincial-level measurement framework for manufacturing industrial chain greenization and empirically quantify environmental regulation’s impacts.
- (2)
- Heterogeneous effects: This study further examines the heterogeneous effects of environmental regulation on the greenization level of manufacturing industrial chains through two novel analytical perspectives: energy consumption structure and the market value share of energy-intensive industries.
- (3)
- Spatial Analysis: We reveal significant spatial spillover effects, demonstrating how environmental regulation in one region positively influences neighboring areas’ industrial chain greenization.
2. Literature Review and Research Hypotheses
2.1. Impact of Environmental Regulation on the Greenization Level of Manufacturing Industrial Chains
2.2. Mechanistic Analysis of Environmental Regulation on Industrial Chain Greenization
2.2.1. Mechanism of Industrial Structure Rationalization
2.2.2. Mechanism of Green Technology Innovation
2.2.3. Mechanism of Industrialization Level
3. Data and Methods
3.1. Model Specification
3.1.1. Benchmark Regression Model
3.1.2. Spatial Autocorrelation Model
3.1.3. Spatial Econometric Model
3.2. Variable Selection
3.2.1. Dependent Variable
3.2.2. Core Explanatory Variable
3.2.3. Control Variables
3.3. Data Sources and Descriptive Statistics
3.4. Data Analysis
4. Regression Results and Analysis
4.1. Analysis of Baseline Regression Results
4.2. Analysis of Control Variables
4.3. Robustness Test
4.4. Endogeneity Test
4.5. Heterogeneity Analysis
4.5.1. Heterogeneity in Energy Consumption Structure
4.5.2. Heterogeneity in Market Value Share of Energy-Intensive Industries
4.5.3. Heterogeneity in Digital Economy Development Level
4.6. Mechanism Tests
5. Analysis of Spatial Spillover Effects
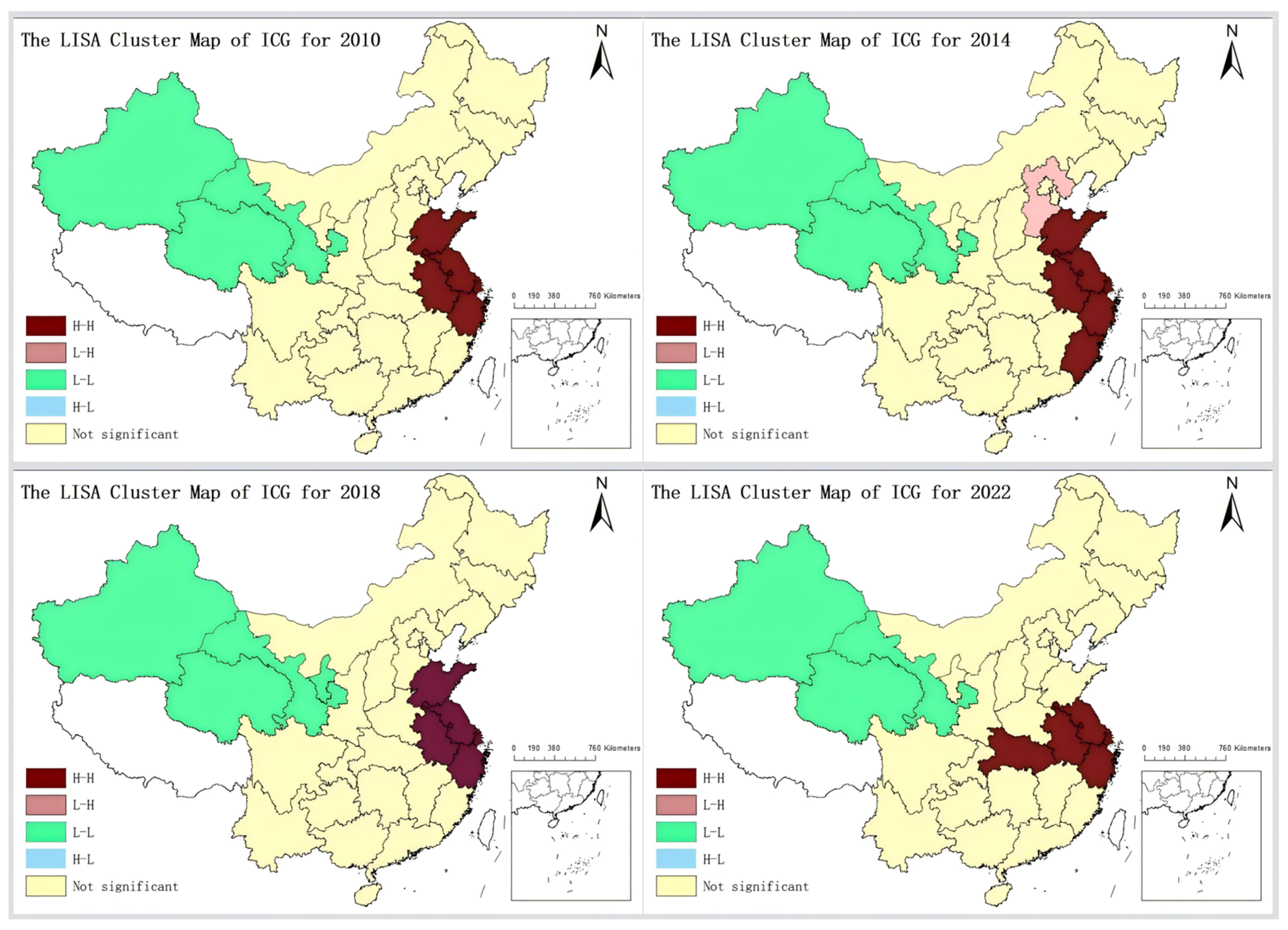
5.1. Spatial Correlation Test
5.2. Spatial Weight Matrix and Econometric Model Selection
5.3. Spatial Econometric Results
6. Discussion and Conclusions
6.1. Conclusions and Recommendations
6.2. Research Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Level 1 Indicator | Level 2 Indicator | Level 3 Indicator | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Digital Infrastructure | Hardware Facilities | Long-distance Optical Cable Line Length | 10,000 km |
| Internet Broadband Access Ports | 10,000 units | ||
| Mobile Phone Base Stations | 10,000 units | ||
| Software Facilities | Number of Internet Domain Names | 10,000 units | |
| Number of IPv4 Addresses | 10,000 units | ||
| Number of Internet Websites | 10,000 units | ||
| Digital Industry Development | Digital Industrialization | Software Business Revenue | 100 million yuan |
| Telecom Business Volume | 100 million yuan | ||
| Number of Electronic Information Manufacturing Enterprises | unit | ||
| Industrial Digitalization | Number of Websites per 100 Enterprises | unit | |
| Proportion of Enterprises with E-commerce Transaction Activities | % | ||
| E-commerce Sales Volume | 100 million yuan | ||
| Number of Computers Used per 100 People | unit | ||
| Digital Economy Environment | Application Environment | Mobile Internet Users | 10,000 households |
| Mobile Phone Users | 10,000 households | ||
| Digital Telephone Users | 10,000 households | ||
| Talent Environment | Proportion of Information-related Employees in Total Employment | % | |
| Number of Undergraduate Graduates | person | ||
| Innovation Environment | R&D Personnel (Full-time equivalent) | person-year | |
| Number of R&D Institutions | unit | ||
| Patents Granted | unit |
References
- Nordhaus, W. Can We Control Carbon Dioxide? (From 1975). Am. Econ. Rev. 2019, 109, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Xiong, X.; Gao, Y. Market-based environmental regulations and green innovation: Evidence from the pilot carbon markets in China. Res. Int. Bus. Financ. 2025, 77, 102896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, R.; Teo, T.S.H. Green technology innovation, environmental externality, and the cleaner upgrading of industrial structure in China—Considering the moderating effect of environmental regulation. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2022, 184, 122020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, Y. Environmental regulation and green transition: Quasi-natural experiment from China’s efforts in sulfur dioxide emissions control. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 434, 139741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Geng, S. Double-edged sword? Heterogeneous effects of digital technology on environmental regulation-driven green transformation. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 389, 125960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Cai, X.; Qian, Q.; Xia, H. How can market-based environmental regulation drive industrial transformation upgrading? Evidence from China’s carbon emissions trading pilot policies. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2025, 102, 104300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yan, X.; Zhang, C.; Yang, M. Research on the spatial spillover effects and mechanisms of environmental regulation on the upgrading of WEEE industrial structure. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 519, 146020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, P. The impact of heterogeneous environmental regulations on traffic carbon emission efficiency. Int. J. Sustain. Transp. 2025, 19, 660–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yu, T.; Lu, G. Does Environmental Regulation Influence Industrial Productivity in China—The Empirical Test Based on DEA and Co-integration Analysis. Econ. Theory Bus. Manag. 2010, 3, 11–17. [Google Scholar]
- Samuelson, P.A. Pure theory aspects of industrial organization and globalization. Jpn. World Econ. 2003, 15, 89–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, M.E.; van der Linde, C. Toward a New Conception of the Environment-Competitiveness Relationship. J. Econ. Perspect. 1995, 9, 97–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- André, F.J.; Ranocchia, C.; Rubio, S.J. Porter Hypothesis vs. Pollution Haven Hypothesis: Can an environmental policy generate a win–win solution? Energy Econ. 2025, 146, 108477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romer, P.M.; Griliches, Z. Implementing a National Technology Strategy with Self-Organizing Industry Investment Boards. Brookings Papers on Economic Activity. Microeconomics 1993, 2, 345–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Q. Research on the Impact of Digital Economy on the Greening of Manufacturing Industry Chain: Empirical Evidence from City Level Chinese. J. Manag. 2025, 38, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathuria, V. Informal regulation of pollution in a developing country: Evidence from India. Ecol. Econ. 2007, 63, 403–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pargal, S.; Wheeler, D. Informal Regulation of Industrial Pollution in Developing Countries: Evidence from Indonesia. J. Political Econ. 1996, 104, 1314–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanoie, P.; Patry, M.; Lajeunesse, R. Environmental regulation and productivity: Testing the porter hypothesis. J. Product. Anal. 2008, 30, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andoh, C.N.; Donkor, P.; Aboagye, J. Ghana’s environmental law and waterbody protection: A critical assessment of plastic pollution regulations. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 380, 125172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domazlicky, B.R.; Weber, W.L. Does Environmental Protection Lead to Slower Productivity Growth in the Chemical Industry? Environ. Resour. Econ. 2004, 3, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldar, B.; Banerjee, N. Impact of informal regulation of pollution on water quality in rivers in India. J. Environ. Manag. 2004, 73, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Hao, H. Environmental regulation and Outward FDI of Chinese listed companies: The role of technological innovations. Econ. Anal. Policy 2025, 87, 1797–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Zhao, X.; Qi, Y. Measurement, Spatial Pattern and regional Difference of Digital Economy Development in China. Ind. Technol. 2023, 42, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, C.; Zheng, R.; Yu, D. An Empirical Study on the Effects of Industrial Structure on Economic Growth and Fluctuations in China. Econ. Res. J. 2011, 46, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S.; Ketcham, J.D.; Kuminoff, N.V. Environmental Regulation, Residential Sorting, and Pollution Exposure among Senior Americans. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2025, 133, 103211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Kahn, M.E.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z. The consequences of spatially differentiated water pollution regulation in China. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2018, 88, 468–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chui, M.; Zheng, Y.; Peng, T.; Shi, D. Impact of environmental regulation intensity and digital economy on regional environmental penalties. Financ. Res. Lett. 2025, 79, 107276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, L. Environmental regulations and the greenwashing of corporate ESG reports. Economic. Anal. Policy 2025, 87, 1469–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, F.; Zhou, Z. National climate change policy, environmental regulation, and media attention: Implications for sustainable investment. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 521, 146235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S. Environmental regulation policy, firm endogenous capability, and green technological innovation: Evidence from a multi-period DID study in heavily polluting industries. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 391, 126436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musonda, J.; Ma, L.; Liu, T.Y.; Shahzad, M.; Ali, A. Megaprojects’ environmental impact mitigation by sustainable construction mediated by sustainable practices and regulations. Clean. Responsible Consum. 2025, 18, 100281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Bian, Z.; Tu, W.; He, J. How environmental regulation policies affect corporate ESG ratings: Latecomer advantage in China’s digital economy. Energy Econ. 2025, 144, 108336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ni, Z.; Yang, J.; Li, H.; Liu, Q. Green shrinkage: The heterogeneous regional effects of environmental regulation on green innovation. Regional. Sci. Policy Pract. 2025, 17, 100216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Qing, Y.; Tao, L.; Li, W.; Wen, C. Spatial spillover effects of environmental regulation on ecological industrialization: Evidence from the upper reaches of the Yangtze River. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2025, 98, 103862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Z.; Liu, C. Does environmental regulation boost corporate sustainability? From the perspective of environmental strategy. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 385, 125625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, V.N. The effect of carbon dioxide emissions, environmental innovation, and market regulation on renewable energy in France. Energy Convers. Manag. X 2025, 27, 101081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Asif, R.; Ilhan, O. Mechanisms of digitalization in reshaping the green transformation of energy firms in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 393, 127047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Zhou, Z.; Hu, X.; Chen, S.; Huang, J. How can urban economic complexity promote green economic growth in China? The perspective of green technology innovation and industrial structure upgrading. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 450, 141807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Qin, L.; He, Z. Corporate green transformation and bankruptcy risk: Empirical evidence from Chinese manufacturing firms. Pac.-Basin Financ. J. 2025, 93, 102889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Liu, Q. Transformation of innovation in heavily polluting enterprises under resource constraints: The role of green finance policy. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2025, 103, 104524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Gao, Y.; Deng, Y.; Zhao, H. Does agricultural green transformation enhance the quality of export products? A perspective of market-oriented environmental regulation. Financ. Res. Lett. 2025, 85 Pt E, 108227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, M.; Yu, Y.; Bu, Y. The impact of digital transformation of resource-based enterprises on green innovation: Mechanism analysis based on TOE framework. Innov. Green Dev. 2025, 4, 100262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bing, L.; Ting, Y. Environmental Regulation Intensity, Financial Mismatch, and Environmental Penalties for Listed Companies. Financ. Res. Lett. 2025, 108707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.; Zhou, Y. Environmental regulation intensity, models, and technological innovation. Financ. Res. Lett. 2025, 85, 108256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluczek, A.; Woźniak, A.; Żegleń, P. National diversity in European energy policy: Analyzing dependencies of changes in energy prices, climate regulations, and technological innovations on economic implications. Energy Strategy Rev. 2025, 62, 101886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beeri, I. The effect of human-wildlife interaction and political factors on support for local environmental morality policies: Thinning, trap–neuter–return and regulation against wild-animals’ feeders. City Environ. Interact. 2025, 27, 100198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Sun, T. Unravelling the impact pathways of green innovation and environmental regulation on China’s green development efficiency goals: Direct and spillover effects. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 168, 112713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Qiu, P. Relationship among environmental regulation costs, corporate accounting policies, and green innovation efficiency. Financ. Res. Lett. 2025, 77, 107056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, K.; Wang, X. Green investor entry and corporate green transformation: Evidence from Chinese resource-based industry. Resour. Policy 2025, 109, 105717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Duan, L. Can informal environmental regulation restrain air pollution? —Evidence from media environmental coverage. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 377, 124637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Liang, E.; Liu, C. “Size-dependent” environmental regulations and spatial labor allocation. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2025, 132, 103158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Lai, X.; Tang, X.; Li, Y. Does environmental regulation affect corporate environmental awareness? A quasi-natural experiment based on low-carbon city pilot policy. Econ. Anal. Policy 2024, 84, 1164–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Xu, Q. Environmental regulation penalties and corporate environmental information disclosure. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2025, 102, 104344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, H.; Du, J.; Farooq Islam, M. Unpacking organizational capabilities and green Innovation for sustainable Performance: The role of environmental regulations in manufacturing industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 507, 145453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, C.; Li, X.; Peng, B.; Li, X. Unlocking Urban Ecological Resilience: The Dual Role of Environmental Regulation and Green Technology Innovation. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2025, 128, 106466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Du, L. Top-down environmental quality regulation and boundary pollution control: Evidence in boundary towns of China. J. Bus. Res. 2025, 194, 115400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Dong, H.; Qi, L. How Directors with Green Backgrounds Drive Corporate Green Innovation: Evidence from China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
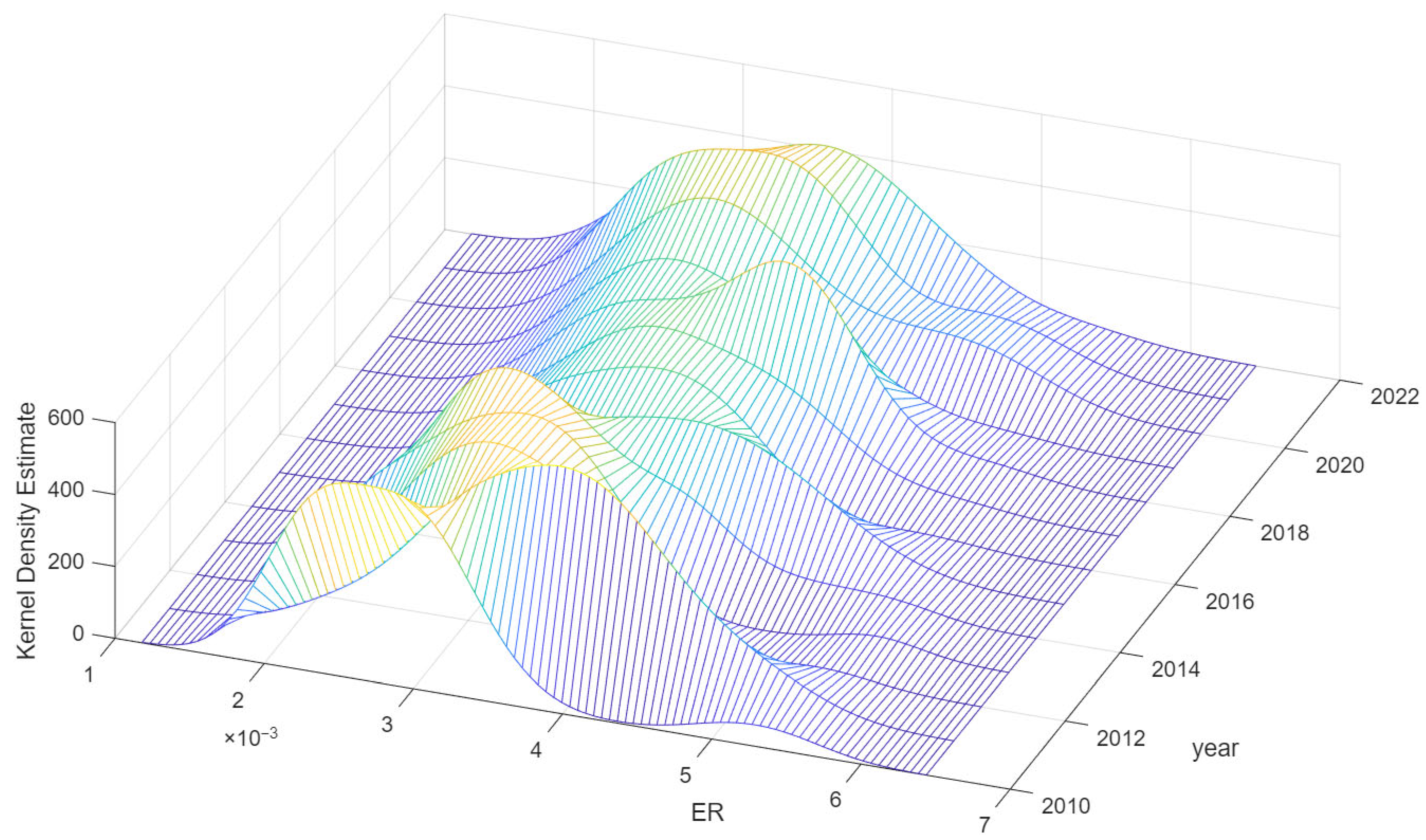
| Tier 1 Indicator | Tier 2 Indicator | Tier 3 Indicator | Polarity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Industrial Chain Greenization | Source Governance | Utilization rate of general industrial solid waste | Positive |
| Logarithm of industrial pollution control investment | Positive | ||
| Energy consumption intensity (per unit GDP) | Negative | ||
| End Governance | Wastewater emissions per unit of industrial added value | Negative | |
| Exhaust gas emissions per unit of industrial added value | Negative | ||
| Smoke and dust emissions per unit of industrial added value | Negative | ||
| Energy consumption per unit of industrial added value | Negative |
| Variable Type | Variable Name | Variable Definition | Measurement Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dependent Variable | ICG | Greenization level of manufacturing industrial chains | Composite index integrating source governance (e.g., solid waste utilization) and end governance (e.g., emission intensity) |
| Core Explanatory Variable | ER | Environmental regulation | Ratio of environmental policy-related term frequency to total word count in provincial government work reports (textual analysis) |
| Control Variable | PD | Population density | Logarithm of resident population per unit administrative area |
| Hum | Human capital level | Ratio of undergraduate/college enrollments to regional resident population | |
| Openness | Openness to globalization | Ratio of total import-export volume to regional GDP | |
| RDI | Research and development intensity | Ratio of internal R&D expenditures to regional GDP | |
| Inf | Informationization level | Ratio of postal service volume to regional GDP (proxy for digital infrastructure) |
| Variable | Obs | Mean | Std. dev | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICG | 390 | 0.651 | 0.167 | 0.192 | 0.959 |
| ER | 390 | 0.003 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.006 |
| lnPD | 390 | 5.463 | 1.285 | 2.053 | 8.282 |
| Hum | 390 | 0.021 | 0.014 | 0.006 | 0.277 |
| Openness | 390 | 0.276 | 0.291 | 0.008 | 1.464 |
| RDI | 390 | 0.018 | 0.011 | 0.003 | 0.068 |
| Inf | 390 | 0.06 | 0.052 | 0.015 | 0.29 |
| OLS | Two-Way Fixed Effects | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | |
| Variables | ICG | ICG | ICG | ICG | ICG | ICG | ICG |
| ER | 11.33 ** | 9.474 * | 10.32 ** | 9.759 ** | 9.303 ** | 8.834 * | 8.249 * |
| (5.353) | (4.850) | (4.864) | (4.800) | (4.717) | (4.749) | (4.696) | |
| lnPD | 0.0883 *** | 0.295 *** | 0.290 *** | 0.337 *** | 0.366 *** | 0.344 *** | |
| (0.00512) | (0.0940) | (0.0949) | (0.0916) | (0.102) | (0.103) | ||
| Hum | −0.516 | −0.638 *** | −0.549 *** | −0.535 *** | −0.451 *** | ||
| (0.414) | (0.124) | (0.130) | (0.126) | (0.119) | |||
| Openness | 0.0799 *** | 0.0951 ** | 0.0923 ** | 0.0792 * | |||
| (0.0280) | (0.0412) | (0.0404) | (0.0404) | ||||
| RDI | 0.716 | −1.327 | −1.233 | ||||
| (0.898) | (1.348) | (1.343) | |||||
| Inf | −0.226 ** | 0.422 ** | |||||
| (0.102) | (0.165) | ||||||
| Individual-FE | NO | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Time-FE | NO | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Constant | 0.123 *** | 0.621 *** | −0.995 * | −0.949 * | −1.234 ** | −1.369 ** | −1.271 ** |
| (0.0301) | (0.0153) | (0.518) | (0.523) | (0.506) | (0.549) | (0.554) | |
| Observation | 390 | 390 | 390 | 390 | 390 | 390 | 390 |
| R-squared | 0.649 | 0.914 | 0.917 | 0.919 | 0.921 | 0.921 | 0.923 |
| Winsorization | Model Replacement | Additional Control Variable | Proxy Variable Replacement | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VARIABLES | ICG | ICG | ICG | ICG |
| ER | 10.25 ** | 8.249 ** | 8.497 * | |
| (4.496) | (4.012) | (4.676) | ||
| ERnew | 2.794 * | |||
| (1.588) | ||||
| lnPD | 0.332 *** | 0.344 *** | 0.369 *** | 0.343 *** |
| (0.102) | (0.0862) | (0.115) | (0.102) | |
| Hum | −0.306 | −0.451 ** | −0.448 *** | −0.450 *** |
| (0.859) | (0.201) | (0.119) | (0.119) | |
| Openness | 0.0934 ** | 0.0792 ** | 0.0822 ** | 0.0798 ** |
| (0.0426) | (0.0340) | (0.0413) | (0.0405) | |
| RDI | −1.063 | −1.233 | −1.417 | −1.246 |
| (1.285) | (1.218) | (1.448) | (1.345) | |
| Inf | 0.460 ** | 0.422 *** | 0.414 ** | 0.422 ** |
| (0.182) | (0.141) | (0.166) | (0.165) | |
| var(e.ICG) | 0.00216 *** | |||
| (0.000155) | ||||
| FD | 0.00687 | |||
| (0.0126) | ||||
| Constant | −1.224 ** | −1.769 *** | −1.430 ** | −1.262 ** |
| (0.554) | (0.606) | (0.639) | (0.553) | |
| Observations | 390 | 390 | 390 | 390 |
| VARIABLES | ICG | ICG |
|---|---|---|
| L.ER | 13.42 *** | 12.14 ** |
| (4.944) | (4.691) | |
| lnPD | 0.314 *** | |
| (0.105) | ||
| Hum | −0.536 *** | |
| (0.129) | ||
| Openness | 0.0745 * | |
| (0.0449) | ||
| RDI | −0.352 | |
| (1.277) | ||
| Inf | 0.361 ** | |
| (0.158) | ||
| Constant | 0.611 *** | −1.123 * |
| (0.0157) | (0.571) | |
| Observations | 360 | 360 |
| R-squared | 0.920 | 0.927 |
| (1) | (2) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VARIABLES | ICG | ICG | ICG | ICG |
| ER | 27.93 *** | 18.73 ** | 4.775 | 0.449 |
| (9.957) | (7.690) | (5.562) | (5.463) | |
| lnPD | 0.564 *** | −0.193 | ||
| (0.117) | (0.152) | |||
| Hum | 2.302 * | −0.540 *** | ||
| (1.372) | (0.125) | |||
| Openness | 0.0819 | 0.0547 | ||
| (0.144) | (0.0462) | |||
| RDI | 2.931 | −2.016 | ||
| (2.390) | (1.663) | |||
| Inf | 0.250 | 0.446 ** | ||
| (0.428) | (0.178) | |||
| Constant | 0.511 *** | −2.364 *** | 0.669 *** | 1.799 ** |
| (0.0290) | (0.576) | (0.0185) | (0.862) | |
| Observations | 143 | 143 | 247 | 247 |
| R-squared | 0.908 | 0.930 | 0.913 | 0.924 |
| High-Share Regions | Low-Share Regions | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VARIABLES | ICG | ICG | ICG | ICG |
| ER | −2.511 | −5.412 | 14.07 ** | 13.28 ** |
| (6.518) | (6.334) | (6.988) | (6.149) | |
| lnPD | −0.177 | 0.472 *** | ||
| (0.166) | (0.115) | |||
| Hum | −3.829 ** | −0.413 *** | ||
| (1.762) | (0.132) | |||
| Openness | −0.0323 | 0.0765 * | ||
| (0.175) | (0.0443) | |||
| RDI | −2.947 | −0.786 | ||
| (2.413) | (1.666) | |||
| Inf | 0.362 * | 0.688 *** | ||
| (0.208) | (0.237) | |||
| Constant | 0.533 *** | 1.404 * | 0.671 *** | −2.198 *** |
| (0.0220) | (0.738) | (0.0215) | (0.672) | |
| Observations | 130 | 130 | 260 | 260 |
| R-squared | 0.924 | 0.931 | 0.869 | 0.890 |
| High Digital Economy | Low Digital Economy | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VARIABLES | ICG | ICG | ICG | ICG |
| ER | 2.099 | 0.910 | 13.20 ** | 10.75 * |
| (8.121) | (7.826) | (6.259) | (5.846) | |
| lnPD | −0.335 | 0.507 *** | ||
| (0.227) | (0.120) | |||
| Hum | −0.595 *** | −0.358 | ||
| (0.147) | (0.891) | |||
| Openness | 0.0136 | 5.29 × 10−5 | ||
| (0.0702) | (0.0676) | |||
| RDI | 2.491 | −1.566 | ||
| (3.139) | (1.540) | |||
| Inf | 0.876 * | 0.324 | ||
| (0.446) | (0.216) | |||
| Constant | 0.756 *** | 2.783 * | 0.535 *** | −1.921 *** |
| (0.0254) | (1.446) | (0.0199) | (0.579) | |
| Observations | 156 | 156 | 234 | 234 |
| R-squared | 0.854 | 0.873 | 0.898 | 0.912 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VARIABLES | TL | TL | GP | GP | ID | ID |
| ER | −10.29 * | −8.459 * | 44.14 ** | 38.63 ** | 8.582 *** | 8.334 *** |
| (5.413) | (5.074) | (18.90) | (18.44) | (2.069) | (1.924) | |
| lnPD | −0.292 ** | 2.711 *** | 0.225 *** | |||
| (0.125) | (0.434) | (0.0642) | ||||
| Hum | −0.263 ** | −0.176 | 0.143 *** | |||
| (0.106) | (0.341) | (0.0479) | ||||
| Openness | −0.220 *** | 0.509 *** | −0.0109 | |||
| (0.0388) | (0.135) | (0.0142) | ||||
| RDI | 0.659 | −15.17 *** | −2.571 *** | |||
| (1.242) | (5.555) | (0.656) | ||||
| Inf | −0.614 *** | 1.645 *** | −0.0279 | |||
| (0.178) | (0.570) | (0.0594) | ||||
| Constant | 0.209 *** | 1.891 *** | 7.291 *** | −7.468 *** | 0.311 *** | −0.870 ** |
| (0.0174) | (0.686) | (0.0606) | (2.367) | (0.00632) | (0.350) | |
| Individual FE | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Time FE | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Observations | 390 | 390 | 390 | 390 | 390 | 390 |
| R-squared | 0.820 | 0.844 | 0.981 | 0.984 | 0.926 | 0.934 |
| Year | I | E(I) | Sd(I) | Z | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 0.240 | −0.035 | 0.076 | 3.633 | 0.000 |
| 2011 | 0.213 | −0.035 | 0.076 | 3.249 | 0.001 |
| 2012 | 0.180 | −0.035 | 0.076 | 2.816 | 0.005 |
| 2013 | 0.178 | −0.035 | 0.076 | 2.786 | 0.005 |
| 2014 | 0.182 | −0.035 | 0.077 | 2.826 | 0.005 |
| 2015 | 0.235 | −0.035 | 0.076 | 3.532 | 0.000 |
| 2016 | 0.215 | −0.035 | 0.076 | 3.279 | 0.001 |
| 2017 | 0.292 | −0.035 | 0.076 | 4.281 | 0.000 |
| 2018 | 0.320 | −0.035 | 0.076 | 4.685 | 0.000 |
| 2019 | 0.278 | −0.035 | 0.075 | 4.144 | 0.000 |
| 2020 | 0.260 | −0.035 | 0.076 | 3.853 | 0.000 |
| 2021 | 0.277 | −0.035 | 0.076 | 4.064 | 0.000 |
| 2022 | 0.263 | −0.035 | 0.077 | 3.865 | 0.000 |
| Type | LM-Error | Robust LM-Error | LM-Lag | Robust LM-Lag | Wald Spatial Error | Wald Spatial Lag | LR: SDM vs. SAR | LR: SDM vs. SEM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Statistic | 22.375 | 31.113 | 19.907 | 28.644 | 30.38 | 30.63 | 29.17 | 29.49 |
| p-value | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0001 | 0.0000 |
| Main | Wx | |
|---|---|---|
| VARIABLES | ICG | ICG |
| ER | 7.641 * | 38.84 *** |
| (3.938) | (13.50) | |
| lnPD | 0.259 ** | 0.959 *** |
| (0.101) | (0.356) | |
| Hum | −0.406 ** | −0.413 |
| (0.201) | (0.335) | |
| Openness | 0.0518 | −0.171 ** |
| (0.0355) | (0.0665) | |
| RDI | −2.081 * | −7.757 * |
| (1.227) | (4.177) | |
| Inf | 0.563 *** | −1.003 ** |
| (0.162) | (0.422) | |
| Individual FE | YES | YES |
| Time FE | YES | YES |
| Observations | 390 | 390 |
| R-squared | 0.567 | 0.567 |
| LR_Direct | LR_Indirect | LR_Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| VARIABLES | ICG | ICG | ICG |
| ER | 7.192 * | 33.97 *** | 41.16 *** |
| (4.082) | (12.74) | (13.70) | |
| lnPD | 0.241 ** | 0.816 ** | 1.057 *** |
| (0.102) | (0.318) | (0.275) | |
| Hum | −0.380 ** | −0.291 | −0.671 * |
| (0.192) | (0.291) | (0.355) | |
| Openness | 0.0545 | −0.155 ** | −0.101 |
| (0.0347) | (0.0608) | (0.0622) | |
| RDI | −1.945 * | −6.577 * | −8.523 ** |
| (1.178) | (3.610) | (3.836) | |
| Inf | 0.591 *** | −0.960 ** | −0.369 |
| (0.163) | (0.395) | (0.337) | |
| Individual FE | YES | YES | YES |
| Time FE | YES | YES | YES |
| Observations | 390 | 390 | 390 |
| R-squared | 0.567 | 0.567 | 0.567 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, M.; Dong, Y.; Wu, X. The Impact of Environmental Regulation on Greenization Level of Manufacturing Industrial Chains: A Dual Perspective of Direct Effects and Spatial Spillovers. Sustainability 2025, 17, 9318. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17209318
Han M, Dong Y, Wu X. The Impact of Environmental Regulation on Greenization Level of Manufacturing Industrial Chains: A Dual Perspective of Direct Effects and Spatial Spillovers. Sustainability. 2025; 17(20):9318. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17209318
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Meilan, Yuezhou Dong, and Xiling Wu. 2025. "The Impact of Environmental Regulation on Greenization Level of Manufacturing Industrial Chains: A Dual Perspective of Direct Effects and Spatial Spillovers" Sustainability 17, no. 20: 9318. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17209318
APA StyleHan, M., Dong, Y., & Wu, X. (2025). The Impact of Environmental Regulation on Greenization Level of Manufacturing Industrial Chains: A Dual Perspective of Direct Effects and Spatial Spillovers. Sustainability, 17(20), 9318. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17209318






