From National Averages to Local Realities: A Subnational Vulnerability Index to Guide Sustainable Development in Low- and Middle-Income Countries
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Construction of the SGVI
2.2. Subnational Indicators
2.3. Addressing Missing Data
2.4. Standardization Around National Values
2.5. Constructing the SGVI
3. Results
3.1. Contribution of Indicators
3.2. SGVI Level and Changes
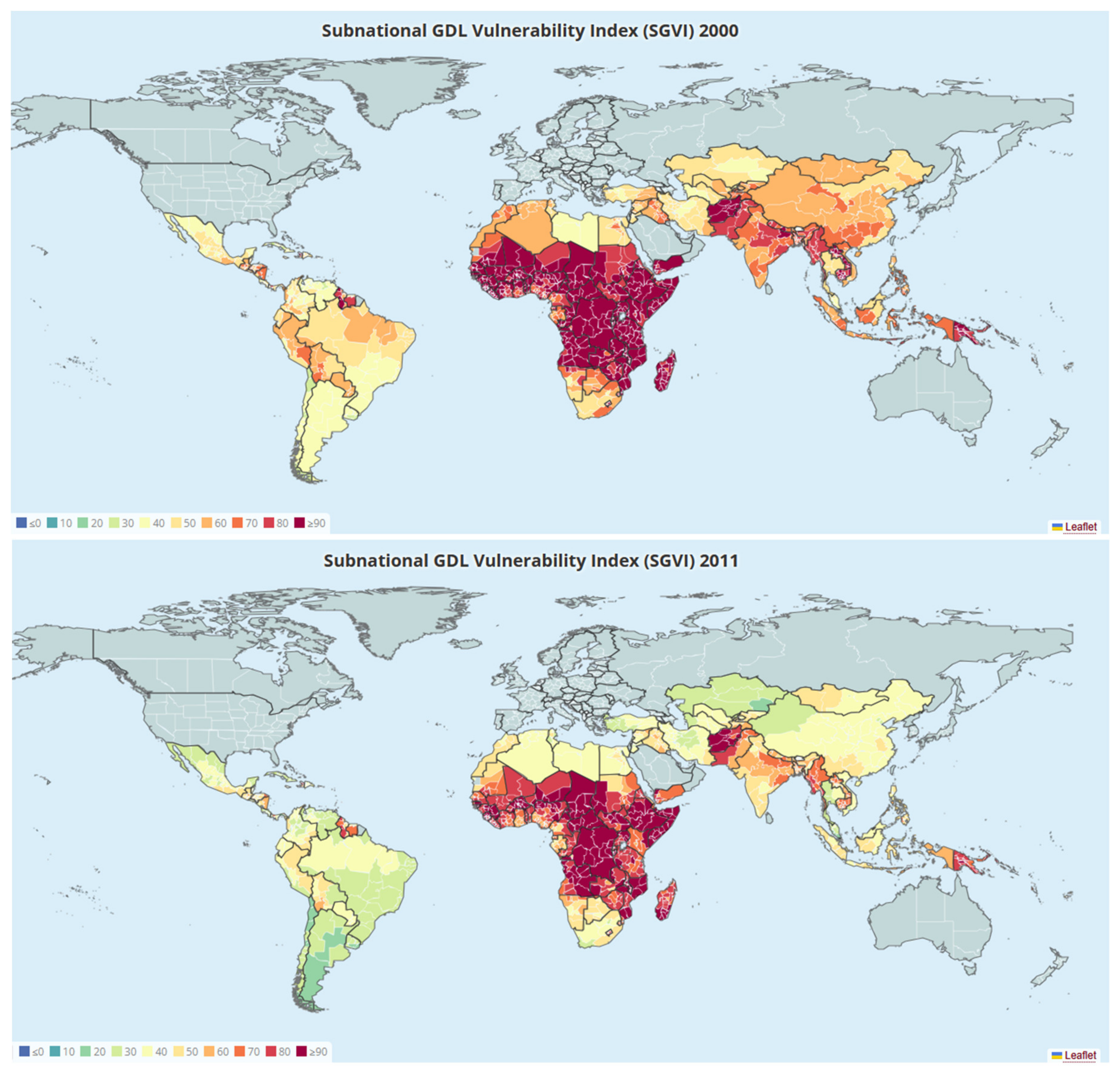
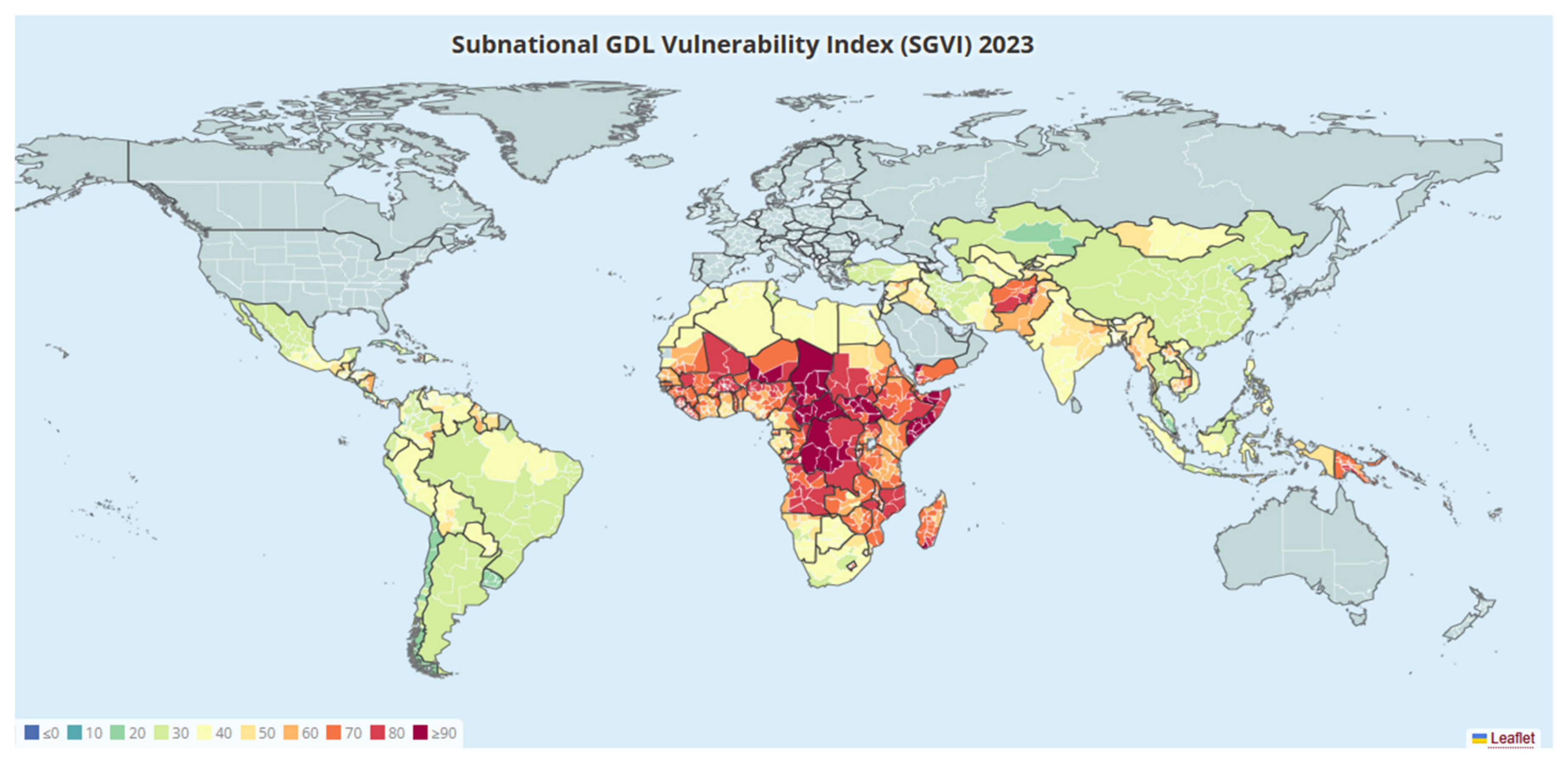
3.3. Decomposing Variation in GVI
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Birkmann, J.; Cardona, O.D.; Carreño, M.L.; Barbat, A.H.; Pelling, M.; Schneiderbauer, S.; Kienberger, S.; Keiler, M.; Alexander, D.; Zeil, P.; et al. Framing vulnerability, risk and societal responses: The MOVE framework. Nat. Hazards 2013, 67, 193–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, M.; Glavac, S.; Hastings, P.; Marshall, G.; McGregor, J.; McNeill, J.; Morley, P.; Reeve, I.; Stayner, R. Top-down assessment of disaster resilience: A conceptual framework using coping and adaptive capacities. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2016, 19, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC; Field, C.B.; Barros, V.R.; Dokken, D.J.; Mach, K.J.; Mastrandrea, M.D.; Bilir, T.E.; Chatterjee, M.; Ebi, K.L.; Estrada, Y.O.; et al. (Eds.) Summary for Policy Makers. In Climate Change 2014: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014; pp. 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC; Pörtner, H.-O.; Roberts, D.C.; Poloczanska, E.S.; Mintenbeck, K.; Tignor, M.; Alegría, A.; Craig, M.; Langsdorf, S.; Löschke, S.; et al. (Eds.) Summary for Policymakers. In Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability; Contribution of Working Group II to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2022; pp. 3–33. [Google Scholar]
- Simpson, N.P.; Mach, K.J.; Constable, A.; Hess, J.; Hogarth, R.; Howden, M.; Lawrence, J.; Lempert, R.J.; Muccione, V.; Mackey, B.; et al. A framework for complex climate change risk assessment. One Earth 2021, 4, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ara Begum, R.; Lempert, R.; Ali, E.; Benjaminsen, T.A.; Bernauer, T.; Cramer, W.; Cui, X.; Mach, K.; Nagy, G.; Stenseth, N.C.; et al. Point of Departure and Key Concepts. In Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability; Contribution of Working Group II to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Pörtner, H.-O., Roberts, D.C., Tignor, M., Poloczanska, E.S., Mintenbeck, K., Alegría, A., Craig, M., Langsdorf, S., Löschke, S., Möller, V., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2023; pp. 121–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, B.; Van Aalst, M.; Zaiton Ibrahim, Z.; Berrang-Ford, L.; Bhadwal, S.; Buhaug, H.; Diaz, D.; Frieler, K.; Garschagen, M.; Magnan, A.K.; et al. Key Risks Across Sectors and Regions. In Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability; Contribution of Working Group II to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Pörtner, H.-O., Roberts, D.C., Tignor, M., Poloczanska, E.S., Mintenbeck, K., Alegría, A., Craig, M., Langsdorf, S., Löschke, S., Möller, V., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2023; pp. 2411–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruane, A.C.; Vautard, R.; Ranasinghe, R.; Sillmann, J.; Coppola, E.; Arnell, N.; Cruz, F.A.; Dessai, S.; Iles, C.E.; Islam, A.K.; et al. The Climatic Impact-Driver Framework for Assessment of Risk-Relevant Climate Information. Earth’s Future 2022, 10, e2022EF002803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muttarak, R.; Lutz, W. Is education a key to reducing vulnerability to natural disasters and hence unavoidable climate change? Ecol. Soc. 2014, 19, 26269470. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/26269470 (accessed on 2 June 2025). [CrossRef]
- Kocur-Bera, K.; Czyza, S. Socio-Economic Vulnerability to Climate Change in Rural Areas in the Context of Green Energy Development—A Study of the Great Masurian Lakes Mesoregion. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallegatte, S.; Fay, M.; Barbier, E.B. Poverty and climate change: Introduction. Environ. Dev. Econ. 2018, 23, 217–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebi, K.; Vanos, J.; Baldwin, J.W.; Bell, J.E.; Hondula, D.M.; Errett, N.A.; Hayes, K.; Reid, C.E.; Saha, S.; Spector, J.; et al. Extreme weather and climate change: Population health and health system implications. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2021, 42, 293–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atwii, F.; Kristin Bergtora, S.; Lotte, K.; Beáta, P.; Katrin, R.; Sören, S.; Daniel, W. World Risk Report 2022; Bündnis Entwicklung Hilft: Berlin, Germany, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Cutter, S.; Boruff, B.; Lynn Shirley, W. Social vulnerability to environmental hazards. Soc. Sci. Q. 2003, 84, 42–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayanlade, A.; Smucker, T.; Nyasimi, M.; Sterly, H.; Weldemariam, L.F.; Simpson, N.P. Complex climate change risk and emerging directions for vulnerability research in Africa. Clim. Risk Manag. 2023, 40, 100497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkmann, J.; Jamshed, A.; McMillan, J.M.; Feldmeyer, D.; Totin, E.; Solecki, W.; Ibrahim, Z.Z.; Roberts, D.; Kerr, R.B.; Poertner, H.-O.; et al. Understanding human vulnerability to climate change: A global perspective on index validation for adaptation planning. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 803, 150065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNDP. HDR Technical Note. 2025. Available online: https://hdr.undp.org/sites/default/files/2025_HDR/HDR25_Technical_Notes.pdf (accessed on 2 June 2025).
- Miola, A. Climate Resilient Development: Theoretical Framework, Selection Criteria and Fit for Purpose Indicators; Institute for Environment and Sustainability, European Commission—Joint Research Centre: Ispra, Italy, 2015; p. JRC94771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin-Ferrer, M.; Vernaccini, L.; Poljansek, K. INFORM Index for Risk Management: Concept and Methodology; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Welle, T.; Birkmann, J. The world risk index—An approach to assess risk and vulnerability on a global scale. J. Extrem. Events 2015, 2, 1550003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Noble, I.; Hellmann, J.; Coffee, J.; Murillo, M.; Chawla, N. University of Notre Dame Global Adaptation Index: Country Index Technical Report; ND-GAIN: South Bend, IN, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Smits, J.; Huisman, J. The GDL Vulnerability Index (GVI). Soc. Indic. Res. 2024, 174, 721–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldmeyer, D.; Wilden, D.; Jamshed, A.; Birkmann, J. Regional climate resilience index: A novel multimethod comparative approach for indicator development, empirical validation and implementation. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 119, 106861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garschagen, M.; Doshi, D.; Reith, J.; Hagenlocher, M. Global patterns of disaster and climate risk-an analysis of the consistency of leading index-based assessments and their results. Clim. Change 2021, 169, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, W.; Saisana, M.; Paruolo, P.; Vandecasteele, I. Weights and importance in composite indicators: Closing the gap. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 80, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Füssel, H.-M. Vulnerability: A general applicable conceptual framework for climate change research. Glob. Environ. Change 2006, 17, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, M.; Harttgen, K.; Klasen, S.; Misselhorn, M. A Human Development Index by Income Groups. World Dev. 2008, 36, 2527–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, M.; Harttgen, K.; Klasen, S.; Misselhorn, M.; Munzi, T.; Smeeding, T. Inequality in Human Development: An Empirical Assessment of 32 Countries. Soc Indic Res 2010, 97, 191–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graetz, N.; Friedman, J.; Osgood-Zimmerman, A.; Burstein, R.; Biehl, M.H.; Shields, C.; Mosser, J.F.; Casey, D.C.; Deshpande, A.; Earl, L.; et al. Mapping local variation in educational attainment across Africa. Nature 2018, 555, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milanovic, B. Global Inequality: A New Approach for the Age of Globalization; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Harttgen, K.; Klasen, S. A Human Development Index at the Household Level, Discussion Papers, No. 75; Georg-August-Universität Göttingen, Courant Research Centre—Poverty, Equity and Growth (CRC-PEG): Göttingen, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Harttgen, K.; Klasen, S. Do Fragile Countries Experience Worse MDG Progress? J. Dev. Stud. 2012, 49, 134–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, Y.; Xian, J. The Correlations Among the World Development Indicators. IEEE-Xplore. 2018. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?arnumber=8632595 (accessed on 2 June 2025).
- Kraemer, G.; Reichstein, M.; Camps-Valls, G.; Smits, J.; Mahecha, M. The Low Dimensionality of Development. Soc. Indic. Res. 2020, 150, 999–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghislandi, S.; Sanderson, W.C.; Scherbov, S. A simple measure of human development: The human life indicator. Popul. Dev. Rev. 2019, 45, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisman, J.; Martyr, R.; Rott, R.; Smits, J. Projections of climate change vulnerability along the Shared Socioeconomic Pathways, 2020–2100. Nature Sci. Data 2025, 12, 1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WDI. The World Bank, World Development Indicators. 2024. Available online: https://databank.worldbank.org/source/world-development-indicators (accessed on 2 June 2025).
- United Nations. Human Development Index Database (HDID); United Nations Development Programme: New York, NY, USA, 2024; Available online: https://hdr.undp.org/data-center/human-development-index#/indicies/HDI (accessed on 2 June 2025).
- UNDP. Human Development Report 2025. In A Matter of Choice: People and Possibilities in the Age of AI; United Nations Development Programme: New York, NY, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Crombach, L.; Smits, J. The demographic window of opportunity and economic growth at sub-national level in 91 developing countries. Soc. Indic. Res. 2021, 161, 171–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WGI. The World Bank, Worldwide Governance Indicators. 2024. Available online: https://databank.worldbank.org/source/worldwide-governance-indicators (accessed on 2 June 2025).
- Vyas, S.; Kumaranayake, L. Constructing Socio-Economic Status Indices: How to Use Principal Components Analysis; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartholomew, D.J.; Steele, F.; Moustaki, I.; Galbraith, J.I. Principal Components Analysis. In The Analysis and Interpretation of Multivariate Data for Social Scientists; Boa Raton: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 115–142. [Google Scholar]
- Global Data Lab. Innovative Instruments for Turning Data into Knowledge. Available online: www.globaldatalab.org (accessed on 29 September 2025).
- Smits, J.; Permanyer, I. The Subnational Human Development Database. Sci. Data 2019, 6, 190038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smits, J.; Permanyer, I. The Subnational Gender Development Database: Uncovering variation in gender inequality within countries. Preprints 2025. [CrossRef]
- Smits, J. GDL Area Database: Sub-National Development Indicators for Research and Policy-Making; GDL Working Paper; Global Data Lab: Nijmegen, The Netherlands, 2016; Available online: https://globaldatalab.org/asset/523/SmitsGDLWorkingPaper16-101v4.4.1(1).pdf (accessed on 2 June 2025).
- Crombach, L.; Smits, J. The Subnational Corruption Database: Grand and petty corruption in 1473 regions of 178 countries, 1995–2022. Sci. Data 2024, 11, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croft, T.N.; Allen, C.K.; Zachary, B.W. Guide to DHS Statistics; ICF: Rockville, MD, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.; Hancioglu, A. Multiple Indicator Cluster Surveys: Delivering Robust Data on Children and Women across the Globe. Stud. Fam. Plan. 2019, 50, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggles, S.; Cleveland, L.; Lovaton, R.; Sarkar, S.; Sobek, M.; Burk, D.; Ehrlich, D.; Lee, J.; Merrill, N. Integrated Public Use Microdata Series, International: Version 7.6; IPUMS: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afrobarometer. Let the People Have a Say: 25 YEARS of Making African Voices Count. 2025. Available online: www.afrobarometer.org (accessed on 2 June 2025).
- LAPOP Lab. Americas Barometers; Center for Global Democracy: Nashville, TN, USA, 2025; Available online: www.vanderbilt.edu/lapop (accessed on 2 June 2025).
- Asian Barometer. Hu Fu Center for East Asia Democratic Studies. 2025. Available online: www.asianbarometer.org/ (accessed on 2 June 2025).
- Smits, J.; Steendijk, R. The International Wealth Index (IWI). Soc. Indic. Res. 2015, 122, 65–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, D.; Kraay, A.C. The Worldwide Governance Indicators: Methodology and 2024 Update (English); Policy Research Working Paper; World Bank Group: Washington, DC, USA, 2024; Available online: http://documents.worldbank.org/curated/en/099005210162424110.
- Gbohoui, W.; Lam, W.R.; Lledo, V.D. The Great Divide: Regional Inequality and Fiscal Policy; IMF Working Paper WP/19/88; IMF: Singapore, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kummu, M.; Taka, M.; Guillaume, J.H. A Gridded global datasets for Gross Domestic Product and Human Development Index over 1990–2015. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snijders, T.A.; Bosker, R.J. Multilevel Analysis: An Introduction to Basic and Advanced Multilevel Modeling, 2nd ed.; SAGE Publishers: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hox, J.J.; Moerbeek, M.; Schoot, R. Multilevel Analysis: Techniques and Applications; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins, S.P.; Van Kerm, P. The Measurement of Economic Inequality. In The Oxford Handbook of Economic Inequality; Nolan, B., Salverda, W., Smeeding, T., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Cowell, F.A. Measuring Inequality, 3rd ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
| Dimension | Indicator(s) | Indicator Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Economy | Gross Domestic Product per capita | Constant 2017 International $ (PPP) |
| Poverty headcount ratio at USD 3.65 a day | % of population below poverty line | |
| Education | Mean years of schooling 25+ population | Number of years |
| Gender | Gender Development Index | Number |
| Health | Life expectancy at birth | Years |
| Infrastructure | Access to clean water | % of population |
| Access to electricity | % of population | |
| Mobile cellular subscriptions per 100 people | Number | |
| Governance | Worldwide Governance Indicators | Standardized (about −3 to +3) |
| Demography | Urbanization | % of population |
| Dependency Ratio | % of population |
| Indicators | Weights |
|---|---|
| GDP per capita (GDPc) | 0.00009511 |
| Poverty headcount at USD 3.65 | −0.09402847 |
| Years of schooling | 0.71349195 |
| Gender Development Index | 25.64387153 |
| Life expectancy at birth | 0.32153768 |
| Access to clean water | 0.15911601 |
| Access to electricity | 0.09070003 |
| Phone subscriptions | 0.06927752 |
| World Governance Index | 2.36889662 |
| Dependency Ratio | −0.13611513 |
| Urbanization | 0.08743449 |
| Constant | −23.46384145 |
| ALL | SSA | LAC | MENAS | CSAP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 54.20 | 53.45 | 54.49 | 54.32 | 54.47 |
| GDPc | −1.00 | −1.49 | −0.91 | −0.85 | −0.78 |
| Poverty365 | 3.02 | 3.17 | 2.61 | 2.73 | 2.45 |
| Education | −2.31 | −2.83 | −2.03 | −2.04 | −1.81 |
| GDI | −1.45 | −1.12 | −2.16 | −2.00 | −2.13 |
| Life expectancy | −2.26 | −2.25 | −2.21 | −2.20 | −2.89 |
| Clean water | −2.83 | −2.85 | −2.88 | −2.90 | −2.87 |
| Electricity | −2.61 | −2.38 | −2.95 | −2.63 | −3.73 |
| Phones | −1.66 | −1.54 | −2.13 | −2.04 | −1.89 |
| Governance | −2.89 | −3.85 | −3.43 | −3.41 | −2.99 |
| Dependency ratio | 2.87 | 2.85 | 2.58 | 2.62 | 2.44 |
| Urbanization | −2.52 | −2.31 | −2.59 | −2.61 | −2.87 |
| All | LAC | SSA | MENAS | CSAP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean SGVI | |||||
| 2000 | 73.1 | 54.6 | 89.8 | 60.1 | 72.2 |
| 2011 | 61.9 | 43.2 | 80.0 | 48.0 | 59.7 |
| 2023 | 54.1 | 39.3 | 70.0 | 44.9 | 48.7 |
| Percentage change in mean SGVI a | |||||
| 2000–2011 | 15.3 | 20.8 | 10.8 | 20.1 | 17.4 |
| 2012–2023 | 12.7 | 9.0 | 12.5 | 6.4 | 18.4 |
| 2000–2023 | 26.0 | 28.0 | 22.0 | 25.2 | 32.6 |
| GINI | Increase in Observed Inequality When Including Subnational Level | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Region | 2000 | 2011 | 2023 | 2000 | 2011 | 2023 |
| All | 0.15 | 0.19 | 0.19 | 16.3 | 18.2 | 20.6 |
| SSA | 0.07 | 0.11 | 0.13 | 83.4 | 77.6 | 72.7 |
| LAC | 0.13 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 30.8 | 39.4 | 56.4 |
| MENAS | 0.10 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 31.9 | 30.0 | 24.0 |
| CSAP | 0.12 | 0.15 | 0.16 | 36.3 | 35.7 | 27.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Smits, J.; Huisman, J. From National Averages to Local Realities: A Subnational Vulnerability Index to Guide Sustainable Development in Low- and Middle-Income Countries. Sustainability 2025, 17, 9313. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17209313
Smits J, Huisman J. From National Averages to Local Realities: A Subnational Vulnerability Index to Guide Sustainable Development in Low- and Middle-Income Countries. Sustainability. 2025; 17(20):9313. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17209313
Chicago/Turabian StyleSmits, Jeroen, and Janine Huisman. 2025. "From National Averages to Local Realities: A Subnational Vulnerability Index to Guide Sustainable Development in Low- and Middle-Income Countries" Sustainability 17, no. 20: 9313. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17209313
APA StyleSmits, J., & Huisman, J. (2025). From National Averages to Local Realities: A Subnational Vulnerability Index to Guide Sustainable Development in Low- and Middle-Income Countries. Sustainability, 17(20), 9313. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17209313






