Abstract
The shipping industry remains heavily dependent on heavy fuel oils, which account for approximately 77% of fuel consumption and contribute significantly to greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. In line with the IMO’s decarbonization targets, ammonia has emerged as a promising carbon-free alternative. This study evaluates the strategic viability of ammonia, especially green production, as a marine fuel through a hybrid SWOT–Best–Worst Method (BWM) analysis, combining literature insights with expert judgment. Data were collected from 17 maritime professionals with an average of 15.7 years of experience, ensuring robust sectoral representation and methodological consistency. The results highlight that opportunities hold the greatest weight (0.352), particularly the criteria “mandatory carbon-free by 2050” (O3:0.106) and “ammonia–hydrogen climate solution” (O2:0.080). Weaknesses rank second (0.270), with “higher toxicity than other marine fuels” (W5:0.077) as the most critical concern. Strengths (0.242) underscore ammonia’s advantage as a “carbon-free and sulfur-free fuel” (S1:0.078), while threats (0.137) remain less influential, though “costly green ammonia” (T3:0.035) and “uncertainty of green ammonia” (T1:0.034) present notable risks. Overall, the analysis suggests that regulatory imperatives and environmental benefits outweigh safety, technical, and economic challenges. Ammonia demonstrates strong potential to serve as viable marine fuel in achieving the maritime sector’s long-term decarbonization goals.
1. Introduction
The maritime industry is increasingly confronted with the challenges of climate change and is accountable for a notable share of global air pollution [1]. The growth of international shipping contributed to greenhouse gas emissions exceeding 1 billion tons in 2018 [2]. To address this, the IMO has committed to reducing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from shipping by at least 50% by 2050, while also aiming to lower carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions per transport work by 40% by 2030 and 70% by 2050, compared to 2008 levels [3]. Achieving these goals will require phasing out fossil fuels and implementing operational and technical measures to reduce fuel consumption, alongside adopting energy carriers with low or near-zero greenhouse gas emissions [4].
Ammonia is increasingly being recognized as a promising hydrogen carrier and alternative marine fuel, owing to its carbon-free combustion properties, which align with the International Maritime Organization’s (IMO) environmental objectives [5]. Furthermore, ammonia is being investigated as a medium for hydrogen storage and transportation, as it permits liquid-phase storage under ambient conditions [6] and provides a higher volumetric hydrogen density compared to liquid hydrogen and other traditional liquid fuels (i.e., methanol, ethanol, gasoline) [7,8]. Compared to hydrogen, ammonia exhibits a moderately higher energy density, making it a more practical option for certain energy storage and transportation applications [9]. Ammonia can be utilized as a fuel in engines primarily through two approaches: by blending it with hydrogen or another highly reactive fuel to facilitate combustion [10].
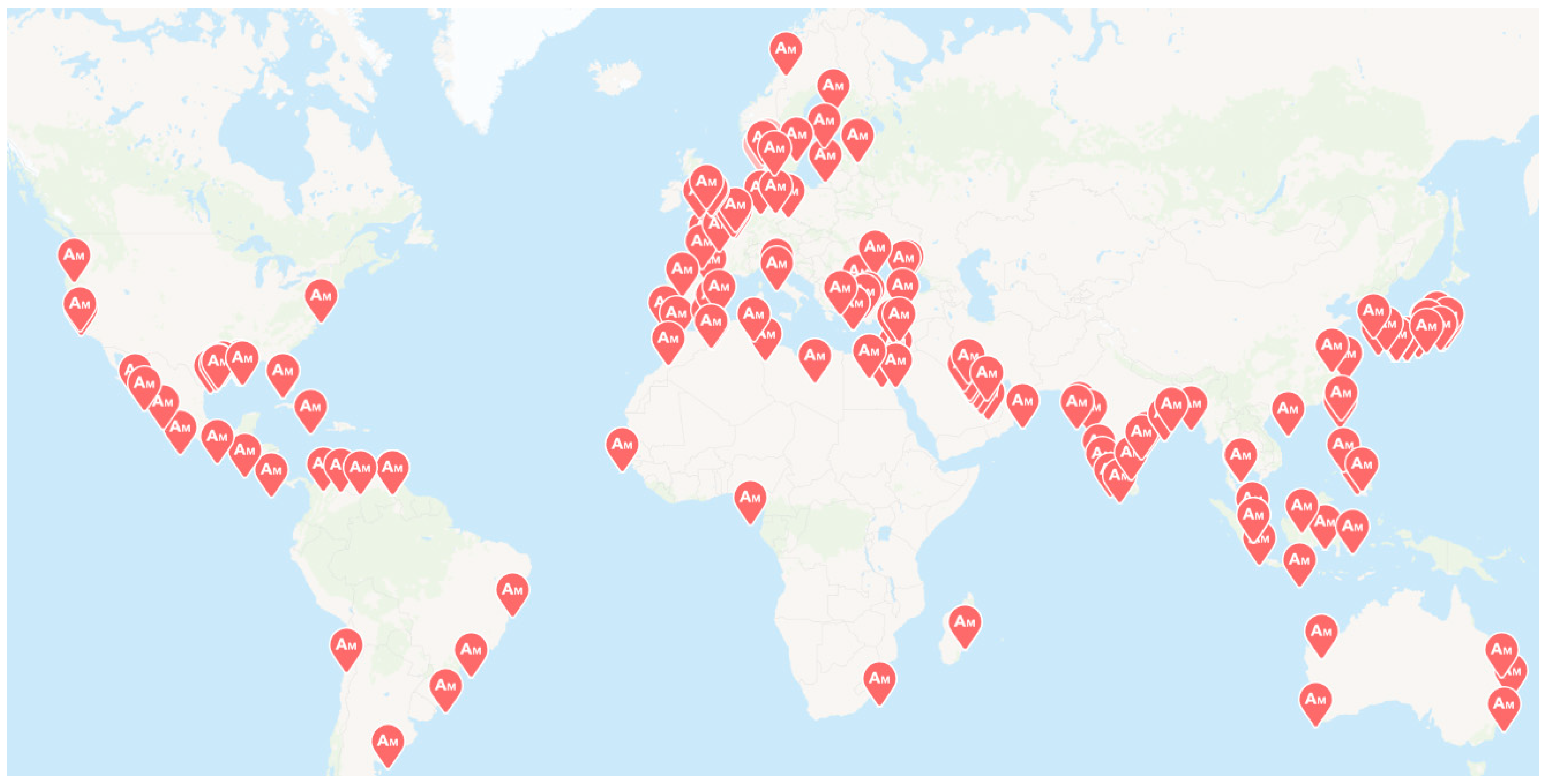
Ammonia has been produced and globally traded for over a century, supported by an established high-capacity infrastructure for liquefied ammonia, including pipelines, bunkering systems, and tank trucks [11]. According to global production statistics, ammonia (NH3) reached an output of approximately 235 million tonnes in 2019, ranking it as the second most-produced chemical commodity after sulfuric acid (H2SO4) [12]. Ammonia plays a vital role in the agricultural sector, primarily as a key raw material in the production of fertilizers. In addition, ammonia serves as a precursor in the synthesis of various industrial products, including polyimides, nitric acid, nylon, pharmaceuticals, explosives, refrigerants, dyes, cleaning agents, and other chemical compounds [13]. Bunkering infrastructure for ammonia worldwide is shown in Figure 1.
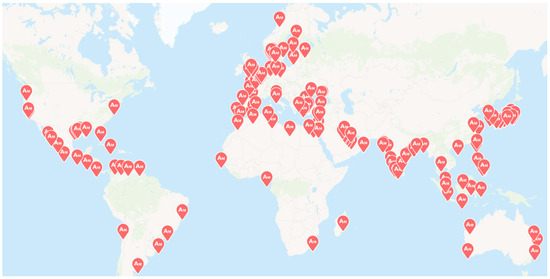
Figure 1.
Bunkering infrastructure for ammonia worldwide [14].
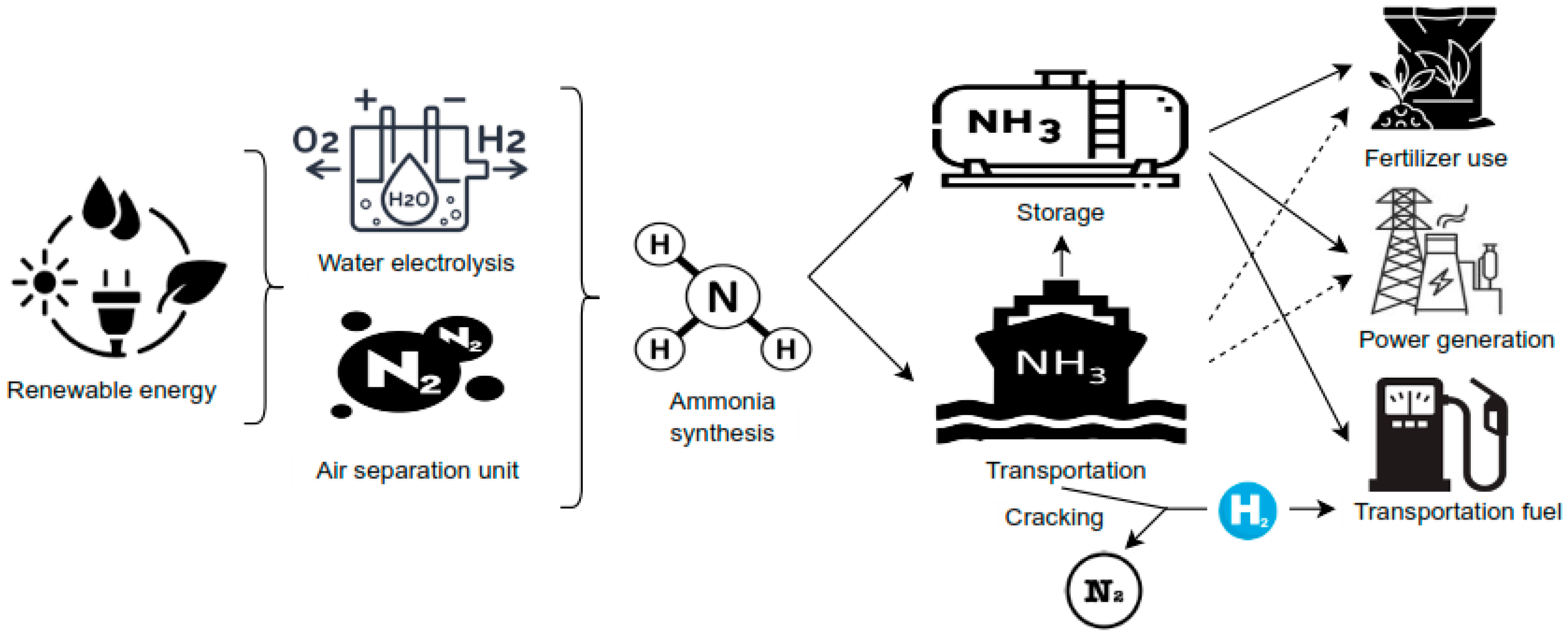
Ammonia production is a mature and extensively developed industrial process. Approximately 85% of global ammonia output is produced via the well-established Haber–Bosch process, which primarily relies on steam reforming of natural gas—an energy-intensive method that accounts for 3–5% of global natural gas consumption [15]. The Haber–Bosch process, despite its long-standing industrial use, contributes an estimated 1.4% to global CO2 emissions [16]. Moreover, this production process generates substantial quantities of nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions, requiring additional mitigation through selective non-catalytic reduction (SNCR) techniques [17]. Consequently, considering the increasing demand for carbon dioxide (CO2) mitigation, reducing the dependence on fossil fuels in ammonia production is essential for it to be considered a fully decarbonized energy carrier. Promising renewable and sustainable alternatives—such as biomass gasification, renewable electricity, and water electrolysis—can enable carbon-free ammonia synthesis pathways [18]. Figure 2 illustrates the pathway for carbon-free ammonia production along with its various end-use applications.
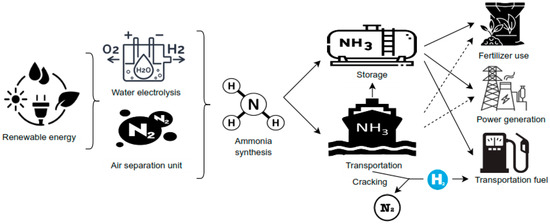
Figure 2.
Roadmap for carbon-free ammonia production and its diverse end-use applications [9].
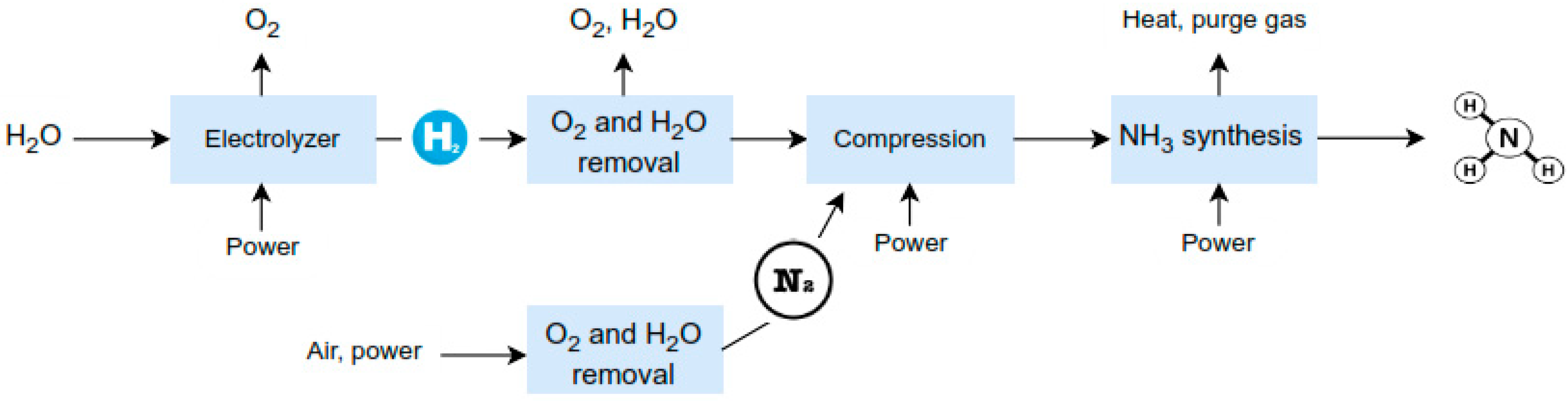
Ammonia production can be classified into three categories based on the feedstock and process employed: brown ammonia, produced entirely from fossil fuels and associated with the highest carbon emissions; blue ammonia, also derived from fossil fuels but with the integration of carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies to reduce emissions; and green ammonia, synthesized using renewable energy, water, and air, resulting in a carbon-free product. Green ammonia is typically produced via an ammonia synthesis loop coupled with electrolysis-based hydrogen generation, as illustrated in Figure 3. Alternatively, biomass-based hydrogen production methods, such as gasification, offer a viable pathway for ammonia synthesis, serving as a substitute for electrolysis-derived hydrogen [9].
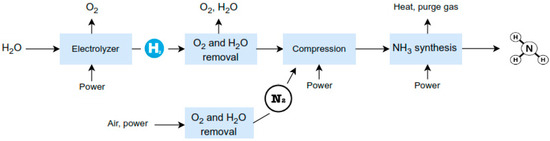
Figure 3.
Schematic illustration of green ammonia production utilizing hydrogen generated via water electrolysis [19].
The use of ammonia in internal combustion engines leads to the formation of nitrogen oxides (NOx) as a byproduct of combustion. To mitigate these emissions, selective catalytic reduction (SCR) systems that are like those installed on modern fossil-fueled vessels to comply with Tier III Emission Control Area (ECA) regulations can be employed. Notably, since SCR systems require either ammonia or urea as a reductant, vessels operating within ECAs are already equipped with the necessary infrastructure and protocols for the storage and handling of these substances [20].
Despite the growing academic and industrial attention to ammonia as a carbon-free marine fuel, the existing literature remains fragmented in terms of comprehensive strategic evaluation. Previous studies have predominantly focused on technical feasibility, combustion behavior, and emission profiles, while lacking a structured analysis that connects environmental, technical, and regulatory perspectives in a unified framework. This research addresses this gap by developing a hybrid SWOT–Best–Worst Method (BWM) approach to systematically assess the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of ammonia adoption in the maritime sector.
The main objective of this study is to identify the key determinants shaping the feasibility and strategic positioning of ammonia as a marine fuel and to prioritize them based on expert judgment. The novelty of this work lies in integrating a qualitative–quantitative decision-making framework, which not only enhances methodological robustness but also provides actionable insights for policymakers, shipowners, and technology developers engaged in the decarbonization of maritime transportation.
Although Balcı et al. [21] identified the structural relationships among success factors for green ammonia adoption using ISM–MICMAC (Interpretive Structural Modelling and Cross-Impact Matrix Multiplication Applied to Classification), their study primarily focused on mapping interdependencies. In contrast, the present study advances the discussion by integrating the SWOT and Best–Worst Method (BWM) to determine the relative significance and strategic priority of factors influencing ammonia’s adoption as a marine fuel. This approach allows for a quantitative assessment of both internal and external dimensions, offering actionable insights for policymakers and industry stakeholders regarding the pathways to accelerate ammonia uptake in the maritime sector.
The remainder of this paper is structured as follows: Section 2 provides a review of the relevant literature; Section 3 outlines the methodology and presents the mathematical formulations; Section 4 presents the results and offer a detailed discussion, respectively; and Section 5 concludes the study and proposes directions for future research.
2. Literature Review
A comprehensive review of the existing literature indicates a substantial body of research in this domain. Accordingly, the literature review is organized into two sections: the first examines studies focused on ammonia as an alternative marine fuel, while the second assesses these studies about the methodological framework adopted in the present study.
2.1. Studies on Ammonia as an Alternative Marine Fuel
Relevant studies on ammonia as an alternative marine fuel were identified through a systematic literature search employing various keyword combinations, including ‘ammonia’, ‘alternative marine fuel’, and ‘ammonia fueled’.
The relevant studies on ammonia as an alternative marine fuel are organized thematically and chronologically. Studies on the use of ammonia as an alternative marine fuel focus on technological feasibility and engine integration [1,7,8,9,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29], environmental & lifecycle assessments [17,23,30,31,32], fuel safety, risk, and toxicity [33,34,35,36], Policy, Economics & Adoption Barriers [37,38,39,40], market potential, future role & strategic perspective [41,42,43,44], and fuel blending and combustion optimization [45,46]. Table 1 presents a summary of studies on ammonia as an alternative marine fuel.

Table 1.
Summary of studies on ammonia as an alternative marine fuel.
The maritime sector’s commitment to achieving significant decarbonization goals has catalyzed a rapid, multi-faceted investment in the necessary technical infrastructure for ammonia adoption [47]. The primary focus of this industrial effort lies in the advancement of engine technology, where major original equipment manufacturers such as MAN Energy Solutions and WinGD are leading the development of dual-fuel, low-speed two-stroke engines [48,49]. These producers are currently subjecting prototype ammonia-fueled engines to extensive testing, with commercial readiness conservatively projected around the 2024–2025 timeframe.
However, the complete technical maturity of ammonia as a viable marine fuel extends beyond the main engine; it is critically dependent on the simultaneous development and certification of various auxiliary and safety systems. This crucial subsystem development includes specialized fuel supply systems, robust storage solutions, effective ventilation equipment, and Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) systems necessary for mitigating the release of toxic NOx and N2O emissions [50]. Consequently, the market deployment and safe operation of ammonia-powered vessels hinge not only on the progress of engine developers but also on the concurrent approval and establishment of standards by Classification Societies [51]. This integrated approach, encompassing both core technology advancement and regulatory compliance, signifies a high level of coordinated investment aimed at ensuring the technical feasibility of ammonia within the mid-2020s maritime landscape.
2.2. Methodological Studies
In the second part of the literature review, relevant studies employing SWOT and MCDM methodologies have been evaluated. Recent studies using decision-making and evaluation approaches have yielded important findings regarding the viability and strategic positioning of ammonia as an alternative marine fuel. Li & Liu [52] and Kumar et al. [53] identify ammonia as a cost-effective and strategically advantageous option despite safety concerns and use integrated LCA-MCDM-SWOT and TEE-SWOT approaches, respectively, to evaluate green hydrogen-based fuels.
Bayraktar et al. [54] state that economic viability rather than carbon neutrality of ammonia comes to the fore in stakeholder assessments, while Rodríguez et al. [55] recommend limiting the ammonia rate in fuel blends to 20% due to NOx and N2O emissions. Syed [56] offers a valuable contribution to the existing body of knowledge by conducting a PESTLE analysis in the context of the European Union, thereby underscoring the pivotal role of green ammonia in the decarbonization of the maritime sector. Finally, Hansson et al. [57] employ the MCDA method to show that stakeholders find ammonia as attractive as hydrogen and biofuels but noted significant barriers to its widespread adoption.
As evidenced by the literature, there is a limited number of multi-criteria decision-making (MCDM) studies focusing on the use of ammonia as an alternative marine fuel. A significant research gap exists in the holistic evaluation of ammonia (NH3) as a marine fuel, particularly in studies that extensively assess both its advantages and disadvantages. This study fills a significant research gap by presenting a novel and holistic framework for investigating ammonia as a potential alternative marine fuel.
The present study employs the SWOT-BWM hybrid methodology to differentiate it methodologically from previous studies, especially those using MCDM methods. Hence, our hybrid approach offers three distinct contributions. First, the SWOT framework is extensively utilized in the literature as a foundational analytical tool. Second, it enables a comprehensive evaluation of ammonia as an alternative marine fuel by systematically identifying and assessing its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Last, in contrast to traditional MCDM methods, the application of the Best–Worst Method (BWM) enhances the consistency and reliability of the results by making comparisons only between the best and worst important criteria. Given the complementary strengths of these two methodologies, the proposed SWOT-BWM approach is expected to yield more robust and dependable outcomes.
The objective of this study is fourfold: firstly, to ascertain the key criteria influencing the preference for ammonia as an alternative marine fuel; secondly, to evaluate the associated operational and managerial constraints; thirdly, to explore opportunities that may support its future viability; and finally, to assess potential threats that could impede its widespread adoption. A hybrid SWOT–BWM framework is employed to evaluate the multifaceted aspects of ammonia as a potential marine fuel.
The panel of 17 experts, with an average of 15.7 years of professional experience in the maritime sector, comprises individuals who possess distinct yet complementary perspectives. Some of them are deeply engaged in academia, contributing to research and policy development, while others represent professionals who are potential users of alternative marine fuels as their adoption becomes more widespread. Their strong interest in alternative fuels provides unique insights into both the practical decision-making and the theoretical understanding of fuel transition processes within the maritime industry.
This study contributes to the literature in three novel ways. First, unlike conventional SWOT analyses, the integration of BWM ensures consistency and robustness by assigning quantitative weights to qualitative expert evaluations. Second, by capturing expert insights across diverse maritime professions, the study provides a more comprehensive sectoral representation than previous works. Third, the combined SWOT–BWM approach enables the identification of priority areas where regulatory, technical, and economic interventions should be concentrated, thereby offering actionable insights for both policymakers and industry stakeholders.
3. Materials and Methods
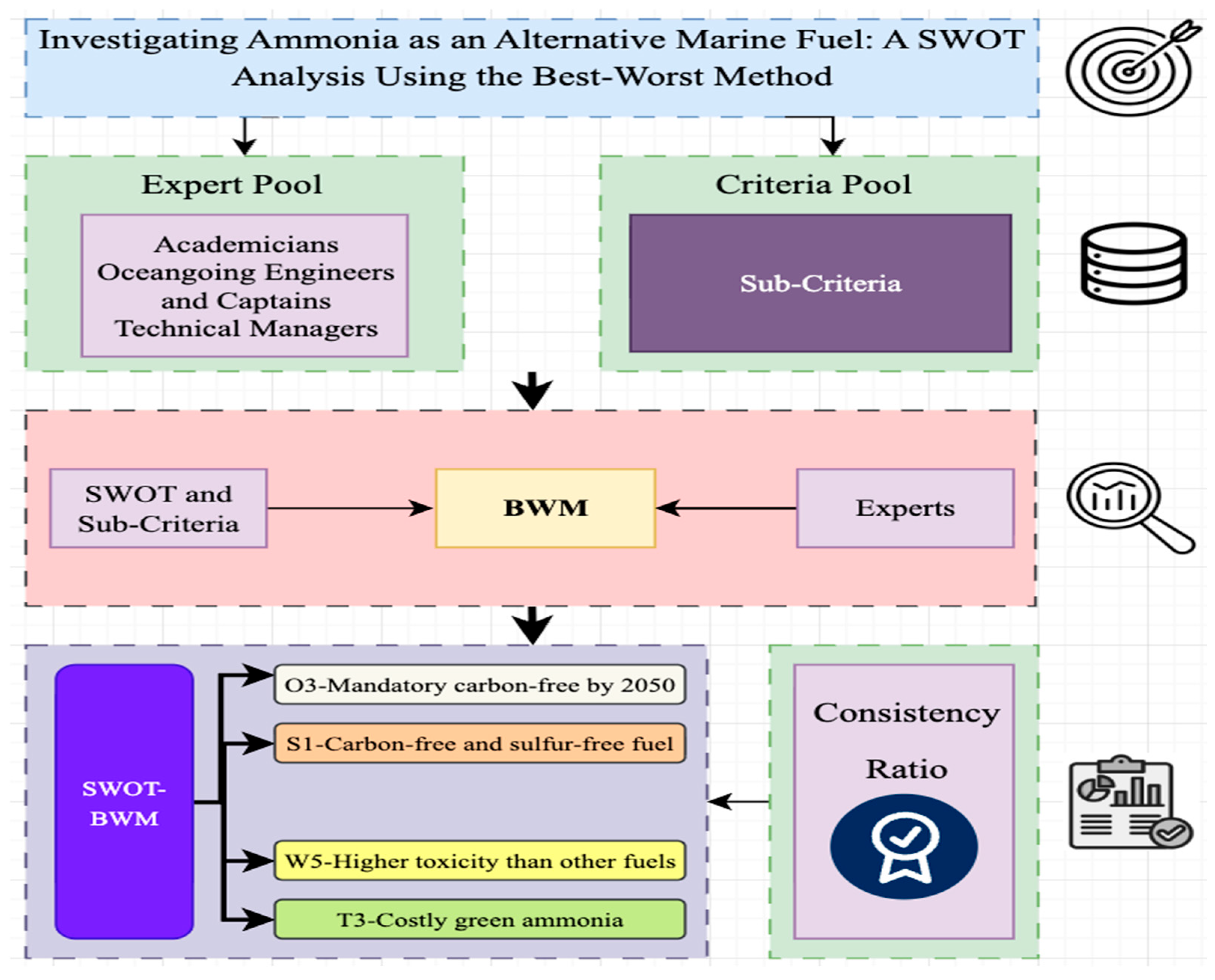
The subsequent section delineates the data collection process and methodology, with a particular emphasis on the SWOT-BWM hybrid technique. The identification of the main and sub-criteria was conducted through the implementation of a questionnaire and the application of the Best–Worst Method (BWM). The data for these criteria were meticulously collected from relevant academic literature and industry reports. The identified SWOT elements were then organized into a 5 × 5 SWOT matrix configuration. Subsequently, the BWM was employed to generate the study’s results. As illustrated in Figure 4, the research model employed in this study comprises several interconnected components.
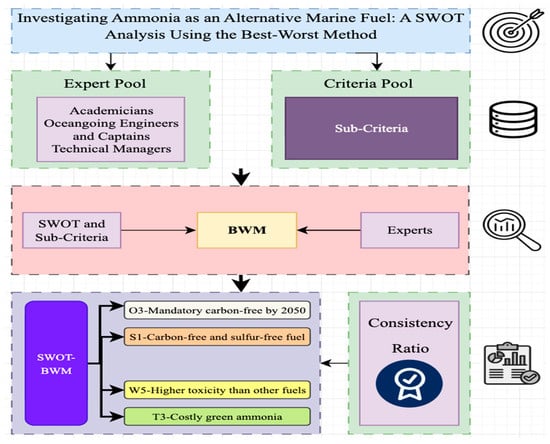
Figure 4.
Research model of the study.
3.1. Data Collection Process
In this study, data collection was conducted in two stages. In the first stage, a 5 × 5 SWOT matrix was developed using secondary data gathered from academic literature on ammonia as an alternative marine fuel, as well as industry reports, expert presentations, statistical publications, conference proceedings, technical documents, and grey literature. In the second stage, a survey was designed based on the constructed SWOT matrix and implemented using the Best–Worst Method (BWM). The survey was administered by maritime professionals, including masters, chief engineers, marine pilots, academicians, officers, surveyors, and engineers studying the maritime sector. The weights of the SWOT criteria and sub-criteria were determined based on the responses obtained from this survey.
Prioritization of SWOT criteria for the use of ammonia as an alternative marine fuel is a qualitative process and requires the contribution of competent experts in the field. In order to increase the reliability and depth of the analysis, it is crucial to carefully select participants who have expertise and can offer a variety of perspectives. In this study, three primary inclusion criteria were applied. First, participants were required to have a minimum of ten years of professional experience in the maritime sector. Second, they were expected to hold at least a bachelor’s degree in a relevant field. Third, to ensure diversity and comprehensive sectoral representation, experts were selected from various specialties within the industry. Accordingly, participants with substantial experience working either at ports or onboard ships were included in the study. The participants’ industry-related experience ranged from 9 to 25 years. Detailed information about the experts is presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
Expert profiles.
3.2. SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis is a strategic management tool used to evaluate the strengths (S), weaknesses (W), opportunities (O), and threats (T) associated with a particular subject or decision-making context [58,59]. The technique involves analyzing both internal and external factors to identify the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats relevant to a given context or decision [60]. A SWOT analysis is an important strategic analysis tool. This tool offers a systematic structure for decision-making processes [61].
A SWOT analysis is a valuable strategic planning tool because it gives a comprehensive overview of the internal and external factors that affect decisions or projects. It helps decision-makers systematically identify and evaluate an organization’s or system’s strengths and weaknesses while also assessing opportunities and threats in the external environment. This dual perspective supports informed decision-making and strategic alignment, enhancing long-term planning by highlighting areas of competitive advantage and vulnerability. SWOT analysis is also widely appreciated for its simplicity, flexibility, and adaptability across various fields. Its accessibility and integrative structure make it one of the most used tools in strategic analysis, particularly in complex or uncertain environments [62].
Strengths refer to internal attributes and resources that offer a competitive advantage in achieving the intended objectives. Weaknesses are internal limitations or deficiencies that may impede progress and undermine performance. Opportunities represent external conditions or trends that can be leveraged to enhance outcomes or support strategic goals. Conversely, threats are external elements that pose potential risks or challenges to the successful execution of a given strategy or initiative. When the objective is to formulate alternative strategies based on the outcomes of a SWOT analysis, the TOWS matrix serves as a highly effective tool. Table 3 presents the TOWS matrix as introduced by Ghazinoory et al. [63].

Table 3.
TOWS matrix.
This framework facilitates the formulation of effective strategies by systematically evaluating the factors identified through the SWOT analysis. SO (Strength–Opportunity) strategies aim to leverage internal strengths to capitalize on external opportunities. WO (Weakness–Opportunity) strategies seek to overcome internal weaknesses by utilizing external opportunities. ST (Strength–Threat) strategies use internal strengths to minimize or avoid exposure to external threats. Finally, WT (Weakness–Threat) strategies focus on developing defensive actions to mitigate the impact of both internal weaknesses and external threats [64].
3.3. BWM
The Best–Worst Method (BWM), initially proposed by Rezaei [65], was utilized to systematically prioritize criteria and evaluate external factors within a structured decision-making framework. Its growing popularity across various domains stems from its efficiency and ability to derive consistent weightings with fewer pairwise comparisons [66,67]. The BWM has gained widespread recognition across diverse disciplines, establishing itself as a robust and preferred approach for prioritizing decisions and comparing evaluation criteria [68,69]. The method has proven particularly useful in maritime-related applications, such as ship recycling, autonomous vessels, supply chains, simulation training, port performance assessment, and sustainable shipping [70,71,72,73,74,75].
The BWM process unfolds in five key steps [65,76]:
Step 1. The decision-maker (DM) first defines the evaluation criteria relevant to the multi-criteria decision-making (MCDM) context.
Step 2. Among the selected criteria, the DM identifies the most important (best) criterion and the least important (worst) criterion .
Step 3. The DM then provides preference ratings of the best criterion over all others using a fixed scale (typically 1 to 9). These ratings constitute the best-to-others vector:
Step 4. Similarly, the DM provides ratings of all criteria in comparison to the worst criterion, forming the others-to-worst vector:
Step 5. To compute the optimal weights = (, ……,), a min–max optimization problem is formulated. This problem seeks to minimize the maximum deviation between the derived weight ratios and the provided preference values, under the condition that the weights are non-negative and sum to one. The optimization model is:
Subject to:
This can also be reformulated by introducing a variable , which represents the maximum absolute deviation:
Finally, the consistency of the comparisons is assessed through a consistency ratio (), calculated as:
where is the optimal value obtained from the optimization model, and is a predefined consistency index. A value closer to 0 denotes higher consistency in the expert’s pairwise comparisons [66].
4. Results and Discussion
In this section, the identification of SWOT sub-criteria and the findings of the SWOT-BWM analysis are discussed under two separate subheadings.
4.1. The Identification of the SWOT Sub-Criteria
The SWOT sub-criteria employed in this study have been obtained from the literature reviewed below. Regarding the strengths of ammonia as an alternative marine fuel, Al-Aboosi et al. [30], Kim et al. [8], McKinlay et al. [43], Zincir [77], Hansson et al. [4], Machaj et al. [42], and Issa-Zadeh and Garay-Rondero [78] highlighted the significant potential of ammonia as a carbon-free and sulfur-free fuel for use in energy systems. Ash & Scarbrough [20], Lövdahl & Magnusson [24], Dimitriou & Javaid [7], Hansson et al. [4], Erdemir & Dincer [79], Morlanés et al. [44], and Machaj et al. [42] suggest that ammonia can be used as a hydrogen carrier; in this approach, hydrogen is obtained from ammonia at the point of use, such as in a fuel cell. DNV GL [80], Kim et al. [8], Valera-Medina et al. [17], and Machaj et al. [42] indicated that ammonia (NH3) offers a more cost-effective storage solution compared to hydrogen.
Aboosi et al. [30], Kim et al. [8], and Morlanés et al. [44] note that ammonia has been widely produced globally for many years and that production, storage, transportation, and supply infrastructure are relatively well established in many ports. Avery [81], Aziz et al. [82], Wijayanta et al. [83], Erdemir & Dincer [79], and Chatterjee et al. [84] emphasize that ammonia provides significant advantages over hydrogen as a vehicle fuel, especially in terms of cost and practicality, thanks to its higher energy density and ease of storage and distribution.
Regarding weaknesses, Lövdahl & Magnusson [24], Zincir [77], Kim et al. [8], and Hansson et al. [4] highlight that ammonia is usually stored in insulated pressure tanks, which require more onboard space compared to other marine fuels. Issa-Zadeh and Garay-Rondero [78] also noted that because alternative fuels have lower energy density than traditional fuels, they would require more space on the ship to travel the same distance, which would limit cargo space. Another weakness in using ammonia as an alternative marine fuel is the engineering difficulties associated with its use. Several engineering challenges must be addressed to ensure the successful use of ammonia as a marine fuel.
The challenges associated with ammonia as a fuel pertain to its non-flammability in air, its requirement for an ignition fuel such as hydrogen or diesel to initiate combustion [4,44], and its vulnerability to unstable combustion under both low and high engine load conditions [8,44]. A further significant weakness is evidenced by the absence of a comprehensive regulatory framework encompassing the utilization of ammonia as a marine fuel [24,80]. Another weakness of ammonia as an alternative marine fuel is that both optimal combustion strategies and aftertreatment systems must be used to control the high NOx emissions [7,43,44,77].
Ammonia is a toxic substance that poses significant health risks when released into the atmosphere at high concentrations and can be lethal depending on the exposure level and duration. It may also contribute to the formation of secondary particulate matter. Additionally, ammonia is hazardous to aquatic organisms, with potential long-term ecological impacts, particularly in cases of direct exposure [4,43,77]. Concurrently, Issa-Zadeh and Garay-Rondero [78] asserted that ammonia is a toxic and corrosive substance, which complicates its handling and storage.
In terms of opportunities, the ongoing work of engine manufacturers such as MAN B&W and Wärtsilä to develop ammonia-powered engines significantly supports the emergence of ammonia as an alternative marine fuel [77,85,86]. Ammonia has the potential to contribute to industrial decarbonization and the clean energy transition as a potentially viable alternative fuel option in the maritime sector, thereby facilitating the achievement of net-zero climate targets [87,88]. It is vital to acknowledge the critical role that carbon-neutral fuels play in achieving the IMO’s 2050 emissions reduction target [78]. In this context, the use of ammonia as an alternative marine fuel is considered a strategic opportunity [89,90].
The rail, road, and pipeline infrastructure found in many countries provides an additional opportunity for the adoption of ammonia as an alternative marine fuel [44]. At the same time, developments in dual-fuel engine technology have emerged as a significant opportunity to promote the use of ammonia as a potential marine fuel [86].
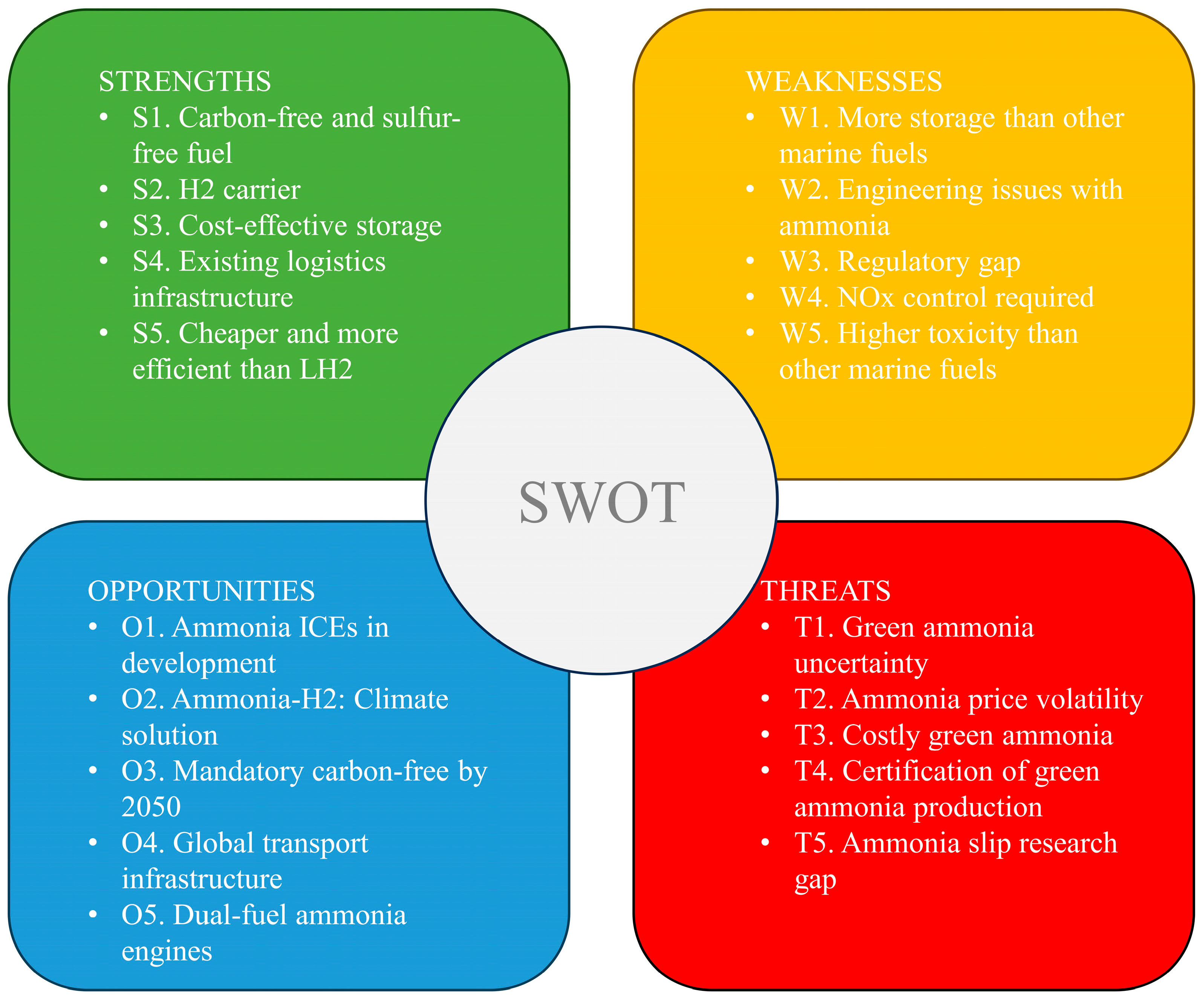
Considering the threats, one of the biggest threats to the adoption of ammonia as an alternative marine fuel appears to be the need to significantly expand green ammonia production at economically viable costs [91,92]. Potential fluctuations in ammonia fuel prices that may arise from future supply–demand imbalances pose another significant threat [85,93]. Issa-Zadeh and Garay-Rondero [78] also noted that ammonia production costs due to the energy-intensive Haber–Bosch manufacturing process increase the price of ammonia. Another significant threat to ammonia uses in the maritime sector is the need to overcome cost and energy efficiency challenges to fully utilize the potential of green ammonia [94,95,96]. Another threat to the use of ammonia as an alternative marine fuel is the concern about ammonia slip and the limited research on its environmental impacts [97]. SWOT sub-criteria have been created in line with the data obtained from the relevant literature and are given in Figure 5.
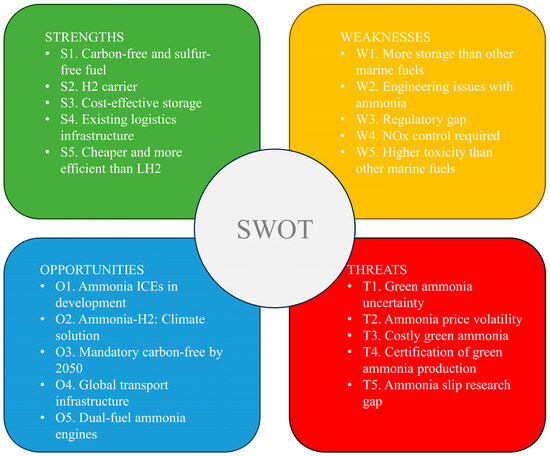
Figure 5.
SWOT sub-criteria for ammonia as an alternative marine fuel.
4.2. The Findings of the SWOT-BWM Analysis
A survey was conducted, which collected the opinions of seventeen experts with an average of 15.7 years of experience in several professions within the maritime field, to identify the best and worst SWOT sub-criteria. The results of the consistency analysis presented in Table 4 indicate that the evaluations of each expert for the main criteria were below 0.132. Accordingly, the proposed methodology is deemed appropriate for evaluating ammonia as an alternative marine fuel. The absence of inconsistency in the experts’ evaluations demonstrates that they possess the requisite knowledge and expertise in their respective domains, thereby allowing their assessments to be regarded as both comprehensive and reliable.

Table 4.
Consistency analysis results.
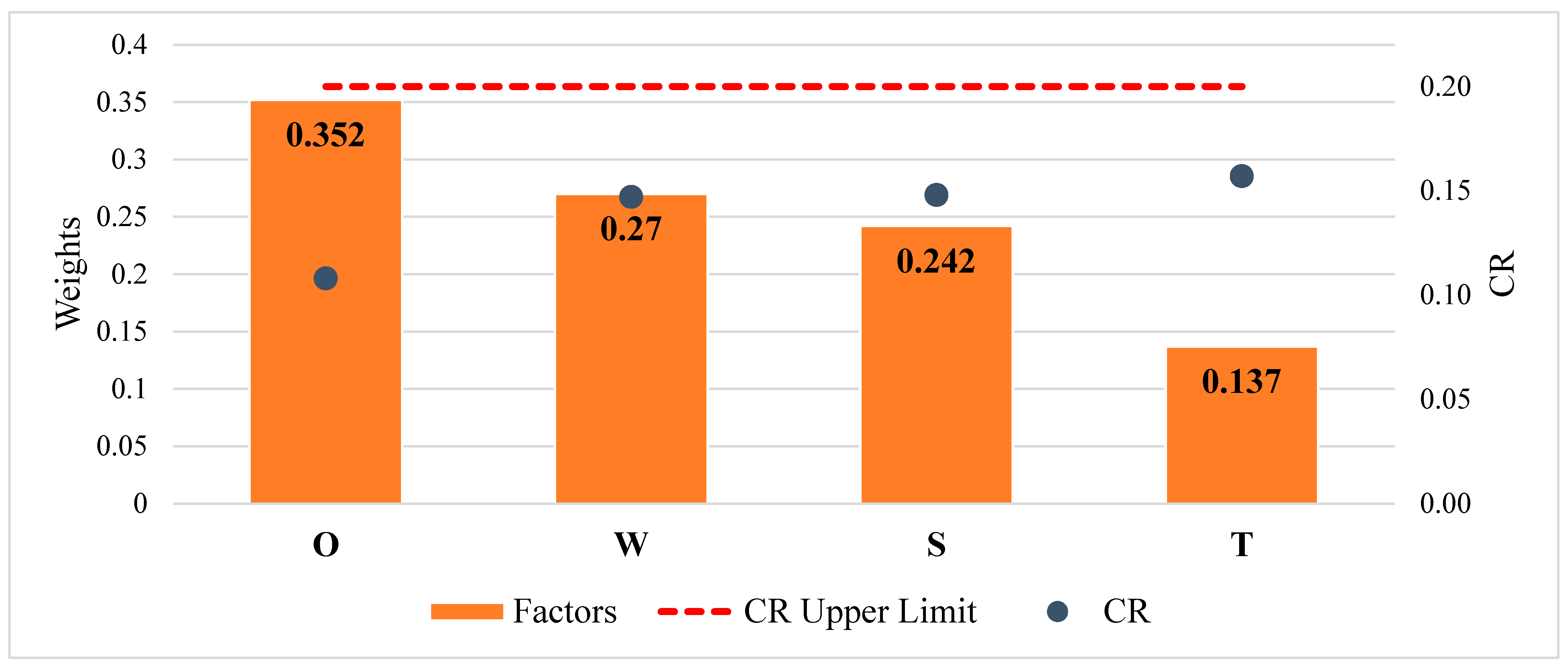
In Table 5, the results and scores for each criterion are presented. The second column reports the weights of the main criteria, while the following columns distinguish between global and local weights and their respective rankings. The consolidation of all criteria into a single framework for global weights enables a comprehensive comparison on an overall basis. In this framework, local weights assess sub-criteria in relation to their respective main criteria, thus highlighting their relative importance within that specified context. With respect to the four SWOT dimensions, as illustrated in Table 5, experts assigned the highest priority to the opportunity criterion (0.352), suggesting that the potential benefits of adopting the strategy outweigh other considerations. This was followed by weakness (0.270) and strength (0.242), indicating that experts highlighted internal limitations to a greater extent than existing advantages. The threat criterion was assigned to have the lowest priority (0.137), indicating that external risks were regarded as less significant in the overall assessment.

Table 5.
Findings of SWOT-BWM analysis.
As demonstrated in Figure 6, the CR values have been derived under the specified conditions to ensure the robustness of the analysis. The values associated with strengths, weaknesses, and threats were found to be relatively similar, whereas the value for opportunities was notably lower. This outcome suggests that the experts demonstrate greater consistency and precision in their assessments of opportunities compared to the other criteria, thereby reinforcing the reliability of the results.
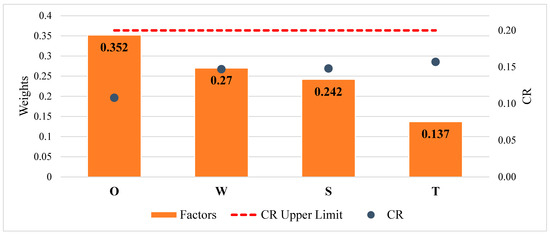
Figure 6.
Rankings, weights, and CR values of SWOT criteria.
The CR values were calculated within the acceptable threshold, thereby confirming the validity of the analysis. As shown in Figure 6, opportunities were assigned the greatest weight, while weaknesses and strengths displayed nearly identical average weights. Threats, in contrast, were weighted lower than the other criteria. This distribution suggests that experts perceive the prospects of ammonia as an alternative marine fuel to outweigh potential risks, while internal limitations and advantages are viewed as being of comparable importance. The superiority of opportunities over threats thus consolidates the strategic viability of ammonia adoption in the maritime sector.
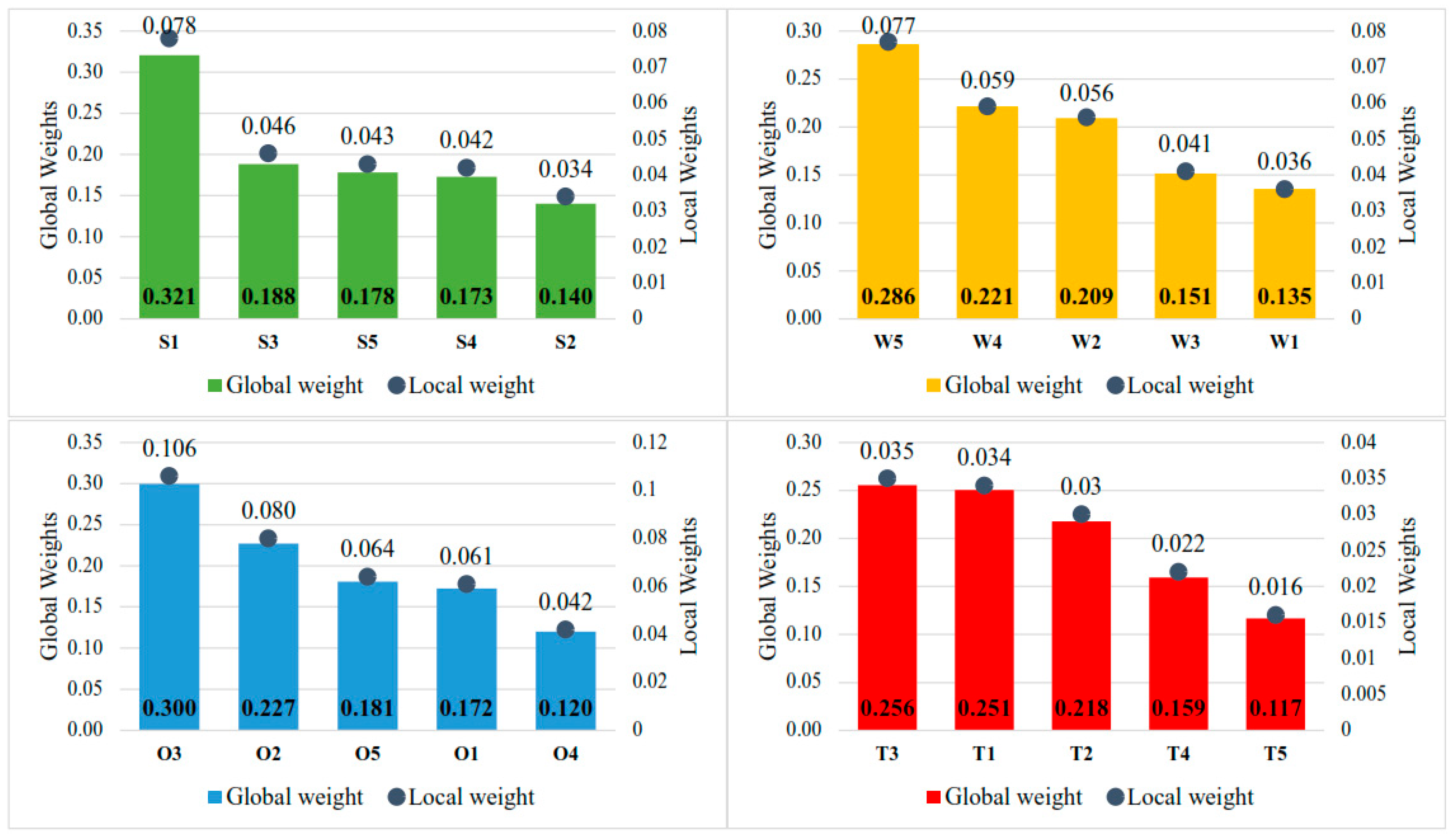
Figure 7 shows the local and global weights of the sub-criteria. Among the strength criteria, “Carbon-free and sulfur-free fuel” (S1) was identified as the most crucial characteristic, underlining the central role of environmental advantages in positioning ammonia as a feasible alternative marine fuel. Bicer and Dincer [23] state that the release of CO2 eq. from geothermal energy-sourced hydrogen and ammonia-fueled transoceanic tankers is approximately 0.98 g and 1.65 g per tonne-kilometer, respectively. By comparison, the release of CO2 eq. from a current conventional heavy fuel oil tanker is approximately 5.33 g/tonne-kilometer. The sub-criteria “Cost-effective storage” (S3), “Cheaper and more efficient than LH2” (S5), and “Existing logistics infrastructure” (S4) carried about equal weights, indicating that economic and logistical considerations are also determining factors in supporting ammonia’s competitiveness. As reported by IEA [98], there are 126 ammonia terminals in 550 ammonia plants located in ports that are equipped to receive and ship this product. Conversely, “H2 carrier” (S2) received the lowest weight, indicating that this feature contributes relatively little to the overall evaluation of ammonia’s strengths in maritime shipping.
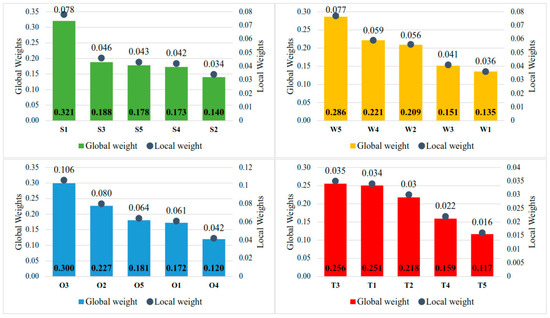
Figure 7.
Global and local weights of each sub-criterion.
Regarding the weakness criteria, “Higher toxicity than other marine fuels” (W5) emerged as the most immediate concern, indicating that health and safety risks are perceived as the basic obstacle to the extensive adoption of ammonia. The sub-criteria “NOx control required” (W4) and “Engineering issues with ammonia” (W2) were weighted nearly equally, demonstrating the technical obstacles that must be overcome to provide both operational efficiency and compliance with emission standards. Meanwhile, “Regulatory gap” (W3) and “More storage than other marine fuels” (W1) received lower but comparable weights, suggesting that although institutional frameworks and volumetric necessities pose challenges, they are currently considered less critical than safety and technical hurdles. These findings imply that improving regulatory standards, coupled with technological solutions to mitigate toxicity and NOx emissions, will be determinant in enabling ammonia’s successful integration into maritime fuels.
Within the opportunity criteria, “Mandatory carbon-free by 2050” (O3) took the highest weight, thus emphasizing the principal role of regulatory mandates in driving the transition towards ammonia-fueled shipping. Furthermore, a comparison of our priority-based findings with the structural analysis by Balci et al. [21], which utilized an Interpretive Structural Model (ISM) to map the adoption roadmap, reveals significant sectoral consensus. Both studies strongly agree that regulatory pressure is the foundational and most influential driver. This underscores the notion that adherence to international decarbonization targets is poised to function as the major catalyst for adoption.
The second-ranked criterion “Ammonia-H2: Climate solution” (O2) represents the potential of ammonia to contribute not only to maritime decarbonization but also to global climate mitigation strategies. The sub-criteria “Dual-fuel ammonia engines” (O5) and “Ammonia ICEs in development” (O1), which were assigned almost equal weights, propose that technological innovation will further expedite adoption as engine solutions develop and become commercially feasible. In a pilot study undertaken within the GSP [99], the viability of an Equinor-chartered ammonia-fueled Aframax tanker was investigated. The anticipated increase in capital expenditure (CAPEX) for a DF ammonia newbuild was estimated to be 19%, equivalent to that for DF LNG. On the contrary, the lowest assigned weight was to “Global transport infrastructure” (O4), remarking that while infrastructure preparedness is advantageous, it is not currently viewed as a decisive factor compared with regulatory and technological drivers.
Within the threat criteria, “Costly green ammonia” (T3) and “Green ammonia uncertainty” (T1) received the highest weights, underscoring the pivotal role of economic and supply-side challenges in constraining ammonia’s near-term competitiveness. However, in the context of long-term competitiveness, DNV GL [50] has forecasted future cost estimates for the production and distribution of green/blue ammonia to range between 1000 USD/tMGOe and 1900 USD/tMGOe in 2050. This is a considerable amount below current green ammonia prices, indicating that forthcoming GHG pricing mechanisms could potentially achieve price parity with MGO. “Ammonia price volatility” (T2) ranked next, reflecting concerns over market stability and long-term cost predictability. The criterion “Certification of green ammonia production” (T4) followed, highlighting the importance of establishing reliable standards to ensure transparency and market confidence. Lastly, “Ammonia slip research gap” (T5) was assigned the lowest weight, suggesting that while it represents a technical and environmental concern, it is currently perceived as less urgent compared to economic and regulatory uncertainties. These results suggest that addressing cost barriers, securing supply stability, and advancing certification frameworks will be critical to mitigating threats and enabling the large-scale adoption of ammonia as a marine fuel.
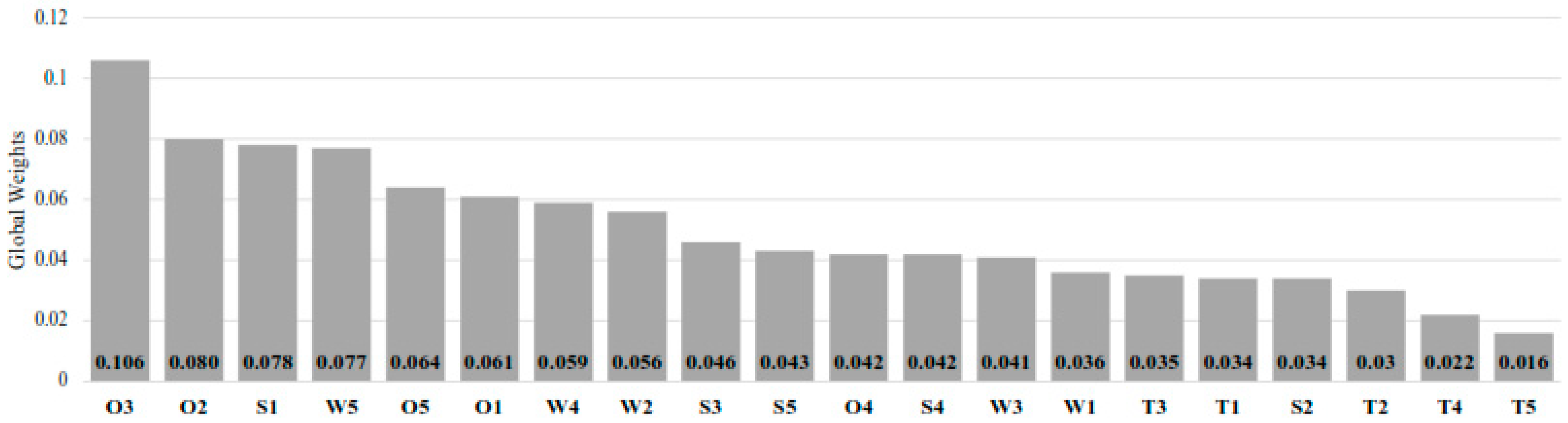
Figure 8 shows global rankings and weights of each sub-criterion. Among all sub-criteria, “Mandatory carbon-free by 2050” (O3) received the highest weight, followed by “Ammonia-H2: Climate solution” (O2), “Carbon-free and sulfur-free fuel” (S1), and “Higher toxicity than other marine fuels” (W5). It is noteworthy that four of the six most heavily weighted sub-criteria have emerged as opportunities, while five of the six least heavily weighted sub-criteria are specified as threats. This case demonstrates the significant potential of ammonia as an alternative marine fuel, with its opportunities outweighing the threats. Regulatory pressure, environmental benefits, and their role in climate strategies appear to be more significant than concerns such as cost or technical barriers. In order to transform this commitment into widespread practical implementation, concerted efforts must be made to confront safety concerns and reduce manufacturing expenses.
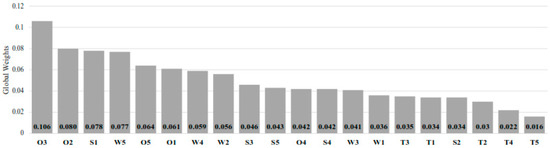
Figure 8.
Global rankings and weights of each sub-criterion.
The SWOT-BWM analysis indicates that the driving forces of ammonia are primarily regulatory imperatives and environmental benefits, as well as its potential role in global climate strategies. Conversely, the most notable issues are related to toxicity, technical difficulties, and high production costs. Notably, opportunities dominated the highest-weight sub-criteria, whereas threats were concentrated among the lowest, suggesting that the benefits of ammonia are perceived to outweigh its risks. For this potential to be achieved in practice, future efforts must focus on mitigating safety challenges, reducing costs, and strengthening certification and regulatory schemes. This will allow ammonia to evolve from a promising concept to a widely adopted marine fuel.
The finding that opportunities had the highest weight, while threats had the lowest, highlights the need to adopt ammonia to minimize GHG emissions in the maritime sector. More specifically, ‘Mandatory carbon-free by 2050’ (O3), Ammonia-H2: Climate Solution’ (O2), and ‘Carbon-free and sulfur-free fuel’ (S1) had the highest overall weights, emphasizing the crucial significance of choosing ammonia as an alternative marine fuel in line with the maritime sector’s decarbonization pathway. AEA [100] supports the study’s findings, emphasizing that alternative fuels such as ammonia are now necessary for ships to comply with regulations.
The sub-criteria ‘Dual-fuel ammonia engines’ (O5) and ‘Ammonia ICEs in development’ (O1) also had high weightings, which supports the importance of advances in ammonia-powered engines for the successful integration of ammonia as an alternative fuel within the maritime sector. Meanwhile, Wartsila, MAN Energy Solutions, and WinGD are carrying on with their research and development of internal combustion ammonia engines and dual-fuel ammonia engines [48,49,50,101]. On the other hand, our analysis revealed some of the weaknesses of ammonia as an alternative marine fuel.
The sub-criteria with the highest weighting for weakness were “Higher toxicity than other marine fuels” (W5), “NOx control required” (W4), and “Engineering issues with ammonia” (W2). Furthermore, advanced quantitative modeling supports the complexity of this transition. Wang and Iris [102], through a two-stage stochastic programming model, concluded that no single alternative fuel will dominate the future maritime fleet; rather, an optimal fleet deployment strategy necessitates a multi-fuel mix, positioning ammonia as a critical component within a broader energy basket alongside fuels like bio-LNG and bio-methanol. Similarly, Wang et al. [103], utilizing an exact algorithm for sustainable alliance operations under the Emissions Trading System (ETS), demonstrate that the ETS directly and significantly influences strategic decisions such as fleet co-deployment, sailing speed optimization, and slot allocation. This quantitative evidence reinforces the finding that the economic feasibility of any alternative fuel, including ammonia, is inseparable from the complexities and imposed costs of mandatory emission management schemes.
In their study, Chavando et al. [14] highlighted that these three sub-criteria present the greatest challenge to the adaptation of ammonia to the maritime industry. Although the threats are low-weighted, the “Costly green ammonia” (T3) and “Green ammonia uncertainty” (T1) sub-criteria are the highest-weighted threats. While our BWM analysis highlighted the cost of green ammonia (T3) as a significant threat, techno-economic supply chain studies [104] offer a forward-looking perspective, projecting that the cost gap between ammonia and competing hydrogen carriers will narrow considerably by 2040 due to predicted reductions in renewable electricity and conversion technology costs. This suggests that the cost threat, while currently critical, may diminish over the long term, particularly for direct-use applications like shipping.
Interestingly, these two sub-criteria also concern green ammonia. Consistent with the results of this study, Proton Ventures [105] stated that the cost of traditional fossil ammonia varies between 200–600 euros per ton, while the cost of green ammonia is up to 1000 euros per ton. Similarly, the Ohio River Valley Institute [106] observed that the outlook for ammonia production is highly uncertain, ranging from modest to explosive growth. They observed that substantial uncertainty exists on the supply side because the growth of ammonia production depends on the speed and scale at which ‘blue’ and ‘green’ ammonia production facilities can be constructed and brought into operation, which in turn depends on the speed and scale at which ‘blue’ and ‘green’ hydrogen production facilities can be constructed and brought into operation.
While our study provides a valuable contribution by highlighting the prominence of opportunities, particularly regulatory drivers and mandatory decarbonization targets, it is crucial to position these findings within the broader academic discourse, where some views differ. Contrary to our results, several studies argue that other factors hold greater weight for industry stakeholders. For instance, the work of Hansson et al. [57] emphasizes that economic considerations, specifically cost, are the most critical criteria in multi-criteria decision-making for marine fuels. Similarly, other research [107,108,109] suggests that the most significant barriers to the adoption of new fuels are infrastructure limitations and inherent safety risks, challenging the notion that opportunities alone are the primary drivers. However, these contrasting views are not entirely disconnected.
Our finding that “mandatory carbon-free by 2050” is a top-weighted opportunity is supported by Q. Wang et al. [28], which asserts that stringent regulatory frameworks, like those from the IMO, are the fundamental force compelling the industry to overcome technological and economic hurdles. This divergence in findings highlights that the future of ammonia is not determined by a single factor but rather by a complex interplay between regulatory pressures, economic feasibility, and practical operational realities.
5. Conclusions
This study involved carrying out a SWOT-BWM analysis to evaluate the use of ammonia as an alternative marine fuel. The SWOT criteria and sub-criteria were identified through a literature review. We identified the significance of each criterion by surveying seventeen maritime experts, each with an average of 15.7 years’ relevant industry experience. The study has two main limitations. Firstly, the experts evaluated only 20 sub-criteria across the four main SWOT criteria. Secondly, the analysis did not specify the academic qualifications of the experts.
The main findings of the study can be outlined as follows: It can be said that positive results have been achieved in adapting ammonia for use as an alternative marine fuel in the maritime sector. The fact that opportunity criteria were found to have the highest weight and that threat criteria were found to have the lowest weight in the analysis shows ammonia’s significant place in the maritime sector as a potential marine fuel.
Decarbonization and climate change, which will determine the future of the maritime industry, stand out as the most important opportunities for the adaptation of ammonia as an alternative marine fuel in the maritime industry. Conversely, the fact that the criteria for strengths and weaknesses carry almost the same weight indicates that there are challenges in adopting ammonia as an alternative marine fuel in the maritime sector, which need to be overcome. The three main weaknesses of ammonia are its toxicity, the difficulty of controlling NOx, and engineering issues. Although the threats to ammonia were the lowest in terms of weight, the uncertainty of green ammonia and the cost of green ammonia stood out as threats that need to be taken into consideration.
According to the weighted TOWS matrix, opportunity-oriented strategies (SO and WO) are prioritized. This suggests that ammonia’s carbon-free and sulfur-free fuel (S1) and its status as a mandatory carbon-free fuel by 2050 (O3) are the main drivers of sectoral transformation. Conversely, factors such as higher toxicity than other marine fuels (W5) and the costly green ammonia (T3) should be managed through technological research and development (R&D) and by strengthening regulatory standards. Therefore, decarbonization-focused innovation, safety certification, and infrastructure alignment are essential for ammonia to become a viable fuel for maritime transport.
Despite its valuable contributions, this study is not without its limitations, which offer avenues for future research. Our assessment of ammonia’s potential as a marine fuel relied primarily on a qualitative and quantitative evaluation using the SWOT-BWM. While this approach provided a structured analysis of its competitive position, it did not incorporate a comprehensive empirical dataset. At the same time, this study was based on green ammonia and WTW (Wheel-to-Wheel) emissions, with SWOT sub-criteria created accordingly.
A more robust understanding of ammonia’s environmental and economic impacts, as well as its operational safety, would require extensive real-world data from pilot projects. Moreover, the reliance on 17 experts, though intentionally selected for their complementary expertise in academia and practical maritime operations, represents a methodological limitation, and expanding the expert pool in future studies would enhance the generalizability and diversity of perspectives. Additionally, the scope of this research was focused solely on ammonia, precluding a direct and holistic comparison with other promising alternative fuels like methanol, hydrogen, and LNG. Future studies could expand this framework to conduct comparative analyses among alternative fuels, which would provide deeper insights into their relative advantages and market competitiveness. Addressing these limitations in subsequent research would provide a more complete and nuanced perspective on ammonia’s role in the decarbonization of the maritime sector.
To improve the academic rigor and depth of this research, for future studies, we propose three key areas for further investigation. First, while this study highlights the zero-carbon and sulfur properties of ammonia, a crucial next step is to perform a detailed performance and emissions analysis of ammonia-fueled marine engines. This research should focus on mitigating nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions and ammonia slip, using either experimental data or advanced numerical simulations. Second, given that the economic feasibility of producing green ammonia is a significant threat, a subsequent study could undertake a comprehensive techno-economic feasibility analysis of the green ammonia production and supply chain. This work would involve developing detailed cost models for production from renewable energy sources and evaluating the infrastructure investments required for a global bunkering network. Finally, to position this research more broadly within the alternative fuels debate, a future paper should conduct a more extensive multi-criteria comparative analysis.
Author Contributions
C.H.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Validation, Formal Analysis, Resources, Writing—Original Draft, Writing Review and Editing, Data Curation, Visualization. A.S.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Validation, Formal Analysis, Resources, Writing Review and Editing, Data Curation. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the editors and anonymous reviewers for their valuable feedback and hard work in helping us to improve our paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ejder, E.; Arslanoğlu, Y. Evaluation of ammonia fueled engine for a bulk carrier in marine decarbonization pathways. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 379, 134688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faber, J.; Hanayama, S.; Zhang, S.; Pereda, P.; Comer, B.; Hauerhof, E.; Yuan, H. Fourth IMO Greenhouse Gas Study. 2020. Available online: https://docs.imo.org/ (accessed on 18 August 2025).
- DNV GL. Ammonia Energy Conference 2020–Ammonia Infrastructure. 2020. Available online: https://www.ammoniaenergy.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/Anthony-Teo.pdf (accessed on 18 August 2025).
- Hansson, J.; Fridell, E.; Brynolf, S. On the Potential of Ammonia as Fuel for Shipping: A Synthesis of Knowledge. Lighthouse Reports. 2020. Available online: https://www.diva-portal.org/smash/get/diva2:1747278/FULLTEXT01.pdf (accessed on 19 August 2025).
- Yang, R.; Liu, J.; Liu, Z.; Liu, J. Applying separate treatment of fuel-and air-borne nitrogen to enhance understanding of in-cylinder nitrogen-based pollutants formation and evolution in ammonia-diesel dual fuel engines. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2024, 69, 103910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, P.A.; Ryu, B.; Kim, C.; Lee, J.; Kang, H. Energy and exergy analysis of an ammonia fuel cell integrated system for marine vessels. Energies 2022, 15, 3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriou, P.; Javaid, R. A review of ammonia as a compression ignition engine fuel. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 7098–7118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Roh, G.; Kim, W.; Chun, K. A Preliminary study on an alternative ship propulsion system fueled by ammonia: Environmental and economic assessments. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, J.S.; Silva, V.; Rocha, R.C.; Hall, M.J.; Costa, M.; Eusébio, D. Ammonia as an energy vector: Current and future prospects for low-carbon fuel applications in internal combustion engines. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 296, 126562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Liu, L. Theoretical investigation of the combustion performance of ammonia/hydrogen mixtures on a marine diesel engine. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 14805–14812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacFarlane, D.R.; Cherepanov, P.V.; Choi, J.; Suryanto, B.H.; Hodgetts, R.Y.; Bakker, J.M.; Vallana, F.M.F.; Simonov, A.N. A Roadmap to the Ammonia Economy. Joule 2020, 4, 1186–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soloveichik, G. Future of ammonia production: Improvement of Haber-Bosch process or electrochemical synthesis. In Proceedings of the 14th Annual NH3 Fuel Conference, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 1–2 November 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ghavam, S.; Vahdati, M.; Wilson, I.A.G.; Styring, P. Sustainable Ammonia Production Processes. Front. Energy Res. 2021, 9, 580808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavando, A.; Silva, V.; Cardoso, J.; Eusebio, D. Advancements and challenges of ammonia as a sustainable fuel for the maritime industry. Energies 2024, 17, 3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frigo, S.; Gentili, R. Analysis of the behaviour of a 4-stroke Si engine fuelled with ammonia and hydrogen. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 1607–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capdevila-Cortada, M. Electrifying the haber–bosch. Nat. Catal. 2019, 2, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valera-Medina, A.; Amer-Hatem, F.; Azad, A.K.; Dedoussi, I.C.; de Joannon, M.; Fernandes, R.X.; Glarborg, P.; Hashemi, H.; He, X.; Mashruk, S.; et al. Review on Ammonia as a Potential Fuel: From Synthesis to Economics. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 6964–7029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.; Hill, A.K.; Torrente-Murciano, L. Current and future role of Haber–Bosch ammonia in a carbon-free energy landscape. Energy Environ. Sci. 2020, 13, 331–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouwenhorst, K.H.R.; Van der Ham, A.G.J.; Mul, G.; Kersten, S.R.A. Islanded ammonia power systems: Technology review & conceptual process design. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 114, 109339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ash, N.; Scarbrough, T. Sailing on Solar: Could Green Ammonia Decarbonise International Shipping; Environmental Defense Fund: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Balci, G.; Phan, T.T.N.; Surucu-Balci, E.; Iris, Ç. A roadmap to alternative fuels for decarbonising shipping: The case of green ammonia. Res. Transp. Bus. Manag. 2024, 53, 101100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldi, F.; Azzi, A.; Maréchal, F. From renewable energy to ship fuel: Ammonia as an energy vector and mean for energy storage. In Computer Aided Chemical Engineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Volume 46, pp. 1747–1752. [Google Scholar]
- Bicer, Y.; Dincer, I. Environmental impact categories of hydrogen and ammonia driven transoceanic maritime vehicles: A comparative evaluation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 4583–4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lövdahl, J.; Magnusson, M. Evaluation of Ammonia as a Potential Marine Fuel; Chalmers University of Technology: Gothenburg, Sweden, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Park, M.; Choi, W. Solid oxide fuel cell-internal combustion engine hybrid system for ships fueled by ammonia. Fuel 2025, 387, 134201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, B.R.; Duong, P.A.; Kang, H. Comparative analysis of the thermodynamic performances of solid oxide fuel cell–gas turbine integrated systems for marine vessels using ammonia and hydrogen as fuels. Int. J. Nav. Arch. Ocean Eng. 2023, 15, 100524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheriff, A.M.; Tall, A. Assessment of Ammonia Ignition as a Maritime Fuel, Using Engine Experiments and Chemical Kinetic Simulations. Master’s Thesis, World Maritime University, Malmö, Sweden, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Huang, J.; Zhang, P. The use of alternative fuels for maritime decarbonization: Special marine environmental risks and solutions from an international law perspective. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 9, 1082453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Lu, S. Inclusion of Maritime into the EU ETS: Implications from the Aviation EU ETS and Aviation Sector. J. Econ. Bus. Manag. 2024, 12, 262–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Aboosi, F.Y.; El-Halwagi, M.M.; Moore, M.; Nielsen, R.B. Renewable ammonia as an alternative fuel for the shipping industry. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2021, 31, 100670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.; Fernandes, R.J.; Turner, J.W.; Emberson, D.R. Life cycle assessment of ammonia and hydrogen as alternative fuels for marine internal combustion engines. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2025, 112, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, H.; Stuart, C.; Spence, S.; Chen, H. Alternative fuel options for low carbon maritime transportation: Pathways to 2050. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 297, 126651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franks, A.; Parkar, S.; Hansen, C.R. Use of quantitative risk assessment to enhance the safety of ships using ammonia as fuel. J. Saf. Sustain. 2024, 1, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Niu, J.; Wu, W.; Zhao, Z.; Du, M.; Chen, L.; Zheng, Q.; Cao, H. Quantitative analysis of toxicity risks in the operation of ammonia-fueled tugboats. Ocean Eng. 2024, 310, 118759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.; Mujeeb-Ahmed, M.; Wang, H.; Park, C.; Hwang, I.; Jeong, B.; Zhou, P.; Papadakis, A.; Giannakis, A.; Sykaras, K. Safety evaluation on ammonia-fueled ship: Gas dispersion analysis through vent mast. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 83, 1060–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zincir, B.; Deniz, C. Assessment of alternative fuels from the aspect of shipboard safety. J. ETA Marit. Sci. 2018, 6, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fullonton, A.; Lea-Langton, A.R.; Madugu, F.; Larkin, A. Green ammonia adoption in shipping: Opportunities and challenges across the fuel supply chain. Mar. Policy 2025, 171, 106444. [Google Scholar]
- Kommers, M. The Potential of Ammonia as an Alternative Fuel in the Marine Industry. Master’s Thesis, Delft University of Technology, Delft, The Netherlands, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Prause, G.; Olaniyi, E.O.; Gerstlberger, W. Ammonia Production as Alternative Energy for the Baltic Sea Region. Energies 2023, 16, 1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreuder, W.; Slootweg, J.C.; van der Zwaan, B. Techno-economic assessment of low-carbon ammonia as fuel for the maritime sector. Appl. Energy Combust. Sci. 2025, 22, 100330. [Google Scholar]
- Duong, P.A.; Kang, H. Ammonia as fuel for marine dual-fuel technology: A comprehensive review. Fuel Process. Technol. 2025, 272, 108205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machaj, K.; Kupecki, J.; Malecha, Z.; Morawski, A.; Skrzypkiewicz, M.; Stanclik, M.; Chorowski, M. Ammonia as a potential marine fuel: A review. Energy Strat. Rev. 2022, 44, 100926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinlay, C.J.; Turnock, S.; Hudson, D. A Comparison of hydrogen and ammonia for future long distance shipping fuels. In Proceedings of the LNG/LPG and Alternative Fuel Ships, London, UK, 29–30 January 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Morlanés, N.; Katikaneni, S.P.; Paglieri, S.N.; Harale, A.; Solami, B.; Sarathy, S.M.; Gascon, J. A technological roadmap to the ammonia energy economy: Current state and missing technologies. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 408, 127310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, W.S.; Bao, Y.; Jin, P.; Tang, G.; Zhou, L. A review on ammonia, ammonia-hydrogen and ammonia-methane fuels. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 147, 111254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Liu, Q.; Wang, L.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J. A review of the port carbon emission sources and related emission reduction technical measures. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 320, 121000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motlagh, H.R.S.; Zadeh, S.B.I.; Garay-Rondero, C.L. Towards International Maritime Organization Carbon Targets: A Multi-Criteria Decision-Making Analysis for Sustainable Container Shipping. Sustainability 2023, 15, 16834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WIN GD. Delivers Exceptional Results in Full Load Ammonia Engine Test. 2025. Available online: https://my.wingd.com/media/vtgkm11c/wingd-full-load-ammonia-tests-deliver-exceptional-results.pdf (accessed on 1 September 2025).
- MAN ES. MITSUI E&S Commences Full-Scale Ammonia Testing. 2025. Available online: https://www.man-es.com/docs/default-source/press-releases-new/pr-mitsui-me-lgia_en.pdf?sfvrsn=18997350_1 (accessed on 26 August 2025).
- DNV GL. Ammonia in Shipping Tracing the Emergence of a New Fuel. 2025. Available online: https://www.dnv.com/maritime/publications/ammonia-in-shipping-download/ (accessed on 2 October 2025).
- Hyundai Heavy. HD Hyundai Heavy Industries Develops Ammonia Dual-Fuel Engine and Receives Approval from 7 Major Classification Societies. 2024. Available online: https://www.hyundai-engine.com/en/media/newsdetail/435 (accessed on 26 August 2025).
- Li, P.; Liu, D. How blue carbon financing can sustain blue carbon ecosystems protection and restoration: A proposed conceptual framework for the blue carbon financing mechanism. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2025, 265, 107644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, L.; Sleiti, A.K.; Al-Ammari, W.A. A techno-economic evaluation and SWOT analysis of various hydrogen energy carriers: Production to distribution. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2025, 142, 1153–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayraktar, M.; Sokukcu, M.; Pamik, M.; Yuksel, O. Evaluating Ammonia as a Marine Fuel: Review and Illustration. Environ. Model. Assess. 2025, 30, 779–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, C.G.; Lamas, M.I.; Rodríguez, J.d.D.; Abbas, A. Multi-Criteria Analysis to Determine the Most Appropriate Fuel Composition in an Ammonia/Diesel Oil Dual Fuel Engine. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, Z. Decarbonizing Maritime Shipping in the EU: A PESTLE and MICMAC Factor Analysis of Green Ammonia (e-NH3) Adoption Using Rogers’ Innovation Decision Process. Master’s Thesis, University of Twente, Enschede, The Netherlands, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Hansson, J.; Månsson, S.; Brynolf, S.; Grahn, M. Alternative marine fuels: Prospects based on multi-criteria decision analysis involving Swedish stakeholders. Biomass-Bioenergy 2019, 126, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, T.; Westbrook, R. SWOT analysis: It’s time for a product recall. Long Range Plan. 1997, 30, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalska-Pyzalska, A.; Kott, J.; Kott, M. Why Polish market of alternative fuel vehicles (AFVs) is the smallest in Europe? SWOT analysis of opportunities and threats. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 133, 110076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I. Evaluating the strategies of compressed natural gas industry using an integrated SWOT and MCDM approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 1035–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickton, D.W.; Wright, S. What’s swot in strategic analysis? Strateg. Change 1998, 7, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurl, E. SWOT analysis: A theoretical review. J. Int. Soc. Res. 2017, 10, 994–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazinoory, S.; Abdi, M.; Azadegan-Mehr, M. Swot methodology: A state-of-the-art review for the past, a framework for the future/ssgg metodologija: Praeities ir ateities analizė. J. Bus. Econ. Manag. 2011, 12, 24–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulen, M.F.; Uflaz, E.; Gumus, F.; Orhan, M.; Arslan, O. An integrated SWOT-based interval type-2 fuzzy AHP and TOPSIS methodology for digital transformation strategy selection in maritime safety. Ocean Eng. 2025, 323, 120518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, J. Best-worst multi-criteria decision-making method. Omega 2015, 53, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, F.; Brunelli, M.; Rezaei, J. Consistency issues in the best worst method: Measurements and thresholds. Omega 2020, 96, 102175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, J. A Concentration ratio for nonlinear best worst method. Int. J. Inf. Technol. Decis. Mak. 2020, 19, 891–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Ma, X.; Liang, Y. Building a consensus for the best-worst method in group decision-making with an optimal allocation of information granularity. Inf. Sci. 2023, 619, 630–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.; Wu, Z.; Pedrycz, W. Priority ranking for the best-worst method. Inf. Sci. 2023, 635, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.; Liu, J.; Chen, J. Scenario-based strategies evaluation for the maritime supply chain resilience. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2023, 124, 103948. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Wiegmans, B.; Wang, X.; Yang, K.; Jiang, L. A Hybrid DEMATEL and Bayesian Best–Worst Method Approach for Inland Port Development Evaluation. Axioms 2023, 12, 1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munim, Z.H.; Chowdhury, M.M.H.; Tusher, H.M.; Notteboom, T. Towards a prioritization of alternative energy sources for sustainable shipping. Mar. Policy 2023, 152, 105579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munim, Z.H.; Notteboom, T.; Haralambides, H.; Schøyen, H. Key determinants for the commercial feasibility of maritime autonomous surface ships (MASS). Mar. Policy 2025, 172, 106482. [Google Scholar]
- Soner, O.; Celik, E.; Akyuz, E. A fuzzy best–worst method (BWM) to assess the potential environmental impacts of the process of ship recycling. Marit. Policy Manag. 2022, 49, 396–409. [Google Scholar]
- Tusher, H.M.; Munim, Z.H.; Nazir, S. An evaluation of maritime simulators from technical, instructional, and organizational perspectives: A hybrid multi-criteria decision-making approach. WMU J. Marit. Aff. 2024, 23, 165–194. [Google Scholar]
- Mi, X.; Tang, M.; Liao, H.; Shen, W.; Lev, B. The state-of-the-art survey on integrations and applications of the best worst method in decision making: Why, what, what for and what’s next? Omega 2019, 87, 205–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zincir, B. A short review of ammonia as an alternative marine fuel for decarbonised maritime transportation. In Proceedings of the ICEESEN2020, Kayseri, Turkey, 19–21 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Issa-Zadeh, S.B.; Garay-Rondero, C.L. Decarbonizing Seaport Maritime Traffic: Finding Hope. World 2025, 6, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdemir, D.; Dincer, I. A perspective on the use of ammonia as a clean fuel: Challenges and solutions. Int. J. Energy Res. 2021, 45, 4827–4834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DNV GL. Comparison of Alternative Marine Fuels. 2019. Available online: https://sea-lng.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/Alternative-Marine-Fuels-Study_final_report_25.09.19.pdf (accessed on 28 August 2025).
- Avery, W. A role for ammonia in the hydrogen economy. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 1988, 13, 761–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, M.; Oda, T.; Kashiwagi, T. Comparison of liquid hydrogen, methylcyclohexane and ammonia on energy efficiency and economy. Energy Procedia 2019, 158, 4086–4091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijayanta, A.T.; Oda, T.; Purnomo, C.W.; Kashiwagi, T.; Aziz, M. Liquid hydrogen, methylcyclohexane, and ammonia as potential hydrogen storage: Comparison review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 15026–15044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Parsapur, R.K.; Huang, K.-W. Limitations of ammonia as a hydrogen energy carrier for the transportation sector. ACS Energy Lett. 2021, 6, 4390–4394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesaro, Z.; Ives, M.; Nayak-Luke, R.; Mason, M.; Bañares-Alcántara, R. Ammonia to power: Forecasting the levelized cost of electricity from green ammonia in large-scale power plants. Appl. Energy 2021, 282, 116009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MAN ES. MAN B&W Two-Stroke Engine Operating on Ammonia. 2025. Available online: https://www.man-es.com/docs/default-source/document-sync/man-b-w-two-stroke-engine-operating-on-ammonia-eng.pdf?sfvrsn=c4bb6fea_5 (accessed on 28 August 2025).
- Boretti, A. Advancing ammonia synthesis: Pathways toward decarbonization and sustainability. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2025, 217, 235–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishaq, H.; Crawford, C. Review of ammonia production and utilization: Enabling clean energy transition and net-zero climate targets. Energy Convers. Manag. 2024, 300, 117869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayramoğlu, K.; Bayraktar, M.; Seyhan, A.; Yuksel, O. Evaluation of techniques to reduce carbon emissions from ships within the scope of revised greenhouse gas emission targets for 2030, 2040, and 2050. Ocean Eng. 2025, 334, 121605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elçiçek, H. Bibliometric analysis on hydrogen and ammonia: A comparative evaluation for achieving IMO’s decarbonization targets. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 21, 7039–7060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehmin, M.N.I.; Kiong, T.S.; Mohamed, H.; Mahlia, T.I.; Aziz, N.A.M.; Timmiati, S.N.; Zakaria, Z. Transition pathway from blue to green ammonia production: Comparative insight into technoeconomic, environmental, and policy framework. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2025, 143, 147–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, G.; Xie, K. Using DPF to Control Particulate Matter Emissions from Ships to Ensure the Sustainable Development of the Shipping Industry. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isella, A.; Lista, A.; Colombo, G.; Ostuni, R.; Manca, D. Gray and hybrid green ammonia price sensitivity to market fluctuations: The Russia-Ukraine war case. In Computer Aided Chemical Engineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; Volume 52, pp. 2285–2290. [Google Scholar]
- Adhari, O.H.K.; Mahmoud, M.; Abdelkareem, M.A.; Olabi, A.G. Green Ammonia: Progress and Challenges. Compr. Green Mater. 2025, 1, 479–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bora, N.; Singh, A.K.; Pal, P.; Sahoo, U.K.; Seth, D.; Rathore, D.; Bhadra, S.; Sevda, S.; Venkatramanan, V.; Prasad, S. Green ammonia production: Process technologies and challenges. Fuel 2024, 369, 131808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidhalter, I.; Mussati, M.C.; Mussati, S.F.; Marcovecchio, M.G.; Aguirre, P.A. Optimal green ammonia system design for minimum levelized costs in Southern Argentina. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2025, 121, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guardiola, C.; Pla, B.; Bares, P.; Mora, J. Model-based ammonia slip observation for scr control and diagnosis. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatronics 2020, 25, 1346–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Energy Agency (IEA). Ammonia Technology Roadmap. Towards More Sustainable Nitrogen Fertilizer Production. 2021. Available online: https://iea.blob.core.windows.net/assets/6ee41bb9-8e81-4b64-8701-2acc064ff6e4/AmmoniaTechnologyRoadmap.pdf (accessed on 29 August 2025).
- Green Shipping Programme (GSP). AMMONIA-POWERED TANKER PILOT. 2023. Available online: https://greenshippingprogramme.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/Ammonia-powered-tanker-pilot.pdf (accessed on 29 August 2025).
- AEA. Ammonia Energy Association-Setting the Scene for Ammonia Maritime Fuel: Regulatory Needs and Timelines to Decarbonize Shipping. 2025. Available online: https://ammoniaenergy.org/articles/setting-the-scene-for-ammonia-maritime-fuel-regulatory-needs-and-timelines-to-decarbonize-shipping/ (accessed on 30 August 2025).
- Wartsila. WARTSILA 25: The Power to Target Net Zero. 2025. Available online: https://brandhub.wartsila.com/m/6ec1690a9bc01222/original/Wartsila-25-Brochure.pdf?utm_source=engines&utm_medium=dfengines&utm_term=w25&utm_content=brochure&utm_campaign=mp-engines-and-generating-sets-brochures (accessed on 1 September 2025).
- Wang, Y.; Iris, Ç. Transition to near-zero emission shipping fleet powered by alternative fuels under uncertainty. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2025, 142, 104689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, S.; Iris, Ç. An exact algorithm for fleet co-deployment and slot co-chartering in a sustainable shipping alliance under emissions trading system. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2025, 327, 450–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genge, L.; Müsgens, F. Green Ammonia: A Techno-Economic Supply Chain Optimization. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2507.02412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proton Ventures. Why Does Green Ammonia Struggle to Kick-Off, & What Can We Do About It? 2025. Available online: https://protonventures.com/news/why-does-green-ammonia-struggle-to-kick-off-what-can-we-do-about-it/ (accessed on 31 August 2025).
- Ohio River Valley Institute. The Uncertain Ammonia Industry, Present & Future. 2025. Available online: https://ohiorivervalleyinstitute.org/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/Ammonia_v5.3-FINAL-1.pdf (accessed on 31 August 2025).
- Christodoulou, A.; Dong, T.; Schönborn, A.; Ölçer, A.I.; Dalaklis, D. A cost-benefit analysis of the use of ammonia and hydrogen as marine fuels. In Proceedings of the International Maritime and Logistics Conference “Marlog 12”, Alexandria, Egypt, 12–14 March 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Park, C.; Hwang, I.; Jang, H.; Jeong, B.; Ha, S.; Kim, J.; Jee, J. Comparative analysis of marine alternative fuels for offshore supply vessels. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 11196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ship & Bunker. A Comparative Analysis of Alternative Fuels for Sustainable Maritime Shipping. 2025. Available online: https://shipandbunker.com/news/world/527976-insight-a-comparative-analysis-of-alternative-fuels-for-sustainable-maritime-shipping (accessed on 1 September 2025).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).