Research on the Cultivation of Sustainable Innovation Dynamics in Private Technology Enterprises Based on Tripartite Evolution Game in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Research on Influencing Factors of Sustainable Innovation Dynamics in Private Technology Enterprises
2.2. Research on the Analysis of Game Entities’ Behaviors
2.2.1. Analysis of Government Behavior
2.2.2. Analysis of Private Technology Enterprise Behavior
2.2.3. Analysis of Market Users’ Behavior
3. Construction of Multi-Entity Evolutionary Game Model for Sustainable Innovation Dynamics of Private Technology Enterprises
3.1. Basic Assumptions
3.2. Game Benefits of Behavior Decisions
3.3. Stability Analysis of Behavior Decision Strategy Evolution
3.4. Update Rules for Behavior Decision Strategies
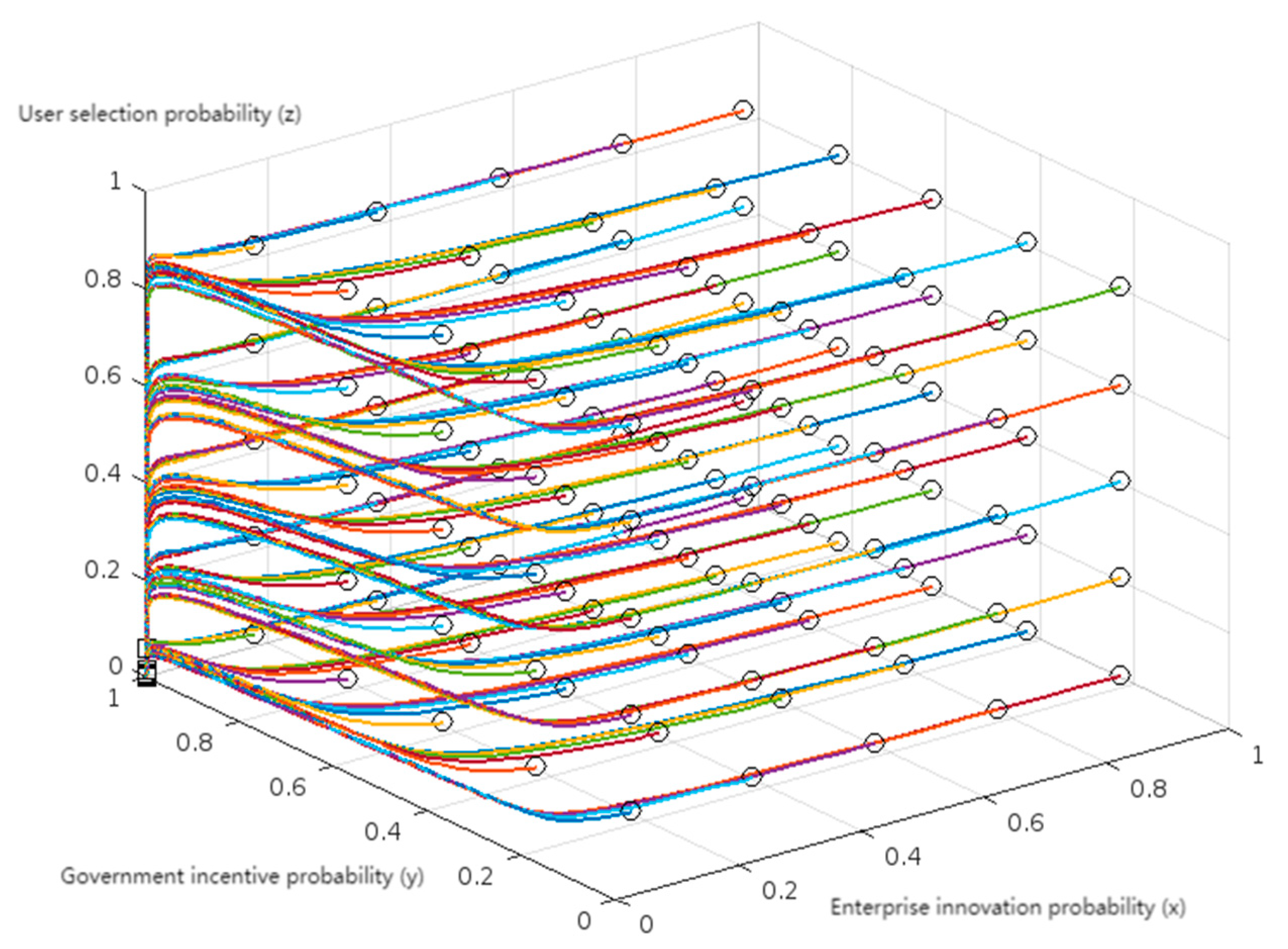
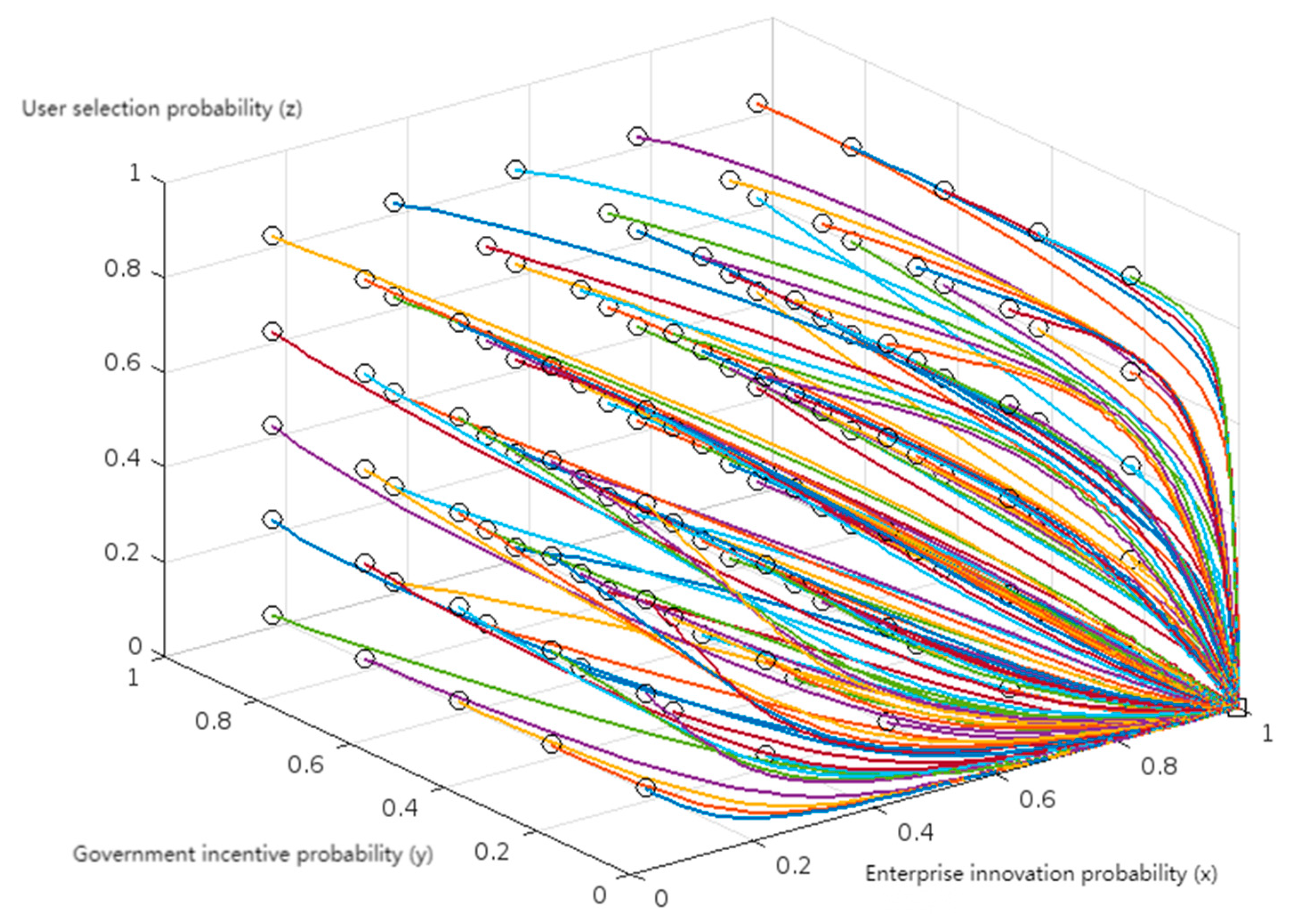
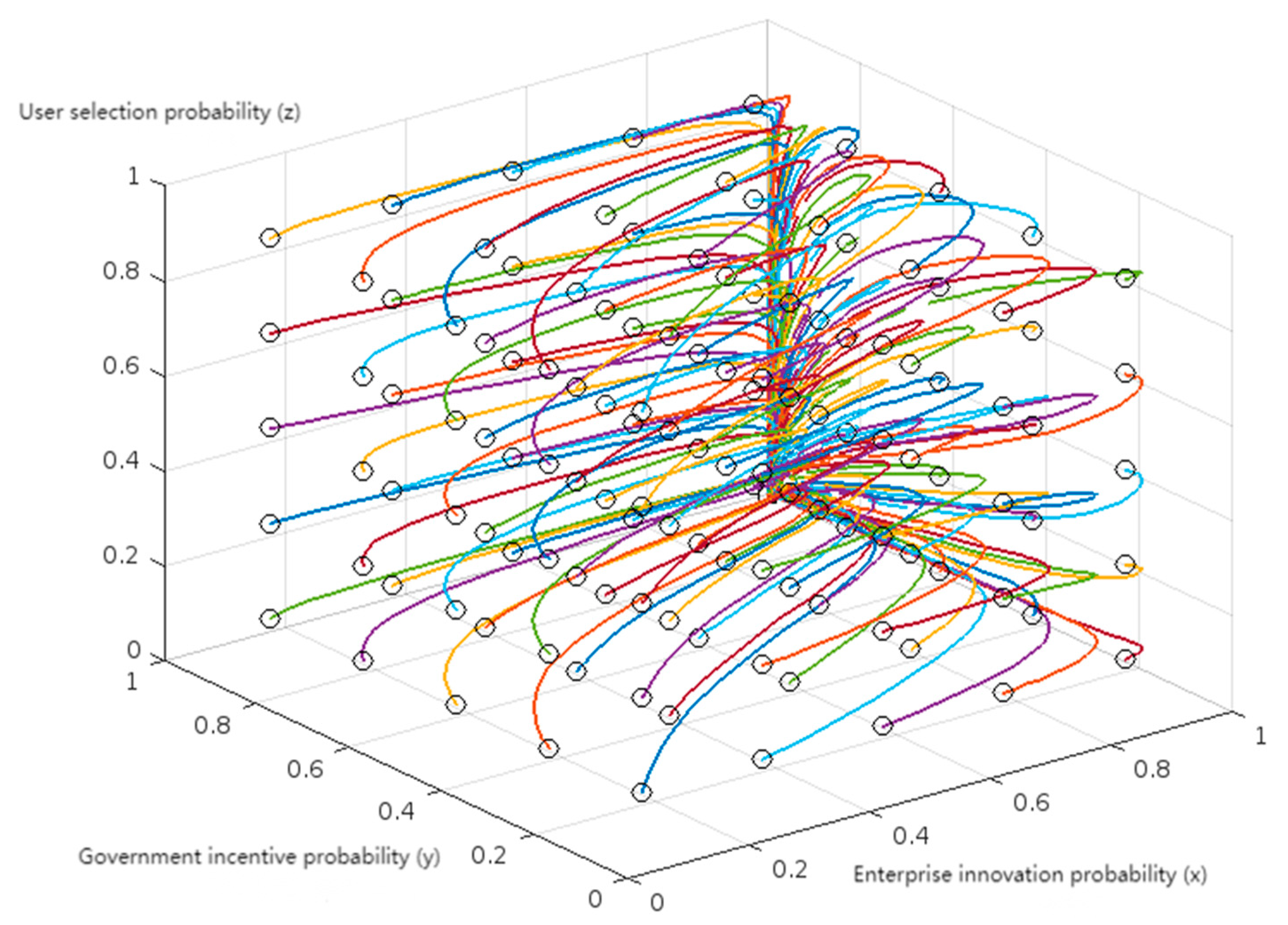
4. Multi-Scenario Numerical Simulation and Result Analysis
4.1. Parameter Setting
4.2. Scenario Simulation and Result Analysis
5. Conclusions and Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Guo, M. Strengthening the main position of private enterprises in scientific and technological innovation. Enterp. Manag. 2023, 9, 10–13. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F. Five Expectations for the Development of Small and Medium-sized Private Science and Technology Enterprises. Enterp. Reform Dev. 2025, 7, 60–62. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, R. Research on Evaluation of Enterprise’s Sustainable Innovation Capability. Bus. Res. 2009, 8, 8–10. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, H. Research on the Influencing Factors of Enterprise’s Continuous Innovation. Sci. Technol. Prog. Countermeas. 2017, 34, 87–93. [Google Scholar]
- García-Morales, J.V.; Lloréns-Montes, J.F.; Verdú-Jover, J.A. Influence of personal mastery on organizational performance through organizational learning and innovation in large firms and SMEs. Technovation 2007, 27, 547–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, M.; Wang, R. How Does Corporate’s Social Responsibility Affect the Persistence of Firm Innovation? China Sci. Technol. Forum 2020, 1, 107–115. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Zhou, H.; Ding, J. Research on the impact of technological diversification on the persistence of innovation at firm-level. Sci. Res. 2017, 35, 1896–1909. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Yue, X.; Huang, H. Cooperation Culture, Enterprise Innovation and Organizational Resilience. Ind. Technol. Econ. 2023, 42, 105–114. [Google Scholar]
- Drucker, P.F.; Noel, J.L. Innovation and Entrepreneurship: Practices and Principles. J. Contin. High. Educ. 1986, 34, 22–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, C. Research on the Driven Path of Ambidextrous Innovation of Science and Technology Enterprises: An Exploration Based on Fuzzy Set Qualitative Comparative Analysis. Math. Probl. Eng. 2022, 2022, 6173263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhai, L.; Jiang, Y. Evolutionary Game Decision in a Platform Supply Chain with Digital Empowerment. J. Manag. 2023, 20, 925–935. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Zheng, Q. Deep Integration of Manufacturing and Logistics Industry and Inter-firm Technological Co-innovation—An Evolutionary Game Analysis with Government Involvement. Bus. Res. 2023, 5, 29–38. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, H.; Fang, D. Government Subsidies, Risk-Taking and Technological Innovation of Private Science and Technology Enterprises. J. Manag. 2021, 34, 45–62. [Google Scholar]
- Teets, J.C.; Hasmath, R.; Lewis, O. The Incentive to Innovate? The Behavior of Local Policymakers in China. J. Chin. Political Sci. 2017, 22, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Xu, X.; Tian, F. Research on the Influencing Factors of Enterprise Technological Innovation in China. Stat. Inf. Forum 2025, 40, 17–28. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.; Zhang, X. Digital empowered business environment and enterprise innovation: Evidence from China. Pac. Basin Financ. J. 2025, 91, 102755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Tao, S. Research on the Impact of US Economic Sanctions on Innovation in Chinese Technology Enterprises—Analysis Based on Enterprise Innovation Decision Theory Model. Mod. Econ. Discuss. 2025, 8, 53–68. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, W. Belt and Road Initiative: Driving innovation in tech enterprises through global value chains. Financ. Res. Lett. 2025, 74, 106796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Huang, C. Government intervention and corporate technological innovation: An evolutionary theory game analysis framework. J. Harbin Univ. Commer. (Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2025, 5, 61–73. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Z.; Xiang, J.; Liu, Q.; Yu, X. Evolutionary Game Analysis of Government Subsidy Mechanism and Enterprise Innovation Strategy—From the Perspective of Stock Price Crash Risk. J. Knowl. Econ. 2024, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Yu, T.; Hong, J.; Shen, Q.G. Making incentive policies more effective: An agent-based model for energy-efficiency retrofit in China. Energy Policy 2019, 126, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Yang, R. Tripartite Evolutionary Game and Simulation Analysis of Green Innovation in Logistics Enterprises under the Background of New Quality Productive Forces. Logist. Res. 2025, 1, 4–13+41. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhu, Q.; Li, X.; Pan, Y. The impact of government subsidy on photovoltaic enterprises independent innovation based on the evolutionary game theory. Energy 2023, 285, 129385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, N.; Li, M. Research on collaborative innovation behavior of enterprise innovation ecosystem under evolutionary game. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2024, 206, 123508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, J.; Ouyang, J.; Wang, L. An evolutionary game analysis of incentive of industrial parks, government support and enterprise innovation willingness in China. Heliyon 2024, 10, e36618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Tulder, R.; van Mil, E. Principles of Sustainable Business: Frameworks for Corporate Action on the SDGs; Taylor and Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polman, P.; Winston, A. Net Positive: How Courageous Companies Thrive by Giving More Than They Take; Chemical Engineering Progress: New York, NY, USA, 2021; Volume 117, p. 53. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Yu, T.; Ma, Y. Game of Government, Enterprise and Consumer Based on Product Quality Regulation Perspective. China Manag. Sci. 2019, 27, 127–135. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H. Game model construction and analysis of different stakeholders-based on the construction of technological innovation mechanism of private enterprises. China Trade 2015, 4, 133–135. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Deng, J.; Su, Y.; Peng, J. On the Mechanism of the Competency Construction under Rapid Changing Environment: A Case Study based on Dynamic Capability. South. Econ. 2019, 11, 113–130. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, X.; Chen, W.; Lin, C. Evolution, Classification, and Relationships of the Theories of Innovation Capabilities. Manag. Q. 2019, 4, 112–150+157. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, X.; Yuan, P. Innovation balance mode selection and enterprise performance: The role of technological diversity and financial redundancy. J. Jinan Univ. (Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2020, 30, 100–108+159. [Google Scholar]
- March, J.G. Exploration and exploitation in organizational learning. Organ. Sci. 1991, 2, 71–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z. An Analysis of the Influencing Factors of the Purchase Decision of New Energy Vehicles. J. Ezhou Univ. 2021, 28, 47–48. [Google Scholar]
- von Hippel, E. Democratizing innovation: The evolving phenomenon of user innovation. J. Betriebswirtsch. 2005, 55, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, E.M. Diffusion of Innovations; The Free Press: New York, NY, USA, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, N.; Tong, Y.; He, H. Evolutionary Game Analysis of SME Social Responsibility Performance under Public Health Emergencies. Mathematics 2023, 11, 1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqudah, Z.M.; García, S.L.; Benau, G.A.M. Influence of ESG among Jordanian fintech businesses: The moderating role of sustainable finance technology. Discov. Sustain. 2024, 5, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Zhang, H.; Hu, J.; Zhang, J. Research on the Evolutionary Mechanism of Non-core Enterprises in the Industrial Innovation Network Based on Evolutionary Game Theory. Tech. Econ. 2022, 41, 52–62. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, N.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Evolutionary Game on Technological Innovation of Enterprises in Complex Product R&D Network. China Manag. Sci. 2024, 32, 242–253. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Bai, C.; Zhou, B. Tripartite Evolutionary Game Analysis of Digital Technology Empowering Enterprise Radical Innovation. Front. Eng. Manag. Sci. Technol. 2025, 1–15. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/34.1336.N.20250626.0937.004 (accessed on 26 June 2025).
- Li, Y.; Wu, L. An Evolutionary Game Study on Multi-Subject Strategy Selection under Government R&D Subsidies. Math. Pract. Theory 2025, 55, 41–56. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Ren, X. Research on credit supervision mechanism of e-commerce platform based on evolutionary game. Syst. Eng. Theory Pract. 2020, 40, 2617–2630. [Google Scholar]
- Barreto, S.L.; Freitas, V.; Paula, D.F.A.V. Sustainable supply chain innovation and market performance: The role of sensing and innovation capabilities. Clean. Responsible Consum. 2024, 14, 100199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Cao, J. Research on the mechanism of sustainable business model innovation driven by the digital platform ecosystem. J. Eng. Technol. Manag. 2023, 68, 101738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Che, X.; Sheng, Y.; Chen, L.; Shi, Q. Study on Government-industry-university-institute Collaborative Innovation Based on Tripartite Evolutionary Game. China Manag. Sci. 2019, 27, 162–173. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Z.; Zheng, Q. An evolutionary game analysis of subsidy strategies in the supply chain of SMEs based on system dynamics. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2022, 199, 1513–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.; Zhang, Z. Coordination Dilemma and Subsidy Strategy of Innovation Diffusion among Heterogeneous User Groups. Tech. Econ. Manag. Res. 2016, 7, 24–28. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Xia, H. Research on Coordination Mechanism of Collaborative Innovation Based on Government Subsidy. Ind. Technol. Econ. 2019, 38, 13–20. [Google Scholar]


| Category | Step | Specific Implementation Points |
|---|---|---|
| Problem Identification & ModelingPreparation | Problem Definition & Agent Identification | To address the triangular dilemma of “low willingness of enterprises to innovate, difficulties in policy implementation, and slow market acceptance,” the government, private technology enterprises, and market users are identified as the boundedly rational players. |
| Model Assumptions & Parameter Definition | Define the strategy spaces for the three agents (Government strategies: strong/weak incentives; Enterprise strategies: active/passive innovation; User strategies: choosing innovative/traditional products). Parameters include Ra, Ca, Rp, Cp, etc. (refer to Table 2 in the paper), with values based on empirical data from the literature. | |
| Theoretical Analysis & ModelConstruction | Payoff Matrix Construction | Construct a 2 × 2 × 2 three-dimensional payoff matrix based on game-theoretic payoff structures, calculating the expected payoffs for all strategy combinations (refer to Table 3 in the paper). |
| Replicator Dynamic Equation Derivation | Derive the replicator dynamic equations for the three agents, e.g., F(x) = dx/dt = x(1 − x)[E11 − E12], describing the strategic evolution path. | |
| Stability Analysis & NumericalVerification | Equilibrium Point Solving & Stability Analysis | Solve the eight pure-strategy equilibrium points and analyze the Evolutionarily Stable Strategy (ESS) by evaluating the eigenvalues of the Jacobian matrix, applying Friedman’s rule: a point is locally asymptotically stable if all eigenvalues λ1, λ2, λ3 < 0; E8 (1, 1, 1) is identified as the optimal ESS for tripartite collaboration (see Section 3.3). |
| Numerical Simulation | Conduct multi-scenario simulations using Matlab software, with parameter settings based on five typical scenarios. | |
| Result Output & Validation | Result Output & Validation | Generate evolutionary path diagrams (time-series plots), output simulation results, and perform sensitivity analysis and policy mapping. |
| Parameter | Parameter Description |
|---|---|
| x | Probability of private technology enterprises adopting the active innovation strategy |
| y | Probability of the government adopting the strong incentive strategy |
| z | Probability of users choosing innovative products |
| Ra | Revenue of private technology enterprises from active innovation |
| Ca | Cost of private technology enterprises for active innovation |
| Rp | Revenue of private technology enterprises from passive innovation |
| Cp | Cost of private technology enterprises for passive innovation |
| P | Penalty imposed by the government on private technology enterprises for passive innovation |
| Rg | Revenue of the government from strong incentives |
| Cg | Cost of the government for strong incentives |
| Rl | Revenue of the government from weak incentives |
| Lg | Reputation loss of the government from weak incentives |
| Va | Revenue of users from choosing innovative products |
| Vp | Revenue of users from choosing traditional products |
| Cu | Additional cost for users to choose innovative products (premium/learning cost) |
| S | Risk loss borne by users choosing innovative products when private technology enterprises passively innovate and the government implements weak incentives |
| K | Subsidy for users choosing innovative products when enterprises actively innovate under strong government incentives |
| Probability of private technology enterprises being penalized for passive innovation |
| Game Entities | Market Users | ||||
| Choose Innovative Products (z) | Choose Traditional Products (1 − z) | ||||
| Private Technology Enterprises | Active Innovation (x) | Government | Strong Incentives (y) | ||
| Weak Incentives (1 − y) | |||||
| Passive Innovation (1 − x) | Government | Strong Incentives (y) | |||
| Weak Incentives (1 − y) | |||||
| Equilibrium Point | Eigenvalues | Stability Conditions | Local Stability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Asymptotic ESS | |||
| λ3 > 0 holds constantly | Unstable Point | ||
| Asymptotic ESS | |||
| λ3 > 0 holds constantly | Unstable Point | ||
| Asymptotic ESS | |||
| λ3 > 0 holds constantly | Unstable Point | ||
| Asymptotic ESS | |||
| Asymptotic ESS |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Hou, R.; Wang, J.; Peng, W.; Liao, Z. Research on the Cultivation of Sustainable Innovation Dynamics in Private Technology Enterprises Based on Tripartite Evolution Game in China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 9217. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17209217
Liu Y, Hou R, Wang J, Peng W, Liao Z. Research on the Cultivation of Sustainable Innovation Dynamics in Private Technology Enterprises Based on Tripartite Evolution Game in China. Sustainability. 2025; 17(20):9217. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17209217
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yue, Renyong Hou, Jinwei Wang, Weihua Peng, and Zhijie Liao. 2025. "Research on the Cultivation of Sustainable Innovation Dynamics in Private Technology Enterprises Based on Tripartite Evolution Game in China" Sustainability 17, no. 20: 9217. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17209217
APA StyleLiu, Y., Hou, R., Wang, J., Peng, W., & Liao, Z. (2025). Research on the Cultivation of Sustainable Innovation Dynamics in Private Technology Enterprises Based on Tripartite Evolution Game in China. Sustainability, 17(20), 9217. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17209217





