Sustainable Digital Transformation in Geotechnical-Related Engineering Disciplines: An Integrated Framework for Türkiye
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (i)
- To develop the SDIM–Geo–TR model as a phased and context-specific framework structuring the digital transformation of geotechnical engineering in Türkiye;
- (ii)
- To establish a five-criteria evaluation framework that operationalizes the model and provides measurable justification;
- (iii)
- To propose a strategic policy roadmap for Türkiye’s geotechnical sector, including recommendations for education, open data governance, software standardization, and platform integration.
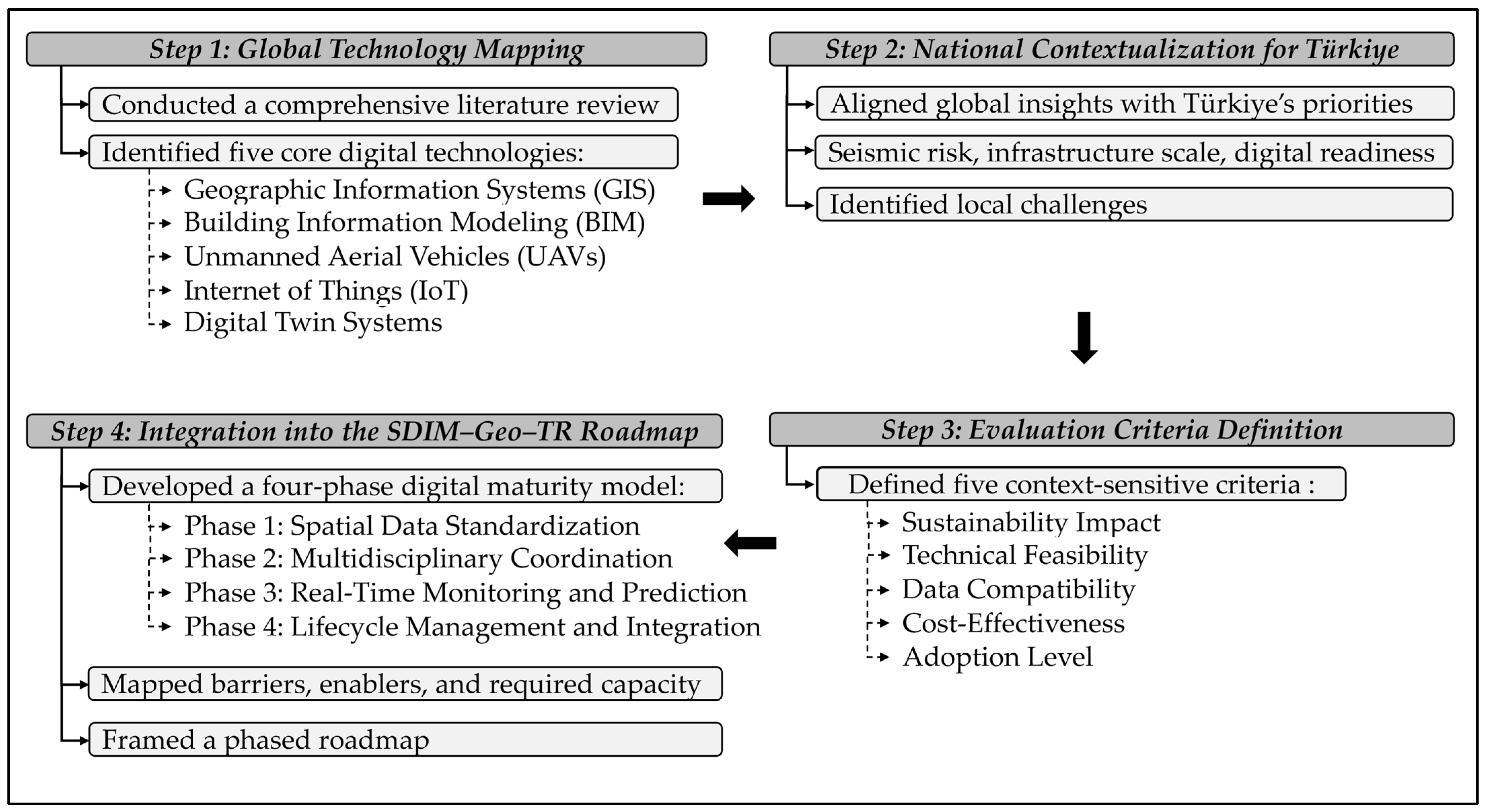
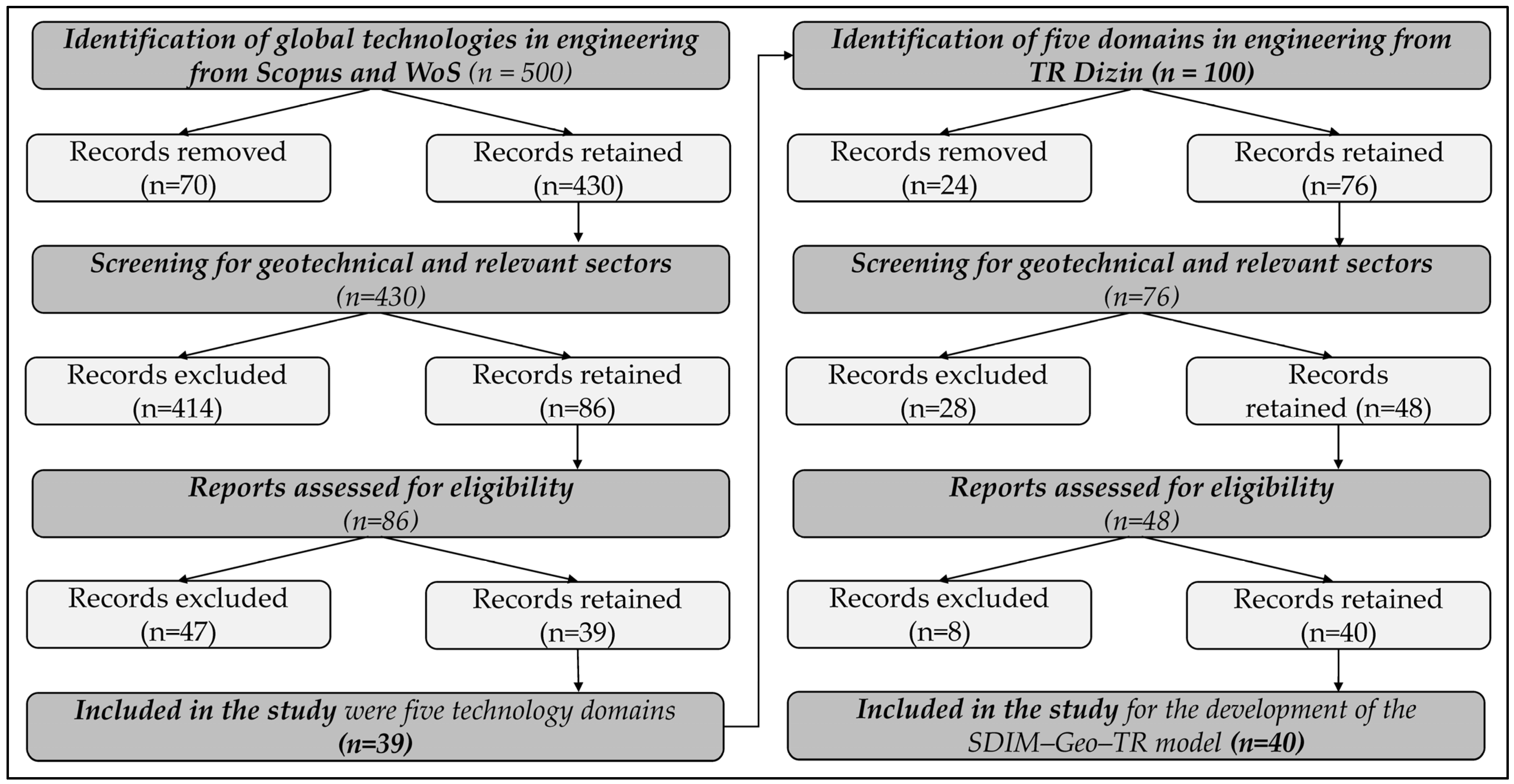
2. Methodology: Framework Design and Contextualization
3. Global Technology Mapping in Geotechnics
3.1. Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
3.2. Building Information Modeling (BIM)
3.3. Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs)
3.4. Internet of Things (IoT)
3.5. Digital Twin
4. National Contextualization for Türkiye
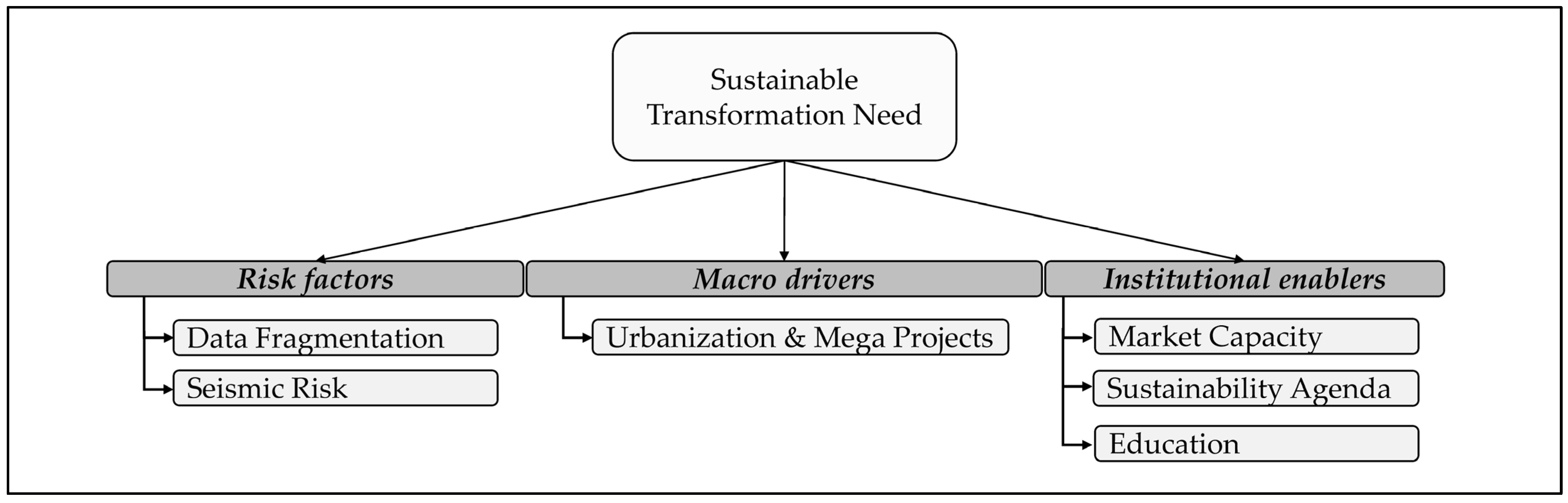
4.1. Contextual Drivers
4.2. Evolution and Current Adoption of Digital Technologies in Türkiye
4.2.1. Adoption Trajectories
4.2.2. Cross-Cutting Patterns and Synthesis
4.3. Implementation Framework: Barriers and Opportunities
4.4. Rationale for the SDIM–Geo–TR Framework
- Standardization of spatial and geotechnical data exchange (addressing interoperability gaps);
- Bridging of design, construction, and monitoring platforms (enabling BIM–GIS–IoT integration);
- Institutionalization of lifecycle feedback through digital twins (transforming pilots into systemic practice).
5. SDIM–GEO–TR Model
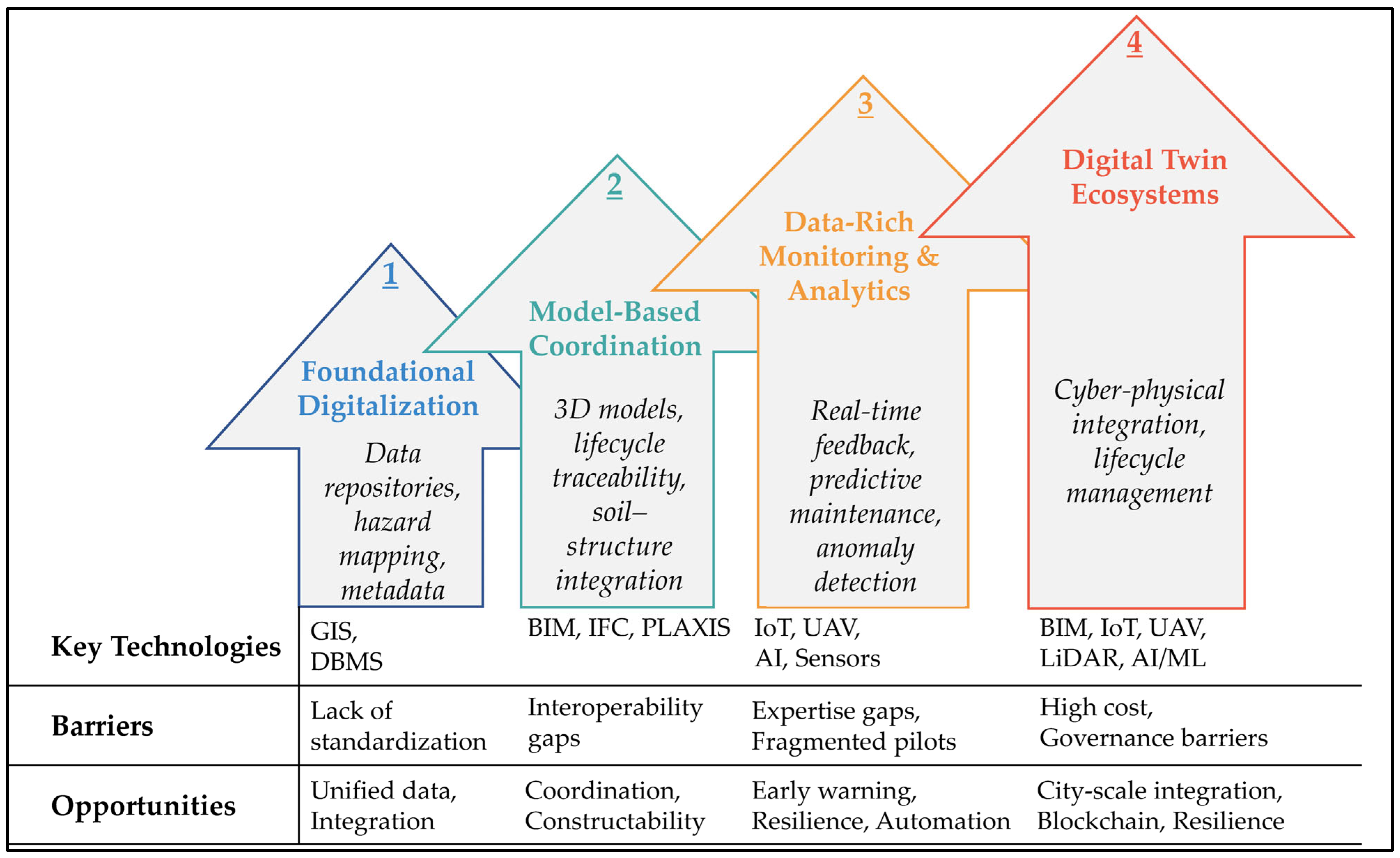
5.1. Four Stages of the SDIM–Geo–TR Framework
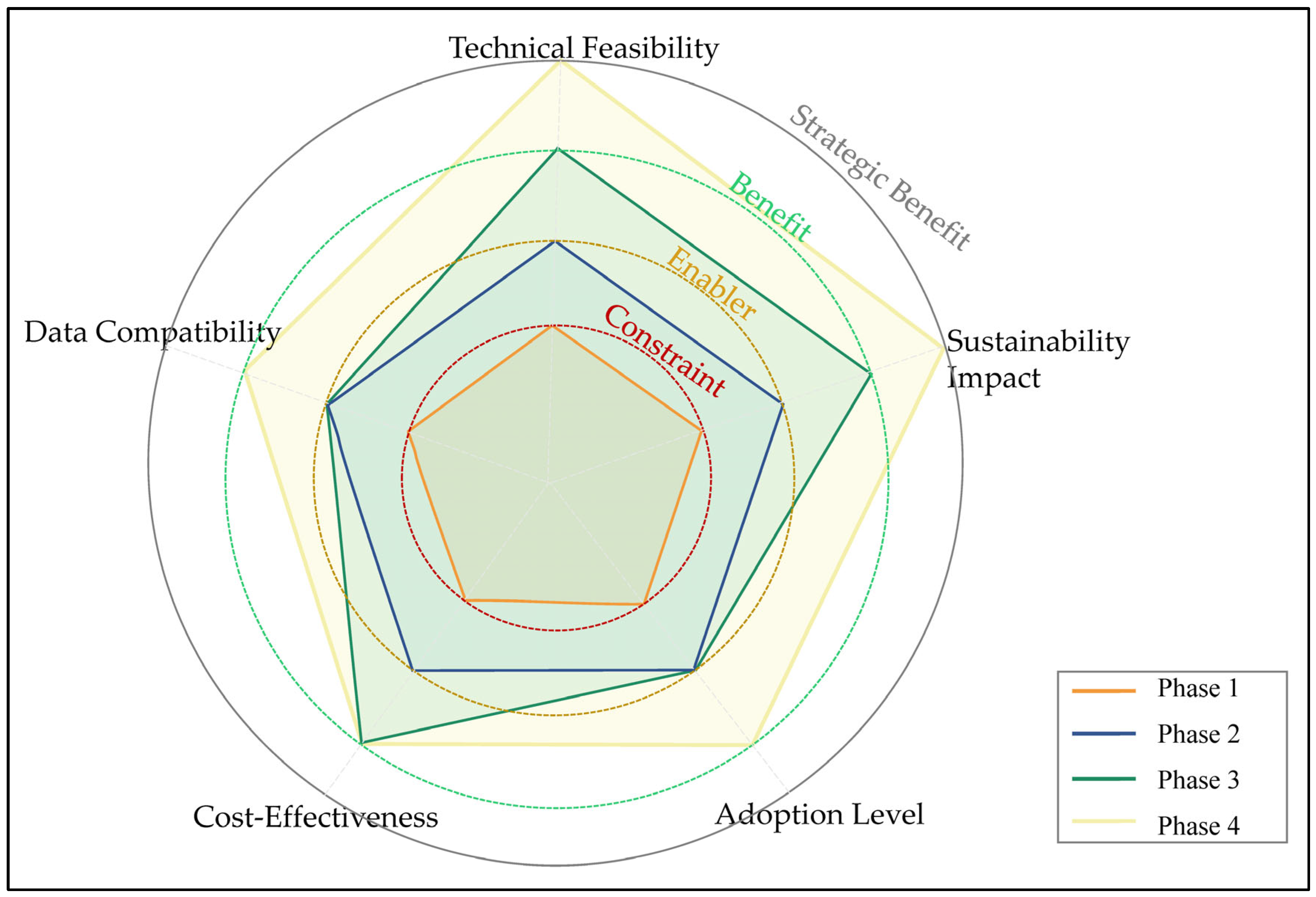
5.2. Evaluation Criteria
- Sustainability Impact: Captures environmental and resilience outcomes such as reduced carbon emissions, lifecycle energy savings, and enhanced disaster preparedness. In Türkiye, examples include UAV-enabled slope monitoring in Rize and life-cycle assessments in dam projects, both of which demonstrate the integration of digital tools with sustainability objectives.
- Technical Feasibility: Reflects the maturity and applicability of technologies under real geotechnical field conditions. It ranges from constraint to enabler, depending on the availability of reliable hardware, software, and local expertise. Practical instances include MEMS-based monitoring systems deployed in Istanbul metro excavations.
- Data Compatibility: Concerns interoperability across geotechnical, structural, and spatial datasets. This includes the capacity of BIM, GIS, and monitoring databases to exchange data in standardized formats such as IFC and CityGML. The ongoing challenges of fragmented datasets archives highlight the need for this criterion in Türkiye.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Evaluates financial performance across the lifecycle of digital systems, including both initial investment and long-term operational savings. UAV-based monitoring in projects illustrates how relatively high upfront costs can be offset by significant efficiency and safety gains.
- Adoption Level: Encompasses ecosystem-wide uptake, digital literacy, and institutional embedding of new technologies. National emerging university–industry curricula collaborations indicate how adoption levels are gradually shifting from isolated pilots to wider diffusion.
5.3. Phase–Criteria Interaction
6. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berawi, M.A.; Miraj, P.; Sari, M. Advancing construction practices: Innovations, efficiency, and safety in the digital era. CSID J. Infrastruct. Dev. 2024, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volk, R.; Rambhia, M.; Naber, E.; Schultmann, F. Urban resource assessment, management, and planning tools for land, ecosystems, urban climate, water, and materials—A review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasso, S.; Massimino, M.R. A GIS for data mining in seismic microzonation studies. Smart Innov. Syst. Technol. 2019, 142, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuhussain, M.A.; Waqar, A.; Khan, A.M.; Othman, I.; Alotaibi, B.S.; Althoey, F.; Abuhussain, M. Integrating Building Information Modeling (BIM) for optimal lifecycle management of complex structures. Structures 2024, 60, 105831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loots, M.; Grobbelaar, S.; Van der Lingen, E. A review of remote-sensing unmanned aerial vehicles in the mining industry. J. S. Afr. Inst. Min. Metall. 2022, 122, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiachío, M.; Megía, M.; Chiachío, J.; Fernandez, J.; Jalón, M.L. Structural digital twin framework: Formulation and technology integration. Autom. Constr. 2022, 140, 104333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida Santos, D.; Luiz Gonçalves Quelhas, O.; Francisco Simões Gomes, C.; Perez Zotes, L.; Luiz Braga França, S.; Vinagre Pinto de Souza, G.; da Silva Carvalho Santos, S. Proposal for a maturity model in sustainability in the supply chain. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadikoglu, E.; Demirkesen, S.; Dal, O.; Seker, O.; Nowak, P.; Toprak, S. Fostering sustainability and resilience in engineering education and practice: Lessons learnt from the 2023 Kahramanmaras earthquakes. Sustainability 2025, 17, 1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connected Places Catapult. Türkiye’s BIM Integration Workshop Report: Current State Analysis, High-Level Strategic Roadmap and Recommended Next Steps; PRO-049086; Connected Places Catapult: London, UK, 13 May 2025. Available online: https://webdosya.csb.gov.tr/db/meslekihizmetler/menu/turkiye-s-bim-integration-workshop-report-english-1_20250716084523.pdf (accessed on 8 October 2025).
- T.C. Kalkınma Bakanlığı. On Birinci Kalkınma Planı (2019–2023): İnşaat, Mühendislik-Mimarlık, Teknik Müşavirlik ve Müteahhitlik Hizmetleri Özel İhtisas Komisyonu Raporu; Yayın No: KB 3001—ÖİK 782; T.C. Kalkınma Bakanlığı: Ankara, Turkey, 2018. Available online: https://www.sbb.gov.tr/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/Insaat-Muhendislik-Mimarlik-Teknik-Musavirlik-ve-Muteahhitlik-Hizmetleri-Ozel-Ihtisas-Komisyonu-Raporu.pdf (accessed on 8 October 2025).
- Brabb, E.E. The San Mateo County California GIS Project for Predicting the Consequences of Hazardous Geologic Processes. In Geographical Information Systems in Assessing Natural Hazards; Carrara, A., Guzzetti, F., Eds.; Advances in Natural and Technological Hazards Research; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1995; Volume 5, pp. 299–334. ISBN 978-90-481-4561-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jibson, R.W.; Harp, E.L.; Michael, J.A. A method for producing digital probabilistic seismic landslide hazard maps. Eng. Geol. 2000, 58, 271–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakellariou, M.G.; Ferentinou, M.D. GIS-based estimation of slope stability. Nat. Hazards Rev. 2001, 2, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunapo, J.; Dasari, G.R.; Phoon, K.K.; Tan, T.S. Development of a web-GIS based geotechnical information system. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 2005, 19, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Westen, C.J. Mapping landslides: Recent developments in the use of digital spatial information. In Proceedings of the 1st North American Landslide Conference, Vail, CO, USA, 3–8 June 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.S.; Park, J.; Seo, J. Geotechnical property modeling and construction safety zoning based on GIS and BIM integration. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadhim, M.M.; Al-Saoudi, N.K.; Ziboon, A.R.T. Digital geotechnical maps of Basrah city using geographical information systems technique. Eng. Technol. J. 2013, 31, 599–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leinauer, J.; Jacobs, B.; Krautblatter, M. High alpine geotechnical real-time monitoring and early warning at a large imminent rock slope failure (Hochvogel, GER/AUT). In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Online, 23–27 August 2021; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2021; Volume 833, p. 012146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal-Páez, P.; Clavero, J.; Droguett, D.; Pérez-Martínez, W.; Briceño-De-Urbaneja, I.; Oliva, P. Landslide Susceptibility Using Remote Sensing Data & GIS in a High Andean Area of Central Chile. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2020-2020 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 17 February 2020; pp. 6604–6607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Noor, S.; Chitra, R.; Gupta, M.; Vel, N.K. GIS applications in geotechnical engineering—Some case studies. Int. J. Latest Trends Eng. Technol. 2015, 5, 36–42. [Google Scholar]
- Player, R.S. Geotechnical use of GIS in transportation projects. In Geotechnical Engineering for Transportation Projects; Ellis, G.W., Zhang, L., Edwards, B., Eds.; ASCE: Reston, VA, USA, 2004; pp. 886–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Player, R.S.V. Geographic information system (GIS) use in geotechnical engineering. In GeoCongress 2006: Geotechnical Engineering in the Information Technology Age; ASCE: Reston, VA, USA, 2006; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraibar, J.M.; De-Paz, J.; Rico, J. Challenges for the Implementation of BIM Methodology in the Execution of Underground Works. Buildings 2022, 12, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Yao, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Lu, G. A Sustainable BIM-Based Multidisciplinary Framework for Underground Pipeline Clash Detection and Analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 374, 133900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, G.; Deaton, S.L.; Chandler, R.; Miles, S. Silvertown Tunnel, London, England—A case study applying BIM principles to the geotechnical process. In Geotechnical Frontiers 2017; ASCE: Reston, VA, USA, 2017; pp. 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelzer, M.; Radoncic, N.; Iserte Llacer, P.L.; Tatar, A.; Holmberg, M. BIM processes and workflows using the example of the subway extension in Stockholm. Geomech. Tunn. 2018, 11, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stascheit, J.; Ninić, J.; Meschke, G.; Hegemann, F.; Maidl, U. Building information modelling in mechanised shield tunnelling—A practitioner’s outlook to the near future: Building information modelling im maschinellen Schildvortrieb—Ein praxisorientierter Blick in die nähere Zukunft. Geomech. Tunn. 2018, 11, 34–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsahly, A.; Hegemann, F.; König, M.; Meschke, G. Integrated BIM-to-FEM approach in mechanised tunnelling. Geomech. Tunn. 2020, 13, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabozzi, S.; Biancardo, S.A.; Veropalumbo, R.; Bilotta, E. I-BIM based approach for geotechnical and numerical modelling of a conventional tunnel excavation. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2021, 108, 103723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinc, R.; Gabršček, D.; Česnik, J.; Žibert, M.; Hostnik, M.; Logar, J. Development of a semiautomatic parametric method for creation of an I-BIM model of a tunnel for use in FEM software. J. Adv. Transp. 2021, 2021, 8843277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.Q.; Zhu, H.M.; Ninić, J.; Zhang, Q.B. Multi-LOD BIM for underground metro station: Interoperability and design-to-design enhancement. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2022, 119, 104232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, H.C.; Liu, Y.Y.; Chang, J.F.; Chou, C.R. Application of BIM in deep excavation projects. In AIJR Proceedings; AIJR: Gujarat, India, 2022; pp. 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erharter, G.H.; Weil, J.; Bacher, L.; Heil, F.; Kompolschek, P. Building information modelling-based ground modelling for tunnel projects—Tunnel Angath/Austria. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2023, 135, 105039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Jin, Y.; Lu, H.; Shi, J. A BIM-based framework for automatic numerical modelling and geotechnical analysis of a large-scale deep excavation for transportation infrastructures. Intell. Transp. Infrastruct. 2023, 2, liad012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igwenagu, U.T.I.; Debnath, R.; Ahmed, A.A.; Alam, M.J.B. An integrated approach for earth infrastructure monitoring using UAV and ERI: A systematic review. Drones 2025, 9, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarino, A.; Valenzuela, H.; Antón, N.; Domínguez, M.; Méndez Cubillos, X.C. UAV applications for monitoring and management of civil infrastructures. Infrastructures 2025, 10, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackney, C.; Clayton, A. Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and their application in geomorphic mapping. In Geomorphological Techniques; British Society for Geomorphology: London, UK, 2015; Chapter 2, Section 1.7. [Google Scholar]
- Caprioli, M.; Trizzino, R.; Mazzone, F.; Scarano, M. Experiences of UAV surveys applied to environmental risk management. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2016, 41, 797–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casagli, N.; Frodella, W.; Morelli, S.; Tofani, V.; Ciampalini, A.; Intrieri, E.; Raspini, F.; Rossi, G.; Tanteri, L.; Lu, P. Spaceborne, UAV and ground-based remote sensing techniques for landslide mapping, monitoring and early warning. Geoenviron. Disasters 2017, 4, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, L.; Helmholz, P.; Belton, D.; Addy, N. Comparison of UAV lidar and imagery for beach monitoring. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2019, 42, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.C.; Cheng, Y.T.; Zhou, T.; Ravi, R.; Hasheminasab, S.M.; Flatt, J.E.; Troy, C.; Habib, A. Evaluation of UAV lidar for mapping coastal environments. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, E.P.; Hendricks, J.; Woodacre, K. Effectiveness of drone-based photogrammetry for on-site quantity assessment. In Proceedings of the Creative Construction Conference 2019, Budapest, Hungary, 29 June–2 July 2019; pp. 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sousa Mello, C.C.; Salim, D.H.C.; Simões, G.F. UAV-based landfill operation monitoring: A year of volume and topographic measurements. Waste Manag. 2022, 137, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspari, F.; Ioli, F.; Barbieri, F.; Belcore, E.; Pinto, L. Integration of UAV-lidar and UAV-photogrammetry for infrastructure monitoring and bridge assessment. In Proceedings of the XXIV ISPRS Congress, Nice, France, 6–11 June 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Yuan, G.; Song, L.; Zhang, H. Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) in landslide investigation and monitoring: A review. Drones 2024, 8, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noroño Sánchez, J.G. How entrepreneurs perceive technology in the digital era: From aversion to adoption. CENIIAC 2025, 1, e0002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacciuttolo, C.; Atencio, E.; Komarizadehasl, S.; Lozano-Galant, J.A. Internet of Things long-range wide-area network-based wireless sensors network for underground mine monitoring: Planning an efficient, safe, and sustainable labor environment. Sensors 2024, 24, 6971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carri, A.; Valletta, A.; Cavalca, E.; Savi, R.; Segalini, A. Advantages of IoT-based geotechnical monitoring systems integrating automatic procedures for data acquisition and elaboration. Sensors 2021, 21, 2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segalini, A.; Savi, R.; Cavalca, E.; Valletta, A.; Carri, A. Innovative application of IoT technologies to improve geotechnical monitoring tools and early warning performances. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Critical Thinking in Sustainable Rehabilitation and Risk Management of the Built Environment, Naples, Italy, 20–22 November 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, M.T.; Satyam, N.; Pradhan, B.; Alamri, A.M. IoT-based geotechnical monitoring of unstable slopes for landslide early warning in the Darjeeling Himalayas. Sensors 2020, 20, 2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Fang, L.; Sun, X.; Peng, W. 5G IoT-based geohazard monitoring and early warning system and its application. EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2021, 2021, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamperl, M.; Singer, J.; Thuro, K. A new IoT geosensor network for cost-effective landslide early warning systems. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly 2021, Online, 19–30 April 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreevidya, P.; Abhilash, C.S.; Paul, J.; Rejithkumar, G. A machine learning-based early landslide warning system using IoT. In Proceedings of the 2021 4th Biennial International Conference on Nascent Technologies in Engineering (ICNTE), Navi Mumbai, India, 15–16 January 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguz, E.A.; Depina, I.; Myhre, B.; Devoli, G.; Rustad, H.; Thakur, V. IoT-based hydrological monitoring of water-induced landslides: A case study in central Norway. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2022, 81, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hazarika, H.; Kanaya, H.; Takiguchi, O.; Murai, M.; Hidayat, M.N.; Kochi, Y. Design and deployment of an IoT-based landslide early warning system. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference and Utility Exhibition on Energy, Environment and Climate Change (ICUE), Pattaya, Thailand, 26–28 October 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharafat, A.; Tanoli, W.A.; Zubair, M.U.; Mazher, K.M. Digital twin-driven stability optimization framework for large underground caverns. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 4481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biegel, G.; Bower, N.; Castelnau, W. The Fuse platform: Integrating data from IoT and other sensors into an industrial spatial digital twin. In Proceedings of the ISPRS TC IV Mid-Term Symposium “Spatial Information to Empower the Metaverse”, Fremantle, Perth, Australia, 22–25 October 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepasgozar, S.M. Differentiating digital twin from digital shadow: Elucidating a paradigm shift to expedite a smart, sustainable built environment. Buildings 2021, 11, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgkinson, J.H.; Elmouttie, M. Cousins, siblings and twins: A review of the geological model’s place in the digital mine. Resources 2020, 9, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmo, D.; Stead, D. Disrupting rock engineering concepts: Is there such a thing as a rock mass digital twin and are machines capable of learning rock mechanics? In Proceedings of the Slope Stability 2020: International Symposium on Slope Stability in Open Pit Mining and Civil Engineering, Perth, Australia, 12–14 May 2020. [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Zhang, T.; Deng, X.; Liu, Z.; Tan, J. Digital twin: A state-of-the-art review of its enabling technologies, applications and challenges. J. Intell. Manuf. Spec. Equip. 2021, 2, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haryono, I.S.; Saw, A.L.; Lee, S.W.; Wong, L.C. Digital twin for geotechnical engineering applications. In Proceedings of the HKIE Geotechnical Division 41st Annual Seminar: Adapt to Challenges, Create to Thrive (GDAS 2021), Hong Kong, China, 18 May 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, R.; Mak, D.; Wei, A.; Yan, J.J.; Pan, Q.H. Integration of BIM and other innovative technologies to enhance the sustainable design of geotechnical works. In Proceedings of the HKIE Geotechnical Division 42nd Annual Seminar: Smart Geotechnics for a Sustainable Future (GDAS 2023), Hong Kong, China, 21 April 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Firoozi, A.A.; Firoozi, A.A. Smart geotechnics: Enhancing infrastructure resilience with IoT and AI. J. Civ. Eng. Urban. 2024, 14, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salzgeber, H.; Ernst, M.; Schneiderbauer, L.; Flora, M. From digital model to digital twin in tunnel construction. Civ. Eng. Des. 2024, 6, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivadeneira-Moreira, J.C. Implementación de gemelos digitales probabilísticos en el monitoreo de infraestructuras geotécnicas. Rev. Cient. Cienc. Método 2024, 2, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.; Wu, S.; Li, Y.; Guo, Q. Digital twins’ application for geotechnical engineering: A review of current status and future directions in China. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 8229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghalzadeh Shishehgarkhaneh, M.; Keivani, A.; Moehler, R.C.; Jelodari, N.; Roshdi Laleh, S. Internet of Things (IoT), Building Information Modeling (BIM), and Digital Twin (DT) in Construction Industry: A Review, Bibliometric, and Network Analysis. Buildings 2022, 12, 1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersoz, A.B.; Pekcan, O.; Altun, M.; Teke, T.; Aydogmus, O. Utilizing digital technologies for rapid damage assessment and reconnaissance: The February 6, 2023 Kahramanmaraş–Türkiye earthquakes (Mw 7.7 and Mw 7.6). Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2024, 22, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajo, A.H.; Akyuz, G.A. Digital transformation implementation challenges in Turkish industrial enterprises. Int. J. Innov. Technol. Manag. 2023, 20, 2350037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koseoglu, O.; Keskin, B.; Ozorhon, B. Challenges and enablers in BIM-enabled digital transformation in mega projects: The Istanbul new airport project case study. Buildings 2019, 9, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yayla, A.; Kayakutlu, G.; Kayalica, M.O. Life cycle assessment with BIM towards sustainable energy policy-making: The case of urban transformation in Istanbul. Int. J. Sustain. Constr. Eng. Technol. 2021, 12, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Hoogen, A.; Fashoro, I.; Calitz, A.P.; Luke, L. A digital transformation framework for smart municipalities. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feroz, A.K.; Zo, H.; Chiravuri, A. Digital transformation and environmental sustainability: A review and research agenda. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Trujillo, A.M.; Gonzalez-Perez, M.A. Digital transformation as a strategy to reach sustainability. Smart Sustain. Built Environ. 2022, 11, 1137–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.K. Exploring the symbiotic relationship between digital transformation, infrastructure, service delivery, and governance for smart sustainable cities. Smart Cities 2024, 7, 806–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Ghrbeia, S.; Alzubi, A. Building micro-foundations for digital transformation: A moderated mediation model of the interplay between digital literacy and digital transformation. Sustainability 2024, 16, 3749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydinoglu, A.C. Modelling, encoding and transforming of open geographic data to examine interoperability between GIS applications. Geocarto Int. 2016, 31, 446–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doe, R.; Kaur, K.; Selway, M.; Stumptner, M. Ecosystem Interoperability for the Architecture, Engineering, Construction & Operations (AECO) Sector. J. Inf. Technol. Constr. 2024, 29, 347–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarigul, F.H.; Gunaydin, H.M. Integrated BIM, GIS and interoperable digital technologies in lifecycle management of building construction projects: Systematic literature review. Smart Sustain. Built Environ. 2025. ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlato, M.; Binni, L.; Durmus, D.; Gatto, C.; Giusti, L.; Massari, A.; Mirarchi, C. Digital platforms for the built environment: A systematic review across sectors and scales. Buildings 2025, 15, 2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayinla, K.O.; Adamu, Z. Bridging the digital divide gap in BIM technology adoption. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2018, 25, 1398–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcan-Deniz, G.; Ozorhon, B.; Kaya, O.C. Building Information Modeling (BIM) Integration in Developing Countries: An In-Depth Examination of Adoption Factors from Public Clients’ Perspectives. Int. J. Archit. Comput. 2025, 23, 481–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Arancibia, J.; Hochstetter-Diez, J.; Bustamante-Mora, A.; Sepúlveda-Cuevas, S.; Albayay, I.; Arango-López, J. Navigating digital transformation and technology adoption: A literature review from small and medium-sized enterprises in developing countries. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, Y.; Gharineiat, Z.; Karimi, A.A.; McDougall, K.; Rossi, A.; Gonizzi Barsanti, S. Digital twin technology in built environment: A review of applications, capabilities and challenges. Smart Cities 2024, 7, 2594–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazrat, M.A.; Hassan, N.M.S.; Chowdhury, A.A.; Rasul, M.G.; Taylor, B.A. Developing a skilled workforce for future industry demand: The potential of digital twin-based teaching and learning practices in engineering education. Sustainability 2023, 15, 16433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumsar, H.; Çelik, S.B.; Kaya, M. Denizli il merkezi yerleşim alanının jeolojik, jeoteknik kent bilgi sistemi (JEO-KBS) [Geological and geotechnical urban information system (GEO-UIS) of the settlement area in Denizli city center]. Pamukkale Univ. J. Eng. Sci. 2004, 10, 25–31. [Google Scholar]
- Kahriman, T.D.A.; Bozdoğan, H.M. İstanbul-Yeniköy yöresindeki bir linyit açık ocağının bilgisayar destekli modellenmesi [Computer-aided modeling of a lignite open-pit mine in the Istanbul–Yeniköy region]. Istanb. Yerbilim. Derg. 2006, 19, 157–167. [Google Scholar]
- Garagon Doğru, A.; Toz, G. Yer bilimlerinde servis odaklı mimari ile coğrafi bilgi sistemi oluşturulması [Development of a geographic information system in earth sciences using service-oriented architecture]. ITU J. Sci. Eng. Ser. D 2011, 8, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Demirci, A.; Karakuyu, M. Afet yönetiminde coğrafi bilgi teknolojilerinin rolü [The role of geographic information technologies in disaster management]. Dogu Geogr. Rev. 2011, 9, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Poyraz, S.A.; Kalafat, D. Sismoloji’de CBS uygulamaları [GIS applications in seismology]. Jeofizik Derg. 2012, 26, 47–58. [Google Scholar]
- Kurnaz, T.; Ramazanoğlu, Ş. Yerleşime uygunluğun coğrafi bilgi sistemleri (CBS) ile sorgulanması, Esenler (İstanbul) örneği [Assessment of settlement suitability using geographic information systems (GIS): The case of Esenler, Istanbul]. Sak. Univ. J. Sci. 2014, 18, 171–182. [Google Scholar]
- Akyol, E.; Alkan, M.; Akgündüz, H. Determining settlement suitability by geographic information systems and analytical hierarchy process. Pamukkale Univ. J. Eng. Sci. 2016, 21, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalçın, C. Tematik coğrafi haritalar ile Edirne’nin sanayi ve Ar-Ge yetenek envanterinin oluşturulması [Creating an inventory of Edirne’s industry and R&D capabilities using thematic geographic maps]. J. Product. 2017, 2, 121–133. [Google Scholar]
- Tün, M.; Pekkan, E.; Mutlu, S. Depremlerde gözlenen etkilerin gönüllü katılımıyla hızlı bir şekilde toplanması [The Rapid collection of observed in the Earthquake by Witnesses]. Eskişehir Tech. Univ. J. Sci. Technol. B-Theor. Sci. 2018, 6, 73–86. [Google Scholar]
- Bol, E.; Sert, S.; Ozocak, A. Coğrafi bilgi sistemlerinin jeoteknik alanında değişken zemin ortamında uygulaması [Application of geographic information systems in geotechnical engineering under variable ground conditions]. Acad. Perspect. Procedia 2018, 1, 1290–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keleş, A.; Keleş, M.K. İnşaat sektöründe kullanımı artan bilgisayar yazılımları ve bilgi teknolojilerinin irdelenmesi [Examination of Computer Software and Information Technologies Whose Usage Increased in the Construction Industry]. El-Cezerî J. Sci. Eng. 2018, 5, 610–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erturan, İ.; Ergin, E. Dijital Denetim ve Dijital Ikiz Yöntemi [Digital Auditing and Digital Twin Method]. World Account. Sci. 2018, 20, 810–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceylan, E.Z. Dijital ikizler ve inşaat sektöründeki yeri [Digital twins and their place in the construction sector]. Yapı Bilgi Model. 2019, 1, 53–61. [Google Scholar]
- Kun, M.; Güler, Ö. İnsansız görüntüleme sistemleri ile elde edilen sayısal yüzey modellerinin mermer madenciliğinde kullanımı [The Usage of Digital Surface Models Obtained by Unmanned Imaging Systems in Marble Mining]. Dokuz Eylül Univ. Fac. Eng. J. Sci. Eng. 2019, 21, 1005–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Küçük, K.; Bayılmış, C.; Sönmez, A.F.; Kaçar, S. IoT Teknolojilerini Kullanan Afet Sonrası Yönetim Sistemi [Post-Disaster Management System Using IoT Technologies]. Acad. Platf. J. Eng. Sci. 2019, 7, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Erdik, M.; Gökuç, Y.T. Türk yapı sektöründe yapı bilgi modellemesinin adaptasyonu [Adaptation of building information modeling in the Turkish construction sector]. J. Balikesir Univ. Inst. Sci. Technol. 2020, 22, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memiş, L.; Babaoğlu, C. Acil durum ve afet yönetiminde süreç yaklaşımı ve teknoloji [Technology and Stages Approach In Emergency and Disaster Management]. J. Fac. Econ. Adm. Sci. 2020, 13, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Demirbilek, M.; Demirbilek, S.Ö. Jeoloji mühendisliği saha çalışmaları için yeni bir model: Gezgin satıcı problemi ve uygulaması [A New Model for Field Studies of Geological Engineering: Travelling Salesman Problem and Application]. Int. J. Manag. Inf. Syst. Comput. Sci. 2021, 5, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alver, O.; Sezen, A.; Eseller-Bayat, E.E. TBDY 2018’e göre geoteknik tasarım: Sıvılaşma ve yapı–kazık–zemin etkileşimi analizleri [Geotechnical Design with Respect to TBDY-2018: Liquefaction and Soil-Pile -Structure Interaction Analyses]. Tech. J. Turk. Chamb. Civ. Eng. 2021, 32, 11197–11226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozkurt, O.; Erenoğlu, R.C. Doğal afetlerin mühendislik yapıları üzerindeki etkilerinin yer bilimleri tabanlı disiplinlerarası bir yaklaşımla erken uyarı sistemi tasarımı [Early Warning System Design with an Earth Science Based Interdisciplinary Approach for the Effects of Natural Disasters on Engineering Structures]. ÇOMÜ LJAR 2021, 2, 77–91. [Google Scholar]
- Şahin, V.; Yılmaz, H.M. Hacim hesaplarında insansız hava aracı (İHA) verilerinin kullanılabilirliğinin araştırılması [Investigation of the usability of unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) data in volume calculations]. Turk. Unmanned Aer. Veh. J. 2021, 3, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uygunoğlu, T.; Kılçık, F.M.; Topçu, İ.B. Nesnelerin internetinin (IoT) inşaat mühendisliğindeki rolü: Gömülü sensör kullanımı [The role of the Internet of Things (IoT) in civil engineering: Use of embedded sensors applications]. Int. J. 3D Print. Technol. Digit. Ind. 2021, 5, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acar, M.C.; Kaya, D. Geographic information system approach in evaluating the geotechnical properties of soils: A case study of Oymaağaç in Kayseri. J. Fac. Eng. Archit. Gazi Univ. 2023, 38, 1079–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delibalta, M.S. Türkiye madencilik sektöründe döngüsel ekonomi ve dijitalleşme uygulamaları [Circular economy and digitalization practices in the mining sector of Turkey]. Nigde Omer Halisdemir Univ. J. Eng. Sci. 2022, 11, 1121–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torlak, S.; Anıktar, S.; Köymen, E. İstanbul geneli altyapı elemanlarının artırılmış gerçeklikle görüntülenmesinin şehircilik ve kent planlamasına etkisi [The Effect of Imaging Infrastructure Elements with Augmented Reality on Urban and Urban Planning in General of Istanbul]. Bartin Univ. Int. J. Nat. Appl. Sci. 2022, 5, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coşandal, M.; Partigöç, N.S. Risk Yönetiminde Bilgi Teknolojilerinin Rolü ve Önemi: Türkiye Örneği [The Role and Importance of Information Technologies in Risk Management: The Case of Turkey]. Resilience 2022, 6, 145–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciritcioğlu, M.G.; Buğday, E. Assessment of Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Use Opportunities in Forest Road Project (Düzce Sample). J. Bartin Fac. For. 2022, 24, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aladağ, H. Türk inşaat sektöründe dijital dönüşüm uygulamaları üzerine bir araştırma [A Research on Digital Transformation Executions in Turkish Construction Industry]. J. Eng. Sci. Des. 2022, 10, 973–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gökçe, H.B.; Subaşı, S.; Kızılay, E.; Hacıcaferoğlu, A.E.; Arıoğlu, S.Ö. Demiryollarında Akıllı Ulaşım Sistemi Çözümleri için Bir Öneri: Dijital Demiryolu [A Proposal for Intelligent Transportation System Solutions in Railways: Digital Railway]. Railw. Eng. 2023, 18, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dereli, C.K.; Çay, R.D.S. Sürdürülebilir yağmur suyu yönetimi üzerine bir inceleme: Edirne örneği [An Examination on Sustainable Rainwater Management: The Case of Edirne]. Düzce Univ. Fac. For. J. For. 2023, 19, 97–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akdeniz, E.; Ofluoğlu, S. Metro istasyonlarında sürdürülebilir tesis yönetimi: BIM destekli dijital ikiz uygulamaları [Sustainable facility management in metro stations: BIM-supported digital twin applications]. Yapı Bilgi Model. 2023, 5, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbay, R.B.; Ökten, B.B.; Üstüner, Y.A. Şantiyelerde bilgi modellemesi ve dijital teknolojilerin kullanımı [The use of information modeling and digital technologies on construction sites]. AJIT-E Acad. J. Inf. Technol. 2023, 14, 298–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eryaman, H.; Akun, E. Yapılarda Yüksekte Çalışma İş Güvenliği Denetimini Kolaylaştırmak İçin Genişletilmiş Gerçeklik ve Yapay Zekânın Entegrasyonu Modeli [An integration model to facilitate occupational safety inspection through augmented reality and artificial intelligence for working at high locations in buildings]. Turk. J. Civ. Eng. 2023, 34, 71–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, Y.; İlerisoy, Z.Y.; Özev, B. Yapı sektöründe dijital dönüşümün 9 yerel yönetim üzerinden karşılaştırmalı analizi [Comparative Analysis of Digital Transformation in the Construction Sector through 9 Local Governments]. PLANARCH-Des. Plan. Res. 2024, 8, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çınar, M.; Aslan, H. Geoteknik uygulamaların yapı bilgi modellemesi ile IFC tabanlı modellenmesi [IFC-based modeling of geotechnical applications with building information modeling]. Artium 2024, 12, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Önal, G.; Fidan, D.; Ulvi, A. Açık Ocak Maden Sahalarının İHA Teknolojisi Kullanılarak Tespiti ve Değerlendirilmesi [Detection and Assessment of Open-Pit Mining Sites Using UAV Technology]. Turk. J. Photogramm. 2024, 6, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiğit, A.Y.; Kaya, Y. Açık Maden Ocağındaki Stok/Pasa Yığınının Hacim Hesaplamasında GNSS/CORS ve İHA Ölçümlerinin Karşılaştırıldığı Bir Çalışma Örneği [A Case Study Comparing GNSS/CORS and UAV Measurements for Volume Calculation of Stockpile in an Open Pit Mine]. Turk. Unmanned Aer. Veh. J. 2024, 6, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozkurt, G.; Ersoy, S.; Yasa, E. Yapı Üretim Süreçlerinde BIM ve VR Uygulamalarının Entegrasyonunun Değerlendirilmesi [Evaluation of integration of BIM and virtual reality applications in building production processes]. Turk. J. Civ. Eng. 2024, 35, 117–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedur, C.; Erbaş, İ. Yapım sektöründe dijital ikiz kavramının yapı yaşam döngüsü kapsamında SWOT analizi ile değerlendirilmesi [Evaluation of the Digital Twin Concept in the Construction Industry with SWOT Analysis within the Scope of the Building Life Cycle]. PLANARCH-Des. Plan. Res. 2024, 8, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekinci, C.E.; Aydın, Ö. Yapıların dijital ikizleri: Kapsamlı bir genel bakış [Digital twins of structures: A comprehensive overview]. Technol. Appl. Sci. 2025, 20, 13–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awange, J.; Kiema, J. Fundamentals of GIS. In Environmental Geoinformatics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Onstein, E. State-of-the-art geospatial information processing in NoSQL databases. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TÜV. ISO 19650 for Building Owners and Operators. Available online: https://www.tuvsud.com/en-us/industries/real-estate/buildings/iso19650 (accessed on 15 September 2025).
- Satyanaga, A.; Aventian, G.D.; Makenova, Y.; Zhakiyeva, A.; Kamaliyeva, Z.; Moon, S.W.; Kim, J. Building information modelling for application in geotechnical engineering. Infrastructures 2023, 8, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Chen, J.; Chen, G.; Wu, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Chen, B.; Ke, W.; Huang, J. Development of data integration and sharing for geotechnical engineering information modeling based on IFC. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2021, 2021, 8884864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodian, M.; Shahrivar, F.; Setunge, S.; Mazaheri, S. Development of Digital Twin for Intelligent Maintenance of Civil Infrastructure. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yitmen, I.; Alizadehsalehi, S.; Akıner, İ.; Akıner, M.E. An adapted model of cognitive digital twins for building lifecycle management. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ay, D.; Demires Ozkul, B. The strange case of earthquake risk mitigation in Istanbul. City 2021, 25, 67–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, G.; Akcamete, A.; Demirors, O. BIM-CAREM: Assessing the BIM capabilities of design, construction and facilities management processes in the construction industry. Comput. Ind. 2023, 147, 103861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrmann, A.; Forster, C.; Liebich, T.; König, M.; Tulke, J. Germany’s governmental BIM initiative–The bim4infra2020 project implementing the BIM roadmap. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computing in Civil and Building Engineering, Cham, Switzerland, 29 June–1 July 2020; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 452–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. Department of Economic and Social Affairs–Sustainable Development. 2015. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/goals (accessed on 15 September 2025).
- Behera, P.; Behera, B.; Sethi, N.; Handoyo, R.D. What drives environmental sustainability? The role of renewable energy, green innovation, and political stability in OECD economies. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2024, 31, 761–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
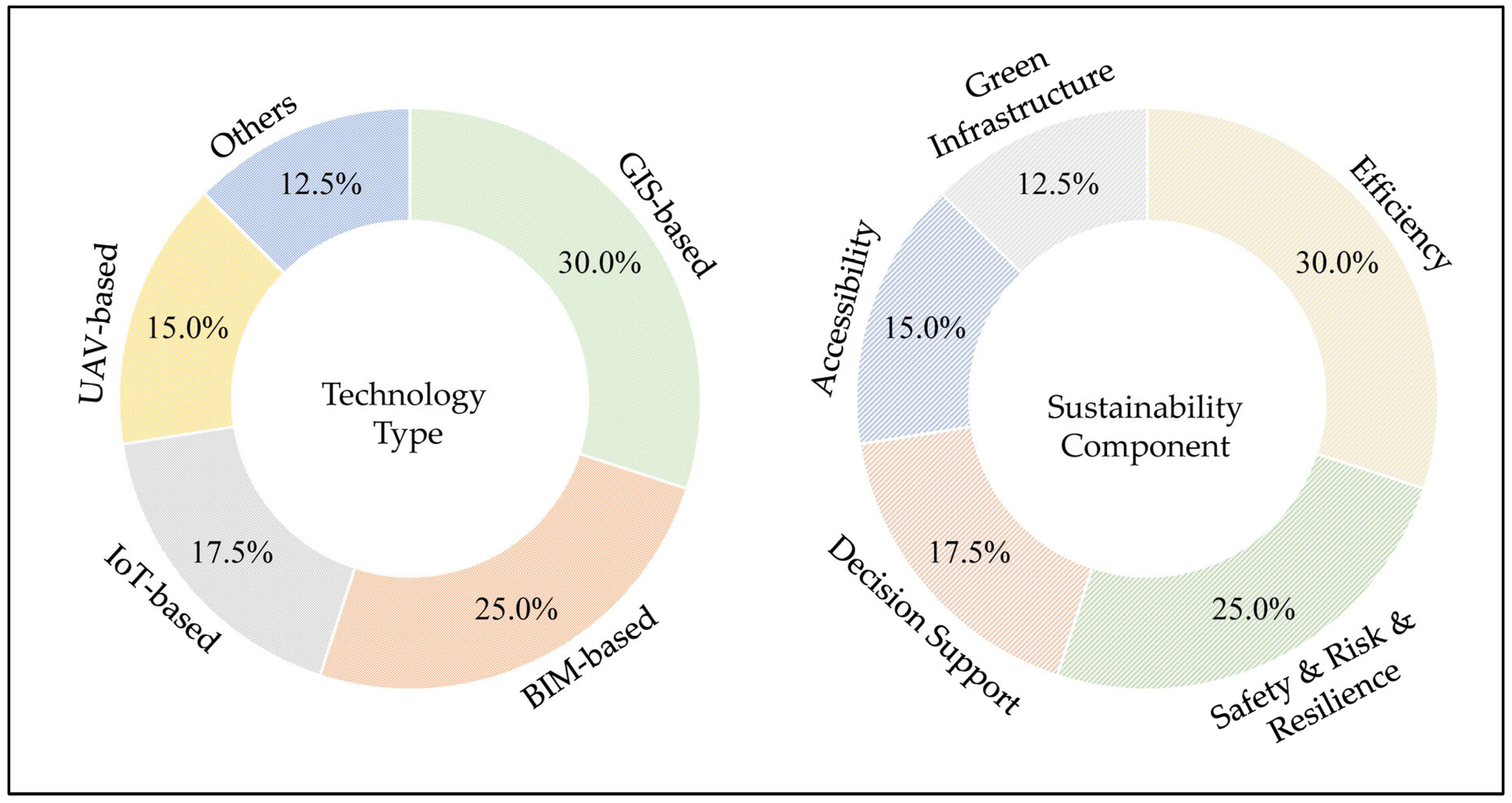
| Study | Application Area | Technologies Integrated | Key Outputs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brabb [11] | Hazard mapping for regional planning | GIS | Seismic hazard zoning |
| Jibson et al. [12] | Seismic landslide hazard assessment | GIS + DEMs + Landslide inventories | Probabilistic risk maps |
| Sakellariou and Ferentinou [13] | Landslide hazard | GIS | Slope stability & Hazard assessment |
| Kunapo et al. [14] | Geotechnical online platform | GIS + Relational DB | Borelog generation & Online analysis |
| Westen et al. [15] | Landslide mapping & Risk assessment | GIS + DEM + LiDAR + Photogrammetry | Landslide susceptibility mapping |
| Khan et al. [16] | 3D modeling & Safety zoning | BIM + GIS | Subsurface modeling & Zoning maps |
| Kadhim et al. [17] | Digital geotechnical mapping | GIS + GPS + Remote Sensing | Maps of bearing capacity & Shear strength |
| Leinauer et al. [18] | Rock slope monitoring & Early warning | GIS + Real-time monitoring | Monitoring & Early warning system |
| Vidal-Páez et al. [19] | Landslide susceptibility mapping | GIS + Fuzzy Logic | Landslide susceptibility mapping |
| Singh [20] | GIS-based data visualization | GIS | Visualization & Integration |
| Player [21,22] | Data communication & Visualization | GIS | Data integration & Stakeholder communication |
| Study | Application Area | Technologies Integrated | Key Outputs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Morin et al. [25] | Tunnel construction | BIM | Collaborative geotechnical workflows |
| Stelzer et al. [26] | Metro & Tunnel construction | BIM + Numerical analysis | Design optimization & Risk minimization |
| Stascheit et al. [27] | Tunnel construction | BIM +3D modeling + Web-based integration | Data management & Design |
| Alsahly et al. [28] | Tunnel & Metro infrastructure | BIM-to-FEM | Streamlined geotechnical & Structural analysis |
| Fabozzi et al. [29] | Tunnel construction | BIM-to-FEM & FEM-to-BIM | Construction scheduling & Time management |
| Klinc et al. [30] | Tunnel construction | BIM-to-FEM + Parametric modeling | Parametric modeling & FEM analysis |
| Huang et al. [31] | Metro infrastructure | Multi-level BIM + IFC interoperability | Numerical modeling & Heuristic workflows |
| Hung et al., [32] | Deep excavation & Metro | 3D/4D BIM + Simulation | Clash detection & Project simulation |
| Erharter et al. [33] | Tunnel construction | BIM ground models + IFC/DAUB alignment | Structured geotechnical data management |
| Shi et al. [34] | Deep excavation | BIM-to-FEM + Python scripting | Automatic modeling & Data repository |
| Study | Application Area | Technologies Integrated | Key Outputs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hackney and Clayton [37] | Pro-glacial topography mapping | UAV + RGB + SfM | High-resolution topographic maps |
| Caprioli et al. [38] | Coastal landslide monitoring | Hexacopter UAV + RGB + SfM + GIS | Landslide hazard mapping |
| Casagli et al. [39] | Landslide mapping & Risk management | UAV-DP + TLS GB-InSAR + Infrared | Landslide monitoring & Risk assessment |
| Shaw et al. [40] | Beach monitoring | DJI UAVs + SfM LiDAR | Shoreline & Change assessment |
| Lin et al. [41] | Coastal erosion monitoring | RGM + LiDAR + DJI M600 | Coastal erosion monitoring |
| Small et al. [42] | Construction site surveying | UAV + RGB + BIM | Construction site volume & Area estimation |
| Mello et al. [43] | Landfill monitoring | UAV + GCPs | Landfill volume & Surface monitoring |
| Gaspari et al. [44] | Bridge/infrastructure monitoring | UAV-LiDAR + SfM + TLS | Bridge/infrastructure inspection |
| Sun et al. [45] | Landslide mapping & Monitoring | UAV + RGB + LiDAR + SAR + GNSS + ML | Landslide hazard mapping & Monitoring |
| Study | Application Area | Technologies Integrated | Key Outputs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Segalini et al. [49] | Rockfall & Structural tilt | Mechanical triggers + Web visualization | Rockfall barrier monitoring & Building tilt alerts |
| Abraham et al. [50] | Landslide | MEMS tilt + VWC sensors + Wireless battLiry modules | Slope stability tracking & Early warnings |
| Li et al. [51] | Landslide monitoring | GNSS + 5G + WSN Groundwater sensors | Multi-level LEWS & Displacement detection |
| Gamperl et al. [52] | Informal settlements | MEMS tilt + LoRa + Groundwater sensors | Low-cost open-source IoT & LEWS for urban zones |
| Sreevidya et al. [53] | ML-based early warnings | Geophysical sensors + ML integration | Slope failure prediction & Accuracy |
| Oguz et al. [54] | Water-induced landslides | VWC sensors + 4G+ Matric suction + piezometers | Real-time pore pressure data & Alert calibration |
| Liu et al. [55] | Embankment slopes | Portable sensors + Mobile routers | All warnings before landslide & Rainfall-triggered detection |
| Study | Application Area | Technologies Integrated | Key Outputs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hodgkinson and Elmouttie [59] | Mining slopes & Geohazards | GPR + LIBS + MOOSE + ML | Digital mining & Slope monitoring |
| Elmo and Stead [60] | Rock slopes & Massifs | IoT + Smart sensors + Numerical simulation | Framework & Slope monitoring |
| Hu et al. [61] | Underground infrastructure | CAD + IoT + 5G + Image recognition | Review of enablers & System interoperability |
| Haryono et al. [62] | Deep excavation | Digital Shadow (BIM only) | Static data flow & Digital coordination |
| Cheng et al. [63] | Tunnel & Slope design | BIM + Handheld LiDAR + UAV + Autodesk tools | Real-time predictive & Sustainable design |
| Firoozi and Firoozi [64] | Tunnels & Bridges | IoT sensors + ML algorithms | Maintenance & Resilience assessment |
| Salzgeber et al. [65] | Tunnel construction | Autodesk Services + IoT sensors | Real-time communication & Data integration |
| Rivadeneira-Moreira [66] | Dams & Tunnels | Bayesian inference + ML + Stochastic models + LiDAR | Predictive monitoring & Real-time risk assessment |
| Tan et al. [67] | General Geotechnical | 3D models + IoT–AI + Lifecycle platforms + | Review of status & Future directions |
| Study | Application Area | Technologies Integrated | Key Outputs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kumsar et al. [87] | Urban geotechnical systems | GIS + DBMS | Structured urban geotechnical database |
| Kahriman and Bozdoğan [88] | Mining | GIS | Mine planning & Data management |
| Garagon and Toz [89] | Geosciences | GIS | Service-oriented GIS & Data sharing |
| Demirci and Karakuyu [90] | Disaster management | GIS + RS | Disaster monitoring & Planning |
| Poyraz and Kalafat [91] | Seismology | GIS | Integrated seismic data & Rapid response |
| Kurnaz and Ramazanoğlu [92] | Settlement suitability | GIS | Risk evaluation & Suitability mapping |
| Akyol et al. [93] | Geotechnical | GIS + AHP | Decision accuracy |
| Yalçın [94] | Industrial inventory | GIS (open source) | Planning & Risk assessment |
| Tün et al. [95] | Disaster management | GIS + Mobile apps | Rapid response & Data integration |
| Bol et al. [96] | Geotechnical assessment | GIS + MapInfo | Decision Support & Efficiency |
| Keleş and Keleş [97] | Construction industry | BIM + GIS + UAV + IoT | Visualization & Design & Management |
| Erturan and Engin [98] | Construction engineering | Digital twin | Efficiency & Process digitalization |
| Ceylan [99] | Construction sector | Digital Twin | Guidance system |
| Kun and Güler [100] | Mining | UAV + Photogrammetry | Efficiency & Waste reduction |
| Küçük et al. [101] | Disaster management | IoT + Fuzzy logic | Building damage & Efficiency |
| Erdik et al. [102] | Construction | BIM | Barriers & Drivers |
| Memiş and Babaoğlu [103] | Disaster & Management | GIS + UAVs + IoT sensors + VR/AR | Process improvement |
| Demirbilek and Demirbilek [104] | Hydrogeology | Python + CPLEX | Route optimization & Cost reduction |
| Alver et al. [105] | Geotechnical Design | Deepsoil + SAP2000 | Earthquake Resilience & Accuracy |
| Bozkurt and Erenoğlu [106] | Railways | IoT + Cloud | Early warning & Monitoring |
| Şahin [107] | Construction & Volume analysis | UAV + GPS | High-accuracy |
| Uygunoğlu et al. [108] | Structural monitoring | IoT | Real-time monitoring & Extended service life |
| Acar and Özdemir [109] | Soil evaluation | GIS + GPS | Urban planning& Disaster preparedness |
| Delibalta [110] | Mining | IT–OT + Smart mining | Resource efficiency& Sustainability |
| Torlak et al. [111] | Infrastructure visualization | AR + GPR | Planning & Accessibility |
| Coşandal and Partigöç [112] | Urban risk management | IoT + GIS + AI + RS | Urban Resilience & Risk reduction |
| Ciritcioğlu et al. [113] | Road design | UAV + GIS + DEM/DTM | Accurate calculations & Planning efficiency |
| Aladağ [114] | Construction industry | BIM | Quality management& Communication |
| Gökçe et al. [115] | Railways | IoT + AI + RFID + Sensors | Efficiency & Safety & Sustainability |
| Dereli and Çay [116] | Infrastructure | GIS + Meteorological SW | Risk reduction & Green infrastructure |
| Akdeniz and Ofluoğlu [117] | Metro stations | Digital Twin | Energy Efficiency & Sustainability |
| Akbay et al. [118] | Construction sites | BIM + VR/AR + Laser scanning | Collaboration& Efficiency |
| Eryaman and Akün [119] | Construction safety | BIM + AR + AI + UAV + VR | Safety & Real-time monitoring |
| Baran et al. [120] | Governance | BIM + GIS | Adoption |
| Çınar and Aslan [121] | Geotechnical modeling | BIM + SketchUp + PLAXIS | Integrated modeling & Risk reduction |
| Önal et al. [122] | Mining | UAV + GIS + Netcad | Monitoring & Safety & Efficiency |
| Yiğit and Kaya [123] | Mining | UAV + Photogrammetry | Accuracy & Cost savings |
| Bozkurt et al. [124] | Building production | BIM + VR | Improved collaboration & Cost barrier |
| Bedur and Erbaş [125] | Construction | Digital Twin | Lifecycle management & Quality |
| Ekinci [126] | Architecture & Construction | Digital Twin + BIM + IoT + AI/ML | Comprehensive overview & Future trends |
| Technology | Current Usage | Barriers | Opportunities |
|---|---|---|---|
| GIS | Widely used in geotechnical disaster management | Data integration & Standardization | Decision support & Rapid response |
| BIM | Growing in construction | High cost & Skill gaps & Data integration | Lifecycle management & Sustainability & Stakeholder engagement |
| UAV | Increasing use in construction | Initial investment & Training needs | High accuracy & Improved safety & Cost savings |
| IoT | Emerging in safety, risk management, and optimization | Data security & System integration & Expertise gaps | Predictive maintenance & Efficiency & Real-time monitoring |
| Digital Twin | Applied in safety and visualization | Hardware/software costs & Training requirements | Enhanced learning & Improved safety & Immersive visualization |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akbas, M. Sustainable Digital Transformation in Geotechnical-Related Engineering Disciplines: An Integrated Framework for Türkiye. Sustainability 2025, 17, 9153. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17209153
Akbas M. Sustainable Digital Transformation in Geotechnical-Related Engineering Disciplines: An Integrated Framework for Türkiye. Sustainability. 2025; 17(20):9153. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17209153
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkbas, Merve. 2025. "Sustainable Digital Transformation in Geotechnical-Related Engineering Disciplines: An Integrated Framework for Türkiye" Sustainability 17, no. 20: 9153. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17209153
APA StyleAkbas, M. (2025). Sustainable Digital Transformation in Geotechnical-Related Engineering Disciplines: An Integrated Framework for Türkiye. Sustainability, 17(20), 9153. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17209153






