Geochemical Baseline, Pollution Evaluation, and Source Apportionment of Topsoil Heavy Metals in Eastern Yongqiao District of Suzhou City, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
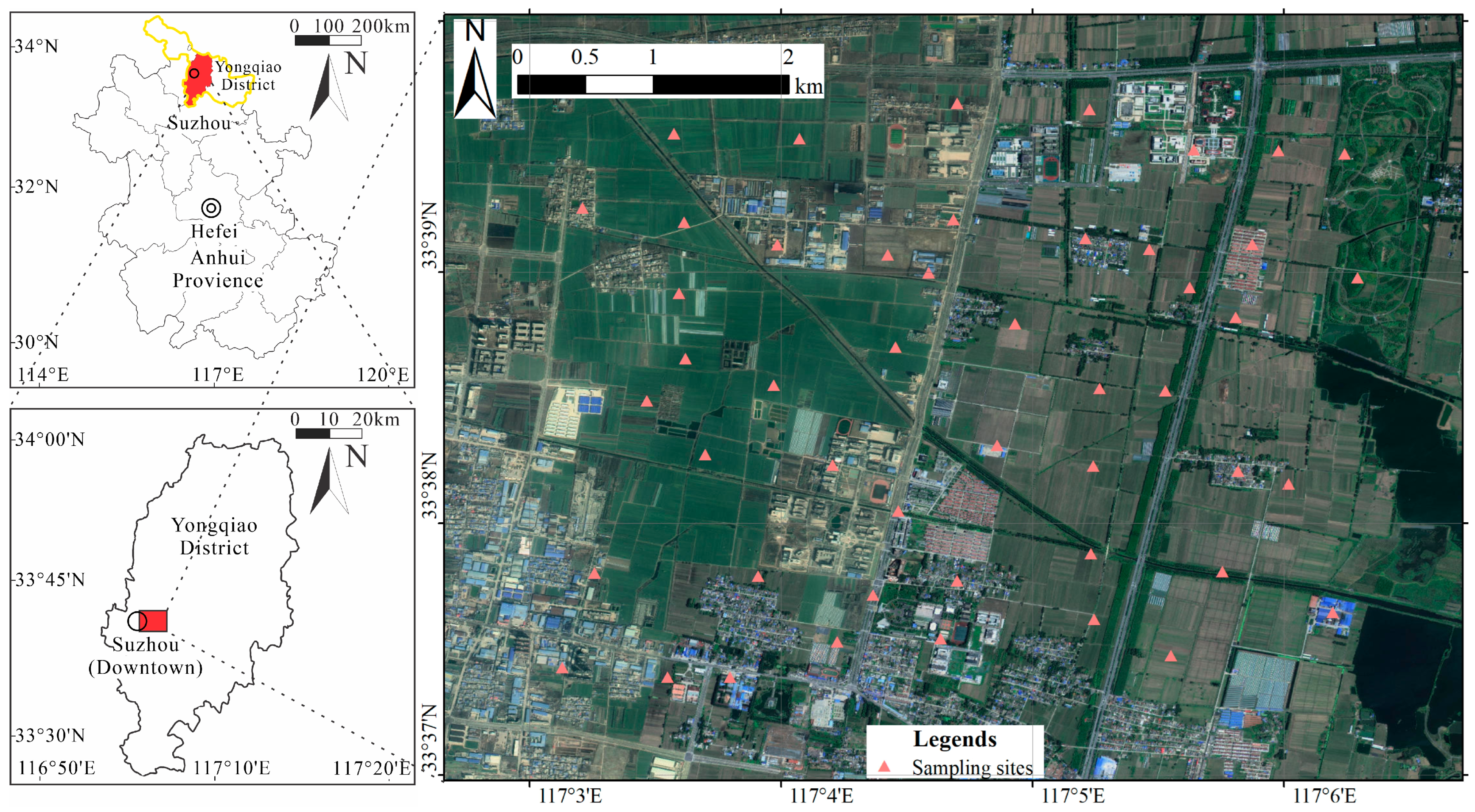
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection and Testing
2.3. Evaluation Method
2.3.1. Assessment Method of Geochemical Baseline
Pollution Assessment of Heavy Metals Based on Igeo
Geostatistical Analysis by Cumulative Frequency Curves
2.3.2. Nemerow Comprehensive Index
2.3.3. Human Health Risk Assessment
2.3.4. Pollution Source Resolution by APCS-MLR
2.4. Data Processing and Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
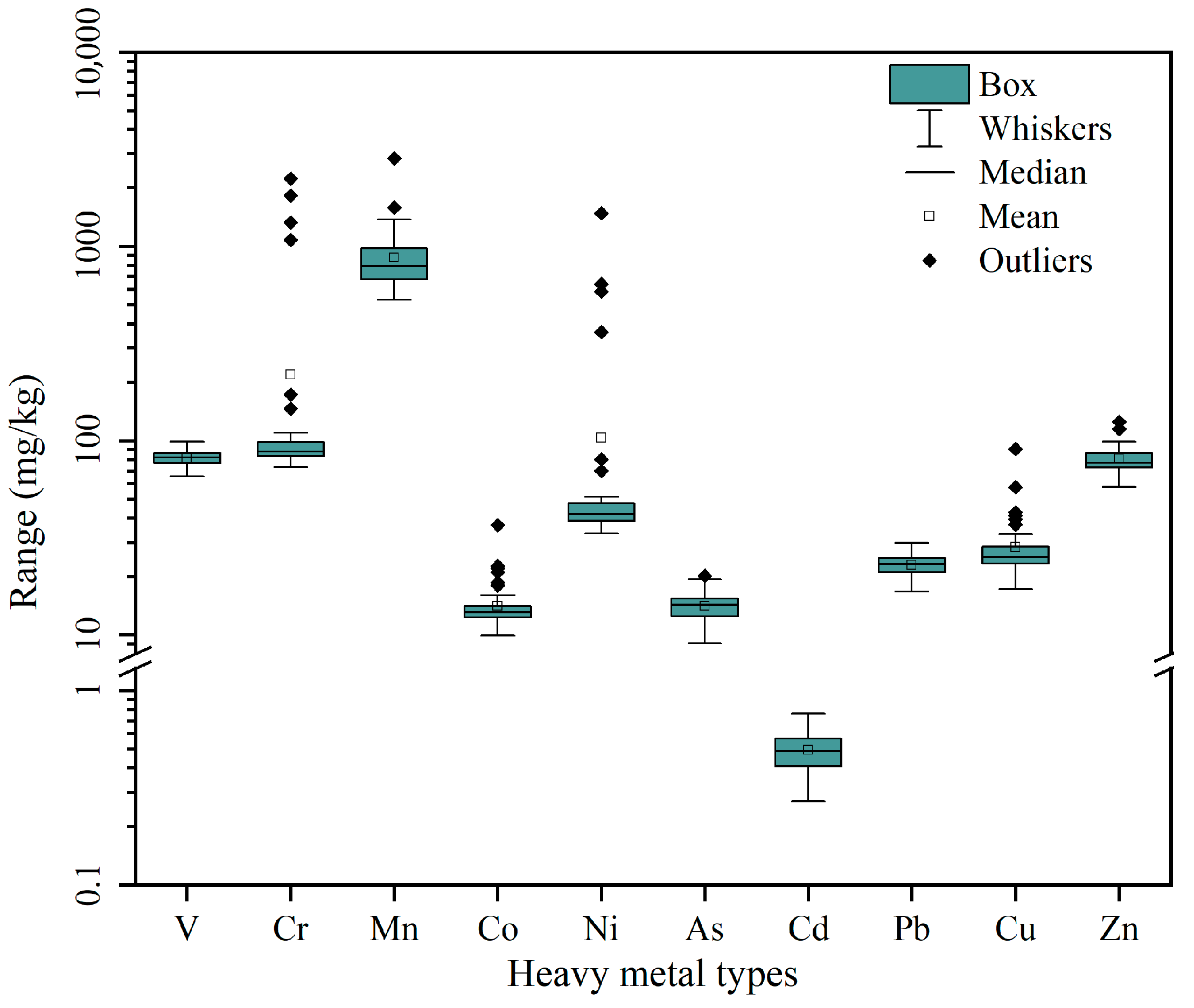
3.1. Descriptive Statistics
3.2. Assessment of Geochemical Baseline
3.3. Heavy Metal Pollution Evaluation
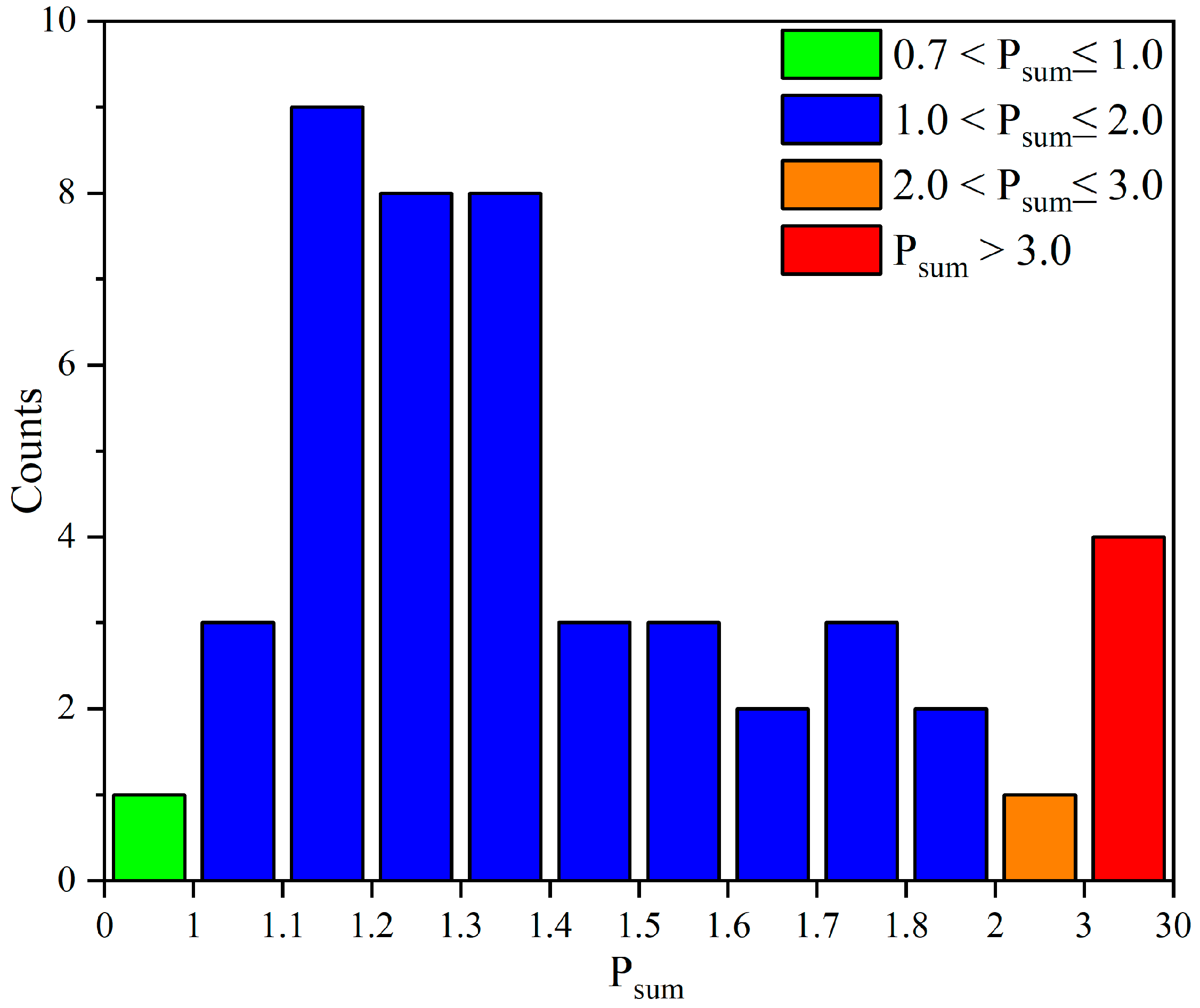
3.4. Nemerow Comprehensive Index Assessment
3.5. Human Health Risk Assessment Results
3.6. Source Apportionment of Heavy Metals
3.6.1. Principal Component 1 (APCS1): Industrial Sources
3.6.2. Principal Component 2 (APCS2): Traffic-Related Sources
3.6.3. Principal Component 3 (APCS3): Natural Sources
3.6.4. Principal Component 4 (APCS4): Agricultural Sources
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Teng, Y.; Ni, S.; Wang, J.; Zuo, R.; Yang, J. A geochemical survey of trace elements in agricultural and non-agricultural topsoil in Dexing area, China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2010, 104, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Hu, T.; Zheng, Y.; Wu, M.; Tang, F.H.M.; Liu, M.; Zhang, B.; Derrible, S.; Chen, Q.; Hu, G.; et al. Global and regional patterns of soil metal(loid) mobility and associated risks. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Tai, L.; Chen, G. Contamination source apportionment and health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil around municipal solid waste incinerator: A case study in North China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631–632, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Wan, R.; Yu, R.; Hu, G.; Lin, C.; Huang, H. A comprehensive analysis on source-specific ecological risk of metal(loid)s in surface sediments of mangrove wetlands in Jiulong River Estuary, China. CATENA 2022, 209, 105817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Wang, H.; Yang, Q.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Delgado Martín, J. An integrated approach for quantifying source apportionment and source-oriented health risk of heavy metals in soils near an old industrial area. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 323, 121271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.; Pan, Z.; Lin, C.; Wang, W.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhou, K.; Lin, H. Integrated insights into potentially hazardous metals in sediments of a typical bay under long-term human impacts: Implications for coastal management. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 364, 132566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Chao, S.; Liu, J.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, A.; Cao, H. Source apportionment and health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil for a township in Jiangsu Province, China. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 1658–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, W.; Yang, T.; Ma, S.; Ni, W. Heavy Metal Pollution of Soils in the Site of a Retired Paint and Ink Factory. Energy Procedia 2012, 16, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Xie, X.; Liu, R. Spatial, sources and risk assessment of heavy metal contamination of urban soils in typical regions of Shenyang, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 174, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, P.; Wang, M.; Liu, J.; Gong, L.; Xia, S. Spatial distribution, source identification, and risk assessment of heavy metals in riparian soils of the Tibetan plateau. Environ. Res. 2023, 237, 116977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zha, X.; Gao, X.; Yu, C. Geochemical characteristics and source apportionment of toxic elements in the Tethys–Himalaya tectonic domain, Tibet, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 831, 154863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, V.B.; Hollas, C.E.; Bortoli, M.; Manosso, F.C.; De Souza, D.Z. Heavy metal contamination in soils of a decommissioned landfill southern Brazil: Ecological and health risk assessment. Chemosphere 2023, 339, 139689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Wu, P.; Yang, F.; Sun, D.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, Y. Assessment of heavy metal pollution and human health risks in urban soils around an electronics manufacturing facility. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 630, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Lu, W.X.; Zhao, H.Q.; Yang, Q.C.; Yang, Z.P. Potential ecological risk assessment and prediction of soil heavy-metal pollution around coal gangue dump. Nat. Hazard. Earth Syst. 2014, 14, 1599–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haji Gholizadeh, M.; Melesse, A.M.; Reddi, L. Water quality assessment and apportionment of pollution sources using APCS-MLR and PMF receptor modeling techniques in three major rivers of South Florida. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566–567, 1552–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thurston, G.D.; Spengler, J.D. A quantitative assessment of source contributions to inhalable particulate matter pollution in metropolitan Boston. Atmos. Environ. (1967) 1985, 19, 9–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, B.; Chi, Q.; Liu, H.; Liu, X.; Zhou, J.; Liu, D.; Cheng, X.; Xu, S.; et al. Concentrations and spatial distribution of chlorine in the pedosphere in China: Based on the China Geochemical Baselines Project. J. Geochem. Explor. 2022, 242, 107089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Yang, J.; Li, K.; Gong, J.; Gao, J.; Wang, Z.; Cai, Y.; Zhao, K.; Hu, S.; Fu, Y.; et al. Differentiating environmental scenarios to establish geochemical baseline values for heavy metals in soil: A case study of Hainan Island, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 898, 165634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarva, J.; Ottesen, R.T.; Tarvainen, T. Geochemical studies on urban soil from two sampling depths in Tampere Central Region, Finland. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 4783–4799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Gao, L.; Wang, X. Characterization of contamination levels of heavy metals in agricultural soils using geochemical baseline concentrations. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 1697–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahams, P. Soils: Their implications to human health. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 291, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klavinš, M.; Briede, A.; Rodinov, V.; Kokorite, I.; Parele, E.; Klavina, I. Heavy metals in rivers of Latvia. Sci. Total Environ. 2000, 262, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossini, H.; Shafie, B.; Niri, A.D.; Nazari, M.; Esfahlan, A.J.; Ahmadpour, M.; Nazmara, Z.; Ahmadimanesh, M.; Makhdoumi, P.; Mirzaei, N.; et al. A comprehensive review on human health effects of chromium: Insights on induced toxicity. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 70686–70705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, C.; Liu, R.; Xu, L.; Wang, Q.; Guo, L.; Miao, Y.; Shen, Z. Source-specific ecological risk analysis and critical source identification of heavy metals in road dust in Beijing, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 388, 121763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Chen, C.; Liu, D.; Wang, M.; Han, Q.; Zhang, X.; Feng, X.; Sun, A.; Mao, P.; Xiong, Q.; et al. Health risk assessment of PM2.5 heavy metals in county units of northern China based on Monte Carlo simulation and APCS-MLR. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 843, 156777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Peng, W.; Lin, M.; Liu, C.; Chen, S.; Wang, X.; Gui, H. Environmental geochemical baseline determination and pollution assessment of heavy metals in farmland soil of typical coal-based cities: A case study of Suzhou City in Anhui Province, China. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Xu, D.; Li, Q. A study on environmental geochemical baselines of heavy metals in the surficial soil of Suzhou. Earth Environ. 2018, 46, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Wang, Z.; Huang, Y. Heavy Metal Pollution and Ecological Risk Assessment of Farmland Soil Around Coal Mine in Suzhou City. J. Shandong Norm. Univ. 2017, 32, 99–104. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, X.; Tu, T.; Zhang, K.; Liu, Q.; Jin, D.; Zhang, B. Simultaneous Determination of 10 Effective State Elements in Soil by Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry with AB-DTPA Extraction. Chin. J. Inorg. Anal. Chem. 2025, 15, 1604–1616. [Google Scholar]
- HJ 832-2017; Soil and Sediment—Digestion of Total Metal Elements—Microwave Assisted Acid Digestion Method. Ministry of Environmental Protection: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Muller, G. Index of Geoaccumulation in Sediments of the Rhine River. Geojournal 1969, 2, 109–118. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Yan, X.; Wang, G.; Gui, H.; Hao, Y.; Xu, X. Geochemical Baseline Establishment, Pollution Assessment, and Source Apportionment of Heavy Metals in Estuary Sediments of Northwestern Taihu Lake, China. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2023, 32, 4653–4663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, I.; Bor, J. Lithogene, geogene und anthropogene Schwermetallgehalte von Lößböden an den Beispielen von Cu, Zn, Ni, Pb, Hg und Cd. Mainz. Geowiss. Mitteilungen 1995, 24, 47–70. [Google Scholar]
- Nemerow, N.L. Scientifc Stream Pollution Analysis; Mcgraw-Hill Companies: New York, NY, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, S.; Li, F.; Liu, S.; You, Y.; Liu, C. Enhanced Assessment of Water Quality and Pollutant Source Apportionment Using APCS-MLR and PMF Models in the Upper Reaches of the Tarim River. Water 2024, 16, 3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Luo, Y.; Jin, K.; He, Q.; Lu, Y. Spatial and temporal distribution characteristics and source apportionment of biogenic elements using APCS-MLR model in the main inlet tributary of Danjiangkou Reservoir. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res 2025, 32, 3729–3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Min, N.; Cheng, C.; Chen, C.; Li, T.; Jiang, J. Current Situation and Evaluation and Analysis of Heavy Metal Pollution in the Soil Around a Power Plant in Northern Anhui Province. J. Henan Univ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 796, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Lin, M.; Peng, W.; Min, N. Evaluation of heavy metal pollution in agricultural soils in coal mining areas based on multiple methods. Environ. Ecol. 2024, 6, 14–18. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Chen, Y.; Yue, X.; Ren, D.; Liu, Y.; Yang, K. Identification and hazard analysis of heavy metal sources in agricultural soils in ancient mining areas: A quantitative method based on the receptor model and risk assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 445, 130528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Gao, L.; Zhao, J. Risk Analysis of Metals in Soil from a Restored Coal Mining Area. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2015, 95, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Zhang, C. Distribution and Evaluation on Potential Ecological Risk of Heavy Metals in Soils of Suzhou. J. Soil Sci. 2013, 44, 232–235. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Xia, Y.; Mu, L.; Liu, W.; Wang, Q.; Su, T.; Yang, Q.; Milinga, A.; Zhang, Y. Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Agricultural Soils Based on Multi-Receptor Modeling Combined with Monte Carlo Simulation. Toxics 2024, 12, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, D.; Jia, X.; Wang, L.; Mcgrath, S.P.; Zhu, Y.; Hu, Q.; Zhao, F.; Bank, M.S.; O’connor, D.; Nriagu, J. Global soil pollution by toxic metals threatens agriculture and human health. Science 2025, 388, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Lu, X. Contamination characteristics and source apportionment of heavy metals in topsoil from an area in Xi’an city, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 151, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Guan, Q.; Tian, J.; Lin, J.; Yang, Y.; Yang, L.; Pan, N. Contamination characteristics, source apportionment, and health risk assessment of heavy metals in agricultural soil in the Hexi Corridor. CATENA 2020, 191, 104573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Wang, H.; Dong, L.; Huang, B.; Borggaard, O.K.; Bruun Hansen, H.C.; He, Y.; Holm, P.E. Source identification of heavy metals in peri-urban agricultural soils of southeast China: An integrated approach. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 237, 650–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Z.; Gong, J.; Gao, J.; Tang, S.; Ma, S.; Duan, Z. Heavy metal pollution in agricultural soils of a typical volcanic area: Risk assessment and source appointment. Chemosphere 2022, 304, 135340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, K.; An, M.; Song, Y.; Fu, G.; Ruan, W.; Wu, D.; Li, X.; Yuan, K.; Wan, X.; Chen, Z.; et al. Soil heavy metals in tropical coastal interface of eastern Hainan Island in China: Distribution, sources and ecological risks. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Cai, L.; Wen, H.; Luo, J.; Wang, Q.; Liu, X. Spatial distribution and source apportionment of heavy metals in soil from a typical county-level city of Guangdong Province, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, L.; Liu, M.; Zhang, J.; Hunag, L.; Chen, Z. Sources of Arsenic in Soil and Affecting Factors of Migration and Release: A Review. Soils 2020, 52, 234–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Fan, F.; Zhang, L.; Qi, J. Research progress on adsorption of heavy metals by manganese oxides and its influencing factors. Appl. Chem. Ind. 2018, 47, 155–159+164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izadi, L.N.; Tamadoni, A.; Siebecker, M.G.; Sricharoenvech, P.; Barreto, M.S.; Fischel, M.H.; Tappero, R.; Sparks, D.L. Hurricanes and turbulent floods threaten arsenic-contaminated coastal soils and vulnerable communities. Environ. Int. 2025, 200, 109479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, W.; Wang, M.; Peng, C. Regional accumulation characteristics of cadmium in vegetables: Influencing factors, transfer model and indication of soil threshold content. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 1036–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nziguheba, G.; Smolders, E. Inputs of trace elements in agricultural soils via phosphate fertilizers in European countries. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 390, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Xiao, K.; Wang, X.; Lv, Z.; Mao, M. Evaluating the distribution and potential ecological risks of heavy metal in coal gangue. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 18604–18615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, G.; Mao, L.; Liu, S.; Mao, Y.; Ye, H.; Huang, T.; Li, F.; Chen, L. Enrichment and sources of trace metals in roadside soils in Shanghai, China: A case study of two urban/rural roads. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631–632, 942–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Chen, X.; Xie, F.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, T.; Dong, X.; Zheng, L. Combining APCS-MLR model to evaluate the distribution and sources of rare earth elements in a large catchment. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 363, 125256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Ge, Y. Excessive Application of Fertilizer, Agricultural Non-Point Source Pollution, and Farmers’ Policy Choice. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Level | Land Accumulation Index Igeo | Pollution Level |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | No pollution | |
| 1 | No pollution to slight pollution | |
| 2 | Slight pollution | |
| 3 | Slight pollution to moderate pollution | |
| 4 | Moderate pollution | |
| 5 | Moderate pollution to strong pollution | |
| 6 | Strong pollution |
| Nemerow Comprehensive Index | Level | Class of Pollution |
|---|---|---|
| ≤ 0.7 | 1 | Safe |
| 0.7 < ≤ 1.0 | 2 | Warning line |
| 1.0 < ≤ 2.0 | 3 | Slight pollution |
| 2.0 < ≤ 3.0 | 4 | Moderate pollution |
| > 3.0 | 5 | Heavy pollution |
| Parameter Symbols | Practical Significance | Reference Values | Unit | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adult | Child | |||
| IngR | Frequency of soil intake | 100 | 200 | mg/d |
| InhR | Respiratory rate | 20 | 7.65 | m/d |
| CF | Conversion frequency | 1 × 10−6 | 1 × 10−6 | kg/mg |
| EF | Exposure frequency | 365 | 365 | d/a |
| ED | Exposure period | 24 | 6 | a |
| PEF | Dust emission factor | 1.36 × 109 | 1.36 × 109 | m3·kg |
| BW | Average weight | 62.1 | 15.9 | kg |
| ATnc | Average exposure time (carcinogenic) | 8769 | 2190 | d |
| ATca | Average exposure time (non-carcinogenic) | 25,550 | 25,550 | d |
| Metals | RFD | SF | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oral Intake | Inhaled | Oral Intake | Inhaled | |
| As | - | - | 1.5 | 3.66 |
| Cd | - | - | 6.1 | 6.1 |
| Cr | - | - | 0.5 | 20 |
| V | 9.00 × 10−3 | 1.79 × 10−3 | - | - |
| Mn | 1.4 | 1.4 | - | - |
| Co | 3.00 × 10−4 | 3.00 × 10−4 | - | - |
| Ni | 0.02 | 5.40 × 10−3 | - | - |
| Pb | 3.50 × 10−3 | 3.52 × 10−4 | - | - |
| Cu | 0.04 | 0.04 | - | - |
| Zn | 0.3 | 0.3 | - | - |
| V | Cr | Mn | Co | Ni | As | Cd | Pb | Cu | Zn | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum value | 98.70 | 2225.77 | 2830.64 | 36.72 | 1476.76 | 20.15 | 0.76 | 29.74 | 90.57 | 124.76 |
| Minimum value | 65.48 | 73.10 | 531.30 | 9.94 | 33.19 | 9.07 | 0.27 | 16.72 | 17.21 | 57.86 |
| Average value | 81.27 | 218.51 | 874.60 | 14.09 | 103.19 | 14.07 | 0.49 | 22.95 | 28.36 | 80.50 |
| Standard deviation | 7.83 | 439.68 | 363.96 | 4.27 | 234.25 | 2.42 | 0.11 | 2.74 | 11.38 | 12.60 |
| Coefficient of variation | 0.10 | 2.01 | 0.42 | 0.30 | 2.27 | 0.17 | 0.22 | 0.12 | 0.40 | 0.16 |
| Background value | 82.4 | 67.5 | 530 | 12.7 | 29.8 | 10.05 | 0.097 | 26.6 | 20.4 | 62 |
| V | Cr | Mn | Co | Ni | As | Cd | Pb | Cu | Zn | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Geochemical baseline values | 75.09 | 81.83 | 583.52 | 12.30 | 36.24 | 11.76 | 0.48 | 20.36 | 21.94 | 74.66 |
| Metal | ADDing Adult | ADDing Child | ADDinh Adult | ADDinh Child |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V | 1.31 × 10−4 | 1.02 × 10−3 | 1.92 × 10−8 | 2.88 × 10−8 |
| Mn | 1.41 × 10−3 | 1.10 × 10−2 | 2.07 × 10−7 | 3.09 × 10−7 |
| Co | 2.27 × 10−5 | 1.77 × 10−4 | 3.33 × 10−9 | 4.99 × 10−9 |
| Ni | 1.66 × 10−4 | 1.30 × 10−3 | 2.44 × 10−8 | 3.65 × 10−8 |
| Pb | 3.69 × 10−5 | 2.89 × 10−4 | 5.43 × 10−9 | 8.12 × 10−9 |
| Cu | 4.56 × 10−5 | 3.57 × 10−4 | 6.71 × 10−9 | 1.00 × 10−8 |
| Zn | 1.29 × 10−4 | 1.01 × 10−3 | 1.90 × 10−8 | 2.85 × 10−8 |
| As | 7.77 × 10−6 | 1.52 × 10−5 | 1.14 × 10−9 | 4.27 × 10−10 |
| Cd | 2.73 × 10−7 | 5.32 × 10−7 | 4.01 × 10−11 | 1.5 × 10−11 |
| Cr | 1.21 × 10−4 | 2.36 × 10−4 | 1.77 × 10−8 | 6.63 × 10−9 |
| Metal | HI Adult | HI Child | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Avg. | 5.86 × 10−1 | 1.14 × 10−1 | |
| V | Min. | 4.72 × 10−1 | 9.15 × 10−2 |
| Max. | 7.11 × 10−1 | 1.38 × 10−1 | |
| Avg. | 8.86 × 10−3 | 7.86 × 10−3 | |
| Mn | Min. | 5.38 × 10−3 | 4.77 × 10−3 |
| Max. | 2.87 × 10−2 | 2.54 × 10−2 | |
| Avg. | 6.66 × 10−1 | 5.91 × 10−1 | |
| Co | Min. | 4.70 × 10−1 | 4.17 × 10−1 |
| Max. | 1.74 × 100 | 1.54 × 100 | |
| Avg. | 2.49 × 10−1 | 6.49 × 10−2 | |
| Ni | Min. | 8.00 × 10−2 | 2.09 × 10−2 |
| Max. | 3.56 × 100 | 9.29 × 10−1 | |
| Avg. | 8.31 × 10−1 | 8.25 × 10−2 | |
| Pb | Min. | 6.05 × 10−1 | 6.01 × 10−2 |
| Max. | 1.08 × 100 | 1.07 × 10−1 | |
| Avg. | 1.01 × 10−2 | 8.92 × 10−3 | |
| Cu | Min. | 6.10 × 10−3 | 5.41 × 10−3 |
| Max. | 3.21 × 10−2 | 2.85 × 10−2 | |
| Avg. | 3.81 × 10−3 | 3.38 × 10−3 | |
| Zn | Min. | 2.74 × 10−3 | 2.43 × 10−3 |
| Max. | 5.90 × 10−3 | 5.23 × 10−3 |
| Metal | RI Adult | RI Child | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Avg. | 6.72 × 10−5 | 2.28 × 10−5 | |
| As | Min. | 4.33 × 10−5 | 1.47 × 10−5 |
| Max. | 9.62 × 10−5 | 3.26 × 10−5 | |
| Avg. | 4.91 × 10−6 | 3.25 × 10−6 | |
| Cd | Min. | 2.68 × 10−6 | 1.77 × 10−6 |
| Max. | 7.57 × 10−6 | 5.01 × 10−6 | |
| Avg. | 9.66 × 10−3 | 9.66 × 10−3 | |
| Cr | Min. | 3.23 × 10−3 | 3.23 × 10−3 |
| Max. | 9.84 × 10−2 | 9.84 × 10−2 |
| Component | Initial Eigenvalues | Extraction Sums of Squared Loadings | Extraction Sums of Squared Loadings | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Variance | Cumulative (%) | Total | Variance | Cumulative (%) | Total | Variance | Cumulative (%) | |
| APCS1 | 4.05 | 40.503 | 40.503 | 4.050 | 40.503 | 40.503 | 3.852 | 38.52 | 38.52 |
| APCS2 | 2.374 | 23.741 | 64.244 | 2.374 | 23.741 | 64.244 | 2.185 | 21.846 | 60.367 |
| APCS3 | 1.263 | 12.629 | 76.873 | 1.263 | 12.629 | 76.873 | 1.576 | 15.762 | 76.129 |
| APCS4 | 0.936 | 9.357 | 86.229 | 0.936 | 9.357 | 86.229 | 1.010 | 10.101 | 86.229 |
| APCS5 | 0.578 | 5.78 | 92.01 | ||||||
| APCS6 | 0.487 | 4.875 | 96.884 | ||||||
| APCS7 | 0.211 | 2.106 | 98.99 | ||||||
| APCS8 | 0.062 | 0.623 | 99.613 | ||||||
| APCS9 | 0.027 | 0.275 | 99.888 | ||||||
| APCS10 | 0.011 | 0.112 | 100 | ||||||
| Heavy Metal Type | APCS1 | APCS2 | APCS3 | APCS4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V | 0.410 | 0.698 | 0.282 | −0.070 |
| Cr | 0.957 | −0.157 | −0.107 | 0.067 |
| Mn | 0.107 | −0.027 | 0.904 | 0.109 |
| Co | 0.926 | 0.093 | 0.332 | 0.094 |
| Ni | 0.984 | −0.069 | −0.051 | 0.048 |
| As | −0.041 | 0.453 | 0.743 | −0.161 |
| Cd | 0.204 | 0.099 | 0.012 | 0.950 |
| Pb | −0.026 | 0.849 | −0.033 | 0.219 |
| Cu | 0.941 | 0.270 | −0.023 | 0.005 |
| Zn | −0.040 | 0.806 | 0.042 | −0.045 |
| Heavy Metal Type | Industrial Sources | Traffic-Related Sources | Natural Sources | Agricultural Sources | Unidentified Sources | R2 | RMSE | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V | 4.64 | 53.28 | 2.90 | 1.77 | 37.40 | 0.74 | 0.53 | <0.01 |
| Cr | 37.27 | 25.69 | 1.23 | 10.32 | 25.49 | 0.96 | 0.22 | <0.01 |
| Mn | 9.58 | 29.96 | 34.38 | 20.77 | 5.31 | 0.84 | 0.42 | <0.01 |
| Co | 23.37 | 22.32 | 7.24 | 6.73 | 40.35 | 0.98 | 0.14 | <0.01 |
| Ni | 65.39 | 11.06 | 0.31 | 12.75 | 10.49 | 0.98 | 0.15 | <0.01 |
| As | 1.26 | 56.50 | 8.94 | 0.22 | 33.09 | 0.80 | 0.46 | <0.01 |
| Cd | 9.30 | 32.88 | 4.30 | 47.87 | 5.65 | 0.61 | 0.65 | <0.01 |
| Pb | 0.72 | 53.71 | 0.61 | 5.03 | 39.93 | 0.78 | 0.49 | <0.01 |
| Cu | 16.20 | 40.72 | 0.51 | 2.47 | 40.10 | 0.96 | 0.21 | <0.01 |
| Zn | 1.11 | 59.18 | 1.42 | 2.32 | 35.97 | 0.66 | 0.61 | <0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Ma, J.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, D.; Wu, C.; Dai, H. Geochemical Baseline, Pollution Evaluation, and Source Apportionment of Topsoil Heavy Metals in Eastern Yongqiao District of Suzhou City, China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 9128. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17209128
Chen Y, Ma J, Yang Y, Liu X, Wang D, Wu C, Dai H. Geochemical Baseline, Pollution Evaluation, and Source Apportionment of Topsoil Heavy Metals in Eastern Yongqiao District of Suzhou City, China. Sustainability. 2025; 17(20):9128. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17209128
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yifei, Jie Ma, Yang Yang, Xianghong Liu, Dingsheng Wang, Cancan Wu, and Hongbao Dai. 2025. "Geochemical Baseline, Pollution Evaluation, and Source Apportionment of Topsoil Heavy Metals in Eastern Yongqiao District of Suzhou City, China" Sustainability 17, no. 20: 9128. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17209128
APA StyleChen, Y., Ma, J., Yang, Y., Liu, X., Wang, D., Wu, C., & Dai, H. (2025). Geochemical Baseline, Pollution Evaluation, and Source Apportionment of Topsoil Heavy Metals in Eastern Yongqiao District of Suzhou City, China. Sustainability, 17(20), 9128. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17209128






