Equitable Allocation of Interprovincial Industrial Carbon Footprints in China Based on Economic and Energy Flow Principles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methodology
2.1. Allocation of Carbon Footprint Transfer Responsibility
2.2. Provincial Carbon Responsibility Accounting Framework
2.2.1. Accounting Framework Based on Benefit–Cost Sharing
2.2.2. NPP-Based Carbon Footprint Measurement
2.2.3. Carbon Footprint Allocation by Benefit Principle
2.2.4. Carbon Footprint Allocation by Energy Flow Principle
2.3. Data Sources and Preprocessing
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Provincial Carbon Footprint Analysis: Production vs. Consumption
3.1.1. Analysis by Province and Industry Sector
3.1.2. Net Carbon Footprint Transfer Analysis
3.2. Carbon Footprint Responsibility Adjustment
3.2.1. Benefit Principle in Responsibility Allocation
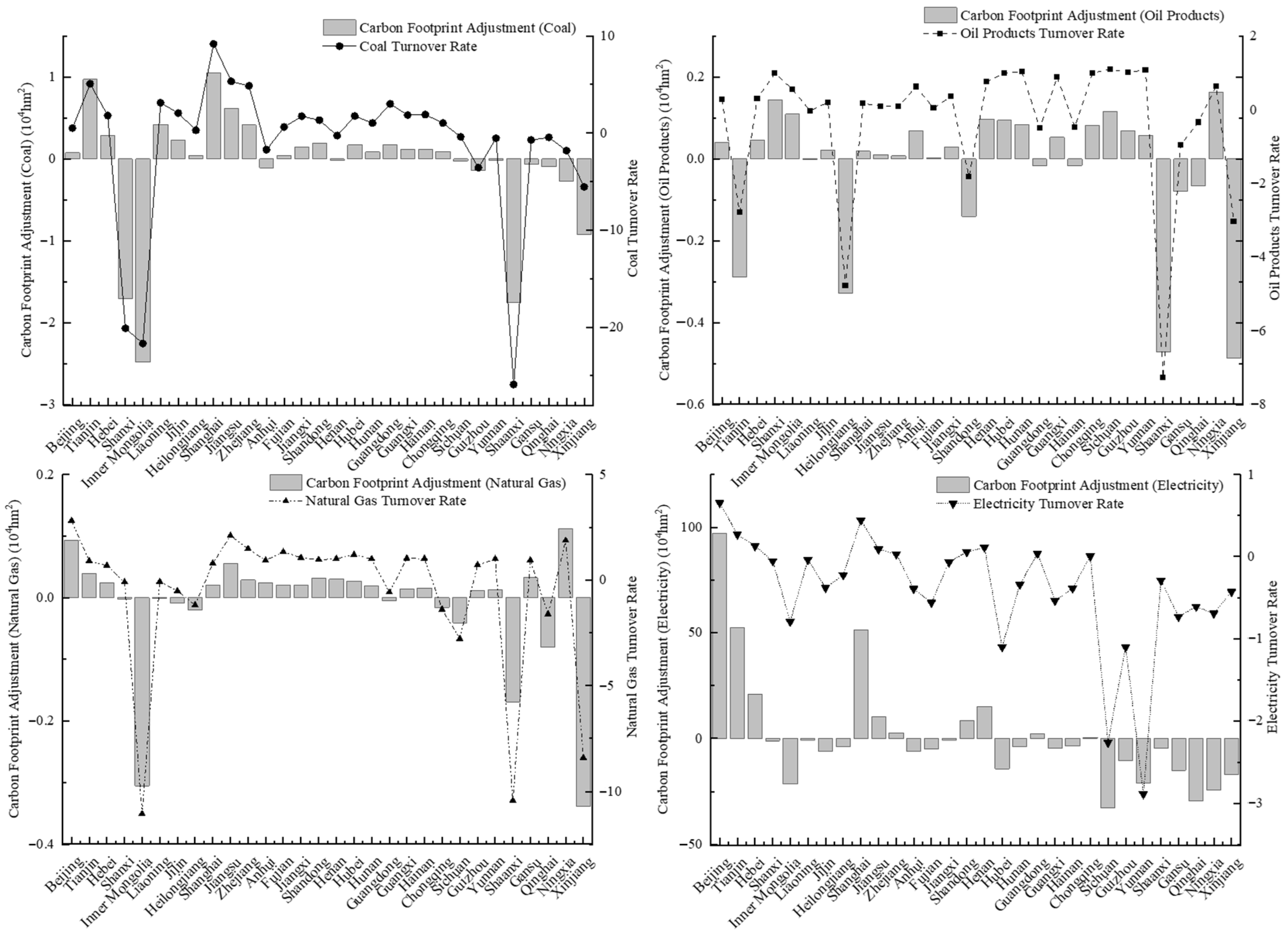
3.2.2. Energy Flow Principle in Carbon Footprint Adjustment
3.3. Effectiveness of Holistic Carbon Footprint Adjustment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Policy Implications
5.1. Conclusions
5.2. Policy Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Yu, Q. Life cycle assessment for carbon dioxide emissions from freeway construction in mountainous area: Primary source, cut-off determination of system boundary. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 140, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, Y. Spatio-temporal evolution characteristics and influencing factors of carbon emission reduction potential in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 59925–59944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danish Ulucak, R.; Khan, S.U.D.; Baloch, M.A.; Li, N. Mitigation pathways toward sustainable development: Is there any trade-off between environmental regulation and carbon emissions reduction? Sustain. Dev. 2020, 28, 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Han, Q.; de Vries, B. A geographic carbon emission estimating framework on the city scale. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 244, 118793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zeng, Y.; Chen, W.; Pan, S.; Du, F.; Zong, G. Spatio-temporal diversification of per capita carbon emissions in China: 2000–2020. Land 2024, 13, 1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z. Research on sustainable development of Xi’an city based on ecological footprint model. Can. Soc. Sci. 2020, 16, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Hu, Y. The measurement and influencing factors of carbon transfers embodied in inter-provincial trade in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 270, 122460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xiong, S.; Li, Z.; Zhou, M.; Li, H. Variation of global fossil-energy carbon footprints based on regional net primary productivity and the gravity model. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 213, 225–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.C.; Li, X.L.; Zhang, Y.Y. Analysis of the Temporal and Spatial Evolution of Carbon Emissions in the Provincial Logistic Industry in China from the Perspective of Shared Responsibility. Environ. Sci. 2025, 46, 2874–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Hertwich, E.G. The flow of embodied carbon through the economies of China, the European Union, and the United States. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 145, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y. Consumption-based CO2 emissions and emissions interregional transfer: A multi-regional input-output approach. J. Ind. Technol. Econ. 2014, 33, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Su, B.; Li, Y.; Yu, S. Reviews of studies on aggregate embodied energy and carbon emission intensities. J. Beijing Inst. Technol. (Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2024, 26, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.; Ang, B.W. Multi-region input–output analysis of CO2 emissions embodied in trade: The feedback effects. Ecol. Econ. 2011, 71, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piñero, P.; Bruckner, M.; Wieland, H.; Pongrácz, E.; Giljum, S. The raw material basis of global value chains: Allocating environmental responsibility based on value generation. Econ. Syst. Res. 2019, 31, 206–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, J.; Domingos, T.; Giljum, S.; Schneider, F. Designing an indicator of environmental responsibility. Ecol. Econ. 2006, 59, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yang, Z.; Cong, J.; Zhang, Y. Optimization of China’s provincial carbon emission responsibility sharing scheme based on the principle of responsibility and benefit matching. Resour. Sci. 2022, 44, 1745–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Dogan, E.; Taskin, D. Production-based and consumption-based approaches for the energy-growth-environment nexus: Evidence from Asian countries. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2020, 23, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Tan, T.; Toktay, L.B. Carbon leakage: The impact of asymmetric regulation on carbon-emitting production. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2021, 30, 1886–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folkers, A. Future Theft: Fossil Capitalization, Ecological Dispossession, and Climate Reparations. Theory Cult. Soc. 2025, preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W. Recalculation of responsibility distribution of China’s provincial consumption-side carbon emissions: Based on the perspectives of shared responsibility and technical compensation. Stat. Res. 2022, 39, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Bai, Y.; Wei, W.; Meng, J.; Zhang, Z.; Song, M.; Guan, D. Chinese provincial multi-regional input-output database for 2012, 2015, and 2017. Sci. Data 2021, 8, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Feng, Z.; Meng, B. Measure of carbon emissions and carbon transfers in 30 provinces of China. J. Quant. Tech. Econ. 2017, 34, 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; He, Y. Responsibility allocation of China’s provincial net carbon transfer from the perspective of value-added. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2021, 31, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Gao, X.; Ahmad, F.; Chandio, A.A.; Khan, S. Carbon compensation and carbon neutrality: Regional variations based on net carbon transfer of trade in China. Geosci. Front. 2024, 15, 101809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wang, B. Carbon footprints and embodied CO2; transfers among provinces in China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 1068–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Ping, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, K. China’s initial allocation of interprovincial carbon emission rights considering historical carbon transfers: Program design and efficiency evaluation. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 121, 106918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Ge, X. Inter-provincial responsibility allocation of carbon emission in China to coordinate regional development. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 7025–7041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Li, Y.; Feng, K.; Meng, J.; Shan, Y.; Guan, D. Carbon emission imbalances and the structural paths of Chinese regions. Appl. Energy 2018, 215, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Q. China’s carbon emissions from the electricity sector: Spatial characteristics and interregional transfer. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2021, 18, 258–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.; Tian, G.; Wu, Z. Examining embodied carbon emission flow relationships among different industrial sectors in China. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2022, 29, 100–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Sheng, X.; Chen, L.; Tang, Y.; Li, Y.; Jia, Y.; Qu, D.; Wang, Q.; Ma, Q.; Zuo, J. Carbon footprint and embodied carbon transfer at the provincial level of the Yellow River Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 803, 149993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.; Li, C.; Liu, Z.; Geng, Y.; Xi, F. Analysis on CO2 emission and urbanization at global level during 1970–2007. Adv. Clim. Change Res. 2011, 7, 423. Available online: https://www.climatechange.cn/EN/Y2011/V7/I6/423 (accessed on 25 August 2025).
- Lv, K.; Feng, X.; Kelly, S.; Zhu, L.; Deng, M. A study on embodied carbon transfer at the provincial level of China from a social network perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 225, 1089–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Cai, Z.; Xu, J.; Song, Y.; Lu, M. Characteristics and mechanisms of carbon emissions in urban agglomerations: A spatiotemporal analysis of Chinese major regions. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2024, 44, 414–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, L.; Ren, H.; Cai, W.; Wu, K.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y. Allocation of carbon emission quotas for China’s provincial public buildings based on principles of equity and efficiency. Build. Environ. 2022, 216, 108994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


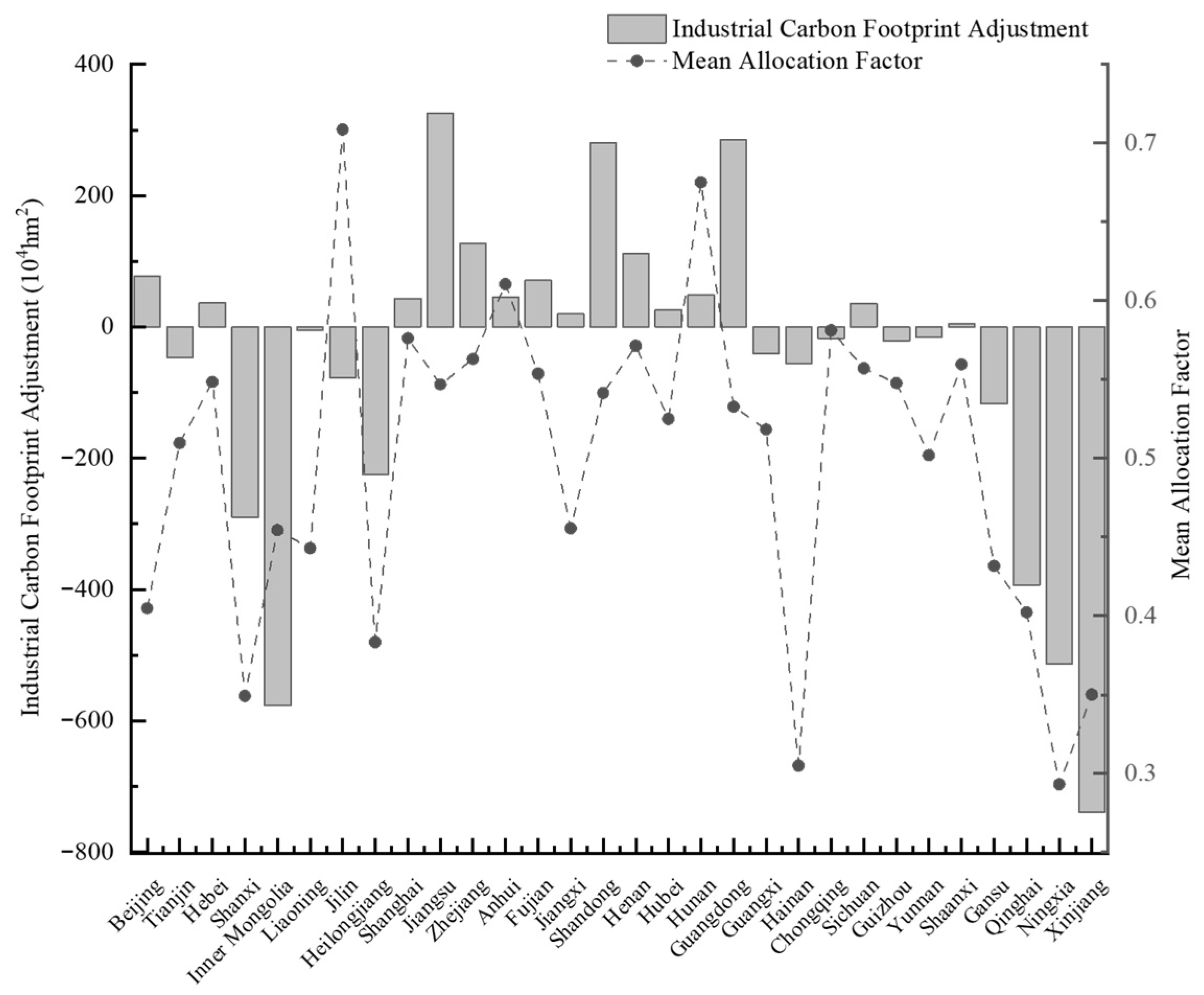
| Industrial Carbon Footprint (104 hm2) | Production-side | Consumption-side | ||||||
| Extractive | Manufacturing | Utilities | Total | Extractive | Manufacturing | Utilities | Total | |
| 7639.05 | 460,883.59 | 404,586.00 | 873,108.63 | 6982.56 | 322,255.29 | 297,833.29 | 627,071.14 | |
| Province | Production-Side Industrial Carbon Footprint (104 hm2) | Consumption-Side Industrial Carbon Footprint (104 hm2) | First Adjusted Industrial Carbon Footprint (104 hm2) | Second Adjusted Industrial Carbon Footprint (104 hm2) | First Adjustment Amount (104 hm2) | Second Adjustment Amount (104 hm2) | NPP (tC·hm−2·a−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing | 2933.75 | 20,430.99 | 3011.34 | 3108.64 | 77.59 | 97.30 | 3.86 |
| Tianjin | 22,505.85 | 13,706.33 | 22,458.94 | 22,511.88 | −46.92 | 52.95 | 2.96 |
| Hebei | 35,660.00 | 38,522.14 | 35,696.76 | 35,717.79 | 36.76 | 21.03 | 3.59 |
| Shanxi | 62,813.01 | 20,656.12 | 62,523.21 | 62,520.56 | −289.80 | −2.65 | 3.76 |
| Inner Mongolia | 117,339.41 | 18,560.69 | 116,762.58 | 116,738.45 | −576.82 | −24.14 | 2.78 |
| Liaoning | 33,100.84 | 34,279.45 | 33,095.90 | 33,095.65 | −4.94 | −0.25 | 4.16 |
| Jilin | 28,627.90 | 5670.23 | 28,551.06 | 28,545.52 | −76.84 | −5.54 | 4.94 |
| Heilongjiang | 46,356.43 | 13,604.89 | 46,131.72 | 46,127.60 | −224.71 | −4.13 | 4.45 |
| Shanghai | 11,058.98 | 16,677.96 | 11,101.94 | 11,154.42 | 42.96 | 52.48 | 4.93 |
| Jiangsu | 17,370.51 | 71,953.29 | 17,695.66 | 17,706.54 | 325.15 | 10.88 | 4.89 |
| Zhejiang | 7433.64 | 28,351.15 | 7560.40 | 7563.45 | 126.76 | 3.05 | 6.66 |
| Anhui | 14,054.79 | 18,877.43 | 14,099.70 | 14,093.83 | 44.91 | −5.87 | 5.05 |
| Fujian | 5579.43 | 17,196.23 | 5650.80 | 5645.93 | 71.37 | −4.86 | 8.58 |
| Jiangxi | 8377.02 | 12,334.43 | 8396.90 | 8396.35 | 19.88 | −0.55 | 6.82 |
| Shandong | 27,005.78 | 74,776.48 | 27,286.65 | 27,295.05 | 280.88 | 8.39 | 3.95 |
| Henan | 16,377.99 | 32,523.64 | 16,489.44 | 16,504.61 | 111.45 | 15.17 | 4.28 |
| Hubei | 13,039.80 | 16,491.25 | 13,066.08 | 13,052.13 | 26.28 | −13.95 | 5.83 |
| Hunan | 11,255.31 | 15,974.00 | 11,303.39 | 11,299.78 | 48.08 | −3.61 | 6.79 |
| Guangdong | 5021.13 | 55,059.19 | 5306.57 | 5308.96 | 285.44 | 2.39 | 9.71 |
| Guangxi | 10,426.92 | 2835.09 | 10,387.06 | 10,382.85 | −39.87 | −4.21 | 9.22 |
| Hainan | 10,079.29 | 1891.32 | 10,023.37 | 10,020.16 | −55.92 | −3.21 | 8.74 |
| Chongqing | 8795.10 | 4648.67 | 8777.84 | 8778.48 | −17.26 | 0.64 | 6.69 |
| Sichuan | 13,200.25 | 17,690.94 | 13,236.35 | 13,203.89 | 36.10 | −32.46 | 5.24 |
| Guizhou | 11,572.69 | 6932.41 | 11,551.41 | 11,541.17 | −21.28 | −10.25 | 8.15 |
| Yunnan | 8817.41 | 5893.24 | 8801.33 | 8780.60 | −16.08 | −20.73 | 10.47 |
| Shaanxi | 19,724.83 | 18,505.50 | 19,730.06 | 19,723.03 | 5.24 | −7.04 | 4.71 |
| Gansu | 27,462.69 | 7895.32 | 27,346.03 | 27,330.96 | −116.65 | −15.07 | 3.69 |
| Qinghai | 72,489.71 | 5183.70 | 72,096.43 | 72,066.74 | −393.28 | −29.69 | 1.56 |
| Ningxia | 79,656.25 | 9724.97 | 79,142.88 | 79,118.53 | −513.37 | −24.35 | 2.15 |
| Xinjiang | 124,971.91 | 20,224.10 | 124,233.10 | 124,214.36 | −738.81 | −18.73 | 1.91 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, J.; Wang, Y.; Shi, X.; Arshad, M.U. Equitable Allocation of Interprovincial Industrial Carbon Footprints in China Based on Economic and Energy Flow Principles. Sustainability 2025, 17, 9036. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17209036
Zhao J, Wang Y, Shi X, Arshad MU. Equitable Allocation of Interprovincial Industrial Carbon Footprints in China Based on Economic and Energy Flow Principles. Sustainability. 2025; 17(20):9036. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17209036
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Jing, Yongyu Wang, Xiaoying Shi, and Muhammad Umer Arshad. 2025. "Equitable Allocation of Interprovincial Industrial Carbon Footprints in China Based on Economic and Energy Flow Principles" Sustainability 17, no. 20: 9036. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17209036
APA StyleZhao, J., Wang, Y., Shi, X., & Arshad, M. U. (2025). Equitable Allocation of Interprovincial Industrial Carbon Footprints in China Based on Economic and Energy Flow Principles. Sustainability, 17(20), 9036. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17209036






