Abstract
We looked into the ways in which the digital economy helps to speed up the convergence of environmentally responsible economic efficiency across China’s regions by facilitating the flow and optimization of R&D resources. We measured the mobility of R&D capital and personnel across 30 provinces in China from 2001 to 2022 using a gravity model, assessed the efficiency of green economic using the SBM method, and determined the influence of the digital economy by the use of a fixed-effects model. (1) We identified the σ convergence (the absolute gap between per capita income or per capita economic efficiency levels of different economies gradually decreasing over time) and β convergence (the negative correlation between the rate of economic efficiency increase among various economies or regions and their initial level of economic efficiency) characteristics of green economic efficiency, discovering that the digital economy has sped up the process of convergence of environmentally responsible economic efficiency in regional areas. (2) We found a latecomer advantage in the convergence of China’s green economic efficiency, along with the advancement of the digital economy; that is, the green economic efficiency more quickly converged in less developed regions and regions with fewer resources. (3) The digital economy is able to accelerate the convergence of regional green economy efficiency through the use of internal mechanisms such as the efficient flow of research and development factors and the reasonable allocation of those factors. By identifying the impact of the digital economy on the gaps in regional green economic efficiency from the new perspective of the flow and allocation of R&D elements, this study contributes to the existing body of literature. It also provides new information regarding the ways in which the digital economy is driving the development of China’s green economy. We offer policy suggestions based on our findings to assist regions in achieving a balance between the digital economy and industrial development through the utilization of resources that are specific to the location.
1. Introduction
Achieving efficient, economical, low-emission, and sustainable development is the main goal of China’s modernization. However, several issues persist in attempts to achieve sustainable development. First, the traditional growth model characterized by high inputs, high emissions, high consumption, lack of recycling, lack of coordination, and low efficiency has not fundamentally changed. As such, technological innovation capabilities need to be strengthened, as the original force driving green economic efficiency is no longer insufficient. Second, underdeveloped regions face challenges in terms of human resources, capital, and infrastructure, resulting in large disparities in the sustainability development level and green economic efficiency compared with developed regions. The regional disparities in green economic development are especially pronounced. General Secretary Xi Jinping has emphasized the need to advance higher-quality regional coordinated development to gradually address the imbalances and inadequacies in regional development, narrow the gaps through enhancing regional development dynamics, and increase the development capabilities of less-developed regions to achieve relative balance among regions. Therefore, a path to high-quality regional green economic development that integrates efficiency enhancement and coordination must be identified in the new stage of sustainability development [1].
The digital economy simultaneously promotes and suppresses growth. The suppressing effects are highlighted by the expansion of regional development disparities due to Matthew’s effect on economic growth, the siphon effect on resource concentration, and the digital divide effect caused by differences in digital technology skills and uptake. Conversely, the promoting effects include the digital economy helping to achieve balanced regional development through the penetration effect of technological empowerment, the allocation effects of resource optimization, and the spillover effects of industrial coordination. Therefore, considering both of these contradictory effects, we must determine whether the digital economy can be used to effectively allocate R&D resources by promoting R&D resource mobility and avoiding resource misallocation. We must also examine whether the digital economy can enhance sustainable development efficiency, namely green economic efficiency, and promote balanced development at the national level.
Taking this into consideration, the purpose of this study is to conduct an empirical investigation into the role that the digital economy plays in the convergence of green economic efficiency in regional areas, as well as the impact pathways that exist between the digital economy, R&D factor allocation, and green economic efficiency. Through the facilitation of the flow of research and development factors and the alleviation of the misallocation of research and development resources, the digital economy is found to significantly promote the convergence of regional green economic efficiency in China, according to the findings of the study. Particularly in the western regions, where the growth rate of green economic efficiency is faster, the development of the digital economy accelerates the narrowing of the efficiency gap between regions with low and high green economic efficiency. This is especially true in regions where the overall rate of green economic efficiency is higher. R&D capital flow and optimization are the primary drivers of the digital economy’s beneficial influence on green economic efficiency; the mobility of R&D talent is only marginally affected. Furthermore, the study emphasizes substantial regional heterogeneity, with different impacts in the western, central, and eastern regions.
The novelty of this study is our in-depth analysis of the effect of the digital economy on gaps in the regional green economic efficiency considering the novel viewpoint of the flow and allocation of R&D resources. We address the limitations in past studies, which only paid attention to the direct link between the digital economy and green economic efficiency, by employing research and development resources as a moderating variable in order to determine the mechanism by which the digital economy stimulates the convergence of environmentally responsible economic efficiency in regional areas. Furthermore, the paper emphasizes the heterogeneity of resource endowments, investigating how the way the digital economy effect green economic efficiency varies across regions with different resource conditions. Given the economic slowdown and increasing pressure to find solutions to this issue, our findings provide a scientific basis for driving China’s green economic development through the digital economy, as well as offer new ideas for addressing industrial development issues while balancing economic growth and environmental improvement. We also provide recommendations regarding how regions can leverage their local advantages to balance the digital economy and industrial development.
What follows is an outline of the rest of the paper: In Section 2, you will find the review of theoretical literature. The review of empirical literature is presented in Section 3. Section 4 delves into the models and provides an explanation of the variables. The primary empirical findings are detailed in Section 5. The discussion is presented in Section 6, and the policy implications are concluded in Section 7.
2. Theoretical Literature Review
2.1. Digital Economy, Factor Allocation, and Green Economic Efficiency
The theory of technological-economic paradigms proposed by Freeman & Perez [2,3,4] offers a unique theoretical perspective for revealing the process and mechanism by which the digital economy drives the reconstruction of the socio-economic system. Digital economy is a new economic form in which data are the major factor of production and modern information technology (for example, cloud computing, big data, AI, and Internet of Things) as the core driving force. It is characterized by efficient connectivity, leveraging digital technologies to break down industry barriers and enable the rapid allocation of resources, and innovation-driven growth, using technological advancements as a driving force to upgrade traditional industries and accelerate the development of emerging sectors.
Developing sustainability development necessitates a focus on green economic efficiency. An all-encompassing view of economic efficiency is green efficiency that accounts for the costs of resources and the environment throughout the growth process, aligning with the current high-quality development principles, unlike traditional total factor productivity and green productivity measures. Studies have been performed on the interplay between the digital economy and green economic efficiency, primarily from three perspectives: industrial adjustment [5], environmental governance [6,7], and upgrading technology [8]. Zhu Jiexi posited that the digital economy can be used to transform traditional industries by optimizing industrial structures, leading to the exit of high-pollution industries from the market and their replacement with high-tech, low-pollution industries. This transformation thus influences potential increases in green economic efficiency. The application of digital technologies promotes the utilization of new energy sources, optimizes the development of clean energy, and increases energy use efficiency, thereby supporting environmental governance [9]. Kim et al. found that information and communication technologies, as foundations of the digital economy, contribute to technological innovation outputs that not only directly promote output growth but also generate economic effects through technological spillover to other industries [10].
The movement of production resources is no longer constrained by administrative and geographic barriers given the national advocacy for the integrated development of the various regions. Central regions have affected their surrounding areas through economic agglomeration, creating a positive feedback loop. However, regions facing continuous net outflows of resources have encountered developmental challenges, which has exacerbated regional disparities. Economic agglomeration has primarily manifested under the digital economy as the concentration of data and research and development (R&D) resources, which has both positively and negatively impacted green economic efficiency, thereby widening regional gaps. Studies on factor mobility and allocation have seldom considered the digital economy’s effect. However, Ren et al. suggested that the digital economy’s growth reduces the misalignment and imbalances of labor, capital, and technology resources, encouraging these resources to flow toward regions with higher development potential and thereby optimizing the allocation structure of traditional resources [11]. From the perspective of labor mobility, the digital labor market imposes fewer geographical and temporal constraints, thus overcoming the limitations caused by labor choice and availability and aligning employment opportunities across different regions and industries, leading to higher-quality job opportunities and a more comprehensive talent pool. This, in turn, facilitates the flow of labor resources. From the capital perspective, digital technologies reduce the costs of information exchange and trade, allowing enterprises to directly engage in commercial activities through internet platforms, thereby enhancing the efficiency of capital resource mobility. From the technology perspective, data resources promote the flow of R&D-related factors among regions, assisting with the most efficient use of available resources; enhancing innovation efficiency; and accelerating the spread of technological innovations, knowledge, experience, and information through spatial spillover effects, thus driving technological upgrades and increases in regional innovation efficiency. Additionally, Bai Junhong et al. found that the internet helps improve high-knowledge labor allocation. R&D capabilities are improved through the digital economy’s optimization of R&D-related factors and R&D human resource allocation, which has an indirect positive effect on regional green economic efficiency. Consequently, the digital economy’s potential to boost green economic efficiency is severely limited by the misallocation of research and development funds and personnel.
The existing research offered valuable insights for this study; however, systematic explorations were lacking the intrinsic transmission mechanisms and effects associated with the growth of the digital economy, R&D resources, and green economic efficiency. During the course of the majority of the research that has been conducted, the primary emphasis has been placed on conducting independent analyses of the digital economy and R&D factors. However, the pathways through which R&D-related factors influence green economic efficiency in the era of the digital economy have been largely ignored. Therefore, we not only address these gaps in the existing research but also provide a deeper and more comprehensive understanding of the interplay between digital economy and green economic efficiency.
2.2. Analysis of the Mechanism of the Digital Economy Affecting the Efficiency Convergence of Regional Green Economy
Figure 1 briefly depicts the path of the effects of the digital economy on the convergence of regional green economic efficiency. The growth in green economic efficiency encompasses three primary dimensions: economic growth, pollution and carbon emission decreases, and resource conservation. The digital economy both positively and negatively influences regional industrial development through impacting various aspects such as industry [11], technology [12,13,14], and the environment [15,16]. Its function as a facilitator of R&D factor flow and a check on resource misallocation mediates this effect. As a result, accomplishing balanced development across regions and enabling the convergence of environmentally friendly economic efficiency are both greatly aided by the digital economy.
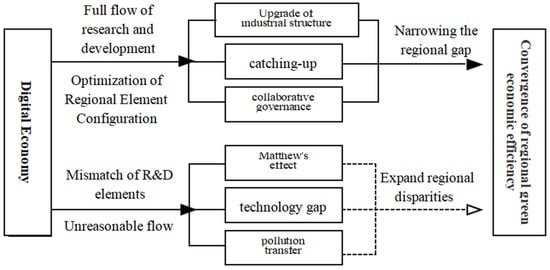
Figure 1.
Digital economy affects the convergence path of regional green economy efficiency.
Through the use of data elements, the digital economy has been responsible for the digitalization of resources, which has helped to address the problems that are brought about by information asymmetry and has sped up the movement of research and development human resources and capital between regions. Because of this dynamic, there is a spillover of knowledge and a diffusion of technology from developed regions to less developed regions, which, in turn, stimulates the provision of factors related to research and development with less developed regions. These agglomeration effects of research and development personnel and capital in inflowing regions can radiate to the surrounding areas, thereby reducing the regional disparities in green economic efficiency. This can be accomplished through optimized industrial structures, balanced technological empowerment, and coordinated environmental governance.
First, the digital economy, leveraging emerging digital technologies and data, accelerates the movement of production resources across industrial sectors, reconfiguring factor resources, optimizing production processes and models, and enhancing energy use and labor productivity, which collectively increases the overall green economic efficiency. Second, late-developing regions, starting with large gaps in terms of institutions and R&D personnel compared with developed regions, should select technology innovation models based on their resource endowments to catch up technologically, according to comparative advantage theory. The digital economy growth has facilitated comprehensive digital transformation in these regions, streamlining the inflow of R&D capital, optimizing the regional innovation layout, and accelerating the adoption of advanced technologies to support technological catch-up. Third, digital technologies enhance the precision and efficiency of environmental governance. The establishment of digital platforms reduces the information asymmetry, effectively promoting the outflow of redundancies from developed regions and the receipt of high-quality resources in less-developed regions, resulting in complementary advantages and advancing collaborative environmental governance, which enhances the overall green economic efficiency.
The agglomeration effects and accumulation of R&D resources in developed regions exacerbate talent drain and the misallocation of resources in economically lagging areas, leading to technology gaps and pollution transfer, intensifying Matthew’s effect and widening the disparities in green economic efficiency within regions. First, the migration of production and R&D resources from less-developed to developed regions reinforces Matthew’s effect, where developed regions become more advanced as lagging regions fall further behind. The digital economy in developed regions can have a crowding out effect on surrounding areas, negatively impacting these surrounding areas and increasing regional disparities. Second, R&D resources may be poorly used and misallocated due to various constraints in less-developed regions, resulting in insufficient innovation output and creating a technology gap with regions with stronger R&D-related factors. This leads to low production efficiency and differences in regional economic growth rates, which hampers the overall economic growth. Lastly, developed regions may shift some of their industrial production to developing regions in response to changes in regional advantages, transferring polluting industries to adjacent areas. This exacerbates the pollution levels in the receiving regions and causes pollution backflow effects, leading to localized pollution transfer. Such phenomena result in environmental degradation and increased resource consumption in less-developed regions, impeding their green economic efficiency to incline and widening the regional gaps in green economic efficiency.
The purpose of this paper is to first investigate, on the basis of the theoretical model analysis that was presented earlier, how the digital economy influences the convergence of green economic efficiency across various regions in China, with a specific emphasis on the role that it plays in reducing regional disparities in green economic efficiency. Subsequently, the analysis investigates the ways in which the mobility of R&D factors, specifically capital, technology, and talent, contributes to the enhancement of green economic efficiency across regions, as well as the ways in which the digital economy contributes to the reduction of excessive allocation of R&D resources. In conclusion, the paper investigates the heterogeneity of these impact mechanisms across regions, providing empirical evidence to support the recommendations that are made regarding policy.
3. Empirical Literature Review
Scholars are increasingly using samples from different regions to assess the impact of the digital economy on economic growth convergence, but no consensus has yet been reached. At the international level, researchers have found that the digital economy, with the internet at its core, has a certain promoting effect on economic growth convergence. Choi and Yi [17] used data from 27 countries from 1991 to 2001 and found that the internet significantly promoted economic growth after controlling for investment rate, government consumption rate, and inflation. Empirical studies by Noh and Yoo [18], which covered 60 countries, and Vicent and Lopez [19], focusing on 27 EU countries, both demonstrate that an increase in internet penetration negatively affects economic development in countries with significant wealth disparities, thereby exacerbating the digital divide.
A number of academics have conducted comprehensive empirical studies on how the digital economy throughout China’s provinces affects economic growth convergence and generally found that the digital economy is beneficial in promoting regional economic convergence [20]. Meanwhile, the robust expansion of the digital industry, including innovative applications in fields such as-commerce and smart manufacturing, has not only directly contributed to the expansion of the local economy, but it has also contributed to the enhancement of the economic vitality of neighboring and less developed regions through the effects of technological spillover [21].
In summary, although some progress has been achieved in the research on the effect of the digital economy on the convergence of green economies, most of the studies have focused on macro analysis with regards to nations or provinces. In-depth explorations are lacking the mechanisms underlying how the digital economy specifically impacts the convergence of green economic efficiency by the allocation of R&D resources. This study provides contributions to filling this gap in the literature in the following aspects: To begin, we looked at the digital economy’s effect on the disparity in regional green economic efficiency through the lens of research and development resource mobility and allocation, since previous studies had only addressed the direct link between the two. Second, we used R&D resources as an intermediary variable. We developed gravity models and fixed-effect models in order to conduct an empirical investigation into the internal mechanism that the digital economy employs in order to facilitate the mobility of research and development resources, prevent the misuse of resources, and speed up the convergence of green economic efficiency in regional institutions. In conclusion, we took into account the heterogeneity of resources and conducted an analysis of the implications of the disparities in the digital economy on the convergence of green economic efficiency in regions that have varying resource endowments. These findings provide a new perspective regarding how the digital economy is driving China’s green economy and offer new ideas for balancing economic growth with environmental improvement. Additionally, from our findings, we provide suggestions to help regions balance the digital economy with industrial development through the use of their resources.
4. Data Sources and Research Methods
4.1. Variable Measures and Data Sources
4.1.1. Dependent Variables
The effectiveness of the green economy served as the dependent variable in this assessment. The methodologies that Yang et al. [22] proposed for measuring the green economic efficiency in China are described below. Subsequently, Qian Zhengming and colleagues offered a more detailed explanation, defining green economic efficiency as a measure of economic efficiency that simultaneously takes into consideration the consumption of resources and the damage of the environment [23]. Our methodology was based on that of Qian Zhengming and colleagues. In order to evaluate the effectiveness of green economic development, we utilized the improved data envelopment analysis (DEA) model that was suggested by Tone et al. [24]. More specifically, we utilized the nonradial, nonangular SBM (Slacks-Based Measure) model.
Stata was utilized in order to determine the overall green economic efficiency. The inputs consisted of labor, capital stock, and energy consumption; the output that was anticipated was gross domestic product (GDP); the output that was not desired was carbon dioxide emissions. For the purpose of representing labor input, the number of employees at the end of the year was used. The total energy consumption in standard coal equivalents was used as the measurement for energy input, and the China Energy Statistical Yearbook was used to obtain this information. In order to calculate the capital stock, annual fixed asset investments were used in conjunction with the perpetual inventory method (PIM), as outlined by Shan et al. [25]. The year 2001 served as the standard for the calculation. In order to acquire information regarding capital inputs, nominal fixed asset investment was deflated by making use of the fixed asset investment price index that was provided by the National Bureau of Statistics.
4.1.2. Explanatory Variables
The explanatory variable was the digital economy. We used data on the GDP of several sectors associated with the digital economy from 30 provinces in China from 2001 to 2022, according to the Statistical Classification of Digital Economy and Its Core Industries 2021 released by the National Bureau of Statistics. Manufacturing computer communication and other electronic equipment, telecommunications, broadcasting, television, internet and related services, software and information technology, and services for satellite transmission were all part of these industries. Using gross value added by industry [26] as a measure for the extent of digital economy development in each province, the data for these sectors were picked from the sections on national economic accounting, industry [27], and services [28] in the Statistical Yearbook of each province.
4.1.3. Mechanism Variables
- (1)
- Net flow of regional R&D factors
The measurement of R&D resource mobility was divided into the movement of R&D personnel and R&D capital. Following the methods of Bai et al. [29], the gravitational model derived from Newton’s law of gravity was employed to calculate the inflow and outflow of R&D personnel and capital. The net resource mobility was measured as the difference between inflow and outflow.
Drawing on the methodology of Li et al. for measuring R&D personnel mobility [23], we considered factors affecting employee movement across economic, employment, cultural, industrial, and innovation environments. The constructed gravitational model was as follows:
where represents the sum of R&D personnel flowing between province j and i, while and represent the full-time equivalent of R&D personnel in provinces i and j, respectively. The gravity model is designed to determine the inflow and outflow of this factor in provinces i and j. refers to the geographical distance between regions i and j, and represents the influence parameter of the distance between regions, usually taken as 1. is the gravitational parameter for personnel size, which generally tends to be equal. The gravity model was designed to measure the inflow and outflow of this factor in provinces i and j. In addition, the other parts of the model represent the gravitational coefficients between province i and province j, where is the per capita GDP of the region, is the wage level of R&D personnel, is the average housing price in the region, job is the unemployment rate, is the population quality measured by the average years of education, is the proportion of the tertiary industry to the GDP of the three industries, and is the number of institutions engaged in research and development work in the region. represents the weight coefficients of various gravitational variables, which are calculated using the entropy method to obtain .
Taking the number of R&D personnel from province j flowing into province i as and considering it as the inflow of R&D personnel from province i as , the outflow of R&D personnel from province i can be expressed as , and the net flow of R&D personnel can be expressed as .
We determined the amount of capital flowing into research and development by taking into account the fact that the factors that most influence capital flow are regional economic development [30], profitability, and the investment climate. For the purpose of measuring R&D-related factor flow, we referred to the method that was developed by Bian et al. [31]. Based on this method, we chose a gravitational variable—the average profit of industrial enterprises—and the financial market environment—expressed as the ratio of the loan balance of regional financial institutions to the capital stock of fixed assets investment. Next, we constructed a gravitational model in the following manner:
refers to the R&D capital flowing from province i to province j, and and represent the capital stock form of R&D expenditure accounted for by the perpetual inventory method in provinces i and j, respectively. refers to the geographical distance between regions i and j, and represents the influence parameter of the distance between regions. Generally, 1 is taken. is the gravitational parameter of capital size, which generally tends to be equal. and , respectively, represent the weight coefficients of the gravitational variable, where . Let us temporarily consider the R&D capital inflow from province as the R&D capital outflow from province i: . Therefore, the R&D capital inflow from province i can be expressed as , and the net R&D capital flow can be expressed as .
- (2)
- R&D resource mismatch index
The mismatch index of R&D resources was divided into R&D personnel mismatch and R&D capital mismatch . We followed the methods of Cui Shuhui to calculate the mismatch index of capital and labor; the output variable was adjusted to the innovation output (represented using the number of patent applications accepted), labor input was replaced with the full-time R&D personnel equivalent, and capital input was replaced with R&D capital stock (using the perpetual inventory method to standardize R&D expenditure as R&D capital stock based on 2001). Here is the exact formula for the calculation:
where and stand for the distortion coefficients of R&D personnel and R&D capital prices, respectively, which are calculated as follows:
refers to the proportion of output in province i to the total output, represents the ratio of R&D capital to the total R&D capital in province i, refers to the amount of R&D capital used in the effective allocation of R&D capital in region i, refers to the output elasticity of R&D capital in each province, estimated using the production function, and is the mismatch index of R&D capital.
4.1.4. Data Sources and Descriptive Statistics
For this empirical econometric study, we gathered panel data from 30 Chinese provinces covering the years 2001–2022. We omitted Xizang, Taiwan, Hong Kong, and Macao from the sample due to incomplete data for each of these regions. In addition to the China Statistical Yearbook, China Science and Technology Statistical Yearbook, and China Environmental Statistical Yearbook, the data were culled from the statistical yearbooks of each province (region, city). You can find the variables’ descriptive statistics in Table 1.

Table 1.
Descriptive statistics of the variables.
4.2. Methods
We constructed a model using the σ and β convergence methods to investigate the growth in regional green economic efficiency in China and the connection between digital economy and regional green economic efficiency after examining the internal mechanism reported in a previous study [32]. σ convergence refers to the trend in the standard deviation of the residuals of the green economic efficiency index in different regions. An σ coefficient that continues to decrease over time indicates σ convergence, meaning that the gap in the green economic efficiency level across regions is narrowing. β convergence refers to economies with lower-efficiency green economy having a faster growth rate in terms of economic output than those with higher efficiency, which can accelerate the catch-up to high-efficiency economic entities. We referred to the approach suggested by Barro et al. [26] and first constructed a basic model of spatial β convergence as follows:
where and represent the green economic efficiency of each province in China during periods t + T and t, respectively, is a constant term with a convergence coefficient , and refers to the error term. < 0 indicates convergence and that the development of the digital economy helps accelerate the convergence of regional green economic efficiency.
was added as a series of control variables to make sure the estimations are robust. Here is the exact model:
To further investigate how the growth of the digital economy influences the efficiency and effects of green economies in different regions, we included the movement and misalignment of R&D funds in the aforementioned spatial convergence model [33]. In addition, we looked at how the growth of the digital economy has affected the movement of funds and researchers between different parts of the world. The following is an analysis of the correlation between the rise of the digital economy, the distribution and misallocation of research and development funds, and a panel regression model:
is the net flow of R&D capital in province i in year t, which can also be expressed as in the formula, representing the net flow of R&D personnel in province t in year t. is the R&D capital mismatch index for year t, which can be replaced with , representing the R&D capital mismatch index. represents the development level of the digital economy, whereas and represent the fixed effects of provinces and time, respectively.
5. Empirical Results and Analysis
5.1. Baseline Regression Results
We employed both σ and β convergence methods to assess the convergence of the green economic efficiency in China. The digital economy was the explanatory variable in the β convergence model to assess its effect on the convergence of regional green economic efficiency in the country.
For the time period under consideration, Figure 2 shows the development of the σ convergence coefficient of the country’s green economic efficiency. Between 2001 and 2022, the coefficient of variation for green economic efficiency dropped significantly across all 30 provinces. Based on these results, it seems that green economic efficiency levels across China’s regions were getting closer to one another or that the gap between them was narrowing.
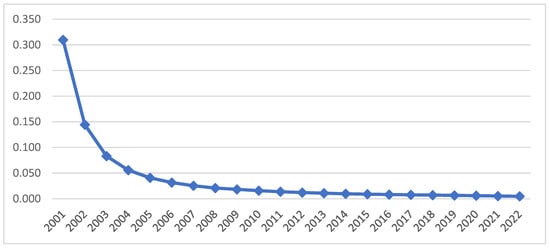
Figure 2.
σ convergence coefficient of green economy efficiency of 30 provinces in China.
In terms of green economy efficiency, we discovered convergence in China. The correlation between digital economy and green economy efficiency was investigated using a spatial panel regression estimation method. The experimental evaluation was conducted using a β conditional convergence model. Table 2 displays the outcomes. Model 1 was the basic model; Model 2 included a series of control such as for environmental infrastructure (), population size (), level of opening up to the outside world (), fiscal decentralization (), industrial structure (), and gross domestic product (), considering the impact of the digital economy.

Table 2.
Results of the β convergence test of green economic efficiency in 30 provinces of China.
According to Table 2, there is β convergence in the increase of national green economic efficiency, as the convergence coefficient of this metric was −0.409 and statistically significant. Taking into account the factors propelling the growth of the digital economy, we discovered a notable convergence in the efficiency of China’s green economy under certain conditions. The development of the digital economy helped accelerate the convergence of China’s green economy efficiency, and regions with lower efficiency needed less time to catch up with regions with higher efficiency. The positive regulatory effect of the development of the digital economy on production resources was stronger than its negative effect. The spatial spillover caused by the accumulation of personnel and capital in developed regions has affected the technological development of underdeveloped regions, which has helped underdeveloped western regions technologically catch up to developed regions. Moreover, the coefficient of digital economy was 0.063, which is considered as significant, indicating that, for every one percentage point increase in national digital economy investment, the convergence speed of regional green economy efficiency increased by six percentage points. (2) The coefficient of the digital economy variable after adding a series of control variables was 0.063, and the estimated results were basically unchanged. The above conclusion aligns with the findings of Liu et al. [34] and Zhang et al. [16], whose studies both found that digital technologies enhance the speed of technological progress and reduce efficiency gaps between regions. However, their studies did not account for the direct role of digital economy investment, focusing instead on broader technological and infrastructural development. The current study’s specific focus on digital economy investment gives a more direct and quantifiable measure of its influence on regional convergence.
5.2. Robustness Test
To ensure the results on the digital economy’s contribution to the convergence of green economic efficiency on a national scale were reliable, we ran them through a battery of robustness checks. To begin, using the methodology of Liu et al. [34], we substituted the revenue ratio of software businesses with the added value of tertiary industry as the digital economy index. The outcomes of this change are shown in Column (1) of Table 3. When compared to the results in Column (2) of Table 2, the impact of the digital economy on the convergence of national green economic efficiency is marginally smaller, but the regression coefficients’ signs and significance levels are unaltered.

Table 3.
Robustness test results.
Second, the digital economy variable was lagged by one period and re-estimated, yielding the results in Column (2) in Table 3. The absolute β value is smaller than that in Column (2) in Table 2 but larger than that in Column (1), which does not include the digital economy variable. This finding denotes that the digital economy still positively impacted the convergence of national green economic efficiency and passed the significance test.
Third, we used a 2% two-sided winsorization on the sample data to reduce the effect of outliers on the regression results. Table 3, Column 3 displays the results. The digital economy hastened the convergence of regional green economic efficiency and reduced the efficiency gap between regions, even though the β convergence coefficient differs significantly from Table 2’s results. This is demonstrated by the final impact, which is minimal [35].
Fourth, robustness was checked by varying the measurement method for the dependent variable, green economic efficiency, and altering the sample period. Using the period from 2004 to 2017, the green total factor productivity of each province was measured using the nonoriented SBM model and the Granger–Morgenstern likelihood (GML) index, which more accurately reflects efficiency changes. The Malmquist model provided the growth rate between periods, more accurately aligning the results with economic reality. The other sample data were from the original dataset from between 2004 and 2017. The results are shown in Column (4). Here, the β convergence coefficient is −0.307 and significant at the 1% level, indicating the digital economy more effectively promoted the convergence of regional efficiency when measured with the SBM-GML model than with the SBM model, which did not capture efficiency changes, thus further validating our findings.
5.3. Endogeneity Test
To tackle the problem of endogeneity and further reduce the impact of endogeneity on the results related to the digital economy, the central explanatory variable, an instrumental variable approach was used. The number of post offices per million people in each province in 1984 was chosen as the instrumental variable, following the methodology of Zhao et al. [36]. We are moving from an industrial to an information-based economy, and the digital economy is driving this change by making use of network communication infrastructure. The expansion of the postal service and the rise of the internet have always gone hand in hand. Green economic efficiency may be affected, though, by the small number of post offices [37].
Since the national information technology service revenue from the previous year and the number of post offices in each province in 1984 are both cross-sectional data points, an interaction term was constructed using these two variables. This interaction term was utilized as the instrumental variable (IV) in a two-stage least squares (2SLS) regression that was conducted using panel data.
Table 4 presents the outcomes of the 2SLS regression using instrumental variables. After controlling for endogeneity, the β convergence coefficient was significantly negative, and its absolute value increased compared with the findings in Table 2, Column 3. This confirmed the existence of β convergence and that the digital economy continued to boost the convergence of green economic efficiency in China. However, the coefficient of the digital economy variable decreased, suggesting that accounting for endogeneity reduced the effect of the digital economy on green economic efficiency. Specifically, a 1 percentage point increase in digital economy investment reduced the growth rate of green economic efficiency from an increase of 6.3 percentage points to 2.5 percentage points.

Table 4.
Endogeneity test results.
6. Further Discussion
6.1. Heterogeneity Analysis
From two different points of view—geographic location and resource endowments—we conducted an analysis of the heterogeneity in the impact of the digital economy on the green economic efficiency of regional economies. Based on the geographical location of the sample, it was divided into three distinct regions: the eastern, the central, and the western regions. A comparison of the results of the β convergence test before and after the inclusion of the digital economy as a core explanatory variable is presented in Table 5.

Table 5.
Results of the regional heterogeneity analysis.
In the east, you will find Beijing, Shandong, Tianjin, Guangdong, Hainan, Fujian, Jiangsu, Liaoning, Hebei, Shanghai, and Zhejiang; in the center, you will find Anhui, Henan, Heilongjiang, Jiangxi, Hunan, Hubei, Jilin, and Shanxi; and in the west, you will find Gansu, Shaanxi, Guizhou, Inner Mongolia, Ningxia, Guangxi, Qinghai, Yunnan, Sichuan, Xinjiang, and Chongqing, along with eleven more.
When the digital economy was taken into consideration, the findings indicated that the influence of β convergence remained significant in all three regions. The western region experienced faster convergence than the central region, which, in turn, converged faster than the eastern region, according to an analysis of the changes in the convergence coefficients. This was discovered by comparing the two regions. This suggests that provinces in the central and western regions that had lower green economic efficiency experienced a faster growth in efficiency than provinces that had a higher efficiency. Furthermore, it took less time to narrow the disparities within the region than it did in the eastern region. It is possible that this finding is due to the fact that the western region had a lower level of green economic efficiency, fewer resources for research and development, and fewer personnel and capital resources involved in the research and development process. As a consequence of this, the effect on the convergence of the green economic efficiency driven by the digital economy was more pronounced in the western region. On the other hand, the convergence coefficient in the eastern region was lower, which may be a result of the heterogeneity in personnel mobility; the green economic efficiency may not be effectively enhanced if an excessive number of people with low levels of skill migrate [38].
Taking into consideration the driving effects of the digital economy, it was found that the convergence speed of the green economic efficiency increased by 5.6, 2.5, and 4.8 percentage points in the eastern, central, and western regions, respectively, for every 1 percentage point increase in investment in the digital economy. Based on this information, it can be deduced that the digital economy had the most significant impact on the green economic efficiency in the eastern region, followed by the western and central regions. The substantial promotion of green economic efficiency by digital economy investment in the eastern region was likely due to data resources driving R&D capital and employees toward areas with higher investment use, maximizing the benefits of the digital economy, and concentrating high-quality resources in the eastern region, where both the overall digital economy level and green economic efficiency were relatively high.
As a result, when introducing new technology, the central and western regions ought to take into consideration their level of regional development, as well as their capacity to assimilate technology. Those advanced digital technologies that have the potential to produce significant economic and social effects, particularly those that make use of skilled human resources, should receive special attention.
Resource endowment is a crucial measure of comparative advantages among regions, where the development of the digital economy and high-quality industrial growth are fundamentally reliant on resource endowments. Differences in resource endowments results in differences in the effectiveness of the digital economy in driving regional green economic efficiency convergence. We evaluated the provincial resource endowments (res) from four aspects: capital, labor, technology, and land. To align with the concepts of the digital economy and sustainability development, we used per capita fixed capital investment to represent capital levels, we measured the labor level using the average years of education, technology was represented by the number of researchers per ten thousand people, and green space area was used to represent land. The provinces were categorized into high- and low-resource endowment regions using the entropy method to integrate the data from these four dimensions. Table 6 reports the results of the heterogeneity analysis of the resource levels. The results of the interaction of the digital economy and resource endowment showed that the development of the digital economy drove the convergence of regional green economic efficiency in both high- and low-resource areas. However, the convergence speed of green economic efficiency slowed as the level of the digital economy increased in regions with higher levels of resources. Conversely, the digital economy accelerated the convergence speed in regions with fewer resources. Specifically, the efficiency convergence rate in low-resource regions increased by 2.5 units for every 1 unit increase in digital economy development. This effect was attributed to the ability of low-resource regions to leverage their latecomer advantage through technological innovation and transformation, enabling leapfrog development and catching up to regions with more resources [39].

Table 6.
Results of the resource endowment heterogeneity analysis.
6.2. Mechanism Analysis
6.2.1. Analysis of the Impact of the Digital Economy on the Flow of R&D Resources
Equation (8) was empirically tested to examine the impact of the digital economy on the net flows of R&D-related factors to thoroughly investigate and determine the reasons for the digital economy’s acceleration of regional green economic efficiency convergence in China. We also aimed to validate the mechanistic analysis in Section 2. The analysis involved performing F, Hausman, and BP tests to assess the model fit; we thus selected a fixed-effects model and used cluster robust standard errors to address heteroscedasticity.
Table 7 reports the regression results for the digital economy with (1) the net flow of R&D capital and (2) the net flow of R&D personnel with fixed provincial effects alone, as well as the results for (3) the net flow of R&D capital and (4) the net flow of R&D personnel with both provincial and time effects fixed.

Table 7.
Digital economy and R & D factor flow fixed-effect model regression results.
Table 7 shows that the development of the digital economy significantly and positively impacted the flow of R&D capital, indicating that the digital economy played a guiding role in the allocation and flow of capital resources. The digital economy has enabled the identification of the mechanism through which various factors affect the economic and social spheres through big data and the internet, reducing barriers to resource mobility in the market and thus accelerating the movement of capital. The digital economy also facilitated the inter-regional movement of R&D personnel. The development of the digital economy can lead to the substitution of low-skilled labor, a disadvantage that outweighs the labor shortage caused by the decrease in the demographic dividend. The application of data technology can stimulate human capital, resulting in the more efficient allocation of human resources. Additionally, the digital economy is characterized by differentiated single-level breakthroughs, with core cities such as Changsha, Chengdu, Chongqing, and Xi’an developing specialized, regional, digital economic hubs that attract human resources, leading to a concentration of skilled workers in these central and western cities.
6.2.2. The Mismatch of R&D-Related Factors in Relation to the Digital Economy
Market barriers, policy restrictions, and information asymmetry between regions have hindered resource mobility, preventing resources from flowing to regions that could use them more effectively, resulting in resource misallocation. Labor and capital are unable to freely flow according to market demand, leading to labor surpluses and capital shortages in some regions, which affect the economic efficiency and development level across regions. Correcting these resource imbalances can increase resource allocation efficiency. Dollar and Wei empirically found that reducing imbalances and increasing the efficacy of capital allocation could increase China’s GDP without additional input, resource use efficiency, and technical investment, thereby increasing the total factor productivity in China. Therefore, reducing the misallocation of R&D resources to maximize resource allocation benefits is a prerequisite for increasing China’s green economic efficiency. One of our study questions was whether the digital economy can promote the growth in green economic efficiency by reducing the misallocation of R&D resources in China. Table 8 presents the fixed-effects regression results of the digital economy and R&D factor misallocation.

Table 8.
Digital economy and R & D factor mismatch fixed-effect model regression results.
The results in columns (1) and (2), which list the fixed provincial effects without fixed time effects, indicate that the digital economy reduced the misallocation of R&D capital but did not robustly reduce the misallocation of R&D personnel. The results of the bidirectional fixed-effects model in column (3) show that the core explanatory variable, the digital economy, reduced the R&D capital misallocation index. The digital economy decreased the misallocation of R&D capital factors. The core issue of resource allocation imbalances lies in information asymmetry, which has led to information silos and information blind spots in traditional production, restricting the rational allocation and full use of R&D resources. However, the dissemination and sharing of information have substantially increased with the rapid development of the digital economy. The new technologies and platforms provided by the digital economy effectively reduce information barriers, facilitating the flow and sharing of information, allowing for the more rational allocation and use of R&D factors within regions [40]. The digital economy offers more information resources and collaborative opportunities for various regions, helping to strengthen cooperation and communication among regions, promoting the cross-regional flow and sharing of R&D resource, and thus increasing the efficiency and innovation capability of R&D resource use.
In summary, the findings of this study reinforce the existing body of literature that underscores the affirmative impact of the digital economy on fostering green economic efficiency convergence across regions. The research, however, sheds new light on the mechanisms by which the digital economy exerts its influence on green economic efficiency, particularly focusing on the movement of R&D factors and the alleviation of capital misallocation. By examining regional disparities in response to investments in the digital economy, especially in regions with varying resource endowments, the study provides a more refined comprehension of how digital economy policies can be customized to suit specific regional settings. Contrary to certain previous studies, this study underscores the substantial potential for leapfrogging in underdeveloped regions, particularly in the western regions and those with low resource endowments. This insight suggests that policies targeting the development of the digital economy should prioritize less developed areas to bridge regional disparities in green economic efficiency.
7. Conclusions and Policy Recommendations
Promoting sustainable development can only be achieved by increasing regions’ green economic efficiency. From the vantage points of the misallocation of research and development funds, as well as the interregional flow of these funds, we examined the effects of China’s digital economy on regional green economic efficiency. Here are the results of our research. The convergence of σ and β in China’s regional green economic efficiency was the first finding. It used to take a lot longer for regions with low green economic efficiency to catch up to regions with high green economic efficiency, but thanks to the rise of the digital economy, that time is now much shorter. Secondly, due to the impact of the digital economy, the convergence speed of green economic efficiency in the three main regions of China—the western, central, and eastern regions—was faster in the western region than in the central region. Similarly, in the eastern region, the convergence speed was faster than in the central region. The eastern region saw the greatest increase in green economic efficiency due to the digital economy, followed by the western region and, finally, the central region. Third, by decreasing resource misallocation and easing the regional flow of R&D-related factors, the digital economy hastened regional convergence and encouraged green economic efficiency growth [41]. Research and development (R&D) capital moved more freely between Chinese provinces as a result of the digital economy, whereas R&D personnel moved less freely. While the rise of the digital economy did a good job of lowering R&D capital misallocation, it failed to significantly forestall R&D personnel misallocation. Consequently, the effect on research and development capital was the principal channel via which the digital economy affected green economic efficiency levels. The growth of the digital economy has improved green economic efficiency and helped bring about convergence in national green economic efficiency by increasing the flow of research and development capital and decreasing its misallocation.
The results show that green economic efficiency is converging faster in the digital economy, especially when it comes to improving the mobility of R&D capital and reducing misallocation. However, there are some limitations that need to be addressed, like the fact that the role of R&D personnel flow has not been thoroughly studied and that there needs to be more research into regional and sectoral differences. To further reduce regional disparities in green economic efficiency, future research should focus on improving our understanding of talent mobility, exploring differences by sector and region, investigating the long-term sustainability of the digital economy’s impact, and studying how digital platforms shape innovation ecosystems.
The growing tensions in China over population, resources, and the environment have worsened in recent years due to the country’s sluggish economic growth. Sustainable development, which aims to balance economic growth with environmental improvement, has emerged as a critical issue for Chinese society and industrial development. The study’s conclusions inform the following policy suggestions.
Make use of the internet’s potential to advance sustainable development: Given the positive effects of digital economy development on green economic efficiency, it is important to acknowledge the role of the digital economy in advancing industrial adjustment, upgrading technology, and environmental governance. To ensure that production meets demand, policymakers should map out specific areas for the digital economy to flourish in, aggressively promote digital technologies, and take advantage of big data’s benefits. During sustainability development, it is possible to reap the benefits of information technology by reducing pollution and carbon emissions through the use of digital and intelligent technologies [42].
To encourage the nationwide convergence of environmentally friendly economic growth and efficiency, the federal government should provide financial and other resources to states so that they can establish sustainability development plans that are both unique and adaptable. By reducing internal regional efficiency disparities and rationally allocating resources according to local endowments and development conditions, the eastern regions can avoid the siphoning effect [43]. In order to improve green economic efficiency, the western regions should utilize digital technologies to steer environmental governance, boost innovation output by capitalizing on the digital economy, and speed up technological catch-up with the eastern regions.
In order to boost digital momentum, it is possible to set up systems for sharing innovation resources with nearby regions. In order to foster innovation [44] and sustainability development [45], data flow should propel R&D-related elements to relocate across regions. By lowering obstacles to information transfer across sectors and geographical areas, the digital economy can be advantageous to research and development personnel and capital. In order to lessen regional inequalities in green economic efficiency, it is necessary to encourage technical diffusion and knowledge spillover across regions and sectors [40], foster the cooperative growth of technology-based businesses [46], and strengthen regional linkages.
Center your attention on how the rise of the digital economy has affected research and development workers: It is important to find ways to reduce income inequality between regions and make the most of the opportunities presented by the digital economy for human resources. Regional governments should prioritize the development of human capital in order to recruit qualified research and development workers, establish a transparent and unrestricted flow of human resources, raise wages and benefits for R&D workers, pour more money into high-tech talent and research initiatives, and fortify the building of a digital infrastructure to encourage effective innovation and research.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.Y.; methodology, J.G. and W.Y.; investigation, J.G., W.Y. and Y.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, J.G. and W.Y.; writing—review and editing, G.Y. and X.L.; project administration, X.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 72004060; Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation, grant number 2023A1515010619; Hunan Young Science and Technology Innovation Talents (He Jian), grant number 2023RC3184; Hunan Province degree and postgraduate teaching reform research project, 2022JGYB198; and Research Project on Teaching Reform in Colleges and Universities of Hunan Province, grant number HNJG-20230829.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All relevant data is included in the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ma, D.; Zhu, Q.; Business, J.O. Innovation in emerging economies: Research on the digital economy driving high-quality green development. J. Bus. Res. 2022, 145, 801–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, C.; Freeman, C. Structural Crises of Adjustment business Cycles and Investment Behaviour. In Technical Change and Economuic Theory; Ifias Research Series 6; Pinter Pub Ltd.: London, UK, 1988; pp. 38–66. [Google Scholar]
- Perez, C. Structural Change and Assimilation of New Technologies in the Economic and Social Systems. Futures 1983, 15, 357–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, C. Technological revolutions and financial capital: The dynamics of bubbles and golden ages. Foreign Aff. 2003, 82, 148. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, S.; Ma, X.; Ji, J. The impact of industrial structure efficiency on provincial industrial energy efficiency in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 215, 925–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, M.E.; Linde, C. Toward a new conception of the environment competitiveness relationship. J. Econ. Perspect. 1995, 9, 97–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, S.; Fan, Z. Modeling the role of environmental regulations in regional green economy efficiency of China: Empirical evidence from super efficiency DEA-Tobit model. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 261, 110227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zhou, P.; Hu, D. Influences of the ongoing digital transformation of the Chinese Economy on innovation of sustainable green technologies. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 875, 162708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faisal, F.; Azizullah Tursoy, T. Does ICT lessen CO2 emissions for fast-emerging economies? An application of the heterogeneous panel estimations. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 10778–10789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Li, Z.; Yang, C. Spatial interaction spillover effects between digital financial technology and urban ecological efficiency in China: An empirical study based on spatial simultaneous equations. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, S.; Hao, Y.; Xu, L. Digitalization and energy: How does internet development affect China’s energy consumption? Energy Econ. 2021, 98, 105220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Zhang, R.; Li, G. Environmental decentralization, digital finance and green technology innovation. Struct. Change Econ. Dyn. 2022, 61, 101927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, Z.; Robaina, M.; Botelho, A. The role of ICT in energy consumption and environment: An empirical investigation of Asian economies with cluster analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 32913–32932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Xu, Z.; Xie, X. Exploring the Role of Digital Economy in Enhanced Green Productivity in China’s Manufacturing Sector: Fresh Evidence for Achieving Sustainable Development Goals. Sustainability 2024, 16, 4314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wu, H.; Jiang, J.; Zong, Q. Digital finance and the low-carbon energy transition (LCET) from the perspective of capital-biased technical progress. Energy Econ. 2023, 120, 106623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Mu, R.; Zhan, Y. Digital economy, energy efficiency, and carbon emissions: Evidence from provincial panel data in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 852, 158403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, C.; Yi, M.H. The Effect of the Internet on Economic Growth: Evidence from Cross-country Panel Data. Econ. Lett. 2009, 105, 39–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, Y.H.; Yoo, K. Internet, Inequality and Growth. J. Policy Model. 2008, 30, 1005–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, M.R.; Lopez, A.J. Assessing the Regional Digital Divide Across the European Union-27. Telecommun. Policy 2011, 35, 220–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Li, J. Digital economy development and green economic efficiency: Evidence from province-level empirical data in China. Sustainability 2022, 15, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Qiu, S.; Zhu, L. Effects of Environmental Regulations on Technological Innovation Efficiency in China’s Industrial Enterprises: A Spatial Analysis. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Hu, X.Z. Analysis on Regional differences and convergence of the efficiency of China’s green economy based on DEA. Economist 2010, 11, 46–54. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, Z.M.; Liu, X.C. Regional Differences in China’s Green Economic Efficiency and Their Determinants. China Popul. Resouces Environ. 2013, 23, 104–109. [Google Scholar]
- Tone, K. A slacks-based measure of efficiency in data envelopment analysis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2001, 130, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, H.J. Reestimating the Capital Stock of China: 1952–2006. J. Quant. Technol. Econ. 2008, 25, 17–31. [Google Scholar]
- Bukht, R.; Heeks, R. Defining, Conceptualising and Measuring the Digital Economy. GDI Dev. Inform. Work. Paper. 2017, 68, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barro, R.J.; Sala-i-Martin, X. Technological Diffusion, Convergence, and Growth. J. Econ. Growth. 1997, 2, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dollar, D.; Wei, S.J. Das (Wasted) Kapital: Firm Ownership and Investment Efficiency in China. NBER Work. Pap. 2007, 13103. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, J.H.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, F.X. R&D Element Flow, Spatial Knowledge Spillovers and Economic Growth. Econ. Res. J. 2017, 52, 109–123. [Google Scholar]
- Czernich, N.; Falck, O.; Kretschmer, T. Broadband Infrastructure and Economic Growth. Econ. J. 2011, 121, 505–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Y.C.; Wu, L.H.; Bai, J.H. Does the Competition of Fiscal S&T Expenditure Improve the Regional Innovation Performance? —Based on the Perspective of R&D Factor Flow. Publ. Fin. Res. 2020, 1, 45–58. [Google Scholar]
- Krugman, P.R. Increasing Returns and Economic Geography. J. Polit. Econ. 1991, 99, 483–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, I.S. Migration and Metropolitan Growth: Two Analytical Models; Chandler Pub., Co.: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Ma, Y.R.; Xu, S.X. Has the development of digital economy improved the efficiency of China’s green economy? China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2022, 32, 72–85. [Google Scholar]
- Roback, J. Wages, Rents, and the Quality of Life. J. Polit. Econ. 1982, 90, 1257–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, S. Digital Economy, Entrepreneurship, and High-Quality Economic Development: Empirical Evidence from Urban China. J. Manag. World 2020, 36, 65–75. [Google Scholar]
- Rosen, S. Wage-based Indexes of Urban Quality of Life. In Current Issues in Urban Economics; Mieszkowski, P., Strazheim, M., Eds.; Johns Hopkins University Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Tapscott, D. The Digital Economy: Promise and Peril in the Age of Networked Intelligence; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.L.; Shao, Q.L.; Nathwani, J. Measuring wellbeing performance of carbon emissions using hybrid measure and meta-frontier techniques: Empirical tests for G20 countries and implications for China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 237, 117758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietz, T.; Rosa, E.A.; York, R. Environmentally efficient well-being: Is there a Kuznets curve? Appl. Geogr. 2012, 32, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgenson, A.K.; Alejseyko, A.; Giedraitis, V. Energy consumption, human well-being and economic development in central and eastern European nations: A cautionary tale of sustainability. Energy Policy 2014, 66, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Cai, J. Carbon emissions and the development of digital economy: A perspective of spatial evolution. J. Environ. Prot. Ecol. 2022, 23, 409–416. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Luo, Y.; Wang, S.Y. Spatial effects of economic performance on the carbon intensity of human well-being: The environmental Kuznets curve in Chinese provinces. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 233, 681–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.X.; Venevsky, S.; Shi, X.L. Econometrics of the environmental Kuznets curve: Testing advancement to carbon intensity-oriented sustainability for eight economic zones in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 283, 124561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Y.; Wang, S.J.; Zhou, C.S. Consumption-based carbon intensity of human well-being and its socioeconomic drivers in countries globally. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 366, 132886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.J.; Xie, Z.H. WUR How does urbanization affect the carbon intensity of human well-being? A global assessment. Appl. Energy 2022, 312, 118798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).