Generative AI and Sustainable Performance in Manufacturing Firms: Roles of Innovations and AI Regulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
Research Gaps and Theoretical Contributions
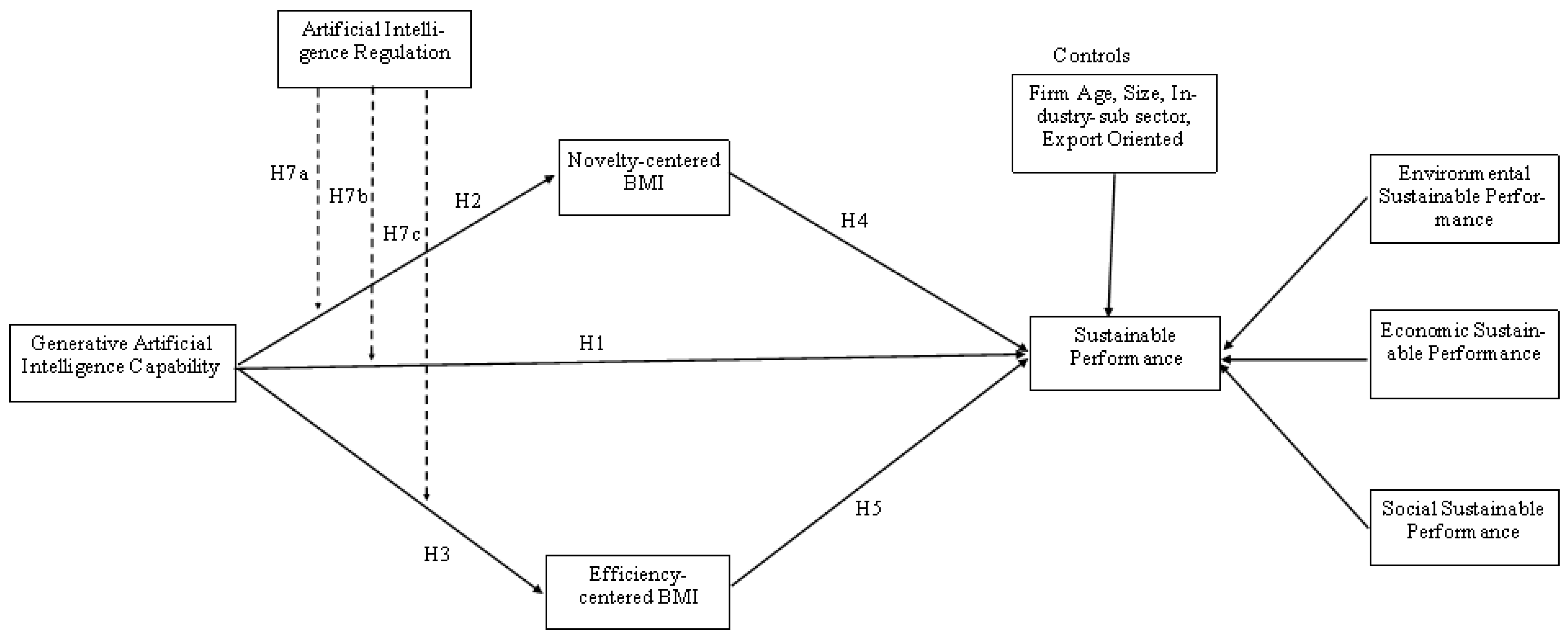
3. Hypothesis Development
3.1. GenAI and Sustainable Performance
3.2. GenAI and Novelty-Centered BMI
3.3. GenAI and Efficiency-Centered BMI
3.4. Novelty-Centered BMI and Firm Sustainability Performance
3.5. Efficiency-Centered BMI and Firm Sustainability Performance
3.6. Mediation Effects
3.7. Moderation Effects of AI Regulation
4. Methodology
4.1. Data Collection
4.2. Measures
4.3. Control Variables
5. Results
5.1. Common Method Bias (CMB)
5.2. Measurement Model
5.3. Model Fit
5.4. Structural Model
5.5. Post Hoc Analysis
5.6. Robustness Check
5.7. Discussion
6. Conclusions
6.1. Theoretical Implications
6.2. Implications for Practice
6.3. Future Research Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ullah, S.; Mehmood, T.; Ahmad, T. Green intellectual capital and green HRM enabling organizations go green: Mediating role of green innovation. Int. J. Innov. Sci. 2023, 15, 245–259. [Google Scholar]
- Ullah, S.; Kukreti, M.; Sami, A.; Shaukat, M.R. Leveraging technological readiness and green dynamic capability to enhance sustainability performance in manufacturing firms. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2025, 36, 714–730. [Google Scholar]
- Karadimas, G.; Pagone, E.; Salonitis, K. Comparative Life Cycle Assessment of Swarf Cleaning Methods for Sustainable Manufacturing. Procedia CIRP 2025, 134, 1005–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, G.; Si, D.; Ahmad, M.; Gu, X. Advancing Environmental Sustainability: A Study on Energy and Resource Efficiency through Technological Innovation in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2024, 18, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badurdeen, F.; Jawahir, I.S. Strategies for value creation through sustainable manufacturing. Procedia Manuf. 2017, 8, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Sun, D.; Warraich, M.A.; Waheed, A. Does industry 5.0 model optimize sustainable performance of Agri-enterprises? Real-time investigation from the realm of stakeholder theory and domain. Sustain. Dev. 2023, 31, 2507–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narkhede, G.; Dohale, V.; Mahajan, Y. Darker side of industry 4.0 and its impact on triple-bottom-line sustainability. Sustain. Dev. 2024, 32, 5999–6016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, T.; Islam, R.; Pitafi, A.H.; Xiaobei, L.; Rehmani, M.; Irfan, M.; Mubarak, M.S. The impact of corporate social responsibility on customer loyalty: The mediating role of corporate reputation, customer satisfaction, and trust. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2021, 25, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.T. Corporate social responsibility and SMEs’ performance: Mediating role of corporate image, corporate reputation and customer loyalty. Int. J. Emerg. Mark. 2023, 18, 4565–4590. [Google Scholar]
- Hosta, M.; Zabkar, V. Antecedents of environmentally and socially responsible sustainable consumer behavior. J. Bus. Ethics 2021, 171, 273–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbie, I. Identifying challenges facing manufacturing enterprises toward implementing sustainability in newly industrialized countries. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2017, 28, 928–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, H. Generative artificial intelligence and internationalization green innovation: Roles of supply chain innovations and AI regulation for SMEs. Technol. Soc. 2025, 82, 102898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şahin, O.; Karayel, D. Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) in Business: A Systematic Review on the Threshold of Transformation. J. Smart Syst. Res. 2024, 5, 156–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäntysaari, K. GenAI Assisted Incremental Innovation and Practices. Bachelor’s Thesis, University of Oulu, Oulu, Finland, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, N.; Chaudhary, V.; Singh, N.; Soni, N.; Kapoor, A. Transforming business with generative ai: Research, innovation, market deployment and future shifts in business models. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2411.14437. [Google Scholar]
- Golder, S.S.; Das, S.; Mondal, S. Revolutionizing Industrial Manufacturing with Big Data and Generative AI: A Path to Predictive Efficiency. J. Comput. Anal. Appl. 2024, 33, 1520. [Google Scholar]
- Janssen, M. Responsible governance of generative AI: Conceptualizing GenAI as complex adaptive systems. Policy Soc. 2025, 44, 38–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi-Tavani, Z.; Zantidou, E.; Leonidou, C.N.; Zeriti, A. Business model innovation and export performance. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2025, 56, 360–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooi, K.-B.; Tan, G.W.-H.; Al-Emran, M.; Al-Sharafi, M.A.; Capatina, A.; Chakraborty, A.; Dwivedi, Y.K.; Huang, T.-L.; Kar, A.K.; Lee, V.-H.; et al. The Potential of Generative Artificial Intelligence Across Disciplines: Perspectives and Future Directions. J. Comput. Inf. Syst. 2025, 65, 76–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente-Almendros, J.A.; Nicoara-Popescu, D.; Pastor-Sanz, I. Digital transformation in SMEs: Understanding its determinants and size heterogeneity. Technol. Soc. 2024, 77, 102483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, S. A study on supply chain system of manufacturing steel industry. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2025, 13, 2395–4752. [Google Scholar]
- Ghebrehiwet, I.; Zaki, N.; Damseh, R.; Mohamad, M.S. Revolutionizing personalized medicine with generative AI: A systematic review. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2024, 57, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abadi, M.M.K.F.; Liu, C.; Zhang, M.; Hu, Y.; Xu, Y. Leveraging AI for energy-efficient manufacturing systems: Review and future prospectives. J. Manuf. Syst. 2025, 78, 153–177. [Google Scholar]
- Vatin, N.I.; Negi, G.S.; Yellanki, V.S.; Mohan, C.; Singla, N. Sustainability Measures: An Experimental Analysis of AI and Big Data Insights in Industry 5.0. In Proceedings of the BIO Web of Conferences, Copenhagen, Denmark, 25–30 August 2024; p. 01072. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Emran, M.; Abu-Hijleh, B.; Alsewari, A.A. Examining the impact of Generative AI on social sustainability by integrating the information system success model and technology-environmental, economic, and social sustainability theory. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2025, 30, 9405–9426. [Google Scholar]
- Sinha, P.; Sharma, M.; Agrawal, R. AI enabled business decisions that enhance sustainability impact of an apparel and fashion supply chain. Technol. Anal. Strateg. Manag. 2024, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judijanto, L.; Winarko, T.; Tahir, U.; Vandika, A.; Sarungallo, A. The effect of AI-based technology implementation, green energy sustainability, and product innovation on economic growth of the manufacturing industry in Indonesia. West Sci. Nat. Technol 2024, 2, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A. AI-Driven Innovations for Enabling a Circular Economy: Optimizing Resource Efficiency and Sustainability. In Innovating Sustainability Through Digital Circular Economy; IGI Global Scientific Publishing: Hershey, PA, USA, 2025; pp. 47–64. [Google Scholar]
- Waltersmann, L.; Kiemel, S.; Stuhlsatz, J.; Sauer, A.; Miehe, R. Artificial intelligence applications for increasing resource efficiency in manufacturing companies—A comprehensive review. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khakurel, J.; Penzenstadler, B.; Porras, J.; Knutas, A.; Zhang, W. The rise of artificial intelligence under the lens of sustainability. Technologies 2018, 6, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakholia, R.; Suárez-Cetrulo, A.L.; Singh, M.; Carbajo, R.S. Advancing Manufacturing Through Artificial Intelligence: Current Landscape, Perspectives, Best Practices, Challenges and Future Direction. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 131621–131637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghobakhloo, M.; Fathi, M.; Iranmanesh, M.; Vilkas, M.; Grybauskas, A.; Amran, A. Generative artificial intelligence in manufacturing: Opportunities for actualizing Industry 5.0 sustainability goals. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2024, 35, 94–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanal, S.; Zhang, H.; Taeihagh, A. Development of new generation of artificial intelligence in China: When Beijing’s global ambitions meet local realities. J. Contemp. China 2025, 34, 19–42. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, W. High-Quality Manufacturing for China’s Stable Growth. China Econ. Transit. Dangdai Zhongguo Jingji Zhuanxing Yanjiu 2020, 3, 120–125. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, S.; Wang, B.; Tang, Y.; Qian, F. Opportunities and challenges of artificial intelligence for green manufacturing in the process industry. Engineering 2019, 5, 995–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barney, J. Firm resources and sustained competitive advantage. J. Manag. 1991, 17, 99–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniuk, D.; Koliada, O. Ensuring Sustainable Use of Generative Artificial Intelligence by Enterprises Based On Resource Consumption Optimization. East.-Eur. J. Enterp. Technol. 2025, 135, 68. [Google Scholar]
- Rajaram, K.; Tinguely, P.N. Generative artificial intelligence in small and medium enterprises: Navigating its promises and challenges. Bus. Horiz. 2024, 67, 629–648. [Google Scholar]
- Gazi, M.A.I.; Rahman, M.K.H.; Masud, A.A.; Amin, M.B.; Chaity, N.S.; Senathirajah, A.R.B.S.; Abdullah, M. AI capability and sustainable performance: Unveiling the mediating effects of organizational creativity and green innovation with knowledge sharing culture as a moderator. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, H.; Jiang, H.; Pan, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wu, Z.; Shu, P.; Tian, J.; Yang, T.; Xu, S. Large language models for manufacturing. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.21418. [Google Scholar]
- Ghobakhloo, M.; Iranmanesh, M.; Fathi, M.; Rejeb, A.; Foroughi, B.; Nikbin, D. Beyond Industry 4.0: A systematic review of Industry 5.0 technologies and implications for social, environmental and economic sustainability. Asia-Pac. J. Bus. Adm. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, S.; Vladimirova, D.; Holgado, M.; Van Fossen, K.; Yang, M.; Silva, E.A.; Barlow, C.Y. Business model innovation for sustainability: Towards a unified perspective for creation of sustainable business models. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2017, 26, 597–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, J.; Abraham, R.; Meske, C.; Brocke, J.V. AI governance for businesses. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2011.10672. [Google Scholar]
- Humble, N.; Mozelius, P. Generative Artificial Intelligence and the Impact on Sustainability. In Proceedings of the International Conference on AI Research, Lisbon, Portugal, 5–6 December 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.; Chen, S. Influence of Artificial intelligent in Industrial Economic sustainability development problems and Countermeasures. Heliyon 2024, 10, e25079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirikkaleli, D.; Ali, K.; Zhang, Q.; Kirikkaleli, N.O. Environmental Sustainability in the USA: Role of Artificial Intelligence. Sustain. Futures 2025, 9, 100823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konya, A.; Nematzadeh, P. Recent applications of AI to environmental disciplines: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torrent-Sellens, J.; Enache-Zegheru, M.; Ficapal-Cusí, P. Promoting the European Sustainable Firm: How Economic, Social, and Green Innovation and the AI-Based Technologies Create Pathways of Social and Environmental Sustainability. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ye, X.; Huang, C.; Li, H. To Be the New Collaborative Partner? The Effect of Generative AI on Dual Innovation in Companies. In Academy of Management Proceedings; Academy of Management: Valhalla, NY, USA, 2025; p. 15962. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, C.; Lyu, J.; Cheng, W. Unlocking Innovation Novelty Through AI Adoption: The Impact of Human-AI Collaboration. In Academy of Management Proceedings; Academy of Management: Valhalla, NY, USA, 2025; p. 14783. [Google Scholar]
- Kanungo, R.P.; Liu, R.; Gupta, S. Cognitive analytics enabled responsible artificial intelligence for business model innovation: A multilayer perceptron neural networks estimation. J. Bus. Res. 2024, 182, 114788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orth, H.G.; Hoke, J. Generative AI Innovation and CEO—TMT Dynamics: A Double-Edged Sword. In Academy of Management Proceedings; Academy of Management: Valhalla, NY, USA, 2025; p. 19139. [Google Scholar]
- Javed, A. Human Agents vs. GPU-Powered GenAI in Customer Service Platforms. J. Comput. Sci. Technol. Stud. 2025, 7, 301–308. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Zuo, J.; Yang, S. Research on the impact of generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) on enterprise innovation performance: A knowledge management perspective. J. Knowl. Manag. 2025, 29, 2238–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljaafreh, S.A. Harnessing Business Intelligence in the Era of Generative Artificial Intelligence. In Generative AI in Creative Industries; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2025; pp. 333–343. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, G.; Ji, X.; Zhang, A. Novelty and Sustainability: The Generation Process of Original Business Model Innovation. Sustainability 2023, 15, 14182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajtazi, K.; Rexhepi, G.; Sharif, A.; Ozturk, I. Business model innovation and its impact on corporate sustainability. J. Bus. Res. 2023, 166, 114082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Principato, L.; Trevisan, C.; Formentini, M.; Secondi, L.; Comis, C.; Pratesi, C.A. The influence of sustainability and digitalisation on business model innovation: The case of a multi-sided platform for food surplus redistribution. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2023, 115, 156–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammirato, S.; Linzalone, R.; Felicetti, A.M. Business model innovation drivers as antecedents of performance. Meas. Bus. Excell. 2022, 26, 6–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teece, D.J.; Pisano, G.; Shuen, A. Dynamic capabilities and strategic management. Strateg. Manag. J. 1997, 18, 509–533. [Google Scholar]
- Teece, D.J. Managing the university: Why “organized anarchy” is unacceptable in the age of massive open online courses. Strateg. Organ. 2018, 16, 92–102. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.; Mehmood, S.; Khan, S.U. Navigating innovation in the age of AI: How generative AI and innovation influence organizational performance in the manufacturing sector. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2025, 36, 597–620. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Cui, L.; Wu, L.; Lowry, P.B.; Kumar, A.; Tan, K.H. Digitalization and network capability as enablers of business model innovation and sustainability performance: The moderating effect of environmental dynamism. J. Inf. Technol. 2024, 39, 687–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Liaqat, I. AI for Sustainability: How Governance and Management Shape Environmental Performance. In Academy of Management Proceedings; Academy of Management: Valhalla, NY, USA, 2025; p. 16697. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, C.; Ma, H.; Wang, Z.; Li, G. The sustainable development of innovative cities in China: Comprehensive assessment and future configuration. J. Geogr. Sci. 2014, 24, 1095–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, N.; Lee, H.; Ford, J. Who is ‘the middle manager’? Hum. Relat. 2014, 67, 1213–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bruggen, G.H.; Lilien, G.L.; Kacker, M. Informants in organizational marketing research: Why use multiple informants and how to aggregate responses. J. Mark. Res. 2002, 39, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-H. How organizational green culture influences green performance and competitive advantage: The mediating role of green innovation. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2019, 30, 666–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F., Jr.; Hult, G.T.M.; Ringle, C.M.; Sarstedt, M.; Danks, N.P.; Ray, S. An introduction to structural equation modeling. In Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM) Using R: A Workbook; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Podsakoff, P.M.; Podsakoff, N.P.; Williams, L.J.; Huang, C.; Yang, J. Common method bias: It’s bad, it’s complex, it’s widespread, and it’s not easy to fix. Annu. Rev. Organ. Psychol. Organ. Behav. 2024, 11, 17–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarstedt, M.; Ringle, C.M.; Hair, J.F. Partial least squares structural equation modeling. In Handbook of Market Research; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 587–632. [Google Scholar]
- Fornell, C.; Larcker, D.F. Structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error: Algebra and statistics. J. Mark. Res. 1981, 18, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F.; Risher, J.J.; Sarstedt, M.; Ringle, C.M. When to use and how to report the results of PLS-SEM. Eur. Bus. Rev. 2019, 31, 2–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henseler, J.; Ringle, C.M.; Sarstedt, M. A new criterion for assessing discriminant validity in variance-based structural equation modeling. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2015, 43, 115–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, G.; Ferro, C.; Høgevold, N.; Padin, C.; Varela, J.C.S.; Sarstedt, M. Framing the triple bottom line approach: Direct and mediation effects between economic, social and environmental elements. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 197, 972–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsey, J.B. Tests for specification errors in classical linear least-squares regression analysis. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 1969, 31, 350–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simo, A.; Dzitac, S.; Ferestyan, L.; Dumitru, C.D.; Gligor, A. Optimizing Electric Vehicle Performance: Advances in Battery Management Systems for Enhanced Efficiency and Longevity. Int. J. Comput. Commun. Control 2024, 19, 6794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiarno, Y.; Novita, D. Resources-based view (RBV) as a strategy of company competitive advantage: A literature review. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Economics Business Management and Accounting (ICOEMA), Tanjungpinang, Indonesia, 17 December 2022; pp. 656–666. [Google Scholar]
- Florek-Paszkowska, A.; Ujwary-Gil, A. The Digital-Sustainability Ecosystem: A conceptual framework for digital transformation and sustainable innovation. J. Entrep. Manag. Innov. 2025, 21, 116–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
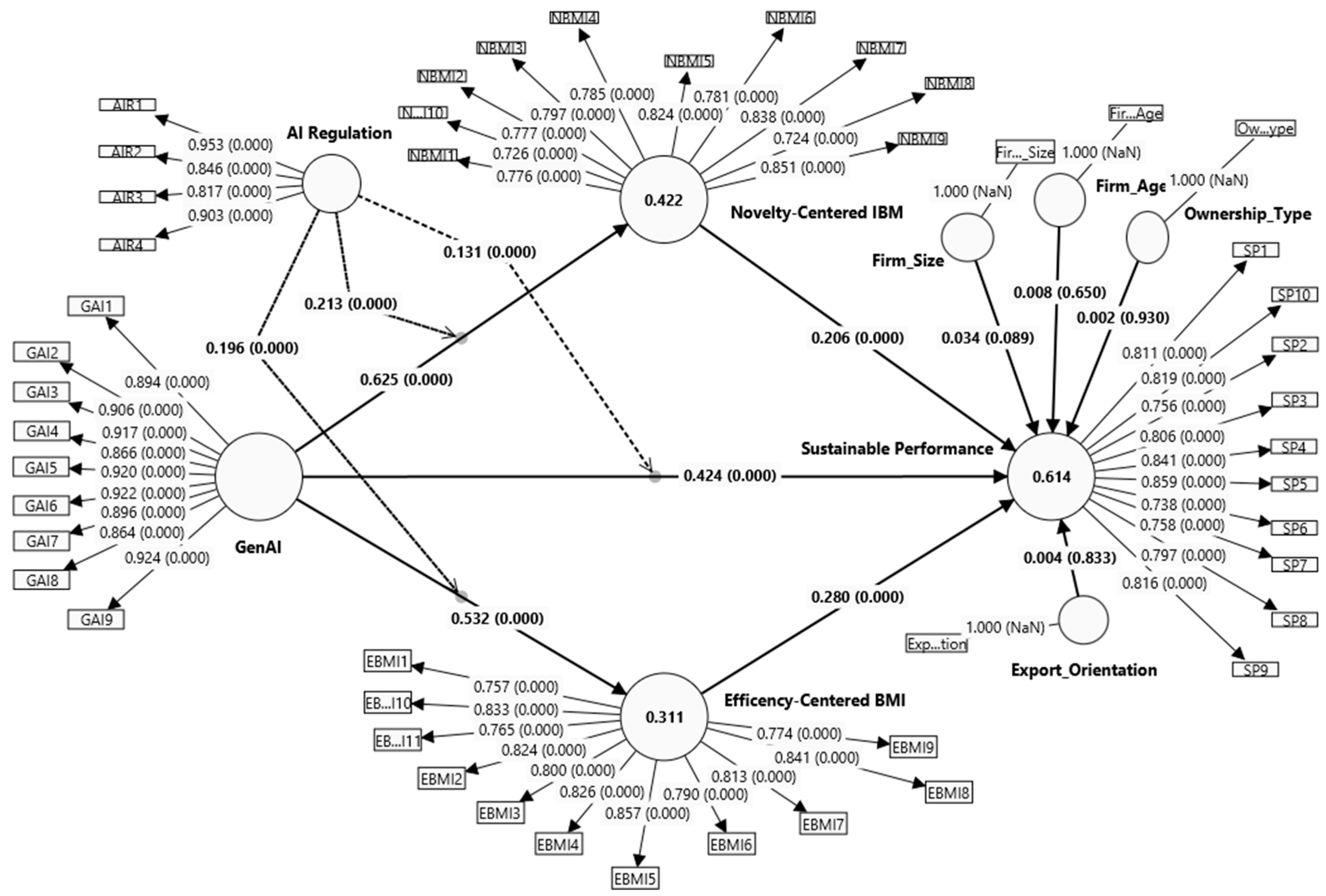
| Construct | Items | FL | VIF | α | Cr | AVE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AI Regulation | AIR1 | 0.953 | 3.597 | 0.92 | 0.933 | 0.776 |
| AIR2 | 0.846 | 3.107 | ||||
| AIR3 | 0.817 | 2.953 | ||||
| AIR4 | 0.903 | 2.614 | ||||
| Efficiency-Centered IBM | EBMI1 | 0.757 | 2.023 | 0.947 | 0.954 | 0.653 |
| EBMI10 | 0.833 | 2.682 | ||||
| EBMI11 | 0.765 | 2.064 | ||||
| EBMI2 | 0.824 | 2.61 | ||||
| EBMI3 | 0.8 | 2.34 | ||||
| EBMI4 | 0.826 | 2.624 | ||||
| EBMI5 | 0.857 | 3.057 | ||||
| EBMI6 | 0.79 | 2.261 | ||||
| EBMI7 | 0.813 | 2.442 | ||||
| EBMI8 | 0.841 | 2.801 | ||||
| EBMI9 | 0.774 | 2.13 | ||||
| GenAI | GnAI1 | 0.894 | 3.994 | 0.971 | 0.975 | 0.812 |
| GnAI2 | 0.906 | 4.489 | ||||
| GnAI3 | 0.917 | 4.989 | ||||
| GnAI4 | 0.866 | 3.237 | ||||
| GnAI5 | 0.92 | 4.15 | ||||
| GnAI6 | 0.922 | 3.256 | ||||
| GnAI7 | 0.896 | 4.09 | ||||
| GnAI8 | 0.864 | 3.235 | ||||
| GnAI9 | 0.924 | 3.421 | ||||
| Novelty-centered IBM | NBMI1 | 0.776 | 2.073 | 0.932 | 0.943 | 0.623 |
| NBMI10 | 0.726 | 1.802 | ||||
| NBMI2 | 0.777 | 2.113 | ||||
| NBMI3 | 0.797 | 2.233 | ||||
| NBMI4 | 0.785 | 2.172 | ||||
| NBMI5 | 0.824 | 2.504 | ||||
| NBMI6 | 0.781 | 2.13 | ||||
| NBMI7 | 0.838 | 2.683 | ||||
| NBMI8 | 0.724 | 1.799 | ||||
| NBMI9 | 0.851 | 2.864 | ||||
| Sustainable Performance | SPr1 | 0.811 | 2.391 | 0.938 | 0.947 | 0.642 |
| SPr10 | 0.819 | 2.463 | ||||
| SPr2 | 0.756 | 1.964 | ||||
| SPr3 | 0.806 | 2.338 | ||||
| SPr4 | 0.841 | 2.725 | ||||
| SPr5 | 0.859 | 2.992 | ||||
| SPr6 | 0.738 | 1.878 | ||||
| SPr7 | 0.758 | 1.977 | ||||
| SPr8 | 0.797 | 2.266 | ||||
| SPr9 | 0.816 | 2.44 |
| Construct | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. AI Regulation | 0.881 | ||||
| 2. Efficiency-Centered BMI | 0.023 | 0.808 | |||
| 3. GenAI | 0.025 | 0.524 | 0.901 | ||
| 4. Novelty-Centered IBM | 0.008 | 0.42 | 0.615 | 0.789 | |
| 5. Sustainable Performance | 0.026 | 0.61 | 0.691 | 0.606 | 0.801 |
| HTMT | |||||
| 1. AI Regulation | |||||
| 2. Efficiency-Centered BMI | 0.022 | ||||
| 3. GenAI | 0.024 | 0.546 | |||
| 4. Novelty-Centered IBM | 0.024 | 0.447 | 0.645 | ||
| 5. Sustainable Performance | 0.026 | 0.645 | 0.723 | 0.646 | |
| Estimated Model | |
| SRMR | 0.026 |
| d_ULS | 0.778 |
| d_G | 0.241 |
| Chi-square | 1645.101 |
| NFI | 0.962 |
| Path | Direct Effects | Moderating Effects | Indirect Effects | f2 | Supported |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control Effects | |||||
| Firm Age → sustainable performance | 0.008 (0.454) | — | — | 0.001 | - |
| Firm size → sustainable performance | 0.034 (0.089) | — | — | 0.003 | - |
| Export oriented → sustainable performance | 0.004 (0.535) | — | — | 0.001 | - |
| Ownership type → sustainable performance | 0.002 (0.93) | — | — | 0.001 | - |
| Main Effects | |||||
| GenAI → Sustainable performance | 0.424 (0.000) | 0.131 (0.000) | — | 0.232 | Yes |
| GenAI → Novelty-centered BMI | 0.625 (0.000) | 0.213 (0.000) | — | 0.673 | Yes |
| Novelty-centered BMI → Sustainable performance | 0.206 (0.000) | — | — | 0.063 | Yes |
| Efficiency-centered BMI → Sustainable performance | 0.280 (0.000) | — | — | 0.138 | Yes |
| GenAI → Efficiency-centered BMI | 0.532 (0.000) | 0.196 (0.000) | — | 0.410 | Yes |
| GenAI → Novelty-centered BMI → sustainable performance | — | — | 0.155 (0.000) | Yes | |
| GenAI → Efficiency-centered BMI → sustainable performance | — | — | 0.231 (0.000) | Yes |
| Path | β | T Value | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Efficiency-Centered BMI → Economic SP | 0.272 | 10.779 | 0.000 |
| Efficiency-Centered BMI → Environmental SP | 0.27 | 10.53 | 0.000 |
| Efficiency-Centered BMI → Social SP | 0.251 | 9.593 | 0.000 |
| GenAI → Economic SP | 0.401 | 14.872 | 0.000 |
| GenAI → Efficiency-Centered BMI | 0.532 | 28.036 | 0.000 |
| GenAI → Environmental SP | 0.389 | 13.929 | 0.000 |
| GenAI → Novelty-Centered IBM | 0.625 | 36.818 | 0.000 |
| GenAI → Social SP | 0.41 | 14.192 | 0.000 |
| Novelty-Centered IBM → Economic SP | 0.191 | 6.867 | 0.000 |
| Novelty-Centered IBM → Environmental SP | 0.215 | 7.757 | 0.000 |
| Novelty-Centered IBM → Social SP | 0.174 | 6.014 | 0.000 |
| AIR × GenAI → Economic SP | 0.128 | 4.67 | 0.000 |
| AIR × GenAI → Efficiency-Centered BMI | 0.193 | 5.054 | 0.000 |
| AIR × GenAI → Environmental SP | 0.123 | 4.563 | 0.000 |
| AIR × GenAI → Novelty-Centered IBM | 0.212 | 5.452 | 0.000 |
| AIR × GenAI → Social SP | 0.122 | 4.286 | 0.000 |
| Efficiency-Centered BMI → Economic SP | 0.272 | 10.779 | 0.000 |
| GenAI → Novelty-Centered IBM → Environmental SP | 0.134 | 7.701 | 0.000 |
| GenAI → Efficiency-Centered BMI → Economic SP | 0.145 | 9.934 | 0.000 |
| GenAI → Efficiency-Centered BMI → Environmental SP | 0.144 | 9.746 | 0.000 |
| GenAI → Novelty-Centered IBM → Social SP | 0.109 | 6.018 | 0.000 |
| GenAI → Efficiency-Centered BMI → Social SP | 0.134 | 8.898 | 0.000 |
| GenAI → Novelty-Centered IBM → Economic SP | 0.12 | 6.868 | 0.000 |
| Nonlinear Relationship | Coefficient | p Value | f2 | Ramsey’s RESET |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| QE (GenAI) → Efficiency-Centered BMI | −0.028 | 0.192 | 0.002 | F = 1.265, p = 0.284 |
| QE (GenAI) → Novelty-Centered IBM | −0.01 | 0.662 | 0.001 | |
| QE (GenAI) → Sustainable Performance | −0.024 | 0.174 | 0.002 | |
| QE (Novelty-Centered IBM) → Sustainable Performance | −0.014 | 0.318 | 0.001 | F = 1.36, p = 0.259 |
| QE (Efficiency-Centered BMI) → Sustainable Performance | 0.023 | 0.077 | 0.003 | F = 0.543, p = 0.582 |
| Mediation | |||||
| Path | Effect | BootSE | Confidence Intervals | ||
| GenAI → Novelty-Centered IBM → Sustainable Performance | 0.104 | 0.012 | (0.0817, 0.1280) | ||
| GenAI → Efficiency-Centered BMI → Sustainable Performance | 0.113 | 0.011 | (0.0909, 0.1360) | ||
| Moderation | |||||
| Path | β | se | t value | p value | Confidence Intervals |
| GenAI*AI regulation → Sustainable Performance | 0.134 | 0.012 | 11.498 | 0.000 | (0.1109, 0.1566) |
| GenAI*AI regulation → Novelty-Centered IBM | 0.111 | 0.011 | 9.437 | 0.000 | (0.0878, 0.1339) |
| GenAI*AI regulation → Efficiency-Centered BMI | 0.112 | 0.014 | 8.279 | 0.000 | (0.0853, 0.1383) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, T.; Badulescu, A. Generative AI and Sustainable Performance in Manufacturing Firms: Roles of Innovations and AI Regulation. Sustainability 2025, 17, 8661. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17198661
Shen T, Badulescu A. Generative AI and Sustainable Performance in Manufacturing Firms: Roles of Innovations and AI Regulation. Sustainability. 2025; 17(19):8661. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17198661
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Tengfei, and Alina Badulescu. 2025. "Generative AI and Sustainable Performance in Manufacturing Firms: Roles of Innovations and AI Regulation" Sustainability 17, no. 19: 8661. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17198661
APA StyleShen, T., & Badulescu, A. (2025). Generative AI and Sustainable Performance in Manufacturing Firms: Roles of Innovations and AI Regulation. Sustainability, 17(19), 8661. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17198661







