Abstract
Potato (Solanum tuberosum) is an important food crop. However, intensive cultivation has led to increased reliance on chemical fertilizers, raising environmental and economic concerns. One of the concerns in potato plantations is phosphorus, which often exhibits low availability due to leaching and poor use efficiency, coupled with rising fertilizer production costs. This study investigates the agronomic and economic impacts of using natural rock amendments combined with plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) as sustainable alternatives to chemical fertilizers on the yield and tuber quality of potato. A field experiment assessed three treatments: conventional chemical fertilizers (T1), reduced chemical fertilizers combined with PGPR (Bacillus megaterium, Bacillus mucilaginosus, and Azotobacter) (T2), and natural rock amendments of potassium feldspar and rock phosphate combined with PGPR (T3). Results showed that T2 and T3 demonstrated improved tuber quality compared to T1, with T3 achieving the highest starch content (314.05 mg/g FW) and reduced sugar content (102.03 mg/g FW). Furthermore, T3 improved soil quality after the growing season, showing higher phosphorus and potassium availability compared to T1. Economically, T3 reduced operating costs by 11% and achieved the highest yield (42 tons/ha). The return on investment for T3 reached approximately 79.48% (USD 3988/ha), with a 40.9% profit increase compared to T1 (USD 2460/ha) These findings confirm that integrating PGPR with natural rock fertilizers offers a cost-effective and durable alternative to conventional fertilization practices, enhancing productivity and profitability while providing significant opportunities for achieving the Sustainable Development Goals and promoting long-term soil sustainability.
1. Introduction
Potato (Solanum tuberosum) is a staple food crop worldwide, contributing significantly to food security and agricultural economies. Potato output exceeds 370 million metric tons yearly, making it the world’s third most important food crop after rice and wheat [1]. Potatoes are grown in over 100 nations in varied agro-ecological zones [2]. Chinese production exceeds 94 million tons per year, followed by India, Russia, and Ukraine. The global potato sector has grown by approximately 20% in the past decade to suit increased domestic and processing demands [3,4]. Egypt’s potato cultivation plays a major role in both domestic consumption and global export markets, showing both agricultural and economic importance in the potato sector. In 2023, Egypt produced approximately 6.87 million tons of potatoes from a total cultivated area of 230,000 hectares, accounting for about 20.7% of Africa’s total potato production [5]. Major importers of Egyptian potatoes include Lebanon and Greece, which source 44.02% and 42.63% of their potato imports from Egypt, respectively. Other key markets include England (6.15%), Germany (11.29%), Italy (15.1%), and Russia (17.13%) [6]. Overall, Egypt stands as a leading potato producer in Africa and a competitive exporter on the international stage, hence its need for more economical and sustainable improvements in potato cultivation.
Traditional agricultural practices rely heavily on chemical fertilizers, which, while effective, pose significant environmental challenges, including soil degradation, water contamination, and greenhouse gas emissions. A common practice among farmers is the excessive application of fertilizers, often surpassing the crop’s actual nutrient requirements. This overapplication frequently results in fertilizer leaching into surrounding water resources, negatively impacting ecosystems [7].
One of the essential minerals needed by the potato crop is phosphorus, as lack of adequate phosphorus fertilization results in reduced tuber yield and size. Its deficiency during early crop development delays tuber initiation and maturity [8]. Potatoes have a high phosphorus demand due to their low phosphorus use efficiency (PUE). This inefficiency arises from their shallow root systems, which reside predominantly in the top 60 cm of soil, limiting their ability to access phosphorus reserves and other minerals in the soil [9,10]. Consequently, farmers often apply excessive amounts of phosphorus fertilizer to meet crop demands, despite the high costs, and this leads to the risk of unused fertilizer leaching out of the soil [11]. This inefficient fertilization practice not only strains farmers economically but also can impact national economies and environmental health. These challenges underscore the urgent need for a more efficient and sustainable phosphorus fertilization approach, one that improves phosphorus use efficiency while promoting ecological sustainability.
Fertilization plays a pivotal role in ensuring food security; however, over-fertilization adversely impacts agricultural systems by accelerating soil acidification, increasing greenhouse gas emissions, and ultimately reducing economic returns. In contrast, sustainable agriculture offers alternatives that maintain productivity while mitigating environmental harm. Sustainable alternatives include natural rocks, such as rock phosphate and feldspar, and biological inoculants like plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF), which both offer promising solutions. Several studies have explored the impact of AMF and natural rocks on various crops, including carob trees [12], robusta coffee [13], tomato [14], potato [15], and wheat [16,17]. These studies collectively highlight improvements in crop performance, such as enhanced root system development and improved plant physiological parameters. These enhancements reflect better nutrient assimilation.
Natural rocks, such as rock phosphate (RP) and feldspar, serve as primary sources of phosphorus (P) and potassium (K) fertilizers, respectively. However, their direct application to crops as P and K sources is often constrained due to the high soil pH, which renders these minerals insoluble and inaccessible to plants. To address this, these natural resources often undergo chemical treatments and high-temperature processes to convert their insoluble forms into soluble, plant-available nutrients. Alternatively, AMF and PGPR offer a sustainable biological approach to solubilize these natural mineral forms, bypassing the need for expensive industrial processing [18,19,20]. PGPR play a vital role in bridging this gap by forming a symbiotic relationship with plants.
PGPR mostly live in symbiosis with the plant, and they have been found to stimulate root growth and therefore enhance the plant’s ability to uptake the nutrients needed from soil [17]. PGPR such as Bacillus megaterium have been known to solubilize essential minerals, such as P and K, and have the ability to fix nitrogen, thereby enhancing nutrient availability and uptake [21,22]. Bacillus mucilaginosus solubilizes insoluble potassium minerals, such as feldspar, into plant-available forms through organic acids and enzymes, enhancing soil fertility and crop growth [23]. Similarly, Azotobacter plays a crucial role in nitrogen fixation, converting atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia, which plants can absorb, thereby reducing the need for chemical fertilizers [24]. The significant volatility in global fertilizer markets, highlighted by an 80% price increase from 2020 to 2023 resulting from supply chain disruptions, energy crises, and export limitations [25], has increased the demand for sustainable alternatives that stabilize long-term input prices [26].
Therefore, this study aimed to assess the agronomic and economic potential of substituting or reducing chemical fertilizers with natural rocks inoculated with PGPR in the cultivation of potato variety Cara. The primary objective of this study is to explore the impact of the different tested fertilization treatments on plant growth, tuber quality, and yield through a field experiment. The second objective is to assess the cost-effectiveness and operational efficiency of the treatments applied. In terms of the economic impact of the treatments, a multi-year economic projection based on fertilizer price index trends is included to assess the long-term financial viability of integrating PGPR-coated natural rocks. The approach examined in this study aims to provide a sustainable and economically resilient alternative to traditional fertilization practices in potato production.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design and Plantation
The field experiment was conducted at Sphinx research station in Menoufia, Egypt, during the 2024 growing season. The soil type at the site was clay with a pH of 7.2. The field was prepared by ploughing and harrowing to create a fine seedbed. After the soil was tilled 25 cm deep, mixed manure was applied at 0.70 m3 per plot three weeks before planting. A mix of micro-nutrients was added to prevent any deficiencies; no chemical pesticides were used. Instead, soil and foliar application of copper lignosulfonate and sulfur were applied as protectives against fungal diseases. The field experiment was laid out with three treatments and 15 replicates. The treatments were as follows: chemical fertilizers without rocks or biological inoculants (T1); chemical fertilizers inoculated with PGPR, without rocks (T2); and rocks inoculated with PGPR, without chemical fertilizers (T3). The chemical fertilizer treatment received a recommended dose of NPK (nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium) fertilizers, while the rock treatments received equivalent amounts of nutrients in the form of rock phosphate and feldspar. PGPR inoculants were applied as per the treatments and were applied as a soil drench at a concentration of 108 CFU mL−1 (Table 1). Potato seeds of the Cara variety are commercially available and were acquired from local vendors (AGROFOOD, Giza, Egypt). The seeds were planted after cutting each tuber to about 3–5 pieces with at least one eye. The cut tubers were planted in rows with a spacing of 50 cm between rows and 30 cm between plants. Each plot measured 72 m × 40 m. Soil samples were taken before planting and after harvest to analyze the availability of elements such as N, P, K, Fe, Zn, and organic matter.

Table 1.
Composition of chemical and rock fertilizers per treatment per hectare (ha).
2.2. Soil Physicochemical Properties
The total phosphorus (P) content was determined using the method described by Olsen and Sommers (1982) [27]. This involved digestion with nitric acid, perchloric acid, and ammonium molybdovanadate, followed by spectrophotometric measurement at a wavelength of 420 nm [28,29]. Exchangeable potassium (K) content was determined by extracting exchangeable cations from soil samples using 1N ammonium acetate. The resulting extract was analyzed to quantify the exchangeable K present in the soil using an atomic absorption spectrophotometer at 776 nm [30]. Zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), iron (Fe), and manganese (Mn) were determined by treating 10 g of soil with 20 mL of DTPA extracting solution (0.005 M DTPA, 0.1 M TEA, and 0.01 M CaCl2, adjusted to pH 7.3). The soil and DTPA solution were mixed for two hours and then filtered. The extract was then analyzed for metals with an inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometer. Calcium (Ca) and magnesium (Mg) were extracted and determined from the soil by mixing 10 mL of 1 N ammonium acetate with 10 g of soil and mixing for 5 min. The filtered extract was analyzed with an inductively coupled plasma–atomic emission spectrometer for calcium and magnesium. The results are reported in parts per million (ppm) in the soil.
2.3. Evaluation of Vegetative Growth Parameters
After 50 days of planting, the following plant growth parameters were measured: plant height (cm), stem diameter (cm) using a digital caliper, and stem branching. Spectral vegetative indices for evaluating plant health were also assessed using a portable leaf spectrometer (CI-710; CID, Camas, WA, USA), calibrated according to the manufacturer’s specifications. For measuring reflectance spectra, five leaves on the second and third nodes from the top of the plant were placed individually between the clip of the measuring head following the manufacturer’s instructions. Using the leaf spectrometer, the indices measured included the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) [31], Normalized Pheophytization Index (NPQI) [32], Normalized Chlorophyll Pigment Ratio Index (NPCI) [33], Photochemical Reflectance Index (PRI) [34], Flavanol Reflectance Index (FRI) [35], Structure Independent Pigment Index (SIPI) [32,36], Plant Senescence Reflectance Index (PSRI) [33], total chlorophyll content (ChlT), chlorophyll a (ChlA), and chlorophyll b (ChlB) [37,38]. Measurements were taken from five plants per treatment in three plots.
2.4. Tuber Yield and Post-Harvest Measurements
2.4.1. Determination of Dry Matter Content (DMC)
Potato tubers were peeled, grated, and weighed before being placed in a pre-weighed crucible. The samples were then dried in an oven at 105 °C for 24 h until a constant weight was achieved. The DMC was calculated as the percentage ratio of the weight of the dried sample to the weight of the fresh sample.
2.4.2. Reducing Sugar Content Determination
Reducing sugars were extracted from 1 g potato tuber samples by homogenization in 5 mL of 80% ethanol at 80 °C, followed by centrifugation at 10,000× g for 10 min. This extraction process was repeated five times to maximize sugar recovery. The supernatant containing the extracted sugars was subjected to the phenol-sulfuric acid method and the absorbance of the resulting solution was measured at 490 nm using a spectrophotometer. The remaining pellet was used to determine the starch content. A standard curve prepared with known glucose concentrations was used to quantify the reducing sugar content in the potato samples [39].
2.4.3. Starch Content Determination
Starch content was determined in the remaining pellet obtained after sugar extraction. The pellet, enriched in starch, underwent hydrolysis to convert starch into glucose. This was performed using the anthrone method, in which 5 mL of freshly prepared anthrone reagent (2 g.L−1 prepared in sulfuric acid) was mixed well with the pellet and then placed in boiling water bath for 10 min and cooled to room temperature before measuring absorbance at 630 nm using a spectrophotometer [40]. A standard curve generated using known glucose concentrations was used to calculate the starch content in the potato samples.
2.5. Cost–Benefit Analysis
Cost–benefit analysis was conducted to evaluate the applicability of the fertilization protocols in potato production. The cost analysis was conducted in US dollars ($). The total cost was split into fixed and variable cost calculated per hectare to evaluate total operating cost (TOC). The following parameters were also evaluated: total revenue, profitability and benefit–cost ratio (BCR) [41]. To assess economic performance, return on investment (ROI) was first calculated for the base year (2024) using actual field data on total operating cost (TOC) and net profit per treatment. A multi-year projection of net phosphorus (P) cost and ROI was conducted for 2024–2026 to capture the impact of fertilizer price volatility on economic sustainability. Fertilizer prices were adjusted annually using World Bank index multipliers as following: +3.9% for 2024, +7.1% for 2025, and +5.0% for 2026 [25]. ROI was recalculated annually using the updated TOC to evaluate the economic trajectory of each fertilization strategy over time, with 10% Residual P Decline per Year [42,43].
2.6. Statistical Analysis
For yield and plant biometric data, statistical analysis and graphs were conducted using GraphPad Prism 9 software. The data underwent two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), followed by a post hoc Tukey HSD test, with significance determined at p < 0.05. Two-way ANOVA was used to assess the impact of treatments, ensuring that observed differences were attributable to the treatments rather than plot variations. Principal component analysis (PCA) was performed to evaluate multivariate variability introduced by different treatments across spectral indices, morphological traits of the crop and tubers, and tuber yield. Pearson correlation analysis was utilized to describe the relationships between factors. A correlation heatmap was created by calculating Pearson’s correlation coefficients (p ≤ 0.05). Principal component analysis (PCA) and the correlation heatmap were performed using R version 4.1.3 using the factoextra and corrplot packages, respectively [44].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of the Fertilization Treatments on Plant Vegetative Growth Parameters
On day 50 after potato planting, a general plant health assessment was conducted to evaluate the potential impact of treatments during the vegetative growth stage. Measurements included plant height, stem diameter, and stem number. The tallest plants were observed in T2 (reduced chemical fertilizer with PGPR) and T3 (natural rocks inoculated with PGPR), with average heights of 48.48 cm and 48.44 cm, respectively (Figure 1A). Plants in T1 (enriched with chemical fertilizers but without rocks or biological inoculants) had a slightly lower average height of 45.5 cm (Figure 1B). The number of stems was highest in T1, followed by T3 and T2. Stem diameter was consistent across all treatments with T1 (11.64 cm), T2 (11.62 cm), and T3 (11.40 cm) (Figure 1C). No statistically significant differences were observed across treatments during the vegetative stage, and plants showed no signs of disease (Figure 1D), confirming that the experimental treatments and conventional chemical fertilizer practices did not adversely affect normal growth. Additionally, this consistency implies that any differences observed in subsequent analyses would be attributed to the treatments rather than the plant establishment phase.
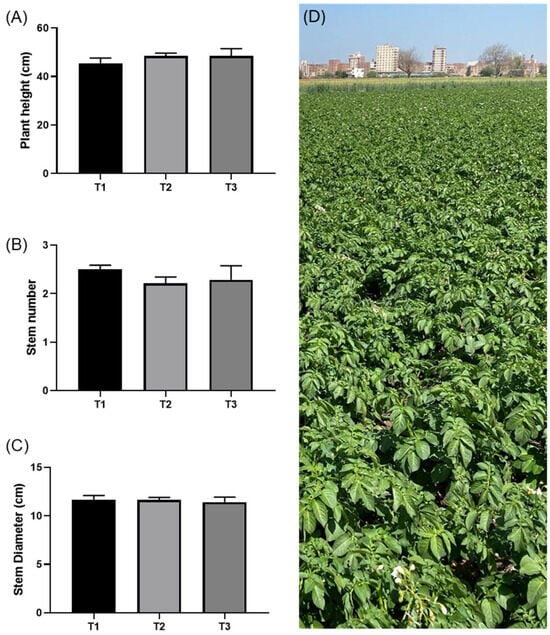
Figure 1.
Impact of the chemical and rock fertilizers on plant growth dynamics 50 days after planting. T1 (enriched with chemical fertilizers but without rocks or biological inoculants), T2 (reduced chemical fertilizer with PGPR), and T3 (natural rocks inoculated with PGPR. (A) Plant height above ground in cm, (B) number of stems per plant, (C) average stem diameter in cm, and (D) field image of the potato plantation on the day of data collection.
Spectral vegetative indices were evaluated to assess plant health at day 50 after transplantation. Total chlorophyll (ChlT), chlorophyll a (ChlA), and chlorophyll b (ChlB) levels were evaluated using the spectral method, with ChlT and ChlA significantly higher in T3 compared to T1 (p < 0.001), and T2 (p < 0.05) (Figure 2A), while ChlB content was the lowest in T1 (16.45 µg cm−3) and highest in T3 (17.20 µg cm−3) with a p-value < 0.05. ChlB content is crucial in harvesting light around the 450 nm wavelength, which cannot be captured by ChlA, increasing the light-harvesting capacity of the plant [45]. The Normalized Pigment Chlorophyll Index (NPCI) is a chlorophyll-normalized vegetative index that further confirms chlorophyll content and plant health. Across all treatments in our field experiment, NPCI was above 0.06, indicating good crop health and a lack of infestation (Figure 2B). Chlorophyll content, a major indicator of plant health, reflects overall vegetation health, as its loss signifies reduced vitality, confirming overall crop health and the absence of pest or disease infestation [46,47]. The Normalized Pheophytinization Index (NPQI) is a measure of chlorophyll degradation due to the formation of phaeopigments; this index was slightly higher in T2 (0.08) than in T1 and T3 (both 0.06). However, this difference was not statistically significant between the treatment and was still within the acceptable healthy range (Figure 2B) [48]. The Photochemical Reflectance Index (PRI) is an indicator of the chlorophyll-to-carotenoid ratio, specifically xanthophyll (a carotenoid pigment). The increase in xanthophyll pigment in plants relative to chlorophyll is often associated with plant stress and can be used as an indication of photosynthetic efficiency [49]. The PRI was consistent (~0.02) across the treatments (Figure 2C). This suggests minimal long-term heat stress, as a higher PRI typically corresponds to reduced stress and greater photosynthetic efficiency [36,50,51]. The Flavonol Reflectance Index (FRI) was lowest in T1 (1.67) compared to T2 (2.42) and T3 (2.48) (Figure 2D). While lower FRI values generally indicate higher photosynthetic efficiency and lower stress [52], the observed differences were not statistically significant, suggesting that higher FRI values in T2 and T3 do not imply plant stress. The Structure Intensive Pigment Index (SIPI) and Plant Senescence Reflectance Index (PSRI) were also measured to further evaluate plant health by analyzing the carotenoid-to-chlorophyll ratio. Both indices, which are sensitive to early senescence and stress, indicated that plants across all treatments maintained healthy chlorophyll levels without external stress effects (Figure 2E,F). Chlorophyll degradation, often associated with chloroplast dismantling during senescence, is typically linked to carotenoid production, an early marker of photosystem protection during stress [33,53,54]. Finally, the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) values were significantly higher in T2 and T3 compared to T1 (p < 0.05) (Figure 2G). The higher the NDVI value, the healthier the vegetation, indicating a lack of drought stress [55]. Collectively, these spectral indices confirm that all treatments supported comparable vegetative health at day 50 post-transplantation, with no detectable adverse effects on plant growth that could influence yield or tuber quality.
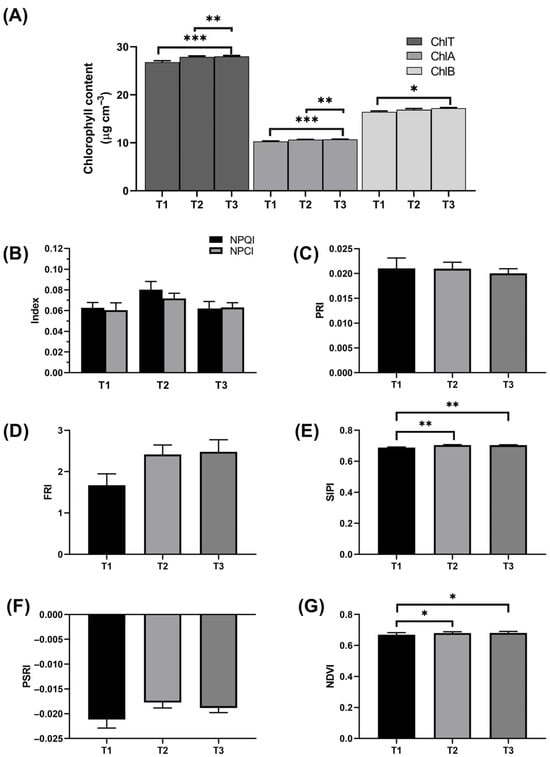
Figure 2.
Impact of fertilization treatments on chlorophyll content and vegetation indices in potato plants. (A) Total chlorophyll content (ChlT) and chlorophyll a (ChlA) and chlorophyll b (ChlB) content in µg.cm−3, (B) NPQI and NPCI (black bar representing NPQI and gray bar representing NPCI), (C) PRI, (D) FRI, (E) SIPI, (F) PSRI, and (G) NDVI. Each bar represents the mean value for the respective treatment with error bars indicating the standard error of the mean (SEM). Measurements were taken from five plants per treatment in three plots. The asterisk indicates statistically significant differences (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, and *** p < 0.001).
3.2. Effect of the Fertilization Treatments on Tuber Yield and Quality
Tuber yield and quality per treatment were assessed after harvest (Figure 3A). The average yield per treatment was 37.2 tons per hectare (t·ha −1) for T1, compared to 34.1 and 42.0 t·ha−1 for T2 and T3, respectively (Figure 3B). Tuber numbers are influenced by nitrogen application rates, as higher nitrogen levels have been shown to enhance tuber yield. In this study, the nitrogen application rate in T1 (176.8 kg N ha−1) resulted in a tuber yield comparable to those observed in other studies with high nitrogen input [56]. Yet, despite receiving reduced nitrogen application, T2 and T3 achieved comparable tuber yields, suggesting that the applied PGPR added, B. mucilaginosus, B. megaterium, and Azotobacter, effectively fixed sufficient nitrogen for potato vegetative growth and hence produced higher potato tuber yield compared to the high N input T1 [57,58,59]. This highlights the potential of PGPR in enhancing nitrogen availability while reducing reliance on synthetic fertilizers.
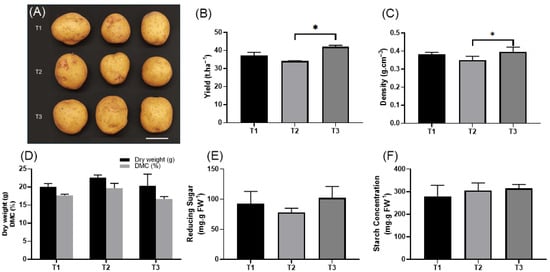
Figure 3.
Effect of chemical fertilizers, PGPR inoculation, and rock amendments on potato tuber morphology and quality traits. (A) Potato tubers harvested from three treatments: T1, chemical fertilizers without rocks or biological inoculants; T2, chemical fertilizers inoculated with PGPR, without rocks; T3, rocks inoculated with PGPR, without chemical fertilizers. Scale bar: 5 cm. (B) Yield (t·ha −1). (C) Tuber density (g.ml−1). (D) Dry weight (g) (black bars) and DMC (%) (gray bars). (E) Reducing sugar content (mg.g FW−1). (F) Starch content identified in tubers per treatment (mg.g FW−1). Each bar represents the mean value for the respective treatment with error bars indicating the standard error of the mean (SEM). The asterisk indicates statistically significant differences (* p < 0.05).
Tuber density and moisture content both play an important role in tuber quality. Between the three treatments, nitrogen (N) along with potassium (K) application also plays an important role in tuber yield and quality [60]. Tuber quality is often determined using dry matter content and is often related to N and K fertilization and availability. Both T1 and T3 showed equivalent dry weights, at 20.04 g and 20.33 g, respectively. However, the water content differed across treatments with DMC percentage: T1 had 17.67%, while T3 had 16.67%. T2 tubers exhibited the lowest water content (DMC 19.67%), whereas T3 retained the highest water relative to its fresh weight, with no significant differences observed between the treatments (Figure 3D). DMC between all the treatments is within the recommended 18–20% DMC, which makes it ideal for consumer usage [61,62].
Starch and reducing sugar contents are other critical parameters for assessing tuber quality. T3 exhibited the highest starch content at 314.05 mg·g of fresh weight (FW) and had the highest reduced sugar content of 102.03 mg·g FW−1, followed by T2 at 302.17 mg·g FW−1 starch content and 77.80 mg·g FW−1 reducing sugar. T1 showed the lowest starch content at 279.90 mg·g FW−1 and reducing sugar at 92.73 mg·g FW−1 (Figure 3E,F). These results indicate that all three treatments produced high-quality tubers with no negative impact on tuber quality. The superior carbohydrate storage observed across treatments suggests enhanced suitability for processing applications and improved overall nutritional value [63,64].
The observed differences in density, coupled with starch content, highlight the variation in tuber composition among the treatments. The denser structure and higher starch content in T3 suggest enhanced structural integrity and energy reserves, making these tubers particularly advantageous for specific processing and storage requirements. The ability of T3 treatment to produce equivalent or superior quality tubers compared to T1 and T2 highlights the potential of using natural rocks and B. mucilaginosus B. megaterium inoculation as PGPR to effectively replace or reduce the application of chemical fertilizers. The results demonstrate that PGPR can enhance vegetative growth and tuber formation in potato crops by increasing the bioavailability of essential nutrients such as phosphorus (P), potassium (K) from the applied natural rocks, and other key elements [22,65]. Importantly, this approach does not compromise potato yield or quality, underscoring its viability as a sustainable agricultural practice.
3.3. Effect of the Fertilization Treatments on Soil Composition Post-Harvest
The soil analysis indicates that most macro- and microelements were near or within the optimum range before plantation with high amount of potassium. According to FAO and the Soil Science Society of America (SSSA), nitrogen availability is dynamic as it is influenced by soil organic matter, microbial activity, and environmental conditions [66]. Optimal N levels in soil typically range around 4–10 ppm for most crops during the growing season. The phosphorus level was about 10 ppm, which is considered the lowest accepted range for available P as the range of P for most crops is from 10 to 40 ppm.
Post-harvest soil analysis for all treatments showed an increase in available phosphorus levels, with T2 having the highest soil phosphorus content (16.33 ppm) (Table 2). This can be attributed to the synergistic effect of chemical fertilizers and PGPR applied in T2. The chemical fertilizers, single superphosphate and phosphoric acid, provided an immediate and readily available source of phosphorus. At the same time, the PGPR enhanced the solubilization of fixed phosphorus in the soil, making more phosphorus accessible to plants. Additionally, T3 demonstrated a substantial increase in total phosphorus, primarily due to the application of rock phosphate and PGPR. Although rock phosphate is less soluble than single superphosphate, the presence of PGPR in T3 facilitated the gradual release of phosphorus over time, enriching the soil with phosphorus in the long term. PGPR, such as B. megaterium, play a vital role in solubilizing P from rock phosphate, making it accessible to plants while preventing it from being washed away or becoming unavailable. This approach not only enhances soil fertility and crop productivity but also addresses significant environmental challenges associated with chemical fertilizers. This finding aligns with the study by Liao et al., which emphasized that traditional chemical fertilizers often lead to P leaching due to their high solubility, while rock phosphate and PGPR reduce P loss and improve P use efficiency [11]. The gradual release of P in T3 is further supported by [22], who demonstrated that B. megaterium significantly improves the solubilization of P from rock phosphate, making it available to plants in a controlled manner. Similarly, [17] found that PGPR-enhanced P availability could reduce the need for chemical P fertilizers, as the P release is synchronized with plant uptake, minimizing waste and environmental impact.

Table 2.
Soil analysis before treatment application and post-harvest (in ppm).
On the other hand, T1 and T2 received the same amount of potassium in the form of potassium sulfate (Table 1), whereas T3 was supplemented with K-feldspar, an insoluble potassium source, along with PGPR known for their capability to solubilize insoluble potassium [19,58,67]. Despite this difference, T3 exhibited a post-harvest soil potassium level of 407.00 ppm and produced comparable tuber yield and DMC, indicating similar tuber quality. In contrast, T1 and T2 retained higher residual soil potassium post-harvest, with 425.00 and 412.33 ppm, respectively. Moreover, the comparable residual nitrogen levels in the soil indicate minimal nitrogen wastage, ensuring efficient nutrient utilization and sustainability for subsequent plantings (Table 2).
The analysis of trace elements before plantation showed that iron (Fe), zinc (Zn), manganese (Mn), and copper (Cu) were present at adequate levels for planting, with initial values of 2.91 ppm, 1.40 ppm, 0.17 ppm, and 0.16 ppm, respectively. Post-harvest results revealed that some elements increased while others remained stable. For instance, iron (Fe) and copper (Cu) showed a slight increase, while zinc (Zn) and manganese (Mn) remained relatively stable. This variation could be attributed to the addition of a complex of trace elements during the cultivation period.
3.4. Multivariate Analysis of Plant, Yield, and Soil Parameters
Principal component analysis (PCA) was performed to visualize the distribution of fertilization treatments based on their impact on the studied vegetative indices and yield-related parameters such as starch content, reducing sugar concentration, and total production. The first two principal components (PC1 and PC2) explained 28.7% and 17.7% of the total variance, respectively, accounting for a cumulative 46.4% of the overall variability (Figure 4A). The PCA biplot revealed a clear separation among the three treatment groups, T1 (blue circles), T2 (orange triangles), and T3 (pink squares), each forming distinct clusters. This pattern indicates that the different fertilization strategies exerted unique influences on plant physiology and productivity. Nutrient variables such as nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) contributed remarkably to the separation along PC1 and PC2. Phosphorus and reducing sugar were aligned along PC1 and associated with T3, suggesting that the phosphorus-rich, PGPR-inoculated treatment had the strongest positive influence on starch accumulation and sugar content. T2 appeared intermediately between T1 and T3, likely reflecting the combined influence of chemical and biological amendments. These findings were further supported by the correlation analysis (Figure 4B), which illustrated the relationships between vegetative indices, soil nutrients, and yield parameters. Phosphorus showed a strong positive correlation with both starch content (r = 0.70) and production (r = 0.92), confirming its pivotal role in enhancing both yield and tuber quality. PGPR inoculation (T3) also showed strong associations with starch content (r = 0.97) and production (r = 0.50), indicating its synergistic effect when combined with rock phosphate. Furthermore, reducing sugar content was positively correlated with starch (r = 0.79) and yield (r = 0.97), reinforcing its role as an indicator of improved productivity. On the other hand, nitrogen (N) exhibited a strong negative correlation with starch content (r = –0.97) and a slight negative correlation with yield (r = –0.12), suggesting that excessive nitrogen may impair carbohydrate accumulation. Potassium (K) was also negatively correlated with yield (r = –0.92), reducing sugar (r = –0.79), and starch content (r = –0.70), indicating a potential opposed effect on tuber quality under the tested treatments.
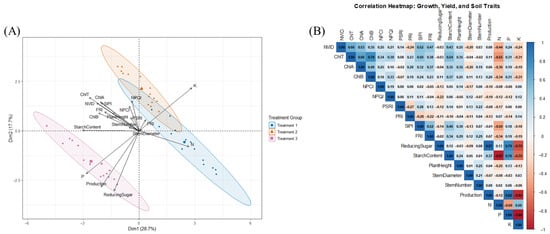
Figure 4.
Multivariate analysis of spectral indices, morphological characteristics, and yield under different treatments. (A) Principal component analysis (PCA) biplot showing the relationship between treatments applied, tuber quality (reducing sugar and starch content), and yield among the three treatments: blue circles (T1), orange triangles (T2), and pink squares (T3). Arrows represent factor loadings of principal components of individual soil quality indicators. (B) Heatmap of the correlation matrix displaying the pairwise Pearson correlation coefficients amongst the treatments applied, tuber quality (reducing sugar and starch content), and yield. The color gradient from light green to dark green represents the correlation values, with dark green indicating strong positive correlations and light green indicating weaker correlations.
3.5. Cost–Benefit Analysis
Evaluating the economic feasibility of the different studied fertilization treatments is another crucial parameter in potato production. Through conducting a cost–benefit analysis study, the total operating cost (TOC), revenue, and profitability across the three fertilization treatments (T1, T2, and T3) were assessed to identify the most cost-effective fertilization treatment (Table 3). T2 had the highest TOC (USD 5006.40 per hectare), mainly due to the cost of fertilization (combined chemical and natural fertilizers), and had the lowest yield (34.20 t ha−1) observed between the three treatments, generating a net profit of USD 1813.60 per hectare. T1 had a TOC of USD 4980 per hectare but resulted in a yield of 37.20 t ha−1. The lowest TOC and highest yield were USD 4411.90 per hectare and 42.0 tons per hectare, respectively. To further evaluate the economic efficiency of the different treatments, the benefit–cost ratio (BCR) was calculated. The calculated BCR of the three treatments T1, T2, and T3 are 1.49, 1.36, and 1.90, respectively. The higher the BCR, the more cost-effective the treatment; hence, T3 is considered the most efficient fertilization strategy in terms of the cost analysis [68,69].

Table 3.
Cost and profitability analysis.
Economic analysis demonstrates that T3 delivers unparalleled economic and ecological benefits. By combining rock phosphate (1040 kg/ha) with synergistic strains of PGPR (B. megaterium, B. mucilaginosus, and Azotobacter at 173 L ha−1), they achieved an 89% reduction in phosphorus costs at just USD 1.15 per kg P2O5 compared to conventional fertilizers (USD 10.19–USD 10.45 per kg). The annual savings are USD 700–750 per hectare (Table 4). Microbial solubilization plays a role in phosphorus plant availability, while the PGPR consortium enhances soil health by producing organic acids which improve P availability, diversifying beneficial soil microbiota and reducing P leaching losses. Unlike conventional systems that deplete soil ecosystems, this approach builds long-term phosphorus reserves while fostering a resilient, biologically active rhizosphere critical for sustainable intensification under harsh conditions and achieving superior agronomic performance [70]. Field trials demonstrate that these soils in Egypt have an average total phosphorus content of 0.1026% (range: 0.052% min.–0.139% max) [71]. This approach not only surpasses agronomic benchmarks but also builds soil health, with rock phosphate maintaining P levels above Egypt’s recorded maximum (0.139%) without chemical depletion.

Table 4.
Phosphorus cost and return on investment (ROI %) for each treatment.
Estimation computations with a 10% annual reduction in P demonstrate that T3 (rock phosphate + PGPR) yields a 79.48–64.38% return on investment (2024–2026), approximately double that of T1 (51.97–42.09%) and T2 (38.55–31.23%). Utilizing T3 leads to an 89% reduction in phosphorus prices (USD 1.15/kg P2O5) and elevated soil phosphorus concentrations (0.172%, 23% above Egypt’s maximum) attributable to microbial phosphorus recycling. T3 sustains phosphorus in the soil for subsequent seasons’ output through efficient nutrient cycling (Table 5). In this economic projection, fertilizer prices were modeled as changing annually to capture market volatility, while crop market prices, land rent, and labor costs were kept constant, based on the observation that these variables typically change more gradually in the study area.

Table 5.
Return on investment (ROI %) for each treatment with 10% Residual P Decline per Year.
3.6. Alignment of the Fertilization Treatments with Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
These findings highlight the potential of sustainable fertilization strategies to optimize both productivity and profitability while reducing reliance on chemical fertilization. This strategy is essential due to the increasing concerns over climate change and the depletion of many of the fossil resources. Adopting sustainable fertilization practices is necessary as it plays an important role in enhancing and protecting soil health, which is critical for long-term agricultural sustainability. Hence, this research aligns with several United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly SDG 2 (Zero Hunger) since the increase in potato yield achieved with a low total operational cost (TOC) demonstrates that sustainable fertilization can improve food security while remaining economically accessible to farming communities. This supports efforts to ensure food availability without increasing input costs or environmental burden. In relation to SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production), by replacing part of the chemical fertilizer inputs with locally available natural rocks and PGPR, this study promotes the efficient use of natural resources. Furthermore, it encourages circular and locally adaptable production systems, reducing overdependence on synthetic inputs. Finally, this study also supports SDG 13 (Climate Action) and SDG 15 (Life on Land). Reducing chemical fertilizer usage helps lower greenhouse gas emissions and fossil-based resource consumption, while the addition of PGPR and natural minerals can enhance soil health and fertility through enhancement of soil microbiome biodiversity.
4. Conclusions
This study demonstrates the agronomic and economic benefits of integrating PGPR and natural rock fertilizers into potato cultivation. Among the three fertilization treatments, the use of natural rock coated with PGPR emerged as the most efficient (T3), yielding the highest production while maintaining the lowest total operational cost. In contrast, the conventional chemical fertilization protocols, which had the highest TOC, resulted in a lower yield, while T2 (reduced chemical + PGPR) had the lowest yield and net profit. The economic evaluation through the benefit–cost ratio further supports the advantage of T3 over T1 and T2, reinforcing the cost-effectiveness of combining PGPR with rock fertilizers. Moreover, the fertilization applied also played a crucial role in shaping yield and quality. Phosphorus fertilization was strongly correlated with higher yield and starch content, emphasizing its importance in enhancing production. On the contrary, nitrogen application negatively impacted starch accumulation, indicating that excessive N fertilization could hinder tuber quality. These findings would promote resource-efficient utilization and climate-resilient agricultural practices, ensuring long-term agricultural sustainability. Future work could further strengthen these findings through conducting similar experiments across different growing seasons, using different potato varieties and at different geographic locations to account for environmental variability. Additionally, incorporating metagenomic analyses would provide a better understanding of the PGPR’s dynamics and their influences on the soil microbial community.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.A.Y. and W.M.F.; methodology, A.A.Y. and W.M.F.; formal analysis, A.A.Y., A.A.B., and W.M.F.; data curation, A.A.Y., A.A.B. and W.M.F.; writing—original draft preparation, A.A.Y. and A.A.B.; writing—review and editing, A.A.Y., A.A.B., and W.M.F.; visualization A.A.Y. and A.A.B.; supervision, W.M.F.; funding acquisition, W.M.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Bartlett Fund for Critical Challenges, Agreement Number: Bartlett-Cycle 4-SSE-BIOL-W.F.03. The Article Processing Charge (APC) was covered by Intramural Support Grants, The American University in Cairo.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We extend our sincere gratitude to Magdy Nasr El-Deen (Menoufia Governorate) for generously providing the field site and essential facilities necessary to carry out this experiment. We also acknowledge Sphinx for Fertilizer and Chemical Industries for their valuable support in supplying the materials used in this research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Defauw, S.L.; He, Z.; Larkin, R.P.; Mansour, S.A. Sustainable potato production and global food security. In Sustainable Potato Production: Global Case Studies; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- FAOSTAT. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QCL (accessed on 22 June 2025).
- Abdellaah, Y.H. An Economic Analysis of Potato Production and Consumption in Egypt: A Case Study of Sohag. J. Sustain. Agric. Sci. 2021, 47, 315–324. [Google Scholar]
- Nasir, M.W.; Toth, Z. Effect of Drought Stress on Potato Production: A Review. Agronomy 2022, 12, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potato Production and Consumption. Available online: https://www.potatopro.com/potato-markets/egypt (accessed on 7 August 2025).
- Tameem, M.M.A.S.; Ahmed, D.A.B.; Ahmed, S.A.M.; Rahim, H.O.A.; Hashem, A.A. An Economic Study of the Competitiveness of Egyptian Potato Exports. Middle East J. Agric. Res. 2024, 13, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Rupp, H.; Tauchnitz, N.; Meissner, R. The influence of increasing mineral fertilizer application on nitrogen leaching of arable land and grassland—Results of a long-term lysimeter study. Front. Soil Sci. 2024, 4, 1345073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, B.G.; Rosen, C.J.; Shiffler, A.K.; Taysom, T.W. Enhanced Efficiency Fertilizers for Improved Nutrient Management: Potato (Solanum tuberosum). Crop. Manag. 2008, 7, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochmuth, G.; Weingartner, P.; Hutchinson, C.; Tilton, A.; Jesseman, D. Potato Yield and Tuber Quality Did Not Respond to Phosphorus Fertilization of Soils Testing High in Phosphorus Content. HortTechnology 2002, 12, 420–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, J.; George, T.S.; Brown, L.K.; Ramsay, G.; Bradshaw, J.E.; White, P.J.; Gregory, P.J. Measuring variation in potato roots in both field and glasshouse: The search for useful yield predictors and a simple screen for root traits. Plant Soil 2013, 368, 231–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Liu, G.; Hogue, B.; Li, Y.; Nicholson, F. Phosphorus availability and environmental risks in potato fields in North Florida. Soil Use Manag. 2015, 31, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutasknit, A.; Ait-El-Mokhtar, M.; Fassih, B.; Ben-Laouane, R.; Wahbi, S.; Meddich, A. Effect of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi and Rock Phosphate on Growth, Physiology, and Biochemistry of Carob under Water Stress and after Rehydration in Vermicompost-Amended Soil. Metabolites 2024, 14, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaitieng, S.; Sinma, K.; Rungcharoenthong, P.; Amkha, S. Arbuscular mycorrhiza fungi applications and rock phosphate fertilizers enhance available phosphorus in soil and promote plant immunity in robusta coffee. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2021, 67, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcel, R.; Zamarreño, Á.M.; García-Mina, J.M.; Aroca, R. Involvement of plant endogenous ABA in Bacillus megaterium PGPR activity in tomato plants. BMC Plant Biol. 2014, 14, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ordoñez, Y.M.; Fernandez, B.R.; Lara, L.S.; Rodriguez, A.; Uribe-Vélez, D.; Sanders, I.R.; Aroca, R. Bacteria with Phosphate Solubilizing Capacity Alter Mycorrhizal Fungal Growth Both Inside and Outside the Root and in the Presence of Native Microbial Communities. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazzoumi, Z.; Azaroual, S.E.; El Mernissi, N.; Zaroual, Y.; Duponnois, R.; Bouizgarne, B.; Kadmiri, I.M. Effect of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi Isolated from Rock Phosphate Mine and Agricultural Soil on the Improvement of Wheat Plant Growth. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 881442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaharoona, B.; Naveed, M.; Arshad, M.; Zahir, Z.A. Fertilizer-dependent efficiency of Pseudomonads for improving growth, yield, and nutrient use efficiency of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 79, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, Z.; Yahya, M.; Hussain, H.S.; Tabbasum, S.; Jalaluddin, S.; Khaliq, S.; Yasmin, S. Development of bacteria-based bioorganic phosphate fertilizer enriched with rock phosphate for sustainable wheat production. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1361574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhao, L.; Huang, Y.; Fu, L.; Ma, L.; Chen, K.; Gu, Z. Review on K-Feldspar Mineral Processing for Extracting Metallic Potassium as a Fertilizer Resource. Minerals 2024, 14, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nacoon, S.; Jogloy, S.; Riddech, N.; Mongkolthanaruk, W.; Ekprasert, J.; Cooper, J.; Boonlue, S. Combination of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and phosphate solubilizing bacteria on growth and production of Helianthus tuberosus under field condition. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, J.-A.; Song, J.; Choe, S.; Jang, G.; Kim, Y. Plant growth-promoting rhizobacterium Bacillus megaterium modulates the expression of antioxidant-related and drought-responsive genes to protect rice (Oryza sativa L.) from drought. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1430546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Mao, X.; Zhang, M.; Yang, W.; Di, H.J.; Ma, L.; Liu, W.; Li, B. The application of Bacillus megaterium alters soil microbial community composition, bioavailability of soil phosphorus and potassium, and cucumber growth in the plastic shed system of North China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 307, 107236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, X. Growth promotion and increased potassium uptake of cotton and rape by a potassium releasing strain of Bacillus edaphicus. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2005, 37, 1918–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, P.N.; Jha, D.K. Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR): Emergence in agriculture. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 28, 1327–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Bank. Commodity Markets Outlook, October 2024. © World Bank. 2024. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10986/42219 (accessed on 22 June 2025).
- Mwakiwa, E.; Wineman, A.; Agyei-Holmes, A.; Fall, M.G.; Kirimi, L.; Mpenda, Z.; Mutandwa, E.; Ogunbayo, I.; Tschirley, D. Price shocks and associated policy responses stemming from the Russia-Ukraine War and other global crises: Evidence from six African countries. Glob. Food Secur. 2025, 45, 100861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, S.R.; Sommers, L.E. Phosphorus. In Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 2: Chemical and Microbiological Properties, 2nd ed.; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1982; pp. 403–430. [Google Scholar]
- O’Halloran, I.; Cade-Menun, B. Total and Organic Phosphorus. In Soil Sampling and Methods of Analysis, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Twine, J.R.; Williams, C.H. The determination of phosphorus in Kjeldahl digests of plant material by automatic analysis. Commun. Soil. Sci. Plant Anal. 1971, 2, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khasawneh, F.E.; Doll, E.C. The Use of Phosphate Rock for Direct Application to Soils. Adv. Agron. 1979, 30, 159–206. [Google Scholar]
- Wiegand, C.; Gerbermann, A.; Gallo, K.; Blad, B.; Dusek, D. Multisite analyses of spectral-biophysical data for corn. Remote Sens. Environ. 1990, 33, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peñuelas, J.; Filella, I.; Lloret, P.; MunoZ, F.; Vilajeliu, M. Reflectance assessment of mite effects on apple trees. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1995, 16, 2727–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penuelas, J.; Baret, F.; Filella, I. Semi-empirical indices to assess carotenoids/chlorophyll a ratio from leaf spectral reflectance. Photosynthetica 1995, 31, 221–230. [Google Scholar]
- Gamon, J.A.; Serrano, L.; Surfus, J.S. The photochemical reflectance index: An optical indicator of photosynthetic radiation use efficiency across species, functional types, and nutrient levels. Oecologia 1997, 112, 492–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merzlyak, M.N.; Solovchenko, A.E.; Smagin, A.I.; Gitelson, A.A. Apple flavonols during fruit adaptation to solar radiation: Spectral features and technique for non-destructive assessment. J. Plant Physiol. 2005, 162, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, D.A.; Gamon, J.A. Relationships between leaf pigment content and spectral reflectance across a wide range of species, leaf structures and developmental stages. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 81, 337–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, J.D.; Balaguer, L.; Manrique, E.; Elvira, S.; Davison, A.W. A reappraisal of the use of DMSO for the extraction and determination of chlorophylls a and b in lichens and higher plants. Environ. Exp. Bot. 1992, 32, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.-D.; Wang, W.-Z.; Hu, J.-D.; Zhang, X.-M.; Wang, J.-B.; Wang, B.-S. Nondestructive Determination of Total Chlorophyll Content in Maize Using Three-Wavelength Diffuse Reflectance. J. Appl. Spectrosc. 2016, 83, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, S.S. Phenol-Sulfuric Acid Method for Total Carbohydrates. In Food Analysis Laboratory Manual, 1st ed.; Nielsen, S.S., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 47–53. [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig, T.G.; Goldberg, H.J. The Anthrone Method for the Determination of Carbohydrates in Foods and in Oral Rinsing. J. Dent. Res. 1956, 35, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obiero, K.; Mboya, J.B.; Ouko, K.O.; Okech, D. Economic feasibility of fish cage culture in Lake Victoria, Kenya. Aquac. Fish Fish. 2022, 2, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Shapiro, C.; Iqbal, J. Long-term comparison of targeted soil test values and crop removal as a phosphorus fertilization strategy in corn. Agron. J. 2024, 116, 3240–3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojeniyi, K.; Ngonidzashe, C.; Devkota, K.; Madukwe, D. Optimizing split-fertilizer applications for enhanced maize yield and nutrient use efficiency in Nigeria’s Middle-belt. Heliyon 2024, 10, e37747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R. The R Project for Statistical Computing. Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 22 June 2025).
- Khan, I.; Zada, A.; Jia, T.; Hu, X. Effect of the Enhanced Production of Chlorophyll b on the Light Acclimation of Tomato. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heikal, N.H.; Rady, M.H.; Merdan, B.A.; El-Abbassi, T.S.; El-Genaidy, M.A.; Azazy, A.M.; Yones, M.S.; Essa, E.E. Early detection of Bactrocera zonata infestation in peach fruit using remote sensing technique and application of nematodes for its control. Kuwait J. Sci. 2024, 51, 100191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hoseny, M.M.; Dahi, H.F.; El Shafei, A.M.; Yones, M.S. Spectroradiometer and thermal imaging as tools from remote sensing used for early detection of spiny bollworm, Earias insulana (Boisd.) infestation. Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2023, 43, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mevy, J.-P.; Biryol, C.; Boiteau-Barral, M.; Miglietta, F. The Optical Response of a Mediterranean Shrubland to Climate Change: Hyperspectral Reflectance Measurements during Spring. Plants 2022, 11, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garbulsky, M.F.; Peñuelas, J.; Gamon, J.; Inoue, Y.; Filella, I. The photochemical reflectance index (PRI) and the remote sensing of leaf, canopy and ecosystem radiation use efficiencies—A review and meta-analysis. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filella, I.; Peñuelas, J.; Llorens, L.; Estiarte, M. Reflectance assessment of seasonal and annual changes in biomass and CO2 uptake of a Mediterranean shrubland submitted to experimental warming and drought. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 90, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Filella, I.; Liu, D.; Ogaya, R.; Llusià, J.; Asensio, D.; Peñuelas, J. Photochemical Reflectance Index (PRI) for Detecting Responses of Diurnal and Seasonal Photosynthetic Activity to Experimental Drought and Warming in a Mediterranean Shrubland. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupčinskienė, A.; Brazaitytė, A.; Rasiukevičiūtė, N.; Valiuškaitė, A.; Morkeliūnė, A.; Vaštakaitė-Kairienė, V. Vegetation Indices for Early Grey Mould Detection in Lettuce Grown under Different Lighting Conditions. Plants 2023, 12, 4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderegg, J.; Yu, K.; Aasen, H.; Walter, A.; Liebisch, F.; Hund, A. Spectral Vegetation Indices to Track Senescence Dynamics in Diverse Wheat Germplasm. Front. Plant Sci 2020, 10, 466315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llorente, B.; Torres-Montilla, S.; Morelli, L.; Florez-Sarasa, I.; Matus, J.T.; Ezquerro, M.; D’Andrea, L.; Houhou, F.; Majer, E.; Picó, B.; et al. Synthetic conversion of leaf chloroplasts into carotenoid-rich plastids reveals mechanistic basis of natural chromoplast development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 21796–21803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polivova, M.; Brook, A.; Polivova, M.; Brook, A. Detailed Investigation of Spectral Vegetation Indices for Fine Field-Scale Phenotyping. In Vegetation Index and Dynamics; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zewide, I.; Mohammed, A.; Tulu, S. Effect of Different Rates of Nitrogen and Phosphorus on Yield and Yield Components of Potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) at Masha District, Southwestern Ethiopia. Int. J. Soil Sci. 2012, 7, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solanki, K.; Choudhary, S.K.; Aakash; Singh, V.; Nath, H.; Anshuman, K. Response of Bacillus megaterium and Bacillus mucilaginosus Strains on Growth and Nutrient Uptake of Soybean. Int. J. Plant Soil Sci. 2023, 35, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, B.B.; Biswas, D.R. Influence of potassium solubilizing microorganism (Bacillus mucilaginosus) and waste mica on potassium uptake dynamics by sudan grass (Sorghum vulgare Pers.) grown under two Alfisols. Plant Soil 2008, 317, 235–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.-J.; Xue, A.-Q.; Cao, Z.-Y.; Yang, S.-J.; Hu, X.-F. Diversity of plant growth-promoting Paenibacillus mucilaginosus isolated from vegetable fields in Zhejiang, China. Ann. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 1745–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucci, G.; Lacolla, G. Effects of Different Fertilizing Formulae on Potato. Ital. J. Agron. 2007, 2, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dingenen, J.; Hanzalova, K.; Salem, M.A.A.; Abel, C.; Seibert, T.; Giavalisco, P.; Wahl, V. Limited nitrogen availability has cultivar-dependent effects on potato tuber yield and tuber quality traits. Food Chem. 2019, 288, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storey, M. The Harvested Crop. In Potato Biology and Biotechnology: Advances and Perspectives; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 441–470. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, M.; Naznin, S.; Naznin, A.; Uddin, N.; Amin, N.; Rahman, M.; Tipu, M.M.H.; Alsuhaibani, A.M.; Gaber, A.; Ahmed, S. Dry Matter, Starch Content, Reducing Sugar, Color and Crispiness Are Key Parameters of Potatoes Required for Chip Processing. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brążkiewicz, K.; Pobereżny, J.; Wszelaczyńska, E.; Bogucka, B. Potato starch quality in relation to the treatments and long-term storage of tubers. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawwam, G.E.; Elbeltagy, A.; Emara, H.M.; Abbas, I.H.; Hassan, M.M. Beneficial effect of plant growth promoting bacteria isolated from the roots of potato plant. Ann. Agric. Sci. 2013, 58, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.; Kleber, M. The contentious nature of soil organic matter. Nature 2015, 528, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahid, M.; Razzaque, A.; Bhuiyan, M.N.I.B.; Islam, M.A.; Begum, R.; Roy, T.S. Effects of Nitrogen and Potassium on Yield and Quality of Potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) Cultivars. Bangladesh J. Bot. 2023, 52, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghimire, S.; Koirala, B.; Devkota, S.; Basnet, G. Economic analysis of commercial banana cultivation and supply chain analysis in Chitwan, Nepal. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2019, 5, 190–195. [Google Scholar]
- de Moraes Rego, C.R.; Ribeiro Reis, V.R.; Wander, A.E.; Cantanhêde, I.; Costa, J.B.; Muniz, L.C.; Costa, B.; de Herrera, J.L. Cost Analysis of Corn Cultivation in the Setup of the Crop-Livestock-Forest Integration System to Recover Degraded Pastures. J. Agric. Sci. 2017, 9, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kishore, N.; Pindi, P.K.; Reddy, S.R. Phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms: A critical review. In Plant Biology and Biotechnology: Plant Diversity, Organization, Function and Improvement; Spinger: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; Volume 1, pp. 307–333. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Farid, I.M. Phosphorus Fractions in some Calcareous Soils of Egypt as Affected by Aging and their Properties. Egypt J. Soil Sci. 2013, 53, 555–566. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).