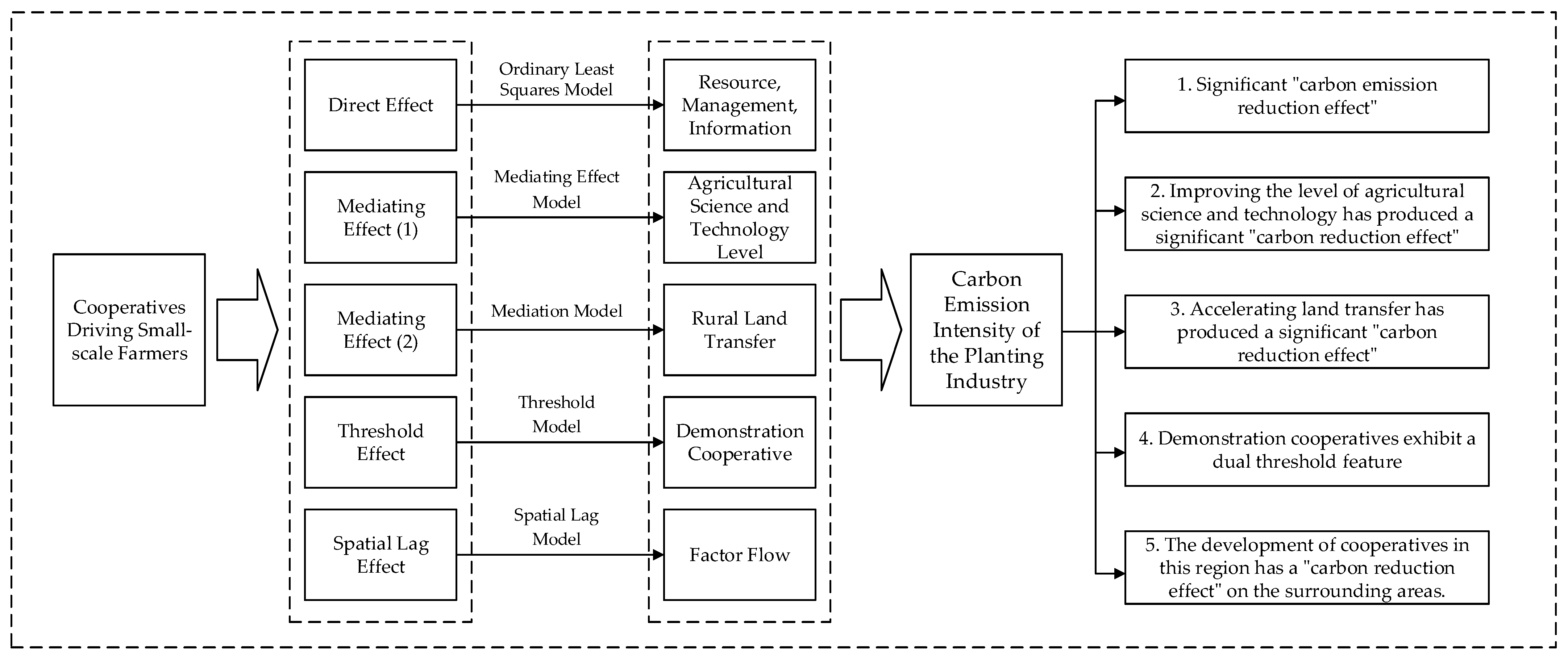
How Can Cooperatives Drive Small-Scale Farmers to Achieve a “Carbon Reduction Effect” in the Planting Industry: Evidence from China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Research on Carbon Emissions in Agriculture
2.2. Research on the Aspect of Cooperatives Driving Farmers
3. Theoretical Analysis and Research Hypotheses
3.1. Analysis of the Direct Impact Effect of Cooperatives on Small-Scale Farmers
3.2. Analysis of the Mediating Effect of Cooperatives in Driving Small-Scale Farmers
3.2.1. Analysis of the Mediating Effect of Agricultural Science and Technology Level
3.2.2. Analysis of the Mediating Effect of Rural Land Transfer
3.3. Analysis of the Threshold Effect on the Development Level of Demonstration Cooperatives
3.4. Analysis of the Spatial Spillover Effect of Carbon Emissions in the Planting Industry
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Model Design
4.1.1. Benchmark Regression Model
4.1.2. Mediating Effect Model
4.1.3. Threshold Effect Model
4.1.4. Spatial Lag Model
4.2. Variable Settings
4.2.1. Explained Variable
4.2.2. Explanatory Variable
4.2.3. Mediating Variable
4.2.4. Threshold Variable
4.2.5. Control Variables
4.3. Data Sources
5. Analysis of Empirical Results
5.1. Analysis of Benchmark Test Results
5.2. Analysis of Robustness Test Results
5.3. Analysis of Heterogeneity Test Results
5.4. Analysis of Mechanism Path Verification Results
5.5. Analysis of the Threshold Effect Test Results
6. Extended Analysis
6.1. Analysis of Global Autocorrelation Test Results
6.2. Analysis of the Test Results of Spatial Spillover Effects
7. Research Findings, Recommendations, and Limitations
7.1. Research Findings
7.2. Research Recommendations
7.3. Research Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, K.; Shi, L. Impact of rural industrial integration on agricultural carbon emissions: Mechanism path and spatial spillover effect analysis. Chin. J. Agric. Resour. Reg. Plan. 2024, 45, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Fu, G.H.; Liu, Y.Z. Agricultural greenhouse gas emissions at county level in Jiangsu Province: Temporal and spatial differences and trend evolution. Resour. Sci. 2018, 40, 1084–1094. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, J.H.; Li, X.M. Promote the development of moderate-scale agricultural operations through the reorganization of small-scale farmers. Expand. Horiz. 2024, 40, 58–66. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, D.T. Research on the practical difficulties and countermeasures of small-scale farmers in adapting to agricultural modernization. Mod. Agric. Res. 2019, 25, 40–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Y. Resilient small-scale farmers: Historical continuity and modern transformation—The vitality and independent responsibility mechanism of small-scale farmers in China. Soc. Sci. China 2019, 40, 82–99+201. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Pu, S.; Zhou, L. Empirical analysis on agricultural non-point source pollution and agricultural growth in Sichuan Province. Rural Econ. 2016, 34, 56–60. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.X. The organic connection between cooperatives driving small-scale farmers and modern agriculture—Based on the investigation of Nongfeng Vegetable and Fruit Planting Professional Cooperatives in Lingyuan City, Liaoning Province. China Farmers Coop. 2018, 10, 42–43. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.H.; Zhang, K.Y.; Hu, N.Y.; Wu, L.P. A review on the measurement of agricultural carbon emissions in China. Chin. J. Eco Agric. 2023, 31, 163–176. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Yin, M.H. Re-measurement of agricultural carbon emissions in China: Basic status, dynamic evolution and spatial spillover effect. Chin. Rural Econ. 2022, 38, 104–127. [Google Scholar]
- Ba, X.R. The orientation and release of agricultural functions in the new stage—Thoughts on “Production Development” in the construction of new countryside. Study Explor. 2008, 30, 162–164. [Google Scholar]
- Woomer, P.L.; Tieszen, L.L.; Tappan, G.; Toure, A.; Sall, M. Land use change and terrestrial carbon stocks in Senegal. J. Arid Environ. 2004, 59, 625–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalf, G.E.; Reilly, J.M. Policy options for controlling greenhouse gas emissions: Implications for agriculture. Choices 2008, 23, 34–37. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.Y.; Hu, H. Impact of industrial agglomeration on agricultural carbon emissions in China. Shandong Soc. Sci. 2016, 30, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Liao, H. The impact of digital economy on agricultural carbon emissions and its mechanism. Reform 2024, 40, 84–99. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, X.Q.; Li, Z.Q.; Zhang, Y.S. Impact of farmland transfer on agricultural carbon emissions and its spatial characteristics. Resour. Sci. 2023, 45, 77–90. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, G.S.; Wang, Q.Z.; Zhi, H.B. Effect analysis of digital inclusive finance on agricultural carbon emission intensity. Econ. Probl. 2024, 46, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.B.; Wang, S. Rural labor outflow, agricultural scale management and agricultural carbon emissions. Econ. Manag. 2022, 36, 43–49. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.E.; Chen, W. Research on the relationship between agricultural mechanization, industrial upgrading and agricultural carbon emissions—Empirical analysis based on dynamic panel data model. J. Agrotech. Econ. 2018, 37, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, H.W.; Liu, X.Y.; Gong, Y.H.; Wang, Z.W. Internet of things development, technological innovation and agricultural carbon emission intensity. Econ. Probl. 2024, 46, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paustian, K.; Six, J.; Elliott, E.T.; Hunt, H.W. Management options for reducing CO2 emissions from agricultural soils. Biogeochemistry 2000, 48, 147–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.X.; Wang, H.L. Environmental regulation, agricultural technology innovation and agricultural carbon emissions. J. Hubei Univ. (Philos. Soc. Sci.) 2020, 47, 147–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zhang, J.H. Carbon emission reduction effect of policy oriented agricultural insurance—Evidence from the pilot implementation of full cost insurance and income insurance. Insur. Stud. 2023, 30, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Zhang, Q. Theoretical mechanism and practical approach of coordinated development between new agricultural business entities and small-scale farmers. J. Hainan Univ. (Humanit. Soc. Sci.) 2024, 42, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Xia, Y.; Sun, D.S. “Digital to the countryside”: E-commerce transformation of farmers’ cooperatives. Contemp. Econ. Manag. 2022, 44, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.H.; Wu, Y.; Cai, Y.X. The dilemma and strategy analysis of the connection between small-scale farmers and modern agriculture under the background of digitalization. Agric. Technol. 2023, 43, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.H.; Yang, C.Y.; Min, R. Can the new agricultural business entity drive the green transformation of small farmers’ production—Analysis based on 454 survey data of small farmers. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2024, 38, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Han, Z.M.; Liu, W.H. Is the development of new agricultural management subject inclusive of small farmers? Econ. Theory Bus. Manag. 2024, 44, 37–56. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.H.; Shao, K.; Sun, C.C.; Yang, Y.W. The mechanism, practice mode and policy suggestions of farmers’ cooperatives driving the development of small-scale farmers. Farmer Sci. Technol. Train. 2019, 19, 29–32. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.Y. Agricultural product brokers and cash crop product circulation: A study of village embeddedness in local markets. Chin. Rural Econ. 2018, 34, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.L. Gaomi, Shandong: The ability of cooperatives to drive small farmers continues to increase. China Farmers Coop. 2020, 12, 10–11. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Shi, L.; Zhang, H. The impact of the development of new agricultural business entities on agricultural carbon emission intensity in China: “carbon reduction effect” or “carbon increase effect”. J. Agrotech. Eco. 2024, 43, 51–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, R.F.; Liang, F.; Li, X.Z.; Ma, H.Y. Study on the willingness of small farmers to organically connect with new agricultural business entities—A case study of Linzhou City, Henan Province. J. Chin. Agric. Mech. 2024, 45, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.X.; Tan, H.Y.; Gao, L.L. Empirical analysis of new agricultural business entities and their behavior of joining cooperatives—Based on the panel data of 795 planting family farms in China. J. Beijing Univ. Technol. (Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2019, 19, 60–73. [Google Scholar]
- Du, X.S.; Wang, H.N.; Ning, A.Z. Research on the promotion of green agriculture development by farmers’ professional cooperatives: A case analysis based on two cooperatives. Rural Financ. Res. 2021, 42, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q. Risk-sharing mechanism for cluster financing of small and medium-sized enterprises based on symbiosis theory. Commer. Sci. Res. 2010, 17, 65–69. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.Z.; Zhang, L.L.; Wang, M.Z. Research on the impact of cooperative intervention on agricultural product supply chain cooperation. J. Ind. Eng. Eng. Manag. 2024, 38, 182–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.L. Channels, risks and prevention and control paths of green agricultural technology diffusion led by farmers’ cooperatives. Heilongjiang Grain 2024, 31, 145–148. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Z.Y. Research on the impact of agricultural science and technology progress on agricultural carbon emissions from the provincial perspective. Stud. Sci. Sci. 2013, 31, 674–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.B.; Wang, Q.B.; Dong, X.R.; Yu, G.F.; Sun, Y. Differences of farmers’ land use behavior in urban rural fringe and its policy implications—A case study of 238 farmers in Sujiatun District of Shenyang City. Econ. Geogr. 2012, 32, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Gao, M.F. Research on the impact of agricultural mechanization and rural labor transfer on agricultural total factor productivity—An empirical test based on the panel data of 31 Provinces (Cities, Autonomous Regions) in mainland China. Fujian Trib. 2021, 38, 59–71. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Song, G. The impact of rural labor transfer scale on farmland transfer. Econ. Geogr. 2020, 40, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.T.; Huang, W.H.; Qi, Z.H.; Ji, H.; Zuo, Z.P. The determination of farmers’ willingness to transfer land management rights: Cost benefit or policy environment—From the perspective of differentiation between small farmers and large grain growers. J. China Agric. Univ. 2019, 24, 191–201. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, L.; Jin, Y.T.; Cheng, M. Land transfer and agricultural carbon emissions: Theoretical mechanism and empirical test. East China Econ. Manag. 2020, 39, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F. Some Understandings on the implementation of intensive operation in China’s commercial banks. Financ. Sci. 1998, 11, 23–26. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, B.Y.; Peng, H.L. The enhancing effect and mechanism of green agriculture on family farms by joining cooperatives. J. Kunming Univ. 2025, 47, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, E.L. Entropy law and exhaustion of natural resources Is Nicholas Georgescu-Roegen’s paradigm defensible. Ecol. Econ. 1990, 2, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.Y.; Liu, S.J. The impact of innovation factor flow on agricultural green development and its spatial spillover effect. West Forum Econ. Manag. 2023, 34, 48–58+79. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.Q.; Cheng, X.Y.; Wang, F. Research on regional spillover effect of agricultural carbon emissions from the perspective of technology diffusion. J. Agrotech. Econ. 2022, 41, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.L.; Zhang, L.; Hou, J.T.; Liu, H.Y. Mediating effect test procedure and its application. Acta Psychol. Sin. 2004, 49, 614–620. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, B.E. Threshold effects in non-dynamic panels: Estimation, testing, and inference. J. Econom. 1999, 93, 345–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, D.A. Spatial Econometrics: Methods and Models. Econ. Geogr. 1988, 65, 160–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, G.Y.; Chen, W.H.; Qian, H.H. The impact of agricultural technical efficiency on agricultural carbon emissions—Based on the analysis of spatial spillover effect and threshold effect. Chin. J. Eco Agric. 2023, 31, 226–240. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Zhang, J.B.; Li, H.P. Spatio-temporal characteristics and influencing factors decomposition of agricultural carbon emissions in China. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2011, 21, 80–86. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.H.; Li, K. Cooperatives to drive non-members small farmers to urban and rural integration. China Bus. Mark. 2025, 39, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Zhang, F. Formation mechanism and incentive effect of vertical fiscal imbalance. J. Manag. World 2019, 35, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable Name | N | Mean | Std | Min | Max | VIF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pl | 540 | 0.3080 | 0.1440 | 0.0827 | 0.7370 | 2.2300 |
| cooper | 540 | 0.0843 | 0.0513 | 0.0077 | 0.2460 | 1.3000 |
| sci-tec | 540 | 4.2890 | 1.3020 | 1.0990 | 7.0710 | 2.9100 |
| transf | 540 | 15.5900 | 1.3370 | 11.8600 | 17.9900 | 3.4900 |
| demon | 540 | 2.2410 | 2.1910 | 0.0479 | 11.5900 | 1.3400 |
| stru | 540 | 0.6530 | 0.1490 | 0.3660 | 1.0240 | 1.5500 |
| disa | 540 | 6.1100 | 1.5470 | 1.2810 | 8.3320 | 2.6100 |
| openness | 540 | 0.0153 | 0.0141 | 0.0007 | 0.0535 | 2.2300 |
| consum | 540 | 4.7590 | 1.3350 | 1.4040 | 7.5430 | 2.6300 |
| per | 540 | 1.6430 | 1.1340 | 0.2340 | 6.1500 | 1.9900 |
| Variable Name | Carbon Emission Intensity of the Planting Industry | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OLS | System GMM | IV | ||
| cooper | −0.2349 *** (0.0703) | −0.2427 *** (0.0709) | −0.1904 * (0.0759) | −0.4750 *** (0.1269) |
| pl(T−1) | 0.5249 *** (0.1205) | |||
| stru | −0.1449 * (0.0664) | 0.5420 ** (0.1723) | −0.1426 * (0.0640) | |
| disa | 0.0014 (0.0029) | −0.0404 ** (0.0141) | 0.0009 (0.0028) | |
| openness | −0.0343 (0.5353) | −8.9107 *** (2.7078) | 0.3904 (0.4855) | |
| consum | −0.0107 (0.0099) | 0.0301 ** (0.0106) | −0.0193 * (0.0092) | |
| per | −0.0041 (0.0048) | −0.0192 (0.0118) | −0.0072 (0.0049) | |
| individual fixed effects | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| time fixed effects | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| intercept term | 0.4470 *** (0.0186) | 0.5733 *** (0.0730) | −0.0091 (0.0397) | 0.3931 *** (0.0742) |
| Obs | 540 | 540 | 510 | 510 |
| Variable Name | Increase Rice Cultivation | Replace Variable | High-Dimensional Fixation | Lag Period | Add Control Variables | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pl | pl | pl | pl | L. pl | pl | |
| cooper | −5.2867 ** (2.0365) | −0.2877 * (0.1358) | −0.2060 ** (0.0702) | −0.2475 *** (0.0715) | ||
| cooper (1) | −0.0164 ** (0.0055) | |||||
| L. cooper | −0.2314 *** (0.0669) | |||||
| control variables | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| individual fixed effects | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| time fixed effects | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| individual # time | NO | NO | YES | NO | NO | NO |
| intercept term | 5.9527 *** (1.6456) | 0.6104 *** (0.0766) | 0.6464 (0.3885) | 0.5167 *** (0.0736) | 0.5739 *** (0.0728) | 0.6339 *** (0.1148) |
| Obs | 540 | 540 | 540 | 510 | 510 | 540 |
| Variable Name | Carbon Emission Intensity of the Planting Industry | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eastern Region | Central Region | Western Region | Major Grain-Producing Areas | Non-Grain Production Areas | |
| cooper | −0.2209 *** (0.0511) | −0.2819 * (0.1264) | −0.0829 (0.1101) | −0.2699 ** (0.1005) | −0.2769 ** (0.1050) |
| control variables | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| individual fixed effects | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| time fixed effects | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| intercept term | 0.5768 *** (0.0446) | 1.6565 *** (0.2001) | 0.0140 (0.1938) | 1.2644 *** (0.1452) | 0.3763 *** (0.0927) |
| Goodness of Fit | 0.9649 | 0.9572 | 0.9328 | 0.9435 | 0.9329 |
| Obs | 198 | 144 | 198 | 234 | 306 |
| Variable Name | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| sci-tec | pl | transf | pl | |
| cooper | 2.4150 *** (0.6947) | −0.2039 ** (0.0693) | 1.3444 *** (0.3798) | −0.2074 ** (0.0717) |
| sci-tec | −0.0161 ** (0.0052) | |||
| transf | −0.0263 *** (0.0078) | |||
| control variables | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| individual fixed effects | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| time fixed effects | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| intercept term | 2.3686 ** (0.8056) | 0.6114 *** (0.0713) | 13.2429 *** (0.7510) | 0.9219 *** (0.1306) |
| Goodness of Fit | 0.9158 | 0.9290 | 0.9558 | 0.9299 |
| Obs | 540 | 540 | 540 | 540 |
| Variable Name | Threshold Inspection | Threshold Value | F Value | p Value | Critical Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10% | 5% | 1% | |||||
| demon | the first threshold | 0.8058 | 83.58 | 0.0000 | 29.8013 | 34.8860 | 40.6194 |
| the second threshold | 5.5118 | 25.14 | 0.0750 | 23.3678 | 27.6723 | 33.0669 | |
| the third threshold | 10.3702 | 19.26 | 0.3400 | 30.0693 | 38.0956 | 59.0664 | |
| Variable Name | Cooper | Std | 95% Confidence Interval | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| demon < 0.8058 | 0.5184 *** | (0.1212) | 0.2802 | 0.7565 |
| 0.8058 < demon ≤ 5.5118 | −0.2806 *** | (0.0667) | −0.4117 | −0.1495 |
| demon > 5.5118 | −0.7925 *** | (0.1132) | −1.0148 | −0.5702 |
| control variables | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| intercept term | 0.9285 *** | (0.0814) | −3.3943 | −1.7199 |
| Goodness of Fit | 0.8216 | |||
| Obs | 540 | |||
| Year | Carbon Emission Intensity of the Planting Industry | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Moran Value | Z Value | p Value | |
| 2006 | 0.1780 | 1.7620 | 0.0390 |
| 2007 | 0.1630 | 1.6120 | 0.0530 |
| 2008 | 0.0910 | 1.0350 | 0.1500 |
| 2009 | 0.1450 | 1.4710 | 0.0710 |
| 2010 | 0.1150 | 1.2490 | 0.1060 |
| 2011 | 0.1000 | 1.1690 | 0.1210 |
| 2012 | 0.1170 | 1.3130 | 0.0950 |
| 2013 | 0.0960 | 1.1390 | 0.1270 |
| 2014 | 0.1030 | 1.1850 | 0.1180 |
| 2015 | 0.1380 | 1.4720 | 0.0710 |
| 2016 | 0.1640 | 1.6700 | 0.0470 |
| 2017 | 0.1620 | 1.6210 | 0.0520 |
| 2018 | 0.1510 | 1.5340 | 0.0630 |
| 2019 | 0.1750 | 1.7250 | 0.0420 |
| 2020 | 0.1990 | 1.9180 | 0.0280 |
| 2021 | 0.2430 | 2.2870 | 0.0110 |
| 2022 | 0.2240 | 2.1500 | 0.0160 |
| 2023 | 0.1580 | 1.5920 | 0.0560 |
| Variable Name | Carbon Emission Intensity of the Planting Industry | |
|---|---|---|
| SAR | OLS | |
| cooper | −0.2229 *** (0.0542) | −0.2427 *** (0.0709) |
| pl | −0.1611 ** (0.0497) | −0.1449 * (0.0664) |
| disa | 0.0010 (0.0029) | 0.0014 (0.0029) |
| openness | −0.1467 (0.5361) | −0.0343 (0.5353) |
| consum | −0.0086 (0.0088) | −0.0107 (0.0099) |
| per | −0.0040 (0.0038) | −0.0041 (0.0048) |
| L. pl | 0.1668 ** (0.0574) | |
| Diff in individual effect characteristics | 0.0015 *** (0.0001) | |
| Obs | 540 | 540 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Wei, F.; Lai, J.; Xiao, H.; Li, K. How Can Cooperatives Drive Small-Scale Farmers to Achieve a “Carbon Reduction Effect” in the Planting Industry: Evidence from China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 8479. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17188479
Zhang H, Wei F, Lai J, Xiao H, Li K. How Can Cooperatives Drive Small-Scale Farmers to Achieve a “Carbon Reduction Effect” in the Planting Industry: Evidence from China. Sustainability. 2025; 17(18):8479. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17188479
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Hong, Fulin Wei, Jixiang Lai, Han Xiao, and Kuan Li. 2025. "How Can Cooperatives Drive Small-Scale Farmers to Achieve a “Carbon Reduction Effect” in the Planting Industry: Evidence from China" Sustainability 17, no. 18: 8479. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17188479
APA StyleZhang, H., Wei, F., Lai, J., Xiao, H., & Li, K. (2025). How Can Cooperatives Drive Small-Scale Farmers to Achieve a “Carbon Reduction Effect” in the Planting Industry: Evidence from China. Sustainability, 17(18), 8479. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17188479






