Understanding the Efficiency of Catalytic Ozonation for the Degradation of Synthetic Dyes in Water: A Study of Degradation Mechanism and Pathways
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Experimental Procedure
Preparation of Sample Solution
2.3. Reaction Setup
2.3.1. Ozonation Experiment
2.3.2. Sample Collection
2.4. LC-MS Sample Preparation
2.5. Instruments and Data Analysis
3. Results
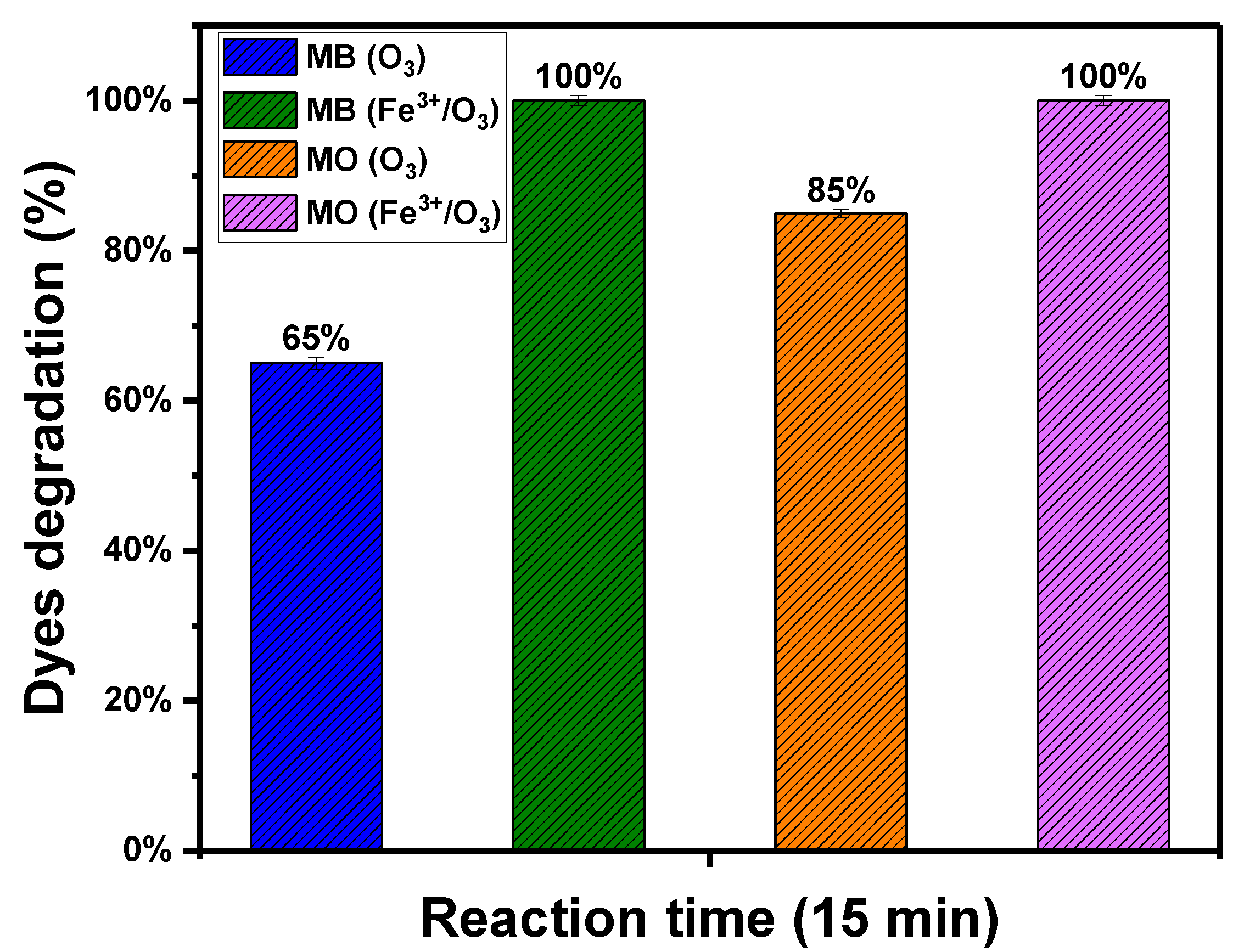
3.1. Degradation of MB and MO by O3 and Fe3+/O3
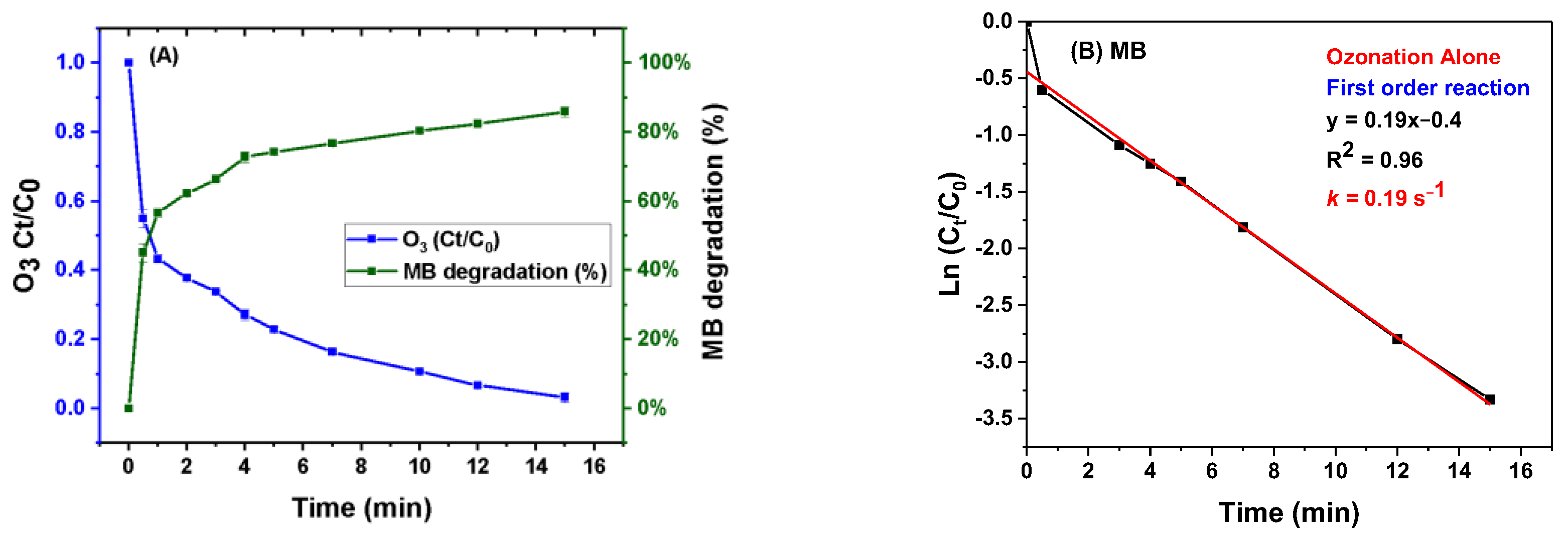
3.2. Degradation of MB
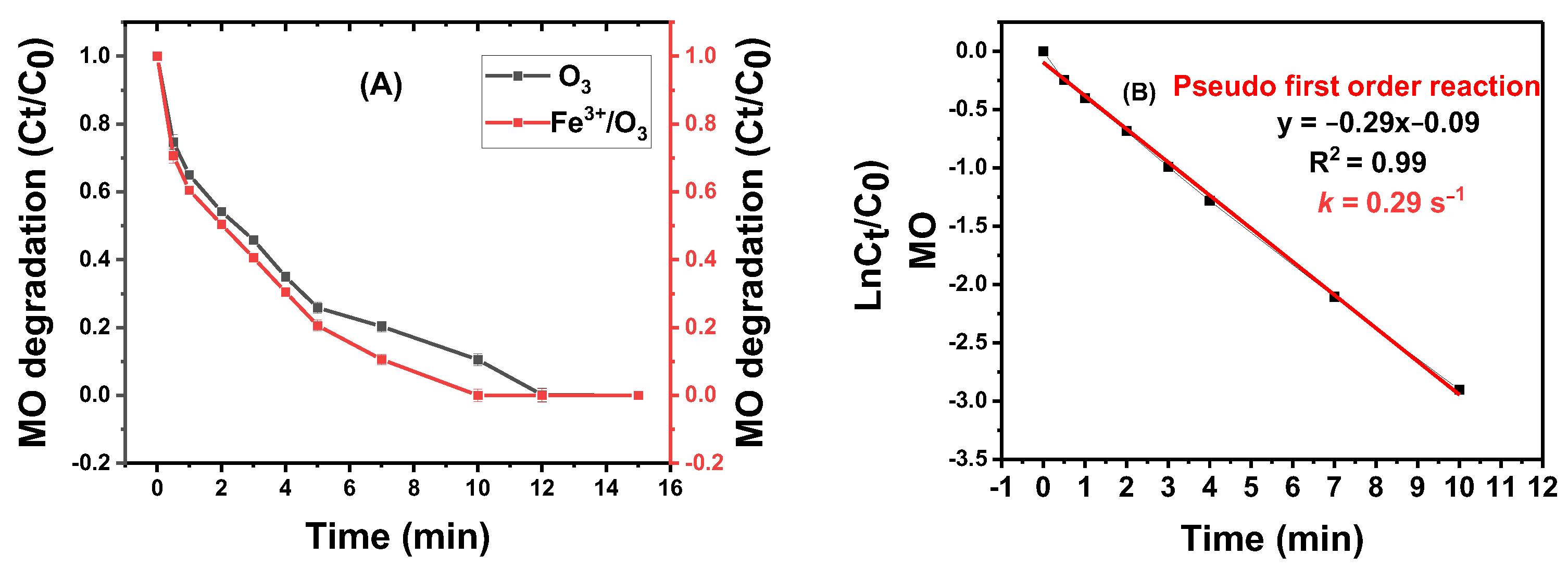
3.3. Degradation of MO
3.4. Reaction Kinetics of MB Degradation
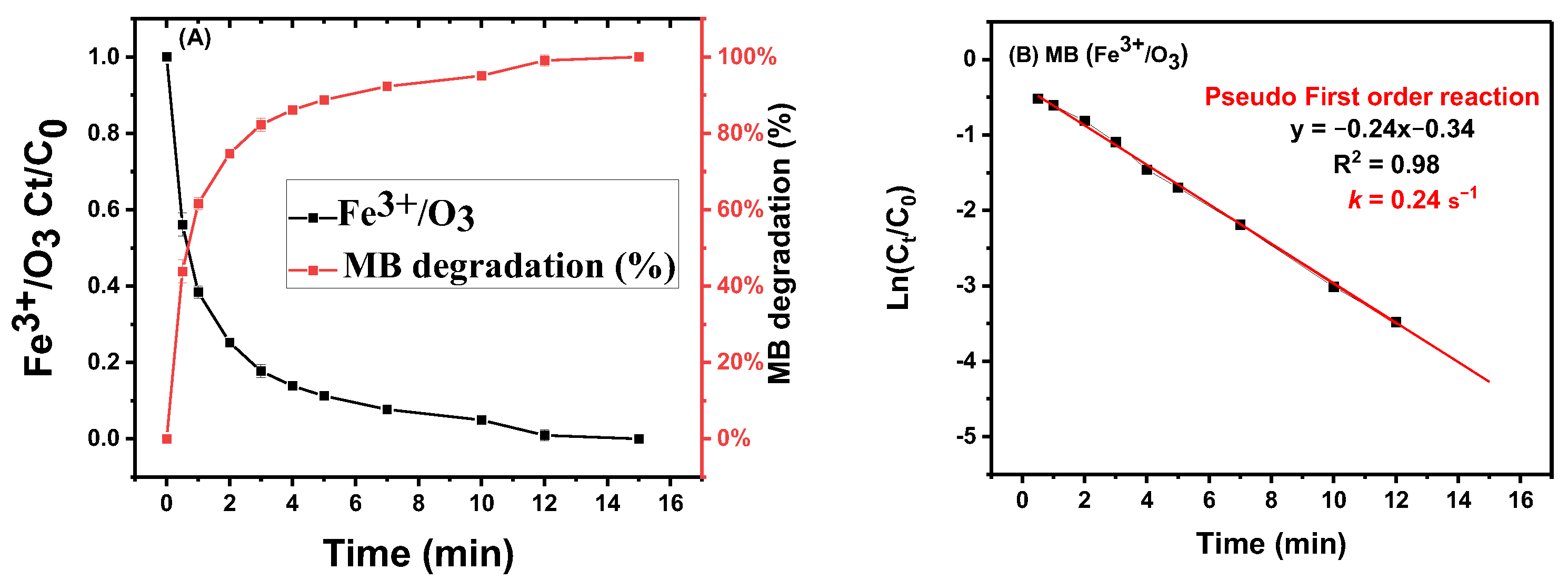
3.5. Ferric Catalyzed Ozonation of MB Degradation
3.6. Effect of pH on the Degradation of MB
3.7. Reaction Kinetics of MO Degradation
3.7.1. Degradation via Ozonation and Ferric Catalyzed Ozonation
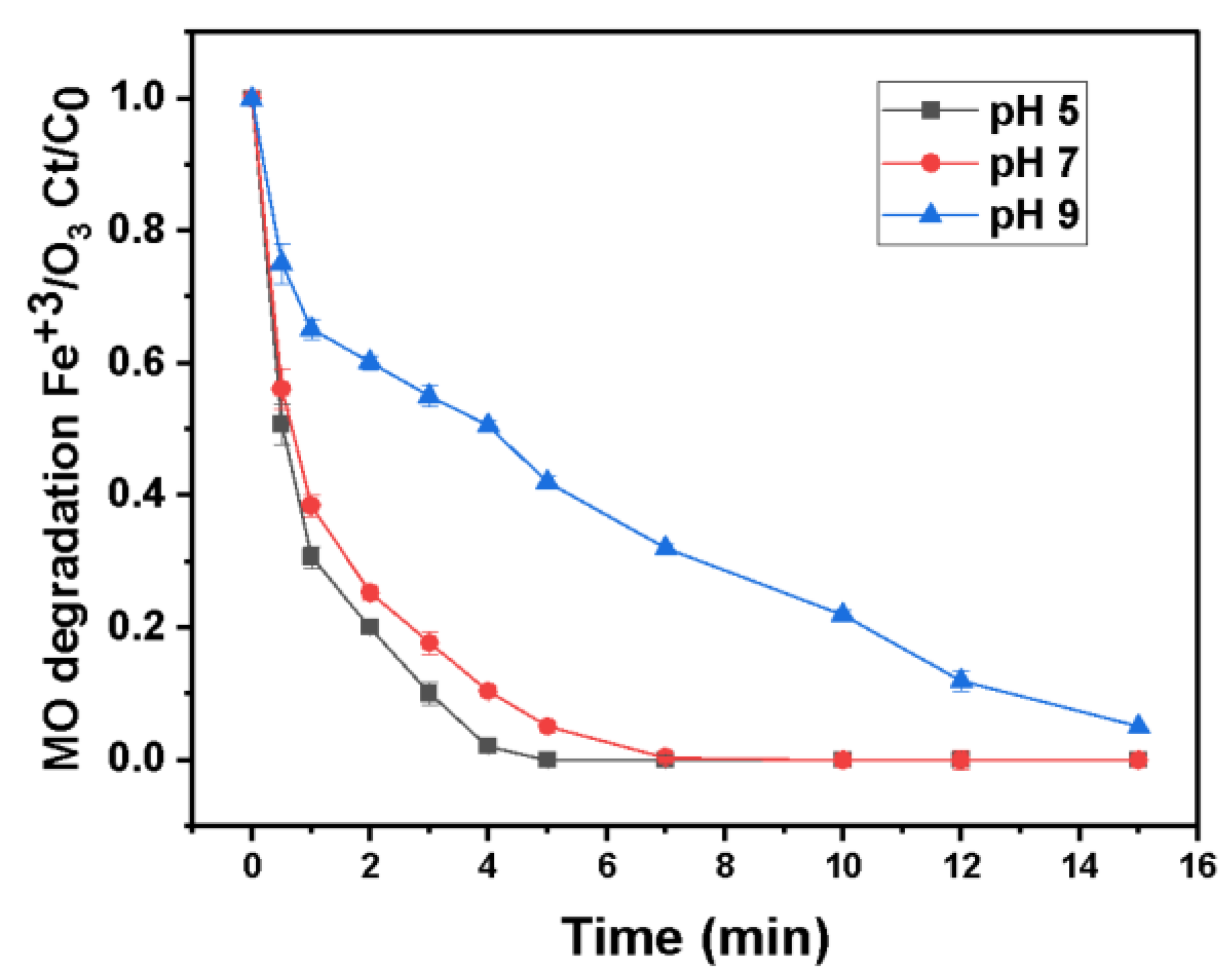
3.7.2. Effect of pH on the Degradation of MO
3.8. Product Identification
3.9. Hydroxylated Product (P1)
3.10. Proposed Degradation Pathways
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AOPs | Advanced Oxidation Processes |
| HPLC | High-Performance Liquid Chromatography |
| LC-MS | Liquid Chromatography–Mass spectrometry |
| SPE | Solid Phase Extraction |
References
- Hong, J.; Bao, J.; Liu, Y. Removal of Methylene Blue from Simulated Wastewater Based upon Hydrothermal Carbon Activated by Phosphoric Acid. Water 2025, 17, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Guo, Z.; Mao, L.; Feng, J.; Huang, J.; Tao, H. Impact of Textile Industries on Surface Water Contamination by Sb and Other Potential Toxic Elements: A Case Study in Taihu Lake Basin, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, T.; Bilal, M.; Nabeel, F.; Adeel, M.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Environmentally-related contaminants of high concern: Potential sources and analytical modalities for detection, quantification, and treatment. Environ. Int. 2019, 122, 52–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negi, A. Environmental Impact of Textile Materials: Challenges in Fiber–Dye Chemistry and Implication of Microbial Biodegradation. Polymers 2025, 17, 871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djaballah, M.L.; Belghit, A.; Dehane, A.; Merouani, S.; Hamdaoui, O.; Ashokkumar, M. Radicals (OH, Cl, ClO and Cl2−) concentration profiles in the intensified degradation of reactive green 12 by UV/chlorine process: Chemical kinetic analysis using a validated model. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2023, 439, 114557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavithra, K.G.; Kumar, P.S.; Jaikumar, V.; Rajan, P.S. Removal of colorants from wastewater: A review on sources and treatment strategies. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 75, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaseen, D.A.; Scholz, M. Textile dye wastewater characteristics and constituents of synthetic effluents: A critical review. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 1193–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shad, A.; Chen, J.; Qu, R.; Dar, A.A.; Bin-Jumah, M.; Allam, A.A.; Wang, Z. Degradation of sulfadimethoxine in phosphate buffer solution by UV alone, UV/PMS and UV/H2O2: Kinetics, degradation products, and reaction pathways. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 398, 125357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Luo, H.; Luo, D.; Chen, Y.; Tang, J.; Ma, H.; Pu, S. New insights into the degradation of nitrobenzene by activated persulfate with sulfidated nanoscale zero-valent iron: Synergistic effects of reduction and reactive oxygen species oxidation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 322, 124252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Yang, J.; Chen, J.; Luo, H.; Ma, H.; Pu, S. Enhancement of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol degradation in groundwater via natural pyrite-activated percarbonate: Mechanistic insights and efficiency evaluation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 116048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Ren, J.; Sun, X.; Chen, X.; Liu, G.; Wang, S.; Yang, H. Strong evidence for interface-field-induced photocarrier separation in new AgFeO2-BiVO4 heterostructures and their efficient photo-Fenton degradation of ciprofoxacin. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2025, 679, 161275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Sun, X.; Zhu, W.; Liu, G.; Xian, T.; Yang, H. Design of CdZnS/BiOCl heterostructure as a highly-efficient piezo-photocatalyst for removal of antibiotic. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 114405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Do, J.Y.; Kim, J.; Kang, M. Fast and highly efficient removal of dye from aqueous solution using natural locust bean gum based hydrogels as adsorbent. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 143, 60–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekhate, C.V.; Srivastava, J.K. Recent advances in ozone-based advanced oxidation processes for treatment of wastewater- A review. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2020, 3, 100031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boczkaj, G.; Fernandes, A. Wastewater treatment by means of advanced oxidation processes at basic pH conditions: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 320, 608–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.U.H.; Gul, N.S.; Sabahat, S.; Sun, J.; Tahir, K.; Shah, N.S.; Muhammad, N.; Rahim, A.; Imran, M.; Iqbal, J.; et al. Removal of organic pollutants through hydroxyl radical-based advanced oxidation processes. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 267, 115564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorov, K.; Rayaroth, M.P.; Shah, N.S.; Boczkaj, G. Activated sodium percarbonate-ozone (SPC/O3) hybrid hydrodynamic cavitation system for advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) of 1,4-dioxane in water. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 456, 141027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slama, H.B.; Chenari Bouket, A.; Pourhassan, Z.; Alenezi, F.N.; Silini, A.; Cherif-Silini, H.; Oszako, T.; Luptakova, L.; Golińska, P.; Belbahri, L. Diversity of Synthetic Dyes from Textile Industries, Discharge Impacts and Treatment Methods. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladoye, P.O.; Ajiboye, T.O.; Wanyonyi, W.C.; Omotola, E.O.; Oladipo, M.E. Ozonation, electrochemical, and biological methods for the remediation of malachite green dye wastewaters: A mini review. Sustain. Chem. Environ. 2023, 3, 100033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Cheng, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Tang, J.; Qiu, F. Efficient degradation of dye wastewater by catalytic ozonation reactive ceramic membrane with facile spraying of nano TiMn oxides: A pilot scale attempt. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 55, 104143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.P.; Dhara, S.; Samanta, N.S.; Purkait, M.K. Advancements on ozonation process for wastewater treatment: A comprehensive review. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2024, 202, 109852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issaka, E.; AMU-Darko, J.N.-O.; Yakubu, S.; Fapohunda, F.O.; Ali, N.; Bilal, M. Advanced catalytic ozonation for degradation of pharmaceutical pollutants―A review. Chemosphere 2022, 289, 133208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masjidin, N.N.; Joseph, C.G.; Teo, S.H.; Gansau, J.A.; Sarbatly, R.; Ramakrishnan, S.; Sillanpää, M. Application of Photocatalytic Ozonation for the Remediation of Aquaculture Effluents: A Review. Catalysts 2024, 14, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epelle, E.I.; Macfarlane, A.; Cusack, M.; Burns, A.; Okolie, J.A.; Mackay, W.; Rateb, M.; Yaseen, M. Ozone application in different industries: A review of recent developments. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 454, 140188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tehrani-Bagha, A.R.; Mahmoodi, N.M.; Menger, F.M. Degradation of a persistent organic dye from colored textile wastewater by ozonation. Desalination 2010, 260, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.-J.; Guo, W.-Q.; Yang, S.-S.; Zheng, H.-S.; Ren, N.-Q. Ultrasonic-assisted ozone oxidation process of triphenylmethane dye degradation: Evidence for the promotion effects of ultrasonic on malachite green decolorization and degradation mechanism. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 128, 827–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, Y.-P.; Liang, Y.-Y.; Chang, C.-N.; Chao, A.C. Differentiating ozone direct and indirect reactions on decomposition of humic substances. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 2395–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Fu, L.; Chen, F.; Zhao, S.; Zhu, J.; Yin, C. Application of Heterogeneous Catalytic Ozonation in Wastewater Treatment: An Overview. Catalysts 2023, 13, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.K.; Mentha, S.S.; Misra, Y.; Dwivedi, N. Emerging pollutants of severe environmental concern in water and wastewater: A comprehensive review on current developments and future research. Water-Energy Nexus 2023, 6, 74–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido-Cardenas, J.A.; Esteban-García, B.; Agüera, A.; Sánchez-Pérez, J.A.; Manzano-Agugliaro, F. Wastewater Treatment by Advanced Oxidation Process and Their Worldwide Research Trends. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.-Y.; Lee, D.-Y.; Oh, K.-Y.; Jeong, D.-K.; Lee, D.-Y.; Kim, J.-H. Photochemical advanced oxidative process treatment effect on the pesticide residues reduction and quality changes in dried red peppers. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 4444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, H.; Mahalvar, A.; Pradhan, M.; Yadav, K.; Kumar Sahu, K.; Yadav, R. Exploring the potential of phytochemicals and nanomaterial: A boon to antimicrobial treatment. Med. Drug Discov. 2023, 17, 100151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Ávila, F.; Zambrano-Jaramillo, A.; Velecela-Garay, C.; Coronel-Sánchez, K.; Valdiviezo-Gonzales, L. Effectiveness of membrane technologies in removing emerging contaminants from wastewater: Reverse Osmosis and Nanofiltration. Water Cycle 2025, 6, 357–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Shi, J.L.; von Gunten, U.; McCurry, D.L. Ozonation of organic compounds in water and wastewater: A critical review. Water Res. 2022, 213, 118053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, S.N.; Ghosh, P.C.; Vaidya, A.N.; Mudliar, S.N. Hybrid ozonation process for industrial wastewater treatment: Principles and applications: A review. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 35, 101193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baruah, M.J.; Dutta, R.; Zaki, M.E.A.; Bania, K.K. Heterogeneous Iron-Based Catalysts for Organic Transformation Reactions: A Brief Overview. Molecules 2024, 29, 3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrán, F.J.; Rivas, F.J.; Montero-de-Espinosa, R. Iron type catalysts for the ozonation of oxalic acid in water. Water Res. 2005, 39, 3553–3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, P.; Kumar, A. ADVANCED OXIDATION PROCESS: A remediation technique for organic and non-biodegradable pollutant. Results Surf. Interfaces 2023, 11, 100122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Majumder, S.K. Degradation kinetics of 4-nitrophenol and its control by ozone bubble with and without nanocatalyst in an ozone bubble column reactor. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 117471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Pan, S.; Xu, F.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, C.; Xu, X.; Gao, B.; Li, Q. Revealing the fundamental role of MoO2 in promoting efficient and stable activation of persulfate by iron carbon based catalysts: Efficient Fe2+/Fe3+ cycling to generate reactive species. Water Res. 2022, 225, 119142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fijołek, L.; Świetlik, J.; Frankowski, M. Ozonation and catalytic ozonation—Sources of error. What do we need to know? J. Environ. Manage. 2024, 370, 123031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, J.E.; Sahoo, M.K. A review on effect of operational parameters for the degradation of azo dyes by some advanced oxidation processes. Sustain. Chem. Environ. 2025, 11, 100274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadollahfardi, G.; Salehi, A.; Cheraghi, S.; Keneshlo, S.; Vatannia, S. Impact of treated industrial wastewater’s pH on different characteristics of self-compacting concrete. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2024, 9, 100696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulou, G.; Evgenidou, E.; Lambropoulou, D. Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Photo-Fenton-Based Photocatalytic Techniques for the Degradation of Nile Blue Dye. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 7917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.; Ghanbari, F.; Moradi, M. Photocatalysis assisted by peroxymonosulfate and persulfate for benzotriazole degradation: Effect of pH on sulfate and hydroxyl radicals. Water Sci. Technol. 2015, 72, 2095–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Sun, M.; Liang, J.; Xiong, Z.; Liu, Y.; Peng, J.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, P.; Lai, B. pH-modulated oxidation of organic pollutants for water decontamination: A deep insight into reactivity and oxidation pathway. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 471, 134393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yang, Z.; Chen, S.; Sun, W.; Sun, Y. Ozonation Treatment of Simulated Wastewater Containing Characteristic Pollutants from the Petrochemical Industry. Water 2025, 17, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayaroth, M.P.; Aravindakumar, C.T.; Shah, N.S.; Boczkaj, G. Advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) based wastewater treatment—Unexpected nitration side reactions—A serious environmental issue: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 133002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Z.; Liang, Y.; Dong, S.; Li, M.; Chen, J.; Chen, H.; Xie, H.; et al. Substantial emissions of nitrated aromatic compounds in the particle and gas phases in the waste gases from eight industries. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 283, 117132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokal-Dembowska, A.; Jarmakiewicz-Czaja, S.; Tabarkiewicz, J.; Filip, R. Nitrate and Nitrite in the Diet: Protective and Harmful Effects in Health and Disease. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2025, 14, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Mode | Products | Retention Time (min) | Molecular Formula | Detected m/z | Calculated m/z | Error (ppm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | P1 | 9 | C16H18ClN3OS | 335.05 | 335.051 | 0.44 |
| P2 | 10.93 | C9H14NO | 152.143 | 152.144 | −0.5 | |
| P3 | 4.47 | C8H14N | 124.111 | 124.11 | −2.56 | |
| P4 | 6.01 | C15H16ClN3OS | 355.073 | 321.074 | −0.5813 | |
| P5 | 2.8 | C14H12ClN3O2S | 321.033 | 321.034 | −0.531 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Altoom, N.G. Understanding the Efficiency of Catalytic Ozonation for the Degradation of Synthetic Dyes in Water: A Study of Degradation Mechanism and Pathways. Sustainability 2025, 17, 8349. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17188349
Altoom NG. Understanding the Efficiency of Catalytic Ozonation for the Degradation of Synthetic Dyes in Water: A Study of Degradation Mechanism and Pathways. Sustainability. 2025; 17(18):8349. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17188349
Chicago/Turabian StyleAltoom, Naif Ghazi. 2025. "Understanding the Efficiency of Catalytic Ozonation for the Degradation of Synthetic Dyes in Water: A Study of Degradation Mechanism and Pathways" Sustainability 17, no. 18: 8349. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17188349
APA StyleAltoom, N. G. (2025). Understanding the Efficiency of Catalytic Ozonation for the Degradation of Synthetic Dyes in Water: A Study of Degradation Mechanism and Pathways. Sustainability, 17(18), 8349. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17188349






