The Impact of Renewable Energy Use, Financial Development, and Industrialization on CO2 Emissions in Middle-Income Economies—A GMM-PVAR Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Renewable Energy and Carbon Emissions
2.2. Financial Development and Carbon Emissions
2.3. Industrialization and Carbon Emissions
2.4. Mechanisms Linking Renewable Energy, Financial Development, Industrialization, and CO2 Emissions
2.5. Literature Gaps
3. Methods and Data Analysis
3.1. Data
3.2. Model Specification
3.3. Estimation Procedure
3.3.1. Cross-Sectional Dependence
3.3.2. Panel Unit Root Tests
3.3.3. Westerlund Cointegration Test
3.3.4. GMM-PVAR Model
3.3.5. Panel Granger Causality
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Upper Middle-Income Countries
4.2. Lower Middle-Income Countries
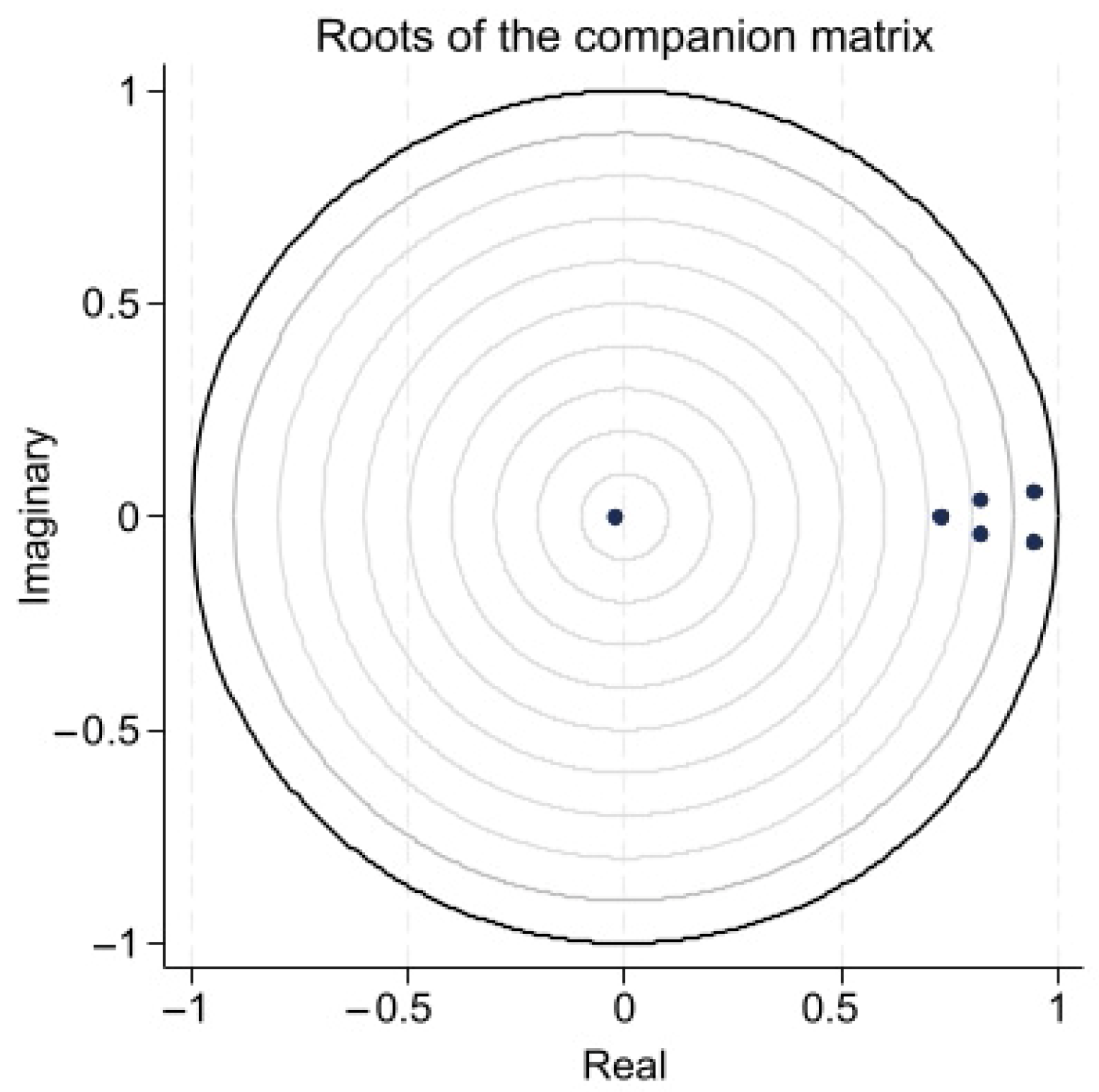
4.3. Robustness Check
5. Conclusions
6. Policy Recommendations
6.1. Upper Middle-Income Countries
6.2. Lower Middle-Income Countries
7. Limitations and Future Research Directions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GMM-PVAR | Generalized Method of Moments Panel Vector Autoregression |
| GNI | Gross National Income |
| IPCC | The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change |
| COP | Conferences of the Parties |
| GDP | Global Gross Domestic Product |
| MICs | Middle-Income Economies |
| FMOLS | Fully Modified Ordinary Least Squares |
| GW | Gigawatt |
| MENA | Middle East and North Africa |
| CCEMG | Common Correlated Effects Mean Group |
| AMG | Augmented Mean Group |
| WDI | World Development Indicators |
| CD | Cross-sectional dependence |
| CADF | Cross-Section Augmented Dickey–Fuller |
| CIPS | Cross-Section Im-Pesaran-Shin |
| RE | Renewable Energy |
| FD | Financial Development |
| IND | Industrialization |
| PS | Political Stability |
| VIF | Variance Inflation Factor |
| MMSC | Moment Selection Criteria. |
| MMSC-HQIC | Hannan-Quinn Information Criterion |
| MMSC-BIC | Bayesian Information Criterion |
| DOLS | Dynamic Ordinary Least Squares |
References
- Grant, L.; Vanderkelen, I.; Gudmundsson, L.; Fischer, E.; Seneviratne, S.I.; Thiery, W. Global Emergence of Unprecedented Lifetime Exposure to Climate Extremes. Nature 2025, 641, 374–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukoba, K.; Onisuru, O.R.; Jen, T.C.; Madyira, D.M.; Olatunji, K.O. Predictive Modeling of Climate Change Impacts Using Artificial Intelligence: A Review for Equitable Governance and Sustainable Outcome. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2025, 32, 10705–10724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, D.; Hall, C.M.; Rushton, B.; Gössling, S. A Review of the IPCC Sixth Assessment and Implications for Tourism Development and Sectoral Climate Action. J. Sustain. Tour. 2024, 32, 1725–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, P. COP28: Ambitions, Realities, and Future. Environ. Sustain. 2024, 7, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, S.; Hu, X. Filling the Climate Finance Gap: Holistic Approaches to Mobilise Private Finance in Developing Economies. npj Clim. Action 2025, 4, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandiramani, J.; Tripathi, S.; Benara Misra, S.; Patil, G.; Shende, A. Does Inequality Exist in Attaining Sustainable Development Goals within a City? A Case Study in Pune City, India. Int. J. Urban Sci. 2024, 29, 627–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andriesse, E.; Dinh, T.L.T.; Kittitornkool, J.; Kodir, A.; Kongkaew, C.; Markphol, A.; Pham, Q.T.N.; Sumadio, W. Immiserizing Growth and the Middle-Income Trap in Rural South East Asia: Comparing Exclusion and Coping Mechanisms among Farming and Fishing Communities. World Dev. 2025, 185, 106783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkat, K.; Alsamara, M.; Mimouni, K. Beyond Economic Growth Goals: Can Foreign Aid Mitigate Carbon Dioxide Emissions in Developing Countries? J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 471, 143411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saqib, N.; Usman, M.; Ozturk, I.; Sharif, A. Harnessing the Synergistic Impacts of Environmental Innovations, Financial Development, Green Growth, and Ecological Footprint through the Lens of SDGs Policies for Countries Exhibiting High Ecological Footprints. Energy Policy 2024, 184, 113863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEA. Global Energy Review 2025; IEA: Paris, France, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Prakash, N. Income Disparities and Environmental Dynamics: Exploring Varied Impacts of Renewable Energy, Innovations, and Economic Growth on CO2 Emissions. Renew. Energy 2025, 243, 122596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEA. Renewables 2024; IEA: Paris, France, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Kumari, D.; Shashwat, S.; Verma, P.K.; Giri, A.K. Examining the Nexus between Carbon Dioxide Emissions, Economic Growth, Fossil Fuel Energy Use, Urbanization and Renewable Energy towards Achieving Environmental Sustainability in India. Int. J. Energy Sect. Manag. 2024, 19, 731–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, X.; Linghu, K.; Jiang, G.; Chang, T.H.; Liu, F.P.; Chiu, Y.H. China’s Energy Efficiency Improvement Considering Renewable Energy Substitution: Applying a Dynamic Two-Stage Undesirable Non-Radial Directional Distance Function. J. Power Sources 2025, 629, 235946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, M.C.; Nadaleti, W.C.; Cardozob, E.; Bittencourt, J.; da Silva, C.; de Souza, E.; Vieira, B.; Escobar, C.; Przybyla, G. Biogas and Biohydrogen from Peach Pomace: Renewable Energy Potential in Southern Brazil. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2025, 210, 115210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishore, T.S.; Kumar, P.U.; Ippili, V. Review of Global Sustainable Solar Energy Policies: Significance and Impact. Innov. Green Dev. 2025, 4, 100224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zeng, B.; Zhao, X.; Zeng, S.; Jiang, S. Impact of Green Finance on Green Energy Efficiency: A Pathway to Sustainable Development in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 450, 141943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbass, K.; Amin, N.; Khan, F.; Begum, H.; Song, H. Driving Sustainability: The Nexus of Financial Development, Economic Globalization, and Renewable Energy in Fostering a Greener Future. Energy Environ. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Xie, Y. How Does Digital Finance Drive Energy Transition? A Green Investment-Based Perspective. Financ. Innov. 2025, 11, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donou-Adonsou, F.; Basnet, H.; Mathey, S. Energy Poverty and Financial Development: Evidence from Developing Countries. Energy Econ. 2025, 147, 108563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Kartal, M.T.; Ullah, S. Pathways to Environmental Sustainability: The Asymmetric Effects of Green Technology Innovation, Policy Stringency, and Industrialization in the United States. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 502, 145376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Ge, Y.; Li, R. Does Improving Economic Efficiency Reduce Ecological Footprint? The Role of Financial Development, Renewable Energy, and Industrialization. Energy Environ. 2025, 36, 729–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, A.; Saadaoui Mallek, R.; Ozturk, I. International Emigration and Economic Complexity: Evidence from the Dynamic GMM Panel VAR Approach. J. Int. Trade Econ. Dev. 2024, 34, 102–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owjimehr, S.; Meybodi, M.E. Dynamic Relationship between Climate Policy Uncertainty Shocks and Financial Stress: A GMM-Panel VAR Approach. Reg. Sci. Policy Pract. 2025, 17, 100181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, S.; Han, V.; Özsolak, B. How Do Renewable Energy, Gross Capital Formation, and Natural Resource Rent Affect Economic Growth in G7 Countries? Evidence from the Novel GMM-PVAR Approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 78438–78448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.A.; Tao, Z.; Agyekum, E.B.; Fahad, S.; Tahir, M.; Salman, M. Sustainable Rural Electrification: Energy-Economic Feasibility Analysis of Autonomous Hydrogen-Based Hybrid Energy System. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2025, 141, 460–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uğurlu, E. Impacts of Renewable Energy on CO Emission: Evidence from the Visegrad Group Countries. Politics Cent. Eur. 2022, 18, 295–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguir Bargaoui, S. The Impact of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energies on Environmental Quality in OECD Countries. J. Knowl. Econ. 2022, 13, 3424–3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhtarov, S.; Aliyev, F.; Aliyev, J.; Ajayi, R. Renewable Energy Consumption and Carbon Emissions: Evidence from an Oil-Rich Economy. Sustainability 2023, 15, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mentel, G.; Tarczyński, W.; Dylewski, M.; Salahodjaev, R. Does Renewable Energy Sector Affect Industrialization-CO2 Emissions Nexus in Europe and Central Asia? Energies 2022, 15, 5877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Huang, K.; Li, L.; Wang, X. Renewable Energy for Balancing Carbon Emissions and Reducing Carbon Transfer under Global Value Chains: A Way Forward. Sustainability 2022, 15, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahanger, A.; Ozturk, I.; Chukwuma Onwe, J.; Joseph, T.E.; Razib Hossain, M. Do Technology and Renewable Energy Contribute to Energy Efficiency and Carbon Neutrality? Evidence from Top Ten Manufacturing Countries. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2023, 56, 103084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Lo, K. China’s Renewable Energy and Energy Efficiency Policies toward Carbon Neutrality: A Systematic Cross-Sectoral Review. Energy Environ. 2024, 35, 491–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apergis, N.; Kuziboev, B.; Abdullaev, I.; Rajabov, A. Investigating the Association among CO2 Emissions, Renewable and Non-Renewable Energy Consumption in Uzbekistan: An ARDL Approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 39666–39679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gierałtowska, U.; Asyngier, R.; Nakonieczny, J.; Salahodjaev, R. Renewable Energy, Urbanization, and CO2 Emissions: A Global Test. Energies 2022, 15, 3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majewski, S.; Mentel, G.; Dylewski, M.; Salahodjaev, R. Renewable Energy, Agriculture and CO2 Emissions: Empirical Evidence From the Middle-Income Countries. Front. Energy Res. 2022, 10, 921166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, S.; Nsiah, C. Reducing Carbon Dioxide Emissions; Does Renewable Energy Matter? Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 693, 133288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raihan, A.; Tuspekova, A. Dynamic Impacts of Economic Growth, Renewable Energy Use, Urbanization, Industrialization, Tourism, Agriculture, and Forests on Carbon Emissions in Turkey. Carbon Res. 2022, 1, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, T.; Jia, W.; Shahidehpour, M.; Han, O.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Z. Review of Optimization Methods for Energy Hub Planning, Operation, Trading, and Control. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2022, 13, 1802–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, X.; Parisio, A. A Corrective Control Framework for Mitigating Voltage Fluctuations and Congestion in Distribution Networks with High Renewable Energy Penetration. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2025, 165, 110508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, T.Z.; Salem, M.; Kamarol, M.; Das, H.S.; Nazari, M.A.; Prabaharan, N. A Comprehensive Study of Renewable Energy Sources: Classifications, Challenges and Suggestions. Energy Strategy Rev. 2022, 43, 100939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basit, M.A.; Dilshad, S.; Badar, R.; Sami ur Rehman, S.M. Limitations, Challenges, and Solution Approaches in Grid-Connected Renewable Energy Systems. Int. J. Energy Res. 2020, 44, 4132–4162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stram, B.N. Key Challenges to Expanding Renewable Energy. Energy Policy 2016, 96, 728–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidi, K.; Ben Mbarek, M. Nuclear Energy, Renewable Energy, CO2 Emissions, and Economic Growth for Nine Developed Countries: Evidence from Panel Granger Causality Tests. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2016, 88, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, S.; Andriamahery, A.; Qamruzzaman, M.; Kor, S. Effects of Financial Development, FDI and Good Governance on Environmental Degradation in the Arab Nation: Dose Technological Innovation Matters? Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1094976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Song, P.; Yang, D.; Gao, C. Does Governance Impact on the Financial Development-Carbon Dioxide Emissions Nexus in G20 Countries. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0273546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charfeddine, L.; Kahia, M. Impact of Renewable Energy Consumption and Financial Development on CO2 Emissions and Economic Growth in the MENA Region: A Panel Vector Autoregressive (PVAR) Analysis. Renew. Energy 2019, 139, 198–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Sheng, M.S.; Wen, L. How Does Financial Development Influence Carbon Emission Intensity in the OECD Countries: Some Insights from the Information and Communication Technology Perspective. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 335, 117553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akan, T. Explaining and Modeling the Mediating Role of Energy Consumption between Financial Development and Carbon Emissions. Energy 2023, 274, 127312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habiba, U.; Xinbang, C.; Ali, S. Investigating the Impact of Financial Development on Carbon Emissions: Does the Use of Renewable Energy and Green Technology Really Contribute to Achieving Low-Carbon Economies? Gondwana Res. 2023, 121, 472–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Zhao, M.; Yuan, R.; Li, N. Influence Mechanism of Financial Development on Carbon Emissions from Multiple Perspectives. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2023, 39, 357–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, T.; Jiang, Q.; Ma, X. To Facilitate or Curb? The Role of Financial Development in China’s Carbon Emissions Reduction Process: A Novel Approach. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahiani, A. Is Financial Development Good for the Environment? An Asymmetric Analysis with CO2 Emissions in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 7901–7909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aluko, O.A.; Obalade, A.A. Financial Development and Environmental Quality in Sub-Saharan Africa: Is There a Technology Effect? Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 747, 141515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omri, A.; Daly, S.; Rault, C.; Chaibi, A. Financial Development, Environmental Quality, Trade and Economic Growth: What Causes What in MENA Countries. Energy Econ. 2015, 48, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acheampong, A.O.; Amponsah, M.; Boateng, E. Does Financial Development Mitigate Carbon Emissions? Evidence from Heterogeneous Financial Economies. Energy Econ. 2020, 88, 104768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamel, L.; Maktouf, S. The Nexus between Economic Growth, Financial Development, Trade Openness, and CO2 Emissions in European Countries. Cogent Econ. Financ. 2017, 5, 1341456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Li, Y.; An, D.; Han, Y.; Xu, S.; Lu, Z.; Crittenden, J. Mining of the Association Rules between Industrialization Level and Air Quality to Inform High-Quality Development in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 246, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Bae, J. Urbanization and Industrialization Impact of CO2 Emissions in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; Ozturk, I.; Usman, A.; Majeed, M.T.; Akhtar, P. On the Asymmetric Effects of Premature Deindustrialization on CO2 Emissions: Evidence from Pakistan. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 13692–13702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appiah, M.; Li, F.; Korankye, B. Modeling the Linkages among CO2 Emission, Energy Consumption, and Industrialization in Sub-Saharan African (SSA) Countries. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 38506–38521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, H.; Alkhateeb, T.T.Y.; Furqan, M. Industrialization, Urbanization and CO2 Emissions in Saudi Arabia: Asymmetry Analysis. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 1553–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, J.; Zikhali, P. The Bittersweet Fruits of Industrialization in Rural China: The Cost of Environment and the Benefit from off-Farm Employment. China Econ. Rev. 2016, 38, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Li, X.; Liao, G. Business Cycles and Energy Intensity. Evidence from Emerging Economies. Borsa Istanb. Rev. 2022, 22, 560–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boya-Lara, C. Integrating Electric Mobility and Distributed Solar in Carbon-Negative Panama: Readiness Assessment and Policy Roadmap for Sustainable Energy Transition. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2025, 87, 101747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.R.; Rao, A.; Sharma, G.D.; Dev, D.; Kharbanda, A. Empowering Energy Transition: Green Innovation, Digital Finance, and the Path to Sustainable Prosperity through Green Finance Initiatives. Energy Econ. 2024, 136, 107736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raihan, A.; Mainul Bari, A.B.M. Energy-Economy-Environment Nexus in China: The Role of Renewable Energies toward Carbon Neutrality. Innov. Green Dev. 2024, 3, 100139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seraj, M.; Seraj, F.T. The Impact of Sustainable Financial Development and Green Energy Transition on Climate Change in the World’s Highest Carbon-Emitting Countries. Sustainability 2025, 17, 3781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Z.; Xia, H.; He, Y. Rewiring Sustainability: How Digital Transformation and Fintech Innovation Reshape Environmental Trajectories in the Industry 4.0 Era. Systems 2025, 13, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Wang, J. The Impact of Digital Economic Growth and Financial Expansion on CO2 Mitigation Strategies in Leading Emitting Countries. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 10515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalakrishnan, T.; Miller, J. New Climate Dis-Economies: The Political Economy of Energy Transitions in Fragile Fossil Fuel Producers. Environ. Secur. 2024, 2, 348–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassani, A.A.; Imran, M.; Khan, S.; Zaman, K.; Khan, H.u.R.; Haffar, M. Financial Integration and Economic Growth: Impact of Renewable Energy Investments, Technology Transfer, and Climate Change on Europe and Central Asian Economies. Financ. Innov. 2025, 11, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahanger, A.; Hossain, M.R.; Awan, A.; Sunday Adebayo, T.; Zubair Chishti, M. Linking Tourist’s Footprint and Environmental Tragedy through Transportation, Globalization and Energy Choice in BIMSTEC Region: Directions for a Sustainable Solution Using Novel GMM-PVAR Approach. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 345, 118551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzeremes, P.; Dogan, E.; Alavijeh, N.K. Analyzing the Nexus between Energy Transition, Environment and ICT: A Step towards COP26 Targets. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 326, 116598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dogan, E.; Chishti, M.Z.; Karimi Alavijeh, N.; Tzeremes, P. The Roles of Technology and Kyoto Protocol in Energy Transition towards COP26 Targets: Evidence from the Novel GMM-PVAR Approach for G-7 Countries. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2022, 181, 121756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hounyo, U.; Kao, C.; Kim, M.S. Serial Dependence Robust Bootstrap Test for Cross-Sectional Correlation. Econom. J. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daghbagi, H.; Hasni, R.; Ben Jebli, M. The Assessment of Economic Complexity and Financial Development on Environmental Quality: Evidence for Panel Cointegration Approach. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2025, 18, 2111–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anavatan, A.; Ispir, M.S. Stochastic Convergence Behaviour in Carbon Dioxide Emissions: Fourier Panel Unit Root Approach. Appl. Econ. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesaran, M.H. A Simple Panel Unit Root Test in the Presence of Cross-Section Dependence. J. Appl. Econom. 2007, 22, 265–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerlund, J. Testing for Error Correction in Panel Data*. Oxf. Bull. Econ. Stat. 2007, 69, 709–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigmund, M.; Ferstl, R. Panel Vector Autoregression in R with the Package Panelvar. Q. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2021, 80, 693–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.; Abid, N.; Aftab, J.; Javed, A. Tracing the Trajectories of Energy Intensity, Environmental Tax Revenues, and Environmental Neutrality in Major European Economies. Energy Strategy Rev. 2025, 58, 101650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickell, S. Biases in Dynamic Models with Fixed Effects. Econometrica 1981, 49, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, D.W.K.; Lu, B. Consistent Model and Moment Selection Procedures for GMM Estimation with Application to Dynamic Panel Data Models. J. Econom. 2001, 101, 123–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Q.; Fan, X.; Zou, S. Threshold Effects of Renewable Energy Investment on the Energy Efficiency–Fossil Fuel Consumption Nexus: Evidence from 71 Countries. Energies 2025, 18, 2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.; Jahanger, A.; Makhdum, M.S.A.; Balsalobre-Lorente, D.; Bashir, A. How Do Financial Development, Energy Consumption, Natural Resources, and Globalization Affect Arctic Countries’ Economic Growth and Environmental Quality? An Advanced Panel Data Simulation. Energy 2022, 241, 122515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jianguo, D.; Ali, K.; Alnori, F.; Ullah, S. The Nexus of Financial Development, Technological Innovation, Institutional Quality, and Environmental Quality: Evidence from OECD Economies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 58179–58200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesaran, M.H. General Diagnostic Tests for Cross-Sectional Dependence in Panels. Empir. Econ. 2020, 60, 13–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, L.; Behera, B.; Sethi, N. Do Green Finance, Green Technology Innovation, and Institutional Quality Help Achieve Environmental Sustainability? Evidence from the Developing Economies. Sustain. Dev. 2024, 32, 2709–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacıimamoğlu, T.; Sungur, O. How Do Economic Growth, Renewable Energy Consumption, and Political Stability Affect Environmental Sustainability in the United States? Insights from a Modified Ecological Footprint Model. J. Knowl. Econ. 2024, 15, 20649–20676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.; Bekun, F.V.; Ozturk, I.; Ferreira, P.J.S.; Karalinc, T. Unravelling the Role of Financial Development in Shaping Renewable Energy Consumption Patterns: Insights from BRICS Countries. Energy Strategy Rev. 2024, 54, 101434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamah, M.; Riti, J.S.; Bin, P. Inclusive Growth and Environmental Sustainability: The Role of Institutional Quality in Sub-Saharan Africa. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 34885–34901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, A.; Hussain, F. From Investment to Emissions: Unveiling the Rebound Effect of Renewable Energy Consumption on Energy Efficiency in Asia-Pacific Economies. Int. J. Energy Sect. Manag. 2025, 19, 455–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özsoy, T. The “Energy Rebound Effect” within the Framework of Environmental Sustainability. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Energy Environ. 2024, 13, e517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaedi, M.; Foukolaei, P.Z.; Alizadeh Asari, F.; Khazaei, M.; Gholian-Jouybari, F.; Hajiaghaei-Keshteli, M. Pricing Electricity from Blue Hydrogen to Mitigate the Energy Rebound Effect: A Case Study in Agriculture and Livestock. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 84, 993–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawn, S.; Manideep, S.; Rekha, S.S.; Rao, C.R.; Rao, K.D.; Al Mansur, A.; Ustun, T.S. Advancing Renewable Energy Integration in Deregulated Markets: The Role of Energy Storage, EVs, and Policy Frameworks. Energy Explor. Exploit. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| CO2 | RE | FD | GDP | IND | PS | VIF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upper Middle-Income Countries | |||||||
| CO2 | 1 | ||||||
| RE | −0.697 | 1 | 1.49 | ||||
| FD | 0.384 | −0.265 | 1 | 1.31 | |||
| GDP | 0.719 | −0.550 | 0.448 | 1 | 2.19 | ||
| IND | 0.579 | −0.339 | 0.325 | 0.607 | 1 | 1.79 | |
| PS | 0.029 | 0.044 | 0.261 | 0.174 | 0.369 | 1 | 1.26 |
| Lower Middle-Income Countries | |||||||
| CO2 | 1 | ||||||
| RE | −0.552 | 1 | 1.93 | ||||
| FD | 0.141 | 0.055 | 1 | 1.56 | |||
| GDP | 0.417 | −0.167 | 0.064 | 1 | 3.04 | ||
| IND | 0.467 | −0.118 | 0.231 | 0.436 | 1 | 1.69 | |
| PS | −0.096 | 0.241 | 0.337 | 0.146 | 0.255 | 1 | 1.27 |
| Upper Middle-Income Countries | Lower Middle-Income Countries | |
|---|---|---|
| CO2 | 133.98 *** | 47.52 *** |
| RE | 34.71 *** | 4.12 *** |
| FD | 106.38 *** | 49.77 *** |
| GDP | 140.62 *** | 57.12 *** |
| IND | 119.83 *** | 47.12 *** |
| PS | 78.48 *** | 37.32 *** |
| CIPS | CADF | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level | First Difference | Level | First Difference | |
| Upper Middle-Income Countries | ||||
| CO2 | −1.596 | −3.413 *** | −1.527 | −2.672 *** |
| RE | −2.076 | −3.195 *** | −1.425 | −3.419 *** |
| FD | −2.133 | −3.329 *** | −1.882 | −2.396 *** |
| GDP | −1.824 | −2.986 *** | −1.532 | −2.193 *** |
| IND | −1.879 | −4.404 *** | −2.003 | −2.891 *** |
| PS | −2.021 | −4.012 *** | −1.780 | −3.135 *** |
| Lower Middle-Income Countries | ||||
| CO2 | −1.772 | −4.024 ** | −1.356 | −2.945 *** |
| RE | −1.625 | −3.680 *** | −1.176 | −3.079 *** |
| FD | −1.964 | −3.509 *** | −1.800 | −2.230 ** |
| GDP | −1.978 | −3.126 *** | −1.337 | −2.384 *** |
| IND | −1.310 | −4.674 *** | −1.350 | −3.342 *** |
| PS | −1.821 | −3.902 ** | −1.602 | −2.794 *** |
| CO2 | RE | FD | GDP | IND | PS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upper Middle-Income Countries | ||||||
| L1.CO2 | −0.054 | −0.135 | 0.869 *** | −0.647 *** | 0.602 *** | −0.568 ** |
| L1.RE | −0.013 | 0.299 *** | 0.136 | −0.126 | 0.039 | −0.023 |
| L1.FD | −0.087*** | −0.022 | 0.947 *** | −0.035 | −0.064 *** | −0.114 *** |
| L1.GDP | 0.126 *** | 0.074 | −0.056 | 0.948 *** | 0.064 | 0.106 |
| L1.IND | 2.030 ** | 0.104 | 0.210 | −0.004 | 0.493 *** | −0.330 ** |
| L1.PS | 0.083 ** | −0.079 * | −0.036 | 0.113 *** | 0.074 | 0.877 *** |
| Lower Middle-Income Countries | ||||||
| L1.CO2 | 0.105 | −0.186 | 0.129 * | −0.558 * | 0.041 | 0.076 |
| L1.RE | 0.047 | 0.895 *** | 0.008 | −0.090 | 0.054 | −0.058 |
| L1.FD | −0.069 ** | −0.046 | 0.904 *** | −0.062 | −0.065 *** | −0.116 ** |
| L1.GDP | 0.081 | 0.164 * | −0.218 | 0.967 *** | −0.021 | 0.009 |
| L1.IND | 0.196 | 0.013 | 0.182 | 0.002 | 0.242 | −0.383 * |
| L1.PS | 0.184 ** | −0.079 | −0.211 | 0.089 | 0.076 | 0.828 *** |
| CO2 | RE | FD | GDP | IND | PS | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upper Middle-Income Countries | CO2 | 0.419 | 9.533 *** | 18.630 *** | 10.359 *** | 5.659 ** | |
| RE | 0.070 | 2.014 | 2.732 | 0.667 | 0.062 | ||
| FD | 15.741 *** | 1.152 | 0.53 | 1.433 | 11.050 *** | 11.889 *** | |
| GDP | 8.690 *** | 2.216 | 2.183 | 2.828 | |||
| IND | 4.610 ** | 0.766 | 1.574 | 0.003 | 6.162 *** | ||
| PS | 4.15 ** | 2.836 | 0.234 | 7.413 | 58.131 | ||
| Lower Middle-Income Countries | CO2 | 0.217 | 3.354 * | 3.377 * | 0.014 | 0.032 | |
| RE | 0.466 | 0.003 | 0.538 | 1.130 | 0.211 | ||
| FD | 4.892 ** | 1.837 | 1.302 | 10.740 *** | 4.545 ** | ||
| GDP | 1.174 | 3.704 * | 2.293 | 0.008 | |||
| IND | 2.368 | 0.005 | 0.775 | 0.000 | 0.126 | 3.009 * | |
| PS | 4.297 ** | 0.513 | 1.276 | 0.097 | 0.408 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Haloui, I.; Amzil, H.; Yang, G.; Fourati, I.; Li, Y. The Impact of Renewable Energy Use, Financial Development, and Industrialization on CO2 Emissions in Middle-Income Economies—A GMM-PVAR Analysis. Sustainability 2025, 17, 8178. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17188178
Haloui I, Amzil H, Yang G, Fourati I, Li Y. The Impact of Renewable Energy Use, Financial Development, and Industrialization on CO2 Emissions in Middle-Income Economies—A GMM-PVAR Analysis. Sustainability. 2025; 17(18):8178. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17188178
Chicago/Turabian StyleHaloui, Ismail, Hayat Amzil, Guosongrui Yang, Ibrahim Fourati, and Yang Li. 2025. "The Impact of Renewable Energy Use, Financial Development, and Industrialization on CO2 Emissions in Middle-Income Economies—A GMM-PVAR Analysis" Sustainability 17, no. 18: 8178. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17188178
APA StyleHaloui, I., Amzil, H., Yang, G., Fourati, I., & Li, Y. (2025). The Impact of Renewable Energy Use, Financial Development, and Industrialization on CO2 Emissions in Middle-Income Economies—A GMM-PVAR Analysis. Sustainability, 17(18), 8178. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17188178






