Abstract
Forest parks are vital terrestrial ecosystems that provide multiple ecosystem services (ESs) to both society and nature, including carbon storage, water conservation, soil retention, and tourism-related cultural services. These services are essential for maintaining ecological security and supporting socio-economic development. However, little is known about how ESs vary across forest parks situated in different karst landforms, and integrated re-search on the combined effects of climate, vegetation, karst surface characteristics, and tourism remains limited. In this study, we examine forest parks in Guizhou Province, China, selecting four key ESs—water conservation, soil retention, carbon storage, and cultural services associated with tourism—and evaluate their levels through a comprehensive ecosystem services index (CES). We apply a structural equation model (PLS-SEM) to disentangle how climate, vegetation, karst surface features, and tourism activities drive spatial heterogeneity in CES. The results reveal significant differences among karst land-form units: carbon storage is relatively low in karst plateaus and gorges, whereas water conservation is highest in non-karst areas. Together, the four categories of driving factors explain 71.6–74.2% of the variance in CES, with climate emerging as the dominant contributor to spatial variation. For individual services, the principal drivers differ: normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) and tourist numbers are jointly shaped by karst surface characteristics and climate, while multi-year average spring precipitation is the most influential factor across forest parks. This study provides new evidence of the socio-ecological mechanisms regulating ESs in karst mountain forestscapes and offers a scientific reference for enhancing and regeneratively managing ecosystem services in these fragile regions.
1. Introduction
Forest ecosystems contribute substantially to regulating essential biophysical processes—such as carbon storage, soil retention, and water regulation—thereby underpinning both ecological integrity and socio-economic resilience at a global scale [1]. However, rapid economic development, climate change and extensive forest management have led to a series of ecological problems such as biodiversity reduction, soil erosion and ecosystem degradation [2,3,4]. The widespread decline of forest ecosystem services (FES) poses significant risks to ecological balance and human well-being, prompting growing global concern [5,6]. Strengthening the conservation and rehabilitation of FES is essential to maintain ecosystem functionality and support long-term sustainability.
Mountain forests provide diverse ecosystem services, including carbon sequestration, hydrological regulation, soil stabilization, and biodiversity support, alongside cultural benefits such as recreation and aesthetic enjoyment [7,8]. Globally, the cultural services of mountain forests—ranging from aesthetic landscapes to spiritual and recreational values—are increasingly recognized as irreplaceable for sustaining human well-being and cultural identity [9,10]. In karst regions, these cultural functions are particularly significant, as unique landscapes, fragile ecological bases, and rich biodiversity foster tourism and shape distinctive socio–ecological interactions [11]. Recognizing these dimensions is essential for understanding the ecological and socio-economic value of karst forest parks [12,13]. This dual ecological and cultural importance makes forest parks in karst regions particularly valuable for both conservation and sustainable development [14,15,16].
A forest park refers to a designated forest area legally approved for conservation, public recreation, and educational purposes. It integrates ecological protection with cultural and tourism functions in accordance with national policy frameworks [17,18]. As significant contributors to FES, forest parks play an irreplaceable role in maintaining climate balance, regulating water sources, preserving biodiversity, conserving soil, carbon sequestration and ecological restoration [16,19,20]. A comprehensive review of research on forest parks within domestic and international contexts reveals that scholars have primarily directed their studies towards vegetative resource conditions, the landscape preferences, motivations, and satisfaction of recreationists [21], spatial evolutionary features [17], and the health benefits associated with forest therapeutics [22]. Recent studies also highlight national-scale connectivity analysis of forest networks using graph-theoretical approaches, providing insights into the spatial optimization of conservation networks in China [23]. Nevertheless, few relevant studies have focused on the mechanisms driving forest park ecosystem services (FPES); internationally, studies such as the RAFL framework in Portugal [24] and governance innovations for sustaining forest ecosystem services in Europe [25] have provided useful insights into integrating cultural services and adaptive management. Simultaneously, the mechanisms by which multiple factors drive the spatial distribution of ecosystem services in karst areas forest parks remain poorly understood. Therefore, undertaking the aforementioned research is conducive to the protection and utilization of forest park resources, and promotes the stable augmentation of the ecosystem services provided by forest parks.
Among many factors, climate change and human activities are commonly identified as predominant factors influencing these services [26,27,28] stated that climatic conditions can impact ecosystem services by altering ecosystems’ distributions and biophysical processes [29]. Particularly, precipitation patterns and temperature changes have significant effects on water yield and soil retention services; an increase in temperature combined with decreased rainfall can lead to vegetation loss and soil degradation, precipitating a cascade of environmental issues [30]. Therefore, incorporating climatic factors into the assessment of ecosystem services is imperative, especially those services related to hydrology [31,32]. Secondarily, human activities introduce socio-economic elements into the ecological setting, where the intensity of such activities directly influences the alterations in ecosystem structure and function, thereby affecting ecosystem services [33,34]. Irrational human activities are highly detrimental to the continuous provisioning of ecosystem services. This is predominantly manifested in activities that have adverse impacts on ecosystems, such as extraction of forest products, deforestation, and unregulated grazing, particularly prevalent in underdeveloped regions. In recent years, the burgeoning forest tourism and wellness activities have catered to human demands for ecosystem services, where the public not only enjoys the conveniences provided by forest resources (e.g., tourism, health and wellness pursuits) but also influences Forest Park ecosystems in return. However, within research focusing on forest ecosystem services, the driving effects of tourism activities on ecosystem services have seldom been discussed.
While regional geographical location determines the locational natural and socio-economic factors, geology and geomorphology exert a macro-control over regional environmental characteristics, constraining the provision of ecosystem services [35]. For instance, under the influence of altitude, regional vegetation types exhibit marked vertical heterogeneity, thereby affecting the diversity of ecosystem services [4]. In the karst areas of southern China, fragile ecological baseline conditions, unique hydrogeological circumstances, and climatic factors jointly dictate the fragmented terrain features [2,26], resulting in extensive exposure of bedrock, thin soil layers, and widespread karstification [27,36]. The local populace is highly dependent on ecosystem services provided by forests [37]. However, the differential progression of socio-economic development and population expansion, along with unsustainable exploitation of natural resources, has led to a reduction in forest area and a decline in forest quality, posing a threat to the equilibrium of forest ecosystems. Nevertheless, in karst areas, there remains a significant knowledge gap regarding the factors influencing FPES. In particular, studies on key geomorphological characteristics—such as rock exposure, soil thickness, and elevation—are scarce, which limits the ability of decision-makers to develop locally adapted strategies for ecological protection and restoration. Moreover, the distribution of forest parks varies across different karst landscape zones, which may also lead to differences in their associated ecosystem services. Therefore, it is necessary to understand the relationship between karst landscape characteristic factors and ecosystem services and reveal the relevant laws, so as to explore the reasons for the differences in FPES in different geomorphological zones.
Guizhou Province, a representative karst region in southern China, features distinctive topographic characteristics and developed karst morphology that result in complex interactions among ecosystem services [38]. Forest parks, as one of the principal types of nature reserves in the country, serve as vital ecological barriers. In this study, we focus on four representative ecosystem services—water retention, soil conservation, carbon storage, and tourism-related cultural services—because they capture the core ecological functions and socio-economic values of forest parks, consistent with MEA/IPBES frameworks. To identify their social–ecological drivers, we selected 19 influencing factors across four dimensions (climate, vegetation, geomorphology, and tourism), based on the SES framework and regional empirical studies, thereby systematically incorporating both natural constraints and human pressures. Specifically, this study aims to (i) evaluate FPES differences across geomorphological zones in Guizhou’s karst region, linking them with associated forest types and ecological functions; (ii) disentangle the socio–ecological drivers of these differences by integrating climatic, vegetative, geomorphological, and tourism dimensions; and (iii) construct a differentiated management framework that combines ecological conservation with sustainable tourism development, thereby providing guidance for zone-specific protection strategies in fragile karst landscapes.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
Guizhou Province, located in inland Southwest China along the eastern edge of the Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau (103°36′–109°35′ E, 24°37′–29°13′ N; Figure 1a), covers approximately 176,200 km2, accounting for 1.84% of China’s landmass. Over 60% of its surface is composed of carbonate rock, earning it the title of a “karst-dominated province” [39]. The terrain is predominantly mountainous and hilly, comprising 92.5% of the land, with elevations ranging from 147 m to 2900 m and averaging around 1100 m, sloping generally from west to east. The province has a humid subtropical climate with ample heat and precipitation (1100–1400 mm annually), a frost-free period that spans much of the year, and an average temperature between 14 °C and 17 °C. Harsh environmental conditions have resulted in shallow, discontinuous soils with low organic matter, exposed bedrock, and extensive erosion and rocky desertification, all of which intensify the pressure between land and human activities [26,36]. Based on the topography, lithology, geological structure, and development of karst features, Guizhou can be divided into six geomorphological zones: karst gorge, karst plateaus, karst trough valley, karst basins, peak-cluster depressions, and non-karst areas. (Figure 1b). These landform types cover the majority of the province’s surface and represent the heterogeneity of karst terrain. For reference, small non-karst areas also exist in the eastern margin of the province, but they are not the focus of this study. The area and proportional representation of each geomorphological zone are presented in Table 1.
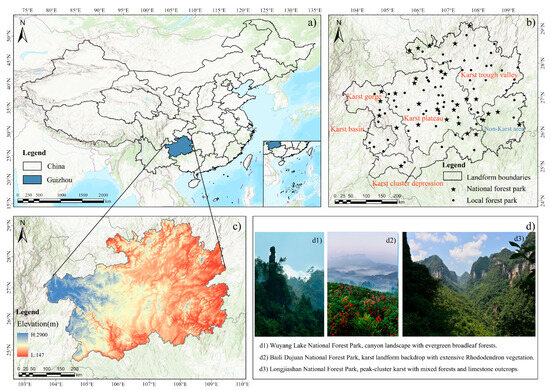
Figure 1.
Geographical location, geomorphic division, and representative karst forest landscapes in Guizhou Province. (a) Location of Guizhou Province in China. (b) Distribution of forest parks in different geomorphic areas of Guizhou Province. (c) Elevation map of Guizhou Province. (d) Representative karst forest landscapes.

Table 1.
Area proportion of different geomorphic types.
In addition to their proportional distribution, each geomorphological zone in Guizhou has distinctive ecological features and dominant forest types. Karst gorges are deeply incised valleys retaining evergreen–deciduous mixed forests [40]; karst plateaus have shallow soils and extensive rock exposure, mainly supporting Masson pine plantations and scrub [41]; karst trough valleys are low-lying corridors with fertile soils and riparian evergreen broadleaf forests; karst basins feature enclosed depressions with deeper soils and secondary broadleaf forests mixed with farmland; peak-cluster depressions combine tower karst with mixed conifer–broadleaf forests and shrublands [42]; while non-karst areas consist of more stable soils covered by dense secondary evergreen broadleaf forests [38]. These ecological differences underpin the heterogeneity of forest park ecosystem services across geomorphological zones. Further detailed descriptions of the ecological and tourism characteristics of each geomorphological zone are provided in Supplementary Note S1.1, and representative examples of forest parks illustrating dominant forest types, key ecological attributes, and tourism activities are summarized in Supplementary Table S1.2.
As of 2019, Guizhou Province harbors a total of 97 forest parks, comprising 30 national-level parks (including 1 national ecological park and 1 national arboretum and flower garden), 67 Local-level parks. According to the statistical data compiled by the Guizhou Provincial Forestry Bureau’s comprehensive monitoring of forests, grasslands, and wetlands by the end of 2022, the forest coverage rate in Guizhou Province has reached 62.81% [43]. The spatial distribution of forest parks in Guizhou Province is illustrated in Figure 1b.
2.2. Data Source
In this study, vector data and related information (e.g., tourist numbers, tourism revenue) for 97 forest parks in Guizhou Province were obtained from the Guizhou Forestry Bureau, included details such as the name, area, type, and geomorphic area of each forest park (Supplementary Table S1). To further capture the heterogeneity of tourism-related cultural services, remote sensing and GIS-based proxies were incorporated, including night-time light intensity (NLI, from NPP-VIIRS), road network density (RND, from the National Basic Geographic Information Center), and viewshed analysis (derived from DEM-based visibility modeling of scenic spots). These indicators together reflect both realized and potential tourism intensity and accessibility and were integrated into the GIS-based accessibility–visibility model to quantify tourism cultural services (TC) for each forest park.
Complementary datasets encompassed land use, digital elevation model (DEM), vegetation indices (e.g., NDVI), soil, meteorological, and socio-economic data. To ensure consistency, the analysis period was restricted to 2000–2020, the overlapping time span across all datasets. For example, meteorological records at daily/monthly resolution and tourism statistics at monthly resolution were aggregated to annual values over this period. The complete list of data sources, temporal spans, spatial resolutions, and processing steps is provided in Table 2 and Supplementary Table S2.

Table 2.
Data Sources and Processing.
All spatial data were uniformly transformed to the WGS_1984_UTM_Zone_48N projection and resampled to 30 m × 30 m resolution. Continuous rasters (e.g., NDVI, precipitation, temperature) were resampled using bilinear interpolation, while categorical rasters (e.g., land use types) used nearest-neighbor assignment. County-level tourism statistics were downscaled to forest-park polygons using a asymetric mapping approach with road-density and point-of-interest (POI) layers as weighting factors; an area-weighted alternative was also tested for robustness. Spatial overlay uncertainty was evaluated by applying ±30 m buffers to park boundaries and recomputing zonal summaries, which showed only minor differences in CES values.
In addition, Supplementary Tables S7–S10 provides a detailed specification of data inputs and model parameters for each ecosystem service (water retention, soil conservation, carbon storage, and tourism cultural services), as well as associated socio-ecological drivers. This ensures that the data sources and processing steps are transparent and reproducible. The weighting scheme used for CES construction is introduced in Section 2.3.2, with its robustness verified through sensitivity analysis.
2.3. Research Methods
2.3.1. Quantification of Ecosystem Services
Guizhou Province, situated in the upper reaches of both the Yangtze and Pearl River basins, functions as a vital ecological barrier for these major river systems. Its unique karst terrain is recognized as a biodiversity hotspot [44,45]. The province’s extensive forest cover plays a critical role in regulating global carbon cycles, maintaining water sources, and conserving soil and water. In light of these ecological attributes, this study focuses on quantifying four key ecosystem services (ESs): water retention (WR), soil conservation (SC), carbon sequestration (CS), and tourism-related cultural services (TC). These four ESs were selected because they represent the most critical regulating, supporting, and cultural services in karst forest parks, and align with international frameworks such as the Millennium Ecosystem Assessment and IPBES. This selection does not aim to cover all possible ESs, but to capture the most representative socio–ecological functions in karst forest parks, balancing ecological processes and human benefits. Together, they reflect both ecological processes (water, soil, and carbon dynamics) and human benefits (tourism and cultural value), thereby capturing the socio–ecological interactions specific to fragile karst landscapes.
For transparency and reproducibility, the detailed data inputs and parameter settings for each ecosystem service model (WR, SC, CS, and TC) are documented in Supplementary Tables S7–S10, which provide specific values, sources, and processing steps.
- (1)
- Water conservation
Water retention was assessed using the InVEST model’s water yield module, which estimates annual runoff based on the Budyko framework of water-energy balance. This approach incorporates average annual precipitation, effective soil depth, and plant-available water content. The core algorithm operates at the pixel level, integrating climatic and edaphic variables, along with actual evapotranspiration, to estimate runoff generation on a spatially explicit basis. The formula for annual water yield is as follows:
WYxj represents the water yield (mm) for land cover type j in grid x; AETxj represents the annual actual evapotranspiration (mm) for land cover type j in grid x; Px represents the annual precipitation (mm) in grid x; PETx represents the potential evapotranspiration (mm); ET represents the reference evapotranspiration, mainly reflecting the local climate conditions; Kc(x) is the plant (vegetation) coefficient, primarily determined by the vegetation type; w(x) is an empirical parameter; AWC(x) represents the plant-available water content (mm), determined by soil texture and effective root depth; Z denotes the seasonal constant characterizing the multi-year average precipitation [46]. In addition, the InVEST model incorporates a digital elevation model (DEM) as a fundamental input to derive slope, flow direction, and watershed boundaries. Through this process, terrain effects such as topographic shielding and runoff redistribution are implicitly accounted for in the spatial assessment of ecosystem service values.
Based on the estimated water yield (WY) results, the water source conservation can be further obtained through a correction model composed of the topographic index, soil saturated hydraulic conductivity, and flow velocity coefficient. The calculation formula is as follows:
In the formula, WR represents water source conservation (mm); Velocity represents flow velocity coefficient; TI represents topographic index, unitless; Ksat represents soil saturated hydraulic conductivity (mm/d); WYxj represents water yield; Darea represents the number of grid cells in the catchment area; Soildep represents soil depth (mm); Pslope represents percent slope.
- (2)
- Soil conservation
Soil conservation (SC) represents the portion of soil preserved within an ecosystem and is commonly defined as the difference between potential and actual soil erosion. In this study, we applied the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) model to estimate SC. The calculation is expressed as follows:
where SC represents soil conservation (t/ha), R represents rainfall erosivity factor [MJ·mm/(ha−1·h−1·a−1)], K represents soil erodibility factor [t·ha2·h/(ha−1·MJ−1·mm−1)], LS represents topographic factor (L represents slope length factor, S represents slope steepness factor), unitless, C represents vegetation cover and crop management factor, unitless, ranging from 0 to 1, and P represents the conservation practice factor, unitless, ranging from 0 to 1.
The calculation of the R factor was based on the method proposed by [47], and the K factor was calculated using the EPIC (erosion-productivity impact calculator) model. For the LS factor calculation, this study utilized an improved slope algorithm initially proposed by [48] and later modified by [49] to calculate the L factor. The calculation of the S factor was based on the empirical formula proposed by [47]. This study referred to previous research in assigning values to the C and P factors for different land use types [50].
- (3)
- Carbon storage
The carbon storage module of InVEST model is mainly based on land use and the corresponding carbon density of each land use type [51], and its calculation formula is as follows:
where Ctot represents the total carbon storage; Cabove indicates the carbon storage in above-ground biomass; Cbelow denotes the carbon storage in below-ground biomass; Csoil stands for the carbon storage in soil; and Cdead represents the carbon storage in dead organic matter.
- (4)
- Tourism and cultural services
Tourism cultural services refer to the tourism and cultural experiential value provided by the ecosystem to visitors [52,53]. This is primarily manifested by certain specific pixels within a certain range providing higher tourism services compared to others, and the factors influencing the tourism cultural services of a specific pixel mainly include two aspects: the accessibility (distance) and visibility of the scenic spots. Tourism cultural services decrease as the distance from the scenic spots increases, and increase with the visibility of the scenic spots. Assuming that the influence of the scenic spot accessibility on tourism revenue is consistent, quantitative analysis of tourism cultural services is conducted through buffer analysis and accessibility analysis using ArcGIS software (10.8.2), combined with field investigations (Forestry Bureau data) and remote sensing data. This leads to the calculation of the tourism cultural services of each forest park. For comparability across geomorphic zones, the pixel-level values within each park were aggregated, and the mean value was taken as the indicator of average tourism cultural services. To ensure comparability with other ecosystem service indicators (e.g., SC, CS, WR), all raw tourism-related variables were normalized to a 0–1 scale using min–max standardization, and the aggregated index is therefore dimensionless (unitless).
We also recognize that climatic variables may indirectly influence tourism cultural services through their impact on tourist flows, which may introduce a potential endogeneity issue between climate factors and tourism activities. While the available dataset does not permit the application of instrumental variable approaches (e.g., 2SLS), this limitation has been carefully considered when interpreting the results, and it is further discussed in the Section 4.
2.3.2. Comprehensive Ecosystem Services Index
The Comprehensive Ecosystem Services Index (CES) serves as a key metric to evaluate the integrated performance of multiple ecosystem service functions, including water conservation, soil retention, carbon sequestration, among others. To make ES indicators with different units and scales directly comparable, all raw values were first standardized using min–max normalization, which transformed them into a dimensionless score ranging from 0 to 1 (Equation (10)). This step ensured that variations in ES indicators (e.g., mm for water conservation, t/ha for carbon sequestration, mg/ha for soil conservation, and person-times for cultural services) were placed on the same scale [54].
For comparability across geomorphic zones, the pixel-level standardized values within each forest park were aggregated, and the mean value was used as the representative indicator of each ES at the park level. Subsequently, the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) was applied to assign relative weights to each ES according to expert judgment and insights from previous studies [55]. This procedure allowed the integration of heterogeneous ES indicators into a single comparable framework, ensuring that the CES reflects the relative contribution of each ES at the park level. To further capture the particularities of karst landscapes, the CES framework explicitly incorporated karst-specific environmental constraints, including bedrock exposure, soil thickness, and rocky desertification. These variables directly shape soil retention, water conservation, and vegetation growth in karst terrains, ensuring that the integrated index reflects not only general ES functions but also the distinctive hydro-ecological characteristics of karst regions. Finally, the CES was calculated as the weighted sum of the standardized ES scores (Equation (9)), representing the integrated performance of multiple ESs in each park.
where CES represents the Comprehensive Ecosystem Services Index; Wi is the weight of the i-th ecosystem service; Si is the standardized value of the i-th ecosystem service; and n is the number of types of ecosystem services.
This standardization procedure eliminated the unit-related differences among ES indicators and ensured that all variables contributed comparably to the CES calculation, thereby avoiding potential bias caused by heterogeneous measurement units. The normalization formula is expressed as follows:
where Si represents the normalized score of the i-th service; Ei denotes the value of the i-th ES; Max(Ei) and Min(Ei) are the maximum and minimum values of the i-th ES, respectively. This process ensured comparability across variables. The relative importance of individual ESs was determined using AHP, and the robustness of the weighting scheme was verified through sensitivity analysis under alternative weighting scenarios. The CES rankings remained largely consistent, demonstrating the reliability of the results (Supplementary Table S6). It should be noted that no Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA) framework was applied in this study; instead, the CES index was constructed by AHP weighting.
2.3.3. Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Model
Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM) is a causal analysis technique grounded in partial least squares theory. It employs iterative estimation by integrating principal component analysis and multiple regression, making it suitable for modeling complex relationships between variables [56]. PLS-SEM typically consists of two components: the measurement (outer) model and the structural (inner) model. The structural model, which evaluates the relationships among endogenous latent variables, is expressed as:
where represents the vector of all latent variables, and represents the path coefficients that can test the relationships between adjacent and non-adjacent variables [57]. The results of this test can demonstrate the correlation and strength of correlation between explanatory variables and response variables. The measurement model is composed of manifest variables and latent variables in an explanatory model [58], represented by the following formula:
To ensure the robustness of the PLS-SEM results, we additionally evaluated construct reliability, convergent validity, discriminant validity, and collinearity, and verified the stability of path estimates through bootstrapping. Detailed results are reported in Supplementary Tables S3–S5. Collinearity was assessed using VIF at both indicator and construct levels, and all values were below 3.0 (Supplementary Table S4), confirming no multicollinearity Given the relatively small sample size (n = 97) and potential non-normal distribution of the data, PLS-SEM was selected instead of CB-SEM, as it is more appropriate for prediction-oriented and exploratory analyses under such conditions. The significance of path coefficients was tested using a bootstrapping procedure with 5000 resamples, and detailed results are reported in Supplementary Table S5.
Formulas (12) and (13) represent exogenous and endogenous indicators, respectively. and are measurement errors, represents the relationship between manifest variables and latent variables; the structural model (or internal model) is a path diagram that reflects the relationships between latent variable effects [59]. This study takes 97 forest parks in Guizhou Province as an example, with vegetation factors, karst surface characteristic factors, climate factors, and tourism activity factors as latent variables, considering a total of 19 manifest variables including NDVI, altitude, slope, rock exposure, rainfall, temperature, tourism revenue, and tourist arrivals, detailed influencing factors are shown in Table 3. The selection of the 19 manifest variables (Table 3) was based on the socio–ecological systems (SES) framework, which emphasizes the coupled interactions between ecological subsystems and human activities [39]. Vegetation (e.g., forest coverage rate, NDVI) and climatic variables (e.g., precipitation, temperature, humidity) represent the ecological processes that regulate carbon, water, and soil dynamics. Karst surface features (e.g., rock exposure, soil depth, surface roughness) capture the geomorphological constraints unique to fragile karst environments. Tourism activity indicators (e.g., ATA, ATI, NLI, RND) represent the human subsystem, reflecting accessibility, intensity of use, and cultural service demand. Together, these indicators constitute a comprehensive set of socio–ecological drivers that jointly determine the availability and quality of ecosystem services in karst forest parks.

Table 3.
Selection table of influencing factors.
2.3.4. Pearson Correlation Analysis
To further examine the pairwise linear relationships between individual ecosystem services (ESs) and potential socio-ecological drivers, we applied Pearson correlation analysis. This method quantifies the strength and direction of association between two continuous variables and [60]. The Pearson correlation coefficient r is defined as:
where and are the observed values of the two variables, and represent their sample means, and nnn is the number of paired observations. The coefficient rrr ranges from −1 to +1, with values close to +1 or −1 indicating strong positive or negative linear relationships, respectively, while values near 0 suggest little or no linear association.
In this study, correlation coefficients were calculated to explore the direct associations among ecosystem service indicators (WR, SC, C, TC) and the 19 manifest variables representing vegetation, landform, climate, and tourism activities. Statistical significance was assessed at the 95% confidence level (p < 0.05). All correlation analyses were conducted using SPSS Statistics 26.0. In this study, tourist arrivals were used as the primary proxy for tourism intensity due to data availability [61].
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Differentiation Characteristics of FPES in Different Geomorphological Areas
Differences exist in the ecosystem services of forest parks in different geomorphic regions in terms of SC, C, WR, and TC, as shown in Figure 2. In terms of SC supply, non-karst forest parks have the highest average SC value of 16.54 mg·ha−1, while the karst gorge region has the lowest SC value of 7.62 mg·ha−1, with a difference of 8.92 mg·ha−1 between the two. Regarding C supply, the six geomorphic regions are relatively similar, with the highest carbon storage in karst basin forest parks at 257.68 t·ha−1, while the karst plateau has a relatively lower carbon storage of 238.03 t·ha−1. Non-karst area and karst gorge have the highest and lowest WR values, respectively, with WR value of 67.71mm for non-karst forest parks and 41.48mm for karst gorge region. As for TC value, the ranking order of forest parks in different geomorphic regions in the karst gorge area is as follows: karst gorge > non-karst area > peak cluster depression > karst plateau > karst trough valley > karst basin. From the evaluation of the comprehensive CES index, the ranking order of forest parks in different karst geomorphic regions from high to low CES is as follows: non-karst area > peak cluster depression > karst trough valley > karst basin > karst gorge > karst plateau (Figure 3). Sensitivity analysis under alternative weighting schemes confirmed that the CES rankings remained largely consistent, indicating the robustness of the results (Supplementary Table S6).
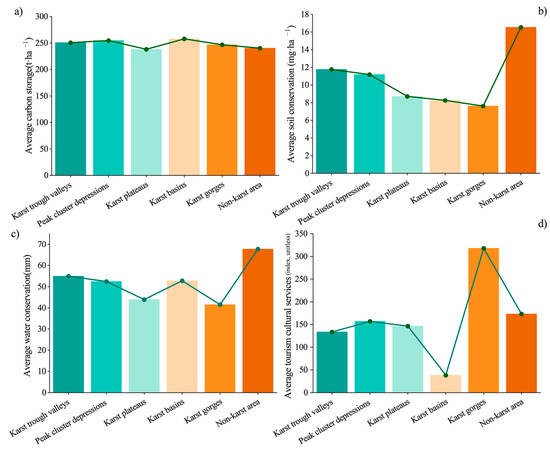
Figure 2.
Ecosystem services of forest parks in different landform areas. (a) SC; (b) C; (c) WR; (d) TC.
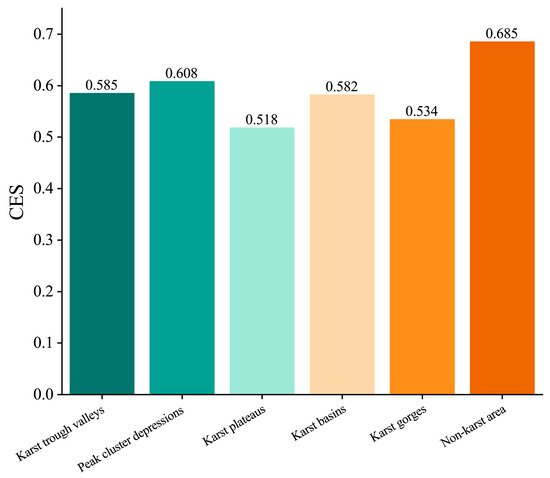
Figure 3.
Comprehensive ecosystem services of forest parks in different landform areas.
These differences are closely related to geomorphological and ecological conditions. Non-karst regions generally have deeper soils and higher vegetation coverage, supporting stronger water and soil conservation, while karst plateaus and canyons suffer from shallow soil layers, high rock exposure, and intense human disturbance, which jointly constrain CES performance. This demonstrates that the spatial heterogeneity of CES is shaped by differences in soil depth, vegetation cover, rock exposure, and human disturbance across geomorphological zones.
3.2. Analysis of the Correlation Between Driving Factors and FPES
The factors influencing different ESs vary. This study investigated the correlation between different ESs in forest parks and potential influencing factors based on Pearson correlation analysis (Figure 4). Correlation analysis showed that NDVI, tourist visits, slope, surface roughness, road density, soil thickness, and nighttime light index exhibited strong statistical associations with carbon sequestration, with correlation coefficients ranging from 0.51 to 0.91. Among them, NDVI and tourist visits showed the highest correlation coefficients (0.91 and −0.83, respectively), which are 0.91 and −0.83, respectively. This indicates that NDVI is positively related to carbon sequestration capacity, while higher tourist visits are associated with reduced carbon storage. However, these correlations should not be interpreted as direct causal effects; rather, they reflect potential associations that may be influenced by multiple interacting factors.
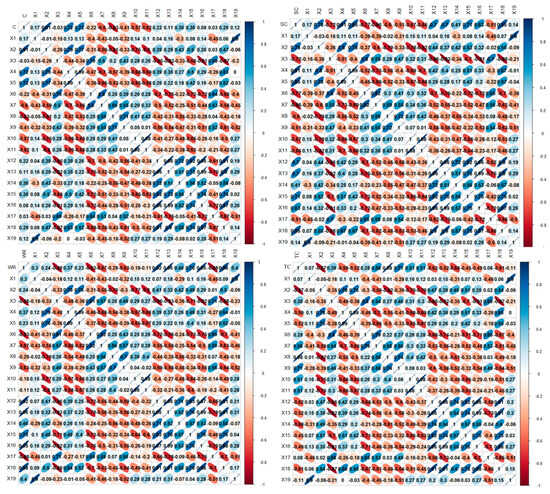
Figure 4.
The correlation between different ecosystem services and influencing factors.
The soil conservation function of forest parks is significantly correlated with NDVI, topographic factors, and climatic factors, with correlation coefficients as low as 0.7. However, the correlation coefficient with tourist activity factors ranges from 0.51 to 0.67, showing a negative correlation, indicating that tourist activity factors have a counteractive effect on the soil conservation capacity of forest parks. The most influential factors affecting soil conservation function include slope (0.91), soil thickness (−0.86), surface roughness (0.85), multi-year average temperature (0.85), NDVI (0.78), and rock exposure (−0.77). Thus, it can be observed that soil conservation function is highly correlated with topographic factors.
The correlation of water resource conservation (WR) with various influencing factors ranks from largest to smallest as follows: multi-year average spring rainfall (0.96), multi-year average winter rainfall (0.95), multi-year average rainfall (0.92), multi-year average temperature (0.88), multi-year average evapotranspiration (−0.88), altitude (−0.88), rock exposure (−0.83), multi-year average autumn rainfall (0.75). We found that WR is positively correlated with multi-year average rainfall, but negatively correlated with evapotranspiration, indicating that the amount of rainfall determines the ability of forest parks to store water for WR, while higher evapotranspiration rates will affect the park’s water storage capacity.
The factors influencing tourism and cultural services in forest parks are primarily the number of tourist visits, with a correlation coefficient of 0.98, indicating that the more tourist visits, the better the tourism and cultural services in the park can be provided. Next is NDVI (−0.87), which is negatively correlated with tourism and cultural services, reflecting that the enhancement of tourism and cultural services will have a counteractive effect on the vegetation in the park. Other factors related to tourism and cultural services include tourism revenue (0.71), multi-year average summer rainfall (−0.68), and multi-year average rainfall (−0.62). The magnitude of rainfall will counteract tourism and cultural service, affecting this service. Taken together, these correlations provide the mechanistic basis for the spatial heterogeneity observed in CES values across geomorphological regions, linking ecological processes (e.g., vegetation growth, soil conservation) and human activities (e.g., tourism pressure) to differences in service supply.
3.3. Analysis of the Driving Mechanisms of CES Differentiation
The PLS-SEM model comprehensively explains the contributions of climate-vegetation-karst surface characteristics and tourism activities to the comprehensive ecosystem services of forest parks (Figure 5). The four paths explain 72.1%, 73.3%, 72.2%, and 73.6% of the variance, respectively, meaning that the climate factors, tourism activity factors, vegetation factors, and karst surface characteristics together explain 72.1–73.6% of the CES variance. The model results show that the total effects of climate-vegetation-karst surface characteristics and tourism activities on CES are climate (0.550–0.568), karst surface characteristics (0.295–0.321), vegetation (0.280–0.344), and tourism activities (0.096–0.153). Among them, climate is the main factor affecting the CES of forest parks. Notably, in models 2, 3, and 4, karst surface characteristics have a positive impact on vegetation, while in model 1, the path coefficient of karst surface characteristics on vegetation changed to a negative impact (−0.440), which is due to the indirect negative impact of climate on vegetation through karst surface characteristics. Additionally, tourism activities have a positive impact on the CES of forest parks, with path coefficients of 0.153 and 0.100, 0.096, and 0.147, respectively.
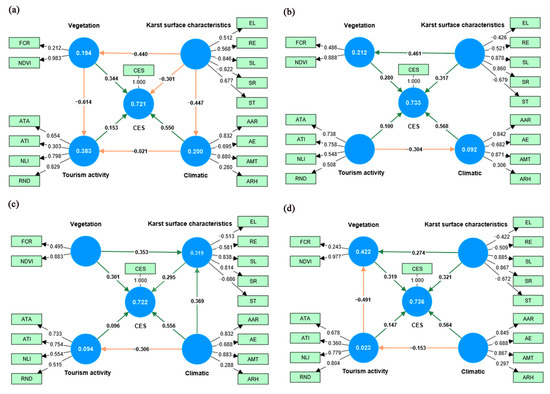
Figure 5.
PLS-SEM model analysis diagrams (a) Model 1 (b) Model 2 (c) Model 3 (d) Model 4.
The indirect effects of the PLS-SEM model are shown in Figure 5 In Model 1, in addition to the four direct pathways affecting the CES of the forest park, among others, climate negatively affects tourism activities through indirect effects on karst surface characteristics as well as vegetation; karst surface characteristics have a positive indirect impact on CES through their influence on vegetation. Model 2 indicates that climate factors indirectly negatively impact CES through their influence on tourism activity factors. Model 3 demonstrates that vegetation factors have a positive indirect impact on CES through their influence on karst surface feature factors, while model 4 shows that climate factors indirectly negatively impact vegetation factors through their influence on tourism activity factors.
In addition, robustness checks confirmed the reliability and validity of the PLS-SEM results. Cronbach’s α, composite reliability (CR), and average variance extracted (AVE) indicated adequate construct reliability and convergent validity (Supplementary Table S3). Discriminant validity was supported by the Fornell–Larcker criterion and HTMT ratios, while all indicator- and construct-level VIFs were below 3.0, suggesting no multicollinearity issue (Supplementary Table S4). Moreover, bootstrapping with 5000 resamples further verified the robustness of the estimated path coefficients (Supplementary Table S5). Climatic variables exhibited a relatively strong association with cultural ecosystem services, suggesting that they play an important—though potentially indirect—role, partly through their influence on tourism flows.
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Karst Landforms on FPESs
Geomorphological structures play a key role in shaping macro-scale ecological patterns and regulating regional erosion dynamics, while also governing the spatial distribution of water and thermal resources at meso- and local scales [31]. There are differences in the degree of karst development, the degree of rock desertification and human activities in different karst geomorphological zones, which lead to differences in vegetation, soil and other conditions, resulting in different ecosystem service functions in different karst geomorphological zones [38]. The results showed that SC and WR were higher in the non-karst area than in other geomorphological zones, while SC and WR in the karst canyon area were the lowest among all geomorphological zones, but TC services were the highest among all geomorphological zones. It indicates that the karst canyon area’s is affected by human activities and reacts sharply. The fragile ecological problems in karst areas are mainly rocky desertification, which is the loss of surface soil, bedrock exposure and ecological degradation caused by soil erosion [39], so soil conservation and water retention services are indispensable ecological cores in the study of karst ecosystems. Meanwhile, soil conservation supports the continuous supply of water and nutrients in the soil, which is an inevitable requirement for vegetation growth and carbon sequestration [21]. The non-karst areas do not have serious rock desertification problems, and at the same time have abundant vegetation resources, so the soil conservation and water conservation services are better compared to other karst geomorphological areas. Karst canyon area is a geomorphological area formed by the dissolution and erosion of surface water along the rock fissures, and the dichotomous leakage environment above and below the ground in karst is significantly manifested in the canyon area [38]. Facing serious soil erosion problems and intense human activities in geomorphological zones can lead to the degradation and decline of SC services and WR services [36]. In canyon environments, tourism development, road construction, and agricultural expansion often intensify vegetation loss and soil disturbance, which further accelerates surface erosion and subsurface leakage. These habitats typically respond with reduced vegetation resilience, weakened soil–water retention, and heightened sensitivity to external climatic fluctuations [8,62]. In terms of carbon sink services in different geomorphological zones, we found that the karst plateau zone has the lowest carbon sink services, and we can see through the study area map and Table 1 that the karst plateau zone has the highest percentage of area (31.36%) and the number of forest parks among all the geomorphological zones, and this geomorphological zone is located in the urban belt of Qianzhong, and the development of the socio-economy is better than that of other geomorphological zones. In addition, the lower TC services in this geomorphological area also indicate the high human activities in the karst plateau area. The supply of nutrients supported by regional soils is impaired by karst development and tourism activities (anthropogenic activities), and the carbon sequestration function of forest vegetation decreases as a result [6,63].
Beyond these spatial patterns, it is also necessary to clarify the hydrological mechanisms through which karst landforms shape water retention services. In karst terrains, precipitation rapidly infiltrates through fissures, sinkholes, and conduits, leading to weak surface runoff but strong subsurface flow. The discontinuous and shallow soil layers constrain water storage capacity, while the high connectivity of underground drainage accelerates subsurface discharge [64]. Vegetation modulates water regulation mainly through canopy interception and root-mediated infiltration, but its role is limited in areas with extensive rock exposure [65]. As a result, water conservation in karst areas depends more directly on precipitation and subsurface hydrological pathways than in non-karst systems. Furthermore, severe rocky desertification exacerbates the reduction in soil and vegetation cover, diminishing infiltration–retention processes and accelerating hydrological losses. These mechanisms explain why climatic factors emerge as the dominant drivers of water-related ecosystem services in our results, whereas vegetation plays a comparatively weaker role. These hydrological and ecological mechanisms highlight the necessity of incorporating karst-specific constraints into the CES framework [40].
Furthermore, it is important to emphasize that the CES framework employed in this study explicitly incorporated karst-specific constraints, such as bedrock exposure, soil thickness, and rocky desertification. These variables are critical determinants of ecosystem processes in karst terrains, directly shaping soil retention, water conservation, and vegetation growth, while also reflecting the distinct hydro-ecological vulnerabilities of karst systems [66]. As a result, the CES values presented here not only capture general ecosystem service functions but also embody the particular ecological constraints of karst landscapes, thereby providing a more accurate and context-specific evaluation of forest park ecosystem services in Guizhou Province [67].
4.2. Influence of Climate-Vegetation-Karst Surface Characteristics-Tourism Activity Factors on Ecosystem Services in Forest Parks
This study incorporated 19 variables across four dimensions—climate, vegetation, karst surface features, and tourism—to explore the underlying drivers of ecosystem service variation in Guizhou’s forest parks. Results from the PLS-SEM model indicated that these factors collectively accounted for 72.1% to 73.6% of the variance in cultural ecosystem services. The contributions of the total effect of CES in forest parks were climate factor (0.550–0.568), karst surface feature factor (0.295–0.321), vegetation factor (0.280–0.344), and tourism activity factor (0.096–0.153). There is a complex relationship between climate-vegetation-karst surface characteristics-tourism activities, surface features (elevation, slope and soil thickness) are closely related to local climate, and the interaction between the two can have a great influence on vegetation [37,68], while the combined effect of climate change and human activities is the cause of vegetation changes, but climate factors are dominant [69]. Thus, climatic factors have been widely recognized as the main factors affecting forests and ESs [1].
The distribution of forests in the Southwest Karst Region is generally at higher elevations and steeper slopes [31]. Topographic and geomorphological features strongly influence local climatic conditions, such as temperature and precipitation patterns, which in turn affect FPES. Among these factors, elevation shows a particularly significant effect on soil conservation (SC) and water regulation (WR), with a negative correlation, i.e., the service function of SC and WR of FPES decreases with increasing elevation. This is because at higher elevations, the density of the forest tree-irrigation layer is lower, and the water generated from the decay of dead leaves and branches in the forest understory decreases, and the soil and water conservation function of the forest decreases, resulting in a decline in the SC and WR services of forest parks [70]; topographic features are closely related to the climate, whereas rocky outcrops and the thickness of the soil layer limit the restoration of the vegetation cover [26]. Therefore, rock exposure in karst areas has a more significant effect on SC and WR in a negative direction, while soil thickness is one of the main effects of SC and WR, which is consistent with the positive correlation between the two. Therefore, climatic and topographic factors control the supply and maintenance of major ecosystem services of forest parks in karst areas.
In addition, we found that tourism activity factors did not have a significant effect on the CES of the forest parks, with an explanatory degree of only 0.096–0.153. Through correlation analysis, the factors related to the CES of tourism included tourist arrivals (0.98), NDVI (−0.87), tourism income (0.71), multi-year average summer precipitation (−0.68), and multi-year average precipitation (−0.62). From the results of the study, on the one hand, summer is a concentrated season for people to enter forest parks for recreation and holiday, and the NDVI value of the forest is one of the main references that people use as a way to conduct tourism, as confirmed by the studies of [71,72]. Tourism activities reflect to some extent the disturbance of ecosystems by human activities, which often have negative impacts on ES [73]. Therefore, tourism and cultural services are negatively correlated with NDVI; on the other hand, the influence of tourism activity factors on FPES is not obvious due to the relatively backward socio-economic development of Guizhou Province, which has a relatively low degree of population aggregation and a low level of economic development compared with rapidly urbanizing regions. However, this situation may change as tourism infrastructure and economic development improve, potentially amplifying the role of tourism activities in shaping FPES. It should be emphasized that the observed correlation between tourist arrivals and carbon sequestration does not imply a direct causal relationship. Rather, this pattern may reflect indirect ecological pressures consistent with international findings on tourism–ecosystem interactions [61,74]. Consequently, while tourism can influence cultural ecosystem services directly, the dominant drivers of FPES in this region remain climatic and geomorphological factors.
4.3. Strategies and Policy Framework for Improving the Ecosystem Service Function of Forest Parks
Firstly, in line with the principle of ecological priority, restoration-oriented and nature-based measures can be adopted to optimize vegetation structure to improve the regional microclimate, promote the natural succession of forest communities, and improve the stability of forest ecosystem services. These measures do not replace natural forests; rather, they encourage native-species regeneration, reduce monocultures, and foster community diversity, thereby strengthening ecosystem resilience while maintaining the integrity of natural capital. Our results show that both vegetation and climate positively affect CES in forest parks, with climate being the dominant factor. Since climate exerts indirect effects on CES via vegetation, we recommend promoting vegetation restoration and diversification—e.g., assisting natural regeneration, enrichment planting with site-adapted native species, and low-intensity thinning of over-dense stands—to increase canopy cover, enhance evapotranspiration, moderate temperature, and raise humidity, thereby improving the regional microclimate. Such microclimate improvements further promote vegetation growth and positive ecological succession [69]. Specifically, in parks dominated by even-aged monoculture stands (e.g., pure conifer plantations), phased, low-intensity measures—such as selective thinning, small canopy-gap creation, and underplanting/enrichment with site-adapted native broadleaf species—can increase structural diversity and develop multi-layered canopies, thereby strengthening resistance to external stressors (e.g., climate extremes, pests, and diseases) and enhancing interactions among species and vegetation strata. Secondly, site-specific native trees, shrubs, and herbs should be used to increase ground cover, reduce bare soil, and raise soil moisture, thereby building a multi-layered, multifunctional forest ecosystem that improves the local microclimate.
To address the inherent trade-offs and potential synergies among ecosystem services, it is essential to implement coordinated governance strategies. Establishing ecological compensation frameworks can facilitate integrated development across multiple service domains. For instance, enhancing forest coverage through afforestation, curbing indiscriminate logging, and restoring degraded lands can collectively reinforce water and soil conservation capacities. These practices help to stabilize the ecological structure by increasing root density and vegetation cover, thereby fostering a resilient pattern of soil–water interactions [20]. Empirical findings suggest that the effectiveness of soil conservation (SC) within forest parks is closely associated with karst terrain attributes such as elevation, slope gradient, surface rock exposure, and soil depth. Consequently, employing ecological engineering practices like terracing and vegetative berms on steep, rocky slopes—supported by conservation and restoration measures—has proven beneficial in promoting the joint improvement of soil and water retention capacities.
Ecotourism, a core function of forest parks, contributes not only to recreational services but also to the enhancement of ecosystem functions. While emphasizing ecosystem service improvement, it is important to incorporate the aesthetic and ecological value of forest vegetation in tourism planning [22]. Although trade-offs may exist between tourism-related cultural services and other ecosystem functions, research indicates that tourism activities generally exert a positive influence on the cultural ecosystem services of forest parks. To further leverage these benefits, the promotion of ecotourism should adhere to ecological prioritization. Vegetation restoration efforts should emphasize landscape enhancement by fostering visually appealing and ecologically resilient forest structures. This approach helps improve forest health, visual diversity, and multifunctionality, ultimately maximizing ecosystem service delivery. It also supports the integration of ecological and economic benefits by offering visitors access to rich and scenic environments [21]. In addition, sustainable tourism models—such as mixed-species forest trails, wildlife-based recreation, and biodiversity education—can be developed based on local ecological characteristics. By strategically allocating tourism infrastructure across diverse forest types, the long-term stability of ecosystem services can be strengthened alongside improvements in both tourism quality and cultural service value.
Finally, to ensure that these scientific strategies can be effectively translated into practice, it is necessary to construct a comprehensive policy action framework. This framework should emphasize multi-level governance coordination by establishing cross-sectoral mechanisms linking forestry, tourism, and environmental protection departments to achieve integrated planning and implementation. It should also incorporate financial and incentive mechanisms, such as ecological compensation schemes, targeted subsidies, and green financing tools, to encourage local communities and park managers to participate in ecosystem restoration and sustainable tourism. In particular, ecological compensation requires clear standards for benefit calculation, diversified funding sources (e.g., fiscal transfers, ecological protection funds, and market-based green finance), and participatory consultation mechanisms to ensure fairness, transparency, and long-term stability. In addition, monitoring and adaptive management systems should be developed, including long-term ecological monitoring platforms and policy evaluation processes, to enable dynamic adjustment of strategies according to ecological feedback and socio-economic outcomes. Such a policy framework will bridge the gap between ecological strategies and actionable governance, providing decision-makers with a more operable pathway to strengthen the ecological and socio-economic functions of karst forest parks.
4.4. Limitations and Prospects
This study explored the differences in ecosystem services across geomorphological zones in Guizhou’s karst forest parks and quantified the impacts of climate, vegetation, karst surface characteristics, and tourism activities. The findings provide an important reference for sustainable development in karst mountain forestscapes. Nevertheless, several limitations should be acknowledged. First, the selection of ecosystem services and management strategies was constrained by data availability and methodological scope. Services such as biodiversity conservation, timber use, and habitat quality were not included. Moreover, while vegetation structure adjustment was highlighted as a strategy, the study did not provide a detailed list of suitable tree species or an integrated eco-economic evaluation model. These omissions may underestimate ecosystem multifunctionality and reduce the practical operability of the proposed management recommendations. Second, while the analysis incorporated major natural and anthropogenic drivers, it did not explicitly account for ecological restoration projects such as rocky desertification control or relevant policy interventions. These management practices can significantly shape ecosystem functions and may have introduced unobserved effects. Third, the study did not fully examine the trade-offs and synergies among different services, or the cascading impacts of interactions between service pairs on regional socio-ecological resilience. Fourth, potential endogeneity between climate and tourism may bias the estimated effect of climate on cultural services, as climate can indirectly shape tourism demand. Given data limitations, advanced causal inference methods could not be applied here, so results should be interpreted cautiously. Future research should employ longitudinal tourism datasets or causal approaches to better distinguish direct and indirect effects. Future work should therefore adopt a multi-scale and multi-dimensional framework that integrates ecological, socio-economic, and governance factors. Incorporating biodiversity indicators, land use history, and community-based management practices will provide a more comprehensive understanding of service dynamics. Such efforts will help bridge ecological modeling with practical strategies for the regenerative management of mountain forestscapes, supporting long-term sustainability under climate and human pressures.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we quantified the driving effects of climate, vegetation, karst surface characteristics, and tourism activities on the comprehensive ecosystem services (CES) of forest parks in Guizhou Province and further clarified the differences among geomorphological zones. The results showed pronounced spatial heterogeneity: CES values ranked as non-karst zone (0.685) > peaked depression > karst trough > karst basin > karst canyon (0.534) > karst plateau (0.518). Overall, the observed spatial heterogeneity can be quantitatively explained by differences in soil depth, vegetation cover, rock exposure, and tourism intensity among geomorphological zones, rather than being solely a generic attribute of karst terrain. Notably, the CES of karst plateau and canyon forest parks was significantly lower than that of other geomorphological types, while non-karst areas performed best overall. Correlation analysis between forest park ecosystem services (FPES) and 19 influencing factors revealed distinct drivers for different service types. Carbon storage was mainly regulated by normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI, r = 0.91) and tourist visits (r = −0.83). Soil conservation showed significant associations with NDVI, karst surface characteristics, and climatic variables (minimum r = 0.70). Water regulation was strongly determined by multi-year average spring precipitation (r = 0.96). Cultural services were most sensitive to tourism intensity, with a correlation as high as 0.98. Together, climate, vegetation, karst surface exposure, and tourism factors explained 72.1–73.6% of the total variance in CES. Among them, climate made the largest contribution (55–56.8%), while tourism activities accounted for only 9.6–15.3%, indicating that the development of tourism and cultural services in Guizhou’s forest parks remains limited. Building upon these findings, this research provides strategic guidance to enhance ecosystem services in forest parks and serves as a scientific basis for optimizing landscape planning and adaptive management in karst regions. These conclusions are most relevant to karst forest parks with similar geomorphological and ecological contexts, and their extrapolation to ecosystems with different rocky desertification intensities or vegetation structures should be made with caution. More broadly, the results contribute to fostering integrated ecological and economic sustainability and highlight pathways for the regenerative governance of fragile mountain forestscapes.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/su17188174/s1, Table S1: List of forest parks in Guizhou Province; Table S1.2: Representative Examples of Forest Parks in Each Geomorphological Zones; Note S1.1: Ecological and Tourism Characteristics of Different Geomorphological Zones; Table S2: Data sources, temporal coverage, harmonization, and processing steps; Table S3: Construct reliability and convergent validity; Table S4: Discriminant validity and collinearity; Table S5: Bootstrapping results (a–d, 5000 resamples); Table S6: Sensitivity analysis of CES under different weighting schemes; Table S7: Carbon pool parameters and sources; Table S8: Biophysical parameters for water yield model; Table S9: C and P factors for RUSLE model; Table S10: Data sources, resolutions, and processing methods for socio-ecological indicators.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.L.; Methodology, R.L. and M.C.; Software, Z.L.; Validation, Z.L. and M.C.; Formal analysis, R.L.; Investigation, R.L. and M.C.; Data curation, Z.L.; Writing—original draft, M.C.; Writing—review & editing, R.L.; Visualization, Z.L., R.L. and M.C.; Supervision, R.L.; Project administration, R.L.; Funding acquisition, R.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Guizhou Forestry Bureau (QianLinKeHe[2024]19), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 32360421; No. 32060372), and the Guizhou Province Department of Science and Technology (QianKeHe JiChu-ZK[2023]Key029).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article and Supplementary Materials.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Costanza, R.; d’Arge, R.; de Groot, R.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; O’Neill, R.V.; Paruelo, J.; et al. The Value of the World’s Ecosystem Services and Natural Capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Li, R.; Shu, D.; Zhao, L.; Chen, M.; Jing, J. Effects of Rainfall and Rocky Desertification on Soil Erosion in Karst Area of Southwest China. J. Mt. Sci. 2022, 19, 3118–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wei, X. Deforestation, Forestation, and Water Supply a Systematic Approach Helps to Illuminate the Complex Forestwater Nexus. Science 2021, 371, 990–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, J. Spatial Heterogeneity of Ecosystem Services in Response to Landscape Patterns under the Grain for Green Program: A Case-study in Kaihua County, China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2022, 33, 1901–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Fu, B.; Lu, N.; Zeng, Y.; Wu, B. How Ecological Restoration Alters Ecosystem Services: An Analysis of Carbon Sequestration in China’s Loess Plateau. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Z.; Zheng, H.; Xiao, Y.; Polasky, S.; Liu, J.; Xu, W.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, Y.; Rao, E.; et al. Improvements in Ecosystem Services from Investments in Natural Capital. Science 2016, 352, 1455–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidl, R.; Albrich, K.; Erb, K.; Formayer, H.; Leidinger, D.; Leitinger, G.; Tappeiner, U.; Tasser, E.; Rammer, W. What Drives the Future Supply of Regulating Ecosystem Services in a Mountain Forest Landscape? For. Ecol. Manag. 2019, 445, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndayizeye, G.; Imani, G.; Nkengurutse, J.; Irampagarikiye, R.; Ndihokubwayo, N.; Niyongabo, F.; Cuni-Sanchez, A. Ecosystem Services from Mountain Forests: Local Communities’ Views in Kibira National Park, Burundi. Ecosyst. Serv. 2020, 45, 101171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgroi, F.; Modica, F. Digital Technologies for the Development of Sustainable Tourism in Mountain Areas. Smart Agric. Technol. 2024, 8, 100475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shams, A. Tourism Flow and the Consumption of Aesthetic Landscape Values in High-Elevation Mountain Areas in the Alps: A Cartographic and Spatio-Market Methodology. J. Outdoor Recreat. Tour. 2025, 51, 100911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, K.; Liu, H.; Zhang, C.; Yue, Y.; Qi, X. Effect of Ecological Engineering Projects on Ecosystem Services in a Karst Region: A Case Study of Northwest Guangxi, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 183, 831–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telbisz, T.; Imecs, Z.; Máthé, A.; Mari, L. Empirical Investigation of the Motivation and Perception of Tourists Visiting the Apuseni Nature Park (Romania) and the Relationship of Tourism and Natural Resources. Sustainability 2023, 15, 4181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canedoli, C.; Ferrè, C.; Abu El Khair, D.; Comolli, R.; Liga, C.; Mazzucchelli, F.; Proietto, A.; Rota, N.; Colombo, G.; Bassano, B.; et al. Evaluation of Ecosystem Services in a Protected Mountain Area: Soil Organic Carbon Stock and Biodiversity in Alpine Forests and Grasslands. Ecosyst. Serv. 2020, 44, 101135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, P.; Zhao, X.; Pu, J.; Huang, P.; Shi, X.; Gu, Z. Study on the Evolution Mechanism of Ecosystem Services in Karst Mountainous Areas from the Perspective of Humanities. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 13628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, G.; Wang, K.; Wang, F.; Dong, Y. Analysis of the Tourism-Economy-Ecology Coupling Coordination and High-Quality Development Path in Karst Guizhou Province, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Yang, A.; Jiang, L.; Lawson, G.; Lei, W. Ecological Recreation Across the Jinma Mountain Region: A Comprehensive Evaluation of Suburban Mountain Greenway Networks. Land 2025, 14, 1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Chen, L.; Luo, W.; Jim, C.Y. Species Diversity and Distribution Pattern of Venerable Trees in Tropical Jianfengling National Forest Park (Hainan, China). J. Nat. Conserv. 2024, 77, 126542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhao, B.; Peng, S.; Li, K.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, J. Effects of Cultural Landscape Service Features in Nat.ional Forest Parks on Visitors’ Sentiments: A Nationwide Social Media-Based Analysis in China. Ecosyst. Serv. 2024, 67, 101614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, H.R.; Buhyoff, G.J. The Scenic Beauty Temporal Distribution Method: An Attempt to Make Scenic Beauty Assessments Compatible with Forest Planning Efforts. For. Sci. 1986, 32, 271–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafond, V.; Cordonnier, T.; Mao, Z.; Courbaud, B. Trade-Offs and Synergies between Ecosystem Services in Uneven-Aged Mountain Forests: Evidences Using Pareto Fronts. Eur. J. For. Res. 2017, 136, 997–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, A.T.H.; Chow, A.S.Y.; Cheung, L.T.O.; Liu, S. Self-Determined Travel Motivation and Environmentally Responsible Behaviour of Chinese Visitors to National Forest Protected Areas in South China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2018, 16, e00480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedmák, R.; Scheer, Ľ.; Kúdela, P.; Vencúrik, J.; Modranský, J.; Daniš, D.; Fabrika, M. Multicriteria Optimization of Ecosystem Services as a Base for Participative Forest Management Promoting Recreation near Tourist Centers and Cities. Trees For. People 2025, 21, 100905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Wang, Y.; Lin, Z.; Li, S. National-Scale Connectivity Analysis and Construction of Forest Networks Based on Graph Theory: A Case Study of China. Ecol. Eng. 2025, 216, 107639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abate, D.; Botequim, B.; Marques, S.; Lagoa, C.; Hernández, J.G.; Hengeveld, G.; Hoogstra-Klein, M.; Borges, J.G. Recreational and Aesthetic Values of Forest Landscapes (RAFL): Quantifying Management Impacts and Trade-Offs with Provisioning and Regulatory Ecosystem Services. For. Ecosyst. 2025, 13, 100318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loft, L.; Schleyer, C.; Klingler, M.; Kister, J.; Zoll, F.; Stegmaier, P.; Aukes, E.; Sorge, S.; Mann, C. The Development of Governance Innovations for the Sustainable Provision of Forest Ecosystem Services in Europe: A Comparative Analysis of Four Pilot Innovation Processes. Ecosyst. Serv. 2022, 58, 101481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Gao, J.; He, M.; Jing, J.; Xiong, L.; Chen, M.; Zhao, L. Effect of Rock Exposure on Runoff and Sediment on Karst Slopes under Erosive Rainfall Conditions. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2023, 50, 101525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Yu, C.; Feng, Z.; Zhao, H.; Wu, K.; Ma, X. Spatial Differentiation Characteristics and Driving Factors of Agricultural Eco-Efficiency in Chinese Provinces from the Perspective of Ecosystem Services. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 288, 125466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.H.; Ai, L.; Fang, N.F.; Zhu, H.D. Modeling the Impacts of Integrated Small Watershed Management on Soil Erosion and Sediment Delivery: A Case Study in the Three Gorges Area, China. J. Hydrol. 2012, 438–439, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Wang, S.; Bai, X.; Luo, G.; Xu, Y. Trade-Offs among Ecosystem Services in a Typical Karst Watershed, SW China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566–567, 1297–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Ma, S.; Wang, L.-J.; Lin, C. Impacts of Future Climate Change and Different Management Scenarios on Water-Related Ecosystem Services: A Case Study in the Jianghuai Ecological Economic Zone, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 127, 107732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Tao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, J.; Bai, X. Use of Interpretable Machine Learning for Understanding Ecosystem Service Trade-Offs and Their Driving Mechanisms in Karst Peak-Cluster Depression Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Theau, J. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Water-Related Ecosystem Services under Ecological Restoration Scenarios: A Case Study in Northern Shaanxi, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 720, 137477.1–137477.13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Liu, Y.; Wu, J.; Lv, H.; Hu, X. Linking Ecosystem Services and Landscape Patterns to Assess Urban Ecosystem Health: A Case Study in Shenzhen City, China. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 143, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirmohammadi, B.; Malekian, A.; Salajegheh, A.; Taheri, B.; Azarnivand, H.; Malek, Z.; Verburg, P.H. Impacts of Future Climate and Land Use Change on Water Yield in a Semiarid Basin in Iran. Land Degrad. Dev. 2020, 31, 1252–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanqing, L.; Wei, S. Trade-off Analysis of Ecosystem Services in a Mountainous Karst Area, China. Water 2018, 10, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Gao, J.; Chen, H.; Jing, J.; Li, R. Elevation, Bedrock Exposure, Land Use, Interbedded Limestone and Clastic Rock, and Vegetation Coverage Dominate the Spatiotemporal Variability of Soil Erosion in Karst Basin. J. Mt. Sci. 2023, 20, 2519–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, J.; Song, X.; Lu, Y. Revealing the Main Factors Affecting Global Forest Change at Distinct Altitude Gradients. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 148, 110131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, J.; Li, R.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Q. Identification of Priority Areas for Soil Erosion Control Based on Minimum Administrative Units and Karst Landforms in Karst Areas of Guizhou. Prog. Phys. Geogr. Earth Environ. 2023, 47, 892–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Geng, H.; Luo, G.; Wu, L.; Wang, J.; Wu, Q. Multiscale Characteristics of Ecosystem Service Value Trade-Offs/Synergies and Their Response to Landscape Pattern Evolution in a Typical Karst Basin in Southern China. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 81, 102584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczygieł, J.; Golicz, M.; Hercman, H.; Lynch, E. Geological Constraints on Cave Development in the Plateau-Gorge Karst of South China (Wulong, Chongqing). Geomorphology 2018, 304, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Wang, X.; Hu, Z.; Xu, X.; Dai, Q.; Mei, L.; Gan, F.; Jin, H.; Wang, L.; Huang, C. Exploring the Spatiotemporal Trends of Extreme Sub-Hourly Rainfall Erosivity: Insights from Karst Plateaus in China. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2025, 60, 102590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Jiang, L.; Tan, X.; Gan, F.; Xia, Y.; Li, W.; Xu, X.; Yan, Y.; Fan, Y.; Pu, J. Changes in Vegetation Types Alter Soil Respiration under the Erosion and Deposition Topography in Karst Trough Valley. Catena 2025, 255, 109027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guizhou Provincial Forestry Bureau. Guizhou Province 2022 Forest Coverage Rate of the Whole Province and Nine Prefecture-Level Cities. Available online: https://lyj.guizhou.gov.cn/ztzl/zybh/202306/t20230625_80491927.html (accessed on 25 August 2025).
- Chen, Y.; Cheng, C.; Xiong, K.; Rong, L.; Zhang, S. Quantifying the Biodiversity and Ecosystem Service Outcomes of Karst Ecological Restoration: A Meta-Analysis of South China Karst. Catena 2024, 245, 108278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Liu, B.; Bussmann, R.W.; Guan, X.; Xu, W.; Xue, T.; Xia, C.; Li, J.; Jiang, H.; Wu, L.; et al. Integrated Plant Diversity Hotspots and Long-Term Stable Conservation Strategies in the Unique Karst Area of Southern China under Global Climate Change. For. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 498, 119540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Song, Y.; Deng, X.; Li, Z. Optimization of Functional Zoning and Spatial Patterns of Water Conservation on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau under Different SSP-RCP Scenarios. Anthropocene 2025, 51, 100479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D. Predicting Rainfall Erosion Losses: A Guide to Conservation Planning; Department of Agriculture, Science and Education Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 1978.
- Mccool, D.K.; Brown, L.C.; Foster, G.R.; Mutchler, C.K.; Meyer, L.D. Revised Slope Steepness Factor for the Universal Soil Loss Equation. Trans. ASAE 1987, 30, 1387–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.Y.; Nearing, M.A.; Risse, L.M. Slope Gradient Effects on Soil Loss for Steep Slopes. Trans. ASAE 1994, 37, 1835–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Chen, H.; Polyakov, V.O.; Wang, K.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, W. Soil Erosion Rates in Two Karst Peak-Cluster Depression Basins of Northwest Guangxi, China: Comparison of the RUSLE Model with 137Cs Measurements—ScienceDirect. Geomorphology 2016, 253, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Zhou, Z.; Huang, D.; Zhang, F.; Deng, F.; Yang, Y. The Response of Carbon Stocks to Land Use/Cover Change and a Vulnerability Multi-Scenario Analysis of the Karst Region in Southern China Based on PLUS-InVEST. Forests 2023, 14, 2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, C. The Contribution of Cultural Ecosystem Services to Understanding the Tourism–Nature–Wellbeing Nexus. J. Outdoor Recreat. Tour. 2015, 10, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Feng, R.; Hou, G.; Xi, J. Identifying Cultural Ecosystem Service Flows and Drivers in Ecological Functional Zone. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 392, 126914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, M.; Charrahy, Z.; González-García, A. Mapping Cultural Ecosystem Services Provision: An Integrated Model of Recreation and Ecotourism Opportunities. Land Use Policy 2023, 131, 106732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Fan, F. Assessment of Ecosystem Services in New Perspective: A Comprehensive Ecosystem Service Index (CESI) as a Proxy to Integrate Multiple Ecosystem Services. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 138, 108800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, A.F.; Montoya, A.K.; Rockwood, N.J. The Analysis of Mechanisms and Their Contingencies: PROCESS versus Structural Equation Modeling. Australas. Mark. J. (AMJ) 2017, 25, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grace, J.B. Structural Equation Modeling and Natural Systems; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006; ISBN 978-0-521-54653-9. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, D.; Xiong, D.; Zhang, B.; He, K.; Wu, H.; Zhang, W.; Lu, X. Long-Term Response of Runoff and Sediment Load to Spatiotemporally Varied Rainfall in the Lhasa River Basin, Tibetan Plateau. J. Hydrol. 2023, 618, 129154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ma, L.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, N.; Wang, W. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Wetlands and Their Driving Factors Based on PLS-SEM: A Case Study in Wuhan. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 151310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassun, B.W.; Kallio, M.; Trømborg, E.; Rannestad, M.M. Land Use and Land Cover Change, Trade-Offs, and Synergies between Ecosystem Services in a Dry Afromontane Forest. J. Nat. Conserv. 2025, 85, 126874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, S.; Ali, A.; Umer, M.; Wang, Z. Integrated Assessment of Tourism Driven Ecological Stressors in Mountain Ecosystems of Swat Valley Pakistan. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 521, 146198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xiong, K.; Li, Y.; Song, S.; Xiang, S. Improving Grassland Ecosystem Services for Human Wellbeing in the Karst Desertification Control Area: Anthropogenic Factors Become More Important. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 946, 174199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Hu, X.; Wang, X.; Meersmans, J.; Liu, Y.; Qiu, S. Simulating the Impact of Grain-for-Green Programme on Ecosystem Services Trade-Offs in Northwestern Yunnan, China. Ecosyst. Serv. 2019, 39, 100998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, B.; Gao, Y.; Liu, J.; Yan, X. Revealing the Role That Epikarst Fissures Filled with Soil Play in Soil Erosion and Nutrient Loss in Karst Rocky Desertification Region of Guizhou, China. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2024, 51, 101645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Guo, X.; Zhou, P.; Tang, L.; Lai, J.; Dai, Y.; Yan, W.; Wu, J. Vegetation Restoration Enhancing Soil Carbon Sequestration in Karst Rocky Desertification Ecosystems: A Meta-Analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 370, 122530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Tao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, J. Spatiotemporal Changes and Driving Mechanism of Ecosystem Carbon Sink in Karst Peak Cluster Depression Basin in Southwest Guangxi Based on the Interaction of “Water-Rock-Soil-Air-Biology”. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 83, 102800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Jian, J.; Lu, K. Spatial-Temporal Characteristics Analysis and Ecological Environment Quality Evaluation of Forest Health Care Bases in Yunnan, Guizhou and Sichuan Provinces. Heliyon 2024, 10, e29644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, F.; Xu, X.; Li, Z.; Zeng, X.; Yi, R.; Luo, W.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, C. Relationships between Lithology, Topography, Soil, and Vegetation, and Their Implications for Karst Vegetation Restoration. Catena 2022, 209, 105831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parhizkar, M.; Shabanpour, M.; Miralles, I.; Zema, D.A.; Lucas-Borja, M.E. Effects of Plant Species on Soil Quality in Natural and Planted Areas of a Forest Park in Northern Iran. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 778, 146310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Y. Forest Management Interventions Affect the Trade-Offs of Multiple Vegetation and Soil Ecosystem Services in Walnut Forests in the Taihang Mountains, China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2025, 57, e03420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Ren, Y.; Wang, J.; Yadav, R.; Chen, S.; Liu, C.; Mu, J.; Xue, L.; Mu, Y.; Mellouki, A. Influence of Tourism on the Local Air Quality in the Mountain Laoshan Forest Scenic Areas. Atmos. Environ. 2025, 353, 121229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; An, R.; Yu, M.-M.; He, F. Tourism Efficiency Decomposition and Assessment of Forest Parks in China Using Dynamic Network Data Envelopment Analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 363, 132405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Cai, L.; Bai, B.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J. National Forest Park Visitors’ Connectedness to Nature and pro-Environmental Behavior: The Effects of Cultural Ecosystem Service, Place and Event Attachment. J. Outdoor Recreat. Tour. 2023, 42, 100621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, A.; Wartman, M.; Rifaee Rasheed, A.; Macreadie, P.I. Tourism and Recreation in Blue Carbon Ecosystems: Exploring Synergies, Trade-Offs and Pathways to Sustainability. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2025, 266, 107697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).