The Spatio-Temporal Characteristics and Factors Influencing of the Multidimensional Coupling Relationship Between the Land Price Gradient and Industrial Gradient in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Urban Agglomeration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Logical Mechanism Underlying the Coupling Between Land Price Gradients and Industrial Gradients
3. Study Area and Data Sources
3.1. Overview of the Study Area
3.2. Data Sources and Processing
4. Research Methods
4.1. Index Construction
4.2. Multidimensional Coupling Evaluation Models
4.2.1. Static Coupling Model
4.2.2. Dynamic Coupling Model
4.2.3. Spatial Matching Model
4.3. Influencing Factor Analysis-Gradient Boosting Decision Tree (GBDT) Model
5. Results and Analysis
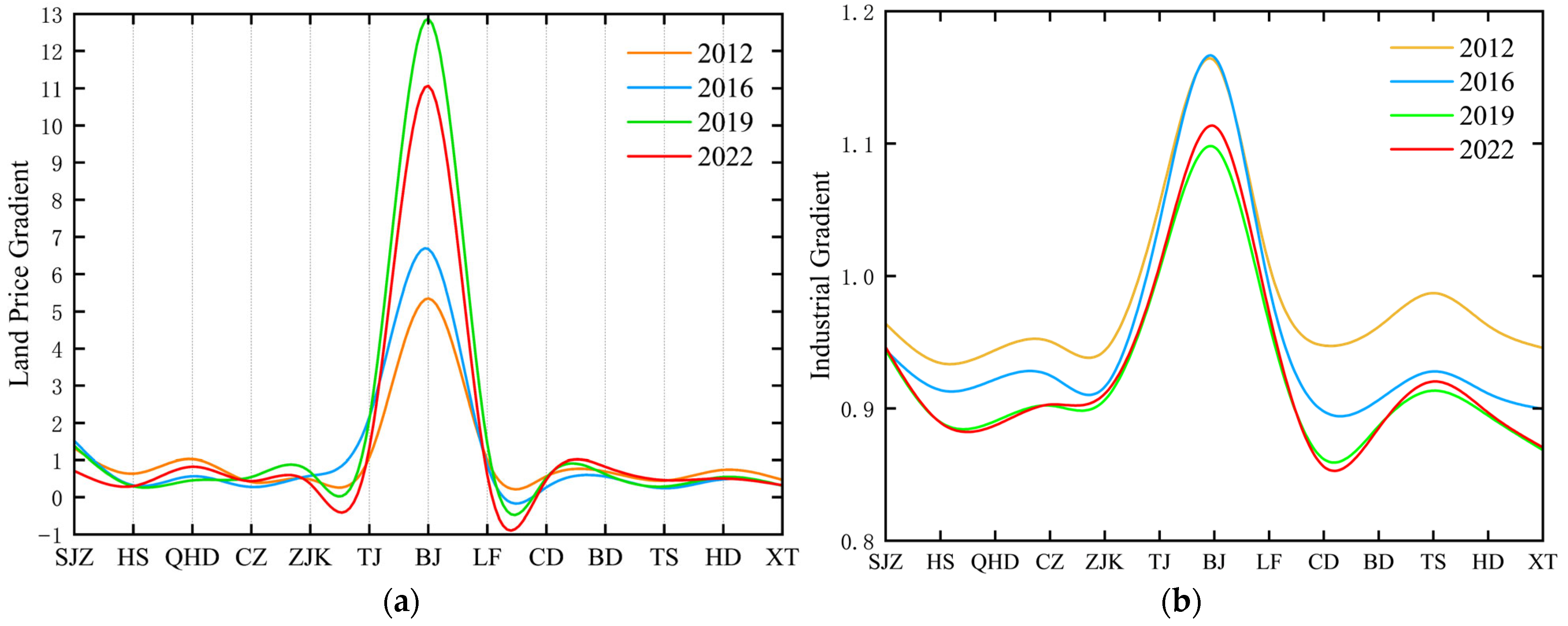
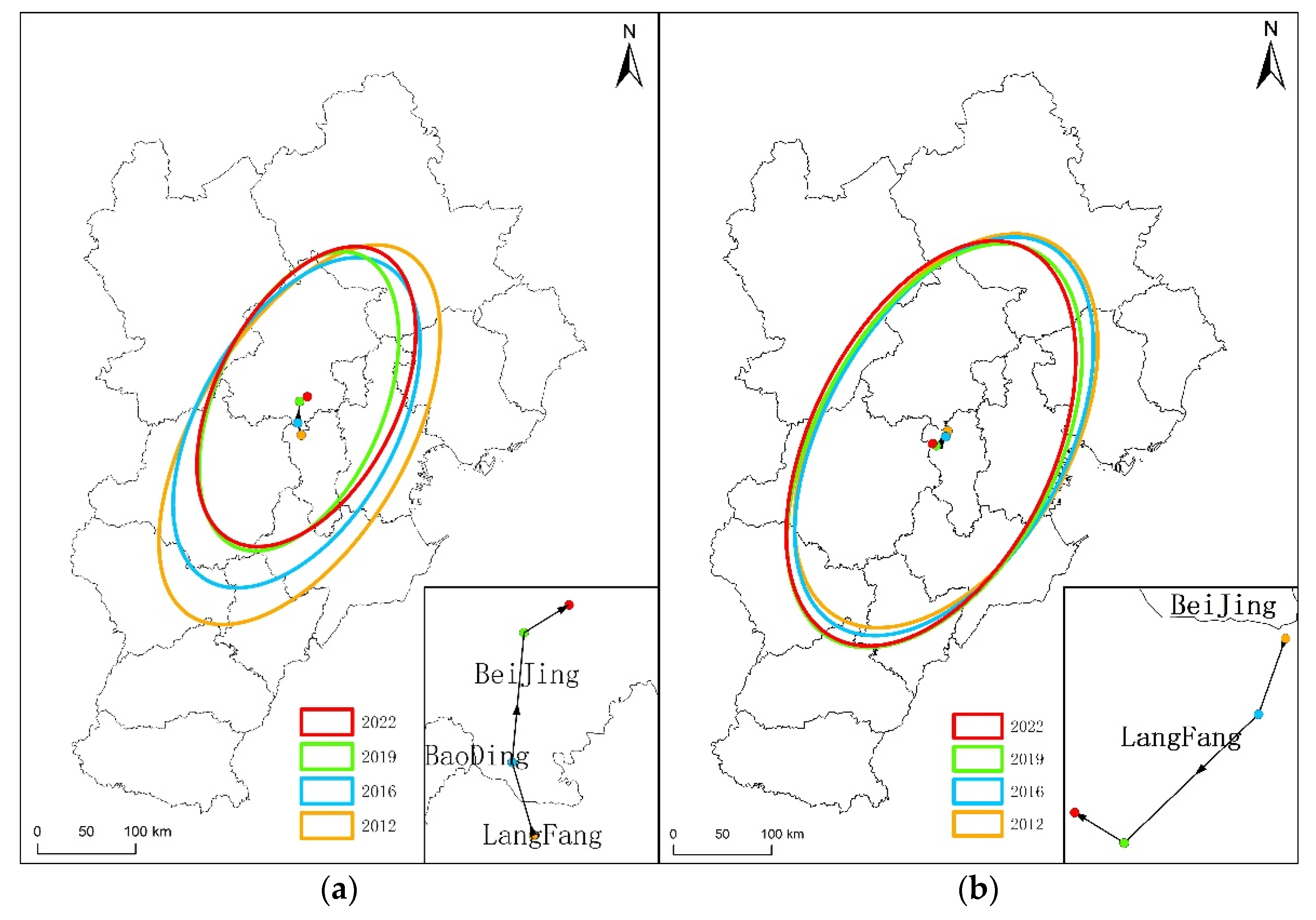
5.1. Spatio-Temporal Distribution Characteristics of Land Price and Industrial Gradients
5.2. Spatio-Temporal Characteristics of the Multidimensional Coupling Between Land Price Gradients and Industrial Gradients
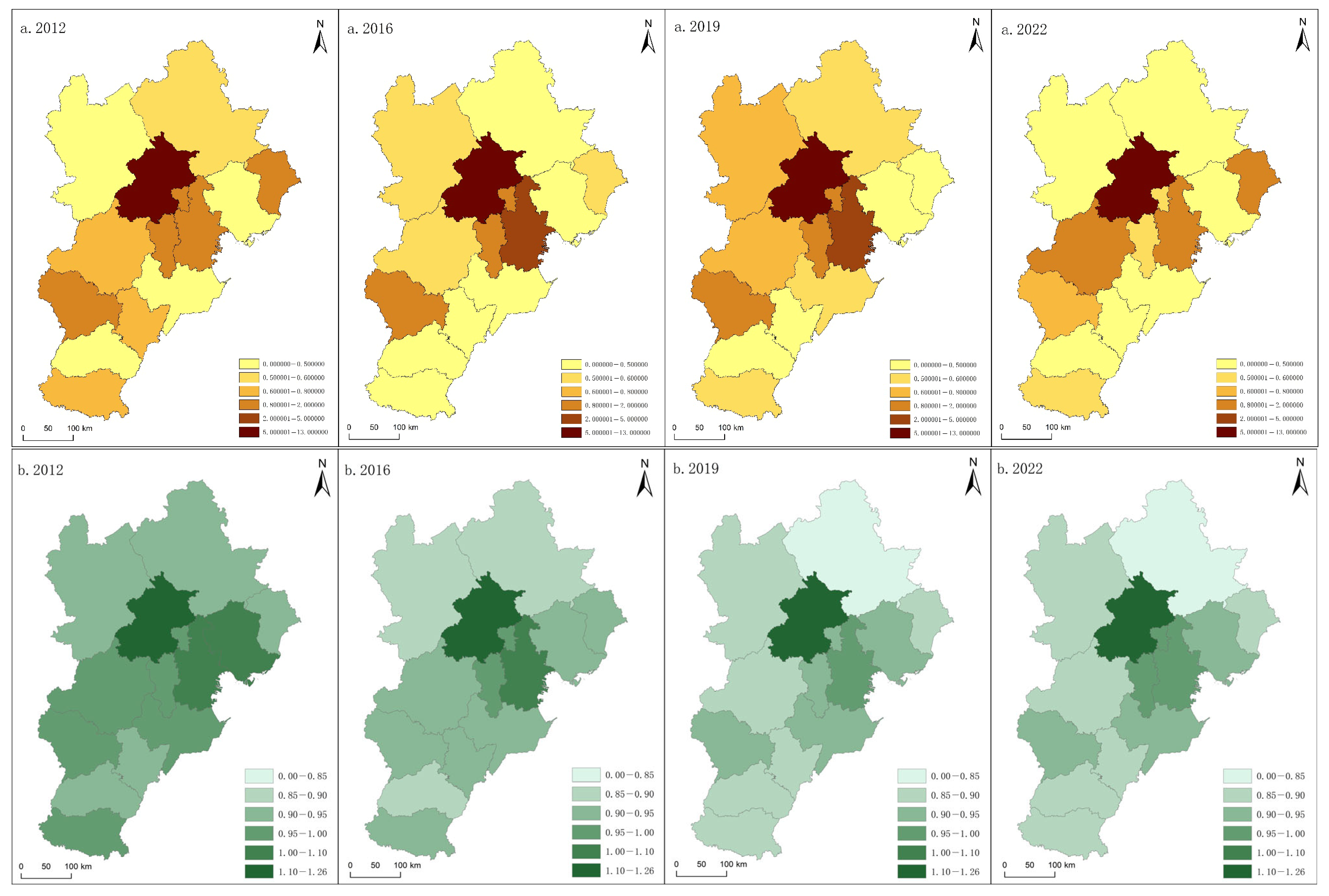
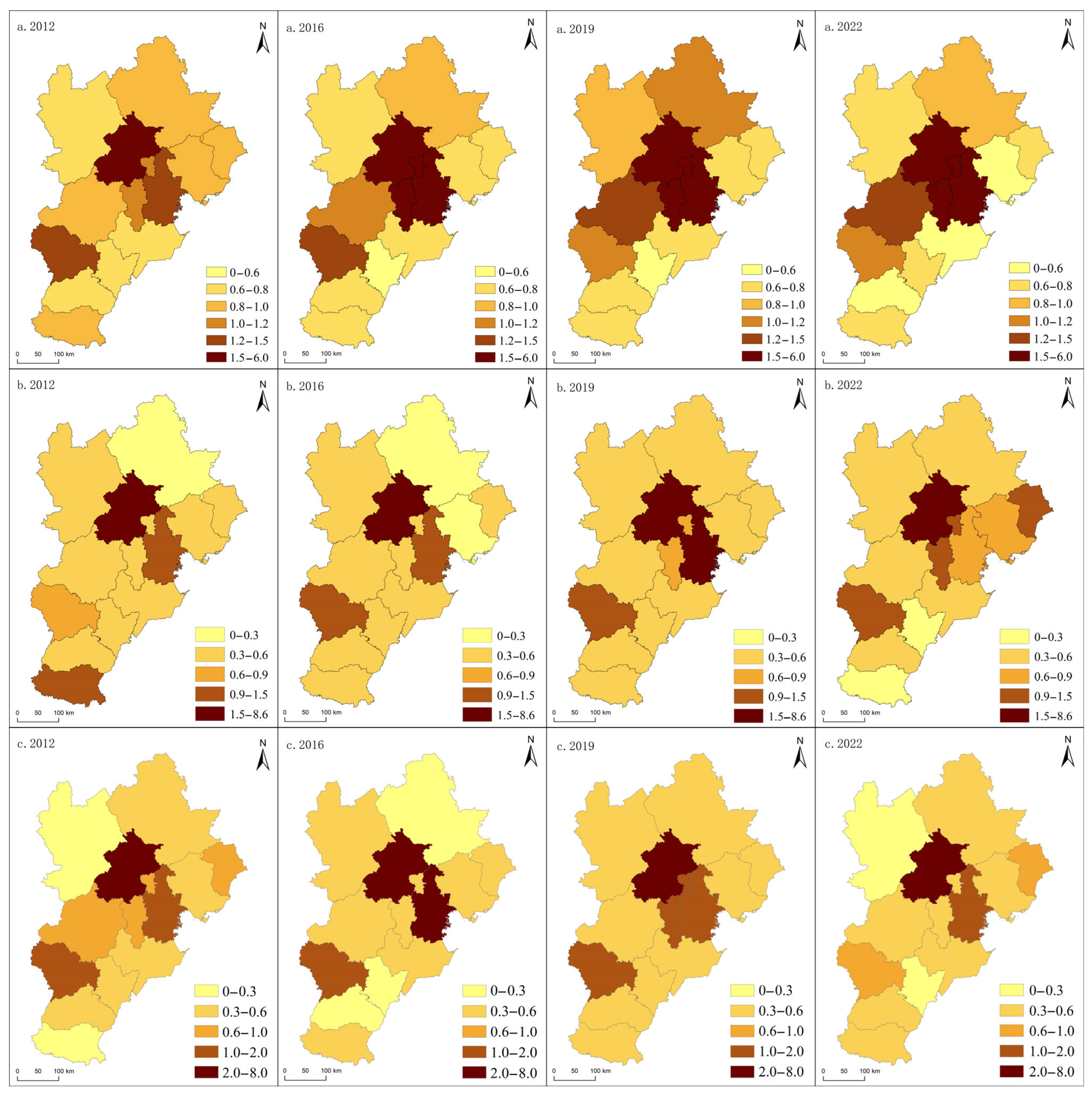
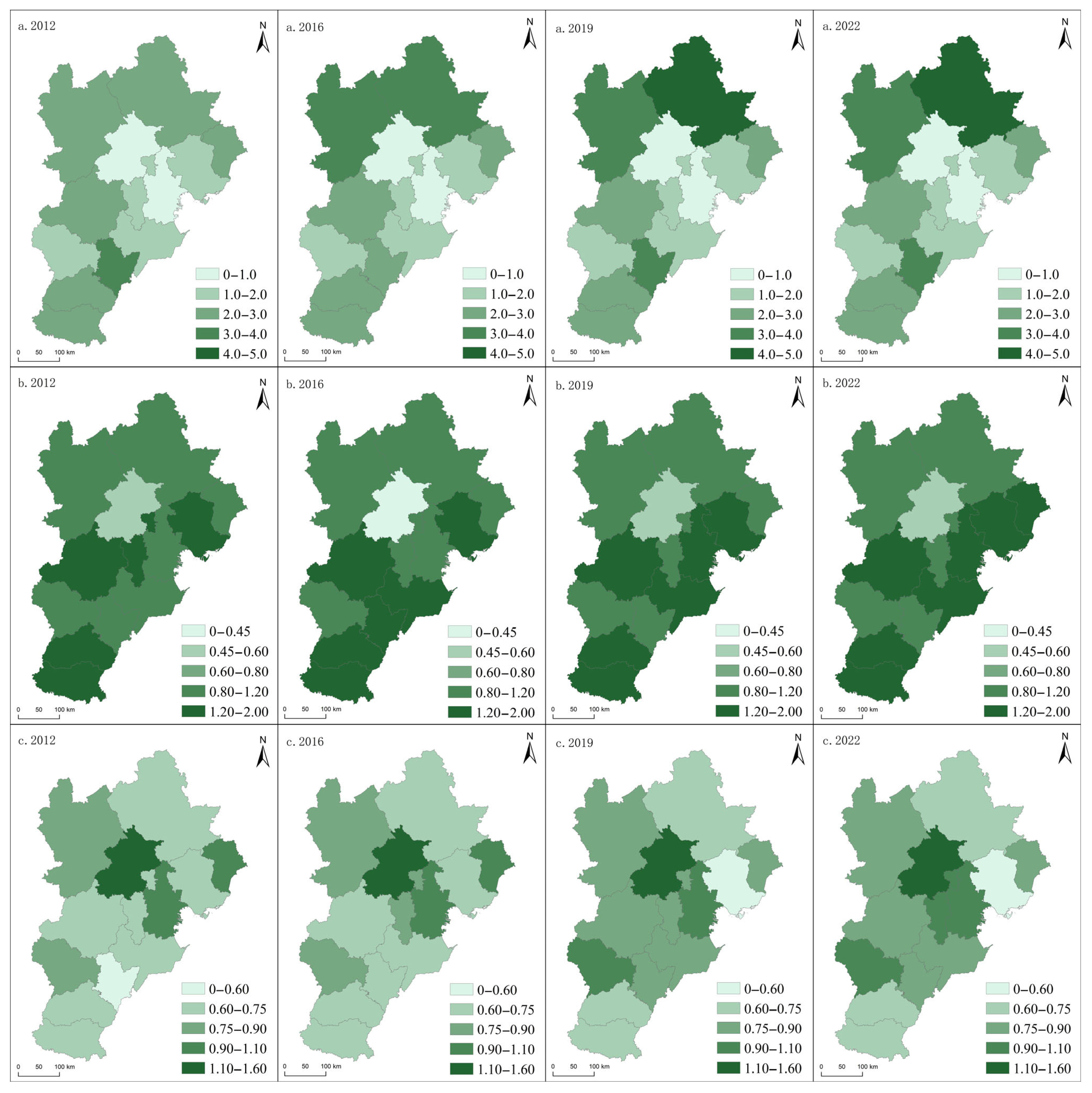
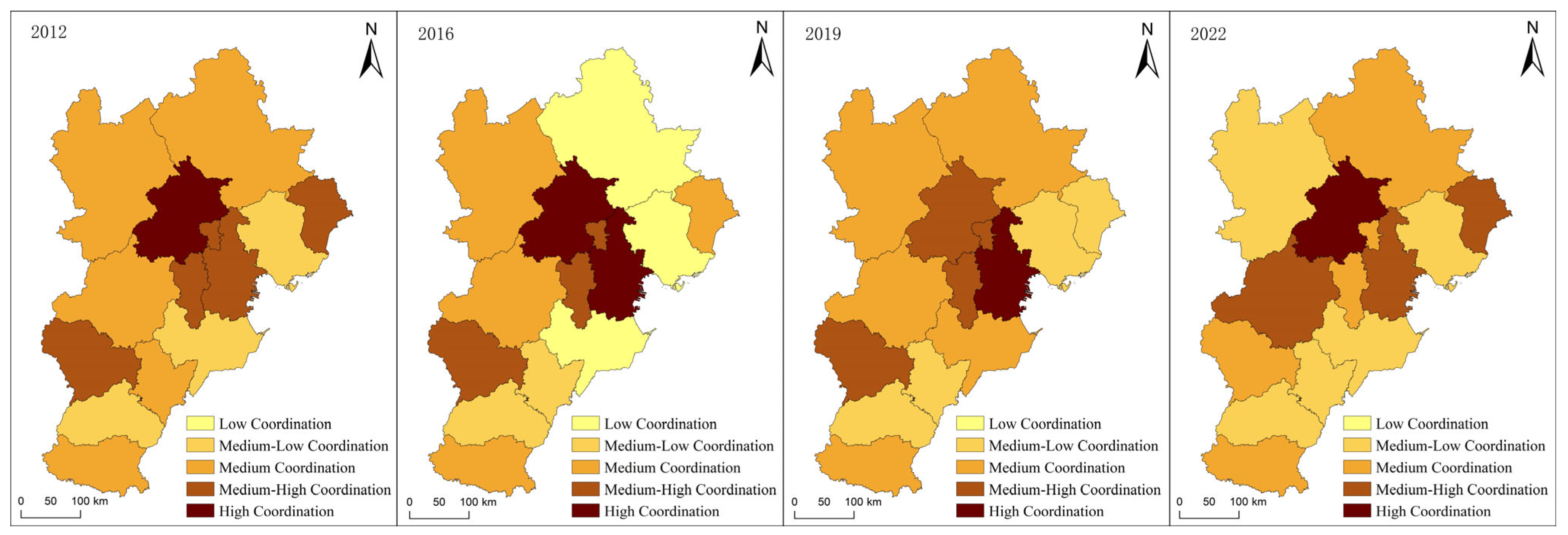
5.2.1. Spatio-Temporal Characteristics of Static Coupling
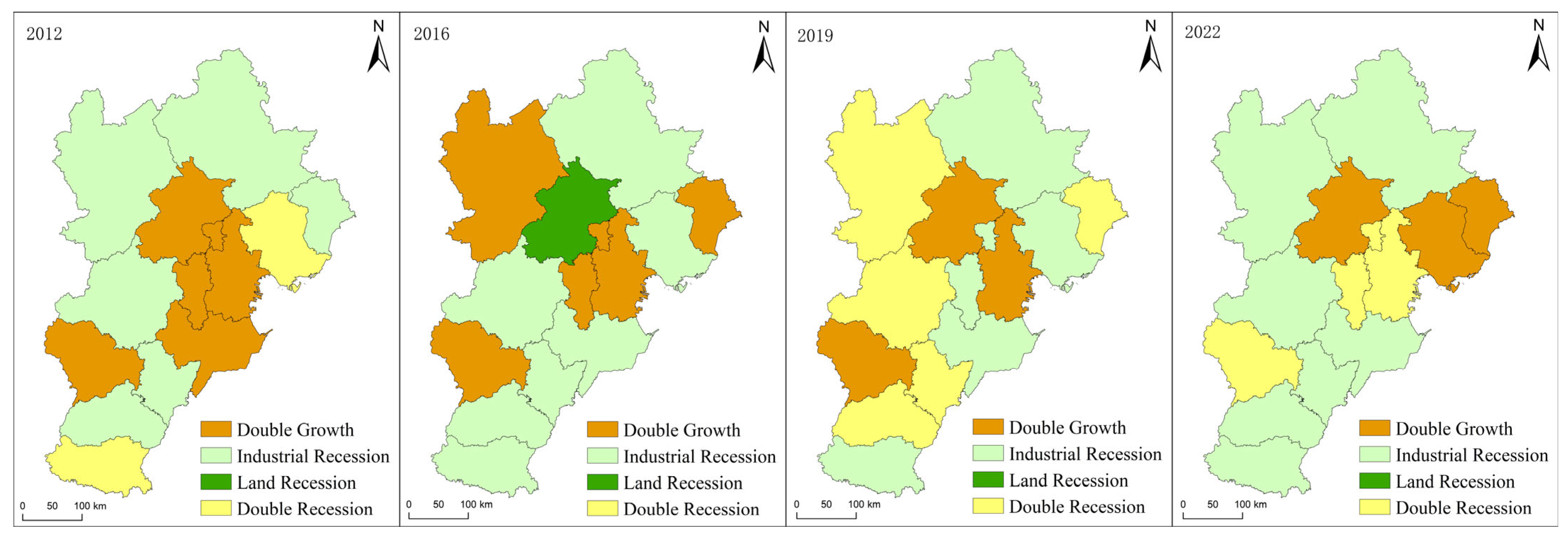
5.2.2. Spatio-Temporal Characteristics of Dynamic Coupling
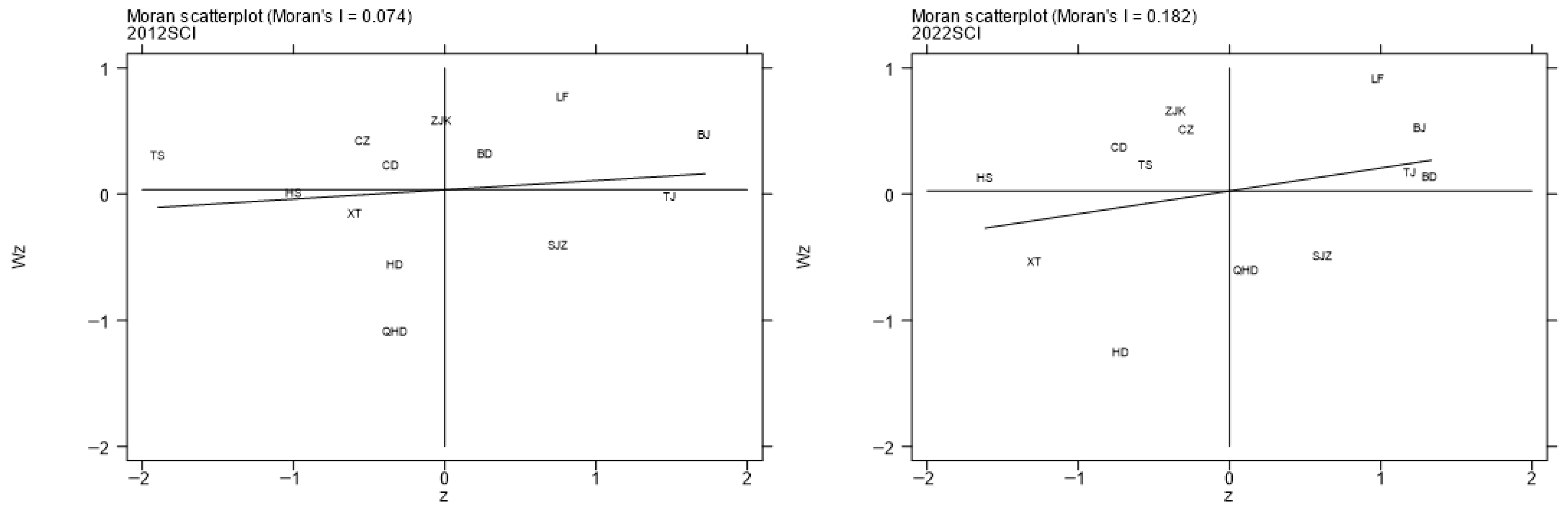
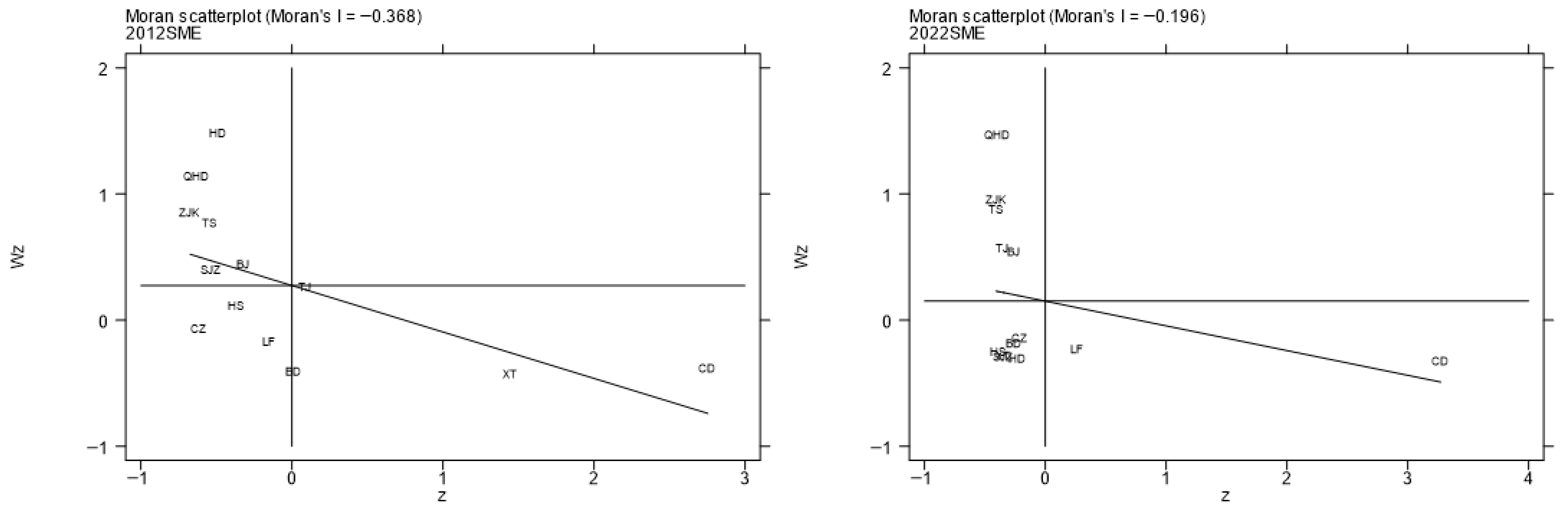
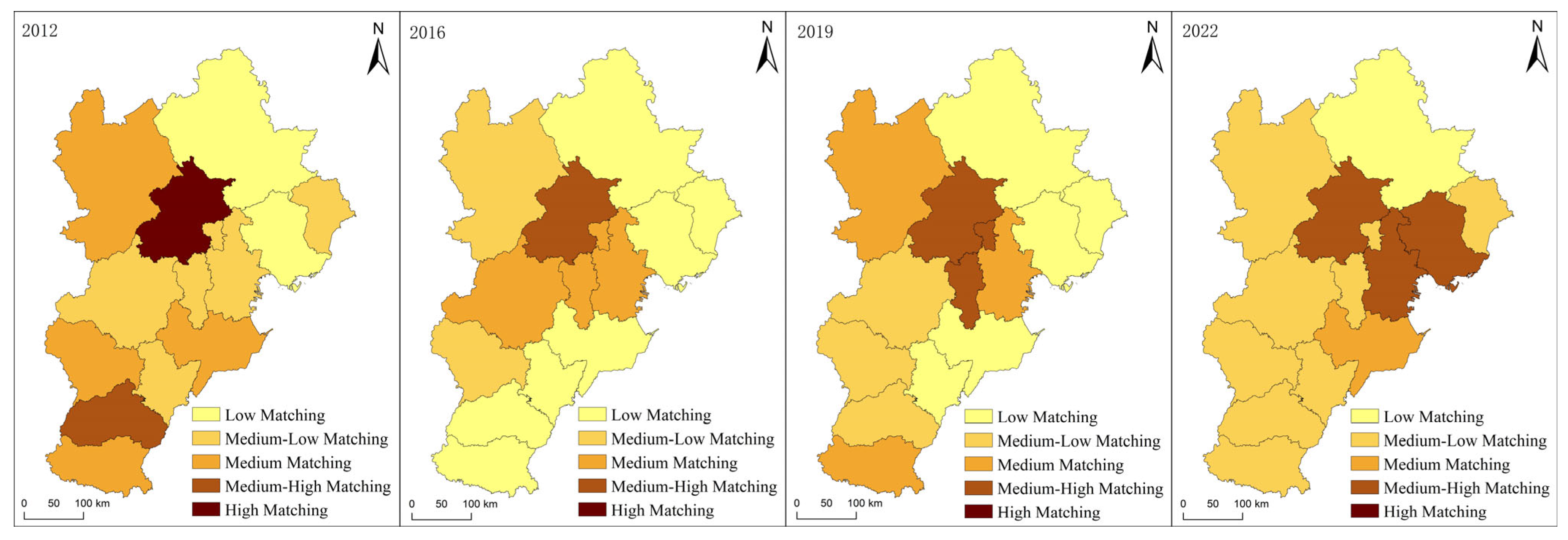
5.2.3. Spatio-Temporal Characteristics of Spatial Matching Degree
5.2.4. Robustness Check
6. Influencing Factors and Nonlinear Mechanisms of the Coupling Relationship
6.1. Variable Selection
6.2. Factor Analysis and Nonlinear Mechanisms
7. Discussion and Conclusions
8. Policy Implications and Research Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, L.; Tang, M.; Wu, Y.; Bao, S.; Wu, Q. Government-led regional integration and economic growth: Evidence from a quasi-natural experiment of urban agglomeration development planning policies in China. Cities 2025, 156, 105482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D. Study on the Optimization of Industrials Land-Use Structure in the Urbanization Agglomeration: A Logical Mechanism Framework. Urban Dev. Stud. 2013, 20, 36–44. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, H.; Wang, Y.; Mao, L.; Hong, N.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, S.; Liao, C. The spatial pattern and governance of Zhongyuan Urban-Rural system in its development trajectory. J. Geogr. Sci. 2022, 32, 1261–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gao, X. Does “involutionary competition” affect the growth of urban total factor productivity?: An empirical study based on 239 prefecture-level cities. China Soft Sci. 2025, 40, 183–195. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Cheng, K.; Fan, Z. Industrial Land Allocation Reform and Urban Land Misallocation—Evidences from Micro Enterprises Land Stock Data. China Econ. Q. 2024, 24, 465–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; He, J.; Chen, D. The Evolution of the Coupling Relationship Between Regional Integration and Land Use Efficiency in the Changzhong Urban Agglomeration. Urban Probl. 2019, 1, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Z.; Shao, Z.; Pan, P. Spatial-Temporal Evolution and Influencing Factors of Land Use Efficiency in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration. Chin. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 16, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Gao, W.; Jiang, W. Evolution Characteristics and Comprehensive Zoning of Territorial Space Efficiency in China. China Land Sci. 2025, 39, 92–104. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Yang, J. Analysis of the Spatiotemporal Differentiation and Influencing Factors of Land Use Efficiency in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Urban Agglomeration. Land 2024, 13, 1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Gao, X.; He, B.-J.; Wu, J.; Wu, K. Coupling Coordination Relationships between Urban-industrial Land Use Efficiency and Accessibility of Highway Networks: Evidence from Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration, China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Zhu, S. The principle of relatedness in China’s regional industrial development. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2020, 75, 2684–2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boschma, R. The geographical dimension of structure change. In New Perspectives on Structural Change: Causes and Consequences of Structural Change in the Global Economy; Alcorta, L., Foster-McGregor, N., Verspagen, B., Szirmai, A., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2021; pp. 172–187. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Liu, X. A Study on the Converging Evolution of Industrial Structure among Cities in the Yangze River Delta Region and Its Influencing Factors. J. Soochow Univ. (Philos. Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2023, 44, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogler, D.F.; Evenhuis, E.; Giuliani, E.; Martin, R.; Uyarra, E.; Boschma, R. Re-imagining evolutionary economic geography. Camb. J. Reg. Econ. Soc. 2023, 16, 373–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, K.; Yuan, S.; Yang, L.; Skitmore, M. Urban–rural construction land transition and its coupling relationship with population flow in China’s urban agglomeration region. Cities 2020, 101, 102701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Song, J.; Duan, H.; Wang, X. Coupling between energy efficiency and industrial structure: An urban agglomeration case. Energy 2021, 234, 121304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Tian, S.; Ma, X.; Zhao, A. Effect of industrial agglomeration on the efficiency of urban productive land allocation: Evidence from China’s nine national-level urban agglomerations. Resour. Sci. 2024, 46, 814–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yu, H.; Hou, Y. How Does Administrative Division Reform Differentially Affect Land Resource Allocation. China Ind. Econ. 2025, 4, 80–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Li, W.; Li, C.; Zheng, Y. The relationship between accessibility and land prices: A focus on accessibility to transit in the 15-min city. Travel Behav. Soc. 2025, 38, 100914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Lui, Z. Spatial-temporal pattern and influencing factors of the urban green development efficiency in Jing-Jin-Ji region of China. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2021, 30, 1079–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, S. Hedonic Prices and Implicit Markets: Product Differentiation in Pure Competition. J. Political Econ. 1974, 82, 34–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L. Assessing Amenity Effects of Urban Landscapes on Housing Price in Hangzhou, China. Urban For. Urban Green. 2015, 14, 1017–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Xiao, W.; Li, L.; Ye, Y.; Song, X. Urban land use efficiency and improvement potential in China: A stochastic frontier analysis. Land Use Policy 2020, 99, 105046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, B.; Wang, J.; Wu, Q.; Wei, Y.D. How does industrial agglomeration affect urban land use efficiency: A spatial analysis of Chinese cities. Land Use Policy 2022, 119, 106178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Yin, J.; Wang, H.; Yang, L. Induced Effect of Resource-based Industry Dependence on Zombie Firms. Econ. Res. J. 2021, 56, 138–154. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Ma, S.; Zheng, Y.; Ma, X.; Duan, K. Do regional integration policies matter? Evidence from a quasi-natural experiment on heterogeneous green innovation. Energy Econ. 2022, 116, 106426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.; Fan, L. The Pattern, Mechanism and Development Direction of Industrial Chain Division of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration. J. Hebei Univ. Econ. Bus. 2024, 45, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y. Market Integration, Specialized Division of Labor, and Industrial Structure Upgrading: Evidence from 18 Urban Agglomerations in China. Stat. Decis. 2025, 41, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Y.; Wang, G.; Liu, Y. Does the Integration of Urban Agglomerations Promote the Improvement of Regional Industrial Structure. Economist 2022, 7, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Q.; Lu, Y.; Wang, J. Exploration on Spatial Non-stationary Pattern and Optimizing Measurement Technology Application of Urban Land Price. China Land Sci. 2023, 37, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, B.; Zheng, T. Study on the Impact of Intercity Transportation Connectivity on the Gap of Urban Residential Land Prices: A Case Study of Megacity Regions in China. Urban Probl. 2023, 7, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhu, D.; Cheng, J.; Jiang, X.; Lun, F.; Zhang, Q. Does regional economic integration promote urban land use efficiency: Evidence from the Yangtze River Delta, China. Habitat Int. 2021, 116, 102404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Li, S.; Du, X. Spatial-Temporal Pattern and Influence Mechanism of Urban Land Prices under the Integrated Development of the Yangtze River Delta. China Land Sci. 2022, 36, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wu, L.; Jin, X.; Fu, H.; Fan, Y.; Ma, G. Spatial synergistic effect of regional integration on urban land use efficiency in Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration. Geogr. Res. 2024, 43, 2104–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; van Dijk, T.; Shao, Y. How Urban Spaces Aect Urban Industry Choices? Case of the Spatial Evolution of Eindhoven, the Netherlands. Urban Plan. Int. 2024, 39, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, W. Three Dimensions of Interpreting Marx’s Labor Theory of Value: A Textual Analysis Based on the London Notebooks. Jianghan Trib. 2023, 8, 23–30. [Google Scholar]
- Marx, K.; Engels, F. Collected Works of Marx and Engels; People’s Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2008; p. 455. [Google Scholar]
- Ricardo, D. On the Principles of Political Economy and Taxation; Yilin Press: Nanjing, China, 2011; pp. 26–28. [Google Scholar]
- Thunen, J. The Isolated State in Relation to Agriculture and Political Economy; Wu, H., Translator; The Commercial Press: Beijing, China, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Alonso, W. Location and Land Use; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Mills, E.S. An aggregative model of resource allocation in a metropolitan area. Am. Econ. Rev. 1967, 57, 197–210. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/1821621 (accessed on 28 June 2025).
- Muth, R.F. Cities and Housing; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Fujita, M.; Ogawa, H. Multiple Equilibria and Structural Transition of Non-Monocentric Urban Configurations. Reg. Sci. Urban Econ. 1982, 12, 161–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helpman, E. The Size of Regions. In Topics in Public Economics: Theoretical and Applied Analysis; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1998; pp. 33–54. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X. A Study on China–Vietnam Cross-Border Agricultural Economic Integration. Soc. Sci. Guangxi 2017, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Du, D.; Duan, D. Spatial distribution characteristics and influencing factors of technology-oriented enterprises in China. Geogr. Sci. 2025, 45, 518–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krugman, P. Increasing returns and economic geography. J. Political Econ. 1999, 99, 483–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilkenny, M. The spatial economy: Cities, regions, and international trade. J. Reg. Sci. 2000, 40, 608–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Sun, B.; Zhang, W. Functional division linkage pattern of urban agglomerations in China: A study from perspective of urban network. Geogr. Sci. 2025, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Peng, D. Spatial Structure of Urban Clusters, Industrial Division and Economic Growth Quality. J. Bus. Econ. 2024, 10, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duranton, G.; Puga, D. From sectoral to functional urban specialization. J. Urban Econ. 2005, 57, 343–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, B.; Zhang, T. Urban producer service functions and geographical distance in Chinese city clusters: A perspective from network externalities. Geogr. Res. 2022, 41, 2418–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Guo, X.; Wang, Y. Industrial Relocation, Elements Agglomeration and Regional Economic Development. J. Manag. World 2018, 34, 47–62+179–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, K. The ‘Flying Geese’ Model of Asian Economic Development: Origin, Theoretical Extensions, and Regional Policy Implications. J. Asian Econ. 2000, 11, 375–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Xiang, K.; Li, P.; Li, J.; Zhong, Y. Specialization and Coordination: New Pattern, New Theory and New Path in China’s Regional Development. China Ind. Econ. 2023, 8, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, J.; Xie, W.; Yang, K. Reshaping China’s spatial economic pattern under the goal of green transformation: Problem identification and path selection. China Soft Sci. 2023, 3, 85–95. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, L.; Zhao, F. Industrial Layout Optimization and High-Quality Development of the Yangtze River Economic Belt: From the Perspective of Interregional Industrial Transfer. Reform 2019, 2, 27–36. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.; Xu, R.; Shi, Y.; Yang, C. Does the industry gradient coefficient correctly reveal the direction of industry relocation? J. Manag. Sci. China 2025, 28, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Li, Z.; Hu, F.; Wu, B. How does land urbanization promote urban eco-efficiency? The mediating effect of industrial structure advancement. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 272, 122798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, X.; Ma, Z. Ecological Environmental Space Control, Land Transaction Price and Green Development: A Quasi-natural Experiment Based on National Key Ecological Function Areas. J. Quant. Technol. Econ. 2025, 42, 69–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Lin, L.; Zhu, Q.; Chen, D.; Ha, W. The effects of new satellite campuses on land prices—Evidence based on micro land transaction data in China. Appl. Geogr. 2025, 176, 103528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, L.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Cui, X.; Li, F.; Yang, J. Exploring the multi-dimensional coordination relationship between population urbanization and land urbanization based on the MDCE model: A case study of the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0253898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.H. Greedy function approximation: A gradient boosting machine. Ann. Stat. 2001, 29, 1189–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Qiu, L.; Song, J.; Geng, Y. Spatial Pattern and Influencing Factors of Population Changes in Counties in the Process of Chinese-style Modernization and Urban-rural Integrated Development. Econ. Geogr. 2025, 45, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojić, A.; Stanić, N.; Vuković, G.; Stanišić, S.; Perišić, M.; Šoštarić, A.; Lazić, L. Explainable extreme gradient boosting tree-based prediction of toluene, ethylbenzene and xylene wet deposition. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 653, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, T.; Wang, J.; Cao, X. Exploring the non-linear associations between spatial attributes and walking distance to transit. J. Transp. Geogr. 2020, 82, 102560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, L. Spatial Differentiation Patterns and Influencing Factors of Urban Land Prices River Economic Belt. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2020, 29, 13–22. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Xin, L. Spatial divergence of urban land prices in China from 2007 to 2019. Geogr. Res. 2022, 41, 1637–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wang, J.; Wu, Q. Study on the Impact of Spatial Mismatch of Industrial Land on Industrial Division of Labor in Urban Agglomeration of the Yangtze River Delta. China Land Sci. 2023, 37, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Xu, H.; Ni, P.; Xu, X. Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Industrial Transfer in Yangtze River Delta. Econ. Geogr. 2023, 43, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yan, Y. China’s Macro-economic Report 2019–2020—China’s Macro-economy in the Period of Structural Adjustment. Econ. Theory Bus. Manag. 2020, 1, 21–41. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X. Massive reserving land, rapid expansion, strong external shocks and default risk identification for real estate developers: Based on random forest model. J. Hainan Univ. (Humanit. Soc. Sci.) 2025, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, R.; Rutherford, B.N.; Edmondson, D.; Matthews, L. Uncertainty in industrial markets: The COVID-19 pandemic. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2022, 102, 364–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmazkuday, H. COVID-19 and housing prices: Evidence from U.S. county-level data. Rev. Reg. Res. 2023, 43, 241–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]










| Indicator | Classification | Type |
|---|---|---|
| SCI | 0 ≤ (SCI) < 0.3 | Low Coordination |
| 0.3 ≤ (SCI) < 0.5 | Medium-Low Coordination | |
| 0.5 ≤ (SCI) < 0.7 | Medium Coordination | |
| 0.7 ≤ (SCI) < 0.9 | Medium-High Coordination | |
| 0.9 ≤ (SCI) ≤ 1 | High Coordination |
| Indicator | Classification | Type |
|---|---|---|
| DCI | 0 ≤ Abs (DCI) < 0.2 | High Coordination |
| 0.2 ≤ Abs (DCI) < 0.4 | Medium-High Coordination | |
| 0.4 ≤ Abs (DCI) < 0.6 | Medium Coordination | |
| 0.6 ≤ Abs (DCI) < 0.8 | Medium-Low Coordination | |
| Abs (DCI) ≥ 0.8 | Low Coordination |
| Indicator | Classification | Type |
|---|---|---|
| DCI > 0 | △LQ > 0; △LGC > 0 | Double Growth |
| △LQ < 0; △LGC < 0 | Double Recession | |
| DCI < 0 | △LQ > 0; △LGC < 0 | Land Recession |
| △LQ < 0; △LGC > 0 | Industrial Recession |
| Indicator | Classification | Type |
|---|---|---|
| SME | 0 ≤ Abs (SME) < 0.1 | High Matching |
| 0.1 ≤ Abs (SME) < 0.3 | Medium-High Matching | |
| 0.3 ≤ Abs (SME) < 0.6 | Medium Matching | |
| 0.6 ≤ Abs (SME) < 0.9 | Medium-Low Matching | |
| Abs (SME) ≥ 0.9 | Low Matching |
| City | MSE-SCI | MSE-DCI | MSE-SME |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing | 0.00077 | 0.015512 | 0.138425 |
| Tianjin | 0.002169 | 0.013683 | 0.038244 |
| Shijiazhuang | 0.004751 | 0.017911 | 0.044073 |
| Tangshan | 0.01254 | 0.111707 | 0.068894 |
| Qinhuangdao | 0.004986 | 0.000756 | 0.059584 |
| Handan | 0.004094 | 0.002736 | 0.062661 |
| Xingtai | 0.002941 | 0.073021 | 0.066068 |
| Baoding | 0.007213 | 0.066271 | 0.065606 |
| Zhangjiakou | 0.009011 | 0.001694 | 0.062054 |
| Chengde | 0.002657 | 0.3928 | 0.065463 |
| Cangzhou | 0.016792 | 0.001405 | 0.068942 |
| Langfang | 0.005884 | 5.702432 | 0.055701 |
| Hengshui | 0.00926 | 0.000758 | 0.067463 |
| Influencing Factors | Indicator Name | Variable Symbol | Variable Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Geographical Conditions | Average elevation | ln(ele) | Calculated as the mean elevation of each city based on DEM data |
| Terrain slope | slope | Calculated as the mean terrain slope within each city’s administrative boundary using DEM data | |
| Urban area | ln(area) | Total administrative area of each city | |
| Locational Conditions | Distance to coastline | ln(disc) | Straight-line distance from each city center to the nearest coastline |
| Distance to core city | ln(dis) | Straight-line distance from each city to the core city | |
| Urban Scale | Economic scale | ln (GDP) | Regional GDP |
| Population scale | ln(pop) | Year-end resident population of each city | |
| Administrative level | adm | Assigned values from 1 to 4 by administrative hierarchy | |
| Public Services and Infrastructure | Basic education | edu | Number of primary and secondary school students per 10,000 population |
| Basic healthcare | hos | Number of hospital beds per 10,000 population | |
| Urban green coverage | green | Green coverage ratio in built-up areas | |
| Economic Development | Average wage | ln(wage) | Average wage of employees in non-private urban units |
| Fiscal expenditure | Ln (Fisc) | Total local general public budget expenditure | |
| Financial development | ln(finan) | Year-end total deposits and loans of financial institutions | |
| Number of patents granted | ln(pat) | Total number of patents granted annually |
| Variable | Obs | Mean | Std | Min | Max | Variable | Obs | Mean | Std | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCI | 143 | 0.556 | 0.227 | 0.009 | 0.999 | Lnpop | 143 | 6.581 | 0.557 | 5.711 | 7.634 |
| DCI | 143 | 0.429 | 1.491 | 0.001 | 13.817 | Adm | 143 | 1.538 | 0.993 | 1 | 4 |
| SME | 143 | 0.869 | 0.148 | 0.036 | 0.999 | Edu | 143 | 0.126 | 0.033 | 0.059 | 0.197 |
| Lnele | 143 | 4.789 | 1.539 | 2.397 | 7.134 | Hos | 143 | 44.329 | 6.553 | 27.323 | 59.912 |
| Slope | 143 | 7.696 | 4.420 | 2.180 | 16.271 | Green | 143 | 0.424 | 0.036 | 0.349 | 0.498 |
| Lnarea | 143 | 9.580 | 0.518 | 8.761 | 10.590 | Lnwage | 143 | 7.256 | 3.123 | 3.295 | 21.508 |
| Lndisc | 143 | 4.947 | 0.755 | 3.641 | 5.846 | Lnfisc | 143 | 15.711 | 0.913 | 14.291 | 18.129 |
| Lndis | 143 | 4.828 | 1.486 | 0.010 | 6.006 | Lnfinan | 143 | 18.566 | 1.132 | 16.941 | 21.848 |
| lngdp | 143 | 17.398 | 0.929 | 16.129 | 19.846 | lnpat | 143 | 8.494 | 1.489 | 5.313 | 12.220 |
| SCI-Top9 | DCI-Top9 | SME-Top9 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Influence | Variable | Influence | Variable | Influence |
| Lnwage | 21.08% | Hos | 33.51% | Lnfisc | 39.40% |
| lnpop | 17.24% | Lnwage | 15.37% | Edu | 16.59% |
| Lndisc | 12.87% | lndis | 12.69% | Lnpop | 12.03% |
| Lnpat | 8.18% | Green | 9.89% | Lnfinan | 10.54% |
| Lnarea | 7.23% | Lngdp | 9.13% | Hos | 4.20% |
| Green | 6.68% | Lnpat | 7.78% | Lnpat | 3.54% |
| Lndis | 5.66% | Lnfisc | 3.25% | Green | 3.42% |
| Hos | 4.97% | Edu | 3.03% | Lngdp | 3.11% |
| edu | 4.33% | lnpop | 2.99% | lnarea | 3.03% |
| Variable | GBDT | RF | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Cross-Validation R2 | Cross-Validation R2 | Mean Cross-Validation R2 | Cross-Validation R2 | |
| SCI | 0.669 | 0.172 | 0.687 | 0.164 |
| DCI | 0.038 | 0.243 | 0.125 | 0.243 |
| SME | 0.381 | 0.321 | 0.426 | 0.170 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, D.; Liang, W. The Spatio-Temporal Characteristics and Factors Influencing of the Multidimensional Coupling Relationship Between the Land Price Gradient and Industrial Gradient in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Urban Agglomeration. Sustainability 2025, 17, 8153. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17188153
Wang D, Liang W. The Spatio-Temporal Characteristics and Factors Influencing of the Multidimensional Coupling Relationship Between the Land Price Gradient and Industrial Gradient in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Urban Agglomeration. Sustainability. 2025; 17(18):8153. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17188153
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Deqi, and Wei Liang. 2025. "The Spatio-Temporal Characteristics and Factors Influencing of the Multidimensional Coupling Relationship Between the Land Price Gradient and Industrial Gradient in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Urban Agglomeration" Sustainability 17, no. 18: 8153. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17188153
APA StyleWang, D., & Liang, W. (2025). The Spatio-Temporal Characteristics and Factors Influencing of the Multidimensional Coupling Relationship Between the Land Price Gradient and Industrial Gradient in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Urban Agglomeration. Sustainability, 17(18), 8153. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17188153





