Identifying the Impact of Climate Policy on Urban Carbon Emissions: New Insights from China’s Environmental Protection Tax Reform
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Factors Affecting Carbon Emissions
2.2. The Implications for Environmental Regulations on the Economy and Environment
2.3. Studies on the Implementation of Difference-in-Differences Methodology
3. Theoretical Analysis
3.1. Institutional Background of EPT
3.2. Theoretical Analysis and Research Hypothesis
4. Materials and Methodology
4.1. The Specification for Benchmark Panel Econometric Model
4.2. Variable Selection and Description
4.2.1. Explained Variable: Per Capita Carbon Emissions (PCE)
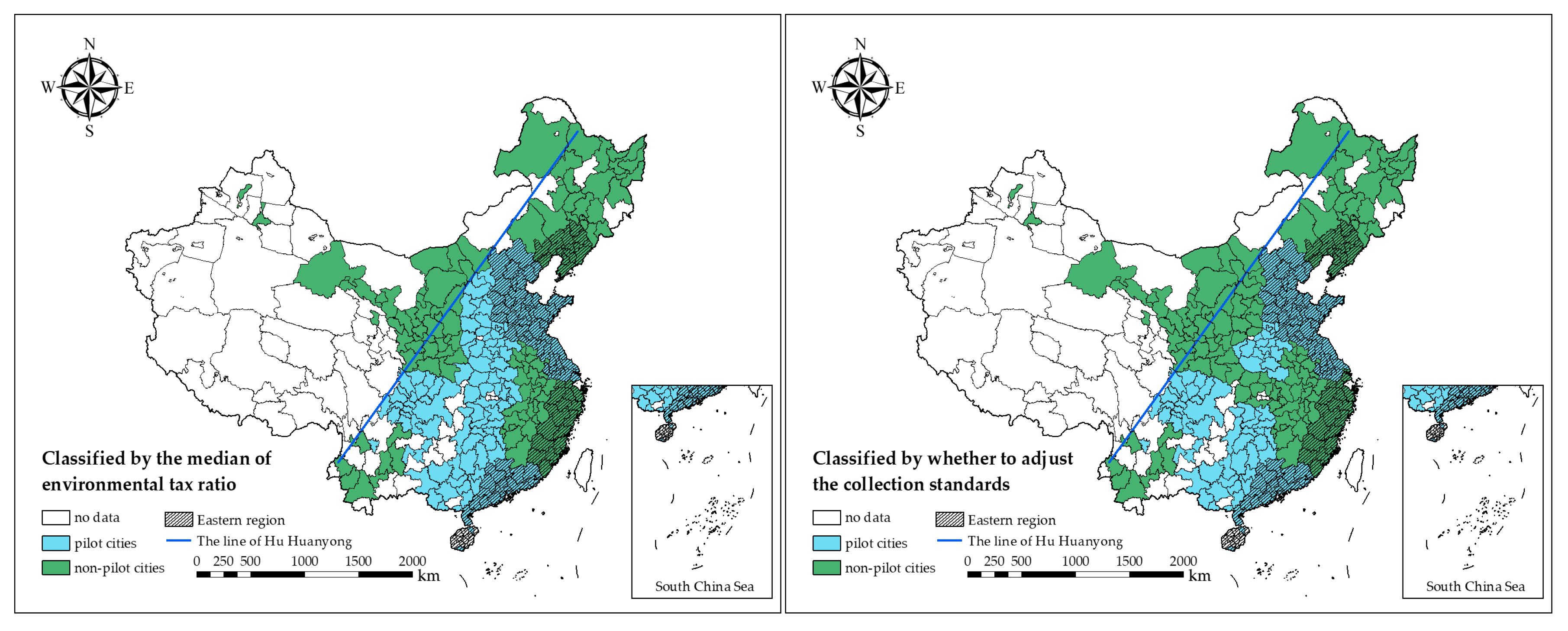
4.2.2. Key Explanatory Variable: Environmental Protection Tax (EPT)
4.2.3. Control Variables
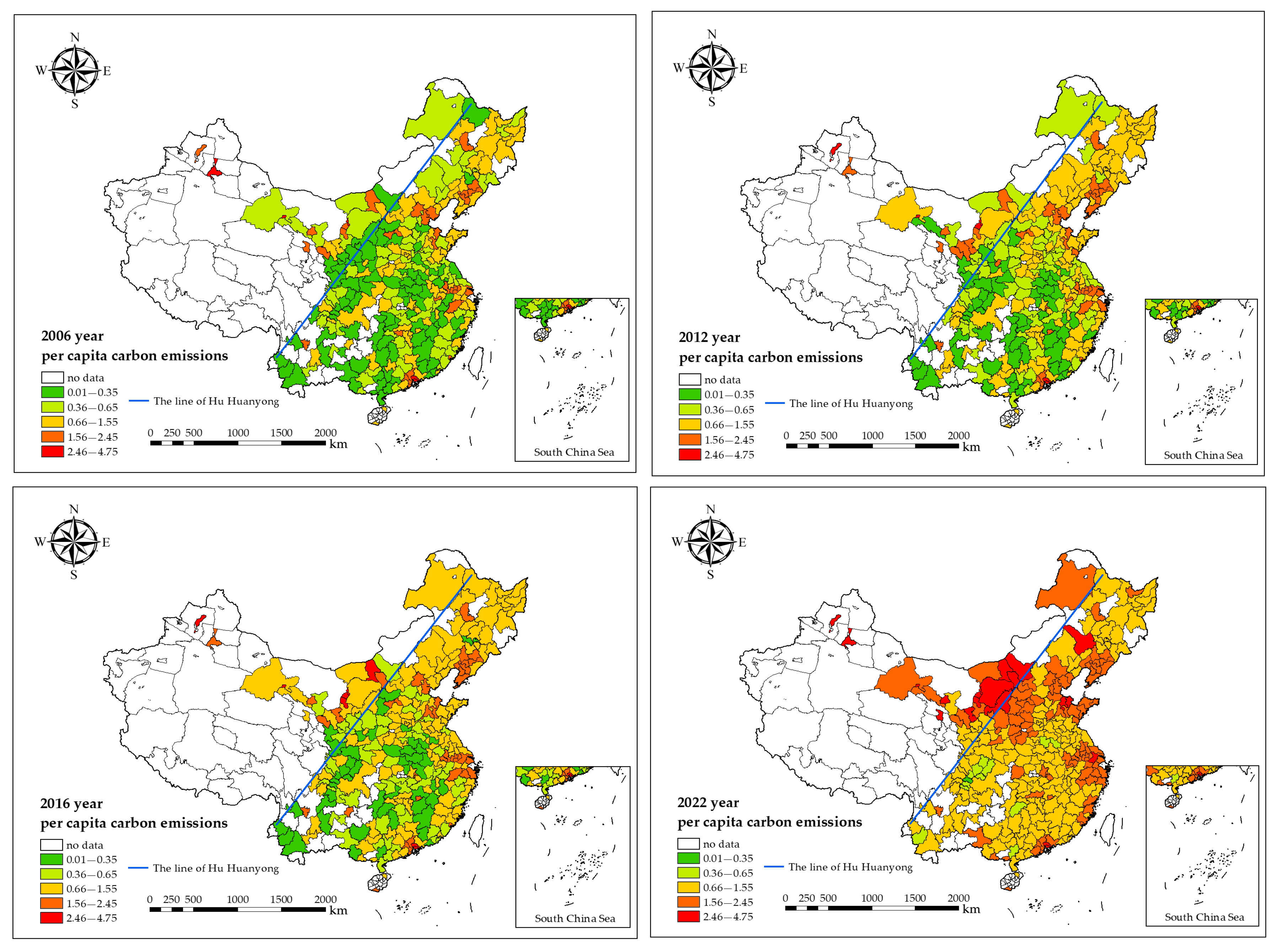
4.3. Data Source and Processing
5. Empirical Results and Analysis
5.1. Baseline Regression Analysis
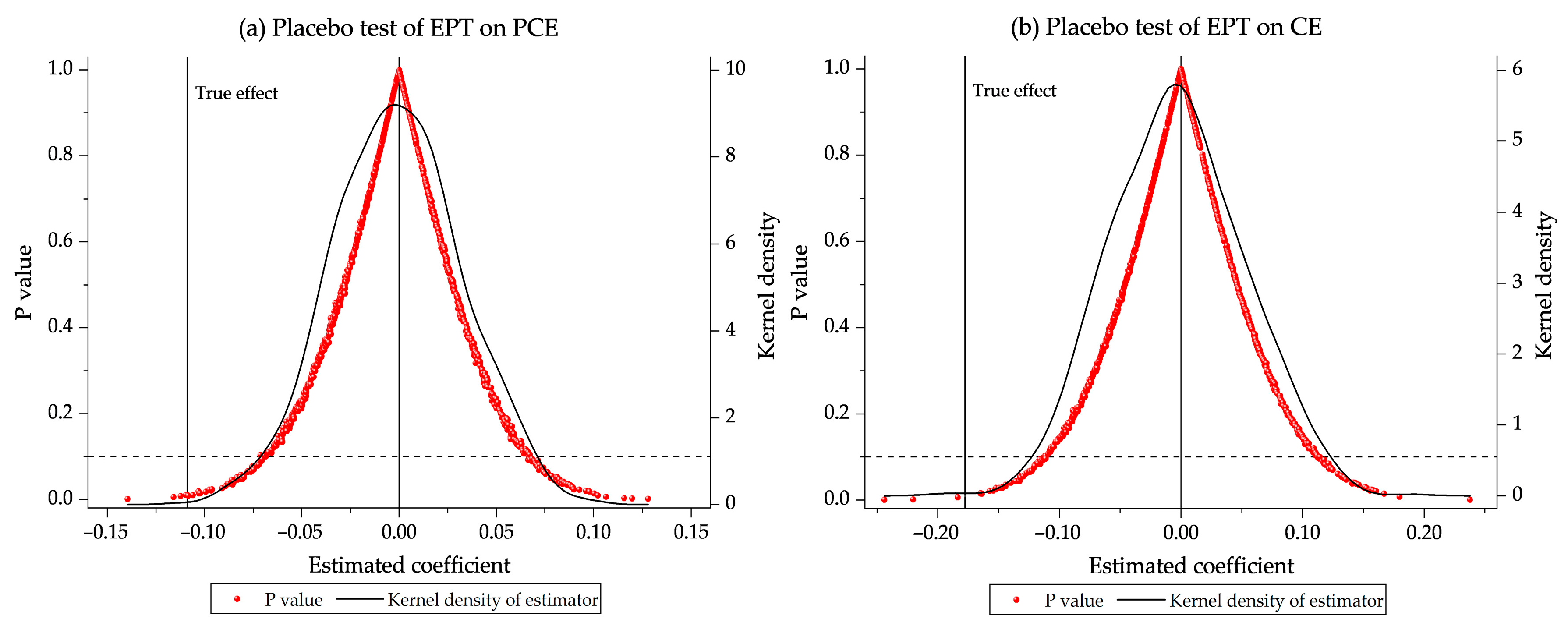
5.2. Parallel Trend Testing and Placebo Testing
5.3. Robustness Analysis
5.4. Policy Uniqueness Test
5.5. Heterogeneity Analysis
5.6. Transmission Mechanism Analysis
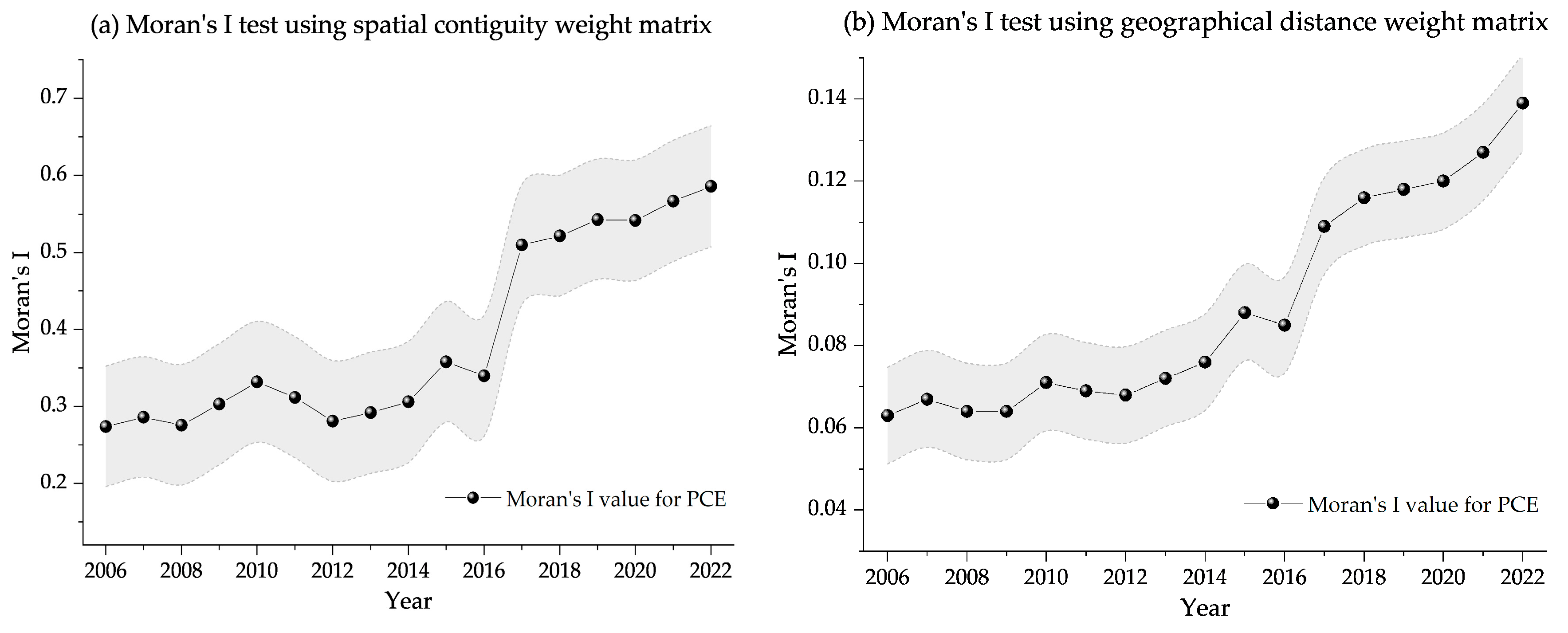
5.7. Spatial Spillover Effects Analysis
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions and Policy Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cui, X.M.; Zhong, Z. Climate change, cropland adjustments, and food security: Evidence from China. J. Dev. Econ. 2024, 167, 103245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, B.G.; Sahadev, S.; Mahanty, A.; Praveensal, C.J.; Asha, G. Trivariate causality between economic growth, energy con-sumption, and carbon emissions: Empirical evidence from India. Energy Effick. 2023, 16, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.F.; Li, Y.; Yu, J. Administrative-led urbanization and urban carbon emission intensity: Evidence from city-county merger in China. Energy Econ. 2024, 136, 107615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakpho, P.; Chitksame, T.; Kaewsompong, N. The effect of environmental taxes and economic growth on carbon emission in G7 countries applying panel kink regression. Energy Rep. 2024, 9, 1384–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.Y.; Xu, Y.Z.; Liu, C.Y. China’s environmental tax reform achieves the co-management of carbon and haze: The role of optimizing energy utilization. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2024, 15, 102180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, F.; Wang, P. The evolution of climate governance in China: Drivers, features, and effectiveness. Environ. Polit. 2021, 30, 141–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.; Oueslati, W.; Rousselière, D. Environmental taxes, reforms and economic growth: An empirical analysis of panel data. Econ. Syst. 2020, 44, 100806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, S.; Morley, B. Environmental taxes and economic growth: Evidence from panel causality tests. Energy Econ. 2014, 42, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Kenjayeva, U.; Mu, G.W.; Iqbal, N.; Chin, F. Evaluating the influence of environmental regulations on green economic growth in China: A focus on renewable energy and energy efficiency guidelines. Energy Strategy Rev. 2024, 56, 101544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.Z.; Li, Z.W.; Wang, B. Can “environmental protection fee to tax” reduce carbon emissions? Evidence from China. Financ. Res. Lett. 2024, 62, 105184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugrinov, S. The effects of environmental taxes on environmental pollution in the member states of the European Union. Econ. Syst. 2025, 49, 101308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.M.; Xin, Z.J.; Wang, Y.F. Effect of the sci-tech finance pilot policy on corporate environmental information disclosuremoderating role of green credit. Financ. Res. Lett. 2024, 62, 105177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W. EKC test study on the relationship between carbon dioxide emission and regional economic growth. Carbon Manag. 2020, 11, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Yue, S.J.; Chen, H.T. Carbon emission efficiency of China’s industry sectors: From the perspective of embodied carbon emissions. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 283, 124655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.L.; Zhao, B.; Fan, T.Z.; Zhang, J.N. Economic growth targets and carbon emissions: Evidence from China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2022, 19, 8053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.B.; Hossain, S. Investigating the connections between China’s economic growth, use of renewable energy, and research and development concerning CO2 emissions: An ARDL Bound Test Approach. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2024, 201, 123220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moutinho, V.; Varum, C.; Madaleno, M. How economic growth affects emissions? An investigation of the environmental Kuznets curve in Portuguese and Spanish economic activity sectors. Energy Policy 2017, 106, 326–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, S.Y.; Ge, W.F.; Yang, P.; Zhang, Y.F. Exploring digital finance, financial regulations and carbon emission nexus: New insight from resources efficiency, industrial structure and green innovation in China. Resour. Policy 2024, 88, 104452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gielen, D.; Boshell, F.; Saygin, D.; Bazilian, M.D.; Wagner, N.; Gorini, R. The role of renewable energy in the global energy transformation. Energy Strategy Rev. 2019, 24, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Wang, B.; Chen, Z.F. Carbon emissions reductions and technology gaps in the world’s factory, 1990–2012. Energy Policy 2016, 91, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jijian, Z.; Twum, A.K.; Agyemang, A.O.; Edziah, B.K.; Ayamba, E.C. Empirical study on the impact of international trade and foreign direct investment on carbon emission for belt and road countries. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 7591–7600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyewo, B. Corporate governance and carbon emissions performance: International evidence on curvilinear relationships. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 334, 117474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.Q.; Nie, Y.M.; Li, H.G.; Wang, H.S. Digital transformation and low-carbon technology innovation in manufacturing firms: The mediating role of dynamic capabilities. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2023, 263, 108969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blohmke, J.; Kemp, R.; Türkeli, S. Disentangling the causal structure behind environmental regulation. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2016, 103, 174–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.Y.; Xie, W.L.; Yang, Y. Dual green innovation capability, environmental regulation intensity, and high-quality eco-nomic development in China: Can green and growth go together? Financ. Res. Lett. 2024, 63, 105275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, R.H.; Yuan, Y.J.; Huang, J.J. Different types of environmental regulations and heterogeneous influence on “green” productivity: Evidence from China. Ecol. Econ. 2017, 132, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Shang, Y.P.; Magazzino, C.; Madaleno, M.; Mallek, S. Multi-step impacts of environmental regulations on green economic growth: Evidence in the lens of natural resource dependence. Resour. Policy 2023, 85, 103919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Zhong, S.H.; Shi, T.; Zhang, X.L. Environmental regulation and haze pollution: Neighbor-companion or neigh-borbeggar? Energy Policy 2021, 151, 112183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.H.; Kong, S.Y. The effect of environmental regulation on green total-factor productivity in China’s industry. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2022, 94, 106757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raff, Z.; Earnhart, D. Employment and environmental protection: The role of regulatory stringency. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 321, 115896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Wang, Y. How does government environmental regulation “unlock” carbon emission effect? —Evidence from China. Chin. J. Popul. Resour. Environ. 2018, 16, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, S. Environmental regulations on air pollution in China and their impact on infant mortality. J. Health Econ. 2015, 42, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.X.; Liao, G.K.; Li, Y.L. The relationship between environmental regulation, pollution and corporate environmental responsibility. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2021, 18, 8018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.J.; Huang, S.F.; Li, W.F.; Wang, Y. Directors? and officers? liability insurance, environmental regulation and firms? environmental responsibility. Ecol. Econ. 2023, 208, 107796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, M.B.; Pulver, S.; Hill, D.T.; Manski, B. Targeted pollution management can significantly reduce toxic emissions while limiting adverse effects on employment in US manufacturing. Environ. Sci. Policy 2023, 139, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, H.C. Competition and ESG practices in emerging markets: Evidence from a difference-in-differences model. Financ. Res. Lett. 2022, 46, 102371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; He, C.Y.; Luo, L. Does the low-carbon city policy make a difference? Empirical evidence of the pilot scheme in China with DEA and PSM-DID. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 122, 107238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.N.; Shao, S.; Yang, L.L. High-speed rail and CO2 emissions in urban China: A spatial difference-in-differences approach. Energy Econ. 2021, 99, 105271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sendstad, L.H.; Hagspiel, V.; Mikkelsen, W.J.; Ravndal, R.; Tveitstol, M. The impact of subsidy retraction on European renewable energy investments. Energy Policy 2022, 160, 112675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Hu, H.Y.; Feng, D.W.; He, X.G. How does broadband infrastructure promote entrepreneurship in China: Evidence from a quasi-natural experiment. Telecommun. Policy 2022, 46, 102440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.T.; Xue, Y.; Hao, Y.; Ren, S.Y. How does internet development affect energy-saving and emission reduction? Evidence from China. Energy Econ. 2021, 102, 105577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.D.; Wang, J.L.; Liu, Y. “Carbon” suppresses “energy”—How does carbon emission right trading policy alleviate the energy trilemma? Energy 2024, 307, 132790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.G.; Bei, H.J.; Wang, C.E.; Chen, G.H. Accelerated Depreciation Tax Credit and Corporate Financialization Based on the PSM-DID Model. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2020, 2020, 6622900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.M.; Sun, S.F. Can environmental protection tax drive manufacturing carbon unlocking? Empirical evidence from China. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 11, 1274785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, M.A.; Seshadri, U.; Kumar, P.; Aqdas, R.; Patwary, A.K.; Riaz, M. Nexus between green finance and climate change mitigation in N-11 and BRICS countries: Empirical estimation through difference in differences (DID) approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 6504–6519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, R.; Tekin, E.; Topalli, V.; Rosenfeld, R. Less Cash, Less Crime: Evidence from the Electronic Benefit Transfer Program. J. Law Econ. 2017, 60, 361–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Ding, Y.G.; Wang, L.Z. Impact of urban-rural medical insurance integration on consumption: Evidence from rural China. Econ. Anal. Policy 2022, 76, 837–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antweiler, W.; Copeland, B.R.; Taylor, M.S. Is free trade good for the environment? Am. Econ. Rev. 2001, 91, 877–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, D.C. Do credit constraints favor dirty production? Theory and plant-level evidence. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2017, 84, 189–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.P.; Song, Y.C. Is There a Conflict between Automation and Environment? Implications of Artificial Intelligence for Carbon Emissions in China. Sustainability. 2023, 15, 12437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Tang, X.; Xi, X.C. The size distribution of firms and industrial water pollution: A quantitative analysis of China. Am. Econ. J.-Macroecon. 2021, 13, 151–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.W.; Liu, L.L.; Luo, D.; Xing, K. The impact of green technology innovation on carbon dioxide emissions: The role of local environmental regulations. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 340, 117990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.P.; Huang, L.Y. How Does Environmental Protection Tax Affect Urban Energy Consumption in China? New Insights from the Intensity Difference-in-Differences Model. Sustainability 2024, 16, 4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.P.; Zhu, Y.Q. Towards Green Development: Identifying the Impact of Population Aging on China’s Carbon Emissions Based on the Provincial Panel Data Analysis. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2024, 33, 4861–4877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, X.L.; Wang, Y.; Ding, Z.Q. Analysis and forecast of the Tianjin industrial carbon dioxide emissions resulted from energy consumption. Int. J. Sustain. Energy 2017, 36, 637–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.H.; Gong, N.J. The estimation of the carbon dioxide emission and driving factors in China based on machine learning methods. Sustain. Prod. Consump 2022, 33, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.Q.; Han, G.; Pei, Z.P.; Yu, H.W.; Li, S.W.; Gong, W. Advanced method for compiling a high-resolution gridded anthro-pogenic CO2 emission inventory at a regional scale. Geo-spat. Inf. Sci. 2025, 28, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, T.; Levine, R.; Levkov, A. Big Bad Banks? The Winners and Losers from Bank Deregulation in the United States. J. Financ. 2012, 65, 1637–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, J.; Sant’Anna, P.H.C. When is parallel trends sensitive to functional form? Econometrica 2023, 91, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambachan, A.; Roth, J. A more credible approach to parallel trends. Rev. Econ. Stud. 2023, 90, 2555–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biasi, B.; Sarsons, H. Flexible wages, bargaining, and the gender gap. Q. J. Econ. 2022, 137, 215–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.D.; Wang, J.L.; Liu, Y. How does auditing outgoing officials’ natural resource asset management policies affect carbon emission efficiency? Evidence from a debiased machine learning model. J. Clean Prod. 2024, 478, 143932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.P.; Meng, Q.Q.; Huang, J. Identifying the Impact of New Digital Infrastructure on Urban Energy Consumption: Evidence from the Broadband China Strategy. Energies 2025, 18, 1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.N.; Feng, Y.; Wang, X. New energy demonstration city and urban pollutant emissions: An analysis based on a spatial difference-in-differences model. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2024, 91, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Variable | Definition | The Entire Sample | Pilot Cities | Non-Pilot Cities | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Obs | Mean | S.D. | VIF | Mean | S.D. | Mean | S.D. | ||
| PCE | Urban carbon emissions | 4794 | 1.074 | 0.701 | — | 1.009 | 0.642 | 1.154 | 0.759 |
| Tax_did | EPT scheme | 4794 | 0.162 | 0.368 | 1.32 | 0.294 | 0.456 | 0 | 0 |
| Pgdp | Economic development | 4794 | 10.529 | 0.722 | 2.00 | 10.542 | 0.704 | 10.514 | 0.743 |
| Indus | The degree of industrialization | 4794 | 0.378 | 0.078 | 1.75 | 0.382 | 0.069 | 0.374 | 0.087 |
| Finance | Financial development | 4794 | 0.643 | 0.254 | 1.99 | 0.606 | 0.242 | 0.689 | 0.261 |
| Revenue | Fiscal revenue | 4794 | 0.069 | 0.025 | 1.60 | 0.067 | 0.026 | 0.071 | 0.024 |
| Sciedu | Science and education level | 4794 | 0.034 | 0.017 | 1.59 | 0.032 | 0.012 | 0.037 | 0.021 |
| Popul | Population density | 4794 | 5.738 | 0.925 | 1.18 | 6.129 | 0.644 | 5.262 | 0.990 |
| Variable | PCE | CE | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | |
| Tax_did | −0.103 *** | −0.111 *** | −0.113 *** | −0.109 *** | −0.178 *** |
| (−7.54) | (−8.14) | (−8.28) | (−7.85) | (−7.39) | |
| Pgdp | 0.108 *** | 0.097 *** | 0.097 *** | 0.756 *** | |
| (4.74) | (4.11) | (4.11) | (18.49) | ||
| Indus | −0.125 | −0.177 | −0.160 | −0.238 | |
| (−1.12) | (−1.59) | (−1.42) | (−1.22) | ||
| Finance | −0.117 *** | −0.129 *** | −0.130 *** | −0.061 | |
| (−3.18) | (−3.45) | (−3.46) | (−0.94) | ||
| Revenue | 1.670 *** | 1.638 *** | 1.490 *** | ||
| (5.45) | (5.34) | (2.80) | |||
| Sciedu | −2.714 *** | −2.604 *** | 0.933 | ||
| (−3.92) | (−3.74) | (0.77) | |||
| Popul | −0.105 * | 0.418 *** | |||
| (−1.70) | (3.90) | ||||
| _Cons | 1.091 *** | 0.078 | 0.201 | 0.794 * | −4.031 *** |
| (286.49) | (0.33) | (0.80) | (1.85) | (−5.43) | |
| ID FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Time FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| R2 | 0.906 | 0.907 | 0.908 | 0.908 | 0.904 |
| F statistic | 56.86 | 27.29 | 24.42 | 21.36 | 77.00 |
| Obs | 4794 | 4794 | 4794 | 4794 | 4794 |
| Variable | CE_GDP | Adjust DID | Adjust Sample | Adjust Interval | PSM-DID | DML | Lag Control | IV Estimation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | |
| Tax_did | −0.065 *** | −0.131 *** | −0.108 ** | −0.089 ** | −0.109 *** | −0.127 *** | −0.109 *** | −0.110 ** |
| (−2.74) | (−3.28) | (−2.45) | (−2.38) | (−2.63) | (−7.89) | (−2.83) | (−2.52) | |
| _Cons | 0.858 | 0.568 | −1.748 | 0.878 | 0.794 | 0.000 | 0.411 | — |
| (1.19) | (0.36) | (−1.29) | (0.54) | (0.50) | (0.07) | (0.24) | — | |
| Control | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| ID FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Time FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| R2 | 0.752 | 0.909 | 0.905 | 0.919 | 0.908 | — | 0.907 | — |
| F statistic | 3.48 | 4.00 | 4.03 | 2.40 | 4.11 | — | 4.19 | 4.07 |
| Obs | 4794 | 4794 | 4199 | 3102 | 4794 | 4794 | 4512 | 4794 |
| K.P.-rk-LM | 251.267 | |||||||
| C.D.-Wald-F | 1.3 × 104 |
| Variable | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tax_did | −0.108 *** | −0.111 *** | −0.111 *** | −0.107 *** | −0.110 *** | −0.187 *** |
| (−2.61) | (−2.67) | (−2.66) | (−2.60) | (−2.63) | (−2.70) | |
| Energy_did | −0.031 | −0.035 | −0.139 ** | |||
| (−0.82) | (−0.94) | (−2.22) | ||||
| Green_did | −0.087 | −0.084 | −0.357 *** | |||
| (−1.08) | (−1.09) | (−3.74) | ||||
| Low_did | −0.025 | −0.018 | −0.088 * | |||
| (−0.85) | (−0.62) | (−1.88) | ||||
| Fiscal_did | −0.122 ** | −0.120 ** | −0.221 *** | |||
| (−2.50) | (−2.45) | (−2.77) | ||||
| _Cons | 0.747 | 0.707 | 0.743 | 0.810 | 0.637 | −4.739 ** |
| (0.48) | (0.44) | (0.47) | (0.53) | (0.42) | (−2.48) | |
| Control | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| ID FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Time FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| R2 | 0.908 | 0.908 | 0.908 | 0.909 | 0.909 | 0.906 |
| F statistic | 3.75 | 3.71 | 3.72 | 4.01 | 3.28 | 10.71 |
| Obs | 4794 | 4794 | 4794 | 4794 | 4794 | 4794 |
| Variable | Geographical Location | Innovation Attribute | Resource Attribute | Industrial Attribute | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| East | Others | Inno | Non-Inno | Non-Res | Res | Non-Old | Old-Ind | |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | |
| Tax_did | −0.001 | −0.169 *** | −0.152 ** | −0.113 ** | −0.182 *** | −0.046 | −0.155 *** | −0.030 |
| (−0.02) | (−3.54) | (−2.42) | (−2.28) | (−3.42) | (−0.66) | (−2.84) | (−0.55) | |
| _Cons | 5.235 *** | −2.174 * | 5.746 *** | −3.106 ** | 5.725 *** | −5.559 *** | 5.338 *** | −3.465 *** |
| (2.88) | (−1.89) | (2.61) | (−2.30) | (3.00) | (−3.82) | (2.67) | (−2.71) | |
| Control | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| ID FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Time FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| R2 | 0.912 | 0.909 | 0.921 | 0.895 | 0.917 | 0.908 | 0.904 | 0.938 |
| F statistic | 11.63 | 7.34 | 6.13 | 3.63 | 3.71 | 5.49 | 4.84 | 3.31 |
| Obs | 1700 | 3094 | 1275 | 3519 | 2856 | 1938 | 3179 | 1615 |
| Variable | Energy Utilization Efficiency | Green Technological Innovation | Industrial Structure Upgrading | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Energy | Energy | PCE | Patent | Patent | PCE | Ind_up | Ind_up | PCE | |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) | |
| Tax_did | 0.183 *** | 0.199 *** | 0.142 *** | 0.182 *** | 0.013 *** | 0.016 *** | |||
| (7.34) | (7.98) | (3.81) | (4.88) | (3.70) | (4.62) | ||||
| Tax_did_high | −0.201 *** | −0.086 *** | −0.089 *** | ||||||
| (−4.28) | (−5.86) | (−6.16) | |||||||
| Tax_did_low | 0.123 *** | −0.021 | 0.002 | ||||||
| (7.71) | (−0.62) | (0.05) | |||||||
| _Cons | 2.939 *** | 3.175 *** | 1.297 *** | −7.888 *** | −7.518 *** | 0.826 ** | 5.199 *** | 5.230 *** | 0.668 |
| (3.82) | (4.11) | (3.21) | (−6.86) | (−6.52) | (2.02) | (47.39) | (47.49) | (1.62) | |
| Control | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| ID FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Time FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| R2 | 0.719 | 0.720 | 0.641 | 0.898 | 0.899 | 0.637 | 0.955 | 0.955 | 0.638 |
| F statistic | 15.04 | 16.46 | 334.14 | 23.24 | 24.61 | 328.62 | 2197.84 | 2202.68 | 329.07 |
| Wald test | 44.47 | 3.20 | 4.56 | ||||||
| Obs | 4794 | 4794 | 4794 | 4794 | 4794 | 4794 | 4794 | 4794 | 4794 |
| Variable | Spatial Contiguity Weight Matrix (W1) | Geographical Distance Weight Matrix (W2) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coefficient | Direct | Indirect | Total | Coefficient | Direct | Indirect | Total | |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | |
| Tax_did | −0.092 *** | −0.093 *** | −0.035 *** | −0.128 *** | −0.097 *** | −0.099 *** | −0.595 *** | −0.694 *** |
| (−7.08) | (−6.87) | (−6.24) | (−6.83) | (−7.46) | (−7.23) | (−3.27) | (−3.68) | |
| ρ | 0.289 *** | 0.854 *** | ||||||
| (17.17) | (26.08) | |||||||
| Control | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| ID FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Time FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| R2 | 0.218 | 0.320 | ||||||
| Log-Lik | 917.841 | 887.261 | ||||||
| Obs | 4794 | 4794 | 4794 | 4794 | 4794 | 4794 | 4794 | 4794 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, X.; Fu, Y.; Meng, Q.; Hu, J. Identifying the Impact of Climate Policy on Urban Carbon Emissions: New Insights from China’s Environmental Protection Tax Reform. Sustainability 2025, 17, 7898. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17177898
Xu X, Fu Y, Meng Q, Hu J. Identifying the Impact of Climate Policy on Urban Carbon Emissions: New Insights from China’s Environmental Protection Tax Reform. Sustainability. 2025; 17(17):7898. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17177898
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Xianpu, Yiqi Fu, Qiqi Meng, and Jiarui Hu. 2025. "Identifying the Impact of Climate Policy on Urban Carbon Emissions: New Insights from China’s Environmental Protection Tax Reform" Sustainability 17, no. 17: 7898. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17177898
APA StyleXu, X., Fu, Y., Meng, Q., & Hu, J. (2025). Identifying the Impact of Climate Policy on Urban Carbon Emissions: New Insights from China’s Environmental Protection Tax Reform. Sustainability, 17(17), 7898. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17177898






