Application of Machine Learning Approaches to Predict Soil Element Background Concentration at Large Region Scale
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
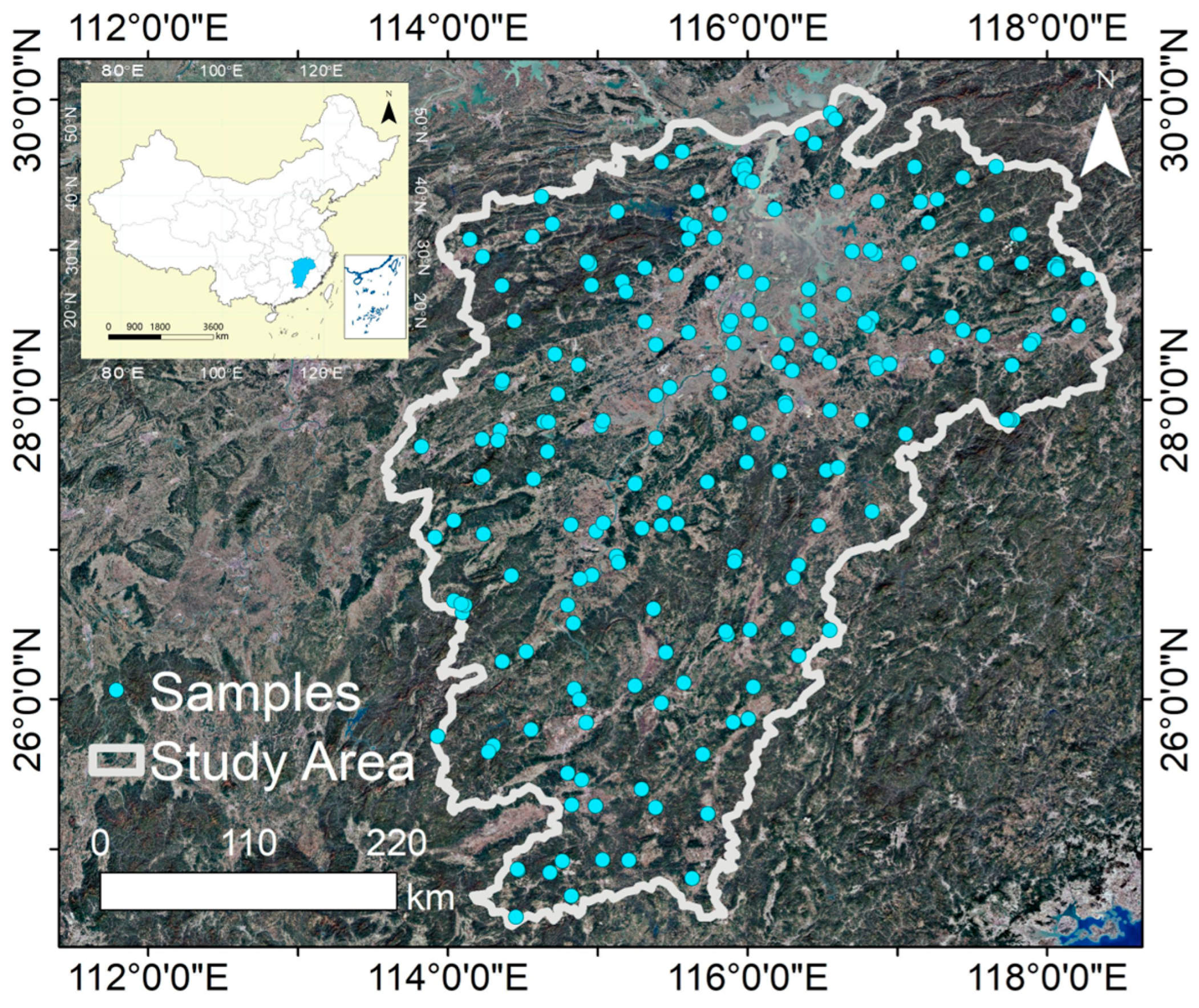
2.1. Study Area and Data Sources
2.2. Theoretical Framework
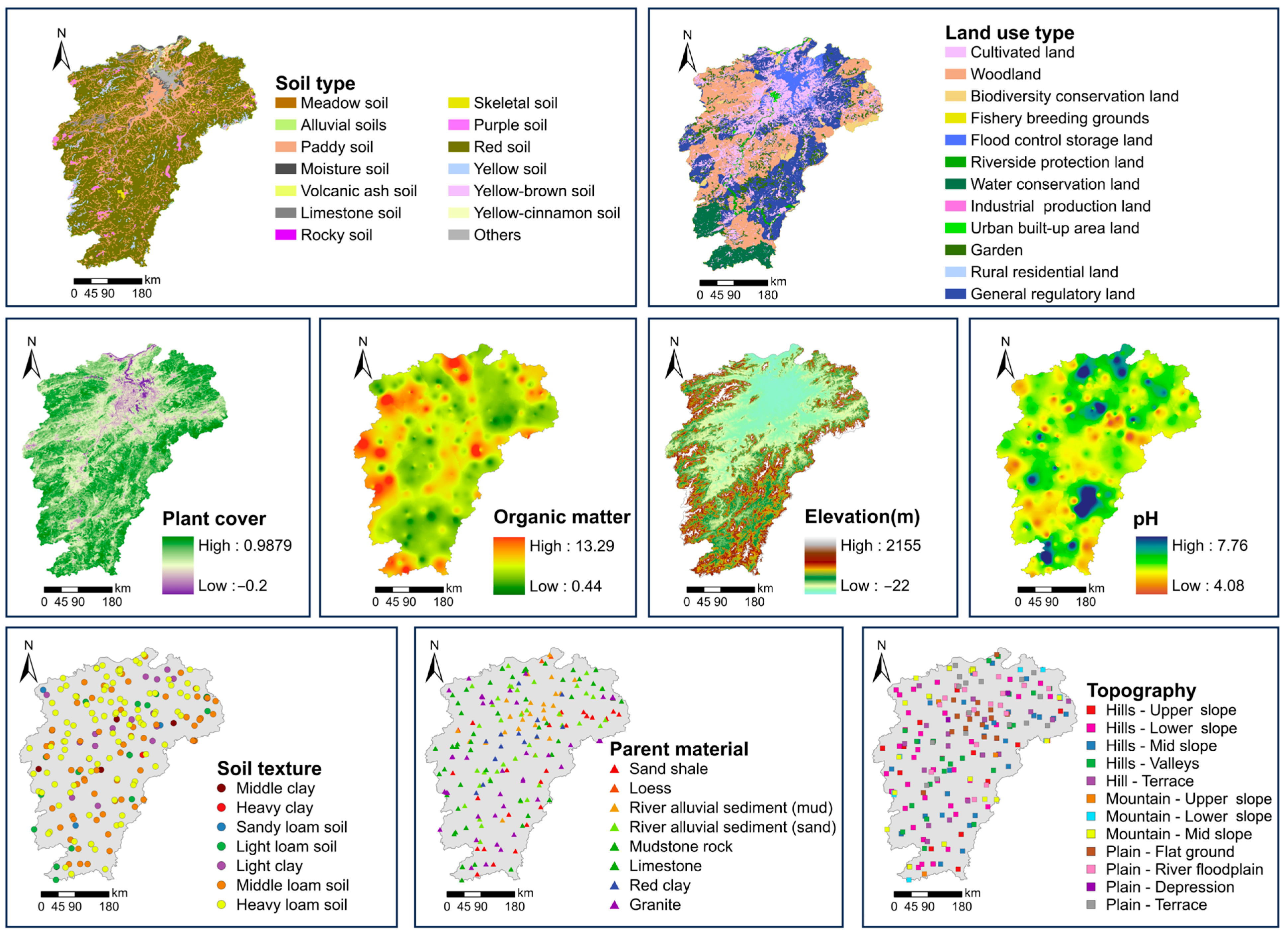
2.3. Digitization of Environmental Variables
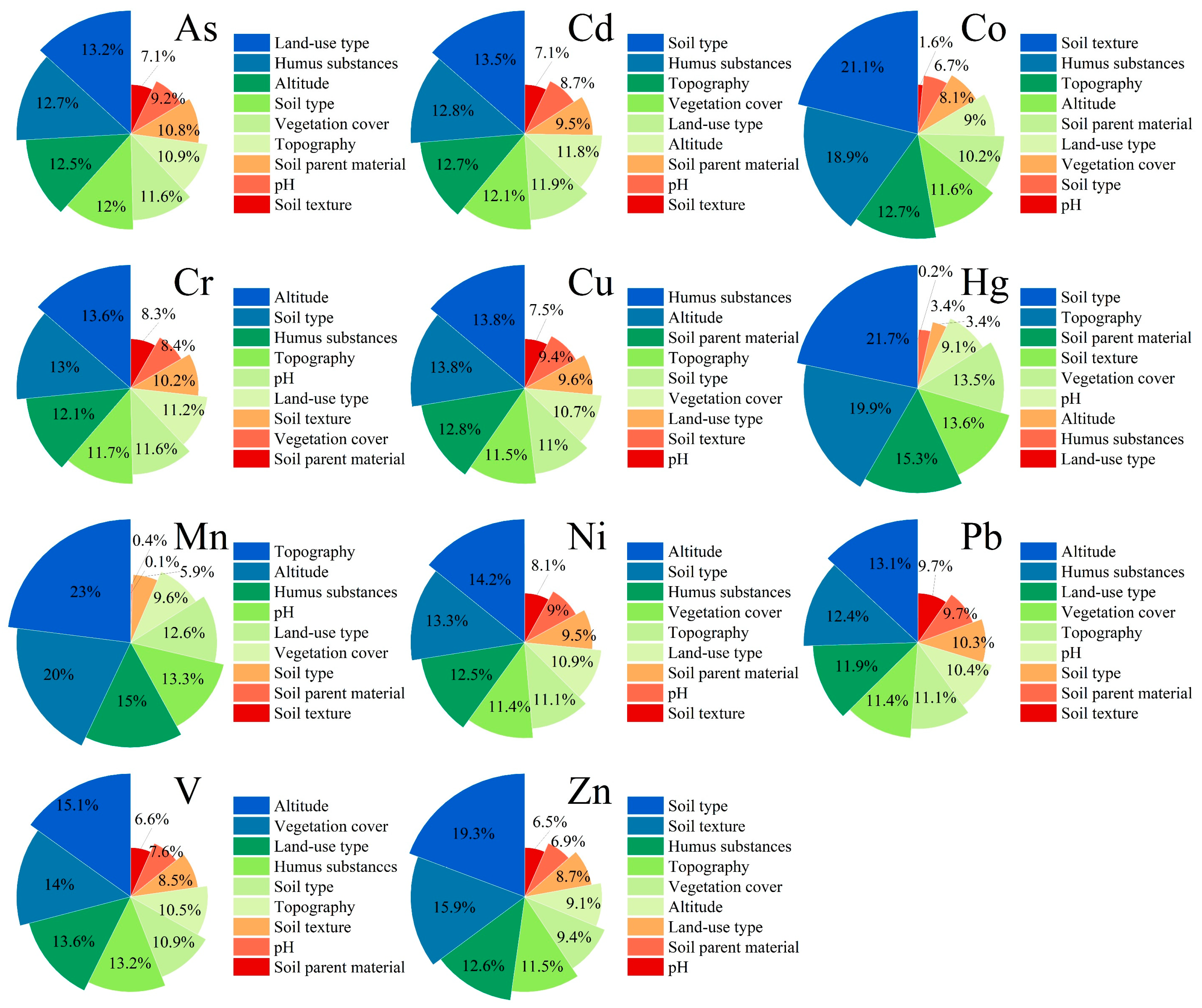
2.4. Identification of Environmental Variables Importance
2.5. Machine Learning Models
2.5.1. Decision Tree
2.5.2. Random Forest
2.5.3. Extreme Gradient Boosting
2.5.4. Support Vector Machine
2.6. Model Implementation and Performance Evaluation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Environmental Variables Affecting Soil Element Background Concentrations
3.1.1. Descriptive Statistics of Soil Element Background Concentrations in Different Environmental Variables
3.1.2. Importance of Environmental Variables for Predicted Results
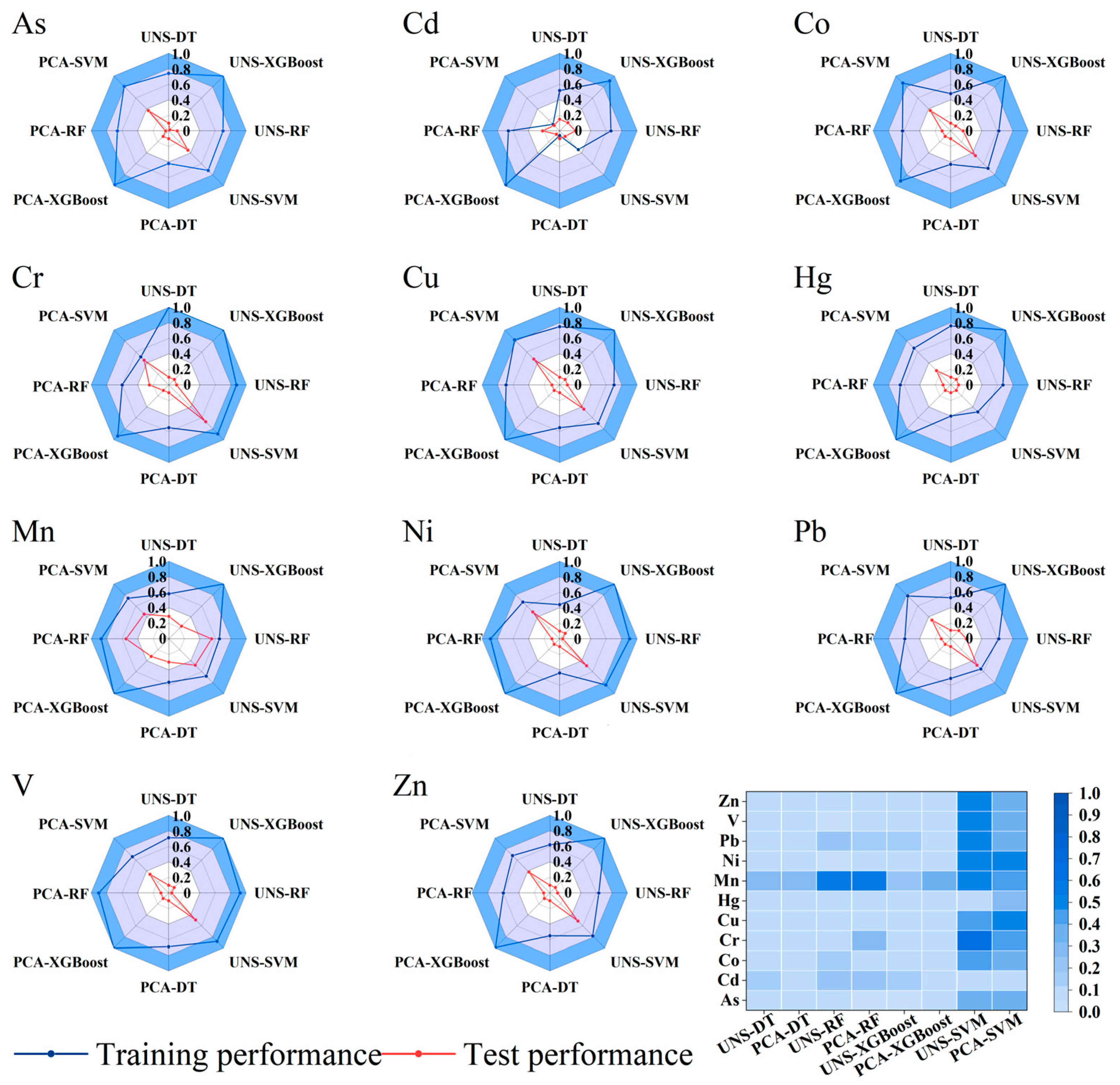
3.2. Comparison of Model Performance
3.2.1. Model Performance Evaluation
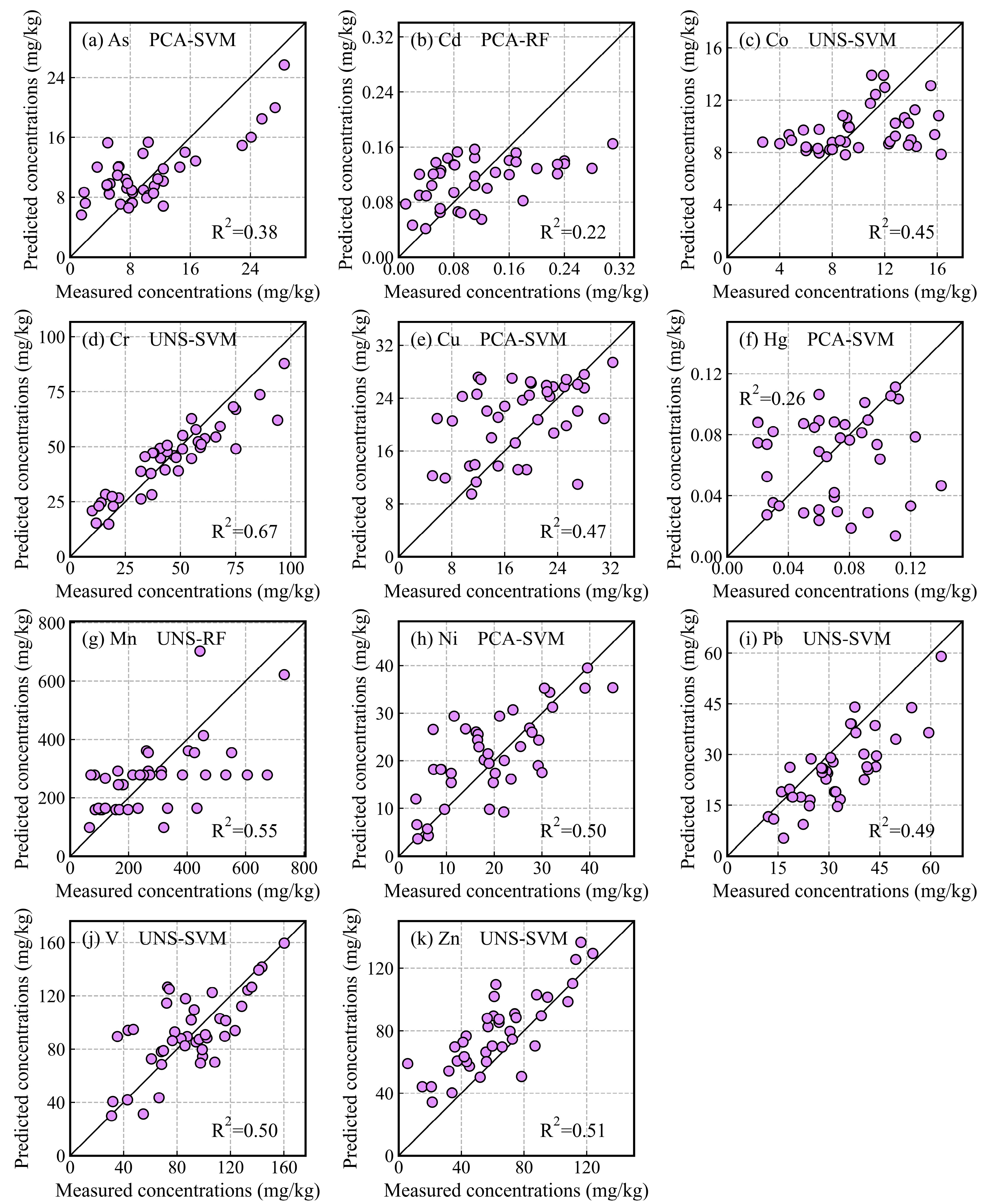
3.2.2. Prediction Accuracy of Heavy Metals in Soil
3.3. Regional Comparisons of SBGs: Validation of Predictive Results
3.4. Advantages, Limitations and Future Research Perspectives
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DT | Decision tree |
| RF | Random forest |
| XGBoost | Extreme gradient boosting |
| SVM | Support vector machine |
| ML | Machine learning |
| As | Arsenic |
| Cd | Cadmium |
| Co | Cobalt |
| Cr | Chromium |
| Cu | Copper |
| Hg | Mercury |
| Mn | Manganese |
| Ni | Nickel |
| Pb | Lead |
| V | Vanadium |
| Zn | Zinc |
| GLM | General linear models |
| DDTC | Diethyldithiocabamate |
| UNS | Unfiltered input |
| PCA | Principal component analysis |
| KMO | Kaiser–Meyer–Olkin |
| MLR | Multiple linear regression |
| R2 | The coefficient of determination |
| RMSE | Root mean squared error |
| MAE | Mean absolute error |
| K–W | Kruskal–Wallis |
References
- Silva, F.L.; Martins E Silva, M.H.; Veiga, J.B.; Silva, A.C.S.; Carvalho, M.A.C.; Weber, O.L.S.; Eguchi, E.S.; López-Alonso, M.; Oliveira-Júnior, E.S.; Guilherme, L.R.G.; et al. Assessing Background Levels of Trace Elements in Soils of Mato Grosso (Brazil) for Environmental and Food Security. Catena 2024, 244, 108267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, V.; Sohrabi, N.; Lak, R.; Tajbakhsh, G. Estimation of Natural Background Levels of Heavy Metals and Major Variables in Groundwater to Ensure the Sustainable Supply of Safe Drinking Water in Fereidan, Iran. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 26, 19807–19832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulieman, M.M.; Kaya, F.; Keshavarzi, A.; Hussein, A.M.; Al-Farraj, A.S.; Brevik, E.C. Spatial Variability of Some Heavy Metals in Arid Harrats Soils: Combining Machine Learning Algorithms and Synthetic Indexes Based-Multitemporal Landsat 8/9 to Establish Background Levels. Catena 2024, 234, 107579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meloni, F.; Nisi, B.; Gozzi, C.; Rimondi, V.; Cabassi, J.; Montegrossi, G.; Rappuoli, D.; Vaselli, O. Background and Geochemical Baseline Values of Chalcophile and Siderophile Elements in Soils around the Former Mining Area of Abbadia San Salvatore (Mt. Amiata, Southern Tuscany, Italy). J. Geochem. Explor. 2023, 255, 107324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Deng, W.; Yang, X. The Background Concentrations of 13 Soil Trace Elements and Their Relationships to Parent Materials and Vegetation in Xizang (Tibet), China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2002, 21, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascarenhas, R.B.; Gloaguen, T.V.; Hadlich, G.M.; Gomes, N.S.; Almeida, M.D.C.; Souza, E.D.S.; Bomfim, M.R.; Costa, O.D.V.; Gonzaga Santos, J.A. The Challenge of Establishing Natural Geochemical Backgrounds in Human-Impacted Mangrove Soils of Northeastern Brazil. Chemosphere 2025, 376, 144261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, X.; Ji, J.; Zhang, C.; Yang, Z.; Shi, H. Carbonate Bedrock Control of Soil Cd Background in Southwestern China: Its Extent and Influencing Factors Based on Spatial Analysis. Chemosphere 2022, 290, 133390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkhordari, M.S.; Qi, C. Prediction of Soil Arsenic Concentration in European Soils: A Dimensionality Reduction and Ensemble Learning Approach. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2025, 17, 100604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Wan, X.; Lei, M.; Gu, G.; Chen, T. Influencing Factors and Prediction of Arsenic Concentration in Pteris Vittata: A Combination of Geodetector and Empirical Models. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 292, 118240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Lu, Y.; Li, L.; Zeng, F.; Li, X.; Li, L.; Yue, J. Elevational Patterns in the Diversity and Composition of Soil Archaeal and Bacterial Communities Depend on Climate, Vegetation, and Soil Properties in an Arid Mountain Ecosystem. Catena 2025, 249, 108679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkpatrick, J.B.; Green, K.; Bridle, K.L.; Venn, S.E. Patterns of Variation in Australian Alpine Soils and Their Relationships to Parent Material, Vegetation Formation, Climate and Topography. Catena 2014, 121, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- More, S.; Dhakate, R. Geogenic and Anthropogenic Sources of Heavy Metals in Soil: An Ecological and Health Risk Assessment in the Granitic Terrain of South India. Catena 2025, 254, 108960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gałązka, A.; Marzec-Grządziel, A.; Grządziel, J.; Varsadiya, M.; Pawlik, Ł. Fungal Genetic Biodiversity and Metabolic Activity as an Indicator of Potential Biological Weathering and Soil Formation—Case Study of towards a Better Understanding of Earth System Dynamics. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 141, 109136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, K.; Mancini, M.; Libohova, Z.; Blackstock, J.; Winzeler, E.; Smith, D.R.; Owens, P.R.; Silva, S.H.G.; Curi, N. Heavy Metals Concentration in Soils across the Conterminous USA: Spatial Prediction, Model Uncertainty, and Influencing Factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 919, 170972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Wang, J.; Zhou, K.; Zhang, W.; Chen, A. Uncertainty in Soil Elemental Prediction Using Machine Learning and Hyperspectral Remote Sensing. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 494, 138502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proshad, R.; Asharaful Abedin Asha, S.M.; Tan, R.; Lu, Y.; Abedin, M.A.; Ding, Z.; Zhang, S.; Li, Z.; Chen, G.; Zhao, Z. Machine Learning Models with Innovative Outlier Detection Techniques for Predicting Heavy Metal Contamination in Soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 481, 136536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Huang, C. Machine Learning-Supported Determination for Site-Specific Natural Background Values of Soil Heavy Metals. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 487, 137276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Huang, G.; Tang, N.; Lu, P.; Jiang, L.; Lv, J.; Qin, Y.; Lin, Y.; Xu, F.; Lei, D. Effects of Heavy Metal Exposure on Hypertension: A Machine Learning Modeling Approach. Chemosphere 2023, 337, 139435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Guan, D.-X.; Zhang, C.; Yu, T.; Li, C.; Wu, Z.; Li, B.; Geng, W.; Wu, T.; Yang, Z. Improved Mapping of Heavy Metals in Agricultural Soils Using Machine Learning Augmented with Spatial Regionalization Indices. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 478, 135407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Yang, Y. Revealing the Synergistic Spatial Effects in Soil Heavy Metal Pollution with Explainable Machine Learning Models. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 482, 136578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barkhordari, M.S.; Qi, C. Prediction of Zinc, Cadmium, and Arsenic in European Soils Using Multi-End Machine Learning Models. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 490, 137800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Hou, H.; Huang, Z.; Zhao, L. Estimation of Heavy Metal Soil Contamination Distribution, Hazard Probability, and Population at Risk by Machine Learning Prediction Modeling in Guangxi, China. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 330, 121607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Wang, X.; Liu, T.; Wei, W.; Zhang, F.; Huang, M.; Liu, H. Enhancing Water Quality Prediction with Advanced Machine Learning Techniques: An Extreme Gradient Boosting Model Based on Long Short-Term Memory and Autoencoder. J. Hydrol. 2024, 644, 132115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.L.; Xu, G.Y.; Zhu, H.M.; Peng, G.H. Study on Soil Enrionmental Background Values in Jiangxi Province; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Hartemink, A.E.; Bockheim, J.G. Soil Genesis and Classification. Catena 2013, 104, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, P.; Zhang, Z.; Gu, Y.; Xiao, L.; Liu, X.; Wang, B. Integrating Machine Learning for Enhanced Spatial Prediction and Risk Assessment of Soil Heavy Metal(Loid)s. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 383, 126919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostami, A.A.; Sedghi, Z.; Nadiri, A.A.; Barzegar, R.; Dimova, N.T.; Senapathi, V.; Islam, A.R.M.T. Harnessing Deep Learning for Fusion-Based Heavy Metal Contamination Index Prediction in Groundwater. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2025, 274, 104672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinlan, J.R. Induction of Decision Trees. Mach. Learn. 1986, 1, 81–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L.; Friedman, J.H.; Olshen, R.A.; Stone, C.J. Classification and Regression Trees, 1st ed.; Routledge: London, UK, 2017; ISBN 978-1-315-13947-0. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Wang, X.; Luo, X.; Huang, G.; Tian, Z.; Li, W.; Liu, F. Delineating and Identifying Risk Zones of Soil Heavy Metal Pollution in an Industrialized Region Using Machine Learning. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 318, 120932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yin, A.; Yang, X.; Fan, M.; Shao, S.; Wu, J.; Wu, P.; Zhang, M.; Gao, C. Use of Machine-Learning and Receptor Models for Prediction and Source Apportionment of Heavy Metals in Coastal Reclaimed Soils. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 122, 107233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.H. Stochastic Gradient Boosting. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2002, 38, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suleymanov, A.; Suleymanov, R.; Kulagin, A.; Yurkevich, M. Mercury Prediction in Urban Soils by Remote Sensing and Relief Data Using Machine Learning Techniques. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. XGBoost: A Scalable Tree Boosting System. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13 August 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-Vector Networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vapnik, V.N. Statistical Learning Theory (Adaptive and Learning Systems for Signal Processing, Communications, and Control); Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1998; ISBN 978-0-471-03003-4. [Google Scholar]
- Park, Y.; Cho, K.H.; Park, J.; Cha, S.M.; Kim, J.H. Development of Early-Warning Protocol for Predicting Chlorophyll-a Concentration Using Machine Learning Models in Freshwater and Estuarine Reservoirs, Korea. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 502, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varley, A.; Tyler, A.; Smith, L.; Dale, P.; Davies, M. Remediating Radium Contaminated Legacy Sites: Advances Made through Machine Learning in Routine Monitoring of “Hot” Particles. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 521, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Guo, G.; Zhang, D.; Lei, M.; Wang, Y. Accurate prediction of spatial distribution of soil potentially toxic elements using machine learning and associated key influencing factors identification: A case study in mining and smelting area in southwestern China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 478, 135454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccolo, A.; Spaccini, R.; De Martino, A.; Scognamiglio, F.; Di Meo, V. Soil Washing with Solutions of Humic Substances from Manure Compost Removes Heavy Metal Contaminants as a Function of Humic Molecular Composition. Chemosphere 2019, 225, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xiong, Z.; Jiang, X.; Liu, G.; Liu, W. Heavy Metal Concentrations in Riparian Soils along the Han River, China: The Importance of Soil Properties, Topography and Upland Land Use. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 97, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackwell, B.D.; Driscoll, C.T. Deposition of Mercury in Forests along a Montane Elevation Gradient. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 5363–5370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Shen, C.; Tang, H.; Huang, Y. Soil Type Data Provide New Methods and Insights for Heavy Metal Pollution Assessment and Driving Factors Analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 135868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xiao, J.; Wang, L.; Liang, T.; Guo, Q.; Guan, Y.; Rinklebe, J. Elucidating the Differentiation of Soil Heavy Metals under Different Land Uses with Geographically Weighted Regression and Self-Organizing Map. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 260, 114065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaşar Korkanç, S.; Korkanç, M.; Amiri, A.F. Effects of Land Use/Cover Change on Heavy Metal Distribution of Soils in Wetlands and Ecological Risk Assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 923, 171603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Chen, Z.; Li, Y.; Ding, K.; Liu, W.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, M.; Baker, A.J.M.; Yang, W.; et al. Factors Influencing Heavy Metal Availability and Risk Assessment of Soils at Typical Metal Mines in Eastern China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 400, 123289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yang, Z.; Guan, D.-X.; Yu, T.; Jiang, Z.; Wu, X.; Yang, Y.; Luan, S.; Xu, H.; Huang, C.; et al. Spatial-Machine Learning Framework for Rapid Identification of Soil Cadmium Risk in High Geochemical Background Areas. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 492, 138091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradpour, S.; Entezari, M.; Ayoubi, S.; Karimi, A.; Naimi, S. Digital Exploration of Selected Heavy Metals Using Random Forest and a Set of Environmental Covariates at the Watershed Scale. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 455, 131609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Ma, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, J.; He, W.; Chen, Y.; Weng, L. Application of Machine Learning Approaches to Predict Ammonium Nitrogen Transport in Different Soil Types and Evaluate the Contribution of Control Factors. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 284, 116867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, X.; Zong, M.; Zhu, X.; Cheng, D. Learning k for kNN Classification. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2017, 8, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| ML Model | Indicator Screening Method | Scenario Settings |
|---|---|---|
| DT | UNS | Scenario 1: UNS-D |
| PCA | Scenario 2: PCA-DT | |
| RF | UNS | Scenario 3: UNS-RF |
| PCA | Scenario 4: PCA-RF | |
| XGBoost | UNS | Scenario 5: UNS-XGBoost |
| PCA | Scenario 6: PCA-XGBoost | |
| SVM | UNS | Scenario 7: UNS-SVM |
| PCA | Scenario 8: PCA-SVM |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Meng, L.; Li, T.; Xue, P.; Wang, H.; Hua, J. Application of Machine Learning Approaches to Predict Soil Element Background Concentration at Large Region Scale. Sustainability 2025, 17, 7853. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17177853
Li J, Meng L, Li T, Xue P, Wang H, Hua J. Application of Machine Learning Approaches to Predict Soil Element Background Concentration at Large Region Scale. Sustainability. 2025; 17(17):7853. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17177853
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jiao, Linglong Meng, Tianran Li, Pengli Xue, Hejing Wang, and Jie Hua. 2025. "Application of Machine Learning Approaches to Predict Soil Element Background Concentration at Large Region Scale" Sustainability 17, no. 17: 7853. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17177853
APA StyleLi, J., Meng, L., Li, T., Xue, P., Wang, H., & Hua, J. (2025). Application of Machine Learning Approaches to Predict Soil Element Background Concentration at Large Region Scale. Sustainability, 17(17), 7853. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17177853





