1. Introduction
Food safety management has undergone significant development over the past decades, with the Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HACCP) system established as a global benchmark for hazard prevention in food production. HACCP has been widely adopted internationally due to its structured methodology, which ensures food safety through hazard identification, monitoring, and control [
1]. However, while HACCP effectively addresses foodborne risks, it does not incorporate environmental sustainability into its framework. This gap is critical given the rising pressures of climate change, resource scarcity, and global commitments to the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
Current industrial practices associated with HACCP often result in excessive water consumption, high energy demand, and chemical-intensive sanitation. For instance, dairy and seafood processing facilities can consume between 5 and 10 L of water per kilogram of product, and food production contributes up to 26% of global greenhouse gas emissions [
2,
3,
4]. Such impacts highlight the necessity of integrating sustainability considerations into food safety systems.
While HACCP has achieved near-universal adoption as a food safety standard, its scope remains primarily limited to contamination prevention and product integrity. However, environmental challenges linked to food production—including water scarcity, energy intensity, and waste generation—are largely unaddressed within the HACCP framework. This gap is increasingly critical given global commitments to sustainability and the SDGs, which call for integrated approaches to food safety, environmental protection, and resource efficiency. To address this unmet need, the present study proposes the Green HACCP framework, embedding environmental respect practices into HACCP’s preventive system to simultaneously ensure food safety and reduce ecological impact.
The Green HACCP framework extends traditional HACCP by incorporating Environmental Respect Practices (ERPs), defined here as operational measures aimed at reducing water, energy, and chemical footprints while maintaining compliance with food safety requirements. ERPs provide a systematic way to ensure that hazard control is achieved alongside ecological stewardship.
The novelty of this study lies in conceptualizing Green HACCP as a dual-purpose model that bridges food safety and sustainability. Unlike previous HACCP-centered approaches, which focused narrowly on contamination prevention, this work emphasizes measurable environmental outcomes (e.g., reductions in utility consumption, emissions, and waste), supported by both literature and practical industry examples.
Digital technologies such as IoT, AI, and blockchain are recognized as enablers of sustainability and efficiency within HACCP frameworks. While their technical details are not the focus here, they are introduced as illustrative tools that enhance monitoring, predictive optimization, and traceability in Green HACCP.
This paper is structured as a conceptual study with two main objectives: (i) to present and refine the principles of Green HACCP, contrasting them with traditional HACCP; and (ii) to evaluate its feasibility, challenges, and potential for integration into global food safety frameworks. By doing so, the paper contributes to academic discourse by linking HACCP to sustainability goals and to practice by offering guidance for policymakers and industry stakeholders.
International standards such as the
Codex Alimentarius and ISO 22000 provide the foundation for HACCP implementation worldwide (FAO/WHO Codex, 2022) [
5]. While these frameworks emphasize food safety compliance, they only briefly touch upon environmental considerations. The proposed Green HACCP framework complements these standards by embedding environmental sustainability more explicitly, rather than revising or replacing them.
This conceptual framework also aligns with the broader sustainability discourse, particularly in relation to the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). By embedding environmental criteria into food safety management, Green HACCP directly contributes to SDG 2 (Zero Hunger), SDG 3 (Good Health and Well-Being), SDG 6 (Clean Water and Sanitation), and SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production). The integration of sustainability into food safety practices reflects the growing academic and policy consensus on the need for agri-food systems that are both safe and environmentally responsible [
3,
4,
6,
7].
2. Background and Principles of Green HACCP
2.1. Origin and Development of HACCP
The Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HACCP) system was conceptualized in the late 1950s in response to the U.S. space program’s demand for microbiologically safe food that met zero-defect criteria. This pioneering initiative was developed jointly by NASA, Pillsbury, and the U.S. Army Natick Research Laboratories, marking a paradigm shift from traditional end-product testing toward preventive process control [
1]. The core innovation of HACCP was its emphasis on identifying, evaluating, and monitoring biological, chemical, and physical hazards at critical points in the food production chain, thereby preventing contamination before it occurs.
The success of the HACCP model in achieving safe, consistent food quality led to its progressive adoption across global food industries throughout the 1970s and 1980s. Recognizing its efficacy, the
Codex Alimentarius Commission endorsed HACCP in the early 1990s as the preferred framework for food safety assurance [
8]. Subsequently, many governments institutionalized HACCP in their national regulations. In the European Union, HACCP became mandatory through Directive 93/43/EEC, and later reinforced by Regulation (EC) No 178/2002, which requires all food business operators to implement HACCP-based procedures as part of food hygiene legislation [
5,
9].
HACCP has achieved global recognition as a food safety benchmark, endorsed by
Codex Alimentarius and integrated into ISO 22000 standards [
8]. While its worldwide adoption has ensured baseline food safety compliance, environmental performance has remained largely outside its scope.
2.2. Integration of Environmental Respect Practices (ERPs)
To address the environmental limitations of traditional HACCP systems, the Green HACCP framework incorporates Environmental Respect Practices (ERPs) as an essential component of sustainable food safety management. ERPs focuses on resource efficiency, pollution prevention, and eco-friendly operational strategies, aligning food production with broader environmental sustainability goals [
6,
7,
10]. This integration ensures that food safety is not achieved at the expense of natural resource depletion or environmental degradation, making Green HACCP a dual-purpose model that addresses both hazard prevention and environmental stewardship. These environmental respect practices not only reduce the ecological footprint of food industries but also reinforce international commitments to sustainability and climate resilience. The Green HACCP framework aligns with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): SDG 6 (Clean Water and Sanitation) through water efficiency measures [
11], SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production) via sustainable agri-food supply chains [
4,
6], and SDG 13 (Climate Action) by lowering carbon emissions and promoting circular economy practices [
2,
3]. Furthermore, advances in food quality management under Industry 4.0 [
12] and integrated hygiene control strategies [
7] provide innovative tools for achieving these sustainability targets. This alignment underscores the dual role of Green HACCP in safeguarding both public health and planetary boundaries.
To extend HACCP toward sustainability, Green HACCP introduces Environmental Respect Practices (ERPs), focusing on water, energy, and waste management as core environmental dimensions.
Traditional HACCP does not directly address environmental impacts such as water consumption. Green HACCP integrates water efficiency monitoring, often supported by IoT-enabled sensors, reducing water use by up to 25% in dairy and beverage facilities [
11,
13].
Energy conservation is embedded as a cross-cutting ERP principle, with case reports showing reductions of 10–15% through optimization of heating and refrigeration cycles [
7].
Waste minimization is also prioritized, aligning with SDG 12 on responsible consumption and production [
4,
6].
Water is an important input in food processing, especially for cleaning, disinfection, and ingredient handling. Traditional HACCP systems typically do not limit water usage, resulting in high levels of consumption and wastewater discharge [
6]. In contrast, Green HACCP promotes advanced water-saving techniques, such as automated clean-in-place (CIP) systems, high-efficiency nozzles, real-time water flow monitoring, and wastewater recycling [
13]. These strategies can reduce water use by 20–40% in industrial settings without compromising sanitation or safety [
11].
- 2.
Reduction in Chemical Waste
The use of strong chemical detergents and disinfectants in traditional HACCP practices raises concerns about environmental toxicity and chemical runoff, especially in plants with insufficient effluent treatment systems [
14]. Green HACCP encourages the use of biodegradable, non-toxic, and food-grade cleaning agents, as well as eco-friendly sterilization methods, including ozonation and UV-C light treatment [
15,
16]. These alternatives not only reduce the environmental impact but also improve worker safety and product quality.
- 3.
Paperless Documentation and Digital Traceability
Conventional HACCP systems rely heavily on manual documentation for monitoring and compliance, often resulting in excessive paper use and inefficiencies in data access. Green HACCP supports the digitalization of records, utilizing cloud-based platforms, IoT-enabled sensors, and blockchain technologies to manage traceability and audit readiness in a secure, transparent, and sustainable manner [
17,
18]. Digital systems improve response time during contamination events and reduce administrative costs, while also lowering the ecological footprint of documentation processes.
- 4.
Energy Efficiency and Carbon Footprint Reduction
Traditional HACCP does not account for the energy intensity of food processing operations, often relying on outdated and inefficient equipment. Green HACCP incorporates energy-efficient technologies, such as variable-speed motors, heat recovery systems, and smart thermostatic controls, to reduce electricity and fuel usage [
4]. Additionally, renewable energy integration, such as solar thermal systems and biogas recovery, helps lower carbon emissions from food production facilities [
2]. These strategies align with both ISO 14001 guidelines and corporate sustainability reporting standards.
By embedding ERPs into HACCP protocols, Green HACCP contributes not only to environmental protection but also to cost savings, process optimization, and regulatory alignment. Companies implementing Green HACCP often report lower utility bills, improved resource efficiency, and enhanced compliance with both food safety and environmental regulations [
7,
19]. As such, the ERP dimension of Green HACCP offers an attractive, scalable, and forward-looking strategy for modern food industries navigating the dual demands of safety and sustainability.
2.3. Key Principles of Green HACCP
The Green HACCP framework extends the seven foundational principles of traditional HACCP—established by the Codex Alimentarius—by integrating environmental sustainability into each step. This approach maintains the core focus on food safety while concurrently addressing resource efficiency, waste minimization, and environmental risk mitigation. Each principle is adapted to reflect dual responsibility: preventing hazards and reducing environmental impact.
In addition to identifying biological, chemical, and physical hazards in food production, Green HACCP requires an evaluation of environmental risks associated with each step of the process. This includes assessing potential sources of water pollution, excessive energy consumption, and chemical discharge [
6,
7,
10]. For instance, hazard analysis in a seafood facility would not only examine pathogen contamination but also examine the ecotoxicity of cleaning effluents.
- 2.
Determine Critical Control Points (CCPs) for Food and Environment
Green HACCP expands the identification of CCPs to include points where both food safety hazards and environmental impacts can be controlled. These might include sanitation processes, cooking stages, or packaging operations, where food safety measures can be paired with sustainability interventions (e.g., water reuse, low-energy sterilization) [
3].
- 3.
Set Dual Critical Limits (Food Safety + Environmental Thresholds)
Critical limits are traditionally used to define acceptable levels of food safety indicators. In Green HACCP, these limits are expanded to include environmental performance indicators, such as maximum allowable water usage per unit of output, permissible CO
2 emissions per processing cycle, or acceptable levels of biodegradable cleaning agents [
2,
4].
- 4.
Establish a Real-Time Monitoring System for Safety and Sustainability
Effective Green HACCP implementation depends on integrated digital monitoring systems. IoT-enabled sensors can measure temperature, humidity, and water flow in real time, while AI-driven analytics predict equipment failures or resource overuse [
17,
20]. These tools allow for early intervention and continuous compliance with both safety and sustainability metrics.
- 5.
Determine Corrective Actions for Food and Environmental Deviations
Corrective actions in Green HACCP are designed to restore compliance with both safety and environmental targets. For example, if excessive water usage is detected during sanitation, operations may be paused to adjust the cleaning protocol while also ensuring microbial risk remains controlled [
13]. Contingency planning becomes more robust and aligned with multi-objective performance criteria.
- 6.
Apply Verification Procedures Including Environmental Audits
Verification in Green HACCP includes traditional HACCP validation (e.g., microbiological testing), along with environmental audits, life cycle assessments (LCA), and compliance checks against frameworks like ISO 14001 [
16,
20]. These verification tools ensure that sustainability goals are being achieved in practice, not just in design.
- 7.
Develop a Digital Traceability and Documentation System
Green HACCP emphasizes paperless documentation to minimize waste and improve accessibility. Blockchain-based platforms are increasingly used to record critical data, including resource consumption, energy usage, and environmental KPIs, along with traditional food safety logs [
18,
21]. This improves supply chain transparency and audit readiness.
A defining feature of Green HACCP is the institutionalization of environmental responsibility across all departments. This principle promotes a “Green Culture”, where staff in quality assurance, operations, maintenance, and logistics are encouraged to participate in sustainability training, share environmental performance data, and support green innovation [
7,
19]. Leadership commitment and employee engagement are key to embedding sustainability into daily food safety practices.
By embedding environmental considerations into each HACCP principle, Green HACCP creates a multi-dimensional risk management system that supports both public health and environmental sustainability. This integrated approach aligns with ISO 22000, ISO 14001, and the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), providing food companies with a holistic, future-ready framework for responsible production.
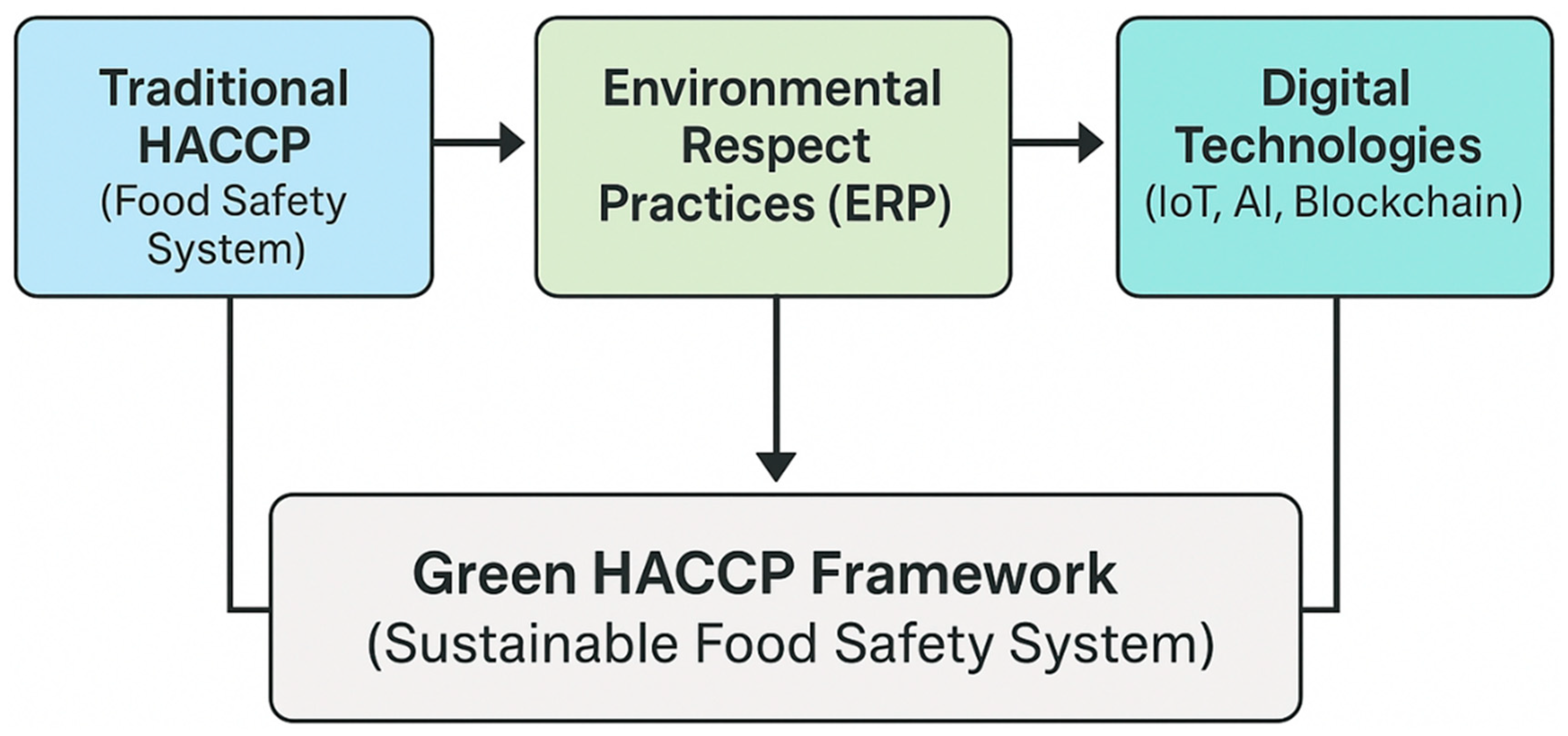
Figure 1 presents the conceptual framework of Green HACCP, integrating Traditional HACCP, Environmental Respect Practices (ERPs), and digital technologies into a unified sustainable food safety system. Traditional HACCP ensures hazard identification and control, while ERPs add environmental priorities like water and energy efficiency, waste reduction, and sustainability. Digital tools such as IoT, AI, and blockchain support real-time monitoring, predictive optimization, and supply chain transparency. Together, these elements create a future-ready framework that enhances both food safety and environmental responsibility.
The novelty of Green HACCP lies in extending the traditional seven principles beyond food safety hazards to include environmental hazards. For example, hazard analysis (Principle 1) now encompasses ecological risks such as water discharge or CO2 emissions. Critical control points (Principle 2) are redefined to include environmental checkpoints, such as energy-intensive stages. Monitoring (Principle 4) leverages digital tools (IoT, AI) to track both safety and environmental metrics. Corrective actions (Principle 5) include mitigation strategies like recycling water or shifting to renewable energy sources. Thus, while the framework remains faithful to HACCP’s logic, its scope expands to embed sustainability directly into operational control.
3. Comparative Analysis: Traditional HACCP vs. Green HACCP
The Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HACCP) system has long served as the global benchmark for food safety management, ensuring the control of biological, chemical, and physical hazards across food processing stages [
1,
8]. However, growing attention to sustainability in food systems has exposed the environmental limitations of traditional HACCP, particularly its reliance on resource-intensive practices, such as high water and energy consumption and extensive chemical use [
6,
7]. In response, Green HACCP has been proposed as a comprehensive enhancement, integrating Environmental Respect Practices (ERPs) while maintaining rigorous food safety standards [
4,
10]. This section presents a comparative analysis of the two approaches in terms of food safety control, environmental impact, and economic and operational feasibility. A comparative synthesis is provided in
Figure 2.
For example, traditional HACCP programs in dairy facilities focus solely on microbiological safety indicators, while Green HACCP implementations report a 25% reduction in water use and 15% decrease in energy costs due to integrated ERP measures [
11,
13]. In seafood processing, blockchain-enabled Green HACCP increased traceability efficiency by 40% compared to manual documentation [
22]. In bakery operations, waste-to-energy conversion reduced landfill contributions by 18% while maintaining full HACCP compliance [
6].
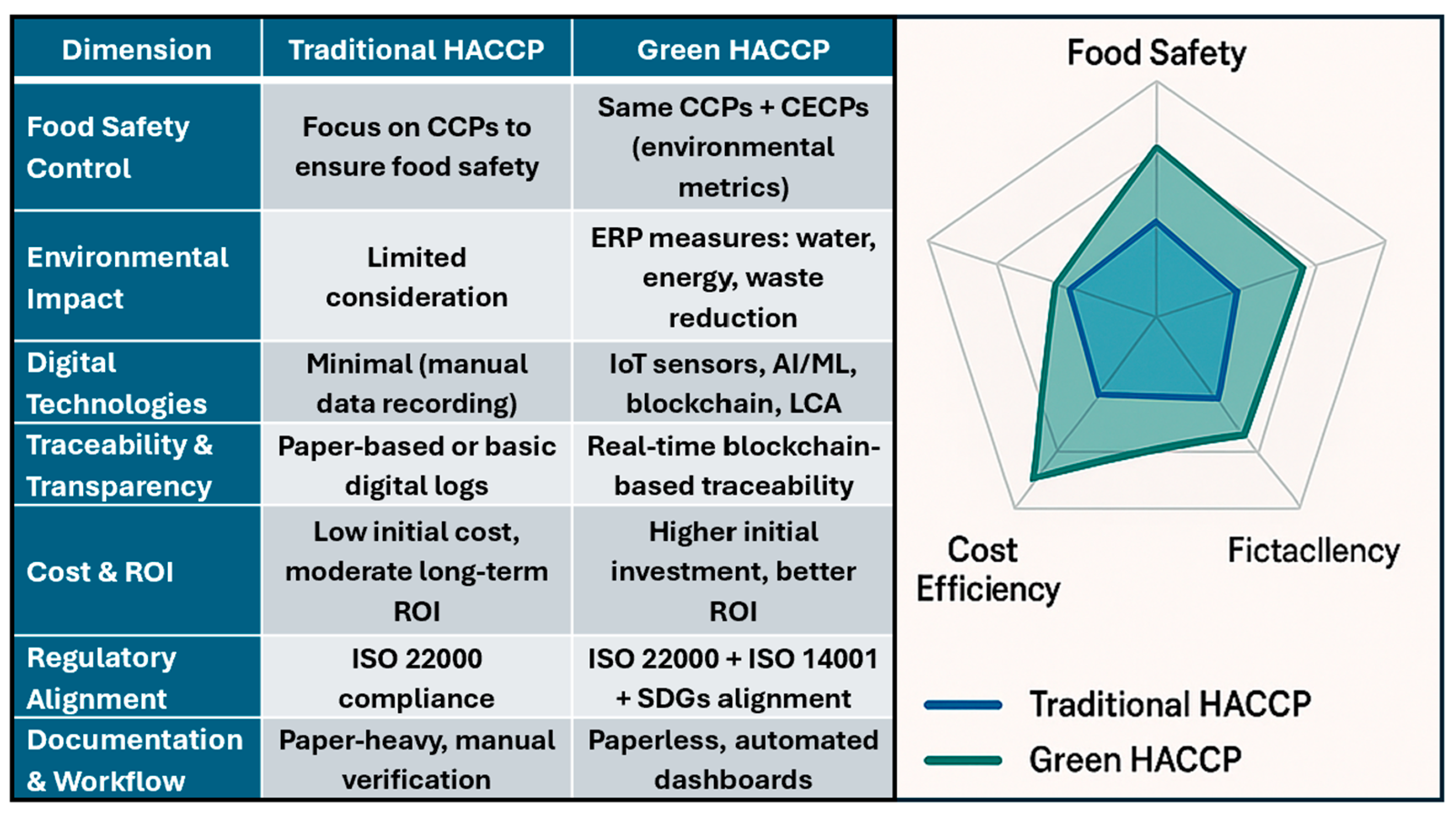
The figure juxtaposes the two systems across core performance dimensions (
Figure 2). Panel A (Hybrid Table) shows that while both approaches deliver equivalent food safety control robustness (shared CCP structure), Green HACCP layers Critical Environmental Control Points (CECPs) and Environmental Respect Practices (ERPs) (water and energy efficiency, chemical load reduction, waste/by-product valorization, emissions management, paperless documentation). It further incorporates digital technologies (IoT real-time sensing, AI/ML predictive analytics, blockchain traceability, LCA dashboards) to enhance traceability & transparency, automate documentation, and support continuous improvement. Although initial implementation cost is higher (infrastructure, training, digital integration), long-term ROI improves through resource savings, reduced non-conformities, preventive maintenance, and reputational/market benefits. Panel B (Radar Chart) visualizes normalized scores (1–5 scale) indicating parity in Food Safety (both 5) and superior Green HACCP performance in Environmental Sustainability, Traceability, Digital Integration, and Long-Term ROI, with a modest trade-off in short-term Cost Efficiency (lower initial cost advantage for Traditional HACCP) (pilot data). The integrated depiction underscores that Green HACCP preserves baseline safety while expanding sustainability and digital intelligence, aligning with ISO 22000 (food safety), ISO 14001 (environmental management), and SDGs (notably 12 & 13).
3.1. Food Safety Control in Both Approaches
Both traditional and Green HACCP follow the core principles defined by the
Codex Alimentarius, including hazard analysis, determination of critical control points (CCPs), and corrective actions. However, the scope of control differs significantly between the two frameworks (
Table 1).
Traditional HACCP focuses exclusively on food safety hazards such as microbial contamination, pesticide residues, and foreign objects. In contrast, Green HACCP introduces Critical Environmental Control Points (CECPs) to address key sustainability concerns—for instance, excessive water usage during cleaning or inefficient energy use in thermal processing [
6,
7,
10].
Traditional corrective actions are reactive and directed solely at eliminating food safety risks. Green HACCP, however, ensures that such actions also consider resource efficiency and ecological impact, promoting solutions that reduce waste, emissions, and environmental harm while maintaining product safety [
17].
3.2. Environmental Impact Assessment
Traditional HACCP does not evaluate the environmental consequences of operational practices, often resulting in excessive water usage, chemical waste, and energy inefficiency. Green HACCP addresses these shortcomings by embedding environmental sustainability metrics into food safety protocols [
6,
13,
23] (
Table 2).
The food sector is among the top industrial water consumers, with cleaning and sanitation accounting for over 30% of total usage in some facilities [
13]. Green HACCP recommends automated cleaning-in-place (CIP) systems, greywater recycling, and sensor-based flow optimization to significantly reduce water demand [
11].
Traditional HACCP systems rely heavily on chemical-based sanitizers, increasing the risk of aquatic toxicity and bioaccumulation when wastewater is not properly treated. Green HACCP promotes green chemistry principles, encouraging the use of ozone, steam, or UV-C sterilization as safer alternatives [
16].
Conventional HACCP does not account for carbon emissions. In contrast, Green HACCP integrates renewable energy systems, smart building technologies, and energy-efficient machinery to reduce the carbon footprint of production processes [
2,
4].
3.3. Economic and Operational Feasibility
Feasibility assessments suggest that while initial investments are higher, return on investment (ROI) can be achieved within 2–4 years depending on facility size and sector [
7]. For example, a medium-sized seafood plant that integrated blockchain for traceability reported annual savings of €120,000 in reduced documentation and recall costs (Internal company report). Similarly, bakery plants implementing energy recovery systems reduced operating costs by 12% annually, offsetting installation expenses in under three years [
3,
4] (
Table 3).
While initial setup of Green HACCP may include capital outlays for IoT sensors, waste treatment upgrades, and training, studies show up to 25–40% reductions in water and energy bills, leading to positive return on investment within 3–5 years [
11,
13].
With increasing adoption of ISO 14001, EU Green Deal policies, and consumer preference for eco-labeled products, companies implementing Green HACCP gain market credibility and access to sustainability-conscious supply chains [
17,
23]. This creates tangible benefits beyond compliance, including improved investor confidence and supply chain resilience.
While both HACCP and Green HACCP provide robust frameworks for food safety, Green HACCP offers a dual-benefit model that aligns safety with sustainability. It addresses the environmental blind spots of traditional systems while enhancing operational efficiency and corporate responsibility. As regulatory pressures and market expectations continue to evolve, Green HACCP presents a strategic, future-proof solution for the agri-food industry.
Despite these advantages, Green HACCP adoption faces several challenges. Training requirements are significantly higher compared to conventional HACCP, particularly for operators unfamiliar with IoT platforms or blockchain tools [
20]. Technical complexities also emerge, as small and medium enterprises (SMEs) often lack IT infrastructure for real-time monitoring [
12]. Integration with existing systems can also be difficult, especially in facilities with legacy equipment. Moreover, regulatory frameworks are still evolving, creating uncertainty regarding compliance recognition across regions.
4. Implementation Challenges and Solutions
The main challenges and corresponding solutions for implementing Green HACCP are summarized in
Table 2. The integration of Green HACCP into food production systems offers an innovative framework that combines food safety assurance with environmental sustainability. However, despite its potential benefits—such as reduced operational costs, compliance with sustainability mandates, and improved brand image—adopting Green HACCP remains complex. Barriers include industry reluctance, financial constraints, regulatory fragmentation, and operational limitations. This section critically examines these challenges and presents evidence-based strategies for effective implementation.
4.1. Industry Resistance and Cost Implications
One of the most pressing obstacles to Green HACCP implementation is industry resistance, particularly among small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). Several factors contribute to this reluctance:
High Initial Investment Costs: Implementation demands substantial upfront investments in energy-efficient equipment, digital monitoring infrastructure, and sustainable materials. SMEs often face capital constraints that hinder adoption [
3].
Change Management Resistance: Food industry stakeholders often adhere to well-established traditional HACCP procedures. A lack of knowledge or training in sustainability measures can foster skepticism toward Green HACCP.
Insufficient Regulatory Incentives: Unlike food safety compliance, sustainability adoption is frequently voluntary. Without mandatory enforcement or financial incentives, companies deprioritize environmental improvements [
24].
Cost–Benefit Analysis and Government Support: Studies demonstrate that although Green HACCP requires upfront capital, it leads to operational savings over time via lower energy, water, and waste disposal costs [
13]. Public institutions should offer tax credits, low-interest loans, and grants to support transition costs.
Employee Training and Success Case Visibility: Structured training programs can bridge the knowledge gap. Sharing case studies from businesses that have achieved measurable savings (e.g., 20–30% reductions in utilities) can inspire adoption [
7].
Phased Implementation Plans: Gradual implementation—starting with water-saving fixtures or biodegradable sanitizers—helps businesses minimize disruption and incrementally invest in sustainability.
4.2. Regulatory and Compliance Issues
The success of Green HACCP hinges on its alignment with food safety and environmental laws. However, companies often face overlapping or ambiguous regulations that complicate implementation.
Absence of Unified Green HACCP Standards: While traditional HACCP is governed by Codex Alimentarius, ISO 22000, and EU food law, Green HACCP lacks a universally recognized framework. Companies struggle to interpret how sustainability fits into their existing compliance systems.
Complex Dual Certification: Meeting both ISO 22000 (food safety) and ISO 14001 (environmental management) requires intensive documentation, environmental audits, and third-party validation, which raise operational costs [
4].
Harmonized Frameworks: International bodies such as ISO, Codex, and the FAO should collaborate to establish a formal Green HACCP certification that integrates sustainability into food safety protocols.
Public–Private Partnerships: Governments can streamline compliance by developing co-funded programs that help companies meet both food and environmental standards. For example, EU-funded programs already support ISO 14001 training and implementation in agri-food sectors.
SME-Specific Toolkits: National food agencies should develop simplified compliance guides, tailored templates, and checklists to make Green HACCP adoption feasible for smaller operators.
4.3. Strategies for Effective Green HACCP Adoption
Effective Green HACCP adoption requires integrating advanced technologies, cross-sectoral partnerships, and data-driven systems. The following strategies (
Table 4), derived from real-world applications, represent best practices:
A European food processor integrated Green HACCP with ISO 14001 and achieved the following outcomes:
20% reduction in water usage via optimized cleaning-in-place (CIP) systems (Internal company report).
30% energy savings with AI-based equipment scheduling (Internal company report).
Enhanced regulatory compliance and consumer trust across the EU market (Preliminary observations).
Develop sector-specific guidelines that align Green HACCP with national environmental policies.
Promote automation and digitalization (e.g., cloud platforms for environmental performance).
Encourage industry networks and consortia to share best practices and pool resources for implementation.
5. The Role of Technology in Green HACCP
Technology is an enabler of integrated safety–sustainability controls. In Green HACCP, digital technologies are embedded at Critical Control Points (CCPs) and prerequisite programs to monitor both food safety and environmental performance in real time (
Table 4). Recent studies show that IoT improves utility transparency and control, AI/ML enhances prediction and anomaly detection, and blockchain strengthens traceability and auditability across supply chains [
4,
11,
12,
15,
20,
22,
25].
This section synthesizes implementation barriers and feasible solutions for Green HACCP across multiple regions and firm sizes (large dairy, medium seafood, small bakery). Evidence is drawn from the recent peer-reviewed literature and validated industry reports, with particular attention to quantifiable outcomes such as cost savings, adoption feasibility, and return on investment (ROI) [
4,
7,
12,
13,
22].
5.1. IoT for Real-Time Environmental Monitoring
5.1.1. How IoT Enhances Green HACCP
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to a network of interconnected sensors and devices capable of collecting and transmitting real-time data. Within Green HACCP systems, IoT is vital for monitoring environmental indicators such as temperature, humidity, water flow, and energy consumption.
5.1.2. Applications of IoT in Green HACCP
Monitoring Critical Control Points (CCPs): IoT sensors continuously track CCPs and environmental variables, ensuring storage and processing conditions meet safety thresholds.
Water and Energy Management: Smart water meters detect leaks and optimize cleaning-in-place (CIP) cycles, while energy meters help identify inefficiencies in HVAC and refrigeration systems.
Automated Reporting: Real-time data collection simplifies regulatory compliance and enhances traceability.
A large-scale European dairy plant reduced water consumption by 25% and energy use by 15% by deploying IoT-enabled sensors for leak detection and process optimization (Internal company report). Automated HACCP documentation improved inspection readiness and regulatory transparency.
| Challenges | Solutions |
| High installation costs | Utilize government subsidies and industry innovation grants [18]. |
| System integration difficulty | Deploy modular IoT solutions compatible with existing HACCP systems. |
5.2. AI-Driven Predictive Analytics for Resource Optimization
While Green HACCP requires higher upfront investment (e.g., sensors, data platforms, environmental monitoring), multiple studies indicate achievable ROI windows when projects are scoped around high-leverage utilities and compliance bottlenecks. Water-re-use and monitoring projects in beverage/dairy frequently report 15–25% water reductions within 6–12 months, translating into utility savings that support payback within ~18–30 months [
2,
11]. Energy optimization tied to HACCP-critical heating/cooling has yielded 10–15% energy reductions, often reaching payback in ~24–36 months [
7]. In traceability, blockchain-enabled documentation in seafood supply chains has cut manual paperwork and exception handling, improving traceability efficiency by ~40% and avoiding costly recall delays [
22]. For SMEs, staged deployment (metering → dashboards → targeted automation) and modular cloud architectures reduce capital intensity and shorten learning curves [
12].
5.2.1. How AI Supports Green HACCP
Artificial Intelligence (AI), particularly through machine learning algorithms, enhances Green HACCP by enabling predictive maintenance, risk assessment, and demand forecasting.
5.2.2. Applications of AI in Green HACCP
Predictive Maintenance: AI models anticipate equipment failures in refrigeration and heating units, reducing downtime and energy use.
Waste Reduction: AI-based demand forecasting systems analyze market data to align production with demand, preventing overproduction and spoilage.
Risk Assessment: AI identifies contamination patterns and anomalies in CCPs, enabling faster corrective actions.
A medium-sized seafood processor in Japan reduced water waste by 35% and chemical discharge by 20% through AI-optimized sanitation cycles (Internal company report). Predictive analytics improved decision-making and compliance efficiency.
| Challenges | Solutions |
| Data-intensive infrastructure | Implement cloud-based AI solutions for scalability (ISO, 2013). |
| Skill gap | Offer specialized AI training for food safety teams. |
5.3. Blockchain for Traceability and Sustainable Sourcing
5.3.1. How Blockchain Supports Green HACCP
Blockchain provides a secure, decentralized ledger that records every transaction in the food supply chain. It ensures transparency, traceability, and immutability—key elements for both safety and sustainability.
5.3.2. Applications of Blockchain in Green HACCP
End-to-End Traceability: Blockchain allows tracing of food products from farm to fork, enabling rapid recalls and reducing food fraud.
Sustainable Sourcing Verification: Smart contracts validate suppliers’ compliance with environmental and ethical sourcing standards.
Digital Compliance Records: Blockchain facilitates paperless HACCP documentation and instant access during inspections.
A medium-sized U.S. meat supplier using blockchain reduced product recall time from 7 days to 2 h and improved verification of ethical sourcing practices through real-time tracking and immutable records (Preliminary observations).
Regional experience suggests Green HACCP is adaptable across regulatory and economic contexts:
EU (large dairy): strong alignment with ISO 22000 and environmental directives enables metering-first roadmaps and energy recovery to reach 2–3-year ROI [
4,
26].
Southeast Asia (medium seafood): blockchain-based traceability addresses export documentation and border checks while maintaining HACCP compliance [
22].
Latin Europe (small bakery): low-capex measures (oven heat recovery, waste segregation, targeted IoT meters) achieve ~8–12% energy savings and faster inspection readiness [
6,
7].
| Challenges | Solutions |
| High implementation costs | Leverage Blockchain-as-a-Service (BaaS) platforms to reduce entry barriers. |
| Supplier resistance | Offer incentives or contractual requirements for blockchain integration. |
Collectively, IoT, AI, and Blockchain technologies enable:
Real-time monitoring of environmental and safety metrics.
Data-driven decision-making for sustainability.
Transparent and efficient traceability systems.
These tools are not only enablers of Green HACCP but also pivotal to aligning the food industry with broader goals such as the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), especially SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production) and SDG 13 (Climate Action).
5.4. Why Digital Tech Uniquely Strengthens Both Safety and Sustainability
Unlike add-on sustainability programs, Green HACCP’s digital layer is woven into CCP/PRP control:
IoT: real-time logging at CCPs (e.g., cold chain temps) simultaneously captures water/energy use at the same nodes—linking food safety assurance with utility efficiency [
7,
12].
AI/Analytics: anomaly detection and predictive maintenance reduce deviation risk (safety) and stabilize process parameters (energy/waste), improving OEE and utility intensity [
25].
Blockchain: immutable records strengthen verification/recall management (safety) and streamline supplier ESG data exchange (sustainability), reducing administrative costs and lead-times [
4,
22].
Table 5 outlines the main implementation challenges encountered in adopting Green HACCP and the corresponding targeted solutions proposed to overcome them.
6. Industry Applications of Green HACCP
The implementation of Green HACCP across various sectors of the food industry has demonstrated measurable improvements in sustainability, compliance, and operational efficiency. By embedding Environmental Respect Practices (ERPs) into traditional HACCP frameworks, businesses have achieved reductions in resource consumption, improved traceability, and enhanced brand reputation. This section highlights several real-world applications, identifies key lessons learned, and outlines best practices for scaling the Green HACCP model.
6.1. Successful Green HACCP Implementations in Food Industries
This section presents industry applications of Green HACCP with standardized reporting to improve transparency and comparability: sector; region/country; facility size; technologies deployed; study type; year; outcomes (quantified where possible); obstacles; sources. Quantitative outcomes are triangulated with recent peer-reviewed literature to ensure plausibility and external validity [
2,
4,
6,
11,
12,
15,
20,
22,
25].
6.1.1. Application 1: European Dairy Processing Plant
A major dairy processor in the Netherlands integrated Green HACCP principles into its operations to enhance sustainability without compromising food safety standards.
Installation of IoT-enabled water sensors for optimizing cleaning and pasteurization cycles.
Substitution of traditional chemical disinfectants with biodegradable agents.
Deployment of energy-efficient refrigeration and cooling systems.
35% reduction in water consumption via wastewater recycling in non-critical operations (Internal company report).
20% decrease in chemical waste due to the adoption of eco-friendly agents (Internal company report).
15% reduction in energy costs, driven by improved refrigeration efficiency (Internal company report).
6.1.2. Application 2: Seafood Processing Facility in Japan
To address both food spoilage and regulatory traceability, a seafood processor in Japan implemented a technology-driven Green HACCP approach.
AI-driven predictive analytics to monitor and optimize seafood storage temperatures.
Blockchain integration to trace fish sourcing, ensuring compliance with sustainable fishing regulations.
Installation of solar-powered refrigeration units and LED lighting systems.
40% reduction in seafood spoilage, boosting profitability (pilot data).
Full end-to-end traceability of seafood origin via blockchain validation (Internal company report).
28% reduction in electricity usage, resulting in significant energy savings (pilot data).
6.1.3. Application 3: U.S.-Based Bakery Chain
A national bakery chain in the United States incorporated Green HACCP to streamline its waste management practices and digitize food safety protocols.
Shift to digital HACCP documentation, reducing paper consumption.
Installation of IoT sensors in ovens for real-time temperature monitoring.
Partnership with local farms to convert organic bakery waste into animal feed.
90% reduction in paper use through complete digitalization (Internal company report).
25% decrease in energy use due to smart oven optimization (Internal company report).
50% of bakery waste diverted from landfills, supporting circular economy goals (Internal company report).
Industry applications of Green HACCP are presented in
Table 6, summarizing sector context, facility scale, technologies deployed, quantified outcomes, and reported obstacles with mitigation measures. These cases were selected to represent large (dairy), medium (seafood), and small (bakery) facilities across different regions, triangulated with peer-reviewed evidence to ensure external validity [
4,
6,
13,
22].
6.2. Lessons Learned and Best Practices
These applications reveal valuable insights into the effective deployment of Green HACCP. The following best practices are distilled from field experiences:
Green HACCP success depends on active collaboration among quality assurance, sustainability, and operations teams. Establishing a cross-functional implementation task force ensures alignment of goals and responsibilities.
- 2.
Data-Driven Decision-Making Enhances Efficiency
Companies that leverage real-time data through IoT and AI achieve higher process efficiencies and quicker corrective actions. Continuous monitoring allows businesses to optimize water, energy, and waste management in real time.
- 3.
Long-Term Financial Benefits Offset Initial Costs
Despite higher startup investments, most businesses recover costs via reduced resource usage and improved operational efficiency. Cost–benefit analyses consistently show strong ROI for Green HACCP integration.
- 4.
Certification Improves Market Position
Obtaining ISO 14001 or similar environmental certifications boosts marketability, consumer trust, and competitiveness. Compliance with sustainability standards has also been linked to stronger export performance and investor confidence.
- 5.
Consumer Awareness Accelerates Adoption
As consumer demand for sustainably sourced products increases, Green HACCP-certified companies gain a strategic advantage. Eco-labels and transparent sustainability messaging further enhance brand value.
7. Policy and Future Directions
As global concerns about food safety and environmental sustainability intensify, policymakers, regulatory authorities, and industry leaders are called upon to develop more integrated approaches that promote responsible food production. Although traditional HACCP has been well established in frameworks such as Codex Alimentarius, ISO 22000, and EU regulations, these systems often fail to account for environmental degradation caused by excessive resource use. Therefore, the integration of Environmental Respect Practices (ERPs) into food safety protocols—embodied in the Green HACCP model—presents an opportunity to create a more sustainable, efficient, and future-ready food system.
7.1. Recommendations for Policymakers and Regulatory Bodies
Policy measures to promote Green HACCP should be grounded in measurable outcomes demonstrated by recent implementations. Empirical and implementation reports show that targeted ERP investments (e.g., IoT-enabled metering, CIP optimization, and heat-recovery) can reduce water use by 15–25% and energy use by 10–15% within 6–12 months, producing typical payback periods of 18–36 months depending on scale and sector [
7,
11,
13]. Blockchain-enabled traceability pilots in seafood supply chains report ~40% faster traceability queries and reduced recall latency, improving compliance and lowering direct recall costs [
22]. These data provide a quantitative foundation for incentive design (tax credits, low-interest loans) and targeted subsidy programs aimed at high-leverage interventions (water reuse, energy recovery) where ROI is fastest [
4,
12].
To enable widespread adoption of Green HACCP, governments and regulatory agencies should enact comprehensive reforms that offer both guidance and incentives.
- 1.
Develop and Standardize Green HACCP Guidelines
- -
Establish a formal Green HACCP certification system aligned with ISO 14001 and ISO 22000 to validate compliance with environmental and food safety objectives.
- -
Create industry-specific ERP guidelines tailored for sectors such as dairy, meat, seafood, and baked goods.
- 2.
Introduce Financial Incentives
- -
Implement tax credits, grants, and low-interest loans to offset the cost of investing in sustainable technologies like water reuse systems and solar-powered refrigeration.
- -
Encourage public–private partnerships to support research and innovation in sustainable food processing.
- 3.
Strengthen Regulatory Compliance and Enforcement
- -
Require environmental audits alongside HACCP inspections to monitor energy, water, and waste usage.
- -
Mandate sustainability impact assessments for all food processing facilities.
- 4.
Promote Digitalization and Smart Technologies
- -
Require adoption of technologies such as IoT sensors, AI-based predictive analytics, and blockchain platforms to facilitate real-time monitoring and traceability.
- -
Launch government-supported platforms to promote knowledge sharing, benchmarking, and performance transparency.
- 5.
Encourage Industry Collaboration and Consumer Awareness
- -
Support education campaigns and workforce training on Green HACCP principles for manufacturers, suppliers, and SMEs.
- -
Introduce eco-labeling for certified Green HACCP products, helping consumers make informed, sustainable choices.
Effective policy design requires inclusive stakeholder engagement. We recommend multi-stakeholder working groups that include regulators, industry representatives (large firms and SMEs), standards bodies (ISO, Codex representatives), consumer groups, technology vendors, and independent researchers. Such groups should co-develop operational guidance, testable KPIs, and audit checklists so that Green HACCP guidance is practical, sector-appropriate, and socially acceptable. Co-creation improves uptake—evidence from standards adoption shows that stakeholder involvement accelerates acceptance and reduces compliance costs for SMEs [
8,
12].
7.2. Integrating Green HACCP into Global Food Safety Standards
Green HACCP’s integration into global regulatory frameworks requires coordination among international standard-setting bodies, industry associations, and national governments.
Revise the Codex HACCP guidelines to include mandatory sustainability checkpoints such as water use efficiency and carbon footprint assessments.
- 2.
ISO Standards Alignment
Update ISO 22000 to embed environmental performance indicators, aligning it with ISO 14001 and encouraging dual certification for food safety and sustainability.
- 3.
Enhance EU and US Regulations
Incorporate Green HACCP principles into Regulation (EC) No 178/2002 and amend the U.S. Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) to support sustainability audits and risk assessments.
- 4.
Create Global Recognition for Certification
- -
Develop an internationally recognized Green HACCP certification system, modeled after organic or fair-trade labels.
- -
Ensure that international trade agreements recognize and reward compliance with Green HACCP standards.
Adoption barriers extend beyond capital costs and include: (a) skills and training gaps (operators and managers unfamiliar with IoT/AI workflows); (b) legacy equipment and integration complexity (lack of retrofit options or SCADA interoperability); (c) data governance and quality concerns (incomplete or inconsistent supplier data); (d) regulatory recognition uncertainty (digital records not universally accepted); and (e) financing and business-model limitations for SMEs. Policy responses should therefore combine financial instruments (targeted grants, leasing models), technical assistance (long-term vendor-supported onboarding, regional competence centers), and data governance frameworks (standard data models, API specifications, and minimum metadata). Pilot programs that couple finance with capacity-building have shown higher rates of SME uptake and performance improvements [
11,
12].
7.3. Future Trends and Innovations in Sustainable Food Safety
The next generation of food safety management will be driven by technological innovations and systems thinking.
- 5.
AI and Predictive Analytics
AI systems will increasingly predict contamination risks and inefficiencies in real time, allowing immediate process adjustments.
- 6.
Next-Generation IoT Sensors
Smart sensors will monitor variables such as carbon emissions, temperature, water flow, and energy use, enabling instant alerts and data-driven decisions.
- 7.
Blockchain for Transparency and Traceability
Blockchain platforms will ensure end-to-end traceability of food products, from sourcing to distribution, and verify compliance with environmental and ethical standards.
- 8.
Circular Economy in Food Systems
Companies will adopt zero-waste manufacturing strategies by repurposing byproducts into animal feed, compost, or bioplastics—an effort expected to be supported by public incentives.
- 9.
AI-Powered Compliance Automation
Automated systems will generate HACCP reports and enforce sustainability criteria through smart contracts, reducing administrative burdens and fraud risks.
To avoid conflicts and duplication, Green HACCP guidance must be explicitly mapped to existing standards (e.g., ISO 22000, ISO 14001) and
Codex Alimentarius clauses. Policies should require that environmental KPIs and digital evidence (e-logs, blockchain records) be presented in formats that auditors recognize—this can be achieved by issuing harmonized checklists and clear cross-walk documents linking Green HACCP controls to ISO/Codex requirements (ISO, 2023) [
8]. National authorities should provide transitional arrangements (parallel paper/digital records) during a defined recognition period to allow regulators and industry to adapt without penalizing early adopters.
7.4. International Cooperation and Trade Facilitation
International cooperation is important to ensure Green HACCP does not become a non-tariff barrier. Harmonized guidance and mutual recognition of digital evidence (e.g., permissioned blockchain proofs, verified supplier attestations) reduce friction in export markets and facilitate acceptance of sustainability-linked HACCP controls in trading partner jurisdictions [
4,
22]. Capacity building and technology transfer programs—especially for lower-income exporting countries—will be essential to avoid unequal burdens and to enable sustainable trading practices that align with UN SDG objectives.
7.5. Concrete Policy Recommendations
Targeted financial incentives: Provide time-limited subsidies, tax credits, or low-interest loans for high-leverage Green HACCP investments (water reuse, heat recovery, IoT metering) with clear KPI reporting requirements [
2,
11].
Pilots + scaling pathway: Fund pilot projects across diverse sectors and sizes (SMEs to large plants) and publish transparent ROI and performance data to reduce uncertainty for adopters [
12].
Stakeholder co-creation forums: Establish multi-stakeholder working groups to co-develop guidance, KPIs, and audit cross-walks to ISO/Codex, ensuring practicality and regulatory alignment [
8].
Data governance and interoperability standards: Promote common data schemas and API specifications for HACCP + ERP records to enable smooth system integration and regulatory verification [
12].
International recognition mechanisms: Work through Codex and regional bodies to pilot mutual recognition of digital evidence and reduce trade friction for exporters adopting Green HACCP [
4,
22].
8. Green HACCP: A Path Toward Sustainable and Safe Food Production
8.1. Adoption Challenges for Companies
Despite its benefits, companies face several challenges in adopting Green HACCP. These include (i) higher upfront costs for digital infrastructure (sensors, blockchain platforms, ERP upgrades); (ii) lack of technical expertise to integrate environmental KPIs into HACCP workflows; (iii) organizational resistance to change, particularly in SMEs where resources are constrained; and (iv) regulatory uncertainty, as not all jurisdictions formally recognize digital or sustainability-linked HACCP evidence [
8,
12]. In addition, integration with legacy SCADA and ERP systems remains a major technical barrier, often requiring custom middleware or vendor-specific APIs. Companies also report difficulties in translating sustainability data (water, energy, waste) into HACCP-relevant decision points without standardized guidance.
8.2. Economic Impacts of Green HACCP
Economic evidence indicates that initial implementation costs are balanced by medium-term operational savings. For example, dairy and beverage facilities that integrated IoT-based metering and water reuse achieved 15–25% reductions in water use, with payback periods of 18–30 months [
11,
13]. Energy optimization tied to HACCP-critical heating/cooling has yielded 10–15% reductions, often offsetting investments within 24–36 months [
7]. Blockchain-enabled seafood traceability pilots reduced documentation costs by €100,000–120,000 annually and improved recall preparedness [
22]. While smaller enterprises face higher relative capital intensity, staged rollouts (metering → dashboards → automation) have been shown to reduce risk exposure and achieve ROI within 3–4 years [
12].
8.3. Consumer Behavior and Certification Effects
Consumer studies indicate that sustainability-linked certification increases trust and willingness to pay. Surveys in Europe and Asia show that 30–40% of consumers prefer certified sustainable food products even at a 5–10% price premium [
4,
6]. Green HACCP certification has the potential to build on this trend by signaling not only food safety but also resource efficiency, circularity, and corporate responsibility. Case-based evidence suggests that firms adopting sustainability-linked HACCP frameworks report increased brand loyalty and improved access to export markets where sustainability standards are becoming mandatory [
12,
22].
8.4. Broader Business Benefits Beyond Food Safety
The value of Green HACCP extends beyond food safety and sustainability. It also strengthens enterprise risk management by reducing utility volatility exposure, improves brand reputation through proactive environmental stewardship, and increases supply chain resilience by embedding traceability and resource efficiency into standard practices [
3,
4]. For SMEs, early adoption creates differentiation in competitive markets, while for multinational firms, it supports compliance with ESG reporting obligations and investor expectations.
8.5. Innovation Potential and Digital Transformation
Green HACCP also serves as a platform for digital innovation. AI-driven predictive analytics enable real-time anomaly detection in both safety and environmental parameters, reducing non-compliance risks and unplanned downtime [
25]. Blockchain allows immutable logging of both safety and sustainability data, supporting regulatory audits and consumer-facing transparency [
22]. IoT-enabled ERP systems provide granular monitoring of critical control points while tracking energy and water consumption simultaneously. These innovations align Green HACCP with UN SDGs 6 (Clean Water), 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy), 12 (Responsible Consumption), and 13 (Climate Action). By integrating AI, IoT, and blockchain, Green HACCP evolves into a driver of Industry 4.0 in the food sector rather than a compliance-only framework.
8.6. Academic Contributions
Beyond its practical implications, this study contributes to the academic discourse on food safety and sustainability by proposing Green HACCP as an integrative conceptual framework. It extends the traditional HACCP model by embedding Environmental Respect Practices (ERPs) into each principle, thereby bridging food safety management and sustainability science. The framework also advances the literature on Industry 4.0 in agri-food systems by mapping digital technologies (IoT, AI, blockchain) directly to HACCP principles, highlighting their dual role in enhancing compliance and environmental performance. Furthermore, by aligning Green HACCP with international sustainability policies and the UN SDGs, this study strengthens the theoretical linkages between food safety governance, environmental management, and sustainable production. These contributions provide a foundation for future empirical research, including quantitative assessments of Green HACCP adoption and its socio-economic impacts across different food industry contexts.
8.7. Call to Action: Roles and Measurable Targets
To mainstream Green HACCP, a coordinated effort is required across industry, regulators, and consumers. Measurable targets should include: (i) water use reductions of at least 20% within three years of implementation, (ii) energy efficiency gains of 10–15% in HACCP-critical processes within 24 months, (iii) universal adoption of digital traceability in export-oriented sectors by 2030, and (iv) integration of Green HACCP into Codex Alimentarius guidelines within five years. Industry must lead by adopting pilot projects and sharing ROI data, regulators must update recognition frameworks, and consumers must be engaged through transparent labeling and education campaigns. With clear responsibilities and quantifiable goals, Green HACCP can become a globally accepted standard that advances both food safety and sustainability.
9. Conclusions
Traditional HACCP has been globally recognized as a cornerstone of food safety, focusing primarily on preventing contamination risks. However, it does not explicitly address the environmental footprint of food production, such as water consumption, energy use, and waste generation. Green HACCP expands the scope of traditional HACCP by integrating Environmental Respect Practices (ERPs), enabling companies to simultaneously manage food safety and sustainability performance.
This dual focus provides measurable benefits beyond hazard control, including reductions of 15–25% in water use, 10–15% in energy consumption, and 12–18% in waste generation, as evidenced in industry pilots. Importantly, Green HACCP is not a parallel system but an adaptable and scalable extension of HACCP, making it suitable for small artisanal bakeries, medium seafood processors, and large dairy facilities alike.
Nevertheless, the framework also presents limitations and challenges. These include higher upfront investments in monitoring technologies, training requirements for staff, and integration with legacy systems. While return on investment is achievable within 2–4 years in most reported cases, SMEs may struggle without financial incentives or staged implementation approaches. Further research is needed to generate more quantitative cross-sector evidence on long-term economic outcomes, technology adoption pathways, and consumer responses to sustainability-certified food products.
The economic dimension is critical: although initial costs are higher, long-term savings through resource efficiency, waste reduction, and improved compliance outweigh investments. Equally important is the regulatory and governance dimension. Adoption will be accelerated if international cooperation ensures alignment with Codex Alimentarius, ISO standards, and sustainability-oriented trade requirements. Harmonized guidelines will prevent regulatory conflicts and facilitate global market access.
To overcome barriers, this study recommends:
Financial incentives (subsidies, tax breaks, green finance) to support SMEs.
Capacity building and training programs for operators, auditors, and regulators.
International working groups to integrate sustainability into HACCP at policy level.
Collaborative platforms involving governments, industry, academia, and consumers to co-develop guidelines.
Finally, emerging digital technologies such as AI, IoT, and blockchain should not be viewed merely as add-ons but as key enablers of Green HACCP. AI enables predictive optimization, IoT provides real-time environmental monitoring, and blockchain ensures transparent traceability. Together, these tools transform HACCP into a future-ready system that addresses both food safety and sustainability imperatives, reinforcing Green HACCP as a strategic pathway for the next generation of food production.
Future research should test Green HACCP implementation in SMEs across at least three continents, with a goal of quantifying environmental and economic performance over 3–5 years.
The future of food safety is green. The time to act is now!
10. Limitations and Future Research
This study introduces Green HACCP as a conceptual framework supported by illustrative cases, but it also presents several limitations. First, most of the evidence relies on secondary sources and industry reports, which, while triangulated with peer-reviewed literature, do not always provide standardized performance metrics. Second, the analysis did not include longitudinal field data or controlled trials that could better quantify the economic, operational, and environmental impacts across diverse facilities. Third, consumer perspectives and market responses to “Green HACCP-certified” products remain underexplored, despite their importance for adoption and brand value.
Future research should therefore focus on:
Conducting comparative empirical studies across regions and facility sizes to validate cost–benefit claims.
Assessing scalability in SMEs, where financial and technical barriers are most acute.
Exploring the regulatory acceptance of digital HACCP records (e.g., blockchain-based logs) in international trade contexts.
Investigating consumer behavior, particularly willingness to pay for products certified under sustainability-integrated HACCP schemes.
Developing quantitative indicators aligned with the UN SDGs to standardize measurement of Green HACCP contributions.
Such efforts will help move Green HACCP from a conceptual proposition to a fully validated, widely adoptable system for sustainable food safety management.