GRACE/GRACE-FO Satellite Assessment of Sown Area Expansion Impacts on Groundwater Sustainability in Jilin Province
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
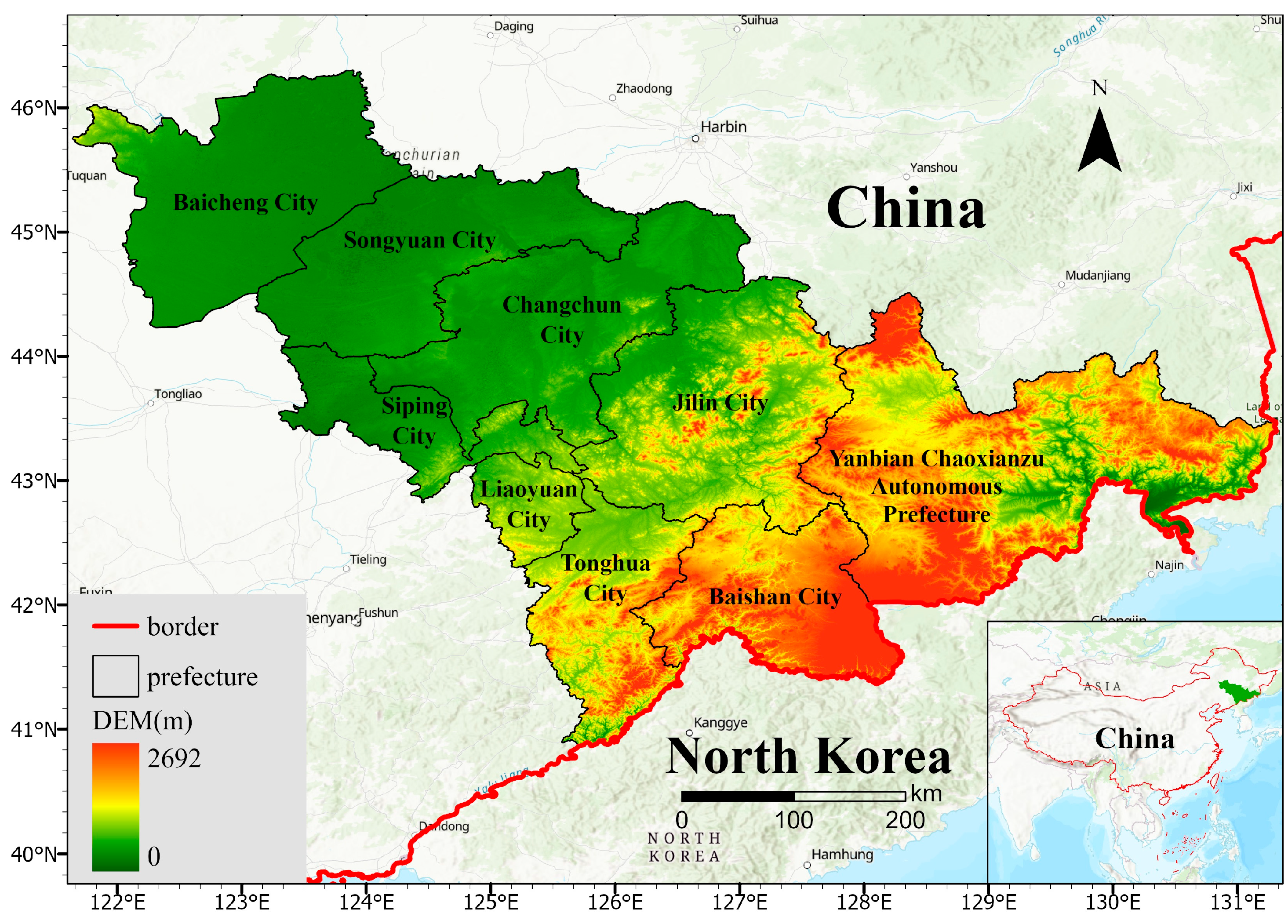
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Datasets
2.2.1. GRACE Data
2.2.2. GLDAS Data
2.2.3. Meteorological Data
2.2.4. Land Use Data
2.2.5. Other Data
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. SSA Interpolation Methods
2.3.2. Groundwater Storage Anomaly
2.3.3. GRACE Groundwater Drought Index (GGDI)
2.3.4. Evaluation of the Groundwater Sustainability
2.3.5. Analysis of Influencing Factors
3. Results
3.1. Spatiotemporal Anomalies in Groundwater Reserves
3.2. Grace Groundwater Drought Index (GGDI)
3.3. Groundwater Sustainability in the Jilin Province
3.4. Analysis of Factors Affecting Groundwater Sustainability
3.4.1. Relationship Between Precipitation and △GWS
3.4.2. Land Use Change
3.4.3. The Impact of Agriculture on △GWS
4. Discussion
4.1. The Impact of Climate Factors on Groundwater Sustainability
4.2. The Impact of Human Activities on Groundwater Sustainability
4.3. Agricultural Policy-Driven Changes in Groundwater Sustainability
4.4. Urbanization Policy-Driven Changes in Groundwater Sustainability
5. Conclusions
- From 2002 to 2022, the ∆GWS in Jilin Province showed an overall downward trend, with the highest average groundwater level in June and the lowest in September.
- The GRACE Groundwater Drought Index (GGDI) for Jilin Province shows that groundwater reserves were in surplus most of the time before September 2010. From October 2010 to August 2018, the reserves fluctuated between surplus and deficit states. Since September 2018, the GGDI has shown a continuous downward trend and entered a state of long-term deficit.
- An assessment was conducted of the sustainability of groundwater in Jilin Province, with the Groundwater Drought Index (GGDI) serving as the primary analytical framework. Prior to 2005, the sustainability of groundwater in Jilin Province was classified as high or extremely high. However, following the first instance of a deficit in groundwater reserves in 2005, the situation experienced a precipitous decline, reaching low sustainability in 2006. By 2011, it had reached an extremely low level of sustainability, with ongoing deterioration.
- The present study employed both MIC analysis and Pearson study to determine the effect of four indicators on the sustainability of groundwater in Jilin Province. The findings suggest that policy-driven expansion of sown areas has the greatest influence on groundwater sustainability. Although increased precipitation positively impacts groundwater levels and sustainability, expansion of sown areas has created irrigation demands that cannot be met. This has led to a negative correlation between precipitation and groundwater sustainability.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jyolsna, P.; Kambhammettu, B.; Gorugantula, S. Application of random forest and multi-linear regression methods in downscaling GRACE derived groundwater storage changes. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2021, 66, 874–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; He, Q.; Liu, K.; Li, J.; Jing, C. Downscaling of GRACE-derived groundwater storage based on the random forest model. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Pan, Y.; Zheng, L.; Li, X.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, C.; Huang, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhou, C. Long-term groundwater storage changes and land subsidence development in the North China Plain (1971–2015). Hydrogeol. J. 2018, 26, 1417–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlon, B.R.; Faunt, C.C.; Longuevergne, L.; Reedy, R.C.; Alley, W.M.; McGuire, V.L.; McMahon, P.B. Groundwater depletion and sustainability of irrigation in the US High Plains and Central Valley. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 9320–9325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alley, W.M.; Reilly, T.E.; Franke, O.L. Sustainability of Ground-Water Resources; US Geological Survey; US Department of the Interior: Washington, DC, USA, 1999; Volume 1186.
- Yuan, Y.J.; Wu, X.Q. Evaluation of groundwater resource sustainability based on GRACE and GLDAS in arid region of Northwest China. Arid Zone Res. 2022, 39, 787–800. [Google Scholar]
- Gorelick, S.M.; Zheng, C. Global change and the groundwater management challenge. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 3031–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusam, K.; Kumari, D.; Pandit, S.; Sharma, P.; Kuila, A. Advancing groundwater sustainability: Strategy combining hydro-chemical analysis, pollution mitigation, and community-based water resource governance. Groundwater. Sust. Dev. 2025, 29, 101433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, C.; Başağaoğlu, H.; Yoosefdoost, I.; Wootten, A.; Chakraborty-Reddy, D.; Bertetti, F.P.; Mirchi, A.; Chakraborty, D. Efficacy of mitigation strategies for aquifer sustainability under climate change. Nat. Sustain. 2025, 8, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Yao, Y.; Ji, Q.; Jin, H.; Wang, T.; Lancia, M.; Meng, X.; Zheng, C.; Yang, D. Groundwater depletion intensified by irrigation and afforestation in the Yellow River Basin: A spatiotemporal analysis using GRACE and well monitoring data with implications for sustainable management. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2025, 59, 102324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascal, C.; Ferrant, S.; Selles, A.; Maréchal, J.-C.; Paswan, A.; Merlin, O. Evaluating downscaling methods of GRACE data: A case study over a fractured crystalline aquifer in South India. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 2022, 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, W.; Zhong, M.; Lemoine, J.M.; Biancale, R.; Hsu, H.T.; Xia, J. Evaluation of groundwater depletion in North China using the Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) data and ground-based measurements. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 2110–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, B.F.; Famiglietti, J.S. Identifying climate-induced groundwater depletion in GRACE observations. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Pei, H.; Shen, Y. Evaluating dynamics of GRACE groundwater and its drought potential in Taihang Mountain Region, China. J. Hydrol. 2022, 612, 128156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Liu, S. Research on agri-environmental technology efficiency—Take Jilin Province in China as an example. Heliyon 2024, 10, e25879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.; Ciais, P.; Huang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Peng, S.; Li, J.; Zhou, L.; Liu, H.; Ma, Y.; Ding, Y. The impacts of climate change on water resources and agriculture in China. Nature 2010, 467, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.A.; Qu, Y.G.; Liu, S.L.; Sun, H.; Wei, Z.C.; Zhang, T. Analysis on the evolution of water resources in Jilin Province. China Flood Disaster Manag. 2020, 30, 62–66+69. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, C.; Liu, Y. Analysis of groundwater storage changes and influencing factors in China based on GRACE data. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Cui, G.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Tong, S.; Zhang, M. GRACE Satellite-based analysis of spatiotemporal evolution and driving factors of groundwater storage in the black soil region of Northeast China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodell, M.; Houser, P.; Jambor, U.; Gottschalck, J.; Mitchell, K.; Meng, C.-J.; Arsenault, K.; Cosgrove, B.; Radakovich, J.; Bosilovich, M. The global land data assimilation system. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2004, 85, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S. 1-km Monthly Precipitation Dataset for China (1901–2023); National Tibetan Plateau/Third Pole Environment Data Center: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, S. 1-km Monthly Potential Evapotranspiration Dataset in China (1901–2022); National Tibetan Plateau Data Center: Beijing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Huang, X. 30 m annual land cover and its dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019. Earth Syst. Sci. Data Discuss. 2021, 13, 3907–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.; Sneeuw, N. Filling the data gaps within GRACE missions using singular spectrum analysis. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2021, 126, e2020JB021227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broomhead, D.S.; King, G.P. Extracting qualitative dynamics from experimental data. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 1986, 20, 217–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.F.; Fang, S.B.; Han, J.H.; Yu, Y.; Wu, D. Analysis of groundwater storage anomaly and multisource influencing factors in the North China Plain. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2025, 29, 677–688. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, T.Y.; Li, X.L.; Shum, C.K.; Ding, H.; Xu, X.Y. The Balance and Abnormal Increase of Global Ocean Mass Change from Land Using GRACE. Earth Space Sci. 2020, 7, e2020EA001104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, B.F.; Famiglietti, J.S.; Landerer, F.W.; Wiese, D.N.; Molotch, N.P.; Argus, D.F. GRACE groundwater drought index: Evaluation of California Central Valley groundwater drought. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 198, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval-Solis, S.; McKinney, D.; Loucks, D.P. Sustainability index for water resources planning and management. Water Resour. Plann. Manag. 2011, 137, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loucks, D.P. Quantifying trends in system sustainability. J. Sci. Hydrol. 1997, 42, 513–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.M.; Wang, Z.T. Detect Songhua River Basin Groundwater Spatiotemporal Variation Characteristics by GRACE and Multi-source Hydrological Data. Geomat. Info. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2023, 48, 1409–1415. [Google Scholar]
- Reshef, D.N.; Reshef, Y.A.; Finucane, H.K.; Grossman, S.R.; McVean, G.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Lander, E.S.; Mitzenmacher, M.; Sabeti, P.C. Detecting novel associations in large data sets. Science 2011, 334, 1518–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshef, D.; Reshef, Y.; Mitzenmacher, M.; Sabeti, P. Equitability analysis of the maximal information coefficient, with comparisons. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1301.6314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milly, P.C.D. Climate, soil water storage, and the average annual water balance. Water Resour. Res. 1994, 30, 2143–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, R.E. The role of infiltration in the hydrologic cycle. Eos Trans. Amer. Geophys. Union. 1933, 14, 446–460. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, G.F.; Yong, L.L.; Zhao, X.; Liu, Y.W.; Zhang, Z.X.; Xu, Y.X.; Sun, Z.G.; Sang, L.Y.; Wang, L. Evaporation, infiltration and storage of soil water in different vegetation zones in the Qilian Mountains: A stable isotope perspective. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 26, 3771–3784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, E.; Porporato, A. A review of soil moisture dynamics: From rainfall infiltration to ecosystem response. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2005, 22, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asoka, A.; Gleeson, T.; Wada, Y.; Mishra, V. Relative contribution of monsoon precipitation and pumping to changes in groundwater storage in India. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Hu, Q. Groundwater influences on soil moisture and surface evaporation. J. Hydrol. 2004, 297, 285–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Wang, S.; Kong, X.; Zheng, W.; Feng, W.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, R.; Song, X.; Sprenger, M. Interaction of surface water and groundwater influenced by groundwater over-extraction, waste water discharge and water transfer in Xiong’an New Area, China. Water 2019, 11, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Pan, Y.; Xu, Y. Spatio-temporal variation of groundwater recharge in response to variability in precipitation, land use and soil in Yanqing Basin, Beijing, China. Hydrogeol. J. 2012, 20, 1331–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, M.; Farrow, C.R. Watershed-scale response of groundwater recharge to inter-annual and inter-decadal variability in precipitation (Alberta, Canada). Hydrogeol. J. 2014, 22, 1825–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asoka, A.; Wada, Y.; Fishman, R.; Mishra, V. Strong linkage between precipitation intensity and monsoon season groundwater recharge in India. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 5536–5544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, R.; Song, Q.; Hao, Y.; Wu, G. Groundwater level declines in Tianjin, North China: Climatic variations and human activities. Environ. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 25, 1899–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Nie, Z.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Cao, L. Change in groundwater table depth caused by natural change and human activities during the past 40 years in the Shiyang River Basin, northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, C.; Fang, C. Water resources flows related to urbanization in China: Challenges and perspectives for water management and urban development. Water Resour. Manag. 2012, 26, 531–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, R.M.A.; Manzoor, M.M.; Mukhtar, S. Urbanization and its effects on water resources: An exploratory analysis. Asian J. Water Environ. Pollut. 2018, 15, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, S.; Camara, G.; Miguel, A.; Monteiro, V.; Quintanilha, J.A.; Elvidge, C.D. Estimating population and energy consumption in Brazilian Amazonia using DMSP night-time satellite data. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2005, 29, 179–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, K.M.; Shi, Y. Nighttime lights and urban expansion: Illuminating the correlation between built-up areas of Lagos City and changes in climate parameters. Buildings 2023, 13, 2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceola, S.; Laio, F.; Montanari, A. Human pressure on rivers is increasing worldwide and threatens water security. Proc. Int. Assoc. Hydrol. Sci. 2015, 366, 109–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.J.; Xu, X.F.; Zheng, L.Y.; Xu, X.L.; Zhang, Y.K. Analysis of the Relationship between Economic Development and Water Resources–Ecological Management Capacity in China Based on Nighttime Lighting Data. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Hao, L. Impact of rapid urbanization on groundwater storage variation amid climate change in the Yangtze River Basin. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2025, 59, 102360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, M.J.; Guo, C.M.; Wang, D.N.; Yuan, F.X.; Qu, S.M.; Ren, J.Q.; Li, Z.H.; Mu, J. Variation of effective precipitation and water deficit index in maize growing season in Jilin Province during 1960–2015. Agric. Res. Arid Areas 2018, 36, 237–243. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Y.L.; Sun, S.K.; Wang, Y.B.; Li, C.; Sun, J.X.; Wu, P.T. Impact of grain virtual water flow on surface water and groundwater in China. Adv. Water Resour. 2021, 150, 103848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, X.; Liu, X.; Bao, X.; Zhang, X.; Yin, B.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhen, W. Effects of spring limited irrigation on grain yield and root characteristics of winter wheat in groundwater-overexploitation areas in the North China Plain. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 294, 108729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Shao, L.; Chen, S.; Wang, J.; Dong, X. Impact of different cropping systems and irrigation schedules on evapotranspiration, grain yield and groundwater level in the North China Plain. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 211, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, D.L.; Burbey, T.J. Regional land subsidence accompanying groundwater extraction. Hydrogeol. J. 2011, 19, 1459–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erban, L.E.; Gorelick, S.M.; Zebker, H.A. Groundwater extraction, la9nd subsidence, and sea-level rise in the Mekong Delta, Vietnam. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 084010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minderhoud, P.S.J.; Erkens, G.; Pham, V.H.; Bui, V.T.; Erban, L.; Kooi, H.; Stouthamer, E. Impacts of 25 years of groundwater extraction on subsidence in the Mekong delta, Vietnam. Environ. Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 064006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, D.; He, X.; Wang, Z.; Tian, Y.; Xiang, H.; Yu, H.; Man, W.; Jia, M.; Ren, C.; Zheng, H. Diverse policies leading to contrasting impacts on land cover and ecosystem services in Northeast China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 240, 117961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongol, N.; Zhang, F.-s. The transformation of agriculture in China: Looking back and looking forward. J. Integr. Agric. 2018, 17, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, K.; Lin, Y.; Shi, W.; Song, Y.; He, X. Balancing green and grain trade. Nat. Geosci. 2015, 8, 739–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J. Rapid urbanization in China: A real challenge to soil protection and food security. Catena 2007, 69, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, Z.; He, C.; Yue, H.; Gou, S. Water shortages raised a legitimate concern over the sustainable development of the drylands of northern China: Evidence from the water stress index. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 590, 739–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Dong, J.; Xiao, X.; Hu, Z.; Sheldon, S. Effectiveness of ecological restoration projects in Horqin Sandy Land, China based on SPOT-VGT NDVI data. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 38, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Grade | Range | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REL | RES | VUL | SI | |
| Extremely low | 0–0.25 | 0–0.20 | 0–0.10 | 0–0.20 |
| Low | 0.25–0.40 | 0.20–0.30 | 0.10–0.40 | 0.20–0.30 |
| Moderate | 0.40–0.60 | 0.30–0.50 | 0.40–0.60 | 0.30–0.50 |
| High | 0.60–0.75 | 0.50–0.75 | 0.60–0.75 | 0.50–0.75 |
| Extremely high | 0.75–1 | 0.75–1 | 0.75–1 | 0.75–1 |
| SA | NTL | PRE | PET | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIC | 0.698 | 0.374 | 0.615 | 0.474 |
| R | −0.78 | −0.708 | −0.363 | −0.417 |
| Year | Land Use Types/km2 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cropland | Forest | Grassland | Water | Barren | Impervious | Wetland | |
| 2002 | 89,206.69 | 84,744.14 | 5763.63 | 2370.56 | 2799.98 | 6018.73 | 18.37 |
| 2012 | 88,926.00 | 82,408.78 | 6589.94 | 2792.28 | 2334.88 | 7858.64 | 11.61 |
| 2022 | 89,817.99 | 82,181.95 | 4967.50 | 3188.23 | 1578.45 | 9178.15 | 9.84 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Dai, C.; Jing, Y.; Ru, Q.; Yan, F.; Zhang, Y. GRACE/GRACE-FO Satellite Assessment of Sown Area Expansion Impacts on Groundwater Sustainability in Jilin Province. Sustainability 2025, 17, 7731. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17177731
Liu Y, Dai C, Jing Y, Ru Q, Yan F, Zhang Y. GRACE/GRACE-FO Satellite Assessment of Sown Area Expansion Impacts on Groundwater Sustainability in Jilin Province. Sustainability. 2025; 17(17):7731. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17177731
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yang, Changlei Dai, Yang Jing, Qing Ru, Feiyang Yan, and Yiding Zhang. 2025. "GRACE/GRACE-FO Satellite Assessment of Sown Area Expansion Impacts on Groundwater Sustainability in Jilin Province" Sustainability 17, no. 17: 7731. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17177731
APA StyleLiu, Y., Dai, C., Jing, Y., Ru, Q., Yan, F., & Zhang, Y. (2025). GRACE/GRACE-FO Satellite Assessment of Sown Area Expansion Impacts on Groundwater Sustainability in Jilin Province. Sustainability, 17(17), 7731. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17177731





