Has Green Technological Innovation Become an Accelerator of Carbon Emission Reductions?
Abstract
1. Introduction
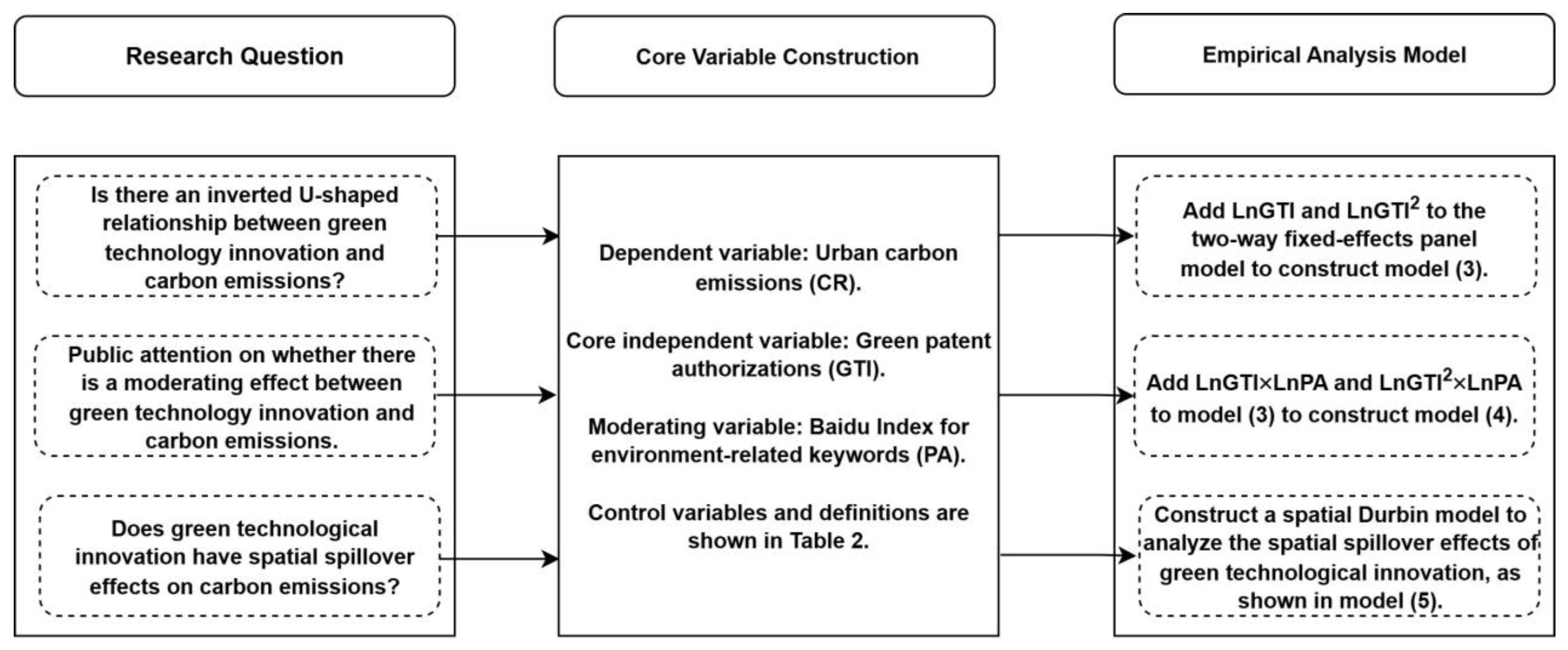
2. Theoretical Analysis and Research Assumptions
2.1. Analysis of Green Technology Innovation’s Impact on Carbon Emissions
2.2. Analysis of Public Concern’s Moderating Effect
2.3. Analysis of Green Technological Innovation’s Spatial Effect
3. Research Design and Data Description
3.1. Variable Selection and Description
3.1.1. Explained Variables
3.1.2. Core Explanatory Variables
3.1.3. Moderating Variables
3.1.4. Control Variables
3.2. Data Sources
3.3. Model Setting
3.3.1. Econometric Model
3.3.2. Moderating Effect Model
3.3.3. Spatial Econometric Modeling
4. Analysis of Empirical Results
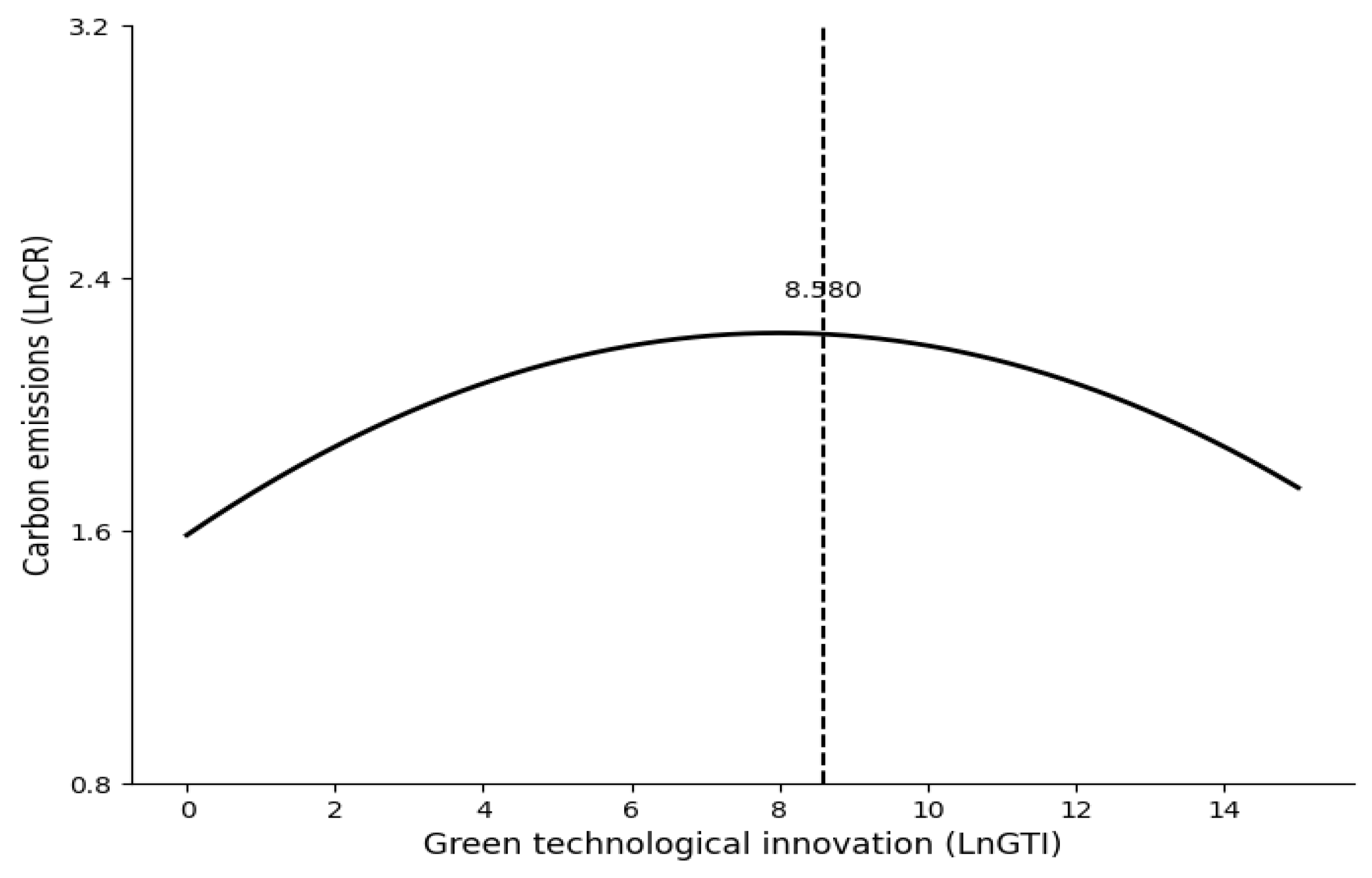
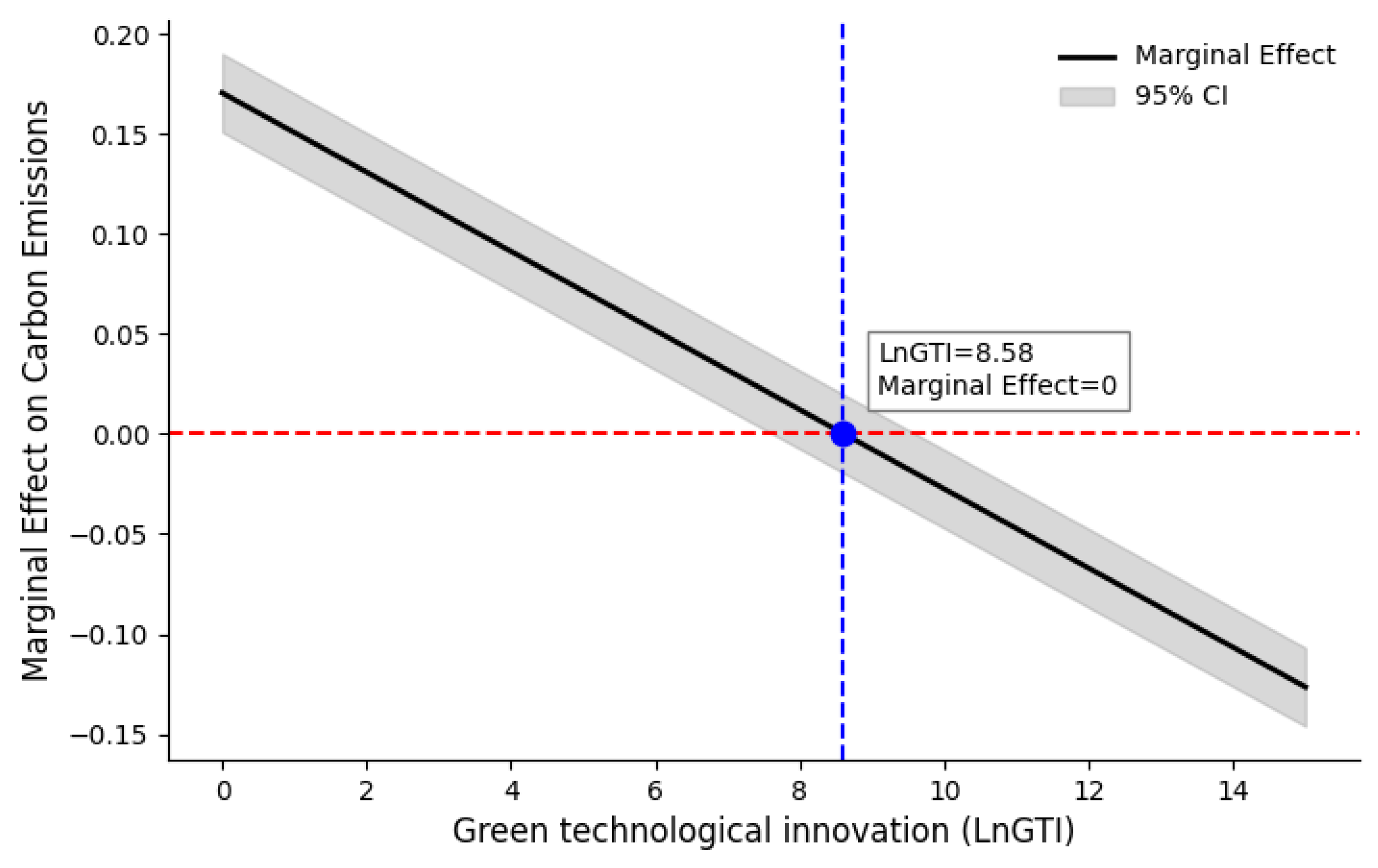
4.1. Benchmark Regression
4.2. Robustness Test
- (1)
- Replacement of Explanatory Variables
- (2)
- Shrinking the sample time range
- (3)
- Eliminate the influence of outliers
4.3. Endogeneity Test
4.4. Regulatory Effect Test
4.5. Heterogeneity Test
4.6. Further Analyses
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions and Recommendations
6.1. Main Conclusions
6.2. Policy Implications
6.3. Research Limitations and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, J.; Cao, G. Do market-based environmental regulations always promote enterprise green innovation commercialization. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 375, 124183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.; Sharif, A. Disruptive solutions for carbon neutrality and sustainable development: Evidence from CS-ARDL approach. Sustain. Dev. 2025, 33, 5374–5389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braungardt, S.; der Wieden, M.B.; Kranzl, L. EU emissions trading in the buildings sector—An ex-ante assessment. Clim. Policy 2025, 25, 208–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP). Emissions Gap Report 2023: Broken Record—Temperatures Hit New Highs, Yet World Fails to Cut Emissions (Again); UNEP: Nairobi, Kenya, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, B.; Ma, R. How does digital finance influence green technology innovation in China? Evidence from the financing constraints perspective. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 320, 115833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United Nations. Net Zero Coalition. Available online: https://www.un.org/en/climatechange/net-zero-coalition (accessed on 9 July 2025).
- Squires, D.; Vestergaard, N. Rethinking the commons problem: Technical change, knowledge spillovers, and social learning. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2018, 91, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Qian, Z.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q. Do green concerns promote corporate green innovation? Evidence from Chinese stock exchange interactive platforms. Manag. Decis. Econ. 2023, 44, 1786–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Hua, G.; AbidAli, R.; Huo, B.; Mahamane, F.; Li, Z. The impact of green low-carbon finance on smog reduction and carbon mitigation: Evidence from a spatial panel simultaneous equations model. Int. J. Urban Sci. 2024, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Ding, H. How public attention drives corporate environmental protection: Effects and channels. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2023, 191, 122486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Lin, Y. Do more hands make work easier? Public supervision and corporate green innovation. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2024, 91, 1064–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- State Council of China, National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC). Action Plan for Carbon Dioxide Peaking Before 2030; State Council: Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Central Committee of the Communist Party of China, State Council of China. Working Guidance for Carbon Dioxide Peaking and Carbon Neutrality in Full and Faithful Implementation of the New Development Philosophy; State Council: Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment (MEE); National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC); Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT); Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development (MOHURD); Ministry of Transport (MOT); Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs (MARA); National Energy Administration (NEA). Implementation Plan for Synergizing Pollution Reduction and Carbon Reduction; Ministry of Ecology and Environment (MEE): Beijing, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, Z.; Yang, T.; Zhang, Z. Assessing the role of public, media, and government attention on air pollution governance in China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 113, 105681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, Z.; Zhao, L.; Elahi, E.; Chang, X. The impact of green management on green innovation in sustainable technology: Moderating roles of executive environmental awareness, regulations, and ownership. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlvik, L.; van den Bijgaart, I. Screening green innovation through carbon pricing. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2024, 124, 102932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geels, F.W. From sectoral systems of innovation to socio-technical systems: Insights about dynamics and change from sociology and institutional theory. Res. Policy 2004, 33, 897–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, A.; Rasool, Z.; Nazar, R.; Anser, M.K. Towards a greener future: How green technology innovation and energy efficiency are transforming sustainability. Energy 2024, 290, 129891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, X.; Zheng, L.; Fan, S.; Zuo, S. Green innovation and carbon emission performance: The role of digital economy. Energy Policy 2024, 195, 114344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Li, X.; Li, S. Green Technology Innovation and Carbon Emission Performance of the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River Urban Agglomeration: Mechanism and Spatio-Temporal Evolution. Energies 2024, 17, 5274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Hong, Q.; Zhu, T.; Yu, W. Influence of green technology innovation and green finance on China’s carbon neutral performance: Do synergistic effects exist? Appl. Econ. 2024, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafeel, K.; Zhou, J.; Phetkhammai, M.; Lu, H.; Sher, K. Green innovation and environmental quality in OECD countries: The mediating role of renewable energy and carbon taxes. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 2214–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Sami, F.; Khan, S.; Alamri, A.M.; Zaidan, A.M. Green innovation and low carbon emission in OECD economies: Sustainable energy technology role in carbon neutrality target. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2023, 59, 103401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, R.E. Strategic Management: A Stakeholder Approach; Pitman: Boston, MA, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, R.K.; Agle, B.R.; Wood, D.J. Toward a theory of stakeholder identification and salience: Defining the principle of who and what really counts. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1997, 22, 853–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etter, M.; Ravasi, D.; Colleoni, E. Social media and the formation of organizational reputation. Acad. Manag. Rev. 2019, 44, 28–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dryzek, J.S. The Politics of the Earth: Environmental Discourses, 3rd ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Castells, M. Communication Power; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Jagodnik, K.M.; Dekel, S.; Bartal, A. Persistence of collective memory of corporate bankruptcy events discussed on X (Twitter) is influenced by pre-bankruptcy public attention. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 6552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laplume, A.O.; Sonpar, K.; Litz, R.A. Stakeholder theory: Reviewing a theory that moves us. J. Bus. Ethics 2008, 83, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaargaren, G.; Mol, A.P.J. Sociology, environment, and modernity: Ecological modernization as a theory of social change. Soc. Nat. Resour. 1992, 5, 323–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etzion, D. Research on organizations and the natural environment, 1992–present: A review. J. Manag. 2007, 33, 637–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, P.; Roth, K. Why companies go green: A model of ecological responsiveness. Acad. Manag. J. 2000, 43, 717–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y. Public environmental concern and green innovation in firms: Evidence from Chinese listed companies. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 421, 139789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzeretti, L.; Capone, F. How proximity matters in innovation networks dynamics along the cluster evolution: A study of the high technology applied to cultural goods. J. Bus. Res. 2016, 69, 5855–5865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Q. An empirical analysis of the impact of green investment on China’s green development level: Based on mediating and spatial spillover effects. Adv. Econ. Manag. Politi-Sci. 2024, 73, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, F. Environmental regulation and spatial spillover effect of green technology innovation: An empirical study using the Spatial Durbin Model. Sustainability 2023, 15, 14133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.; Gao, Z.; Wang, L.; Tian, L. How does green innovation drive urban carbon emission efficiency?—Evidence from the Yangtze River Economic Belt. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 375, 134196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Xia, Z. Digital inclusive finance, green technological innovation, and carbon emissions from a spatial perspective. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 8454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shipan, C.R.; Volden, C. The mechanisms of policy diffusion. Am. J. Politi-Sci. 2008, 52, 840–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). 2006 IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories. Volume 2: Energy; Institute for Global Environmental Strategies (IGES): Hayama, Japan, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC). Notice on the Average Emission Factor of the Regional Power Grid Baseline in 2015; NDRC: Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment (MEE). Notice on the Carbon Emission Factor of China’s Power Grid in 2021 and 2022; MEE: Beijing, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, M. Temporal and spatial variations of carbon intensity from electricity generation in China: Decomposition and scenario analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 363, 132511. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Y.; Zheng, L.; Gu, Y.; Yang, X. Impacts of green technology innovation on carbon emissions: A spatial-based perspective. Technol. Anal. Strat. Manag. 2024, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Fan, L.; Chen, H.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z. Green innovation and carbon emission reduction: Empirical insights from spatial durbin and dynamic threshold models. Int. Rev. Financ. Anal. 2025, 101, 103997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhou, X.; Lu, M.; Cui, Z. Impacts of haze weather on tourist arrivals and destination preference: Analysis based on Baidu Index of 73 scenic spots in Beijing, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 273, 122887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, J.; Bai, Y.; Yang, R. Public environmental concern and enterprise environmental protection investment: From the perspective of enterprise life cycle. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024, 26, 15031–15065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Ma, X.; Fu, T.; Guan, S. Does public concern over haze pollution matter? Evidence from Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, B.; He, Y.; Dong, Z.; Wang, S. Have public environmental appeals inspired green total factor productivity? empirical evidence from Baidu Environmental Search Index. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 30237–30252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xia, W. Public attention and investment efficiency: Incentive effect or deterrent effect? Analysis on heterogeneous bilateral stochastic frontier model. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2022, 185, 122043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Cao, X.; Zhao, S.; Xu, Y. Prediction and lag analysis of public concern about air pollution based on gray relation analysis and bidirectional long short-term memory. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2023, 16, 1037–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haans, R.F.J.; He, Z.L. Thinking about U: Theorizing and testing U- and inverted U-shaped relationships in strategy research. Strat. Manag. J. 2016, 37, 1177–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Geng, Y.-R.; Guo, T. The impact of green technological innovation in urban agglomerations on carbon emissions: The moderating effect of human capital. J. Nat. Resour. 2024, 39, 2121–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, G.; Li, L.; Guo, D. Does the Integration of the Digital Economy and the Real Economy Enhance Urban Green Emission Reduction Efficiency? Evidence from China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2025, 122, 106269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Xu, W.; Xin, D. Digital–Real Economy Integration and Urban Low-Carbon Development in China. Econ. Anal. Policy 2025, 86, 606–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC). Pilot Work Program for Low-Carbon Provinces and Low-Carbon Cities (Batch I, II, III); NDRC: Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- State Council of the People’s Republic of China. Sustainable Development Plan for Resource-Based Cities (2013–2020); State Council: Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, C.; Lee, C.-C. Synergy of Pollution Control and Carbon Reduction in China: Spatial–Temporal Characteristics, Regional Differences, and Convergence. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2023, 101, 107110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, L.; Han, L. The Digital Empowerment Promotes Synergistic Efficiency in Regional Pollution Reduction and Carbon Emission Reduction—Analysis of the Moderating Effects of Market Structure and Government Behavior. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 493, 144867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, N.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Q. The Empowerment of Smart City Construction on the Synergy Effect of Pollution Control and Carbon Reduce in China: Empirical Analysis with Double Machine Learning Method. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 519, 145958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Fang, J.; Li, J.; Wang, X. Research on the Impact of the Integration of Digital Economy and Real Economy on Enterprise Green Innovation. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2024, 200, 123097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Hui, S. Low-Carbon Transition Policy and Employment Structure: Evidence from China’s Low-Carbon City Pilot. Cities 2025, 162, 105985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, Z.; Walker, T.R.; Wilson, J.; Tao, X.; Dong, H.; Zhao, W. Impact of Political Incentives on Urban Green Development: An Analysis of 284 Cities in China. Cities 2025, 161, 105891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, W.; Lan, Y.; Gan, L.; Li, J. How Does New Urbanization Affect Urban Carbon Emissions? Evidence Based on Spatial Spillover Effects and Mechanism Tests. Urban Clim. 2024, 56, 102060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Yin, S. How Does Digital Technology Innovation Drive Synergies for Reducing Pollution and Carbon Emissions? Sustainable Cities and Society 2024. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 116, 105932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, N.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, G.; Wu, L.; Zhang, L. How Does Data Factor Marketization Influence Urban Carbon Emission Efficiency? A New Method Based on Double Machine Learning. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2025, 119, 106106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Xie, J. Digital Economy and Carbon Emission Efficiency in Three Major Urban Agglomerations of China: A U-Shaped Journey towards Green Development. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 373, 123571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.-H.; Wang, X.-Q.; Meng, X.-R. U-Shaped Relationship between Environmental Regulation and the Digital Transformation of the Chinese Coal Industry: Mechanism and Moderating Effects. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 373, 123641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
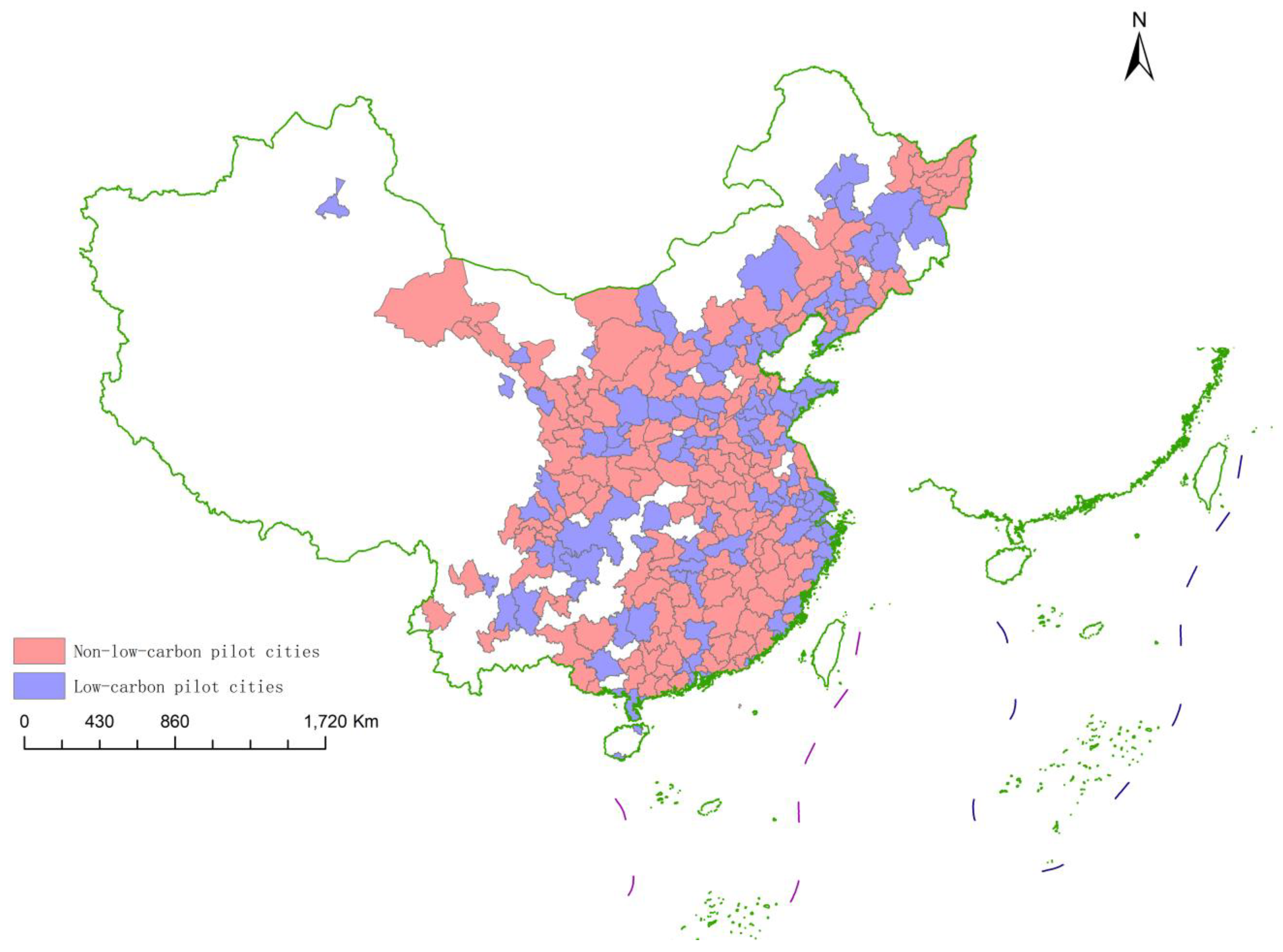
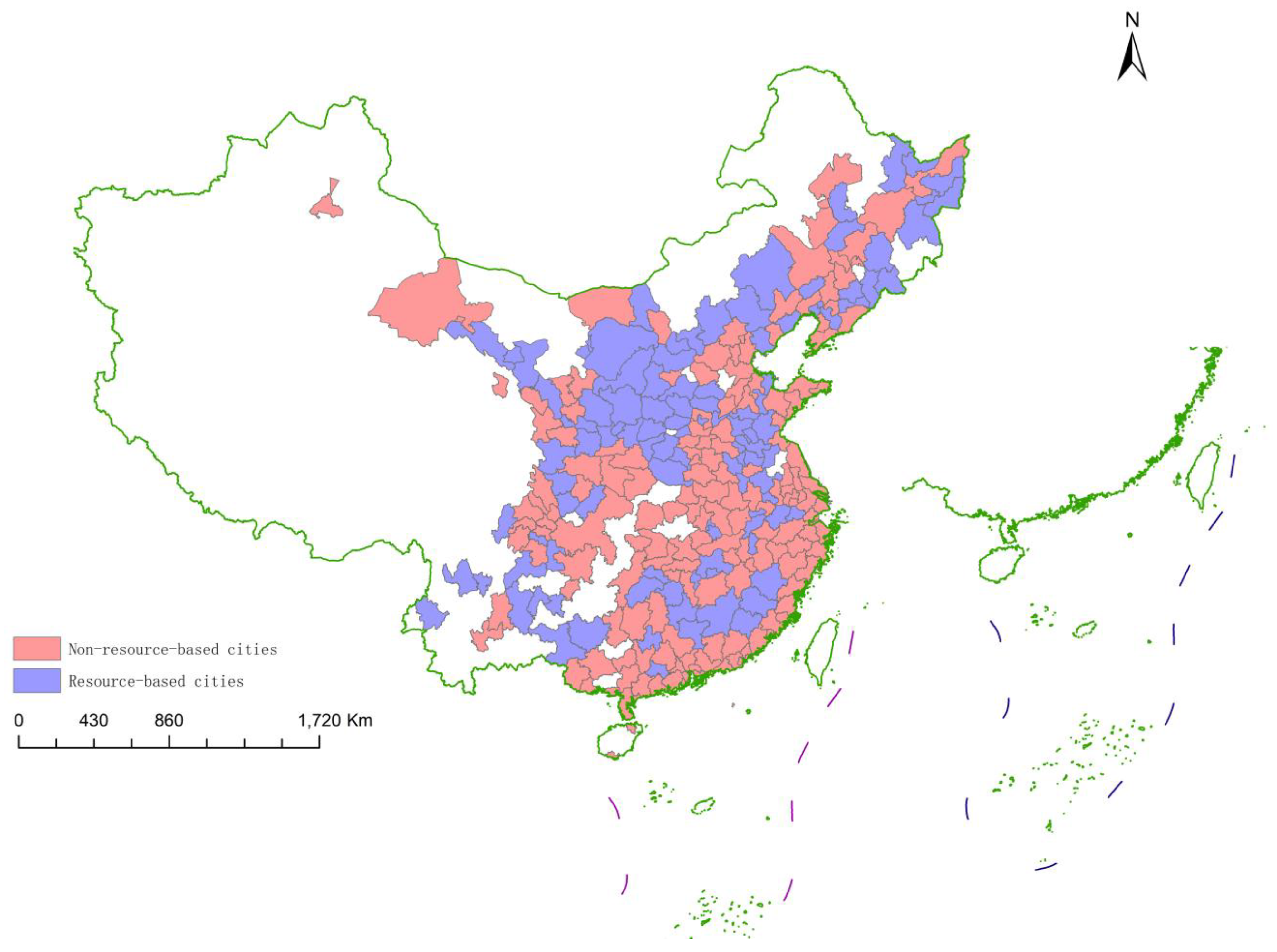
| Symbol | Obs | Mean | SD | Min | Median | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LnCR | 2937 | 2.1726 | 0.7343 | 0.0864 | 2.1269 | 5.3715 |
| LnGTI1 | 2937 | 0.7050 | 1.1000 | 0.0000 | 0.2467 | 4.6052 |
| LnGTI2 | 2937 | 0.9500 | 1.1000 | 0.0449 | 0.3940 | 5.0000 |
| LnPA | 2937 | 0.0530 | 0.0455 | 0.0000 | 0.0374 | 0.7577 |
| OP | 2937 | 0.2200 | 0.2008 | 0.0002 | 0.1571 | 0.5000 |
| LnPS | 2937 | 5.7762 | 0.9061 | 0.6831 | 5.9353 | 7.8816 |
| UL | 2937 | 0.5630 | 0.1480 | 0.1815 | 0.5435 | 1.0000 |
| GV | 2937 | 0.1950 | 0.0900 | 0.0439 | 0.1741 | 0.8055 |
| FD | 2937 | 2.0040 | 1.0000 | 0.5879 | 1.8507 | 4.5000 |
| SD | 2937 | 0.0175 | 0.0178 | 0.0006 | 0.0119 | 0.2068 |
| LnHD | 2937 | 4.8400 | 0.8200 | 2.5000 | 4.7146 | 5.9915 |
| Variable Name | Abbreviation | Definition | Data Source | Variable Type | Time Span | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dependent Variable | Urban Carbon Emissions | LnCR | Total CO2 emissions per 10,000 people (natural logarithm) | China Statistical Yearbook, China Urban Statistical Yearbook, IPCC [42], China Power Grid [42,43,44] | Continuous | 2012–2022 |
| Explanatory Variables | Authorized Green Patents | LnGTI1 | Number of authorized green patents per 10,000 people, log(1 + x) transformed | National Intellectual Property Administration (CNIPA) https://www.cnipa.gov.cn | ||
| Applied Green Patents | LnGTI2 | Number of applied green patents per 10,000 people, log(1 + x) transformed | ||||
| Moderating Variables | Public Environmental Attention | LnPA | Baidu Index for environmental keywords per 10,000 people, log(1 + x) transformed | Baidu Search Index Platform https://index.baidu.com | ||
| Control Variables | Openness to the Outside World | OP | Actual utilized foreign investment/regional GDP | China Urban Statistical Yearbook | ||
| Population Density | LnPS | Natural logarithm of population density (resident population per square kilometer) | ||||
| Urbanization Rate | UL | Urban population/total population | ||||
| Government Intervention | GV | Government expenditure/regional GDP | ||||
| Financial Development | FD | Bank deposits and loans/regional GDP | ||||
| R&D Investment Intensity | SD | Science and technology expenditure/government expenditure | ||||
| Human Capital | LnHD | Number of university students per 10,000 people (natural logarithm) |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LnCR | LnCR | LnCR | LnCR | LnCR | LnCR | LnCR | LnCR | |
| LnGTI | 0.0107 *** | 0.0101 *** | 0.0100 *** | 0.0103 *** | 0.0102 *** | 0.0107 *** | 0.0099 *** | 0.0099 *** |
| (15.8382) | (15.2476) | (14.7649) | (15.1469) | (14.9689) | (15.2518) | (13.5591) | (13.6222) | |
| LnGTI2 | −0.0108 *** | −0.0080 *** | −0.0082 *** | −0.0009 *** | −0.0007 *** | 0.0013 *** | −0.0032 *** | −0.0023 *** |
| (−3.7712) | (−2.8616) | (−2.8505) | (−3.1202) | (−2.9762) | (3.0150) | (−3.0020) | (−2.9286) | |
| OP | −0.2383 *** | −0.2386 *** | −0.2373 *** | −0.2340 *** | −0.2339 *** | −0.2333 *** | −0.2297 *** | |
| (−11.7193) | (−11.7220) | (−11.6892) | (−11.3968) | (−11.4093) | (−11.4099) | (−11.2045) | ||
| PS | 0.0090 | 0.0008 | −0.0012 | 0.0131 | −0.0272 | −0.0372 | ||
| (0.3403) | (0.0302) | (−0.0464) | (0.4854) | (−0.9439) | (−1.2750) | |||
| UL | −0.1275 *** | −0.1247 *** | −0.1298 *** | −0.1266 *** | −0.1196 *** | |||
| (−3.9642) | (−3.8662) | (−4.0223) | (−3.9321) | (−3.7021) | ||||
| GV | −0.0408 | −0.0330 | −0.0339 | −0.0378 | ||||
| (−1.0552) | (−0.8525) | (−0.8794) | (−0.9815) | |||||
| FD | 0.0468 *** | 0.0714 *** | 0.0723 *** | |||||
| (2.9024) | (4.1404) | (4.1916) | ||||||
| SD | 0.0275 *** | 0.0277 *** | ||||||
| (3.9436) | (3.9677) | |||||||
| LnHD | −0.0001 ** | |||||||
| (−2.2443) | ||||||||
| City Fe | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Year Fe | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| _cons | 0.8564 *** | 0.9298 *** | 0.0037 | 0.4985 | 0.4770 | 0.3090 | 1.3537 ** | 1.5860 *** |
| (55.8592) | (56.4990) | (0.0069) | (0.9121) | (0.8696) | (0.5567) | (2.3578) | (2.7269) | |
| N | 2937 | 2937 | 2937 | 2937 | 2937 | 2937 | 2937 | 2937 |
| Lower Bound | Upper Bound | |
|---|---|---|
| Interval | −5.6810 | 3.1955 |
| Slope | −0.1152 | 0.0611 |
| t value | −19.1773 | 7.8061 |
| P | 3.62 × 10−77 | 4.21 × 10−15 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LnCR | LnCR | LnCR | LnCR | |
| LnGT | 0.0458 *** | |||
| (2.5405) | ||||
| LnGT2 | −0.0097 *** | |||
| (−16.9823) | ||||
| LnGTI | 0.0107 *** | 0.0111 *** | 0.0099 *** | |
| (10.3444) | (12.1935) | (13.6222) | ||
| LnGTI2 | −0.0034 *** | −0.0008 *** | −0.0023 *** | |
| (−3.2102) | (−3.0185) | (−3.0588) | ||
| Control | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| City Fe | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Year Fe | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| _cons | 0.9516 *** | 0.7398 | 1.5781 *** | 1.4144 *** |
| (41.9245) | (1.0279) | (2.8062) | (3.1266) | |
| N | 2937 | 2136 | 2937 | 2937 |
| 2SLS | SYS-GMM | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) First-Stage LnGTI | (2) First-Stage LnGTI2 | (3) Second-Stage LnCR | (4) | |
| LnIV | 1.1911 *** | −0.1227 *** | ||
| (33.5400) | (−7.1802) | |||
| LnIV2 | −0.1421 *** | 0.0040 *** | ||
| (−18.0301) | (3.6700) | |||
| LnGTI | 0.0414 *** | 0.0611 *** | ||
| (6.9103) | (2.8510) | |||
| LnGTI2 | −0.0143 *** | −0.0166 *** | ||
| (−15.3903) | (−4.5506) | |||
| AR(1) | −1.92 (0.054) | |||
| AR(2) | 1.15 (0.251) | |||
| Sargan test | 22.16 (0.332) | |||
| F-statistic | 24.55 | |||
| Control | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| City Fe | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| Year Fe | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| N | 2937 | 2937 | 2937 | |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LnCR | LnCR | LnCR | LnCR | |
| LnGTI | 0.0275 *** | 0.0402 *** | 0.1000 *** | 0.0800 *** |
| (6.0470) | (9.4626) | (6.0470) | (9.4626) | |
| LnGTI2 | −0.0053 *** | −0.0049 *** | −0.0200 *** | −0.0500 *** |
| (−5.7571) | (−5.3901) | (−5.7571) | (−5.3901) | |
| LnPA × LnGTI | 0.0008 *** | 0.0007 *** | ||
| (9.1841) | (8.5148) | |||
| LnPA × LnGTI2 | −0.0001 *** | −0.0001 *** | ||
| (−2.8767) | (−3.9048) | |||
| LnPA | 0.0002 ** | 0.0001 *** | ||
| (0.8735) | (0.4802) | |||
| LnMA × LnGTI | 0.0050 *** | 0.0020 *** | ||
| (9.1841) | (8.5148) | |||
| LnPA × LnGTI2 | −0.0020 *** | −0.0010 *** | ||
| (−2.8767) | (−3.9048) | |||
| LnMA | 0.0010 ** | 0.0005 *** | ||
| (0.8735) | (0.4802) | |||
| Control | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| City Fe | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Year Fe | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| _cons | 1.4255 | 0.1537 * | 1.2000 | 0.3000 * |
| (0.6174) | (1.6666) | (0.6174) | (1.6666) | |
| N | 2937 | 1771 | 2937 | 1771 |
| Symbol | Obs | Mean | SD | Min | Median | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LnCR | 1166 | 2.0503 | 0.7100 | 0.2000 | 2.0100 | 4.9500 |
| LnGTI1 | 1166 | 0.8900 | 1.1200 | 0.0000 | 0.3900 | 4.6052 |
| LnGTI2 | 1166 | 1.1300 | 1.1500 | 0.0500 | 0.5300 | 5.0000 |
| LnPA | 1166 | 0.0621 | 0.0480 | 0.0000 | 0.0465 | 0.7577 |
| OP | 1166 | 0.2400 | 0.2000 | 0.0002 | 0.1860 | 0.5000 |
| LnPS | 1166 | 5.9100 | 0.8700 | 1.2400 | 5.9800 | 7.8500 |
| UL | 1166 | 0.5960 | 0.1420 | 0.2600 | 0.5700 | 1.0000 |
| GV | 1166 | 0.1900 | 0.0870 | 0.0439 | 0.1720 | 0.8055 |
| FD | 1166 | 2.1000 | 1.0000 | 0.5879 | 1.9800 | 4.5000 |
| SD | 1166 | 0.0182 | 0.0165 | 0.0010 | 0.0125 | 0.1900 |
| LnHD | 1166 | 4.9700 | 0.7900 | 2.7000 | 4.8500 | 5.9915 |
| Symbol | Obs | Mean | SD | Min | Median | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LnCR | 1771 | 2.2850 | 0.7400 | 0.0864 | 2.2100 | 5.3715 |
| LnGTI1 | 1771 | 0.5700 | 0.9700 | 0.0000 | 0.1700 | 4.1000 |
| LnGTI2 | 1771 | 0.8000 | 1.0700 | 0.0449 | 0.2900 | 4.9000 |
| LnPA | 1771 | 0.0460 | 0.0425 | 0.0000 | 0.0330 | 0.6400 |
| OP | 1771 | 0.2000 | 0.1800 | 0.0003 | 0.1310 | 0.4800 |
| LnPS | 1771 | 5.6400 | 0.9200 | 0.6831 | 5.8111 | 7.6500 |
| UL | 1771 | 0.5320 | 0.1440 | 0.1815 | 0.5100 | 0.9800 |
| GV | 1771 | 0.2020 | 0.0900 | 0.0500 | 0.1800 | 0.8055 |
| FD | 1771 | 1.8700 | 0.9500 | 0.5879 | 1.7300 | 4.2100 |
| SD | 1771 | 0.0160 | 0.0175 | 0.0006 | 0.0105 | 0.2068 |
| LnHD | 1771 | 4.6900 | 0.7800 | 2.5000 | 4.5200 | 5.8500 |
| Symbol | Obs | Mean | SD | Min | Median | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LnCR | 1870 | 2.3700 | 0.7200 | 0.2000 | 2.3100 | 5.2500 |
| LnGTI1 | 1870 | 0.6000 | 1.0300 | 0.0000 | 0.2000 | 4.3000 |
| LnGTI2 | 1870 | 0.7900 | 1.1000 | 0.0450 | 0.3100 | 4.7000 |
| LnPA | 1870 | 0.0450 | 0.0440 | 0.0000 | 0.0340 | 0.7020 |
| OP | 1870 | 0.1700 | 0.1700 | 0.0002 | 0.0900 | 0.4780 |
| LnPS | 1870 | 5.6000 | 0.8900 | 0.6831 | 5.7300 | 7.5811 |
| UL | 1870 | 0.5190 | 0.1400 | 0.1900 | 0.4900 | 0.9600 |
| GV | 1870 | 0.2130 | 0.0950 | 0.0490 | 0.1900 | 0.8055 |
| FD | 1870 | 1.7900 | 0.9100 | 0.5879 | 1.6200 | 4.1000 |
| SD | 1870 | 0.0158 | 0.0170 | 0.0006 | 0.0101 | 0.2000 |
| LnHD | 1870 | 4.6300 | 0.7800 | 2.5000 | 4.5100 | 5.8400 |
| Symbol | Obs | Mean | SD | Min | Median | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LnCR | 1067 | 1.9750 | 0.6920 | 0.0864 | 1.9400 | 4.9911 |
| LnGTI1 | 1067 | 0.8100 | 1.1100 | 0.0000 | 0.4500 | 4.6052 |
| LnGTI2 | 1067 | 1.1200 | 1.1400 | 0.0600 | 0.5800 | 5.0000 |
| LnPA | 1067 | 0.0590 | 0.0460 | 0.0000 | 0.0410 | 0.7577 |
| OP | 1067 | 0.2500 | 0.2100 | 0.0002 | 0.1800 | 0.5000 |
| LnPS | 1067 | 5.9400 | 0.8900 | 1.2412 | 6.0200 | 7.8816 |
| UL | 1067 | 0.6040 | 0.1420 | 0.2600 | 0.5800 | 1.0000 |
| GV | 1067 | 0.1800 | 0.0820 | 0.0439 | 0.1620 | 0.7012 |
| FD | 1067 | 2.1800 | 1.0200 | 0.6170 | 2.1000 | 4.5000 |
| SD | 1067 | 0.0190 | 0.0160 | 0.0012 | 0.0135 | 0.1900 |
| LnHD | 1067 | 5.0200 | 0.7800 | 2.9000 | 4.9100 | 5.9915 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LnCR | LnCR | LnCR | LnCR | |
| LnGTI | 0.0079 | 0.0194 *** | 0.0027 *** | 0.0042 |
| (1.4321) | (3.3499) | (2.8501) | (1.5234) | |
| LnGTI2 | −0.0138 | −0.0057 *** | −0.0078 *** | −0.0113 |
| (−1.4321) | (−5.2980) | (−6.8064) | (−1.3176) | |
| Control | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| City Fe | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Year Fe | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| _cons | 0.4725 *** | 0.5804 *** | 0.5671 *** | 0.5190 *** |
| (13.1422) | (19.0766) | (18.0280) | (15.0895) | |
| N | 1166 | 1771 | 1870 | 1067 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | LR_Direct | LR_Indirect | LR_Total |
| LnGTI | 0.0127 *** | 0.0017 *** | 0.0144 *** |
| (9.8042) | (6.5196) | (5.3271) | |
| LnGTI2 | −0.0027 *** | −0.0003 *** | −0.0030 *** |
| (−7.1143) | (−2.7819) | (−4.4395) | |
| Control | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| City Fe | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Year Fe | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Observations | 2937 | 2937 | 2937 |
| Number of ids | 267 | 267 | 267 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, J.; Yao, W.; Liu, F.; Qi, Y. Has Green Technological Innovation Become an Accelerator of Carbon Emission Reductions? Sustainability 2025, 17, 7499. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167499
Zhu J, Yao W, Liu F, Qi Y. Has Green Technological Innovation Become an Accelerator of Carbon Emission Reductions? Sustainability. 2025; 17(16):7499. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167499
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Jiagui, Weixin Yao, Fang Liu, and Yue Qi. 2025. "Has Green Technological Innovation Become an Accelerator of Carbon Emission Reductions?" Sustainability 17, no. 16: 7499. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167499
APA StyleZhu, J., Yao, W., Liu, F., & Qi, Y. (2025). Has Green Technological Innovation Become an Accelerator of Carbon Emission Reductions? Sustainability, 17(16), 7499. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167499


_Li.png)



