Statistical Characteristics of Hourly Extreme Heavy Rainfall over the Loess Plateau, China: A 43 Year Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
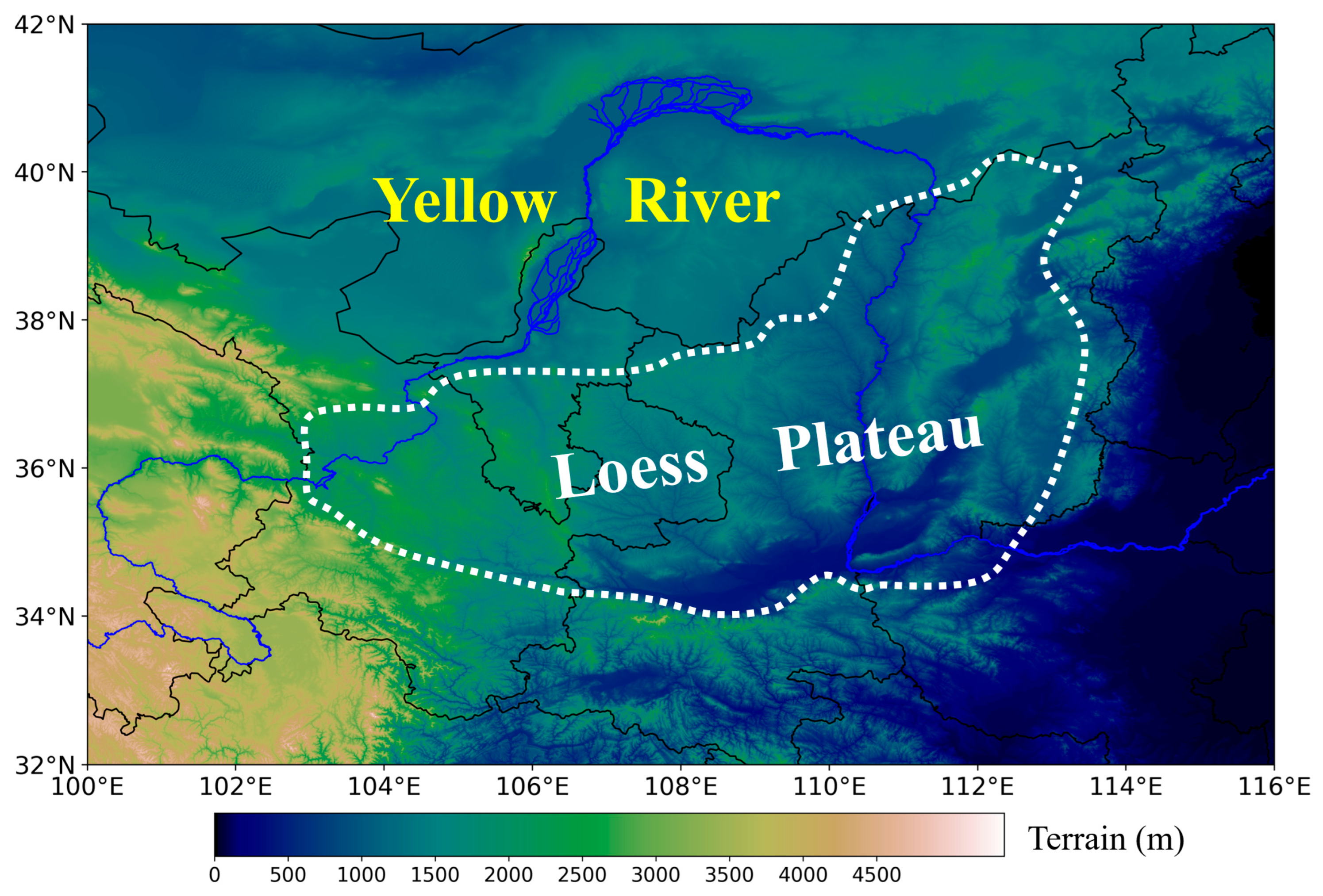
2. Data and Methods
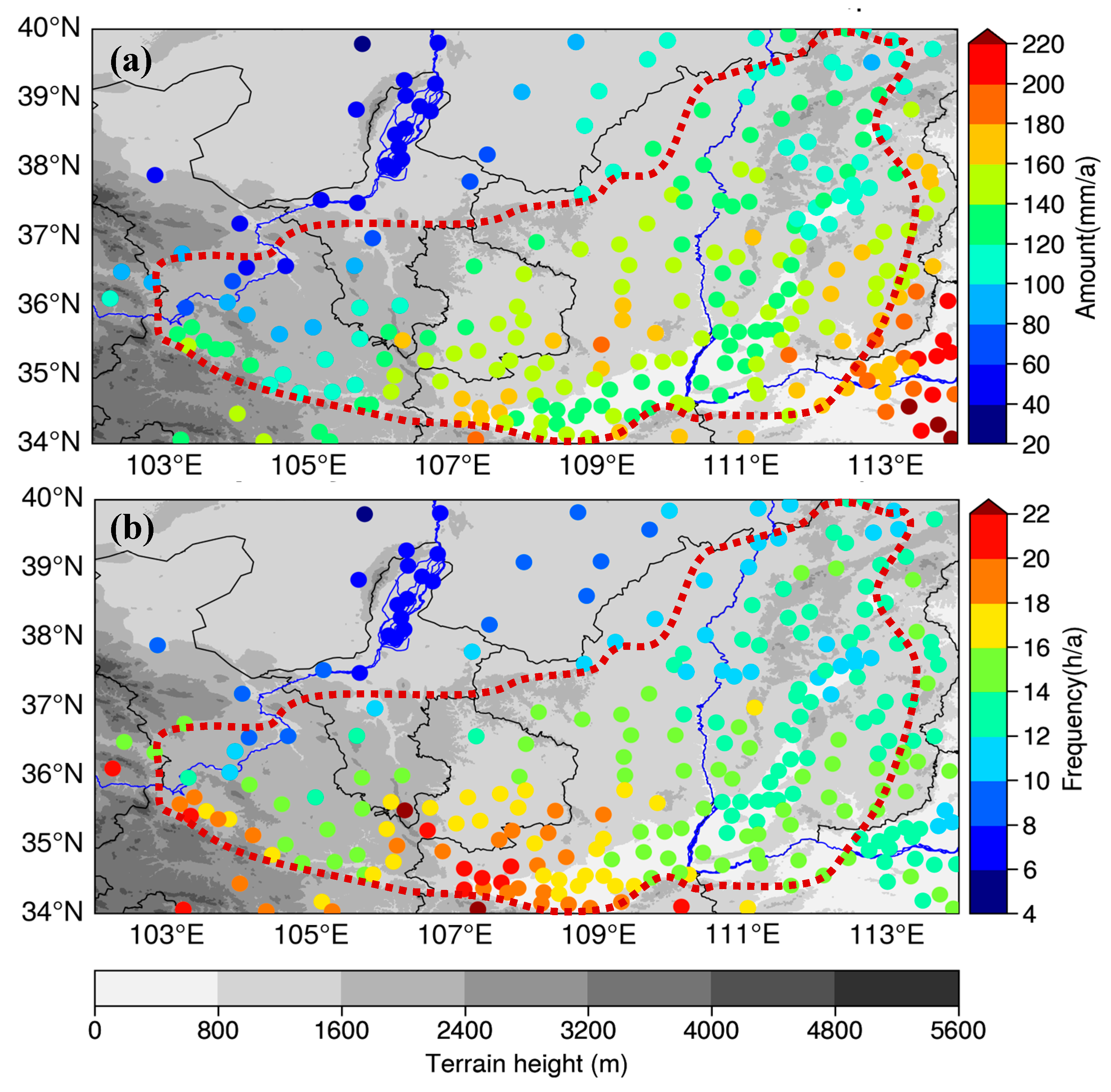
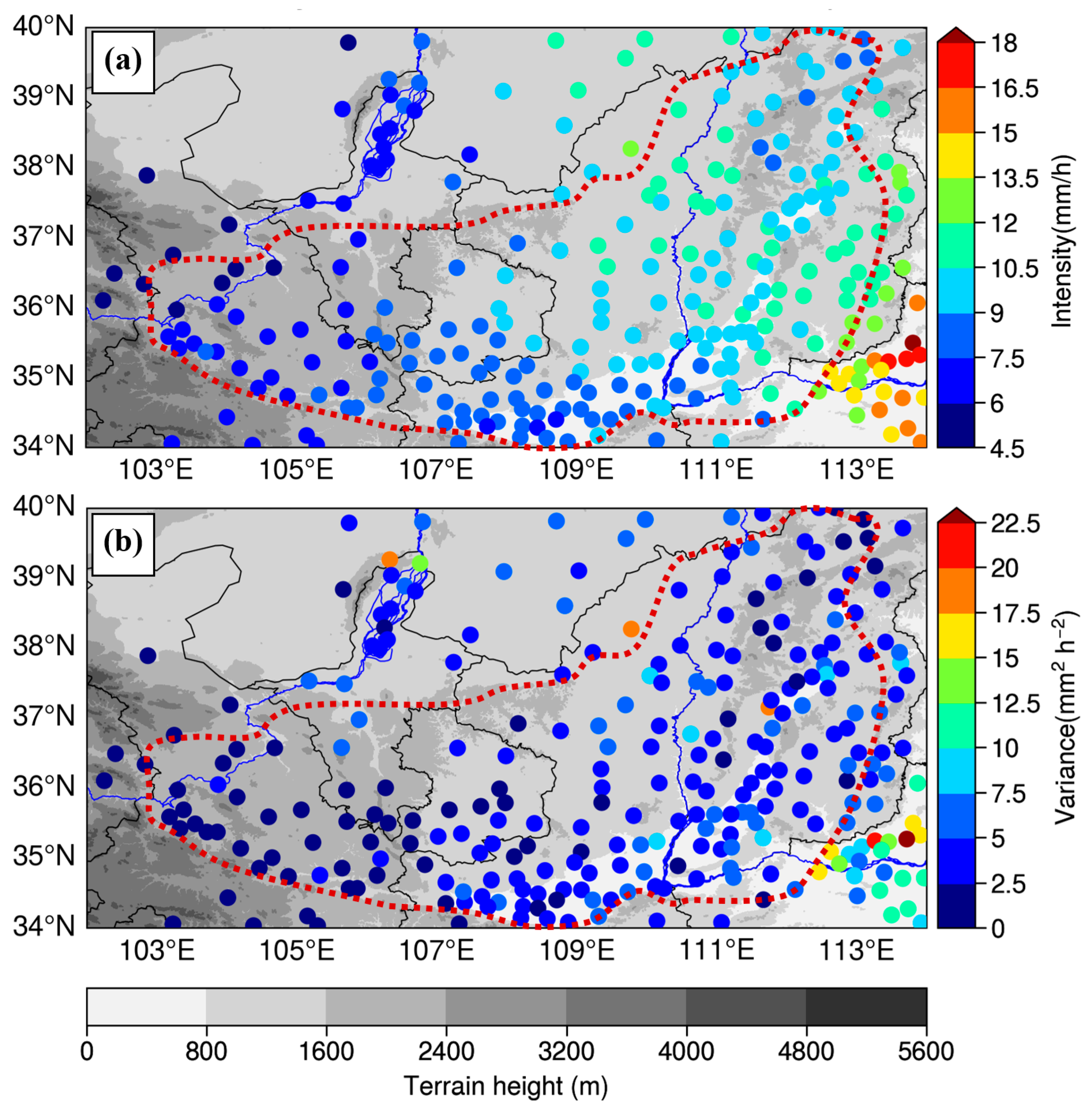
3. Spatial Characteristics
3.1. General Features
3.2. Key Characteristics of Extreme Hourly Rainfall
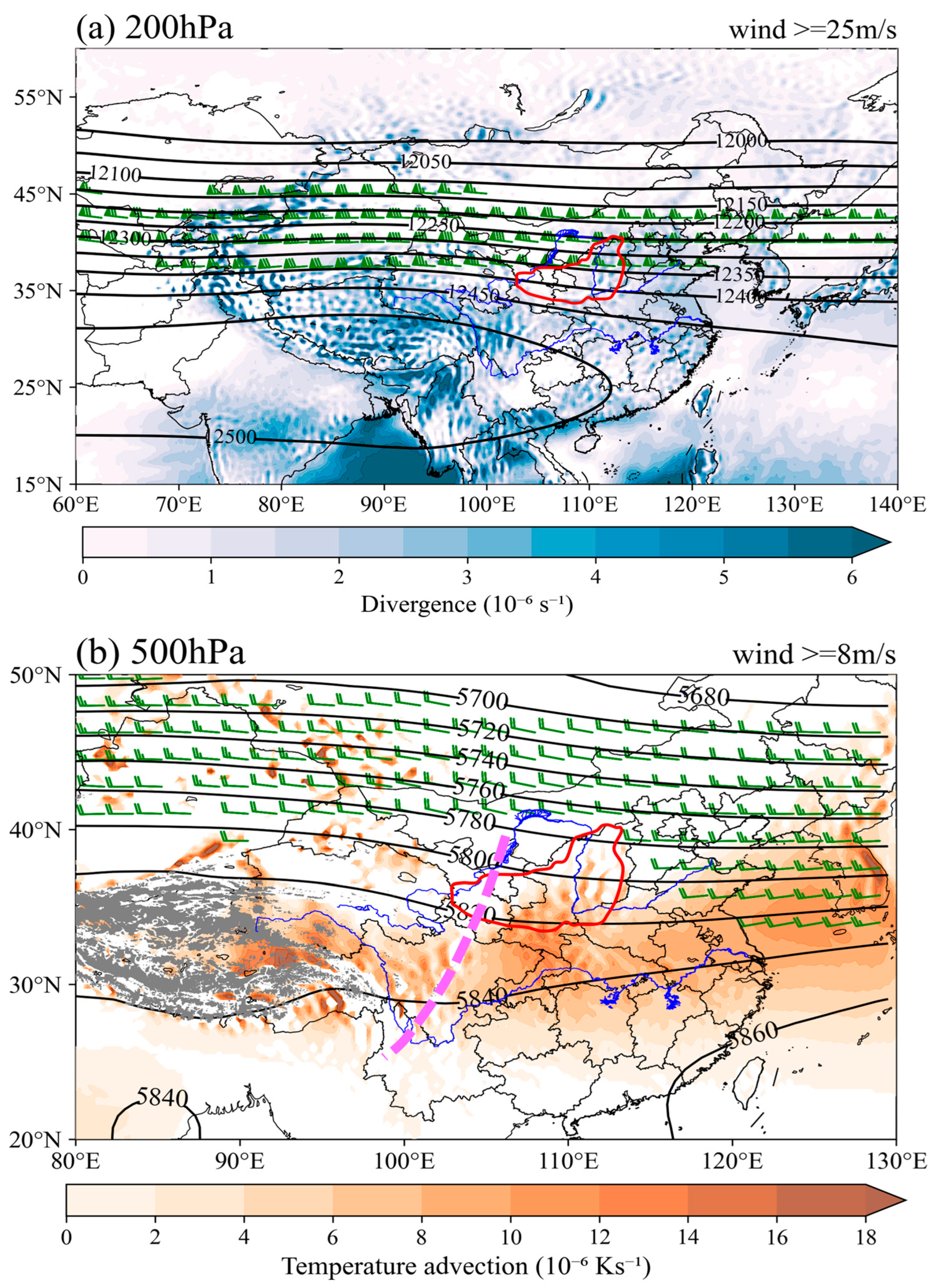
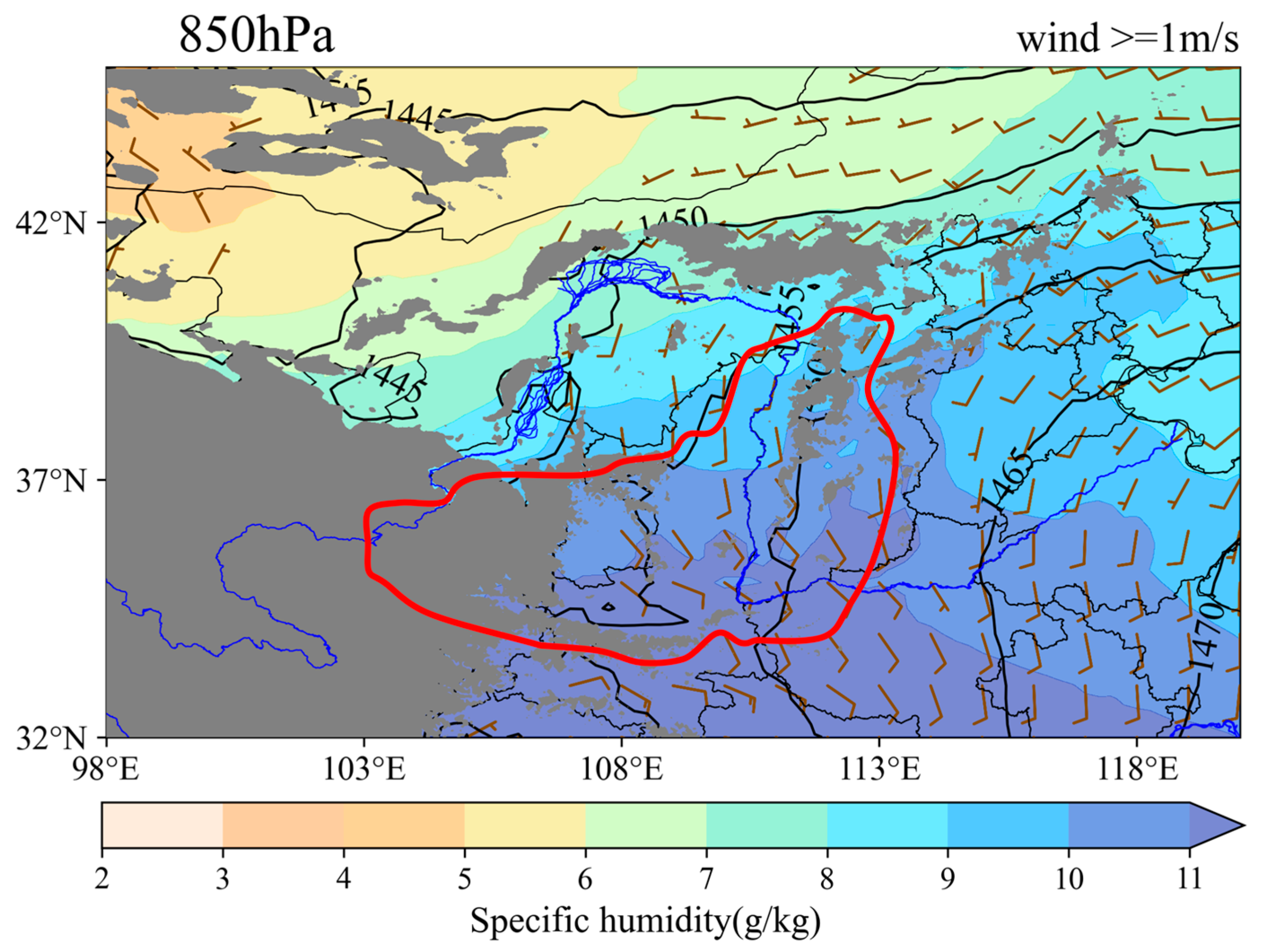
4. Synoptic-Scale Background Environment Features
5. Temporal Features
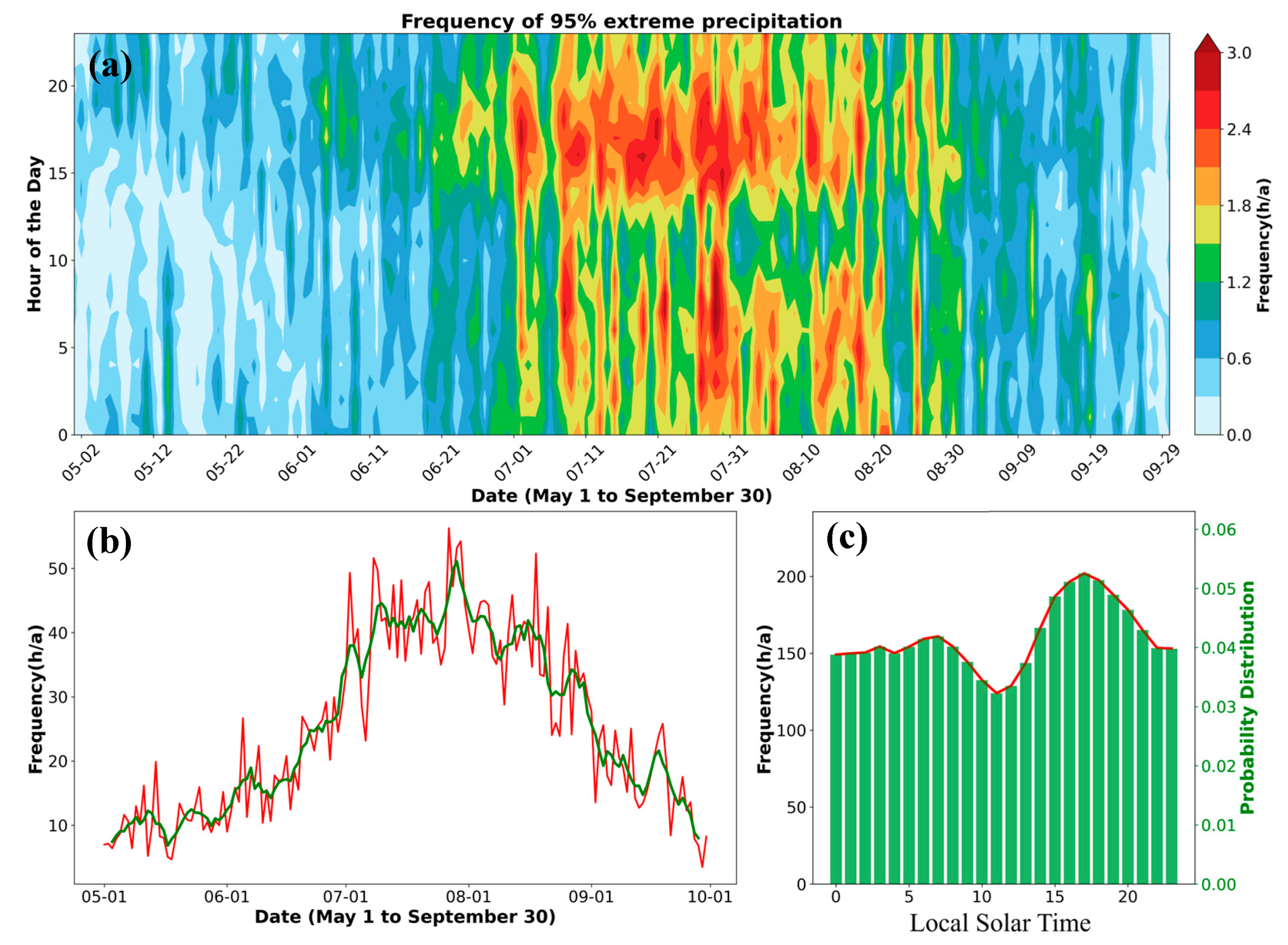
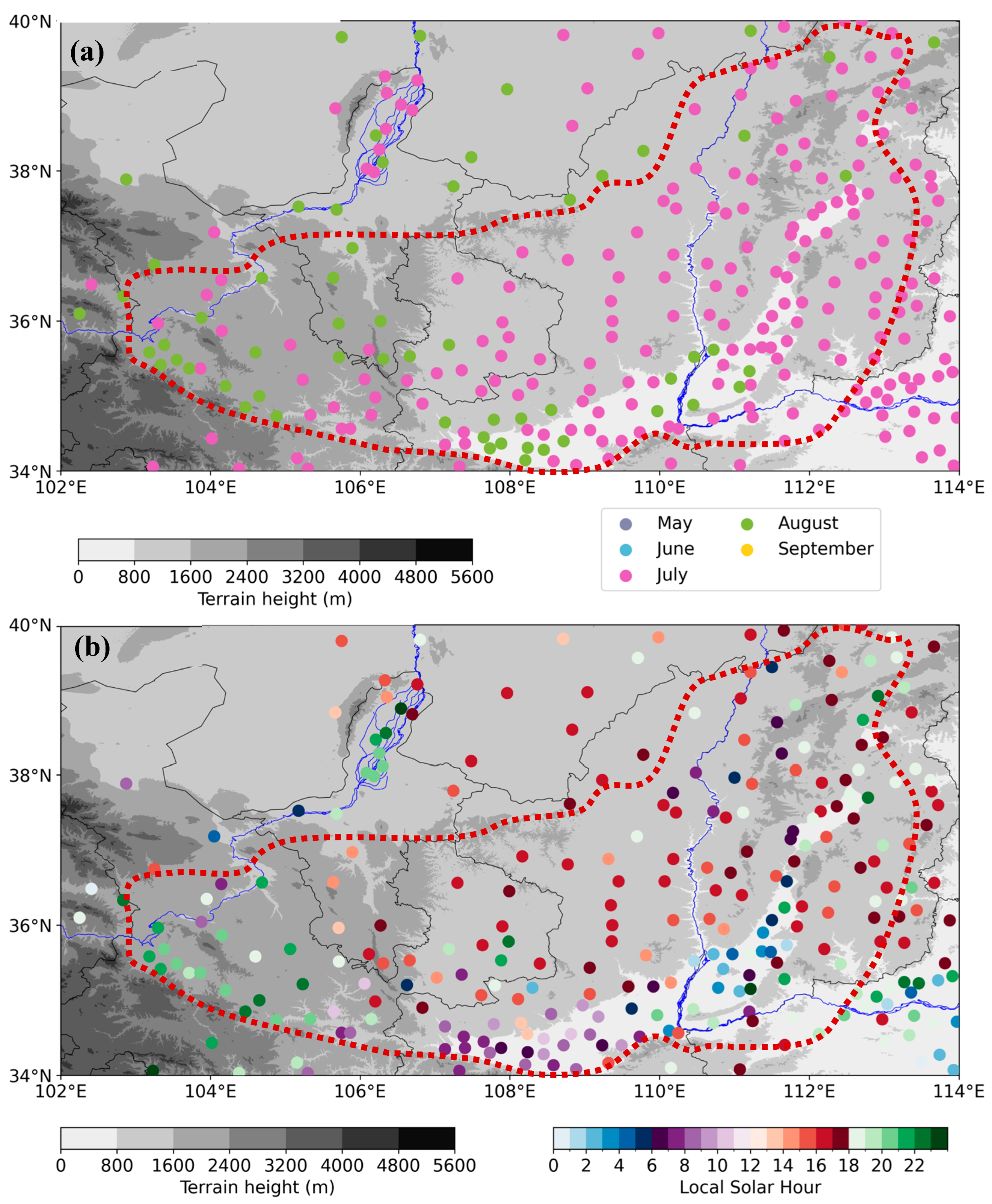
5.1. Monthly and Diurnal Variations
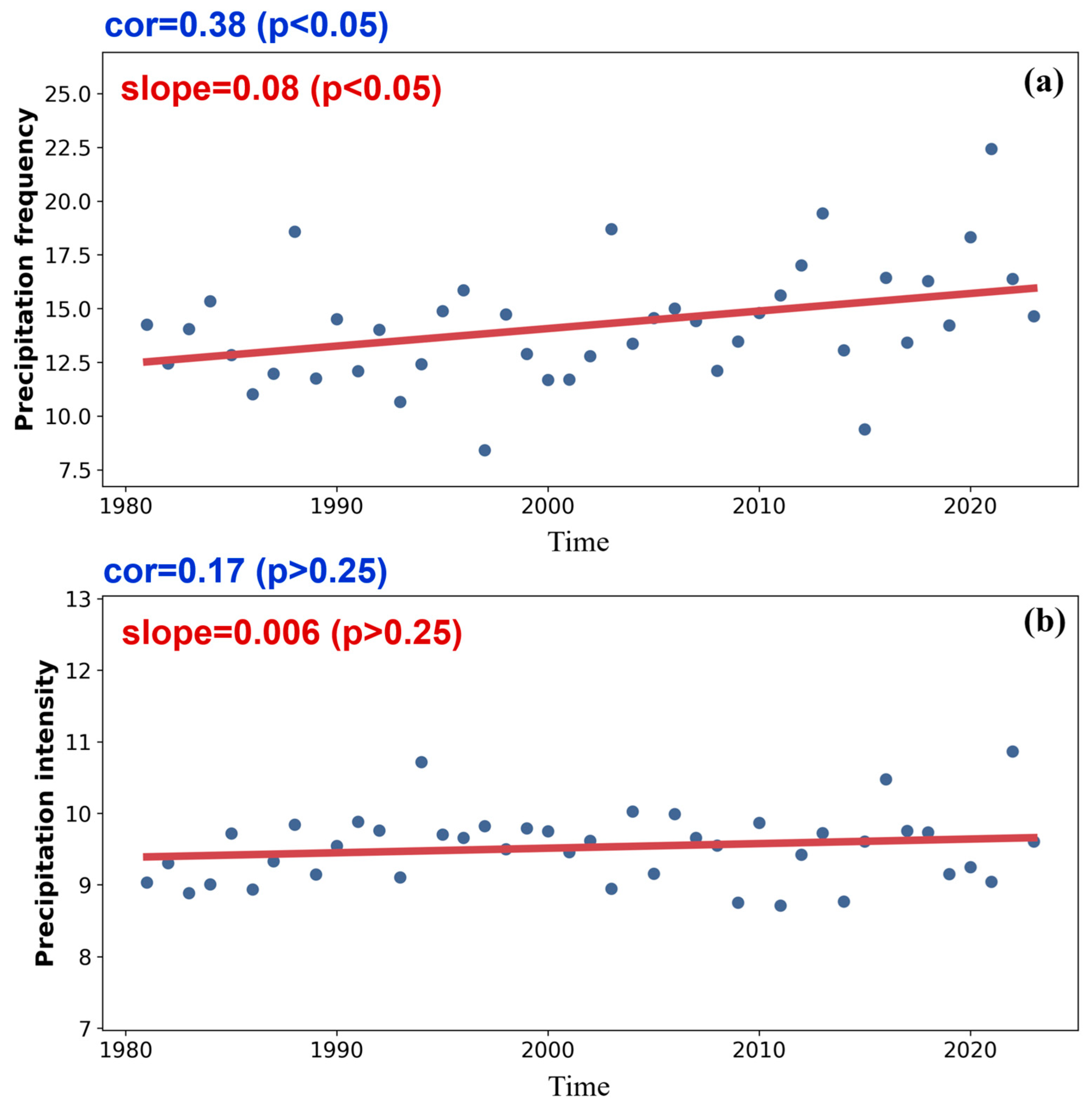
5.2. Long-Term Trends
6. Conclusions and Discussion
6.1. Conclusions
6.2. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Allen, M.R.; Ingram, W.J. Constraints on future changes in climate and the hydrologic cycle. Nature 2002, 419, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Zhang, X.; Zwiers, F.; Westra, S.; Alexander, L.V. A Global, Continental, and Regional Analysis of Changes in Extreme Precipitation. J. Clim. 2021, 34, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, P.; Moseley, C.; Haerter, J.O. Strong Increase in Convective Precipitation in Response to Higher Temperatures. Nat. Geosci. 2013, 6, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabari, H. Climate Change Impact on Flood and Extreme Precipitation Increases with Water Availability. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenberth, K.E.; Dai, A.; Rasmussen, R.M.; Parsons, D.B. The Changing Character of Precipitation. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2003, 84, 1205–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhou, T.; Ye, W.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, L.; Wolski, P.; Risbey, J.; Wang, Z.; Min, S.-K.; Ramsay, H.; et al. A Year Marked by Extreme Precipitation and Floods: Weather and Climate Extremes in 2024. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2025, 42, 1045–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, T.H.; Heard, M.S.; Isaac, N.J.B.; Roy, D.B.; Procter, D.; Eigenbrod, F.; Freckleton, R.; Hector, A.; Orme, C.D.L.; Petchey, O.L.; et al. Biodiversity and Resilience of Ecosystem Services. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2015, 30, 673–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Huang, J.; Guo, N.; Bi, J.; Wang, G. Variability of Soil Moisture and Its Relationship with Surface Albedo and Soil Thermal Parameters over the Loess Plateau. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2009, 26, 692–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, M.; Fan, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhu, S.; Zhao, T. Trends of Temperature and Precipitation Extremes in the Loess Plateau Region of China, 1961–2010. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2017, 129, 949–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Zeng, X.; Li, F. Climate Change Characteristics in Ecological Fragile Zones in China during 1980–2014. Clim. Environ. Res. 2019, 24, 455–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, W.; Zuo, J.; Bi, J.; Shi, J.; Wang, X.; Chang, Z.; Huang, Z.; Yang, S.; Zhang, B. An Overview of the Semi-Arid Climate and Environment Research Observatory over the Loess Plateau. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2008, 25, 906–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Zhang, L.; Bao, J. Turbulence Influenced by Mesoscale Motions in the Stable Boundary Layer over Complex Terrain of the Loess Plateau. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2013, 37, 113–123. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, S.; Gang, C.; Cao, Y.; Chen, Y. Assessment of Climate Change Trends over the Loess Plateau in China from 1901 to 2100. Int. J. Climatol. 2018, 38, 2250–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Huang, Q.; Wang, M. Analysis of the Relationship between Surface Soil Moisture and Precipitation over the Loess Plateau. Plateau Meteorol. 2024, 43, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, D.; Zhang, S.; Jin, C. Analysis of Cloud Characteristics in the Loess Plateau Based on CloudSat-CALIPSO Satellite Data. Plateau Meteorol. 2024, 43, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Fan, Z.; Ren, Y. Flood Risk Assessment in the Loess Plateau: A Case Study of the Quchan Basin, China. Clim. Environ. Res. 2022, 27, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Guo, W.; Wang, W.; Luo, S.; Chen, Z.; Lou, Y.; Fei, J. Characteristics of Shallow Landslides under Extreme Rainfall and Their Effects on Runoff and Sediment on the Loess Plateau. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 7898–7909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Q.; Gong, Y.; Liu, X. Temporal and Spatial Variation Characteristics of Daytime and Nighttime Precipitation in Monsoon and Westerly Regions of the Loess Plateau from 1961 to 2020. Plateau Meteorol. 2023, 42, 1444–1456. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, S.; Hu, Z.; Fu, C. Characteristics and Possible Causes for Extreme Precipitation in Summer over the Loess Plateau. Plateau Meteorol. 2022, 41, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Liu, W. A Preliminary Study of Climate Vulnerability of Agro-Production in the Loess Plateau. Clim. Environ. Res. 2003, 8, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Zhang, X.P.; Ma, Q. Spatiotemporal Characteristics of Precipitation and Extreme Events on the Loess Plateau of China between 1957 and 2009. Hydrol. Process. 2013, 28, 4971–4983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Song, Y.; Ding, D. Variation Characteristics of the Extreme Precipitation Event during the Main Flood Period in Shanxi Province. Clim. Environ. Res. 2010, 15, 433–442. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Deng, H.; Sun, R. Analysis of Spatiotemporal Variation in Precipitation on the Loess Plateau from 1961 to 2016. Sustainability 2024, 16, 11119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, B.; Xiao, W.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, J. Spatio-Temporal Characteristics of Precipitation Days and Intensity with Different Grades in the Loess Plateau during 1961–2017. Arid. Zone Res. 2021, 38, 714–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Yan, H.; Liu, C.; Han, T.; Zhao, N.; Yang, H. Spatio-temporal evolution of extreme precipitation in Loess Plateau during 1960–2017 and its response to atmospheric circulation changes. J. Earth Environ. 2023, 14, 588–602. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.X. Vegetation-Precipitation Thresholds and Ecological Restoration on the Loess Plateau. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2005, 25, 12331239. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, D.; Yang, Y.; Piao, S.; Yang, H.; Lei, H.; Fu, B. Excessive Afforestation and Soil Drying on China’s Loess Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2018, 123, 923–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 Global Reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bretherton, C.S.; Widmann, M.; Dymnikov, V.P.; Wallace, J.M.; Bladé, I. The Effective Number of Spatial Degrees of Freedom of a Time-Varying Field. J. Clim. 1999, 12, 1990–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 33669-2017; Monitoring Indices of Precipitation Extremes. Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China (SAC): Beijing, China, 2017. Available online: https://openstd.samr.gov.cn/ (accessed on 16 March 2025).
- Chen, W.; Wan, W.; He, H.; Liao, D.; Liu, J. Temperature Field Distribution and Numerical Simulation of Improved Freezing Scheme for Shafts in Loose and Soft Stratum. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2024, 57, 2695–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holton, J.R.; Hakim, G.J. An Introduction to Dynamic Meteorology, 5th ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013; p. 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.-M.; Mai, Z.; Sun, J.-H.; Li, W.-L.; Ding, Y.; Wang, Y.-Q. Impacts of Convective Activity over the Tibetan Plateau on Plateau Vortex, Southwest Vortex, and Downstream Precipitation. J. Atmos. Sci. 2019, 76, 3803–3830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.-M.; Zhang, Y.-C.; Wang, H.-J.; Tang, H.; Li, W.-L.; Sun, J.-H. On the Evolution of a Long-Lived Mesoscale Convective Vortex That Acted as a Crucial Condition for the Extremely Strong Hourly Precipitation in Zhengzhou. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2022, 127, e2021JD036233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowski, P.M.; Richardson, Y.P. Mesoscale Meteorology in Midlatitudes; Wiley-Blackwell: Chichester, UK, 2010; p. 407. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, S.-M.; Zhang, J.-P.; Xiao, X.; Huang, T.-T.; Sun, J.-H. A 42-yr Statistic on the Dabie Vortices: Multi-Scale Temporal Characteristics and Associated Mechanisms, and Hourly-Rainfall Features. J. Clim. 2025, 38, 1553–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.M.; Tang, H.; Sun, J.H.; Zhao, T.B.; Li, W.L. Historical Rankings and Vortices’ Activities of the Extreme Mei-yu Seasons: Contrast 2020 to Previous Mei-yu Seasons. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2021GL096590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Fan, Z. Choice of South Asian Summer Monsoon Indices. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1999, 80, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zeng, Q. A Unified Monsoon Index. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.; Zhang, F.; Sun, J. Diurnal Variations of Warm-Season Precipitation East of the Tibetan Plateau over China. Mon. Weather. Rev. 2011, 139, 2790–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, F. Impacts of Mountain–Plains Solenoid on Diurnal Variations of Rainfalls Along the Mei-Yu Front over the East China Plains. Mon. Weather. Rev. 2012, 140, 379–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jiang, W.; Wu, J.; Hou, P.; Dai, Z.; Rao, P.; Ling, Z.; Deng, Y. Extreme Hourly Precipitation Characteristics of Mainland China from 1980 to 2019. Int. J. Climatol. 2023, 43, 2989–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhai, P. Temporal and Spatial Characteristics of Extreme Hourly Precipitation over Eastern China in the Warm Season. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2011, 28, 1177–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Jiang, X.; Zhai, P.; Luo, Y. Detectable Intensification of Hourly and Daily Scale Precipitation Extremes across Eastern China. J. Clim. 2021, 34, 1185–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Zhao, X. Changes of precipitation pattern in China: 1961–2010. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2022, 148, 1005–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platnick, S.; King, M.D.; Ackerman, S.A.; Menzel, W.P.; Baum, B.A.; Riédi, J.C.; Frey, R.A. The MODIS Cloud Products: Algorithms and Examples from Terra. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 459–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.; Tang, F.; Wang, L. All-Sky Assimilation of FY-4A AGRI Water Vapor Channels: An Observing System Experiment Study for South Asian Monsoon Prediction. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2024, 150, 2458–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, H.; Hu, F.; Zhang, W.; Meng, X.; Gao, Y.; Fu, S. Statistical Characteristics of Hourly Extreme Heavy Rainfall over the Loess Plateau, China: A 43 Year Study. Sustainability 2025, 17, 7395. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167395
Yuan H, Hu F, Zhang W, Meng X, Gao Y, Fu S. Statistical Characteristics of Hourly Extreme Heavy Rainfall over the Loess Plateau, China: A 43 Year Study. Sustainability. 2025; 17(16):7395. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167395
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Hui, Fan Hu, Wei Zhang, Xiaokai Meng, Yuan Gao, and Shenming Fu. 2025. "Statistical Characteristics of Hourly Extreme Heavy Rainfall over the Loess Plateau, China: A 43 Year Study" Sustainability 17, no. 16: 7395. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167395
APA StyleYuan, H., Hu, F., Zhang, W., Meng, X., Gao, Y., & Fu, S. (2025). Statistical Characteristics of Hourly Extreme Heavy Rainfall over the Loess Plateau, China: A 43 Year Study. Sustainability, 17(16), 7395. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167395







