Nanofluid-Enhanced HVAC&R Systems (2015–2025): Experimental, Numerical, and AI-Driven Insights with a Strategic Roadmap
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Current Gaps in Review of Nanofluids Applications
- Lack of HVAC&R-Specific Focus: Prior reviews remain largely disconnected from HVAC&R system architectures. None offers a comprehensive assessment of nanofluid integration into evaporators, condensers, compressors, or performance indicators such as the coefficient of performance (COP), cooling load, or pressure drop under real-world operation.
- Emphasis on Isolated Property Prediction: AI and ML tools have been primarily applied to predict isolated thermophysical properties (e.g., viscosity, thermal conductivity), without bridging the implications of these predictions for full-system modeling, design optimization, or operational energy performance in HVAC settings.
- Absence of Methodological Taxonomy: While some papers classify studies by nanoparticle type or performance metric, a structured methodological synthesis—categorizing experimental, numerical, hybrid, and AI-based investigations—is missing. Such a taxonomy is critical to identify research synergies and implementation pathways in HVAC&R.
- Neglect of Practical and Lifecycle Challenges: Viscosity-induced pressure penalties, long-term nanoparticle stability, fouling, and cost-efficiency trade-offs are acknowledged but not critically analyzed in most prior reviews. For instance, optimization is discussed by Basu et al. (2023) [9], yet lacks connection to lifecycle sustainability or technoeconomic feasibility.
- Missing Integration with Smart HVAC Technologies: None of the cited reviews incorporate nanofluid research within the evolving context of smart HVAC systems, including digital twins, adaptive control, or real-time energy analytics—a direction increasingly relevant to energy-aware building management.
1.2. Motivation for This Work
- Component-Specific Relevance: Direct mapping of nanofluid performance metrics to HVAC&R components (e.g., evaporators, condensers) and system-level outputs like COP and thermal load reduction.
- Methodologically Balanced Taxonomy: A structured classification across experimental, numerical, hybrid, and AI/ML-based studies that enables comparative analysis of their strengths, limitations, and evolution.
- Actionable Design Guidance: Synthesized findings are organized by nanoparticle type, base fluid, and operating condition to support engineering design and optimization.
- Deployment-Aware Framing: Particular attention is given to practical challenges—pressure drop penalties, sedimentation, economic feasibility, and integration into smart HVAC systems.
1.3. Novelty of This Review Paper
- HVAC&R Component-Level Focus: This review uniquely concentrates on the integration of nanofluids into specific HVAC&R components—such as condensers, evaporators, compressors, and heat exchangers—linking them to system-level outcomes like coefficient of performance (COP), heat transfer rates, and energy efficiency.
- Structured Methodological Classification: More than 200 peer-reviewed studies are systematically categorized under a comprehensive framework spanning experimental, numerical, theoretical, hybrid, and AI/ML-based methodologies. This taxonomy allows clear benchmarking of research directions and evidence-based insights for future investigations.
- Comparative and Application-Specific Synthesis: The review presents clustered performance comparisons based on nanoparticle types, base fluids, and operational parameters relevant to HVAC&R environments. This structured synthesis aids researchers and engineers in identifying optimal nanofluid configurations for specific use cases.
- Emphasis on Smart HVAC Integration: Beyond conventional heat transfer evaluation, the paper advances the field by incorporating recent developments in AI, digital twins, and intelligent HVAC controls—areas typically underrepresented in past reviews—thus creating a pathway toward smart, adaptive thermal systems.
1.4. Organization of This Paper
- Section 2 presents the core thematic review of nanofluid applications in HVAC systems, categorized into three subdomains:
- Section 2.1 focuses on Thermophysical Properties, evaluating both numerical (Section 2.1.1) and experimental (Section 2.1.2) studies, followed by a Critical Analysis and Research Gaps subsection (Section 2.1.3).
- Section 2.2 reviews advances in Heat Transfer Enhancement, structured into Experimental Studies (Section 2.2.1), Numerical Studies (Section 2.2.2), and AI/ML-Driven Approaches (Section 2.2.3), culminating in a Critical Analysis and Future Directions (Section 2.2.4).
- Section 2.3 synthesizes the broader Research Methodologies and Analytical Trends across the literature, including Experimental Studies (Section 2.3.1), Numerical Investigations (Section 2.3.2), Hybrid Studies (Section 2.3.3), AI/ML-Based Approaches (Section 2.3.4), and Review-Based Papers (Section 2.3.5). It concludes with a Critical Analysis and Future Directions subsection (Section 2.3.6) that integrates methodological gaps and forward-looking insights.
- Section 3 provides a consolidated Conclusion and Future Directions, summarizing the key insights from the review while proposing actionable research trajectories and system-level recommendations for nanofluid deployment in next-generation HVAC&R technologies.
2. Thematic Review of Nanofluid Applications in HVAC Systems
- Refrigeration, Air Conditioning, and HVAC Systems (main application theme, n = 133),
- Heat Transfer Enhancement (supporting subtheme 1, n = 46), and
- Thermophysical Properties (supporting subtheme 2, n = 21).
2.1. Thermophysical Properties
2.1.1. Numerical Investigations
2.1.2. Experimental Investigations
2.1.3. Critical Analysis and Research Gaps
- Idealized assumptions in simulations (e.g., uniform dispersion, constant properties) often overlook real-world phenomena such as agglomeration, phase separation, and surfactant degradation.
- Long-term operational studies assessing thermal cycling effects, corrosion, and stability under HVAC&R-like conditions remain scarce.
- Viscosity and specific heat are underexplored in terms of their coupled impact on system performance, especially under low-to-moderate temperature gradients typical of HVAC&R loops.
| Ref. | Nanoparticle Type | Study Type Distribution | Representative Findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| [18,19,20,21,22] | Al2O3, SiO2 | Numerical | • Density is a less studied property vs. TC and viscosity. |
| [13,17,23,24] | CuO | Numerical, Review | • TC ↑ by ~57%; COP ↑ by ~27% (with R134a/R152a). • Minor viscosity increase observed. |
| [15,23,25,26] | Fe3O4-CoFe2O4 | Experimental, Numerical | • Investigated MHD effects on heat transfer properties. |
| [16,27] | Graphene | Experimental, Experimental/Numerical, Numerical | • ↑ Concentration enhances TC and heat transfer. • ↑ Concentration also increases viscosity and friction. |
| [20,22,23,24,28] | TiO2 | Experimental | • Studied heating effects on viscosity, TC, and absorbance. |
| [14,29,30] | Hybrid/Other | Numerical, Review | Improving adsorbent TC and heat exchange area for compact system optimization. |
| [31,32] | Nanolubricant, Refrigerant | Review | Analyzing thermophysical and hydraulic parameters to enhance refrigeration system COP. |
2.2. Heat Transfer Enhancement
- Brownian motion—Random motion of nanoparticles at the microscale promotes enhanced mixing in the fluid, disrupting thermal boundary layers and facilitating heat transport.
- Thermophoresis—Migration of nanoparticles from hotter to cooler regions due to temperature gradients, redistributing thermal energy more effectively.
- Microconvection—Localized eddies generated by moving nanoparticles amplify fluid agitation and improve convective heat transfer rates.
- Enhanced thermal conductivity—Nanoparticles with inherently higher conductivity than the base fluid (e.g., Al2O3, CuO, graphene) form efficient thermal pathways, accelerating heat transport through the fluid.
- Field-induced effects (optional in specific designs)—Magnetic or electric fields applied to specialized nanofluids can align particles or induce additional motion, further modifying heat transfer behavior.
- Viscous dissipation and porous media effects—Relevant in some configurations where flow resistance or porous structures influence the local energy balance.
- Section 2.2.1 Experimental Studies examine lab-scale evaluations of nanofluid heat transfer in compact exchangers, solar systems, and augmented flow channels.
- Section 2.2.2 Numerical Investigations delve into Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD)-based modeling and simulation of nanofluid behavior under varied boundary conditions and channel geometries.
- Section 2.2.3 AI/ML-Driven Approaches highlight recent advances in artificial intelligence for thermal prediction, surrogate modeling, and optimization.
- Section 2.2.4 Critical Analysis and Future Directions discusses limitations, research gaps, and emerging opportunities.
2.2.1. Experimental Studies
- Nusselt number enhancements routinely exceeded 50%, with some specialized microchannel or hybrid geometries pushing improvements beyond 200%.
- COP increases ranged between 5 and 10%, linked to lower compressor work or elevated evaporator effectiveness when using nanofluids.
- Optimal nanoparticle concentrations typically clustered around 0.3–0.4% by weight or volume, balancing enhanced thermal conductivity with manageable viscosity and pressure drop effects.
- In passive systems, cabinet or internal temperature drops of 15–22% were commonly achieved using TiO2 or ZnO-doped materials.
| Ref. | Nanoparticle Type | Findings |
|---|---|---|
| [36,37,38,39] | TiO2 | ↓ Cabinet temperature up to 21.5% at 125 cm, esp. at 40 °C Optimal at 0.3% doping Provided highest thermal insulation and UV absorption |
| [34,38,40,41,42,43,44,45] | Al2O3 | • ↑ Heat transfer coefficient by 80.5% at 0.4% vol. • ↑ COP by 7.5%, ↓ Power consumption by 5.2% • ↑ Pressure drop by 13.6%, max 25.42 kPa/m |
| [33,46,47] | Al-based (Hybrid) | • ↑ Nusselt number by 210%, heat transfer coefficient ↑ 120% • Mild pressure drop increase (~13%) • Noted optimal performance around 0.4% concentration |
| [48] | Cu/CuO | • PEC reached 1.18 (↑ ~18% over baseline) • Most effective at 0.4 wt.% Cu–water nanofluid • ↑ Heat transfer coefficient and pressure drop across flow rates |
| [36] | ZnO | • Effective UV blocking, better than plain PC • ↓ Refractive index and thermal insulation than TiO2 • Optimal at 0.3% doping for moderate ↓ temperature |
| [36,42,47] | Ag | • ↑ PCM storage performance by 55–184% across heat storage and evaporation metrics • Accelerated charge/discharge in solar still hybrid systems |
| [44] | SWCNT | • ↑ Nusselt number by ~25–35% in nanofluid flows • Slight ↑ viscosity, minimal ΔP rise • Stability achieved with surfactant-assisted dispersion |
| [49] | LCMO manganite | • ↑ Thermal conductivity and heat transfer by ~15–22% • Optimal at 0.1–0.2% volume fraction • Moderate pressure drop, good long-term dispersion stability |
2.2.2. Numerical Studies
| Ref. | Nanoparticle/Hybrid | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|
| [56] | CNT | • Improved microchannel Nusselt and local temperatures |
| [57] | Al2O3 + Cu | • RKF simulation: hybrid more stable vs. mono; HT ↑ with Pr, Eckert; magnetic field raises skin friction |
| [58] | Fe3O4 + Al2O3 + Cu/Ag | • Annular cavity: ↑ Ha ↓ temp ↑ velocity ↑ Nusselt; Cu most responsive; fins moderate convection |
| [59] | TiO2 + SiO2, TiO2 + MoS2, TiO2 + Au | • Solar-assisted flows: ↓ entropy, ↑ efficiency under hybrid blends |
| [60] | Cu, TiO2, Fe3O4 | • Stefan blowing and Soret–Dufour: THNF ↑ HT by 22%, hybrid by 17%, mono by 11%; Yamada–Ota > Hamilton–Crosser |
| [61] | Al2O3 + TiO2 + SiO2 | • Radial magnetic: slip and curvature ↑ temp; activation energy ↑ conc ↓ mass transfer |
| [62] | Fe3O4 + CoFe2O4 | • Magnetic hybrid flows analyzed for entropy and heat transfer |
| [63] | Ag + Cu + TiO2 | • Simulated multi-metal hybrids under laminar regimes |
| [64] | Al2O3 | • Magnetic refrigeration: up to 15% ↑ cooling; small pumping penalty, COP marginal |
| [65] | ZnO | • Subcooled boiling: ↑ vapor gen, wall Nu with ϕ < 1%; bubble dynamics crucial |
| [66] | CuO (LiBr) | • FEM: CuO ↑ mass flux, rate, coefficient in LiBr absorption |
| [67,68] | Cu/CuO | • Barocaloric refrigerator: 10% Cu nanofluid ↑ HT by ~30% • Laminar mixed convection: ↑ ϕ ↑ Nu, rib AR and Ri interplay key for buoyancy vs. forced |
| [69] | Diamond + Cu | • ANFIS + PSO predicted pool boiling HT of refrigerant–oil with nanoparticles |
| [55] | MWCNT | • In interface cooling modules ↓ hotspots, ↑ thermal uniformity |
| [54] | EG + MoS2 + SiO2 | • Inclined magnetic ↑ HT by ~28%, ↓ entropy |
| [52] | GO + Au + Ag | • Wedge boundary layer ↑ HT |
| [53] | Hybrid (Au–Ag) | • Optimal ~0.08 vol% ↑ HT by ~28–41%, balanced vs. shear |
| [51] | SiO2, Al2O3 | • In TEC, hybrid ratios ↓ local temps, extended cooling |
| [50] | TiO2 + Au | • Magnetized non-Newtonian flow ↑ Nusselt, sensitive to field and ϕ |
2.2.3. AI/ML-Driven Approaches
| Ref. | Nanoparticle Type | AI/ML Algorithms | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| [70,75,76] | Al2O3 | ANN, LM, GA | • ANN models predicted nanofluid heat exchanger parameters accurately. • GA optimized volume fraction for max thermal effectiveness. |
| [71,77] | Al2O3 + TiO2 | GPR | • GPR predicted Nusselt number and entropy rates in microchannels. • Achieved surrogate models reducing CFD computation time. |
| [72,78] | Al2O3, CuO, Al, Cu | RNN + LSTM | • LSTM captured time-dependent heat transfer dynamics. • Predicted optimal conditions balancing heat transfer and pressure drop. |
| [73,79] | Al2O3, SWCNT, SWCNT, Au, ZnO | CFNN, ET, QLM, BRNN | • Hybrid AI approaches forecasted thermal conductivity enhancements. • Showed multi-nanoparticle blends raised convective HT coefficients. |
2.2.4. Critical Analysis and Future Directions
- Integrated multi-objective frameworks: Future studies should unify AI/ML optimization with CFD or experimental data streams to jointly minimize entropy, maintain low pressure drops, and maximize Nusselt gains—bridging energy efficiency with operational reliability.
- Stability and fouling resilience: There is a pressing need for dynamic investigations tracking nanoparticle agglomeration, surface fouling, and re-dispersion under cyclic on–off operation typical in HVAC systems. Coupled magnetic or ultrasonic field techniques may offer novel avenues for in situ stability management.
- Next-generation nanomaterials: Graphene derivatives, MXenes, or bio-inspired hybrid composites hold promise for achieving high thermal conductivities at lower concentrations, potentially decoupling the viscosity trade-off that has constrained many oxide-based systems.
- Lifecycle and techno-economic perspectives: Very few studies holistically assess long-term cost-effectiveness, environmental footprint, or regulatory considerations tied to nanoparticle deployment and disposal. These analyses are vital to guide commercial translation.
- Integration into digital twins and adaptive controls: As smart HVAC infrastructures proliferate, embedding AI-driven nanofluid models into real-time digital twin systems could enable predictive adjustments to flow rates, nanoparticle dosing, or auxiliary magnetic fields—dynamically optimizing thermal performance and prolonging system lifespan.
2.3. Research Methodologies and Analytical Trends in Nanofluid-Enhanced HVAC&R Systems
- Experimental studies (n = 69) overwhelmingly dominate the literature and are most commonly applied to refrigeration systems (n = 105) and HVAC systems (n = 23). These studies often focus on evaluating nanofluid-enhanced heat exchangers, condensers, and evaporators under lab or bench-scale conditions.
- Numerical (n = 14) and theoretical investigations (n = 11) are primarily used to model heat transfer, fluid flow, and entropy generation using simulation tools or closed-form analytical methods. These studies complement experimental findings and explore parameter sensitivity under controlled assumptions.
- Hybrid methodologies (n = 5), although less common, serve a vital role in validating numerical models against experimental data. These studies demonstrate the highest methodological robustness but remain underutilized.
- AI/ML-driven research (n = 20) is an emerging area, primarily focused on predictive modeling and performance optimization. These studies show increasing potential for integration into real-time HVAC&R system control and design optimization.
- Review papers (n = 14) synthesize findings across various applications and methodologies, often identifying knowledge gaps or proposing research directions.
- Heat Exchanger studies (n = 1);
- Thermal management applications (n = 2);
- Magnetic nanofluid studies (n = 1).
2.3.1. Experimental Studies
- Experimental Fluid Characterization for System Integration,
- System-Level Performance Enhancement, and
- Comparative and Application-Specific Analysis.
- Experimental Fluid Characterization for System Integration accounts for 26 studies, again with a strong concentration in refrigeration systems (24 articles). These works primarily investigate nanofluid formulation, dispersion stability, and thermophysical properties (e.g., thermal conductivity, viscosity) in application-ready contexts, often under flow or heat load conditions.
- System-Level Performance Enhancement is the most extensively studied category, comprising 31 experimental studies, with the majority (25 articles) focusing on refrigeration systems. These studies commonly aim to validate gains in Coefficient of Performance (COP), energy reduction, or thermal efficiency when nanofluids are used in actual system components, such as evaporators, compressors, or heat exchangers.
- Comparative and Application-Specific Analysis includes 10 studies, split between HVAC&R systems. These studies test multiple nanofluids or operating parameters to evaluate performance differences under controlled comparative conditions.
Experimental Fluid Characterization for System Integration
| Ref. | Nanoparticle Involved | Evaluated Parameter | Refrigerant | Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [85,86,87,88] | Al2O3 | COP | R134a, R600a | ↑ COP (14 to 45%) Power Reduction (5–9%) |
| [80,84,88] | SiO2 | COP | R600a | ↑ COP (15–40%) |
| [80,81,84,88,89,90,91,92] | (25%) TiO2-(75%) SiO2, ZnO | COP, Compressor Power, Cooling Capacity | POE oil, R600a | ↑ COP (14–51%) Power (8–13%) ↑ Refrigerated Capacity (13%) |
| [93,94,95,96,97,98,99,100] | CuO, Ag, Cu | COP, Compressor Power, Refrigerating Capacity | R600a, R134a, R290 | ↑ COP (12.2–35%) Power (1.39–24%) ↑ Refrigerated Capacity (13%) Friction 9.9% |
| [82,83,101] | CNT, MWCNT, Graphene | COP, Compressor Power, Cooling Capacity | POE oil | ↑ COP (12.2–35%) Power (1.39–6.8%) |
| [102,103,104,105,106] | Ag, Diamond, | COP, Cooling Capacity | R600a, R134a, R410A, R32 | ↑ COP (2.4–39.5%) Power (1.39–6.8%) ↑ Refrigeration Capacity (2.4%) |
System-Level Performance Enhancement
| Ref. | Nanoparticle Type | Base Fluid/Refrigerant | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| [87,112,113,114,115] | Hybrid Al2O3/CuO/TiO2 | Zeotropic refrigerant blend (23% R32/25% R125/52% R134a) | ↑ COP 3.10% (at blend 011) ↑ Compressor power coefficient 13.51% ↑ Cooling capacity by 5.78% ↑ TEGWI 1.06 kg/s CO2 ↑ Optimal heat transfer at 0.0075 Vol.% nanoparticle concentration |
| [100,101,107,108,109,110,111,115,116,117,118,119,120] | Al2O3/TiO2 | Chiller fluid (not explicitly stated, inferred to be water-based), Distilled Water, H2O–LiBr, POE (polyol ester) oil, R134a, Water–glycol mixture; Ammonia–water solution, NH3–H2O, NH3–H2O–LiBr, Water | ↑ COP (9.1% to 14%) Energy consumption about 32%, 50.9 tons/year CO2 emission; net LCA benefit of 36.6 tons/year Winter: Avg. ↑ 9.8% Summer: Avg. ↑ 8.9% Al2O3/R134a compared to pure refrigerant COP ↑ to 6.5 (about 15% improvement) ↑ COP 17.27% Absorption efficiency ↑ up to 85% Improved Thermal Performance |
| [88] | Graphene-Based | Polyester Oil (POE) | ↑ COP by ~29% |
| [112,121,122,123] | Binary Nanofluids (e.g., Iron Oxide + LiBr-H2O) | LiBr-H2O; Water–ethylene glycol; H2O–LiBr | ↑ Absorption rate 4.9–7.6% without magnetic field ↑ TC by up to 37.7% over baseline fluid, ↑ Max desorption rate by 7.9% (CNT); ↑ Max SCOP by 14%; ↑ cooling effect up to 6%; Optimal desorber modules: <50, cost cap: EUR 35/module |
| [124,125,126,127] | Noble/Carbon-Based (Ag, MWCNT) | Water; Various compressor oils | ↑ COP with nanofluid absorbent ↑ Overall efficiency from 77.3% to 81% with Ag nanofluid Exergy efficiency of the system: 29% At 50 °C and 0.1% mass conc., ↑ viscosity by 40–90%, depending on base oil; |
| [128,129,130,131] | Hybrid Experimental (Al2O3, CuO, TiO2) | Deionized Water; Water | ↑ Max COP: 24.2% (vs. water) Al2O3/H2O had 6.2% higher COP vs. hybrid TiO2 had 5.6% lower COP vs. hybrid Compression ratio up to 6.9% |
| [130,132] | Copper-Based (Cu, CuO) | SAE50 Oil; Water | Viscosity by up to 15% at low vol. fractions; ↑ by 14% at 1% vol.; ↑ COP by 23% (Al2O3) and 72% (Cu) at 5% volume fraction Higher TC of Cu yielded better performance than Al2O3 |
| [133] | Mixed Metal Oxides (MgO, TiO2) | Water | ↑ COP by 16.7% (MgO) and 11.5% (TiO2) at 1% wt. Max performance at PVC fill, 12 mm, 90° spray angle |
| [134,135,136,137] | TiO2 with Surfactants (SDBS) | NH3–H2O | ↑ COP up to 27% overall ↑ 14–26.2% under challenging conditions (e.g., low evap temp, high cooling water temp); best performance with 0.5% TiO2 + 0.02% SDBS |
Comparative and Application-Specific Analysis
2.3.2. Numerical Investigations
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) Studies
| Ref. | Nanoparticle Type | Base Fluid/Refrigerant | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| [151,153,154,155,156] | Al2O3, SiO2, Fe | R134a, Water | ↑ HVAC system efficiency by approximately 10% Compressor power at 0–5% vol fraction ↑ 10% in thermal performance using nanofluids Maximum COP with 0.2% volume fraction of nanoparticles ↑ 7.6% in effectiveness of a plate heat exchanger 11.6% compressor power 14.6% improvement in COP ↑ cold chain efficiency by reducing energy consumption ↑ Thermal characteristics by inlet velocity, but a higher pressure drop |
| [150] | MWCNT | R1234yf | Analyze the specific heats of the various MWCNT nanoparticle-enhanced [HMIM] cation-based ionic liquids Effect of concentration (0–1%) on COP at assorted Generator temperatures (303–383 K) were obtained experimentally at a temperature and a concentration of 303–383 K and 0–1 wt%, respectively, and were subsequently used for modeling the solubility and absorption refrigeration cycle |
| [152] | Hybrid | Ethyl glycol | Impact of activation parameters and Schmit number on dimensionless concentration for different nanofluids |
| [156,157,158,159,160] | CuO, Cu-based nanofluids | Water, R134a, ethylene-glycol | Optimal performance at 4% nanofluid concentration ↑ cold chain efficiency by energy consumption ↑ COP 20% for CuO/Water, 25% for CuO/water with insulation ↑ Cooling power (about 5%) Simulation results show that, a 9 m2 solar collector, a 0.3 m3 storage tank, and 0.05 m thick polystyrene insulation|The active barocaloric regenerative refrigeration cycle is supposed to work as a domestic refrigerator in temperature range of 255 ÷ 290 K |
| [153,156,158,160,161] | TiO2, MO | R134a, POE Oil, LPG | 0.5 to 1 g TiO2 addiction to the POE oil performs better than that of 1.5 g TiO2. Predicting irreversibility using ANFIS-SC model: RSME = 0.998, MAPE = 0.078% ↑ cold chain efficiency by energy consumption The comparison of variance, root mean square error (RMSE), mean absolute percentage error (MAPE) were 0.996–0.999, 0.0296–0.1726 W, and 0.108–0.176% marginal variability values |
Theoretical Modeling and Analytical Studies
| Ref. | Nanoparticle Type | Base Fluid/Refrigerant | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| [162,164,167,168,169] | AL2O3, CuO-Al2O3/MO | LiBr-H2O, R600a, R134a, R1234yf, R1233ZDE | ↑ COP more than 20%, ↑ max exergy efficiency: 38.48% Power consumption: up to 23%, Exergy destruction up to 49%, ↑ COP by 29%, ↑ Second law efficiency to 28% ↑ COP of the solar cycle by 4.51% ↑ COP range: 16 to 25% |
| [164,165,167,168] | Cu, CuO | R600a, R134a, R1234yf, R1233ZDE | Power consumption: up to 23%, ↑ COP by 29%, ↑ Second law efficiency up to 28% Power consumption by 11%, CO2 emission: 12.5% |
| [166,170,171] | TiO2, FeOTiO2 | POE Oil, NH3–H2O | TiO2 is most effective, Levelized cost ranges USD 0.773/kWh to USD 0.875/kWh ↑ COP, circulation ratio, and internal temperature reached 17%, 57%, and 20% Irreversibility up to 18% |
| [163,165] | CNT, MWCNT | POE Oil, R290/R1233ZDE | Power consumption: up to 16%, Pressure ratio up to 5.6%, COP by 11% |
| [163] | Graphene | POE Oil | Power consumption reduced: up to 16%, Pressure ratio up to 5.6%, ↑ COP by 11% |
| [172,173] | Ag, Fe2O3 | Ethylene glycol/DI-water | ↑ convective HTC increased up to 11% |
2.3.3. Hybrid Studies
2.3.4. AI/ML-Based Approaches
- Developing system-level digital twins for HVAC&R applications that integrate nanofluid property predictions into full-cycle simulations.
- Applying reinforcement learning or advanced control-based AI models for real-time system optimization, considering dynamic environmental loads.
- Creating large-scale datasets through experimental or simulated studies to train generalizable AI models across multiple refrigerants and nanofluids.
| Ref. | Type of Nanoparticle | Method/Technique | Parameter Evaluated | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [148,177,179] | RE2TM2Y ternary intermetallic compounds (e.g., Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm with Ni, Cu, Co and Sn, In, Cd, Ga, A | MOO using (NSGA-II), (GPR) (SVR) with RBF kernel, (SELM), (GSVR) with Gaussian and Polynomial kernels | Thermal and exergy COP, total product cost rate, Relative Cooling Power (RCP), applied magnetic field, ionic radii, RMSE, MAE, correlation coefficient (CC) | GU-GSVR vs. SELM (1–7 T field): RMSE ↓ 27.97% MAE ↓ 76.01% CC ↑ 10.55% R134a Refrigerant: Thermal COP: 10.13% Exergy COP: 0.6530% ↑ 8.5%/12.3% over base case R1234ze Refrigerant: Annual cost reduced to USD 6148 (↓ 2.4%) Optimal nanoparticle fraction: 0.0149–0.041 GPR-RBF Model: Highest predictive accuracy COP improved with 0.5–1.0 g TiO2 Performance declined at 1.5 g TiO2 |
| [182,183,184] | Halloysite nanotubes (HNTs) in SAE 5W40 | RSM, NSGA-II, MLP, ML algorithms, Cascaded Forward Neural Network (CFNN), GPR, ANN, SVM, DT | Dynamic viscosity, TC, density, specific heat capacity | Property Enhancement: Max TC increase: 23.24% at 1 vol.% and 60 °C Max viscosity increase: 21.4% at 1 vol.% and 30 °C Trend: TC and viscosity increase with nanoparticle concentration |
| [183,185,186,187,188,189,190,191,192] | Hybrid nanofluid (Al2O3–Cu–Water) in porous media | (ANN) with (PSO), (ANN) + (GA), (SVR), (RF); CFD-based simulation, SVR, MLP, RF (regressor models) | Temperature, time, NaOH concentration → Nanoparticle size, pressure, substrate thermal effusivity, Nusselt number, heat transfer efficiency, thermal performance factor, Reynolds number, permeability, nanoparticle volume fraction, entropy generation, shear stress | ML Prediction of CHF Trends: MLP: Best performance (mean R2 ~87%) RF: High single-run R2 (90%) but lower mean R2 SVR: Lowest performance Top features: Pressure, nanoparticle size Substrate thermal effusivity: Negligible impact ML models outperformed Kandlikar’s correlation Heat Transfer Enhancement: CNi inserts: 12.5–23.9% improvement CDNi inserts: Up to 32.6% improvement ML trained on 220 CFD + experimental data showed high prediction accuracy ZnO Nanoparticle Synthesis and Efficiency: Predicted size: 5.67 nm at 59 °C, 56 min, 0.08 M NaOH Experimental: 5.3 ± 0.4 nm Photocatalytic efficiency: 74% (vs. 58% for commercial ZnO) Flow and Entropy Analysis: Heat transfer ↑ with Re, permeability, and volume fraction Entropy shows nonmonotonic trend ANN-PSO provided accurate correlations for thermal parameters |
| [148,189,193,194] | Tri-hybrid nanofluid (specific composition not explicitly stated); used as coolant under PV panels | (ANN) trained with Levenberg–(LMA-TNN); combined with Lobatto IIIa numerical solver, Bayesian (BRNN), (QLM), k (ANN) with hyperparameter optimization, combined with CFD using Keller Box Method (KBM) | Temperature, velocity profile, thermal radiation, magnetic field, Casson parameter, ANN regression accuracy, Reynolds number, Deborah number, MSE, regression, ST index, heat transfer rate, shear stress, magnetic field | High model accuracy with errors ranging from 10−7 to 10−11 ANN models reduced computational time and effectively captured flow/temperature behavior ANN and KBM achieved near-perfect regression (R2 ≈ 1.0) PG–water nanofluid showed comparable heat transfer to EG-based nanofluid Curvature and suction increased velocity and decreased temperature in flow regime BRNN addressed uncertainty and reduced overfitting efficiently Magnetic field and curvature enhanced overall heat transfer |
| [179,195,196] | TiO2 nanoparticles in MO oil; LPG refrigerant | ANFIS with GP, SC, FCM clustering; WS optimization, Gene Expression Programming (GEP), and Adaptive Neuro–Fuzzy Inference System (ANFIS), Adaptive Neuro–Fuzzy Inference System (ANFIS) using Grid Partitioning and Subtractive Clustering | Thermal conductivity, viscosity, density, specific heat, temperature (20–60 °C), concentration (0–0.3%), specific heat capacity (SHC), Second-law efficiency, total irreversibility, RMSE, MAPE, variance | ANFIS (subtractive clustering): High accuracy (Var: 0.996–0.999, RMSE: 0.0296–0.1726 W, MAPE: 0.108–0.176%); outperformed ANN GP-ANFIS: Best for SHC (R = 0.99992, MAPE = 0.036%) and TC (R = 0.99833, MAPE = 0.218%) SC-ANFIS: Best for density and viscosity (R ≈ 0.9989) Key sensitivities: Density_np (0.53%), VF (1.9%), SHC_np (1.6%), TC_np (1.7%) GEP vs. ANFIS: GEP more accurate (R > 0.9825, RMSE = 0.79, MAPE < 2.16%) than ANFIS (R > 0.96, RMSE = 1.50, MAPE < 2.93%) |
2.3.5. Review-Based Papers
2.3.6. Critical Analysis and Future Directions
A Critical Appraisal of the Current Research Landscape
- Methodological Imbalance and Limited Synergy: The field is disproportionately reliant on experimental investigations. While empirical data is indispensable, the pronounced scarcity of hybrid studies—which integrate experimental work with validated numerical modeling—suggests a prevailing trial-and-error approach. This underutilization of synergistic methodologies means the predictive and optimization power of computational tools is not being fully leveraged to accelerate discovery and reduce research overhead.
- Asymmetrical Application Focus: There is a distinct and substantial focus on refrigeration systems at the expense of broader HVAC applications. This neglects the significant energy-saving potential in areas such as commercial chillers, large-scale heat pumps, and data center cooling, which constitute a major portion of global energy consumption for thermal management. This represents a strategic misalignment of research effort with the sectors promising the greatest potential impact.
- The Unresolved Challenge of Long-Term Viability: A critical deficiency in the current literature is the predominant focus on short-term performance metrics. Issues of paramount importance for practical implementation—such as long-duration fluid stability, nanoparticle agglomeration and sedimentation, potential for erosion and corrosion of system components, and material compatibility—remain largely unaddressed. Without robust, long-term operational data, the remarkable performance enhancements reported in laboratory settings remain academically compelling but commercially unproven.
- Deficiency in Economic and Lifecycle Analysis: The research convincingly demonstrates that nanofluids can improve thermodynamic efficiency, but it largely fails to address whether this improvement is economically viable or environmentally beneficial over the full lifecycle. The high initial cost of nanomaterials and the energy intensity of fluid preparation processes may offset the economic and environmental gains from operational energy savings. A comprehensive technoeconomic analysis (TEA) and lifecycle assessment (LCA) are conspicuously absent from most studies.
- Nascent Integration of AI and Machine Learning: While the application of AI/ML is a promising development, its current use is rudimentary. Existing models are almost exclusively focused on predicting the thermophysical properties of the nanofluids themselves or the performance of isolated components. A critical gap exists between this foundational, property-level prediction and the development of holistic, system-level models capable of dynamic optimization and control.
3. Conclusions and Future Directions
- Prioritize Long-Term, System-Level Validation: The foremost priority must be to shift from short-term, component-based experiments to long-duration studies on integrated, pilot-scale systems. For example, this involves running a nanofluid-enhanced chiller for a full cooling season (>2000 h) while continuously monitoring for performance degradation, changes in pressure drop, filter clogging, and signs of component erosion. This is the only way to generate conclusive data on fluid stability, material compatibility, and sustained performance under realistic operational cycling.
- Broaden the Application Scope to High-Impact HVAC Systems: Research efforts should be deliberately expanded into under-investigated, high-impact areas where the potential for energy savings is greatest. Specific examples include investigating nanorefrigerants in large-scale commercial chillers for office buildings, employing nanolubricants in the compressors of multi-zone heat pumps, and using nanofluids in the secondary loops of data center cooling systems.
- 3.
- Promote Synergistic Hybrid Methodologies: To move beyond trial-and-error, hybrid studies that couple experimental work with validated numerical simulations (CFD) and theoretical models must become the standard. A practical workflow would involve using CFD to computationally screen and optimize the geometry of a microchannel heat exchanger for a specific nanofluid before fabricating and experimentally testing only the most promising designs. This synergy will enable more rapid and cost-effective optimization.
- 4.
- Advance from Property Prediction to System-Level AI/ML: The research community must leverage AI and machine learning to develop dynamic “digital twins” of entire HVAC&R systems. For instance, an AI model could be trained to predict the onset of nanoparticle agglomeration using real-time sensor data (temperature, pressure, flow rate) and automatically adjust system operation to maintain stability, or forecast the remaining useful life of the fluid for predictive maintenance.
- 5.
- Mandate Technoeconomic and Lifecycle Assessments: To establish commercial viability, rigorous technoeconomic analysis (TEA) and lifecycle assessment (LCA) must be integrated into research projects. This means quantifying whether the operational energy savings from a 15% COP improvement can justify the initial cost of graphene-based nanoparticles and the energy footprint of their synthesis over a 10-year system lifespan.
- 6.
- Foster Innovation in Material Science for Inherent Stability: Foundational research into novel nanomaterials is critical to overcoming the core challenge of stability. This includes developing advanced materials like core-shell nanoparticles, where a highly conductive core (e.g., copper) is coated with a chemically inert shell (e.g., silica) to prevent oxidation and improve long-term dispersion in water–glycol mixtures without relying on potentially degradable surfactant additives.
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| ANFIS | Adaptive Neuro–Fuzzy Inference System |
| ANN | Artificial Neural Network |
| BRNN | Bayesian Regression Neural Network |
| CFNN | Cascaded Forward Neural Network |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| COP | Coefficient of Performance |
| conc | Concentration |
| Da | Darcy Number |
| DT | Decision Tree |
| Ec | Eckert Number |
| EG | Ethylene Glycol |
| ET | Extra Trees Algorithm |
| Fr | Forchheimer Number |
| GA | Genetic Algorithm |
| GEP | Gene Expression Programming |
| GPR | Gaussian Process Regression |
| Ha | Hartmann number |
| HMIM | 1-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium |
| HT | Heat Transfer |
| HTC | Heat Transfer Coefficient |
| HVAC&R | Heating, Ventilation, Air Conditioning, and Refrigeration |
| KBM | Keller Box Method |
| LCA | Lifecycle Analysis |
| LGBM | Light Gradient-Boosting Machine |
| LINMAP | Linear Programming Technique for Multidimensional Analysis of Preference |
| LMA | Levenberg–Marquardt Algorithm |
| LMA-TNN | Levenberg–Marquardt Algorithm Trained Neural Network |
| LMFA NN | Local Mean Field Approximation Neural Network |
| LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory |
| MAPE | Mean Absolute Percentage Error |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| MLP | Multi-Layer Perceptron |
| MO | Mineral Oil |
| MOD | Mean of Deviation |
| np | Nanoparticle |
| NSGA-II | Non-dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm II |
| PCM | Phase Change Material |
| Pe | Peclet Number |
| PG | Propylene Glycol |
| PVP | Polyvinylpyrrolidone |
| QLM | Quasi-Linearization Method |
| RCP | Relative Cooling Power |
| Rd | Radiation parameter |
| RF | Random Forest |
| Ri | Richardson Number |
| RMSE | Root Mean Square Error |
| RNN | Recurrent Neural Network |
| RSM | Response Surface Methodology |
| Sc | Schmidt Number |
| SC | Subtractive Clustering |
| SDS | Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate |
| SHC | Specific Heat Capacity |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
| SWCNT | Single-Wall Carbon Nanotube |
| TC | Thermal Conductivity |
| TDMA | Tri-Diagonal Matrix Algorithm |
| THNF | Trihybrid nanofluid |
| VF | Volume Fraction |
| VST | Dynamic Viscosity |
| WF | Weight Fraction |
| XGB | Extreme Gradient Boosting |
| ZnO | Zinc Oxide |
| ↑ | Increase |
| Decrease | |
| > | Greater or outperform |
| < | Less than |
References
- International Energy Agency. Cooling. IEA. 2023. Available online: https://www.iea.org/energy-system/buildings/cooling (accessed on 15 May 2025).
- Kasaeian, A.; Nasrin, R.; Vatan, S. A review on solar-assisted heat pump systems using nanofluid. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 46, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidur, R.; Leong, K.Y.; Mohammad, H.A. A review on applications and challenges of nanofluids. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 1646–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, J.; Qi, C.; Zhang, W. Review on Coupled Thermo-Hydraulic Performance of Nanofluids and Microchannels. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.K.; Choi, S.U.; Yu, W.; Pradeep, T. Nanofluids: Science and Technology; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Mahian, O.; Kianifar, A.; Sahin, A.Z.; Wongwises, S. A review of the applications of nanofluids in solar energy. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 139, 1205–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.Q.; Wang, L.M.; Li, H.B. Critical review on the stability and thermal conductivity of water-based hybrid nanofluids for heat transfer applications. RSC Adv. 2025, 15, 14088–14125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riyadi, T.; Herawan, S.; Tirta, A.; Ee, Y.; Hananto, A.; Paristiawan, P.; Yusuf, A.; Venu, H.; Veza, I. Nanofluid heat transfer and machine learning: Insightful review of machine learning for nanofluid heat transfer enhancement in porous media and heat exchangers as sustainable and renewable energy solutions. Results Eng. 2024, 24, 103002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, A.; Saha, A.; Banerjee, S.; Roy, P.; Kundu, B. A Review of Artificial Intelligence Methods in Predicting Thermophysical Properties of Nanofluids for Heat Transfer Applications. Energies 2024, 17, 1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, M.; Faiz, M.; Hassan, W.; Abbas, M.; Raza, J.; Kumail, Z.; Nawaz, T.; Shabir, S.; Jan, A.; Li, F. AI-powered optimization and numerical techniques for nanofluid heat transfer systems-a review. Multiscale Multidiscip. Model. Exp. Des. 2025, 8, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smrity, A.; Yin, P. Bridging computational and experimental boundaries: A review of theoretical modeling and experimental validation of hybrid nanofluids in heat transfer applications. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2025, 115, 109873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalatbari, S.; Jalili, P.; Jalili, B.; Ganji, D. Investigating the improvement of heat transfer and flow characteristics of hybrid nanofluids: A comprehensive review. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part E J. Process Mech. Eng. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, D.; Ullah, H.; Fiza, M.; Jan, A.; Akgül, A.; Hendy, A.; Islam, S. Investigating slip velocity effects on thermal and mass transport in magnetized nanoparticle squeeze flow via numerical scheme. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part N J. Nanomater. Nanoeng. Nanosyst. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Jin, Y.; Xu, M.; Liaw, K.L.; Zhang, K.; Mohit, M.; Kurnia, J.; Sasmito, A. Thermal characteristics of nanofluid ice slurry flowing through a spiral tube: A computational study. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2024, 61, 104882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmi, B.; Dharmaiah, G.; Anjum, A.; Samdani; Naheed, M. Influence of Darcy–Forchheimer Fe3O4—CoFe2O4—H2O hybrid nanofluid flow with magnetohydrodynamic and viscous dissipation effects past a permeable stretching sheet: A numerical contribution. Multiscale Multidiscip. Model. Exp. Des. 2024, 8, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Zhao, N.; Li, X.; Liu, J.; Yang, L. Experimental and numerical investigation on heat transfer mechanism and multifunctional thermodynamic properties of supercritical carbon dioxide/amino-functionalized graphene nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2025, 241, 126702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibin, B.S.; Gundabattini, E. Investigation on transport properties, heat transfer characteristics and pressure drop of CuO enhanced R1234yf based refrigerant. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2023, 49, 103229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satheeshkumar, P.; Selwynraj, A.I. Pathways to enhance the performance of adsorption cooling system: An overview. Results Eng. 2024, 23, 102855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, J. A three-dimensional unsteady flow of Casson nanofluid with suspension of microorganisms with variable thermal conductivity: A modified Fourier theory approach. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2024, 63, 105218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibin, B.S.; Gundabattini, E. Investigation on the density of Al2O3/R1234yf, TiO2/R1234yf and CuO/R1234yf nano-refrigerants. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part N J. Nanomater. Nanoeng. Nanosyst. 2022, 237, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Z.; Bhargav, A. Effect of Aggregation Morphology on Thermal Conductivity and Viscosity of Al2O3-CO2 Nanofluid: A Molecular Dynamics Approach. Nanosci. Technol. Int. J. 2021, 12, 19–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawawi, N.; Azmi, W.; Redhwan, A.; Sharif, M.; Samykano, M. Experimental investigation on thermo-physical properties of metal oxide composite nanolubricants. Int. J. Refrig. 2018, 89, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elboughdiri, N.; Fatima, N.; El-Rahman, M.; Abbas, M.; Rashid, R.; Shomurotova, S.; Said, M.; Mahariq, I.; SHendy, A.; MGalal, A. Characteristics of unsteady thermo-bioconvection chemical reactive stagnation point flow of trihybrid nanofluid around rotating sphere with Oxytactic Microorganisms. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2024, 61, 104981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yıldız, G.; Ağbulut, Ü.; Gürel, A. A review of stability, thermophysical properties and impact of using nanofluids on the performance of refrigeration systems. Int. J. Refrig. 2021, 129, 342–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarac, B.; Soprunyuk, V.; Herwig, G.; Gümrükçü, S.; Kaplan, E.; Yüce, E.; Schranz, W.; Eckert, J.; Boesel, L.; Sarac, A. Thermomechanical properties of confined magnetic nanoparticles in electrospun polyacrylonitrile nanofiber matrix exposed to a magnetic environment: Structure, morphology, and stabilization (cyclization). Nanoscale Adv. 2024, 6, 6184–6195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehyo, M.; Özcan, H. Thermophysical Properties of Nanoferrofluid (Fe3O4–Acetone/Znbr2) as a Working Fluid for Use in Absorption Refrigeration Applications. Int. J. Thermodyn. 2021, 24, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sica, L.; Contreras, E.; Bandarra Filho, E.; Parise, J. An experimental viscosity investigation on the use of non-Newtonian graphene heat transfer nanofluids at below-ambient temperatures. Int. J. Energy Res. 2021, 45, 14530–14546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Du, K.; Li, Y.; Yang, L. Experimental investigation on the influence of high temperature on viscosity, thermal conductivity and absorbance of ammonia–water nanofluids. Int. J. Refrig. 2017, 82, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, T. Numerical simulation of heat transfer in williamson hybrid nanofluid (MgO−Ag/water) flow with viscous dissipation effects. Multiscale Multidiscip. Model. Exp. Des. 2025, 8, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, H.; Giddings, D.; Walker, G.; Power, H. CFD assessment of the effect of nanoparticles on the heat transfer properties of acetone/ZnBr2 solution. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2018, 128, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, Z.; Rahman, S.; Sohail, M.; Bibin, B.S. Analysis of thermophysical properties and performance of nanorefrigerants and nanolubricant-refrigerant mixtures in refrigeration systems. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2023, 49, 103274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, Z.; Rahman, S.; Sohail, M.; Bahman, A.; Alim, M.; Shaik, S.; Radwan, A.; El-Sharkawy, I. Nano-refrigerants and nano-lubricants in refrigeration: Synthesis, mechanisms, applications, and challenges. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2023, 233, 121211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Y. Enhanced flow boiling heat transfer study on EDM-modified aluminum surface. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2025, 274, 126642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hadi Attia, M.; Harby, K.; Amin, M.; Abdelgaied, M. Evaluating honeycomb-arranged hollow copper tubes and nanoparticle-coated flax fibers for improved hemispherical solar still performance. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2025, 197, 106986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, A.; Alqsair, U.; Alotaibi, F.; Alrwuais, F.; Omara, Z.; Essa, F. Improving thermal performance of half-cylindrical solar stills with convex/corrugated absorbers, wick materials, reflector, and nano-enhanced phase change materials. J. Energy Storage 2024, 100, 113462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, A.; Chavan, S.; Sutar, K.; Chendake, Y.; Shaikh, I.; Sihna, M. Experimental investigation on climate-control nano-composite polycarbonate sheets enhanced with TiO2, ZnO, and zeolite nanoparticles for polyhouse use. Eng. Res. Express 2024, 6, 045553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Dong, C.; Xiong, P.; Nan, H.; Yan, D.; Li, R.; An, Y.; Lei, J.; Li, Z. Triple Thermal Management Wood–Plastic Composite Plate with Excellent Waterproof and Mechanical Properties. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2024, 64, 453–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuce, P.; Cuce, E.; Guclu, T.; Shaik, S.; Alshahrani, S.; Saleel, C. Effect of using hybrid nanofluids as a coolant on the thermal performance of portable thermoelectric refrigerators. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2022, 53, 102685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiriyasart, S.; Suksusron, P.; Hommalee, C.; Siricharoenpanich, A.; Naphon, P. Heat transfer enhancement of thermoelectric cooling module with nanofluid and ferrofluid as base fluids. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2021, 24, 100877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Salam, B. A review on nanofluid: Preparation, stability, thermophysical properties, heat transfer characteristics and application. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanukrishna, S.S.; Murukan, M.; Reshmi Krishnan, S. Effect of nanoparticles on the flow boiling heat transfer characteristics of refrigerant and performance of refrigeration systems: An experimental investigation. Int. J. Thermofluids 2025, 27, 101263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorfie, E.; Moltot, A.; Zergaw, G.; Dessie, H. Influence of Joule Heating and Nonlinear Thermal Radiation on the Electrical Conductivity of Second-Grade Hybrid Nanofluid Flow Over a Stretching Cylinder. Eng. Rep. 2025, 7, e70129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, U.; Bhattacharyya, D.; Endrino, J.; Fereres, S. The effects of ejector adiabatic absorber on heat and mass transfer of binary nanofluid with heat transfer additives. Emergent Mater. 2021, 4, 1665–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahbubul, I.; Khan, M.; Ibrahim, N.; Ali, H.; Al-Sulaiman, F.; Saidur, R. Carbon nanotube nanofluid in enhancing the efficiency of evacuated tube solar collector. Renew. Energy 2018, 121, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahbubul, I.; Saadah, A.; Saidur, R.; Khairul, M.; Kamyar, A. Thermal performance analysis of Al2O3/R-134a nanorefrigerant. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2015, 85, 1034–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Lum, L.; Kandasamy, R.; Zhao, H.; Ho, J. Flow boiling heat transfer enhancement of R134a in additively manufactured minichannels with microengineered surfaces. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2024, 256, 124150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilic, G. Performance Evaluation of Triply Periodic Minimal Surface Heat Exchangers Using Nanofluids at High Flow Rates for Enhanced Energy Efficiency. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 4140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshvaght-Aliabadi, M.; Alizadeh, A. An experimental study of Cu–water nanofluid flow inside serpentine tubes with variable straight-section lengths. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2015, 61, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagum, M.; Hossen, M.; Chowdhury, F.; Hoque, S. Influence of lightly doped Ca on the structural, magnetic and magnetocaloric properties of LaCaMnO3 nanoparticles. Mater. Charact. 2025, 225, 115153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Lu, D.; Imran, M.; Anwar, M. Numerical insights into enhanced heat transfer mechanisms in TiO2-Au ethylene glycol nanofluids within Darcy porous media using fractional calculus. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2025, 70, 106063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Zhou, L.; Song, C.; Zhang, J. Numerical study of thermoelectric coolers for cooled infrared detectors using microchannel heat sinks and nanofluids. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2025, 266, 125457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, S.; Durgaprasad, P.; Díaz Palencia, J.; Wakif, A.; Raju, C.; Dinesh kumar, M.; Muneerah, A.; Ali, J. Contour Analysis for Heat Transfer Rate in a Wedge Geometry with Non-Uniform Shapes Nanofluid: Gradient Descent Machine Learning Technique. Results Eng. 2024, 23, 102714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balogun, O.; Aslam, M.; Iqbal, M.; Arshad, M. Investigation of gold and silver based hybrid nanofluid with effects of thermal radiation over a stretching sheet. Alex. Eng. J. 2025, 117, 352–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bompally, R.; Gurijala, R.; Reddy, R.; Thumma, T. Effect of inclined magnetic field, non-uniform heat source on hybrid EG-MoS2-SiO2 radiative nanofluid flow with viscous and Joule dissipation over convectively heated elongating surface. Multiscale Multidiscip. Model. Exp. Des. 2025, 8, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Lin, Z.; Luo, X.; Chen, J.; Yang, Z.; Wu, R.; Chen, Y. Bi-objective optimization of thermal interface material-microchannel-nanofluid-based thermal management system design for microchip array. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2025, 274, 126727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Chandel, S.; Shukla, P.; Sinha-Ray, S. Thermal Management of Microelectronics Using Microchannel Heat Sink with Inclined Geometry and Cnt-Based Nanofluid. J. Enhanc. Heat Transf. 2025, 32, 37–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreelakshmi, K.; Mary, G.; Alqsair, U.; Elsemary, I.; Alsayegh, R.; Khan, S.; Kolsi, L. Evaluation of heat transfer for unsteady thin film flow of mono and hybrid nanomaterials with five different shape features. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2024, 62, 105168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkherbache, S.; Amroune, S.; Belaadi, A.; Zergane, S.; Farsi, C. Numerical Analysis of Natural Convection in an Annular Cavity Filled with Hybrid Nanofluids under Magnetic Field. Energies 2024, 17, 4671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, U.; Imran, M.; Noreen, S.; Fatima, N.; Muhammad, T. Heat Transfer Performance of Hybrid Nanofluid Radiative Flow via a Rotating Disk With Heat Source–Sink Effects and Response Surface Methodology. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elboughdiri, N.; Abbas, M.; Ayed, H.; Mouldi, A.; Fatima, N.; Abduvalieva, D.; Said, M.; Mahariq, I.; Hendy, A.; Galal, A. Numerical simulation of Stephan blowing impacts on thermally laminated 3D flow of MHD trihybrid nanofluid with Soret and Dufour effects. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2025, 66, 105460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinwari, W.; Hayat, T.; Abbas, Z.; Momani, S. Trihybrid fluid flow with Arrhenius activation energy and slip conditions in porous space: A numerical analysis. Alex. Eng. J. 2025, 117, 534–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shree, S.; Hanumagowda, B.; Saini, G.; Singh, K.; Kulshreshta, A.; Varma, S.; Punith Gowda, R. Heat and mass transfer in electrically conducting hybrid nanofluid flow between two rotating parallel stretching surfaces: An entropy analysis. Multiscale Multidiscip. Model. Exp. Des. 2024, 8, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hema, S.; Venkatesh, P.; Gireesha, B.; Pavithra, C. Flow and heat transfer analysis of MHD ternary hybrid nanofluid flow through a vertical porous microchannel with slip boundary conditions. Multiscale Multidiscip. Model. Exp. Des. 2025, 8, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpa, F.; Bianco, V. Improving the performance of room temperature magnetic regenerators using Al2O3-water nanofluid. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2024, 236, 121711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, H.; Giddings, D.; Walker, G. CFD simulation of a concentrated salt nanofluid flow boiling in a rectangular tube. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 125, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Mao, F.; Song, Y.; Hong, J.; Yan, Y. Effect of adding copper oxide nanoparticles on the mass/heat transfer in falling film absorption. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2020, 181, 115937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aprea, C.; Greco, A.; Maiorino, A.; Masselli, C. Enhancing the Heat Transfer in an Active Barocaloric Cooling System Using Ethylene-Glycol Based Nanofluids as Secondary Medium. Energies 2019, 12, 2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.; Teamah, M.; El-Maghlany, W. Numerical investigation for heat transfer enhancement using nanofluids over ribbed confined one-end closed flat-plate. Alex. Eng. J. 2017, 56, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saee, A.; Baghban, A.; Zarei, F.; Zhang, Z.; Habibzadeh, S. ANFIS based evolutionary concept for estimating nucleate pool boiling heat transfer of refrigerant-ester oil containing nanoparticles. Int. J. Refrig. 2018, 96, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolghadri, A.; Maddah, H.; Ahmadi, M.; Sharifpur, M. Predicting Parameters of Heat Transfer in a Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger Using Aluminum Oxide Nanofluid with Artificial Neural Network (ANN) and Self-Organizing Map (SOM). Sustainability 2021, 13, 8824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanti, P.; Wanatasanappan, V.; Said, N.; Saini, S.; Mishra, V.; Paramasivam, P.; Yusuf, M. Thermal performance, entropy generation, and machine learning insights of Al2O3-TiO2 hybrid nanofluids in turbulent flow. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 16035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, B.; Bashir, H.; Ahmed, N.; Khan, U.; Kumar, A.; Garayev, M. Enhancing heat transfer in nanofluids: Exploring nanoparticle aggregation using deep learning optimization. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 2025, 39, 2550195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlMohamadi, H.; Rubbab, Q.; Garalleh, H.; Atta, G.; Amjad, M.; Jamshed, W.; ElSeabee, F.; Bayram, M. Artificial intelligence and numerical simulation based assessment of trihybrid structured flow over a curved geometry: Thermalized case analysis. Results Eng. 2025, 25, 103829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, H.; Pasha, A.; Shah, Z.; Zahoor Raja, M.; Algarni, S.; Alqahtani, T.; Irshad, K.; Khan, W. Application of machine learning for thermal exchange of dissipative ternary nanofluid over a stretchable wavy cylinder with thermal slip. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2024, 60, 104599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojjat, M. Nanofluids as coolant in a shell and tube heat exchanger: ANN modeling and multi-objective optimization. Appl. Math. Comput. 2020, 365, 124710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahdat Azad, A.; Vahdat Azad, N. Application of nanofluids for the optimal design of shell and tube heat exchangers using genetic algorithm. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2016, 8, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyothi, K.; Venkateswarlu, B.; Reddy, P.; Kodi, R.; Annapureddy, D. Neural network-driven analysis of MHD boundary layer flow and heat transfer in Sisko nanofluids. Multiscale Multidiscip. Model. Exp. Des. 2025, 8, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, X. Predicting the thermal conductivity enhancement of nanofluids using computational intelligence. Phys. Lett. A 2020, 384, 126500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipour Bonab, S.; Yazdani-Asrami, M. Machine learning-based model for the intelligent estimation of critical heat flux in nanofluids. Nano Express 2024, 5, 025012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; ul Haque, M. Thermophysical Evaluation of Silica Nanoparticles in Refrigerant Compressor Oil for Enhanced Refrigeration Performance. Int. J. Heat Technol. 2025, 43, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Kumar, P.; Goyal, K. A novel approach of using TiO2 and SiO2 nanoparticles and hydrocarbon refrigerant R600a in retrofitted vapour compression refrigeration system for environment protection and system performance enhancement. Appl. Nanosci. 2023, 13, 6299–6317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassim, S.; Hairuddin, A.; Cut, V. The effects of Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube to the performance of a refrigeration system. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2024, 238, 6691–6705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dağıdır, K.; Bilen, K. Experimental investigation of usage of POE lubricants with Al2O3, graphene or CNT nanoparticles in a refrigeration compressor. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2023, 14, 1041–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahsan, M.; Chand, P.; Namrata, K. Comparative Experimental Investigation to Analyze the Use of SiO2 Nanoparticles with R600a and Pure R600a in Vapour Compression Refrigeration System. Recent Pat. Mech. Eng. 2025, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariram, V.; Al Riyami, H.; Nadanakumar, V.; Godwin John, J.; Christu Paul, R.; Nakandhrakumar, R.; Rameshkumar, P. Microstructure and Structural Comparison between Additively Manufactured Metal and Ceramics. Int. J. Veh. Struct. Syst. 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthick, M.; Karuppiah, S.; Kanthan, V. Performance investigation and exergy analysis of vapor compression refrigeration system operated using R600a refrigerant and nanoadditive compressor oil. Therm. Sci. 2020, 24, 2977–2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusof, T.; Arshad, A.; Suziyana, M.; Chui, L.; Basrawi, M. Experimental Study of a Domestic Refrigerator with POE-Al2O3 Nanolubricant. Int. J. Automot. Mech. Eng. 2015, 11, 2243–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohunakin, O.; Adelekan, D.; Babarinde, T.; Leramo, R.; Abam, F.; Diarra, C. Experimental investigation of TiO2-, SiO2- and Al2O3-lubricants for a domestic refrigerator system using LPG as working fluid. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 127, 1469–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindasamy, S.; Kalibangan, M.; Sadhasivam, S.; Kadasari, R. Experimental analysis of domestic refrigeration system using nanorefrigerant [CeO2+ZnO+R134a]. Therm. Sci. 2022, 26, 969–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Yao, S.; Sun, Q. Highly efficient grooved NiTi tube refrigerants for compressive elastocaloric cooling. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2023, 228, 120439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkaya, M.; Menlik, T.; Sözen, A.; Gürü, M. The Effects of Triton X-100 and Tween 80 Surfactants on the Thermal Performance of a Nano-Lubricant: An Experimental Study. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 8, 955–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhamneya, A.; Rajput, S.; Singh, A. Comparative performance analysis of ice plant test rig with TiO2-R-134a nano refrigerant and evaporative cooled condenser. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2018, 11, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthilkumar, A.; Anderson, A.; Sekar, M. Performance analysis of R600a vapour compression refrigeration system using CuO/Al2O3 hybrid nanolubricants. Appl. Nanosci. 2021, 13, 899–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, H.; Camdali, U.; Biyikoglu, A.; Aktas, M. Performance analysis of R134a vapor compression refrigeration system based on CuO/CeO2 mixture nanorefrigerant. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2022, 44, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyakumar, N.; Uthranarayan, C.; Narayanasamy, B. Energy conservation in the refrigeration system through improvement of Coefficient of Performance and power consumption reduction using Nanofluids. Int. J. Ambient Energy 2019, 43, 1120–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Harge, P. Effect of Addition of Different Mass Fractions of CuO Nano Particles in Compressor oil upon COP of the Refrigeration System. Int. J. Recent Technol. Eng. 2019, 8, 3732–3736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, A. Performance evaluation of a refrigeration system using nanolubricant. Appl. Nanosci. 2020, 10, 1667–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, R.; Kundan, L.; Sharma, R. Investigating the Performance of Nanorefrigerant (R134a + CuO)-Based Vapor Compression Cycle: A New Scope. Heat Transf. Res. 2021, 52, 33–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikanden, V.; Avinash, A. An experimental insight into the effects of silver-doped cupric oxide nanoparticles on the performance of hydrocarbon refrigeration system. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanukrishna, S.S.; Vishnu, A.S.; Jose Prakash, M. Nanorefrigerants for energy efficient refrigeration systems. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2017, 31, 3993–4001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, A.; Cárdenas Gómez, A.; Bandarra Filho, E.; Parise, J. Experimental evaluation of SWCNT-water nanofluid as a secondary fluid in a refrigeration system. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 111, 1487–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afolalu, S.; Ikumapayi, O.; Ogedengbe, T.; Adegbenjo, A.; Jen, T. Evaluation and Analysis of an Agro-Based Nano Refrigerant to Improve the Performance of a Domestic Refrigeration System. Int. J. Heat Technol. 2022, 40, 1305–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selimefendigil, F. Experimental Investigation of Nano Compressor Oil Effect on the Cooling Performance of a Vapor-Compression Refrigeration System. J. Therm. Eng. 2018, 5, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcucci Pico, D.; da Silva, L.; Schneider, P.; Bandarra Filho, E. Performance evaluation of diamond nanolubricants applied to a refrigeration system. Int. J. Refrig. 2019, 100, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcucci Pico, D.; da Silva, L.; Hernandez Mendoza, O.; Bandarra Filho, E. Experimental study on thermal and tribological performance of diamond nanolubricants applied to a refrigeration system using R32. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2020, 152, 119493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Zhu, T.; Bao, Y. Thermal performance evaluation of a thermoelectric cooler coupled with corona wind. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2020, 179, 115753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikpe, A.; Udofia Ekpenyong, A. Buhar sıkıştırmalı soğutma sistemindeki hibrit-nanoakışkan zeotropik karışımların termo-fiziksel değerlendirilmesi. Gümüşhane Üniversitesi Fen Bilim. Enstitüsü Derg. 2024, 14, 1021–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Tang, X.; Song, J.; Jia, T.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, L.; Li, S.; Su, W. Experimental study on the influence of adding TiO2 nanoparticles on practical ammonia-water absorption refrigeration system-the generation and rectification processes. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2023, 230, 120763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micali, F.; Milanese, M.; Colangelo, G.; de Risi, A. Reducing CO2 emissions by improving HVAC system efficiency of data centers through nanofluids: A case study. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2025, 275, 126889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milanese, M.; Micali, F.; Colangelo, G.; de Risi, A. Experimental Evaluation of a Full-Scale HVAC System Working with Nanofluid. Energies 2022, 15, 2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavulu, K.; Rasu, N. An Experimental Study on the Improvement of Coefficient of Performance in Vapor Compression Refrigeration System Using Graphene Lubricant Additives. Energy Sources Part A Recover. Util. Environ. Eff. 2021, 47, 6449–6464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Elsaid, A. Effect of hybrid and single nanofluids on the performance characteristics of chilled water air conditioning system. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2019, 163, 114398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venegas, M.; García-Hernando, N.; Zacarías, A.; de Vega, M. Performance of a Solar Absorption Cooling System Using Nanofluids and a Membrane-Based Microchannel Desorber. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.; Ahmed Khan, W.; Nayfeh, J. Experimental Investigation on the Performance of Heat Pump Operating with Copper and Alumina Nanofluids. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2021, 66, 2843–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nourafkan, E.; Asachi, M.; Jin, H.; Wen, D.; Ahmed, W. Stability and photo-thermal conversion performance of binary nanofluids for solar absorption refrigeration systems. Renew. Energy 2019, 140, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elibol, E.; Yilmazoglu, M.; Aksoy, A.; Aktas, F. Thermal analysis of a refrigeration system integrated with a thermoelectric couple and microchannels using TiO2-water nanofluid. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2024, 108, 109491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, R.; Jawahar, C.; Brusly Solomon, A.; Bellos, E.; Ajay Vasanth, X. Experimental investigation of a two-phase closed thermosyphon with Al2O3/R134a nanorefrigerant. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part E J. Process Mech. Eng. 2022, 238, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Li, S.; Zhou, R.; Xu, M.; Jiang, W.; Du, K. Experimental investigation on the effect of TiO2 nanoparticles on the performance of NH3—H2O—LiBr absorption refrigeration system. Int. J. Refrig. 2021, 131, 826–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laplane, C.; Ren, P.; Roberts, R.; Lu, Y.; Volz, T. Inert Shell Coating for Enhanced Laser Refrigeration of Nanoparticles: Application in Levitated Optomechanics. ACS Photonics 2024, 11, 963–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuce, E.; Guclu, T.; Cuce, P. Improving thermal performance of thermoelectric coolers (TECs) through a nanofluid driven water to air heat exchanger design: An experimental research. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 214, 112893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Wang, M.; Jin, Z.; Li, S. Modeling and experimental verification of the enhancement of TiO2 nanofluid on ammonia falling film absorption process. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2022, 184, 107917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Li, S.; Zhou, R.; Xu, M.; Jiang, W.; Du, K. Effects of absorption pressure and temperature on NH3-H2O-LiBr-TiO2 nanofluid absorption performance and system COP. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2023, 219, 119353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sözen, A.; Özbaş, E.; Menlik, T.; Skender, N.; Kılınç, C.; Çakır, M. Performance investigation of a diffusion absorption refrigeration system using nano-size alumina particles in the refrigerant. Int. J. Exergy 2015, 18, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F. Experimental investigation of Al2O3-water nanofluid as a secondary fluid in a refrigeration system. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2021, 26, 101024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safaei, M.; Ranjbarzadeh, R.; Hajizadeh, A.; Bahiraei, M.; Afrand, M.; Karimipour, A. Effects of cobalt ferrite coated with silica nanocomposite on the thermal conductivity of an antifreeze: New nanofluid for refrigeration condensers. Int. J. Refrig. 2019, 102, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourfayaz, F.; Imani, M.; Mehrpooya, M.; Shirmohammadi, R. Process development and exergy analysis of a novel hybrid fuel cell-absorption refrigeration system utilizing nanofluid as the absorbent liquid. Int. J. Refrig. 2019, 97, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalkilic, A.; Mahian, O.; Kucukyildirim, B.; Eker, A.; Ozturk, T.; Jumpholkul, C.; Wongwises, S. Experimental Study on the Stability and Viscosity for the Blends of Functionalized MWCNTs with Refrigeration Compressor Oils. Curr. Nanosci. 2018, 14, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Rincon Ortiz, C. Experimental investigation of the effect of magnetic field on vapour absorption with LiBr–H2O nanofluid. Energy 2020, 193, 116640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondre, D.; Joshi, A.; Shinde, T.; Deshmukh, A.; Dhanawade, K. Experimental Performance and Analysis of Domestic Refrigeration System Using Nano-Refrigerants. In Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talpada, J.; Ramana, P. Experimental Analysis of H2O–LiBr Absorption Refrigeration System Using Al2O3 Nanoparticles. Int. J. Air-Cond. Refrig. 2020, 28, 2050010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatami, M.; Domairry, G.; Mirzababaei, S. Experimental investigation of preparing and using the H2O based nanofluids in the heating process of HVAC system model. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 7820–7825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsaid, A. A novel approach for energy and mass transfer characteristics in wet cooling towers associated with vapor-compression air conditioning system by using MgO and TiO2 based H2O nanofluids. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 204, 112289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, T.; Ahmad, W.; Quadri, I. Performance Evaluation of a Vapor Compression Refrigeration System Using Oxide Nano-particles: Experimental Investigation. Nanosci. Nanotechnol.-Asia 2021, 11, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfe, M.; Dalir, R.; Bakhtiari, R.; Afrand, M. Simultaneous effects of multi-walled carbon nanotubes and copper oxide nanoparticles on the rheological behavior of cooling oil: Application for refrigeration systems. Int. J. Refrig. 2019, 104, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Li, S.; Yang, L.; Du, K. Experimental investigation on performance of ammonia absorption refrigeration system with TiO2 nanofluid. Int. J. Refrig. 2019, 98, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Kim, C.; Kim, N. Steam Condensation on Copper-Enhanced Tubes Used in an Absorption Refrigeration System. J. Enhanc. Heat Transf. 2021, 28, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aramesh, M.; Pourfayaz, F.; Haghir, M.; Kasaeian, A.; Ahmadi, M. Investigating the effect of using nanofluids on the performance of a double-effect absorption refrigeration cycle combined with a solar collector. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part A J. Power Energy 2019, 234, 981–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousif, S.; Al-Obaidi, M.; Al-Muhsen, N. Towards More Efficient Refrigeration: A Study on the Use of TiO2 and Al2O3 Nanoparticles. Int. J. Heat Technol. 2024, 42, 1251–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shewale, V.; Kapse, A.; Sonawane, V. Experimental analysis of vapour compression refrigeration system using nano lubricant with refrigerant R-134a. Therm. Sci. 2024, 28, 3687–3697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, K.; Al-Mirani, A.; Ali, B.; Alomar, O. Impacts of Using AlO Nano Particle to Compressor Oil on Performance of Automobile Air Conditioning System. Front. Heat Mass Transf. 2024, 22, 839–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.; Rajput, S.; Kumar, R.; Sharma, A.; Saxena, K.; Agrawal, M.; Kadhim, I. Experimental and numerical investigation of metal oxide base nano particles for VCRS test rig. Int. J. Interact. Des. Manuf. (IJIDeM) 2023, 18, 5909–5916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasha, K. Controlling the Nusselt Number in a TiO2/R134a Nano-refrigerant System. Int. J. Heat Technol. 2019, 37, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, V.; Parekh, A.; Tailor, P. Experimental investigation of a vapour compression refrigeration system using R134a/Nano-oil mixture. Int. J. Refrig. 2020, 112, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanasarma, S.; Kuzhiveli, B. The effect of silica nanoparticle on thermal, chemical, corrosive, and the nature-friendly properties of refrigerant compressor lubricants—A comparative study. Asia-Pac. J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 15, e2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babarinde, T.; Akinlabi, S.; Madyira, D.; Ekundayo, F. Comparative Study of Energy Performance of R600a/TiO2 and R600a/MWCNT Nanolubricants in a Vapor Compression Refrigeration System. Int. J. Energy A Clean Environ. 2020, 21, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devendra; RaviPrakash, M.; Kapilan, N.; Yadav, S.P.S. Performance of Vapor Compression Refrigeration System using Nanoparticles—Based Mineral Oil Lubricant. Int. J. Recent Technol. Eng. 2019, 8, 730–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Peng, H.; Chang, Z.; Ding, G. Experimental investigation on TiO2 nanoparticle migration from refrigerant–oil mixture to lubricating oil during refrigerant dryout. Int. J. Refrig. 2017, 77, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, A.; Shah, S.; Bahaidarah, H.; Zamir, T.; Aziz, T. Advanced neural network modeling with Levenberg–Marquardt algorithm for optimizing tri-hybrid nanofluid dynamics in solar HVAC systems. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2025, 65, 105609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benazzouz, A.; Ammar, M.; Settou, B.; Marif, Y.; Djemoui, K. Thermal performance analysis of a domestic-size absorption cooling system incorporating nanofluid with thermal insulation in hot climate of Algeria. Int. J. Refrig. 2025, 170, 192–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldoo, T.; Lee, M.; Cho, H. Numerical investigation on thermal performance of absorption refrigeration system using MWCNT nanoparticle-enhanced 1-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium cation-based ionic liquids. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2022, 206, 118093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, W.; Nabwey, H.; EL-Kabeir, S.; Rashad, A.; AbdElnaem, S.; Seddek, L. Solar Energy Encouragement in Solar HVAC Using Eyring-Powell Ternary-Hybrid Nanofluid Flow in Porous Medium with Cattaneo-Christov Heat and Mass Fluxes. Spec. Top. Rev. Porous Media Int. J. 2023, 14, 71–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colangelo, G.; Raho, B.; Milanese, M.; de Risi, A. Numerical Evaluation of a HVAC System Based on a High-Performance Heat Transfer Fluid. Energies 2021, 14, 3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabakaran, R.; Gomathi, B.; Saravanan, A.L.; Jeyalakshmi, P.; Lal, D.M.; Kim, S.C. Machine learning-based performance and optimal refrigerant charge prediction for a split air conditioning system. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2025, 274, 126764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei, S.; Razmi, A.; Soltani, M.; Nathwani, J. Quantifying the effect of nanoparticles addition to a hybrid absorption/recompression refrigeration cycle. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 260, 121084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar Prasad, U.; Mishra, R.; Das, R. Experimental studies of vapour compression refrigeration system with eco-Friendly primary refrigerant and brine mixed with nano particles as secondary refrigerant. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 45, 3857–3859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández Jaramillo, D.; Nieto Londoño, C.; Zapata-Benabithe, Z. Analysis of working nanofluids for a refrigeration system. DYNA 2016, 83, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqaed, S.; Mustafa, J.; Sharifpur, M.; Alharthi, M.A. Numerical simulation and artificial neural network modeling of exergy and energy of parabolic trough solar collectors equipped with innovative turbulators containing hybrid nanofluids. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2023, 148, 8611–8626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aprea, C.; Greco, A.; Maiorino, A.; Masselli, C. The use of barocaloric effect for energy saving in a domestic refrigerator with ethylene-glycol based nanofluids: A numerical analysis and a comparison with a vapor compression cooler. Energy 2020, 190, 116404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talpada, J.S.; Ramana, P.V. The Theoretical Analysis of H2O-LiBr Absorption Refrigeration System using Al2O3 Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mech. Prod. Eng. Res. Dev. 2019, 9, 303–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndoye, F.; Schalbart, P.; Leducq, D.; Alvarez, G. Numerical study of energy performance of nanofluids used in secondary loops of refrigeration systems. Int. J. Refrig. 2015, 52, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, J.; Singh, J.; Ohunakin, O.S.; Adelekan, D.S. Artificial neural network approach for irreversibility performance analysis of domestic refrigerator by utilizing LPG with TiO2–lubricant as replacement of R134a. Int. J. Refrig. 2018, 89, 159–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Lu, J. A Theoretical Comparative Study of Vapor-Compression Refrigeration Cycle using Al2O3 Nanoparticle with Low-GWP Refrigerants. Entropy 2022, 24, 1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, M.; Rajput, S. Energy and exergy analysis of vapour compression test rig using R134a blended with GN- MWCNT/POE hybrid nano-lubricants. Energy Sources Part A Recover. Util. Environ. Eff. 2023, 46, 188–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Rajput, S. Performance of a computerized refrigeration cycle test rig for varying concentrations of (CuO-Al2O3 /MO) hybrid nano-lubricants and R600a refrigerant charges: An energetic and exergetic approach. Energy Sources Part A Recover. Util. Environ. Eff. 2023, 45, 9975–9992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, M.; Cimsit, C.; Keven, A.; Karaali, R. Analysis of cascade vapor compression refrigeration system using nanorefrigerants: Energy, exergy, and environmental (3E). Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2024, 57, 104373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürbüz, E.; Keçebaş, A.; Sözen, A. Exergy and thermoeconomic analyses of the diffusion absorption refrigeration system with various nanoparticles and their different ratios as work fluid. Energy 2022, 248, 123579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgharian, H.; Baniasadi, E.; Colpan, C. Energy, exergy and exergoeconomic analyses of a solar refrigeration cycle using nanofluid. Int. J. Exergy 2019, 30, 63–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, J. Performance improvement of double-tube gas cooler in CO2 refrigeration system using nanofluids. Therm. Sci. 2015, 19, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürbüz, E.; Sözen, A.; Keçebaş, A.; Özbaş, E. Experimental and numerical investigation of diffusion absorption refrigeration system working with ZnOAl2O3 and TiO2 nanoparticles added ammonia/water nanofluid. Exp. Heat Transf. 2020, 35, 197–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özbaş, E. Energy and Exergy Analysis of Using FeOTiO2 Nanofluid in Diffusion Absorption Refrigeration Systems. Heat Transf. Res. 2021, 52, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selimefendigil, F.; Oztop, H. Exergetic performance of vapor-compression refrigeration system with TiO2-nanoadditive in the compressor oil. Therm. Sci. 2021, 25, 637–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragelli, R.; Sanchez, L.; Ingraci Neto, R.; Scalon, V. Refrigeration capacity of silver nanofluids under electrohydrodynamic effect oriented to heat removal in machining process. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2018, 96, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahar, M.; Otanicar, T. Experimental and theoretical description of a technique for the concentration measurement of binary liquids containing nanoparticles. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2015, 85, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhayere, E.; Adebayo, V.; Adedeji, M.; Abid, M.; Kavaz, D.; Dagbasi, M. Investigating the effects of nanorefrigerants in a cascaded vapor compression refrigeration cycle. Int. J. Energy Environ. Eng. 2022, 14, 601–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khetib, Y.; Sait, H.; Habeebullah, B.; Hussain, A. Improving the performance of a lithium-ion battery connected to a solar system using a nano-refrigerant in an ejector refrigeration cycle. J. Energy Storage 2022, 45, 103601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, Q.; Zeng, M.; Xu, R.; Xie, G.; Chu, W. Investigation on mass transfer characteristics of the falling film absorption of LiBr aqueous solution added with nanoparticles. Int. J. Refrig. 2018, 89, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Renault, F.; Gómez, A.; Sarafraz, M.; Khan, H.; Safaei, M.; Filho, E. Nanofluids as secondary fluid in the refrigeration system: Experimental data, regression, ANFIS, and NN modeling. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 144, 118635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsah, S. Relative cooling power modeling of RE2TM2Y ternary intermetallic rare-earth-based magnetocaloric compounds for magnetic refrigeration application using extreme learning machine and hybrid intelligent method. Int. J. Refrig. 2024, 168, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, J.; Singh, J.; Ohunakin, O.; Adelekan, D.; Atiba, O.; Nkiko, M.; Atayero, A. Adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) approach for the irreversibility analysis of a domestic refrigerator system using LPG/TiO2 nanolubricant. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 1405–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, H.; Kumari, S.; Dutt, A.; Kumar, P.; Makhatha, M. A Machine Learning Approach to Predict the Performance of Refrigerator and Air Conditioning Using Gaussian Process Regression and Support Vector Methods. Recent Pat. Mech. Eng. 2021, 14, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyaghchi, F.; Mahmoodnezhad, M.; Sabeti, V. Exergoeconomic analysis and optimization of a solar driven dual-evaporator vapor compression-absorption cascade refrigeration system using water/CuO nanofluid. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 139, 970–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadi, V.; Özmen, Ö.; Caliskan, A.; Karamış, M. Experimental study and computational intelligence on dynamic viscosity and thermal conductivity of HNTs based nanolubricant. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 2022, 74, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiannejad Amiri, M.; Ghorbanzade Zaferani, S.; Sarmasti Emami, M.; Zahmatkesh, S.; Pourhanasa, R.; Sadeghi Namaghi, S.; Klemeš, J.; Bokhari, A.; Hajiaghaei-Keshteli, M. Multi-objective optimization of thermophysical properties GO powders-DW/EG Nf by RSM, NSGA-II, ANN, MLP and ML. Energy 2023, 280, 128176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marulasiddeshi, H.; Kanti, P.; Jamei, M.; Prakash, S.; Sridhara, S.; Said, Z. Experimental study on the thermal properties of Al2O3-CuO/water hybrid nanofluids: Development of an artificial intelligence model. Int. J. Energy Res. 2022, 46, 21066–21083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, R.; Abad, J.; Fattahi, A.; Mohebbi, M.; Doranehgard, M.; Li, L.; Alhajri, E.; Karimi, N. A Machine Learning Approach to Predicting the Heat Convection and Thermodynamics of an External Flow of Hybrid Nanofluid. J. Energy Resour. Technol. 2021, 143, 070908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Ramesh, K.; Parameshwaran, R.; Deshmukh, S. Thermal conductivity prediction of titania-water nanofluid: A case study using different machine learning algorithms. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2022, 30, 101658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Mei, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, C. Prediction of Thermal Conductivity of EG–Al2O3 Nanofluids Using Six Supervised Machine Learning Models. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 6264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bemani, A.; Madani, M.; Kazemi, A. Machine learning-based estimation of nano-lubricants viscosity in different operating conditions. Fuel 2023, 352, 129102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Alsalmah, H.A. Artificial intelligence based evaluation of the tri-hybridized (WS2+Fe3O4+CuS) flow subjected to the thermal performance in porous systems. Results Eng. 2025, 26, 104717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrao, B.; Kim, K.; Duarte, J. Analysis of the Effects of Different Nanofluids on Critical Heat Flux Using Artificial Intelligence. Energies 2023, 16, 4762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, J. Enhancement of Heat Transfer Using Water/Graphene Nanofluid and the Impact of Passive Techniques—Experimental, Numerical, and ML Approaches. Energies 2024, 18, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajila, F.; Manokaran, S.; Ramaswamy, K.; Thiyagarajan, D.; Pappula, P.; Ali, S.; Dillibabu, S.; Kasi, U.; Selvaraju, M. Prediction of nanofluid thermal conductivity and viscosity with machine learning and molecular dynamics. Therm. Sci. 2024, 28, 717–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Khan, M.; Waqas, H.; Al-Mdallal, Q. Optimizing solar collector efficiency and safety: A comparative thermal analysis of non-toxic hybrid nanofluid mixtures using machine learning. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2025, 72, 106221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Vargas, B.; González Rodríguez, L.; Pacheco-Álvarez, M.; Peralta-Hernández, J.; Picos, A. Use of artificial intelligence models for the reduction of nanoparticle size in the synthesis of ZnO. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2023, 98, 1868–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Said, Z.; Memon, S.; Elavarasan, R.; Khalid, M.; Nguyen, X.; Arıcı, M.; Hoang, A.; Nguyen, L. Comparative evaluation of AI-based intelligent GEP and ANFIS models in prediction of thermophysical properties of Fe3O4-coated MWCNT hybrid nanofluids for potential application in energy systems. Int. J. Energy Res. 2022, 46, 19242–19257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Al-Bahrani, M.; Ruhani, B.; Heybatian Ghalehsalimi, H.; Zandy Ilghani, N.; Maleki, H.; Ahmad, N.; Nasajpour-Esfahani, N.; Toghraie, D. Optimized ANFIS models based on grid partitioning, subtractive clustering, and fuzzy C-means to precise prediction of thermophysical properties of hybrid nanofluids. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 471, 144362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattad, A.; Sarkar, J.; Ghosh, P. Improving the performance of refrigeration systems by using nanofluids: A comprehensive review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 3656–3669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilen, K.; Dağidir, K.; Arcaklioğlu, E. The effect of nanorefrigerants on performance of the vapor compression refrigeration system: A comprehensive review. Energy Sources Part A Recover. Util. Environ. Eff. 2022, 44, 3178–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Narendran, G.; Perumal, D. Effects of Nanorefrigerants for Refrigeration System: A review. Nanosci. Technol. Int. J. 2023, 14, 17–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisal, H.; Deulgaonkar, V.; Tamkhade, P.; Desale, A.; Patil, R.; Raut, S. Vapour Absorption Refrigeration System and Nanofluids: Recent Research, Development and Applications. Int. J. Veh. Struct. Syst. 2024, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Song, J.; Jia, T.; Yang, L.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Du, K. A comprehensive review on the pre-research of nanofluids in absorption refrigeration systems. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 3437–3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talpada, J.; Ramana, P. A review on performance of absorption refrigeration system using new working pairs and nano-particles. Int. J. Ambient Energy 2021, 43, 5654–5672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcucci Pico, D.; Parise, J.; Bandarra Filho, E. Nanolubricants in refrigeration systems: A state-of-the-art review and latest developments. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2023, 45, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmi, W.; Sharif, M.; Yusof, T.; Mamat, R.; Redhwan, A. Potential of nanorefrigerant and nanolubricant on energy saving in refrigeration system—A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 69, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, M.; Kim, S.; Seo, J.; Lee, M. Review of the Thermo-Physical Properties and Performance Characteristics of a Refrigeration System Using Refrigerant-Based Nanofluids. Energies 2015, 9, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponticorvo, E.; Iuliano, M.; Cirillo, C.; Maiorino, A.; Aprea, C.; Sarno, M. Fouling Behavior and Dispersion Stability of Nanoparticle-Based Refrigeration Fluid. Energies 2022, 15, 3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praveen Bharathwaj, R.; Shaik, J.; Raju, J.J.; Padmanathan, P.; Satheesh, A. A critical review on nanorefrigerants: Boiling, condensation and tribological properties. Int. J. Refrig. 2021, 128, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, K.; Calautit, J.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Liu, H. A review of the applications of phase change materials in cooling, heating and power generation in different temperature ranges. Appl. Energy 2018, 220, 242–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundan, L.; Singh, K. Improved performance of a nanorefrigerant-based vapor compression refrigeration system: A new alternative. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part A J. Power Energy 2020, 235, 106–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiyandi, S.; Thampi, G. Review on performance analysis in diffusion absorption refrigeration system (DARS) using different working fluids. Int. J. Ambient Energy 2023, 44, 2185–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
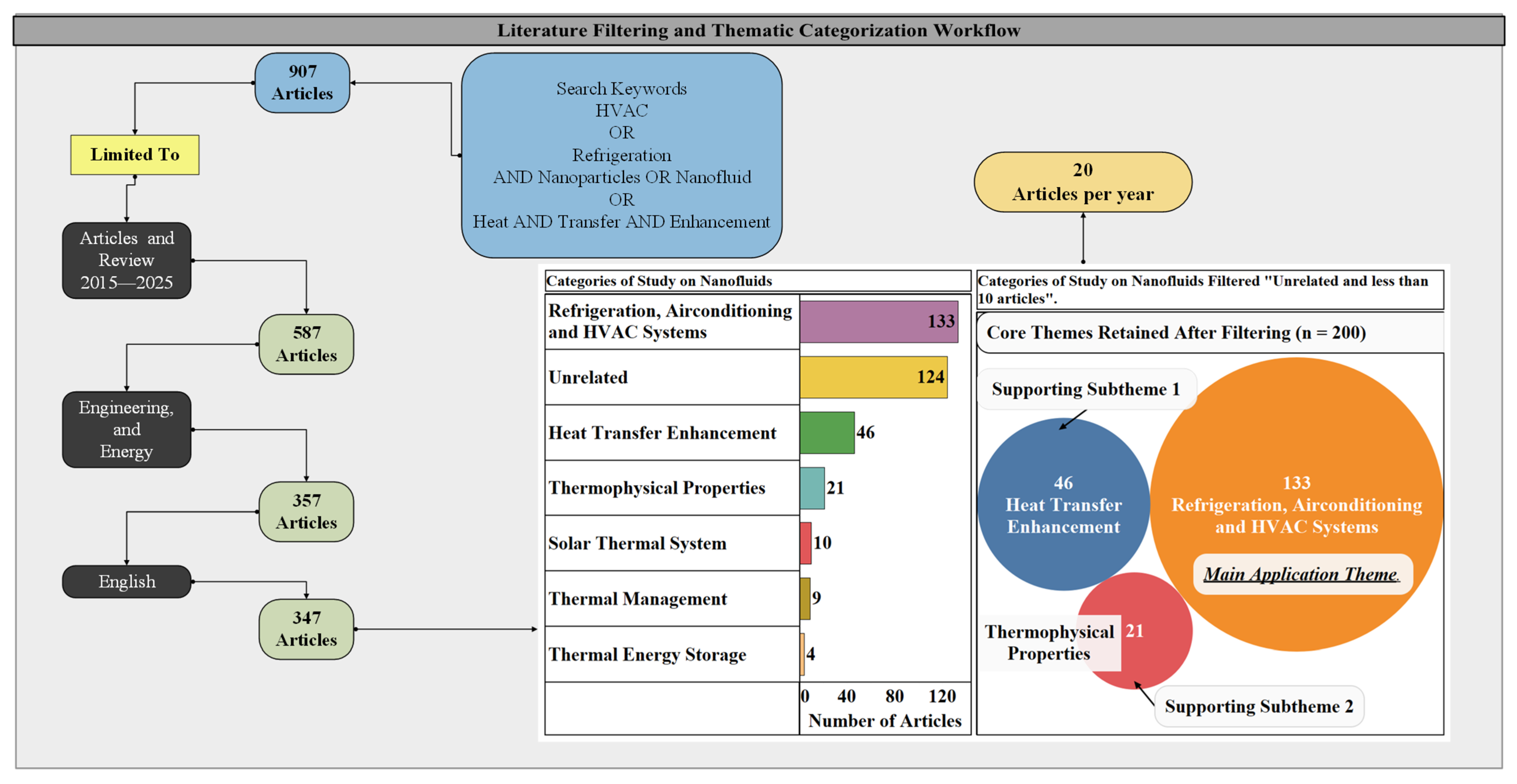
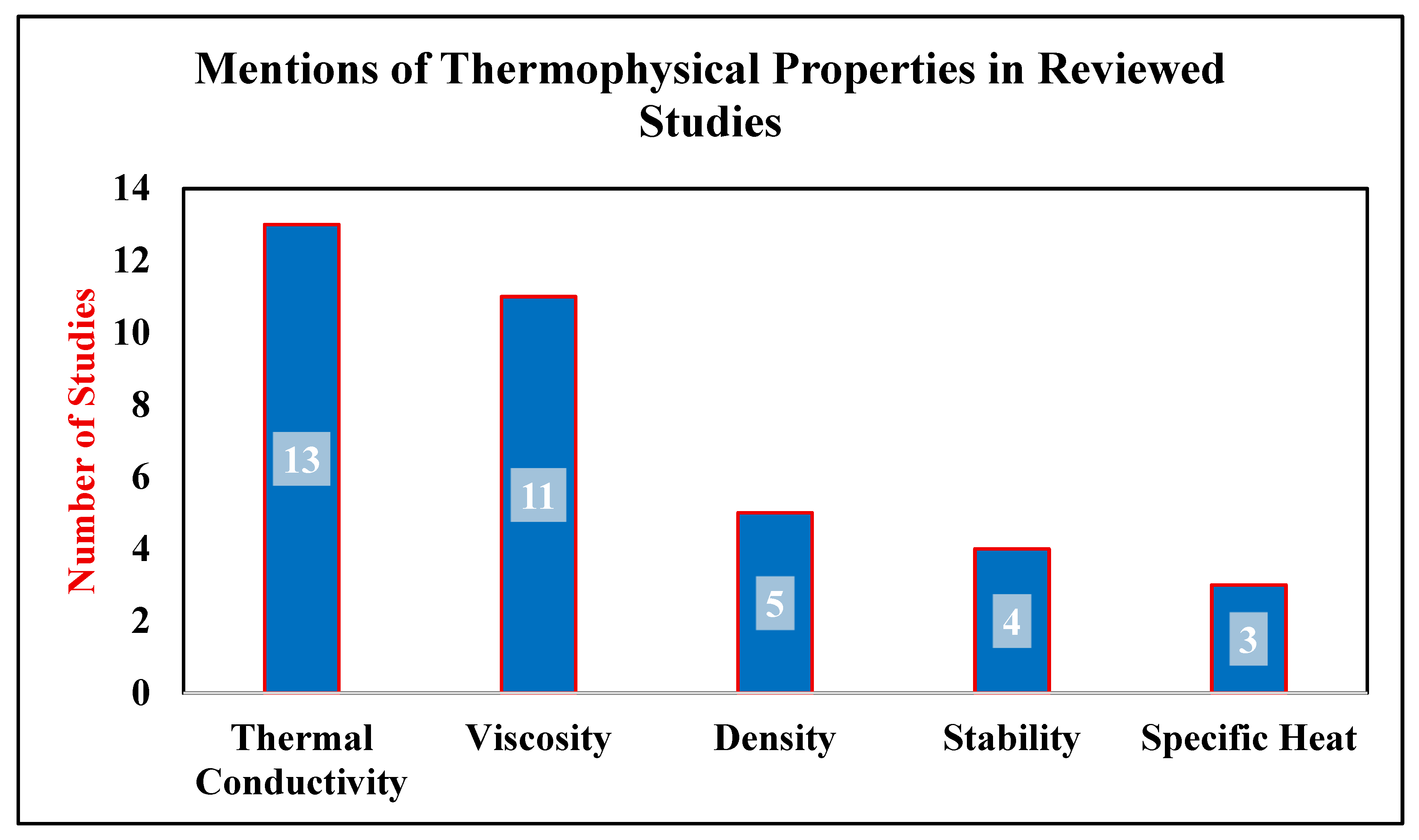
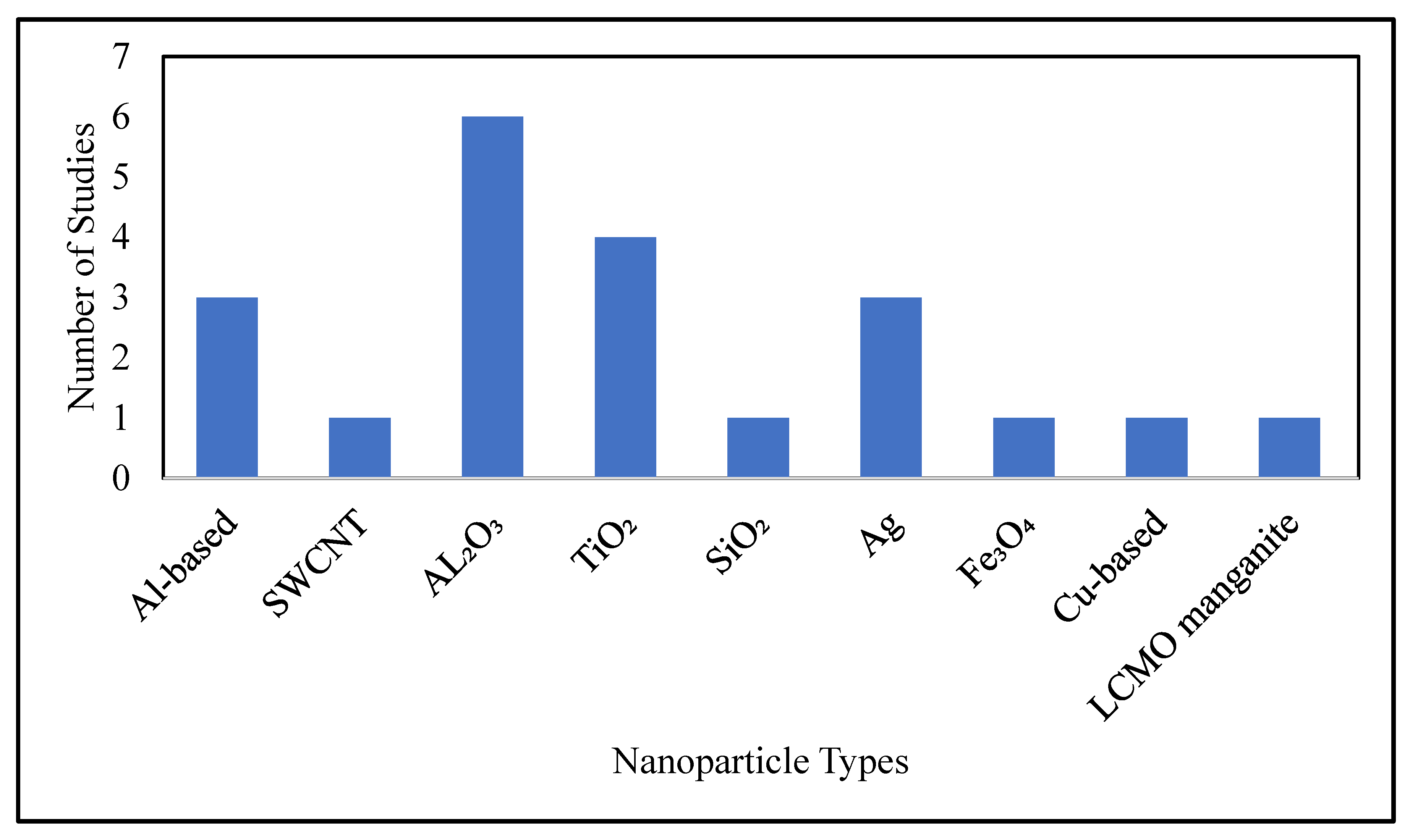
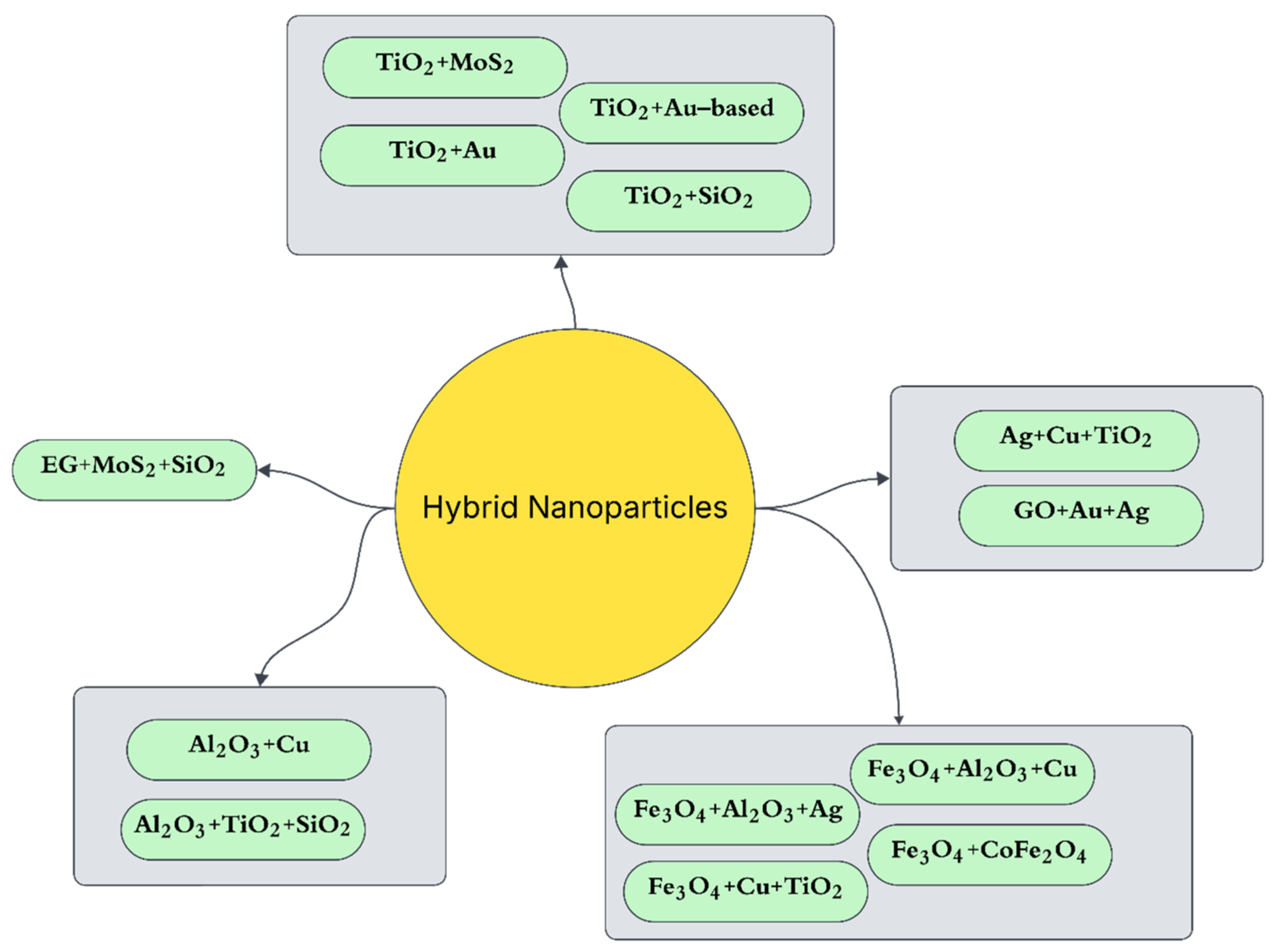
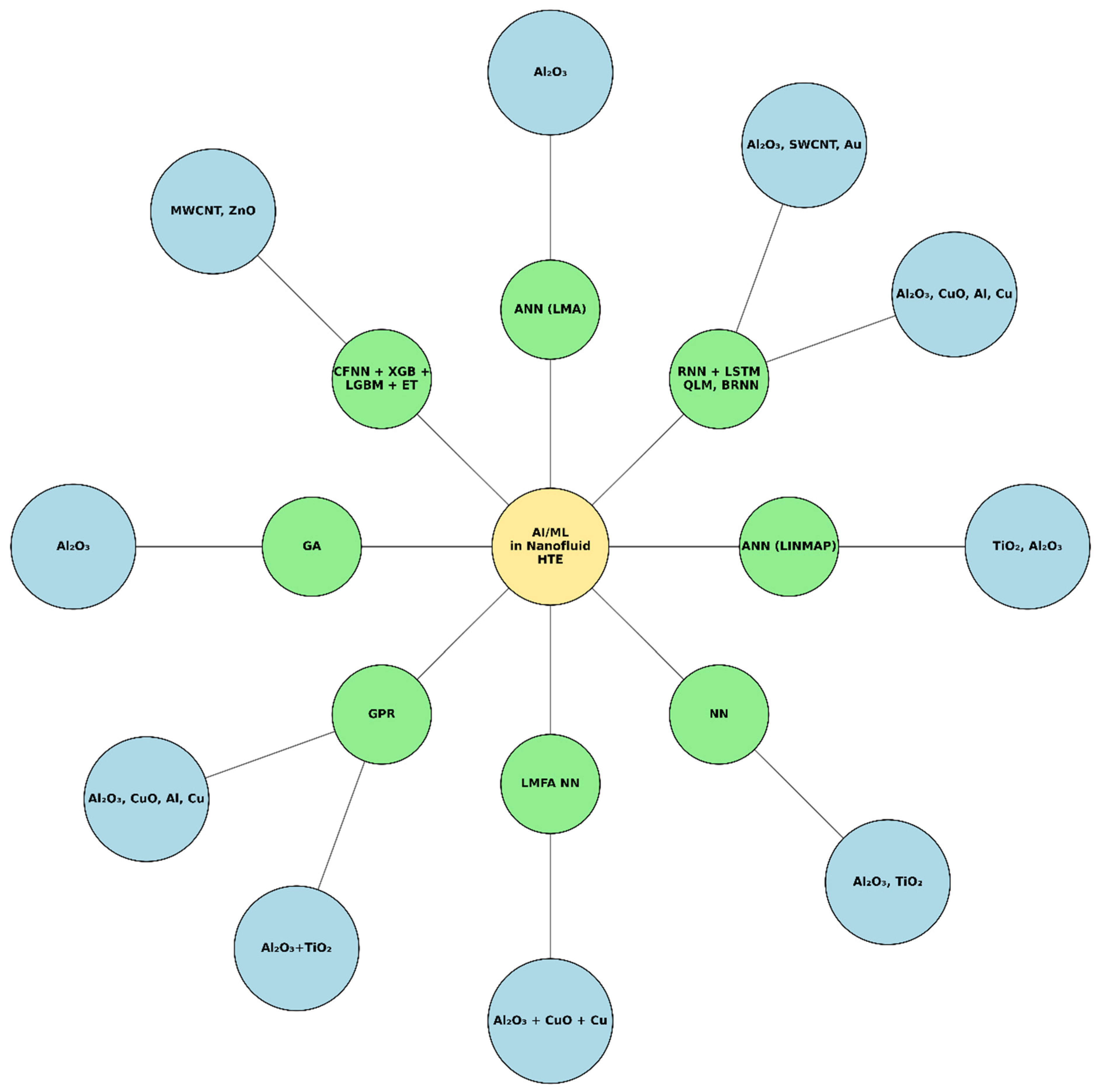
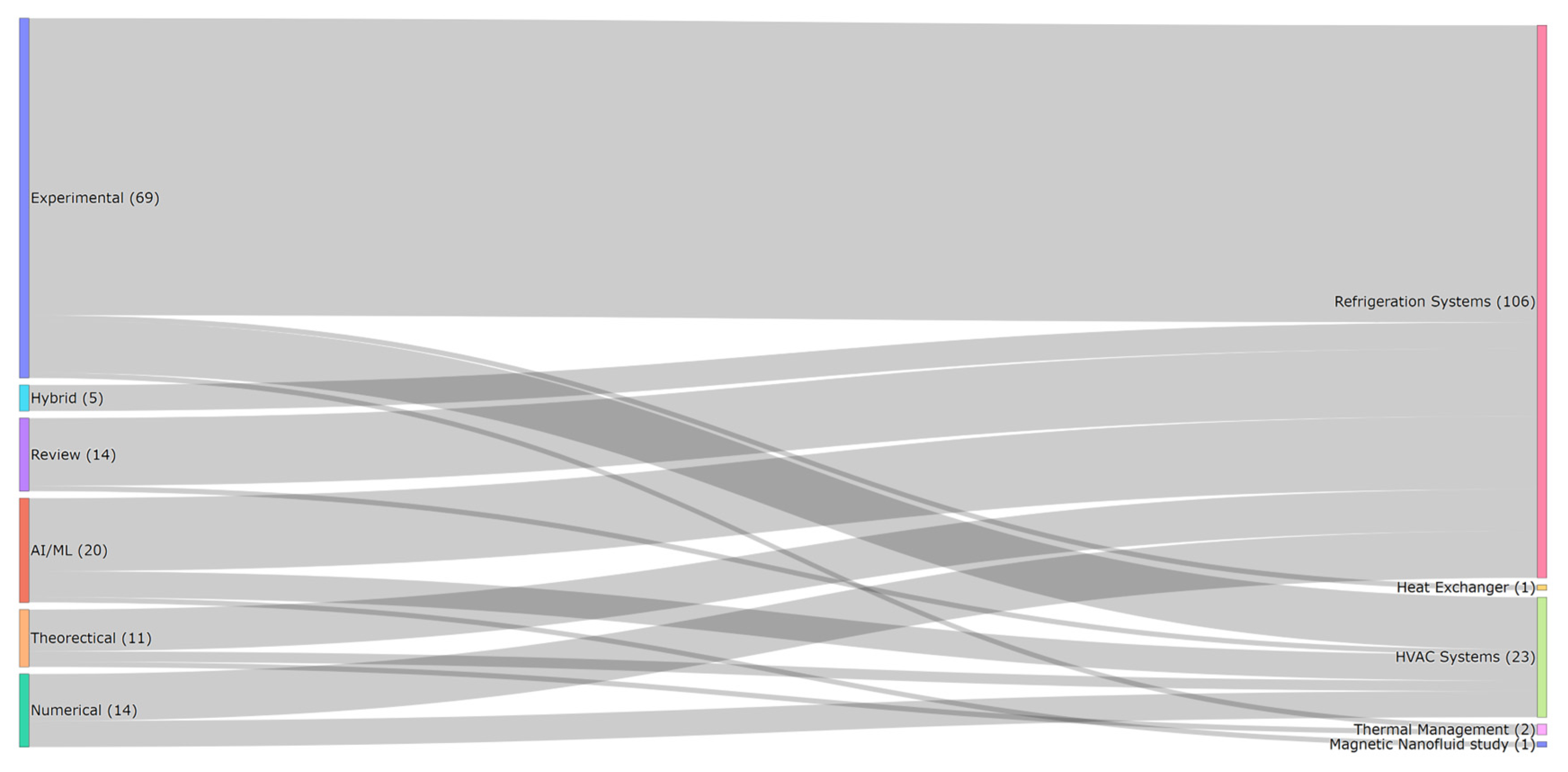
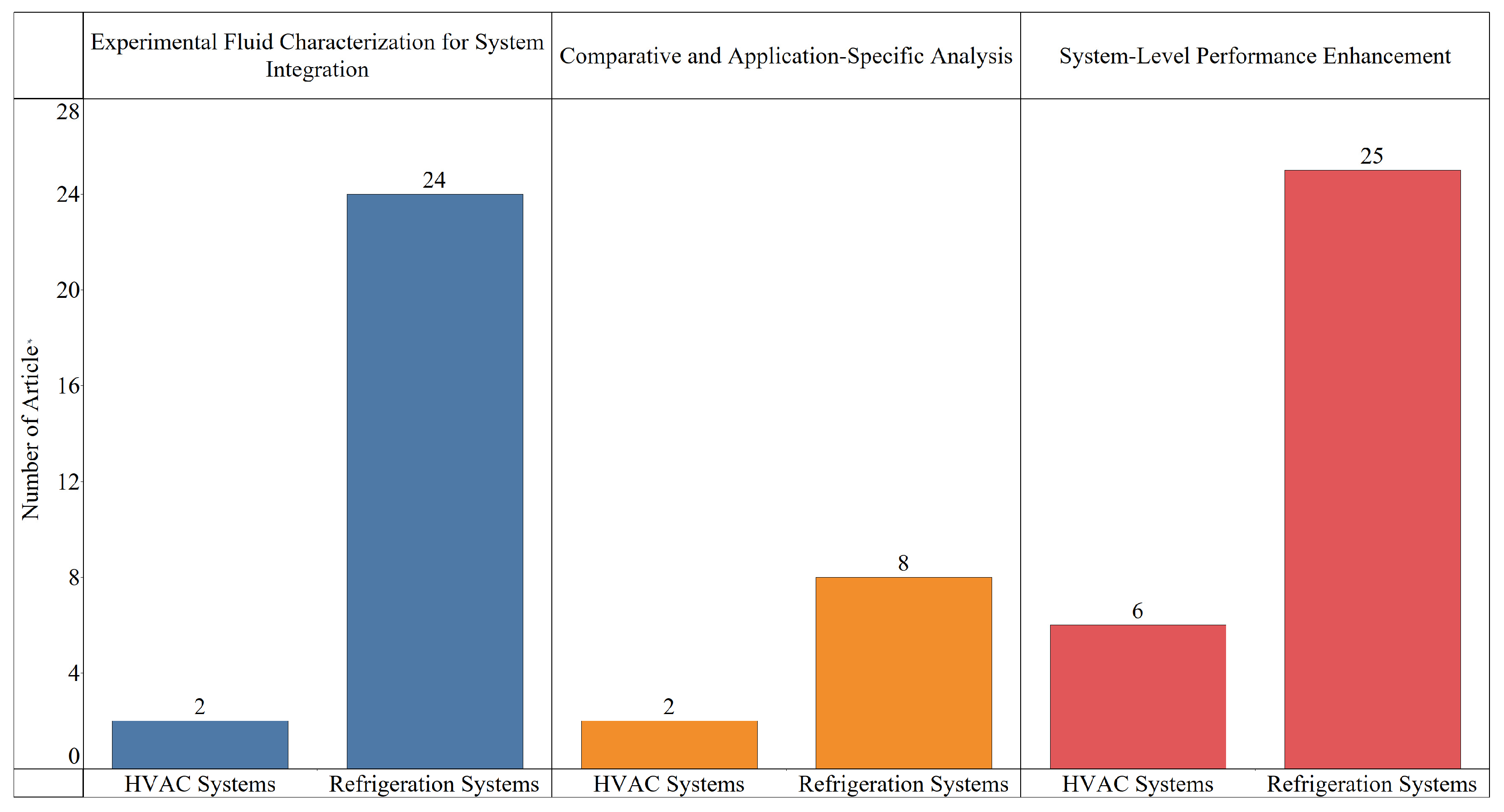
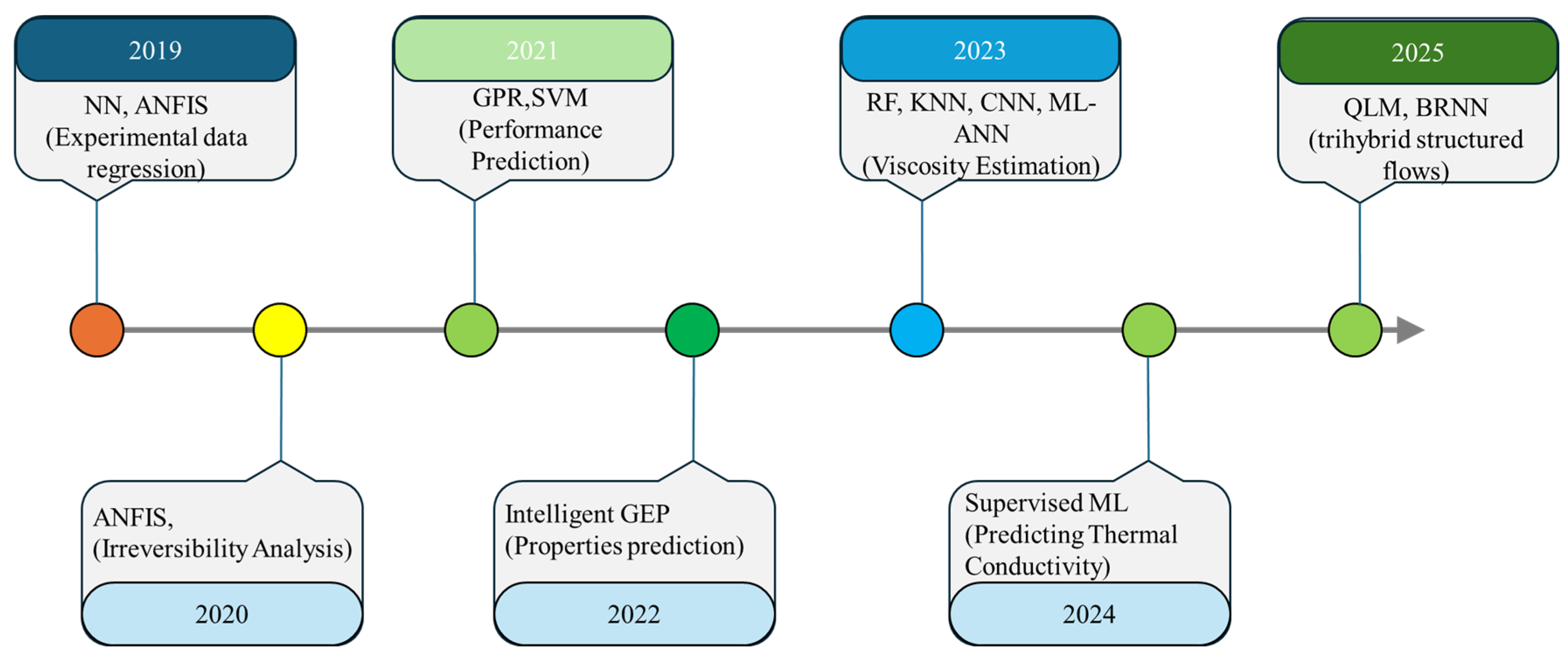
| Feature/Focus Area | Riyadi et al. (2024) [8] | Basu et al. (2023) [9] | Smrity & Yin (2025) [11] | This Study (Present Review) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Application Domain | Porous heat exchangers, solar systems | General heat transfer/nanofluid systems | General modeling–experiment synergy | HVAC&R-specific (evaporators, condensers, COP) |
| AI/ML Integration | Partial (heat exchanger optimization) | Yes (thermophysical property prediction) | Yes (surrogate modeling, data fitting) | Yes (component and system-level modeling + taxonomy) |
| Methodological Classification | No | No | No | Yes (experimental, numerical, hybrid, AI/ML) |
| System-Level Analysis | No | No | No | Yes (COP, pressure drop, energy efficiency) |
| Lifecycle and Technoeconomic Considerations | Brief mention | Not addressed | Not addressed | Discussed (stability, cost, viscosity trade-offs) |
| Focus on Smart HVAC Integration (e.g., digital twins) | No | No | No | Yes (emerging AI-enabled HVAC technologies) |
| Research Gaps and Future Roadmap | General | General | General | Detailed and domain-specific |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Myat, A.; Rahman, M.M.; Akbar, M. Nanofluid-Enhanced HVAC&R Systems (2015–2025): Experimental, Numerical, and AI-Driven Insights with a Strategic Roadmap. Sustainability 2025, 17, 7371. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167371
Myat A, Rahman MM, Akbar M. Nanofluid-Enhanced HVAC&R Systems (2015–2025): Experimental, Numerical, and AI-Driven Insights with a Strategic Roadmap. Sustainability. 2025; 17(16):7371. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167371
Chicago/Turabian StyleMyat, Aung, Md Mashiur Rahman, and Muhammad Akbar. 2025. "Nanofluid-Enhanced HVAC&R Systems (2015–2025): Experimental, Numerical, and AI-Driven Insights with a Strategic Roadmap" Sustainability 17, no. 16: 7371. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167371
APA StyleMyat, A., Rahman, M. M., & Akbar, M. (2025). Nanofluid-Enhanced HVAC&R Systems (2015–2025): Experimental, Numerical, and AI-Driven Insights with a Strategic Roadmap. Sustainability, 17(16), 7371. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167371








