Balancing Safety and Growth: An Ecological Resilience Framework for Great Wall Tourism Towns
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Cultural Heritage and the Great Wall
2.2. Ecological Resilience and Related Assessment Approaches
2.3. Ecological Risks Faced by the Great Wall Heritage Site
3. The Tourism Industry of the Great Wall Cultural Belt in Beijing
3.1. The Great Wall Cultural Belt (GWCB) in Beijing
3.2. Tourism Industry of the GWCB in Beijing

4. Research Framework
4.1. Assessment of Ecological Resilience
4.2. Assessment of Tourism Industry Development
4.3. Coupling and Coordination Degree Model
4.4. The Suitability of the Research Framework
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Ecological Risk
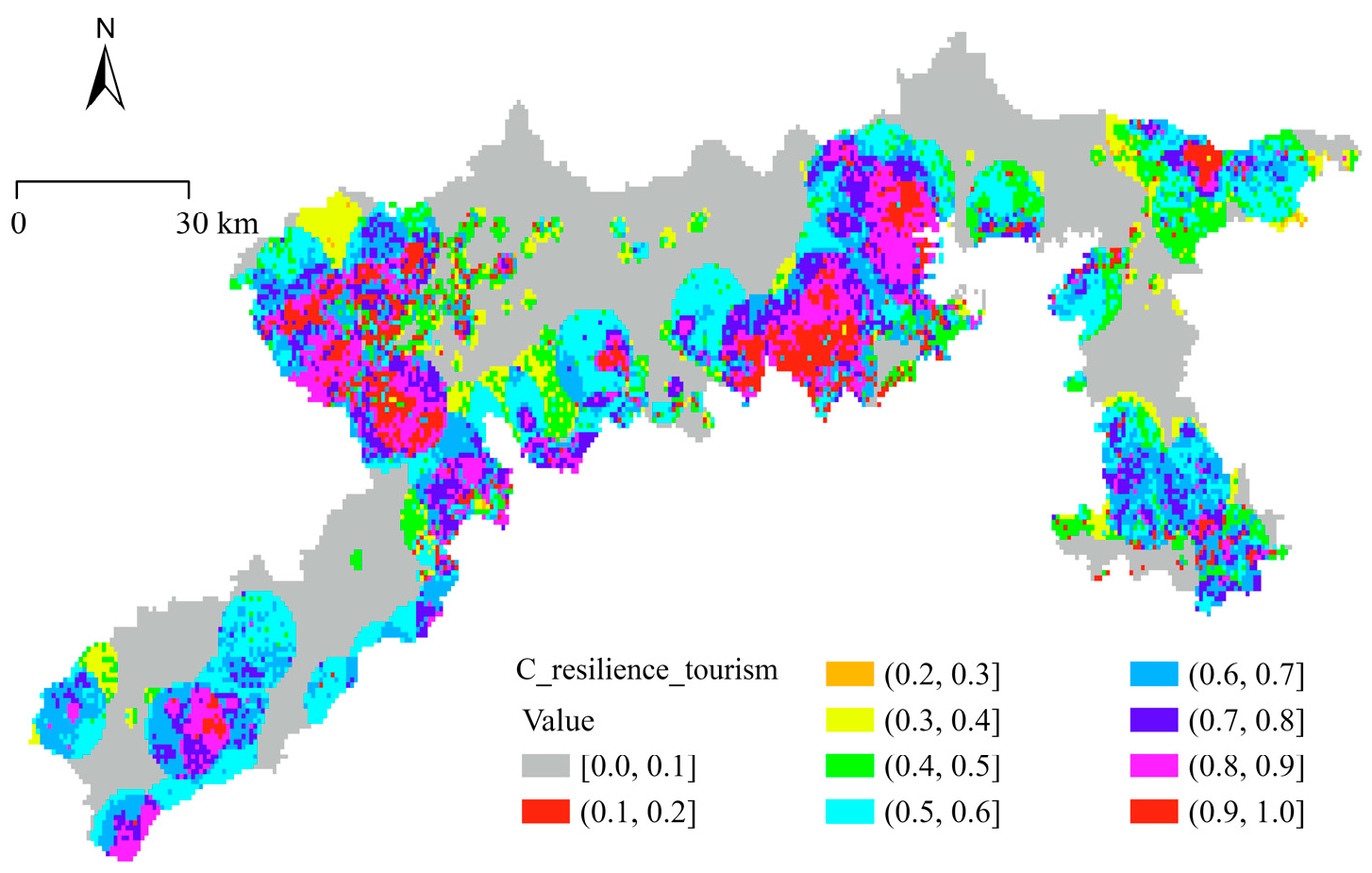
5.2. Ecological Resilience
5.3. Tourism Industry Level
5.4. Coupling Coordination Degree
5.4.1. Coupling Degree
5.4.2. Coordination Degree
6. Conclusions and Suggestions
6.1. Conclusions
6.2. Suggestions
6.2.1. Strategies for Enhancing Ecological Resilience
6.2.2. Strategies for Tourism Management
6.2.3. Discussion of Strategies for Other Similar Industry Development Areas
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yuan, X.F.; Shao, Y.J.; Li, Y.H.; Liu, Y.S.; Wang, Y.S.; Wei, X.D.; Wang, X.F.; Zhao, Y.H. Cultivated land quality improvement to promote revitalization of sandy rural areas along the Great Wall in northern Shaanxi Province, China. J. Rural. Stud. 2022, 93, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.X.; Gao, A.Y. Cultural connotation and epochal value of the Qi Great Wall from the perspective of national culture park. J. Univ. Jinan Soc. Sci. Ed. 2021, 31, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, R.E.; Bucknam, R.C.; Hanks, T.C. Ancient engineering geology projects in China; A canal system in Ganzu province and trenches along the Great Wall in Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region. Eng. Geol. 1994, 36, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.C.; Zhang, Y.C. The fractal structure of the Ming Great Wall Military Defense System: A revised horizon over the relationship between the Great Wall and the military defense settlements. J. Cult. Herit. 2018, 33, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, M.Y.; Luo, J.M. The enlightenment from the lnteractive mechanism between world heritage conservation and Community Development in Britain: A case of the Hadrian’s Wall. Ecol. Econ. 2007, 12, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.M.; Wall, G. Community participation in tourism at a world heritage site: Mutianyu Great Wall, Beijing, China. Int. J. Tour. Res. 2014, 16, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.M.; Wall, G. Global–local relationships and governance issues at the Great Wall World heritage site, China. J. Sustain. Tour. 2012, 20, 1067–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, J. Evaluation of rural tourism development effect and selection of development path along the linear cultural heritage protection area—Take the Beijing Great Wall cultural belt as an example. Urban Dev. Res. 2018, 29, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Zhang, Y.R.; Zhu, X.K.; Xie, W.X.; Wan, Y. Study on spatial distribution and layout of villages in rural areas adjacent to cultural belt of the Great Wall in Beijing. Beijing Surv. Mapp. 2022, 36, 571–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.L. Research on the integration path of the Great Wall national cultural park construction and rural revitalization. Sci. Technol. Inf. 2022, 20, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.Y. Challenges and responses—Protection of the Great Wall under the impact of climate change. Nat. Cult. Herit. Res. 2022, 7, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Ma, Y.; Chen, M.Q.; Wang, S.S. Research on the construction of Gubeikou Great Wall heritage corridor based on ecological suitability evaluation. Beijing Plan. Constr. 2022, 202, 125–139. [Google Scholar]
- Mavhura, E.; Manyangadze, T.; Aryal, K.R. A composite inherent resilience index for zimbabwe: An adaptation of the disaster resilience of place model. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2021, 57, 102152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.M.; Ye, C. Alogical framework of rural-urban governance from the perspective of social-ecological resilience. Prog. Geogr. 2021, 40, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.Y.; Dong, Z.Y.Z.; Chen, B. Spatio-tempora analysis and sinulation of uan eologiea resilienee: A case study of Hamgzhou. Aeta Eeologica Sin. 2022, 42, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.F.; Cao, Y.C.; Yu, J.H. On the method for determining protection range of cultural heritage under the complex geographical environment—Taking the Great Wall as an example. J. Hebei Univ. Geosci. 2017, 40, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.L. Rainstorm Disaster Risk Assessment and Spatial and Temporal Variation Characteristics of the Great Wall Relics in Beijing. Master’s Thesis, Beijing University of Civil Engineering and Architecture, Beijing, China, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.P. Characteristics Identification and Classification of Small Watershed in Beijing Great Wall Cultural Belt Based on Ecology. Master’s Thesis, Beijing University of Civil Engineering and Architecture, Beijing, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, S.S.; Kim, K.J. Toward a framework integrating authenticity and integrity in heritage tourism. J. Sustain. Tour. 2015, 23, 1468–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrage, J.A.; Chamra, C. Geo-landscape and geo-heritage assessment to promote geo-tourism and geo-conservation of Ehden region in north Lebanon. Int. J. Geoheritage Parks 2022, 10, 635–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.H.; Tung, S.W.V. A supply-side angle to understand heritage tourism sites: A value-based assessment approach. J. China Tour. Res. 2024, 20, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nokandeh, J.; Sauer, E.W.; Rekavandi, H.O.; Wilkinson, T.; Abbasi, G.A.; Schweninger, J.L.; Mahmoudi, M.; Parker, D.; Fattahi, M.; Usher-Wilson, L.S.; et al. Linear barriers of northern Iran: The great wall of Gorgan and the wall of Tammishe. Iran 2006, 44, 121–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Liu, F.; Qiao, W. Evaluating industrial heritage value using cloud theory and Dempster–Shafer theory. J. Cult. Herit. 2024, 68, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Pan, Y.; Han, Y. Constructing cultural space and telling cultural stories: A case study of regional cultural heritage preservation in Shichahai, Beijing. Aslib J. Inf. Manag. 2024, 76, 585–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Brown, S. Comparing landscape values and heritage stakeholders: A case study of West Lake cultural landscape of Hangzhou, China. Int. J. Cult. Policy 2023, 29, 184–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.Y.; Liu, Z.Y.; Zhang, M. An initial exploration of the construction of the “Beijing Great Wall Cultural Belt” under the framework of regional collaborative development. J. Beijing Univ. Civ. Eng. Archit. 2016, 32, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Wang, Z.Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Yang, X.; Sun, Z. Research on the spatial distribution characteristics of the Ming Great Wall Heritage in Beijing and its influencing factors. Arid Zone Resour. Environ. 2022, 36, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Shi, Y.N. Research on the cultural value interpretation and dissemination of the Great Wall national cultural park. Hebei Acad. J. 2023, 43, 210–214. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, C.L.; Lei, X.; Yuan, X.B. Research on the cultural heritage display system of the Great Wall national cultural park (Hebei Section). J. Hebei Geol. Univ. 2022, 45, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Wu, D.F.; Wu, J.W. An interpretation framework for large linear cultural heritage under the background of national cultural parks—A case study of the Great Wall. Landsc. Archit. 2023, 30, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Chen, S.Q. Construction of spatial patterns of linear cultural heritage: A case study of the Datong Section of the Ming Great Wall. Landsc. Archit. 2019, 26, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Liu, Y.J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S.S.; He, D. Research on the planning of landscape protection and utilization of cultural heritage sites based on LCA: A case study of the Gubeikou Town in the Beijing Great Wall Cultural Belt. Urban Dev. Stud. 2022, 29, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Lu, L.N.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J. Identification of landscape characteristics of large-scale linear heritage areas: A case study of the Beijing Great Wall Cultural Belt. Landsc. Archit. 2022, 29, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, W.W.; Guo, Z.Q. Study on the spatial regularity of rammed pits of the Ming Great Wall using 3D scanning technique and random forest algorithm. J. Cult. Herit. 2023, 62, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Luo, L.L.; Li, Q.; Chen, Y.Y.; Wu, L.; Wang, X.Y. Auto-identification of linear archaeological traces of the Great Wall in northwest China using improved DeepLabv3+ from very high-resolution aerial imagery. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 113, 102995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.L.; Liu, H.W.; Xu, H.; Zhou, W.; Balz, T.; Chen, P.X.; Zhu, X.K.; Lin, H.; Fang, C.Y.; Parcharidis, I. Deformation monitoring and thematic mapping of the Badaling Great Wall using very high-resolution interferometric synthetic aperture radar data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 105, 102630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Tang, Y.Y.; Maurizio, D.V. Acquisition, analysis, and research on the construction information data of the Ming Great Wall for architectural heritage protection: A case study of the Shixia section of the Great Wall in Yanqing, Beijing. Chin. Cult. Herit. 2017, 80, 92–98. [Google Scholar]
- Sang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Sun, K.; Wang, X.; Meng, X.Y. Research on the digital twin technology framework and application for Great Wall cultural heritage. Sci. Technol. Innov. Appl. 2021, 11, 19–23+27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holling, C.S. Resilience and stability of ecological systems. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1973, 4, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, G.; Allen, C.R.; Holling, C.S. Ecological resilience, biodiversity, and scale. Ecosystems 1998, 1, 6–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunderson, L.H. Ecological resilience: In theory and application. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 2000, 31, 425–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, M.; Marzluff, J.M. Ecological resilience in urban ecosystems: Linking urban patterns to human and ecological functions. Urban Ecosyst. 2004, 7, 241–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickett, S.T.A.; McGrath, B.; Cadenasso, M.L.; Felson, A.J. Ecological resilience and resilient cities. Build. Res. Inf. 2014, 42, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, P.J.G.; Gonçalves, L.A.P.J. Urban resilience: A conceptual framework. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 50, 101625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonson, W.D.; Miller, E.; Jones, A.; García-Rangel, S.; Thornton, H.; McOwen, C. Enhancing climate change resilience of ecological restoration—A framework for action. Perspect. Ecol. Conserv. 2021, 19, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Bose, A.; Singha, N.; Basak, D.; Chowdhury, I.R. Urban waterlogging risk as an undervalued environmental challenge: An integrated MCDA-GIS based modeling approach. Environ. Chall. 2021, 4, 100194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etinay, N.; Egbu, C.; Murray, V. Building urban resilience for disaster risk management and disaster risk reduction. Procedia Eng. 2018, 212, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.T.H.; Friess, D.A.; Todd, P.A.; Mazor, T.; Lovelock, C.E.; Lowe, R.; Gilmour, J.; Chou, L.M.; Bhatia, N.; Jaafar, Z.; et al. Maximising resilience to sea-level rise in urban coastal ecosystems through systematic conservation planning. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2022, 221, 104374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, L.A.; Constas, M.; Matthews, N.; Verkaart, S. Advancing resilience measurement. Nat. Sustain. 2021, 4, 288–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabe, T.; Rao, P.S.C.; Ukkusuri, S.V.; Cutter, S.L. Toward data-driven, dynamical complex systems approaches to disaster resilience. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2111997119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venter, Z.S.; Barton, D.N.; Martinez-Izquierdo, L.; Langemeyer, J.; Baró, F.; McPhearson, T. Interactive spatial planning of urban green infrastructure–retrofitting green roofs where ecosystem services are most needed in Oslo. Ecosyst. Serv. 2021, 50, 101314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, D.L.; Falagán, N.; Hardman, C.A.; Kourmpetli, S.; Liu, L.; Mead, B.R.; Davies, J.A.C. Ecosystem service delivery by urban agriculture and green infrastructure—A systematic review. Ecosyst. Serv. 2022, 54, 101405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manolaki, P.; Zotos, S.; Vogiatzakis, I.N. An integrated ecological and cultural framework for landscape sensitivity assessment in Cyprus. Land Use Policy 2020, 92, 104336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, S.K. Prediction-Adaptation-Resilience (PAR) approach-A new pathway towards future resilience and sustainable development of urban landscape. Geogr. Sustain. 2021, 2, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staccione, A.; Candiago, S.; Mysiak, J. Mapping a green infrastructure network: A framework for spatial connectivity applied in northern Italy. Environ. Sci. Policy 2022, 131, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutra, S.; Mondejar, M.B.; Becue, V. The nexus of ‘urban resilience’ and ‘energy efficiency’ in cities. Curr. Res. Environ. Sustain. 2022, 4, 100118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravagnan, C.; Monardo, B.; Amato, C.; Cerasoli, M. Infrastructures for mobility and urban regeneration. Interpretive paradigms and operational tools for resilient metropolitan cities. In Proceedings of the VI International Congress Isuf-H, Madrid, Spain, 29 September–1 October 2022; pp. 471–484. [Google Scholar]
- Marome, W.; Rodkul, P.; Mitra, B.K.; Dasgupta, R.; Kataoka, Y. Towards a more sustainable and resilient future: Applying the Regional Circulating and Ecological Sphere (R-CES) concept to Udon Thani city region, Thailand. Prog. Disaster Sci. 2022, 14, 100225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Tu, J.Y.; Wu, X.M.; Huang, S.; Li, Y. Thoughts on the Construction of the Great Wall National Cultural Park supported by the “Hydroponic System”. China Cult. Herit. 2021, 105, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.F. Exploration of Ming Dynasty military fort in Hebei. J. Tianjin Univ. Soc. Sci. 2010, 12, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.J. Research on the Landscape Ecological Value Assessment and Spatial Pattern Optimization of Cultural Heritage Sites: Taking the Miyun Section of the Beijing Great Wall Cultural Belt as an Example. Master’s Thesis, Beijing University of Civil Engineering and Architecture, Beijing, China, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.P. Reflections on the “Three Cultural Belts” and the construction of Beijing as a cultural center. J. Beijing Union Univ. 2017, 58, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.J.; Yin, B.B.; Li, J. Protection and construction methods of place name heritages in Beijing Great Wall cultural zone. Urban Dev. Stud. 2021, 28, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.L.; Zhou, G.N.; Yu, S.B. Study on rural ecological resilience measurement and optimization strategy based on PSR-“Taking Weiyuan in Gansu Province as an Example”. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.G.; Zhou, Y.J.; Yin, S.G. Interaction mechanisms of urban ecosystem resilience based on pressure-state-response framework: A case study of the Yangtze River Delta. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duo, L.H.; Li, Y.N.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, Y.X.; Wu, Z.H.; Zhao, D.X. Spatiotemporal pattern evolution of urban ecosystem resilience based on “resistance-adaptation-vitality”: A case study of Nanchang city. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 902444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.Y.; Yuan, M.N.; Wang, Q.; Corcoran, J.; Xu, Z.H.; Peng, J. Dealing with urban floods within a resilience framework regarding disaster stages. Habitat Int. 2023, 136, 102783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Cao, E.; Xie, Y.C.; Xu, C.X.; Li, H.Y.; Yan, L.L. Integrating ecosystem services and landscape ecological risk into adaptive management: Insights from a western mountain-basin area, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 281, 111817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, S.B.; Rodier, D.J.; van der Schalie, W.H.; Wood, W.P.; Slimak, M.W.; Gentile, J.H. A framework for ecological risk assessment at the EPA. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1992, 11, 1663–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Dang, W.X.; Liu, Y.X.; Zong, M.L.; Hu, X.X. Research progress and prospects of landscape ecological risk assessment. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2015, 70, 664–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lange, H.J.; Sala, S.; Vighi, M.; Faber, J.H. Ecological vulnerability in risk assessment—A review and perspectives. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 3871–3879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.H.; Kang, Y.Y.; Deng, W.; Wang, G.M.; Wang, H.K.; Xing, Y.H. Transformation of “Three Lives” land use and landscape ecological risk analysis in the eastern Taihang Mountains: A case study of Pingshan county, Hebei province. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. (Biling.) 2022, 30, 1113–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Cui, B.S.; Liu, J.; Yao, R.H.; Zhai, H.J. The effect of land use and its change on ecological risk in the Lancang River watershed of Yunnan Province at the landscape scale. Acta Sci. Circumstaniae 2008, 28, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Xie, Y.C.; Zhao, C.X.; Gao, Y.J. Landscape ecological risk assessment and its spatiotemporal variation of the Bailongjiang watershed, Gansu. China Environ. Sci. 2014, 34, 2153–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Liu, X.H.; Zhang, S.; Jin, Q. Ecological risk assessment of the Shunyi District, Beijing based on an analysis of the integrated ecological loss. J. Tsinghua Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2008, 48, 366–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.X.; Yang, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.S.; Yan, J.W. Trends and attribution analysis of habitat quality changes in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region over the past 40 years. Remote Sens. Technol. Appl. 2023, 38, 251–263. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, J.M.; Feng, Y.F.; Li, C.; Lv, S.; Ma, J.J. Evolution of habitat quality and landscape pattern in the towns along the Yellow River floodplain under the boundary of river regime. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 6798–6809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.Y.; Zhang, X. 2020 Global 30-Meter Fine Land Cover Products. Aerospace Information Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Sciences 2020. Available online: https://zenodo.org/records/4280923 (accessed on 18 November 2024). [CrossRef]
- Robin, E.; Maksym, B.; Andrew, J.T.; Alessandro, S. Unconstrained National Population Weighted Density in 2000, 2005, 2010, 2015 and 2020 (1 km Resolution); WorldPop, University of Southampton: Southampton, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudaqi, M.H.M.T.; Tong, R.; Xu, B.N.; Zhou, R.Y.; Gong, A.F.; Zeng, J.; Ji, M.F.; Qi, Y.C.; Ni, G.H.; Tian, F.Q. Hindcasting on “July 2023” flood event in Beijing. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2024, 43, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frechtling, D.C. The tourism satellite account: A Primer. Ann. Tour. Res. 2010, 37, 136–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins-Kreiner, N.; Wall, G. Evaluating tourism potential: A SWOT analysis of the Western Negev, Israel. Tourism 2007, 55, 51–63. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.H.; Peng, K.H. Fuzzy Rasch model in TOPSIS: A new approach for generating fuzzy numbers to assess the competitiveness of the tourism industries in Asian countries. Tour. Manag. 2012, 33, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diana, D.; Cecilia, P.I.; Călin, V. An assessment of the relationship between the cultural heritage, travel and tourism and sustainable development in the central and eastern European countries. Ann. Univ. Oradea Econ. Sci. Ser. 2012, 21, 1141–1147. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.H.; Chen, W.W. The impact of informatization on the relationship between the tourism industry and regional economic development. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.D.; Liu, J.M.; Zhang, S.Y.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, X. Spatial pattern and micro-location rules of tourism businesses in historic towns: A case study of Pingyao, China. J. Destin. Mark. Manag. 2022, 25, 100721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Yu, W.T.; Cui, J.S.; Liu, J.M.; Chan, C.S. Comparative analysis of the spatial-temporal distribution and influencing factors of the tourism industry in three cities along Beijing-Hangzhou grand canal in China. J. Resour. Ecol. 2024, 15, 1039–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.J.; Kong, W.; Ren, L.; Zhi, D.D.; Dai, B.T. Research on misuses and modification of coupling coordination degree model in China. J. Nat. Resour. 2021, 36, 793–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.W.; Zhang, X.W.; Ma, H.K.; Wu, J.S. Research progress on landscape ecological risk and an evaluation framework based on ecosystem services: ESRISK. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2018, 73, 843–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.L.; Wu, Y.X.; He, X.L.; Fu, Q.; Wang, Z.L.; Jiang, Q.X. Dynamic simulation and coupling coordination evaluation of water footprint sustainability system in Heilongjiang province, China: A combined system dynamics and coupled coordination degree model. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 380, 135044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinney, M.L. Urbanization, biodiversity, and conservation: The impacts of urbanization on native species are poorly studied, but educating a highly urbanized human population about these impacts can greatly improve species conservation in all ecosystems. Bioscience 2002, 52, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Yang, Y.; Tian, D.J.; Nuo, M.Z.Y. Spatial practice and adaptive reconstruction of rural heritage sites from the perspective of resilience: Taking western royal tombs of the Qing Dynasty in Hebei province as an example. China Anc. City 2022, 36, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H. Application analysis of LID concept in urban waterfront landscape design. Ecol. Econ. 2014, 30, 192–195. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, F.; Zhang, X.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, Y. Spatial structure and corridor construction of intangible cultural heritage: A case study of the Ming Great Wall. Land 2022, 11, 1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.H. Ecological restoration technology of the northern wetland park—Take the Liuli river wetland park as an example. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2022, 46, 1535–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.M. Evaluation and Optimization of Urban Ecological Resilience in Changchun Based on Landscape Pattern. Ph.D. Thesis, Northeast Normal University, Changchun, China, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Gan, Y.L.; Zhu, Y.Y. Spatial value characteristics and governance paths for watersheds guided by harmonious coexistence between human and nature: A case study of Hubei province. J. Nat. Resour. 2025, 40, 367–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wall, G. Heritage tourism in a historic town in China: Opportunities and challenges. J. China Tour. Res. 2021, 18, 1073–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, D.; Hall, C.M.; Gössling, S. Global tourism vulnerability to climate change. Ann. Tour. Res. 2019, 77, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, W.B.; Shi, Y.; Yang, F.; Nan, X.G.; Bao, Z.Y. Study on the construction of mountain landscape resilience system based on comprehensive ecological security pattern: A case study of mogan mountain in Zhejiang province. Chin. Landsc. Archit. 2022, 38, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wu, B.M. Evaluation and spatial differentiation of ecological resilience of rural settlements under climate change. Ecol. Econ. 2023, 39, 110–118. [Google Scholar]
- Linnenluecke, M.K.; Griffiths, A.; Winn, M.I. Firm and industry adaptation to climate change: A review of climate adaptation studies in the business and management field. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Clim. Change 2013, 4, 397–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njoroge, J.M. Climate change and tourism adaptation: Literature review. Tour. Hosp. Manag. 2015, 21, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| Indicators | Formula | Instruction | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ecological risk | (1) | LER is the level of ecological risk; fi is an index of ecological vulnerability indicators and ecological loss levels, including 8 factors in this study; wi is the weight of indicator i. | |
| Normalized differential vegetation index | NDVI = (NIR − Red)/(NIR + Red) | (2) | NDVI is the normalized differential vegetation index; NIR is the near-infrared spectral band in remote sensing images; Red is the visible red light band. |
| Landscape fragmentation | Ci = Ni/Ai | (3) | Ci is landscape fragmentation; Ni is the number of patches; Ai is the area of patches. |
| Landscape separation degree | Si = Din | (4) | Si is the landscape separation degree; Din is the distance from patch i to its nearest patch of a similar land use type n. |
| Landscape fractal index | (5) | Fi is the landscape fractal index; Ai is the area of the patch i; Ci is the perimeter of the patch i. | |
| Dimension | Indicators | Weight |
|---|---|---|
| Habitat vulnerability | NDVI (negative indicator) | 0.10 |
| Slope | 0.25 | |
| Altitude (submergence risk, negative indicator) | 0.10 | |
| Density of population | 0.10 | |
| Peak precipitation | 0.20 | |
| Ecological loss index | Landscape fragmentation | 0.10 |
| Landscape separation index | 0.05 | |
| Landscape fractal index | 0.10 |
| Threat Sources | Maximum Impact Distance/km | Weight | Distance Decay Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | 2 | 0.6 | Linear |
| Urbanization | 1 | 0.9 | Exponential |
| Unused land | 0.5 | 0.4 | Linear |
| Land Use | Habitat | Sensitivity | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cropland | Impervious | Unused Land | ||
| Cropland | 0.5 | 0 | 0.8 | 0.5 |
| Forest | 1 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 0.4 |
| Grassland | 1 | 0.9 | 0.5 | 0.3 |
| Shrubland | 1 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.3 |
| Wet land | 1 | 0.4 | 0.8 | 0.1 |
| Water body | 1 | 0.4 | 0.8 | 0.2 |
| Impervious | 0.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Unused land | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0 |
| Data | Source | Year |
|---|---|---|
| Land use | Liu and Zhang, 2020 [78] | 2020 |
| Remote sensing image | www.gscloud.cn/ | 2020 |
| DEM | www.gscloud.cn/ | 2019 |
| Precipitation | Tudaqi et al., 2024 [80] | 2023 |
| POI | Bigmap software (v1.6.23) | 2021 |
| Data of the Great Wall | www.thegreatwall.com.cn, accessed on 10 November 2024 | / |
| Towns | Max_C_ Risk | Mean_C_Risk | Max_D_ Risk | Mean_D_Risk | Max_C_ Resilience | Mean_C_Resilience | Max_D_ Resilience | Mean_D_ Resilience |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qingshui A1 | 0.8140 | 0.3529 | 0.5126 | 0.2489 | 0.9184 | 0.4090 | 0.4604 | 0.2165 |
| Yanchi A3 | 0.8088 | 0.2489 | 0.3882 | 0.1566 | 0.9441 | 0.2720 | 0.3783 | 0.1380 |
| Zhaitang A2 | 0.9395 | 0.3433 | 0.4869 | 0.2025 | 0.9929 | 0.3878 | 0.4250 | 0.1860 |
| Liucun B1 | 0.7819 | 0.1438 | 0.4993 | 0.1082 | 0.9984 | 0.2006 | 0.4499 | 0.0919 |
| Nankou B2 | 0.9452 | 0.5682 | 0.5575 | 0.3728 | 0.9622 | 0.6484 | 0.4933 | 0.2998 |
| Changling B3 | 0.7990 | 0.4901 | 0.5002 | 0.3500 | 0.9944 | 0.6046 | 0.4587 | 0.3009 |
| Badaling C1 | 0.9998 | 0.6920 | 0.7233 | 0.4789 | 0.9999 | 0.8022 | 0.6365 | 0.3981 |
| Dayushu C6 | 0.8196 | 0.3911 | 0.5883 | 0.3506 | 0.9992 | 0.5892 | 0.5080 | 0.2598 |
| Dazhuangke C3 | 0.5738 | 0.2602 | 0.4139 | 0.2093 | 0.9826 | 0.3375 | 0.4337 | 0.1959 |
| Jingzhuang C2 | 0.7771 | 0.2739 | 0.5644 | 0.2307 | 0.9999 | 0.3637 | 0.5340 | 0.1960 |
| Jiuxian C13 | 0.9123 | 0.2993 | 0.6824 | 0.2702 | 1.0000 | 0.3985 | 0.5507 | 0.2043 |
| Kangzhuang C7 | 0.7323 | 0.5534 | 0.5881 | 0.4707 | 0.9873 | 0.7838 | 0.5560 | 0.3430 |
| Liubinpu C11 | 0.4073 | 0.0299 | 0.3751 | 0.0313 | 0.9929 | 0.0453 | 0.3552 | 0.0255 |
| Sihai C4 | 0.4739 | 0.1091 | 0.3801 | 0.0936 | 0.7096 | 0.1467 | 0.3797 | 0.0861 |
| Xiangying C12 | 0.3666 | 0.0240 | 0.3798 | 0.0290 | 0.9624 | 0.0468 | 0.4344 | 0.0249 |
| Yanqing C8 | 0.8176 | 0.4298 | 0.6080 | 0.4044 | 1.0000 | 0.7459 | 0.5488 | 0.2749 |
| Yongning C5 | 0.7792 | 0.0748 | 0.5884 | 0.0759 | 0.9983 | 0.1178 | 0.5144 | 0.0542 |
| Zhangshanying C14 | 0.7868 | 0.4495 | 0.5852 | 0.3787 | 0.9997 | 0.5766 | 0.6302 | 0.3147 |
| Zhenzhuquan C10 | 0.4675 | 0.0256 | 0.3323 | 0.0237 | 0.5564 | 0.0315 | 0.3269 | 0.0202 |
| Shenjiaying C9 | 0.9991 | 0.3012 | 0.5275 | 0.3121 | 0.9995 | 0.5225 | 0.5490 | 0.2219 |
| Bohai D2 | 0.9764 | 0.4157 | 0.5821 | 0.2829 | 1.0000 | 0.5049 | 0.5426 | 0.2461 |
| Huaibei D4 | 0.9815 | 0.7483 | 0.7435 | 0.4952 | 1.0000 | 0.8446 | 0.6482 | 0.4081 |
| Jiuduhe D1 | 0.9555 | 0.2862 | 0.5764 | 0.2070 | 0.9983 | 0.3716 | 0.4887 | 0.1847 |
| Liulimiao D5 | 0.8688 | 0.1954 | 0.5382 | 0.1477 | 0.9531 | 0.2331 | 0.5022 | 0.1293 |
| Yanqi D3 | 0.9851 | 0.5613 | 0.6534 | 0.3769 | 0.9999 | 0.6175 | 0.5913 | 0.3055 |
| Huangsongyu F5 | 0.7282 | 0.4994 | 0.5356 | 0.4102 | 0.9590 | 0.6404 | 0.5110 | 0.3557 |
| Jinhaihu F4 | 0.7258 | 0.3941 | 0.5439 | 0.3454 | 1.0000 | 0.5367 | 0.5447 | 0.2766 |
| Nandulehe F3 | 0.6906 | 0.3227 | 0.4924 | 0.2719 | 0.9989 | 0.4341 | 0.4239 | 0.2272 |
| Shandongzhuang F2 | 0.6861 | 0.3433 | 0.5008 | 0.2977 | 0.9998 | 0.4800 | 0.4728 | 0.2410 |
| Xiongerzhai F6 | 0.6861 | 0.5215 | 0.5148 | 0.4215 | 0.9339 | 0.6468 | 0.4605 | 0.3652 |
| Zhenluoying F7 | 0.6922 | 0.2861 | 0.5111 | 0.2554 | 0.9742 | 0.3869 | 0.4617 | 0.2232 |
| Wangxinzhuang F1 | 0.6368 | 0.2006 | 0.4781 | 0.2004 | 1.0000 | 0.3049 | 0.4817 | 0.1601 |
| Beizhuang E10 | 0.4658 | 0.1007 | 0.4165 | 0.1039 | 0.9352 | 0.1360 | 0.4992 | 0.0943 |
| Bulaotun E5 | 0.5305 | 0.1905 | 0.4368 | 0.1778 | 0.9994 | 0.2650 | 0.5079 | 0.1504 |
| Dachengzi E11 | 0.4844 | 0.0433 | 0.4195 | 0.0410 | 0.6570 | 0.0525 | 0.3916 | 0.0352 |
| Fengjiayu E4 | 0.5221 | 0.0711 | 0.3995 | 0.0619 | 0.9992 | 0.0806 | 0.4885 | 0.0484 |
| Gaoling E6 | 0.3743 | 0.0508 | 0.3898 | 0.0595 | 0.5778 | 0.0689 | 0.4120 | 0.0540 |
| Gubeikou E7 | 0.9999 | 0.4833 | 0.9337 | 0.4439 | 1.0000 | 0.5665 | 0.8423 | 0.3795 |
| Shicheng E3 | 0.9628 | 0.6222 | 0.6465 | 0.4278 | 0.9999 | 0.7289 | 0.5900 | 0.3806 |
| Taishitun E9 | 0.9043 | 0.3458 | 0.6962 | 0.3229 | 0.9996 | 0.4487 | 0.6405 | 0.2795 |
| Xitiangezhuang E1 | 0.8575 | 0.3822 | 0.5335 | 0.3191 | 0.9991 | 0.5700 | 0.5144 | 0.2545 |
| Xiwengzhuang E2 | 0.7834 | 0.4426 | 0.5316 | 0.3861 | 0.9892 | 0.6109 | 0.4888 | 0.3183 |
| Xinchengzi E8 | 0.9893 | 0.3684 | 0.8259 | 0.3564 | 0.9976 | 0.4556 | 0.7656 | 0.3217 |
| [0, 0.3] | (0.3, 0.5] | (0.5, 0.7] | (0.7, 1] | |||||
| C Value | Discoordination | Medium discoordination | Medium coordination | Coordination | ||||
| D Value | Deterioration | Medium deterioration | Medium development | Development | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, R.; Lou, J.; Huang, S.; Xiao, J.; Long, F. Balancing Safety and Growth: An Ecological Resilience Framework for Great Wall Tourism Towns. Sustainability 2025, 17, 7243. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167243
Wang R, Lou J, Huang S, Xiao J, Long F. Balancing Safety and Growth: An Ecological Resilience Framework for Great Wall Tourism Towns. Sustainability. 2025; 17(16):7243. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167243
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Run, Jiahui Lou, Shengqin Huang, Jiarui Xiao, and Fei Long. 2025. "Balancing Safety and Growth: An Ecological Resilience Framework for Great Wall Tourism Towns" Sustainability 17, no. 16: 7243. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167243
APA StyleWang, R., Lou, J., Huang, S., Xiao, J., & Long, F. (2025). Balancing Safety and Growth: An Ecological Resilience Framework for Great Wall Tourism Towns. Sustainability, 17(16), 7243. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167243





