Sustainable Treatment of Crude Oil-in-Saline Water Emulsion with Licuri (Syagrus coronata) Leaf Fiber
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of Licuri Leaf Fiber
2.2.2. Characterization of the LLF
2.2.3. Preparation of Crude Oil in Saline Water Emulsion
2.2.4. Batch Sorption Experiments
2.2.5. Kinetic and Isotherm Models
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of LLF
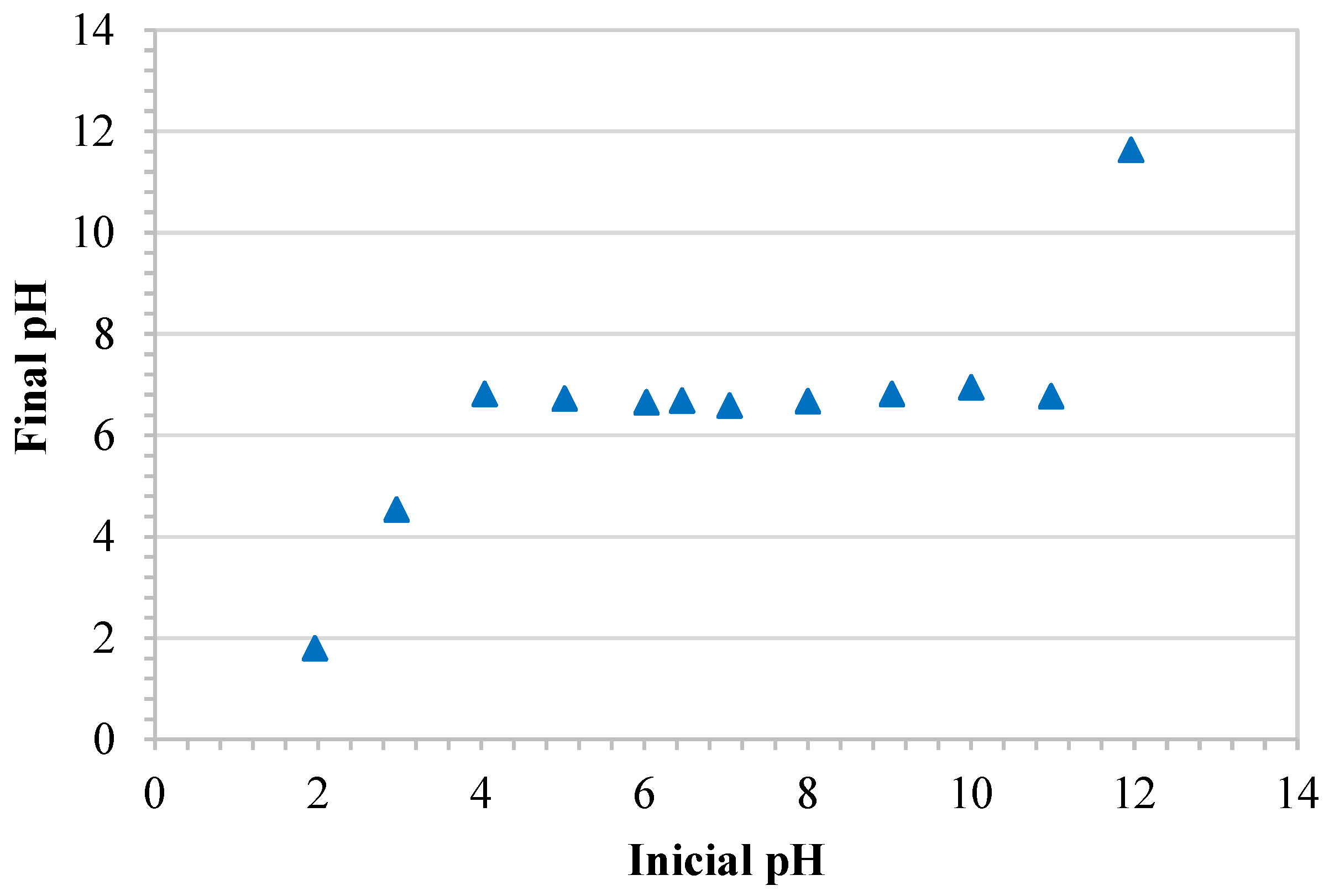
3.1.1. Zero Charge Point Analysis
3.1.2. Compositional Analysis
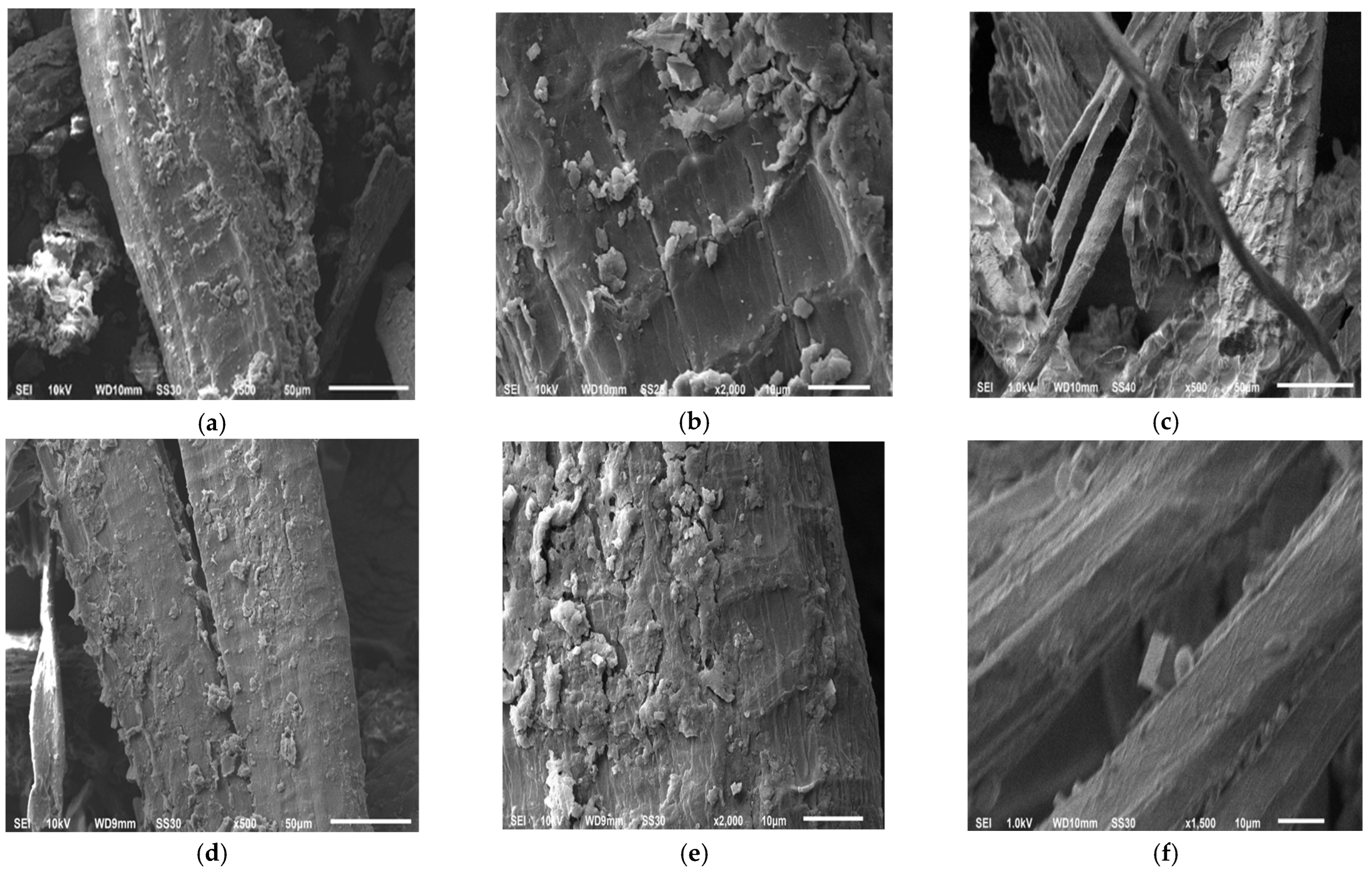
3.1.3. SEM and EDS Analysis
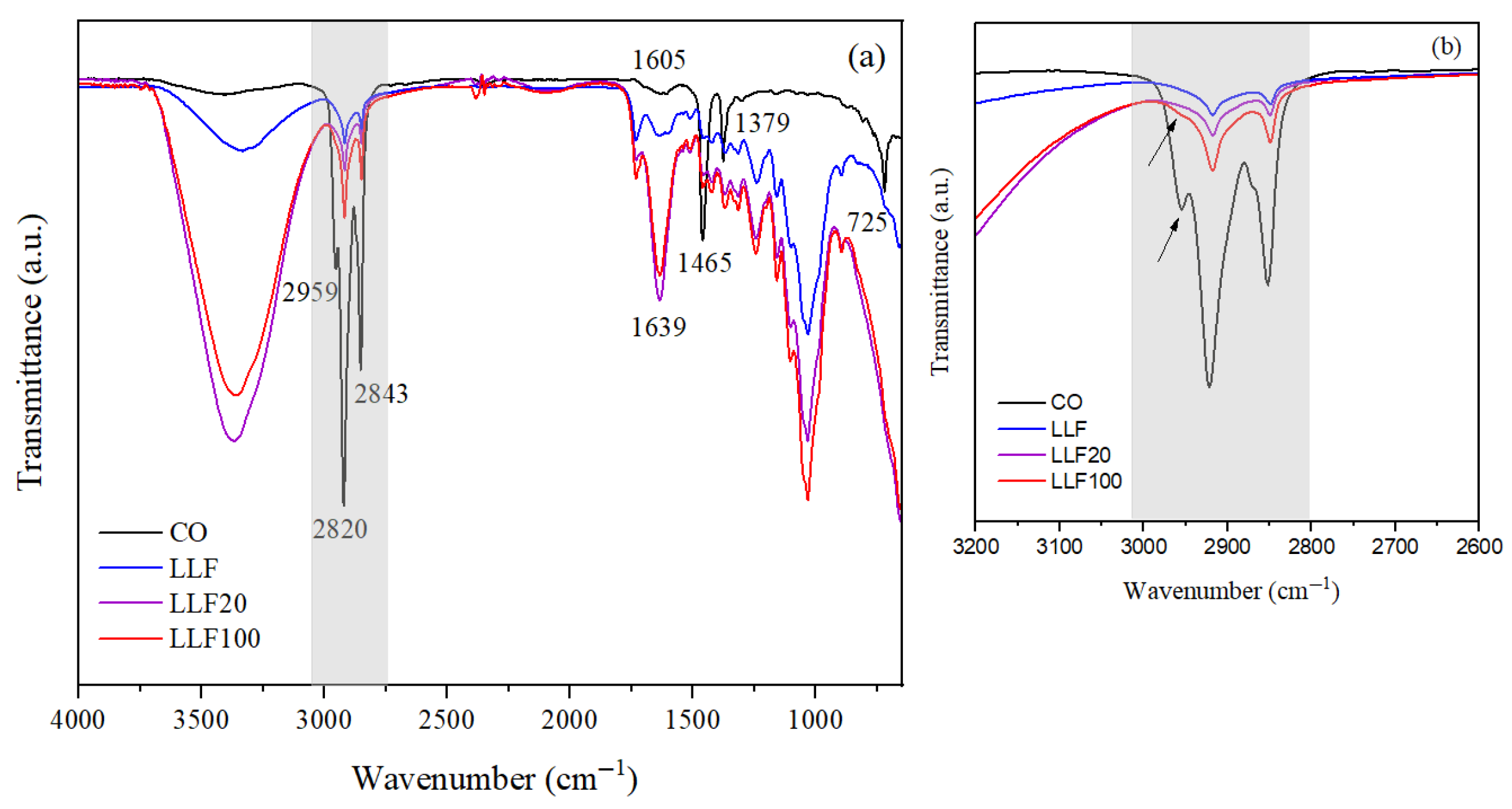
3.1.4. FTIR Analysis
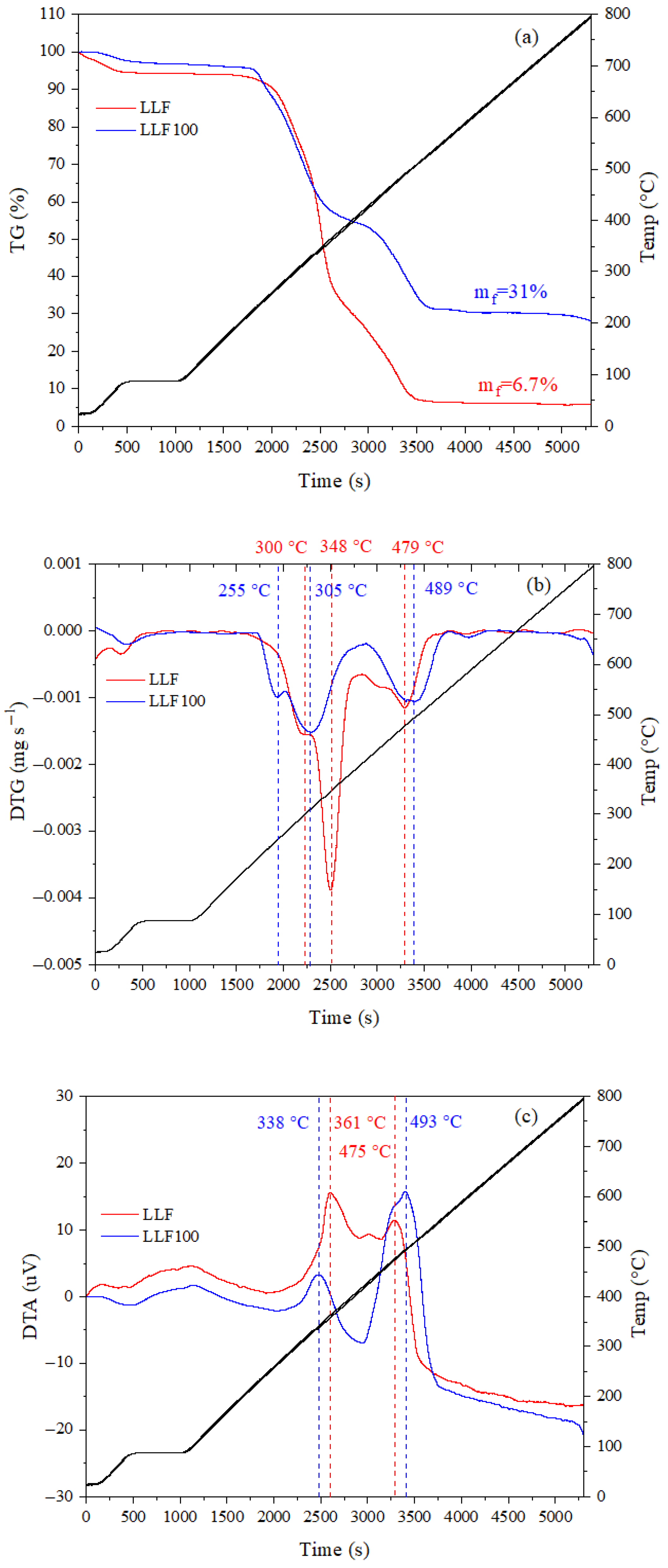
3.1.5. TGA and DTA Analysis
3.2. Batch Experiments
3.2.1. Sorption Kinetics
3.2.2. Model Kinetics
3.2.3. Sorption Isotherm
3.2.4. Isotherm Model
3.2.5. Thermodynamic Parameters
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siwayanan, P.; Ramachandran, D.G.; Jamaluddin, R.; Ahmad, S. Oil spill removal using kenaf core fibers as biosorbent material. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, Proceedings of the 26th Regional Symposium on Chemical Engineering (RSCE 2019), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 30–31 October 2019; IOP Publishing Ltd: Bristol, UK, 2020; Volume 778, p. 012003. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Li, Z.; Lü, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, D.; Li, Q.; Qiu, F. Recent progress and future prospects of oil-absorbing materials. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 27, 1282–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Chen, B.; Zhang, B.; Song, X.; Zeng, G.; Lee, K. Photocatalytic ozonation of offshore produced water by TiO2 nanotube arrays coupled with UV-LED irradiation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 402, 123456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuhasel, K.; Kchaou, M.; Alquraish, M.; Munusamy, Y.; Jeng, Y.T. Oily wastewater treatment: Overview of conventional and modern methods, challenges, and future opportunities. Water 2021, 13, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Kim, Y.; Woo, Y.C.; Hwang, I. Water management and produced water treatment in oil sand plant: A review. Desalination 2023, 567, 116991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amakiri, K.T.; Canon, A.R.; Molinari, M.; Angelis-Dimakis, A. Review of oilfield produced water treatment technologies. Chemosphere 2022, 298, 134064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delanka-Pedige, H.M.; Zhang, Y.; Young, R.B.; Wang, H.; Hu, L.; Danforth, C.; Xu, P. Safe reuse of treated produced water outside oil and gas fields? A review of current practices, challenges, opportunities, and a risk-based pathway for produced water treatment and fit-for-purpose reuse. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2023, 42, 100973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakharian, H.; Ganji, H.; Naderifar, A. Saline produced water treatment using gas hydrates. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 4269–4273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, Q.; Dong, S.; Liu, H.; Dong, K.; Wu, X.; Sui, M.; Zhang, F. Synthesis of mixed-base active material from drilling fluid solid waste and biomass for oil wastewater adsorption and its mechanism. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 66, 106076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerff, B.; Key, D.; Bladergroen, B. A review of the processes associated with the removal of oil in water pollution. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, R.R.L.; Moraes, J.S. Removal of organic pollutants from wastewater using chitosan: A literature review. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 1741–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vianna, L.F. RESOLUÇÃO CONAMA Nº 393. Rev. Bras. Direito Petróleo Gás Energ. 2018, 5, 211–224. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J.; Chen, B.; Thanyamanta, W.; Hawboldt, K.; Zhang, B.; Liu, B. Offshore produced water management: A review of current practice and challenges in harsh/Arctic environments. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 104, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Medeiros, A.D.M.; da Silva Junior, C.J.G.; de Amorim, J.D.P.; Durval, I.J.B.; de Santana Costa, A.F.; Sarubbo, L.A. Oily wastewater treatment: Methods, challenges, and trends. Processes 2022, 10, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jin, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Sun, F.; Ma, H.; Pugazhendhi, A.; Xia, C. A comprehensive review of lignocellulosic biomass derived materials for water/oil separation. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 876, 162549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ani, J.U.; Akpomie, K.G.; Okoro, U.C.; Aneke, L.E.; Onukwuli, O.D.; Ujam, O.T. Potentials of activated carbon produced from biomass materials for sequestration of dyes, heavy metals, and crude oil components from aqueous environment. Appl. Water Sci. 2020, 10, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emenike, E.C.; Adeleke, J.; Iwuozor, K.O.; Ogunniyi, S.; Adeyanju, C.A.; Amusa, V.T.; Okoro, H.K.; Adeniyi, A.G. Adsorption of crude oil from aqueous solution: A review. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 50, 103330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, T.M.; de Jesus, F.A.; da Silva, G.F.; Pontes, L.A.M. Synthesis of activated carbon from oleifera moringa for removal of oils and greases from the produced water. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2020, 14, 100357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toorani, F.; Aghdasinia, H.; Nejatbakhsh, S.; Karimi, A. Removal of hydrocarbon pollutants from aqueous media using hydrophobic cellulose-based adsorbents. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2023, 199, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sam, E.K.; Liu, J.; Lv, X. Biomass-Based/Derived Value-Added Porous Absorbents for Oil/Water Separation. Waste Biomass Valorization 2023, 14, 3147–3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujtaba, M.; Fraceto, L.F.; Fazeli, M.; Mukherjee, S.; Savassa, S.M.; de Medeiros, G.A.; Pereira, A.E.S.; Mancini, S.D.; Lipponen, J.; Vilaplana, F. Lignocellulosic biomass from agricultural waste to the circular economy: A review with focus on biofuels, biocomposites and bioplastics. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 402, 136815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, T.; Wang, F.; Xu, G. Sorption kinetics and mechanism of various oils into kapok assembly. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 91, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, L.M.T.M.; Oliveira, L.F.A.M.; Sonsin, A.F.; Duarte, J.L.S.; Soletti, J.I.; Fonseca, E.J.S.; Ribeiro, L.M.O.; Meili, L. Ultrafast diesel oil spill removal by fibers from silk-cotton tree: Characterization and sorption potential evaluation. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 263, 121448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batzias, F.A.; Sidiras, D.K.; Siontorou, C.G.; Bountri, A.N.; Politi, D.V.; Kopsidas, O.N.; Konstantinou, I.G.; Katsamas, G.N.; Salapa, I.S.; Zervopoulou, S.P. Experimental design for estimating parameter-values of modelling crude oil adsorption on thermo-chemically modified lignocellulosic biomass. Int. J. Arts Sci. 2014, 7, 205. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, M.S.; Frety, R.; Vidal, R.R.L. Cotton linter as biosorbent: Removal study of highly diluted crude oil-in-saline water emulsion. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 20, 2111–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheu, S.C.; Kong, H.; Song, S.T.; Johari, K.; Saman, N.; Yunus, M.A.C.; Mat, H. Separation of dissolved oil from aqueous solution by sorption onto acetylated lignocellulosic biomass-equilibrium, kinetics and mechanism studies. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 864–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.; Wang, S.; Ang, H.M. Removal of emulsified oil from oily wastewater using agricultural waste barley straw. Biochem. Eng. J. 2010, 49, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.J. Agricultural bio-waste for adsorptive removal of crude oil in aqueous solution. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2019, 21, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Najar, J.A.; Al-Humairi, S.T.; Lutfee, T.; Balakrishnan, D.; Veza, I.; Soudagar, M.E.M.; Fattah, I.M. Cost-effective natural adsorbents for remediation of oil-contaminated water. Water 2023, 15, 1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutfee, T.; Al-Najar, J.A.; Abdulla, F.M. Removal of oil from produced water using biosorbent. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Buildings, Construction and Environmental Engineering, Istanbul, Turkey, 7–9 October 2019; IOP Publishing Ltd: Bristol, UK, 2020; Volume 737, p. 012198. [Google Scholar]
- Cavalcanti, C.P.L.; Macedo, T.J.S.; Gois, G.C.; Menezes, V.G.; do Monte, A.P.O.; da Silva, A.D.; da Silva, D.J.M.; da Silva, E.O.; Araújo, G.G.L.; Rodrigues, R.T.S.; et al. Licuri oil improves feedlot performance and modifies ruminal fauna of Santa Inês ewes. Livest. Sci. 2022, 265, 105093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, J.S.; ShiosakI, R.K.; Mendes, M.L.M. Licuri (Syagrus coronata): Características, importâncias, potenciais e perspectivas do pequeno coco do Brasil. Desenvolv. Meio Ambiente 2021, 58, 169–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Ramon, M.V.; Stoeckli, F.; Moreno-Castilla, C.; Carrasco-Marin, F. On the characterization of acidic and basic surface sites on carbons by various techniques. Carbon 1999, 37, 1215–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chun, Y.; Sheng, G.; Huang, M. pH-dependence of pesticide adsorption by wheat-residue-derived black carbon. Langmuir 2024, 20, 6736–6741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Soest, P.J. Use of detergents in the analysis of fibrous feeds. II. A rapid method for the determination of fiber and lignin. J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem. 1990, 73, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Soest, P.V.; Robertson, J.B.; Lewis, B.A. Methods for dietary fiber, neutral detergent fiber, and nonstarch polysaccharides in relation to animal nutrition. J. Dairy Sci. 1991, 74, 3583–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajak, V.K.; Kumar, S.; Thombre, N.V.; Mandal, A. Synthesis of activated charcoal from saw-dust and characterization for adsorptive separation of oil from oil-in-water emulsion. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2018, 205, 897–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Elakneswaran, Y.; Shimokawara, M.; Kato, Y.; Kitamura, R.; Hiroyoshi, N. Impact of the temperature, homogenization condition, and oil property on the formation and stability of crude oil emulsion. Energ. Fuel. 2024, 38, 979–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elanchezhiyan, S.S.; Meenakshi, S. Synthesis and characterization of chitosan/Mg-Al layered double hydroxide composite for the removal of oil particles from oil-in-water emulsion. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 1586–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.S.; Zheng, T.; Wang, P.; Jiang, J.P.; Li, N. Adsorption isotherm, kinetic and mechanism studies of some substituted phenols on activated carbon fibers. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 157, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X. Modeling of experimental adsorption isotherm data. Information 2015, 6, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mall, I.D.; Srivastava, V.C.; Kumar, G.V.A.; Mishra, I.M. Characterization and utilization of mesoporous fertilizer plant waste carbon for adsorptive removal of dyes from aqueous solution. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2006, 278, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.M.; Kwon, H.J.; Moreau, J.P. Cotton nonwovens as oil spill cleanup sorbents. Text. Res. J. 1993, 63, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, I.A.; East, G.C.; Johnson, D.J. Structure–property relationships in natural cellulosic fibres: Part III: Flax—An oil sorbent. J. Text. Inst. 2003, 94, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougherty, M.J.; Tran, H.M.; Stavila, V.; Knierim, B.; George, A.; Auei, M.; Adams, P.D.; Hadi, M.Z. Cellulosic biomass pretreatment and sugar yields as a function of biomass particle size. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isaac, A.; Barboza, V.; Sket, F.I.; D’Almeida, J.R.M.; Montoro, L.A.; Hilger, A.; Manke, I. Towards a deeper understanding of structural biomass recalcitrance using phase-contrast tomography. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2015, 8, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Guo, S.; Deng, X.; Zhao, D.; Zhu, S.; Qu, H.; Li, X.; Zhao, Y. An optimized method for evaluating the preparation of high-quality fuel from various types of biomass through torrefaction. Molecules 2024, 29, 1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lins, U.; Barros, C.F.; Da Cunha, M.; Miguens, F.C. Structure, morphology, and composition of silicon biocomposites in the palm tree Syagrus coronata (Mart.) Becc. Protoplasma 2002, 220, 0089–0096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asemani, M.; Rabbani, A.R. Detailed FTIR spectroscopy characterization of crude oil extracted asphaltenes: Curve resolve of overlapping bands. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2020, 185, 106618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilt, B.K.; Welch, W.T.; Rankin, J.G. Determination of asphaltenes in petroleum crude oils by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Energ. Fuels. 1989, 12, 1008–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christy, A.A.; Dahl, B.; Kvalheim, O.M. Structural features of resins, asphaltenes and kerogen studied by diffuse reflectance infrared spectroscopy. Fuel 1989, 68, 430–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zojaji, I.; Esfandiarian, A.; Taheri-Shakib, J. Toward molecular characterization of asphaltene from different origins under different conditions by means of FT-IR spectroscopy. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 289, 102314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sakhawy, M.; Kamel, S.; Salama, A.; Tohamy, H.A.S. Preparation and infrared study of cellulose based amphiphilic materials. Cellul. Chem. Technol. 2018, 52, 193–200. [Google Scholar]
- De Rosa, I.M.; Kenny, J.M.; Puglia, D.; Santulli, C.; Sarasini, F. Morphological, thermal and mechanical characterization of okra (Abelmoschus esculentus) fibres as potential reinforcement in polymer composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2010, 70, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, F.K.; Hamdan, S.; Rahman, M.R.; Rusop, M.; Lai, J.C.H.; Hossen, M.F.; Rahman, M.M. Synthesis and characterization of cellulose from green bamboo by chemical treatment with mechanical process. J. Chem. 2015, 2015, 212158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludueña, L.N.; Vecchio, A.; Stefani, P.M.; Alvarez, V.A. Extraction of cellulose nanowhiskers from natural fibers and agricultural byproducts. Fibers Polym. 2013, 14, 1118–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-González, D.; Fernandez-Lopez, M.; Valverde, J.L.; Sanchez-Silva, L. Thermogravimetric-mass spectrometric analysis on combustion of lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 143, 562–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, N.S.; Oliveira, V.C.; Fréty, R.; Sales, E.A. Thermal and catalytic fast pyrolysis of oily extracts of microalgae: Production of Biokerosene. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2021, 32, 811–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Yu, S.; Zhu, Y.; Shen, Y.; Gao, X.; Shi, W.; Tay, J.H. Adsorption mechanisms of crude oil onto polytetrafluoroethylene membrane: Kinetics and isotherm, and strategies for adsorption fouling control. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 235, 116212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Shahawy, A.; Heikal, G. Organic pollutants removal from oily wastewater using clean technology economically, friendly biosorbent (Phragmites australis). Ecol. Eng. 2018, 122, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, A.E.D.; Fawzy, M.; Hosny, G.; Obaid, A. Equilibrium, kinetic, and diffusion models of chromium (VI) removal using Phragmites australis and Ziziphus spina-christi biomass. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 18, 2125–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Yu, F.; Zhou, L.; Jin, L.; Yang, M.; Luan, J.; Tang, Y.; Fan, H.; Yuan, Z.; Chen, J. Enhanced adsorptive removal of methyl orange and methylene blue from aqueous solution by alkali-activated multiwalled carbon nanotubes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 5749–5760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osemeahon, S.A.; Dimas, B.J. Removal of crude oil from aqueous medium by sorption on Sterculis setigera. Asian J. Appl. Chem. Res. 2020, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obi, A.I.; Ajiwe, A.C.; Okoye, P.A.C.; Umeh, C.T.; Amadi, E.G. Crude oil sorption performance of native and acetylated Siamese senna seed pods. Sustain. Chem. Environ. 2024, 8, 100173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.S.; Ramalingam, S.; Senthamarai, C.; Niranjanaa, M.; Vijayalakshmi, P.; Sivanesan, S. Adsorption of dye from aqueous solution by cashew nut shell: Studies on equilibrium isotherm, kinetics and thermodynamics of interactions. Desalination 2010, 261, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado-Gómez, E.; Tapia, J.I.; Encinas, A. A sustainable hydrophobic luffa sponge for efficient removal of oils from water. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2021, 28, e00273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Oepen, B.; Kördel, W.; Klein, W. Sorption of nonpolar and polar compounds to soils: Processes, measurements and experience with the applicability of the modified OECD-Guideline 106. Chemosphere 1991, 22, 285–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, E.G.; Oliveira, J.C.; Miranda, C.S.; Jose, N.M. Licuri Fibers Characterization After Treatment to Produce Cellulose Nanocrystals; No. INIS-BR—17511; Associacao Brasileira de Ceramica (ABCERAM): Sao Paulo, Brazil, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ju, X.; Bowden, M.; Brown, E.E.; Zhang, X. An improved X-ray diffraction method for cellulose crystallinity measurement. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 123, 476–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Elements | Content (wt%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Before Sorption | After Sorption | |
| C | 73.4 | 66.8 |
| O | 21.0 | 20.6 |
| K | 0.9 | - |
| Na | - | 1.8 |
| Ca | 1.4 | 3.4 |
| Cl | 0.3 | 7.0 |
| Ci (mg L−1) | qmax (mg g−1) | Pseudo-First Order | Pseudo-Second Order | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qmax,calc (mg g−1) | k1 (h−1) | R2 | qmax,calc (mg g−1) | k2 (g mg−1 h−1) | R2 | ||
| 28 | 25.40 | 4.40 | 0.27 | 0.2726 | 24.15 | 1.07 | 0.9971 |
| 102 | 91.03 | 107.10 | 1.04 | 0.9570 | 114.94 | 0.01 | 0.9173 |
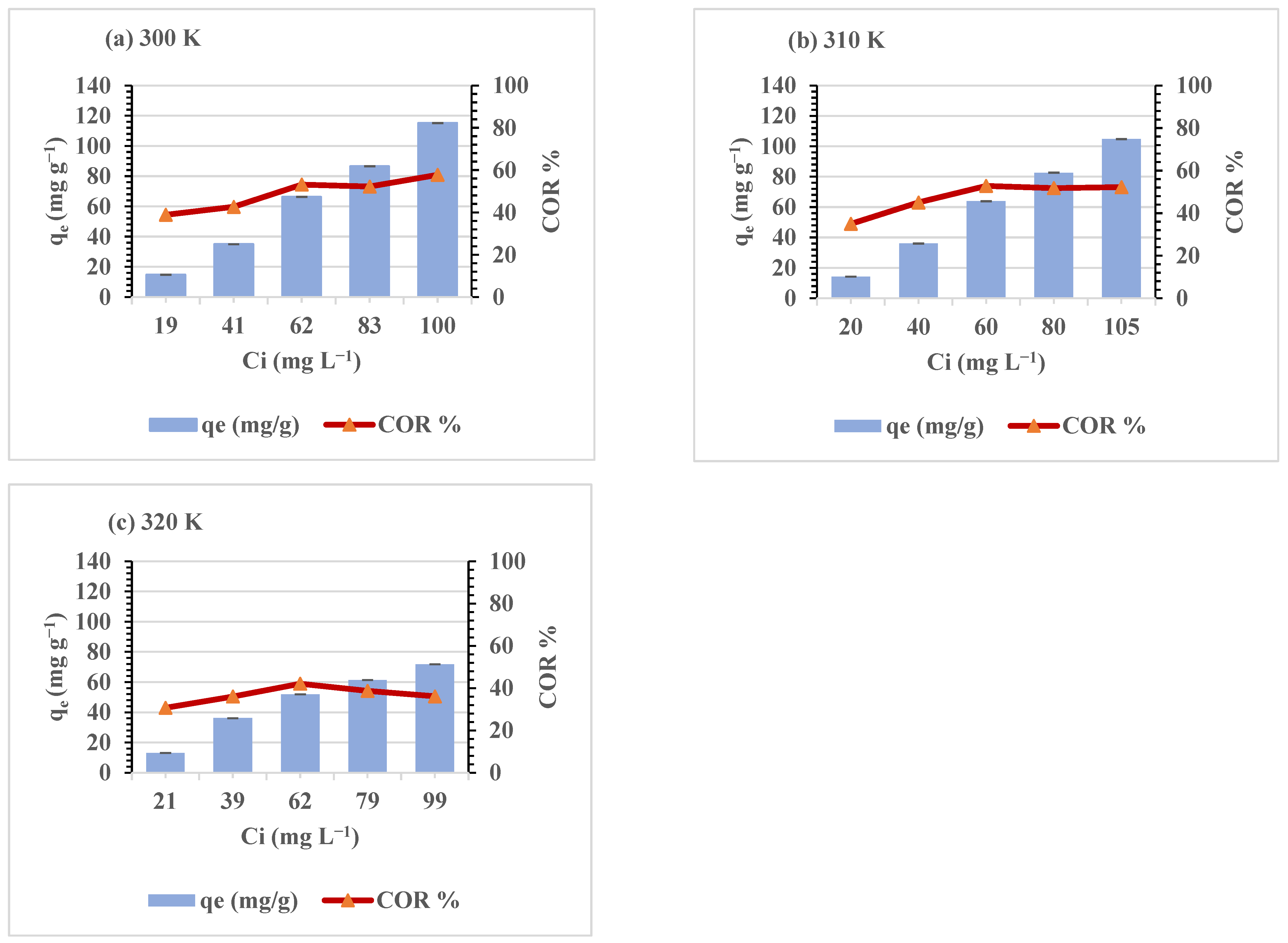
| Temperature (K) | Ci (mg L−1) | Ce (mg L−1) | qe (mg g−1) | COR (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 300 | 19.01 ± 1.07 | 11.60 ± 0.31 | 14.81 ± 1.52 | 38.90 ± 1.82 |
| 41.00 ± 1.42 | 23.51 ± 0.84 | 34.98 ± 1,24 | 42.65 ± 0.39 | |
| 62.39 ± 0.74 | 29.23 ± 0.41 | 66.32 ± 0.66 | 53.15 ± 0.10 | |
| 82.88 ± 1.24 | 39.59 ± 0.74 | 86.58 ± 1.12 | 52.23 ± 0.29 | |
| 99.73 ± 2.69 | 42.15 ± 2.67 | 115.18 ± 2.04 | 57.76 ± 1.11 | |
| 310 | 20.35 ± 1.02 | 13.22 ± 1.27 | 14.25 ± 1.28 | 35.02 ± 0.14 |
| 40.35 ± 1.37 | 24.20 ± 0.54 | 36.05 ± 2.08 | 45.04 ± 3.40 | |
| 60.49 ± 0.82 | 35.91 ± 1.29 | 63.90 ± 0.51 | 52.83 ± 1.25 | |
| 79.84 ± 0.73 | 38.60 ± 0.99 | 82.68 ± 1.48 | 51.77 ± 0.25 | |
| 105.35 ± 2.73 | 50.30 ± 0.81 | 104.79 ± 2.07 | 52.22 ± 1.77 | |
| 320 | 20.81 ± 1.80 | 14.69 ± 0.89 | 13.08 ± 1.40 | 30.73 ± 2.05 |
| 39.29 ± 1.28 | 21.21 ± 0.79 | 36.17 ± 3.50 | 36.03 ± 4.45 | |
| 62.30 ± 0.28 | 35.69 ± 1.74 | 51.85 ± 1.60 | 42.09 ± 1.31 | |
| 79.40 ± 0.55 | 48.58 ± 1.58 | 61.38 ± 2.91 | 38.71 ± 1.77 | |
| 98.90 ± 2.44 | 63.55 ± 2.50 | 71.84 ± 2.19 | 36.12 ± 1.29 |
| Model | Parameters | Temperature (K) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 300 | 310 | 320 | ||
| Langmuir | qo (mg g−1) | 263.16 | 243.90 | 116.28 |
| b (L mg−1) | 0.011 | 0.010 | 0.0207 | |
| R2 | 0.0526 | 0.0594 | 0.2803 | |
| Temkin | KL (L mg−1) | 0.2343 | 0.2312 | 0.2578 |
| B1 | 36.54 | 33.031 | 23.154 | |
| R2 | 0.7410 | 0.7705 | 0.8876 | |
| Freundlich | KF (mg g−1)(mg L−1)1/n | 0.6433 | 0.6779 | 0.9307 |
| n | 0.747 | 0.786 | 0.921 | |
| 1/n | 1.34 | 1.27 | 1.09 | |
| R2 | 0.9849 | 0.9890 | 0.9697 | |
| T (K) | Ci (mg L−1) | Thermodynamic Parameters | ||||
| Kc (L g−1) | ΔG (kJ mol−1) | ΔH (kJ mol−1) | ΔS (kJ mol−1 K−1) | R2 | ||
| 300 | 19.01 ± 1.07 | 1.28 | −0.60 | −14.49 | −0.046 | 0.9969 |
| 310 | 20.35 ± 1.02 | 1.08 | −0.18 | |||
| 320 | 20.81 ± 1.80 | 0.89 | 0.30 | |||
| 300 | 62.39 ± 0.74 | 2.27 | −2.00 | −17.90 | −0.053 | 0.9991 |
| 310 | 60.49 ± 0.82 | 1.78 | −0.77 | |||
| 320 | 62.30 ± 0.28 | 1.45 | −0.97 | |||
| 300 | 82.88 ± 1.24 | 2.19 | −1.91 | −21.84 | −0.066 | 0.7657 |
| 310 | 79.84 ± 0.73 | 2.14 | −1.98 | |||
| 320 | 79.40 ± 0.55 | 1.26 | −0.60 | |||
| 300 | 99.73 ± 2.69 | 2.72 | −2.44 | −34.90 | −0.108 | 0.9437 |
| 310 | 105.35 ± 2.73 | 2.08 | −0.65 | |||
| 320 | 98.90 ± 2.44 | 1.13 | −0.32 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bahia, P.V.B.; Ferreira, G.A.; Mascarenhas, A.J.S.; Castro, F.d.S.; Fréty, R.T.F.; Vidal, R.R.L. Sustainable Treatment of Crude Oil-in-Saline Water Emulsion with Licuri (Syagrus coronata) Leaf Fiber. Sustainability 2025, 17, 7188. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167188
Bahia PVB, Ferreira GA, Mascarenhas AJS, Castro FdS, Fréty RTF, Vidal RRL. Sustainable Treatment of Crude Oil-in-Saline Water Emulsion with Licuri (Syagrus coronata) Leaf Fiber. Sustainability. 2025; 17(16):7188. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167188
Chicago/Turabian StyleBahia, Pedro Victor Bomfim, Guilherme Augusto Ferreira, Artur José Santos Mascarenhas, Fabiana da Silva Castro, Roger Thomas François Fréty, and Rosangela Regia Lima Vidal. 2025. "Sustainable Treatment of Crude Oil-in-Saline Water Emulsion with Licuri (Syagrus coronata) Leaf Fiber" Sustainability 17, no. 16: 7188. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167188
APA StyleBahia, P. V. B., Ferreira, G. A., Mascarenhas, A. J. S., Castro, F. d. S., Fréty, R. T. F., & Vidal, R. R. L. (2025). Sustainable Treatment of Crude Oil-in-Saline Water Emulsion with Licuri (Syagrus coronata) Leaf Fiber. Sustainability, 17(16), 7188. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167188






