Black Soldier Fly Frass Fertilizer Outperforms Traditional Fertilizers in Terms of Plant Growth in Restoration in Madagascar
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Species
2.3. Substrate and Fertilizer
2.4. Experimental Design
2.5. Data Collection
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
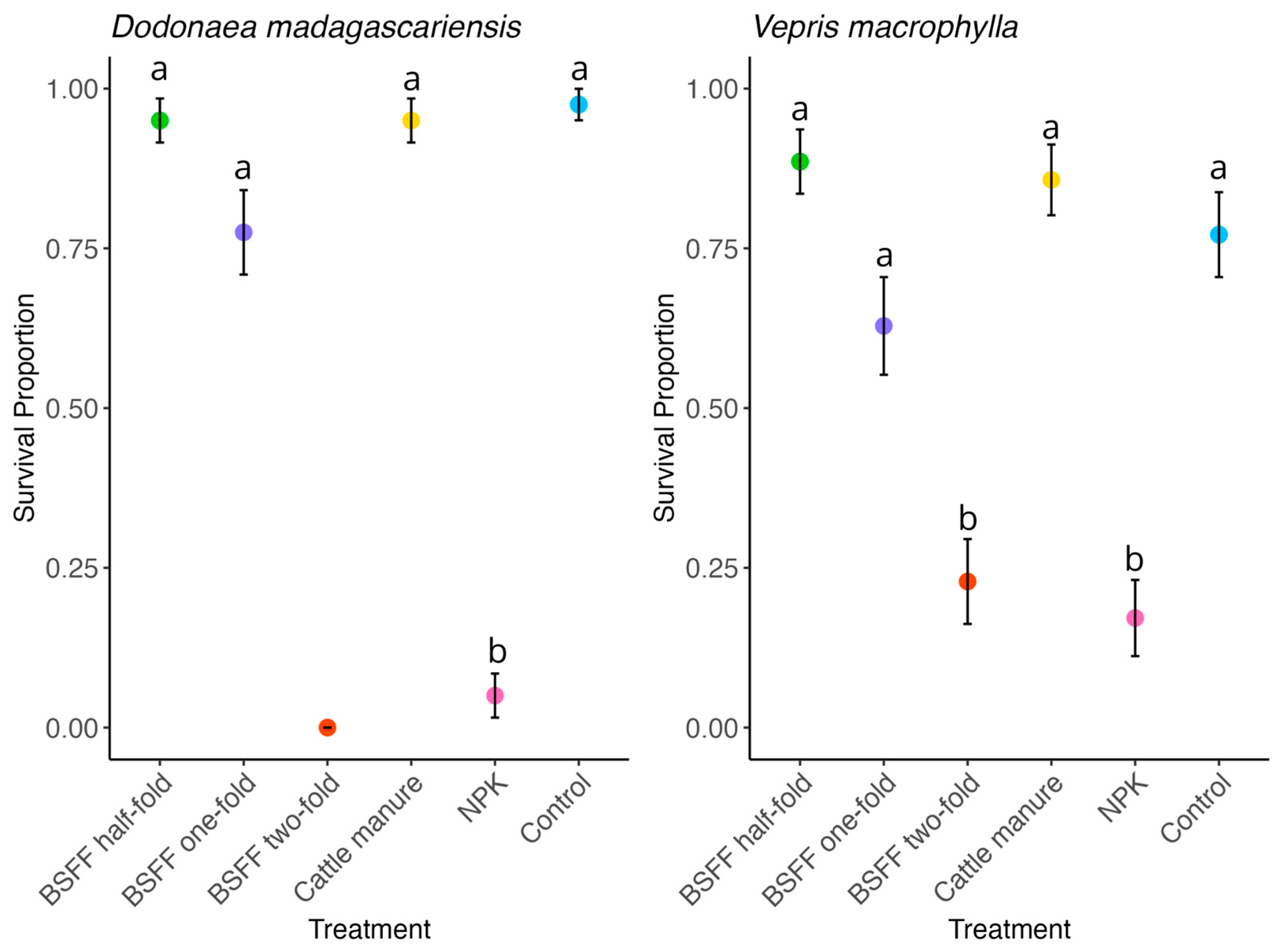
3.1. Seedlings Survival
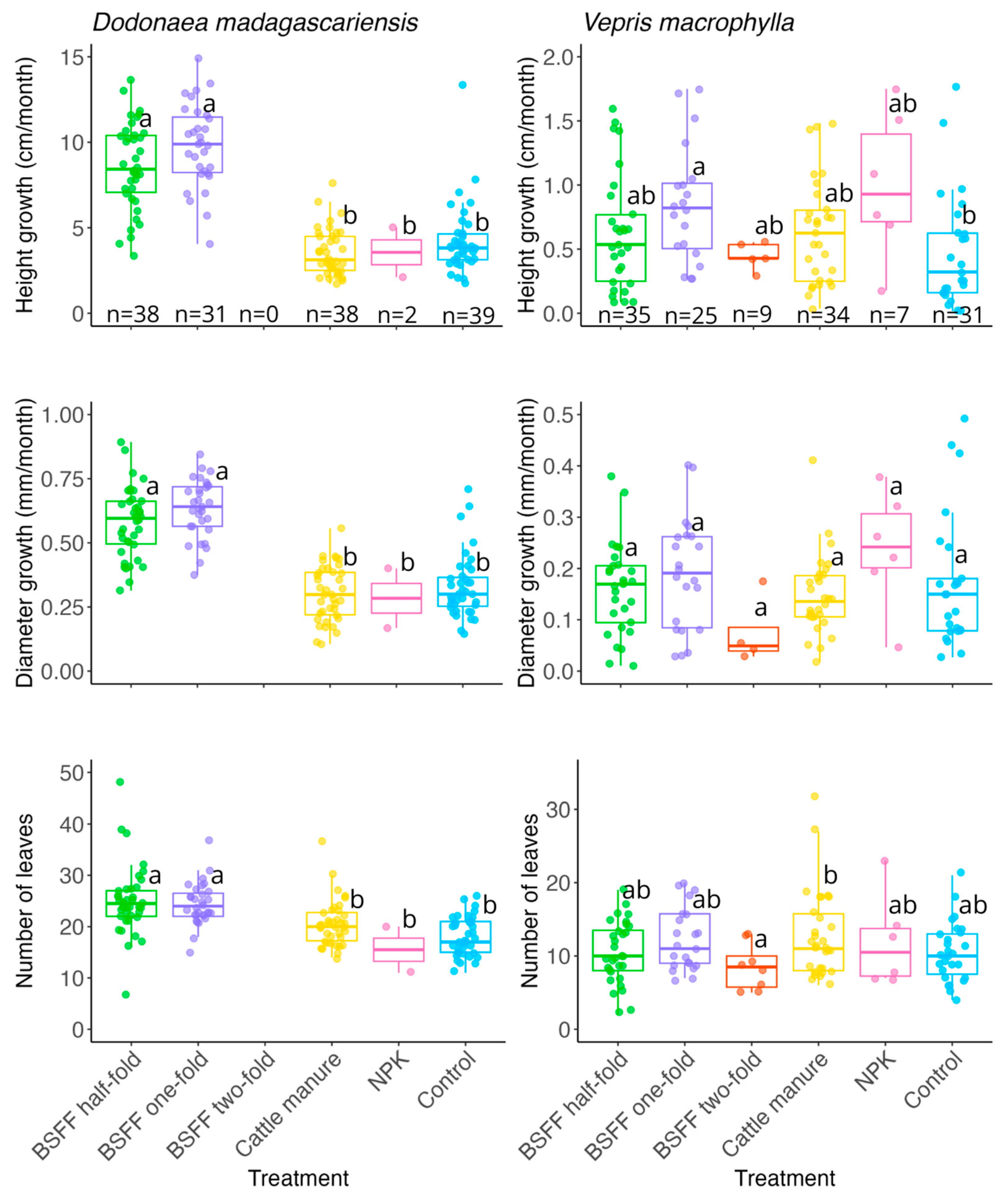
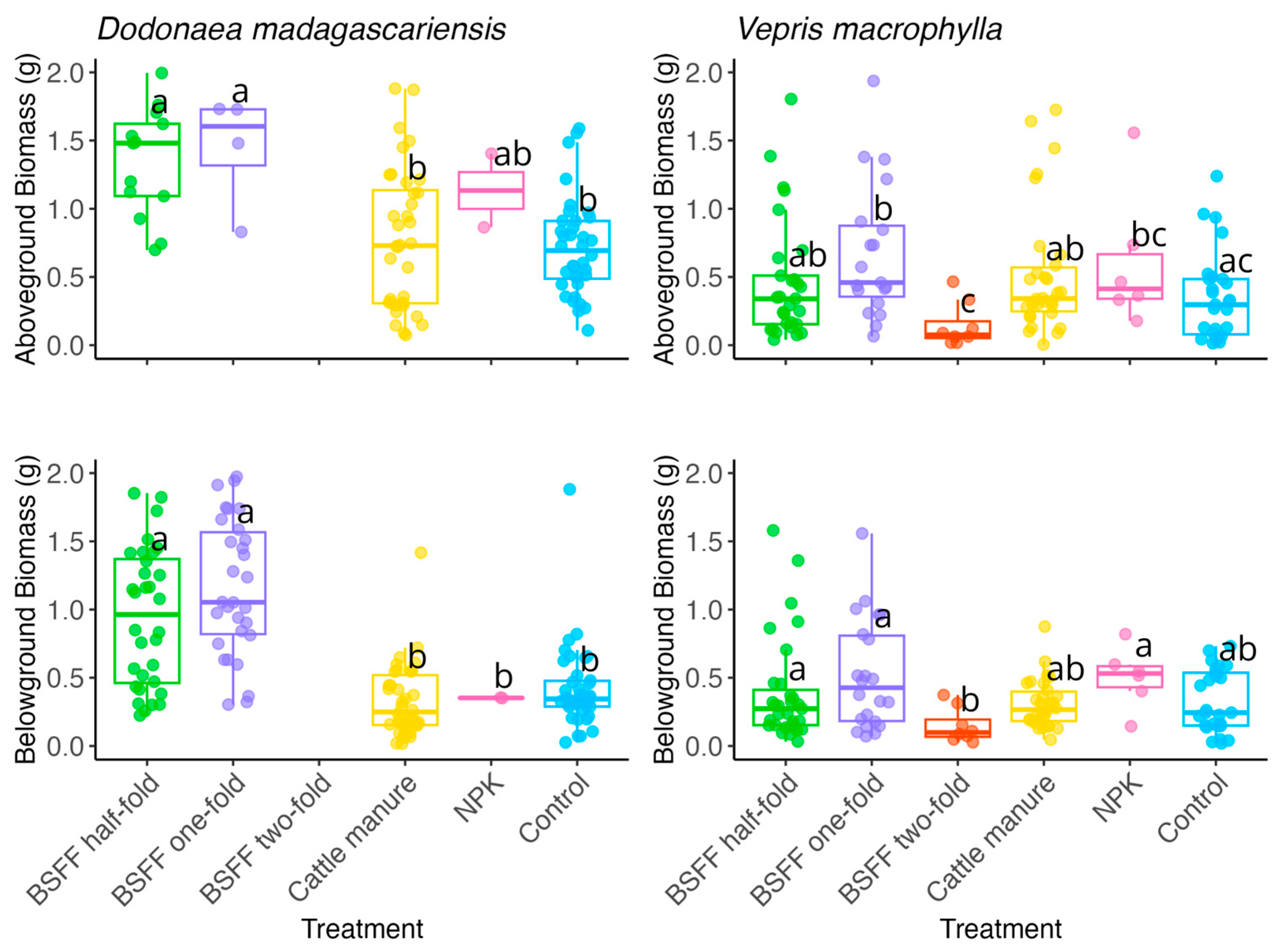
3.2. Seedlings Growth and Biomass
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ganzhorn, J.U.; Lowry, P.P., II; Schatz, G.E.; Sommer, S. The biodiversity of Madagascar: One of the world's hottest hotspots on its way out. Oryx 2001, 35, 346–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, S.M.; Benstead, J.P. Updated estimates of biotic diversity and endemism for Madagascar. Oryx 2005, 39, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allnutt, T.F.; Ferrier, S.; Manion, G.; Powell, G.V.N.; Ricketts, T.H.; Fisher, B.L.; Harper, G.J.; Irwin, M.E.; Kremen, C.; Labat, J.-N.; et al. A method for quantifying biodiversity loss and its application to a 50-year record of deforestation across Madagascar. Conserv. Lett. 2008, 1, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, N.; Mittermeier, R.A.; Mittermeier, C.G.; da Fonseca, G.A.B.; Kent, J. Biodiversity hotspots for conservation priorities. Nature 2000, 403, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, G.J.; Steininger, M.K.; Tucker, C.J.; Juhn, D.; Hawkins, F. Fifty years of deforestation and forest fragmentation in Madagascar. Environ. Conserv. 2007, 34, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieilledent, G.; Grinand, C.; Rakotomalala, F.A.; Ranaivosoa, R.; Rakotoarijaona, J.R.; Allnutt, T.F.; Achard, F. Combining global tree cover loss data with historical national forest cover maps to look at six decades of deforestation and forest fragmentation in Madagascar. Biol. Conserv. 2018, 222, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opdam, P.; Wascher, D. Climate change meets habitat fragmentation: Linking landscape and biogeographical scale levels in research and conservation. Biol. Conserv. 2004, 117, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramiadantsoa, T.; Ovaskainen, O.; Rybicki, J.; Hanski, I. Large-scale habitat corridors for biodiversity conservation: A forest corridor in Madagascar. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0132126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morelli, T.L.; Smith, A.B.; Mancini, A.N.; Balko, E.A.; Borgerson, C.; Dolch, R.; Farris, Z.; Federman, S.; Golden, C.D.; Holmes, S.M.; et al. The fate of Madagascar’s rainforest habitat. Nat. Clim. Change 2020, 10, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brancalion, P.; Niamir, A.; Broadbent, E.; Crouzeilles, R.; Barros, F.; Almeyda, A.M.; Baccini, A.; Aronson, J.; Goetz, S.; Reid, J.L.; et al. Global restoration opportunities in tropical rainforest landscapes. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaav3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strassburg, B.B.N.; Iribarrem, A.; Beyer, H.L.; Cordeiro, C.L.; Crouzeilles, R.; Jakovac, C.C.; Junqueira, A.B.; Lacerda, E.; Latawiec, E.; Balmford, A.; et al. Global priority areas for ecosystem restoration. Nature 2020, 586, 724–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- African Forest Landscape Restoration Initiative (AFR100). Available online: www.wri.org/our-work/project/african-restoration-100 (accessed on 3 June 2025).
- Culbertson, K.A.; Treuer, T.L.; Mondragon-Botero, A.; Ramiadantsoa, T.; Reid, J.L. The eco-evolutionary history of Madagascar presents unique challenges to tropical forest restoration. Biotropica 2022, 54, 1081–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadhurst, L.M.; Lowe, A.; Coates, D.J.; Cunningham, S.A.; McDonald, M.; Vesk, P.A.; Yates, C. Seed supply for broadscale restoration: Maximizing evolutionary potential. Evol. Appl. 2008, 1, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Society for Ecological Restoration International Science & Policy Working Group. The SER International Primer on Ecological Restoration; SER: Boston, MA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Vågen, T.G.; Shepherd, K.D.; Walsh, M.G. Sensing landscape level change in soil fertility following deforestation and conversion in the highlands of Madagascar using Vis-NIR spectroscopy. Geoderma 2006, 133, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pareliussen, I.; Olsson, E.G.A.; Armbruster, W.S. Factors limiting the survival of native tree seedlings used in conservation efforts at the edges of forest fragments in upland Madagascar. Restor. Ecol. 2006, 14, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miandrimanana, C.; Reid, J.L.; Rivoharison, T.; Birkinshaw, C. Planting position and shade enhance native seedling performance in forest restoration for an endangered Malagasy plant. Plant Divers. 2019, 41, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chazdon, R.L. Beyond deforestation: Restoring forests and ecosystem services on degraded lands. Science 2008, 320, 1458–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brancalion, P.H.S.; Viani, R.A.G.; Strassburg, B.B.N.; Rodrigues, R.R. Finding the money for tropical forest restoration. Unasylva 2015, 245, 41–50. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, R.R.; Lima, R.A.F.; Gandolfi, S.; Nave, A.G. On the restoration of high diversity forests: 30 years of experience in the Brazilian Atlantic Forest. Biol. Conserv. 2009, 142, 1242–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, A.C.; Laurance, S.G.W. A review of the use of direct seeding and seedling plantings in restoration: What do we know and where should we go? Appl. Veg. Sci. 2015, 18, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossnickle, S.C. Why seedlings survive: Influence of plant attributes. New For. 2012, 43, 711–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotowa, O.J.; Małek, S.; Jasik, M.; Staszel-Szlachta, K. Substrate and fertilization used in the nursery influence biomass and nutrient allocation in Fagus sylvatica and Quercus robur seedlings after the first year of growth in a newly established forest. Forests 2025, 16, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotowa, O.J.; Małek, S.; Kupka, D.; Pach, M.; Banach, J. Innovative peat-free organic substrates and fertilizers influence growth dynamics and root morphology of Fagus sylvatica L. and Quercus robur L. seedlings one year after planting. Forests 2025, 16, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poveda, J. Insect frass in the development of sustainable agriculture. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 41, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, I.G.; Yong, J.W.; Lalander, C. Frass derived from black soldier fly larvae treatment of biodegradable wastes: A critical review and future perspectives. Waste Manag. 2022, 142, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poveda, J.; Jiménez-Gómez, A.; Saati-Santamaría, Z.; Usategui-Martín, R.; Rivas, R.; García-Fraile, P. Mealworm frass as a potential biofertilizer and abiotic stress tolerance-inductor in plants. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 142, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menino, R.; Felizes, F.; Castelo-Branco, M.A.; Fareleira, P.; Moreira, O.; Nunes, R.; Murta, D. Agricultural value of black soldier fly larvae frass as organic fertilizer on ryegrass. Heliyon 2021, 7, e05855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrianorosoa Ony, C.; Solofondranohatra, C.L.; Ramiadantsoa, T.; Ravelomanana, A.; Ramanampamonjy, R.N.; Hugel, S.; Fisher, B.L. Effect of cricket frass fertilizer on growth and pod production of green beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0303080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalander, C.H.; Fidjeland, J.; Diener, S.; Eriksson, S.; Vinnerås, B. High waste-to-biomass conversion and efficient Salmonella spp. reduction using black soldier fly for waste recycling. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 35, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beesigamukama, D.; Mochoge, B.; Korir, N.K.; Fiaboe, K.K.; Nakimbugwe, D.; Khamis, F.M.; Subramanian, S.; Wangu, M.M.; Dubois, T.; Ekesi, S.; et al. Low-cost technology for recycling agro-industrial waste into nutrient-rich organic fertilizer using black soldier fly. Waste Manag. 2021, 119, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.; Hassanzadeh, N. BSFL frass: A novel biofertilizer for improving plant health while minimizing environmental impact. Can. Sci. Fair J. 2019, 2, 41–46. [Google Scholar]
- Coudron, C.; Spranghers, T.; Elliot, D.; Halstead, J. Insect Breeding: Lab Scale and Pilot Scale Experiments with Mealworm and Black Soldier Fly; BioBoost: Roeselare, Belgium, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Temple, W.D.; Radley, R.; Baker-French, J.; Richardson, F. Use of Enterra Natural Fertilizer (Black Soldier Fly Larvae Digestate) as a Soil Amendment; Enterra Feed Corporation: Langley City, BC, Canada, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Setti, L.; Francia, E.; Pulvirenti, A.; Gigliano, S.; Zaccardelli, M.; Pane, C.; Caradonia, F.; Maistrello, B.S.L.; Ronga, D. Use of black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens (L.), Diptera: Stratiomyidae) larvae processing residue in peat-based growing media. Waste Manag. 2019, 95, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, K.; Kawasaki, T.; Hirayasu, H.; Matsumoto, Y.; Fujitani, Y. Evaluation of fertilizer value of residues obtained after processing household organic waste with black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens). Sustainability 2020, 12, 4920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beesigamukama, D.; Mochoge, B.; Korir, N.; Musyoka, M.; Fiaboa, K.K.M.; Nakimbugwe, D.; Khamis, F.M.; Subramanian, S.; Dubois, T.; Ekesi, S.; et al. Nitrogen fertilizer equivalence of black soldier fly frass fertilizer and synchrony of nitrogen mineralization for maize production. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anyega, A.O.; Korir, N.K.; Beesigamukama, D.; Changeh, G.J.; Nkoba, K.; Subramanian, S.; Van Loon, J.J.A.; Dicke, M.; Tanga, C.M. Black soldier fly-composted organic fertilizer enhances growth, yield, and nutrient quality of three key vegetable crops in Sub-Saharan Africa. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 680312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehan, I.; Lopes, I.G.; Murta, D.; Lidon, F.; Fareleira, P.; Esteves, C.; Moreira, O.; Menino, R. Agronomic potential of Hermetia illucens frass in the cultivation of ryegrass in distinct soils. Insects Food Feed. 2024, 1, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, S.; Gastauer, M.; Cavalcante, R.B.; Ramos, S.J.; Caldeira, C.F., Jr.; Silva, D.; Rodrigues, R.R.; Salomão, R.; Oliveira, M.; Souza-Filho, P.W.M.; et al. Challenges and opportunities for large-scale reforestation in the Eastern Amazon using native species. For. Ecol. Manag. 2020, 466, 118120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haase, D.L.; Davis, A.S. Developing and supporting quality nursery facilities and staff are necessary to meet global forest and landscape restoration needs. Reforesta 2017, 4, 69–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centre de Recherches, D’études et D’appui à L’analyse Économique à Madagascar (CREAM). Monographie Région Analamanga; Centre de Recherches, D’études et D’appui à L’analyse Économique à Madagascar (CREAM): Antananarivo, Madagascar, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Pareliussen, I. Natural and Experimental Tree Establishment in a Fragmented Forest, Ambohitantely Forest Reserve, Madagascar. Ph.D. Thesis, Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Trondheim, Norway, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ramifehiarivo, N.; Brossard, M.; Grinand, C.; Andriamananjara, A.; Razafimbelo, T.; Rasolohery, A.; Razafimahatratra, H.; Seyler, F.; Ranaivoson, N.; Rabenarivo, M.; et al. Mapping soil organic carbon on a national scale: Towards an improved and updated map of Madagascar. Geoderma Reg. 2017, 9, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, I.G.; Wiklicky, V.; Vinnerås, B.; Yong, J.W.H.; Lalander, C. Recirculating frass from food waste bioconversion using black soldier fly larvae: Impacts on process efficiency and product quality. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 366, 121869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020; Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 15 August 2024).
- Greenwood, M. The natural duration of cancer. Rep. Public Health Med. Subj. 1926, 33, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Newton, L.; Sheppard, C.; Watson, D.; Burtle, G.; Dove, R. Using the Black Soldier Fly, Hermetia illucens, as a Value-Added Tool for the Management of Swine Manure; Animal and Poultry Waste Management Center, North Carolina State University: Raleigh, NC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Alattar, M.; Alattar, F.; Popa, R. Effects of microaerobic fermentation and black soldier fly larvae food scrap processing residues on the growth of corn plants (Zea mays). Plant Sci. Today 2016, 3, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Ee, A.W.L.; Tan, J.K.N.; Cheong, J.C.; Chiam, Z.; Arora, S.; Lam, W.N.; Tan, H.T.W. Upcycling food waste using black soldier fly larvae: Effects of further composting on frass quality, fertilizing effect and its global warming potential. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 288, 125664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahalvi, H.N.; Rafiya, L.; Rashid, S.; Nisar, B.; Kamili, A.N. Chemical Fertilizers and Their Impact on Soil Health. In Microbiota and Biofertilizers; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Yaacobi, G.; Shouster-Dagan, I.; Opatovsky, I.; Baron, Y.; Richter, H.; Bashan, I.; Steinberg, S. The Potential of the Black Soldier Fly Bioconverted Rearing Substrate as a Plant Growth Enhancer. In Book of Abstracts Insecta Conference; ATB: Potsdam, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Beesigamukama, D.; Mochoge, B.; Korir, N.; Ghemoh, C.J.; Subramanian, S.; Tanga, C.M. In situ nitrogen mineralization and nutrient release by soil amended with black soldier fly frass fertilizer. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basri, N.E.A.; Azman, N.A.; Ahmad, I.K.; Suja, F.; Jalil, N.A.A.; Amrul, N.F. Potential applications of frass derived from black soldier fly larvae treatment of food waste: A review. Foods 2022, 11, 2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hénault-Ethier, L.; Quinche, M.; Reid, B.; Hotte, N.; Fortin, A.; Normandin, É.; de La Rochelle Renaud, G.; Zadeh, A.R.; Deschamps, M.-H.; Vandenberg, G. Opportunities and challenges in upcycling agri-food byproducts to generate insect manure (frass): A literature review. Waste Manag. 2024, 176, 169–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beesigamukama, D.; Subramanian, S.; Tanga, C.M. Nutrient quality and maturity status of frass fertilizer from nine edible insects. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 7182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surendra, K.; Tomberlin, J.K.; van Huis, A.; Cammack, J.A.; Heckmann, L.-H.L.; Khanal, S.K. Rethinking organic wastes bioconversion: Evaluating the potential of the black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens (L.)) (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) (BSF). Waste Manag. 2020, 117, 58–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houben, D.; Daoulas, G.; Faucon, M.-P.; Dulaurent, A.-M. Potential use of mealworm frass as a fertilizer: Impact on crop growth and soil properties. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez, M.; Uchanski, M. Insect left-over substrate as plant fertiliser. J. Insects Food Feed. 2021, 7, 683–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oonincx, D.G.; De Boer, I.J. Environmental impact of the production of mealworms as a protein source for humans—A life cycle assessment. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smetana, S.; Schmitt, E.; Mathys, A. Sustainable use of Hermetia illucens insect biomass for feed and food: Attributional and consequential life cycle assessment. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 144, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, E.; de Vries, W. Potential benefits of using Hermetia illucens frass as a soil amendment on food production and for environmental impact reduction. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2020, 25, 100335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armson, K.A.; Sadreika, V. Forest Tree Nursery Soil Management and Related Practices; Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources: Toronto, ON, Canada, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Mexal, J.G.; South, D.B. Bareroot Seedling Culture. In Forest Regeneration Manual; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1991; pp. 89–115. [Google Scholar]
- Grossnickle, S.C. Ecophysiology of Northern Spruce Species. The Performance of Planted Seedlings; NRC ResearchPress: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, B.E. Seedling morphological evaluation: What You Can Tell by Looking. In Evaluating Seedling Quality: Principles, Procedures, and Predictive Abilities of Major Tests; Forest Research Laboratory, Oregon State University: Corvallis, OR, USA, 1985; pp. 59–72. [Google Scholar]
- Grossnickle, S.C. Importance of root growth in overcoming planting stress. New For. 2005, 30, 273–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| C (%) | N Total (%) | C/N Ratio | P Total (%) | K (%) | Ca (%) | Na (%) | Mg (%) | Mn (mg/kg) | Cu (mg/kg) | Fe (mg/kg) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 39.7 | 3 | 13.2 | 3.09 | 0.36 | 0.063 | 0.02 | 5.04 | 180.8 | 48.6 | 2563.8 | 7.88 |
| Treatment | BSFF Half-Fold | One-Fold BSFF | BSFF Two-Fold | Cattle Manure | NPK | Control |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N input (g) | 0.325 | 0.65 | 1.3 | 0.65 | 0.65 | 0 |
| Volume of fertilizer (l) | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.12 | 0.27 | 0.01 | 0 |
| Volume of sand (l) | 0.38 | 0.37 | 0.34 | 0.27 | 0.40 | 0.4 |
| Volume of soil (l) | 0.38 | 0.37 | 0.34 | 0.27 | 0.40 | 0.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Solofondranohatra, C.L.; Ramiadantsoa, T.; Hugel, S.; Fisher, B.L. Black Soldier Fly Frass Fertilizer Outperforms Traditional Fertilizers in Terms of Plant Growth in Restoration in Madagascar. Sustainability 2025, 17, 7152. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17157152
Solofondranohatra CL, Ramiadantsoa T, Hugel S, Fisher BL. Black Soldier Fly Frass Fertilizer Outperforms Traditional Fertilizers in Terms of Plant Growth in Restoration in Madagascar. Sustainability. 2025; 17(15):7152. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17157152
Chicago/Turabian StyleSolofondranohatra, Cédrique L., Tanjona Ramiadantsoa, Sylvain Hugel, and Brian L. Fisher. 2025. "Black Soldier Fly Frass Fertilizer Outperforms Traditional Fertilizers in Terms of Plant Growth in Restoration in Madagascar" Sustainability 17, no. 15: 7152. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17157152
APA StyleSolofondranohatra, C. L., Ramiadantsoa, T., Hugel, S., & Fisher, B. L. (2025). Black Soldier Fly Frass Fertilizer Outperforms Traditional Fertilizers in Terms of Plant Growth in Restoration in Madagascar. Sustainability, 17(15), 7152. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17157152






