Sustainable Soil Management in Reservoir Riparian Zones: Impacts of Long-Term Water Level Fluctuations on Aggregate Stability and Land Degradation in Southwestern China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area Overview
2.2. Sample Collection and Pretreatment
2.3. Measurement Indicators and Methods
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Soil Physicochemical Properties
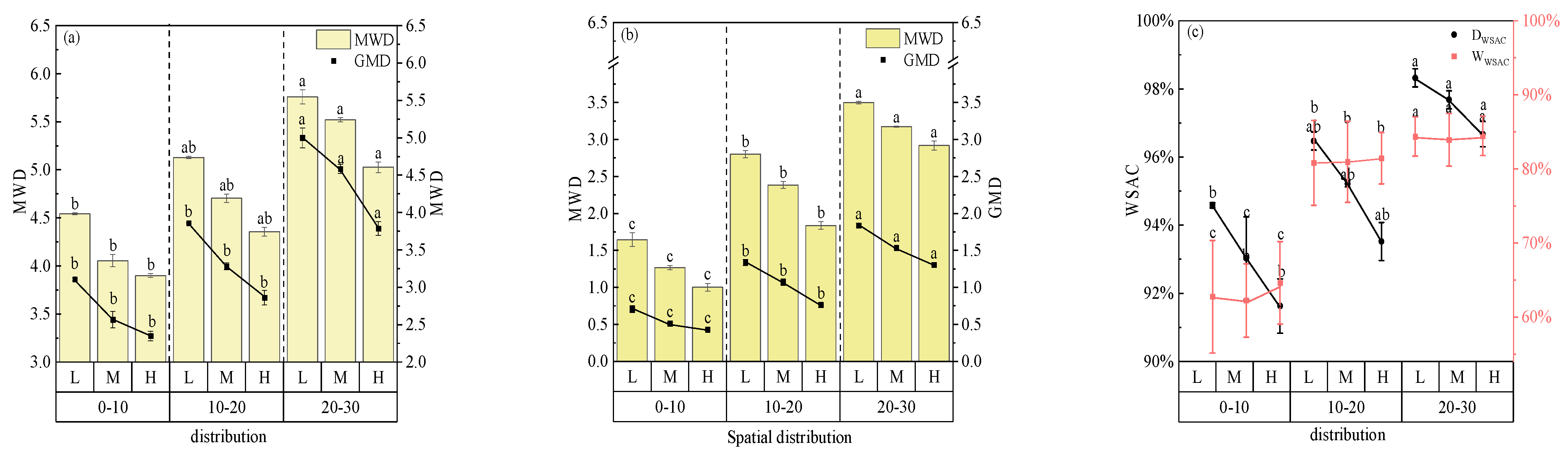
3.2. Distributed Along the Elevationof Soil Aggregate Particle Size Using Dry and Wet Sieving Method
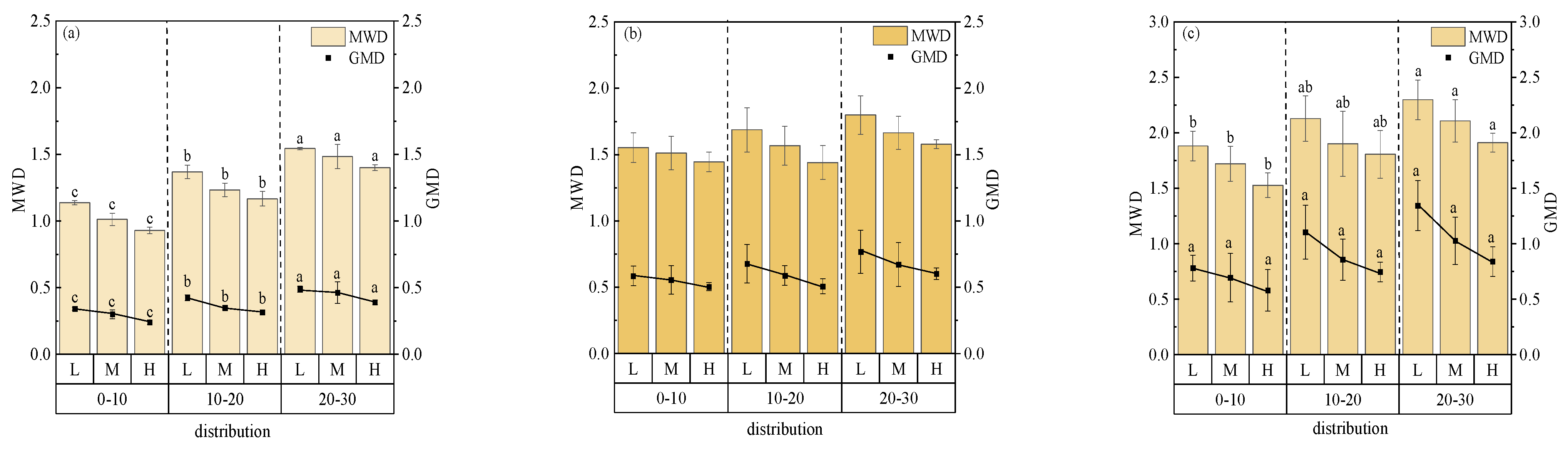
3.3. Determination of the Elevation Distribution of Aggregate Grain Size via the Le Bissonnais Method
3.4. Determination of Aggregate Stability via Dry and Wet Sieving Methods
3.5. Determination of Soil Aggregate Stability via the Le Bissonnais Method
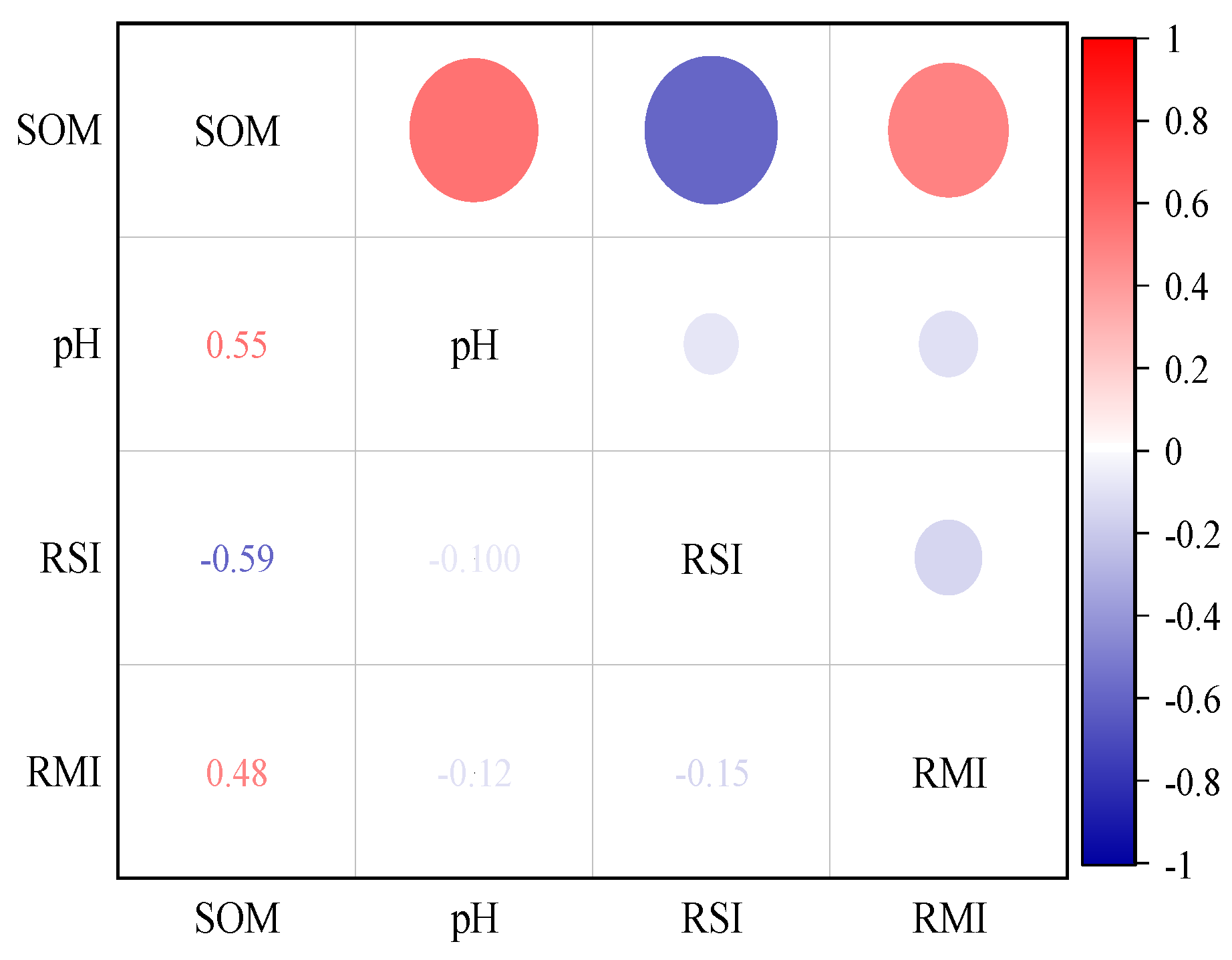
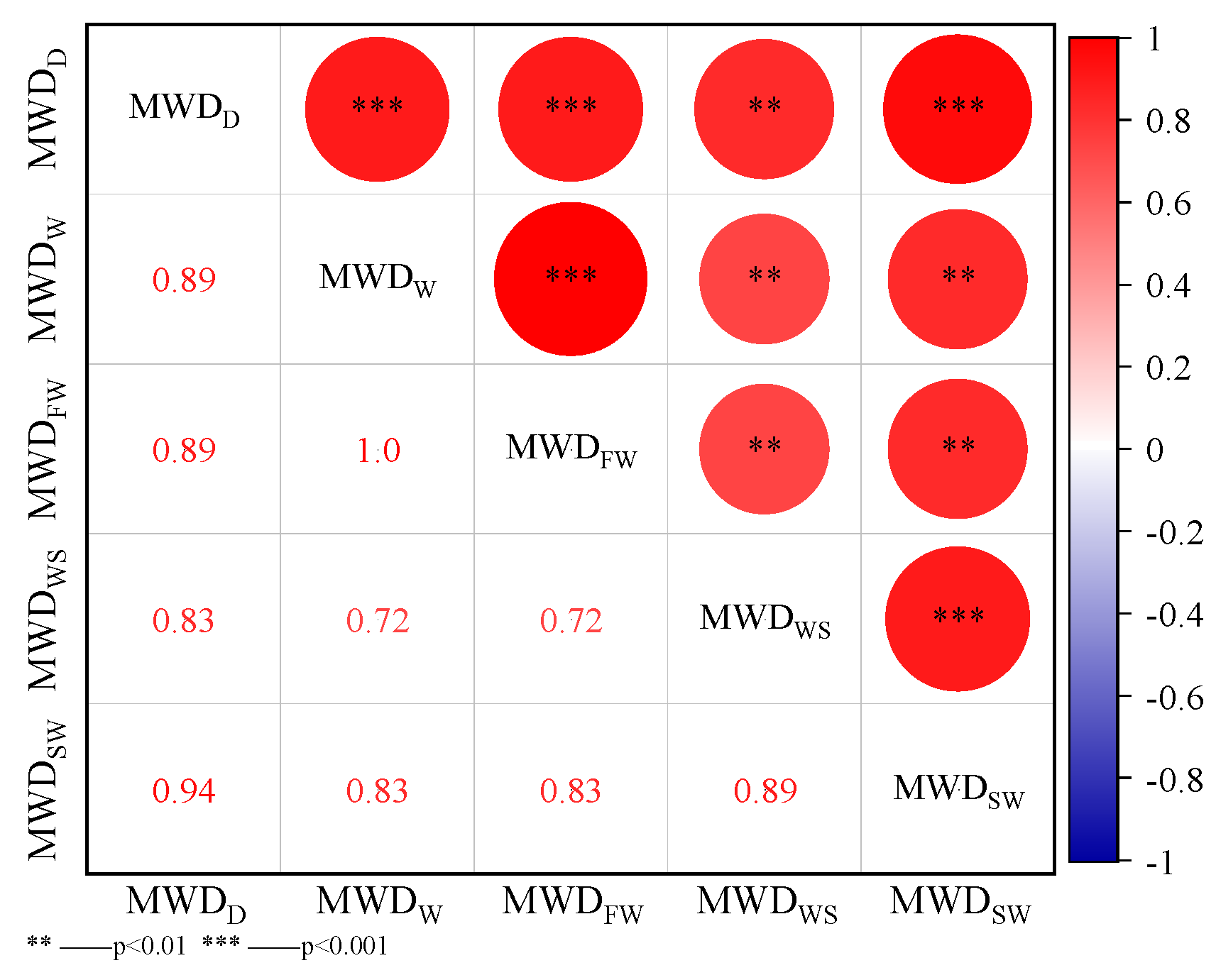
3.6. Correlation Analysis Between the Stability of the Soil Aggregates and Their Contents and Soil Physicochemical Properties Determined via the Five Methods
4. Discussion
4.1. Response of Soil Aggregate Composition to Changes in Water Level
4.2. Comparison of Test Methods for Stability of Soil Aggregates
4.3. Response of Aggregate Fragmentation Indicators to Changes in the Water Table and Soil Stratigraphy
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qin, D.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, D.; Liao, P.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J. Spatial variation of soil phosphorus in the water level fluctuation zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir: Coupling effects of elevation and artificial restoration. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 167000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Sun, R.; Chen, L.; Sun, T. Sensitive indicators of soil nutrients from reservoir effects in the hot-dry valleys of China. Catena 2022, 216, 106421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Mao, C.; Wang, S.; Jia, Z.; Rao, W. Seasonal variation and provenance of organic matter in the surface sediments of the three gorges reservoir: Stable isotope analysis and implications for agricultural management. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 870, 161886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, B.; Xu, X.; Sun, Z.; Zhuo, H.; Yuan, L.; Zhou, Z. Research on partition of phosphorus in the Three Gorges Reservoir on the Yangtze River. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 168442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, Y.; He, X.; Wen, A.; Gao, P.; Tang, Q.; Yan, D.; Long, Y. Dynamic changes of soil erosion in a typical disturbance zone of China’s Three Gorges Reservoir. Catena 2018, 169, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Y.; Wu, S.; Chen, C.; Sun, X.; Huang, P.; Ma, M.; Yi, X. Shift from soil chemical to physical filters in assembling riparian floristic communities along a flooding stress gradient. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 844, 157116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Y.; Ma, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, K.; Yi, X.; Wang, X.; Huang, P. Physicochemical determinants in stabilizing soil aggregates along a hydrological stress gradient on reservoir riparian habitats: Implications to soil restoration. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 143, 105664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nsabimana, G.; Bao, Y.; He, X.; de Dieu Nambajimana, J.; Yang, L.; Li, J.; Ntacyabukura, T. Soil aggregate stability response to hydraulic conditions in water level fluctuation zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Catena 2021, 204, 105387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowdeswell-Downey, E.; Grabowski, R.C.; Rickson, R.J. Do temperature and moisture conditions impact soil microbiology and aggregate stability? J. Soil Sediments 2023, 23, 3706–3719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Wei, X.; Zhu, H.; Fu, W.; Shao, M. Responses of soil aggregate stability, erodibility and nutrient enrichment to simulated extreme heavy rainfall. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 709, 136150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amézketa, E. Soil aggregate stability: A review. J. Sustain. Agric. 1999, 14, 83–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Wang, S.; Gao, Z.; Pan, H.; Zhuge, Y.; Ren, X.; Li, C. Aggregate stability and organic carbon stock under different land uses integrally regulated by binding agents and chemical properties in saline-sodic soils. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 4151–4161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekaran, U.; Sagar, K.L.; Kumar, S. Soil aggregates, aggregate-associated carbon and nitrogen, and water retention as influenced by short and long-term no-till systems. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 208, 104885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Qi, J.Y.; Zhang, X.Z.; Li, S.S.; Virk, A.L.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, H.L. Effects of tillage and residue management on soil aggregates and associated carbon storage in a double paddy cropping system. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 194, 104339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Jiang, X.; Ji, X.; Zhou, L.; Li, S.; Chen, C.; Meng, Q. Distribution of water-stable aggregates under soil tillage practices in a black soil hillslope cropland in Northeast China. J. Soil Sediments 2020, 20, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Deng, Y.; Li, D.; Liu, Z.; Wen, L.; Huang, Z.; Lu, Y. Soil aggregate stability and its response to overland flow in successive Eucalyptus plantations in subtropical China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 151000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Xia, Z.; Yang, Y.; Liu, D.; Xiang, R.; Ding, Y.; Xiao, H. Spatial and temporal evolution and factors influencing soil aggregate stability in the riparian zone during exposure: A case study of the water-level fluctuation zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 957, 177408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, R.; Shi, D.; Ni, S.; Wang, R.; Zhang, J.; Song, G. Effects of soil erosion and soil amendment on soil aggregate stability in the cultivated-layer of sloping farmland in the Three Gorges Reservoir area. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 223, 105447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nsabimana, G.; Hong, L.; Yuhai, B.; de Dieu Nambajimana, J.; Jinlin, L.; Ntacyabukura, T.; Xiubin, H. Soil aggregate disintegration effects on soil erodibility in the water level fluctuation zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Environ. Res. 2023, 217, 114928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.S.; Jiang, N.H.; Zhang, L.D.; Liu, Z.L. Soil Physical and Chemical Analysis and Description of Soil Profiles; China Standard Methods Press: Beijing, China, 1996; pp. 24–266. [Google Scholar]
- Le Bissonnais, Y.L. Aggregate stability and assessment of soil crustability and erodibility: I. Theory and methodology. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 1996, 47, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Horn, R. Mechanisms of aggregate stabilization in Ultisols from subtropical China. Geoderma 2001, 99, 123–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Shrestha, B.M. Stand age, fire and clearcutting affect soil organic carbon and aggregation of mineral soils in boreal forests. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 50, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auerswald, K. Percolation stability of aggregates from arable topsoils. Soil Sci. 1995, 159, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ma, M.; Wu, S.; Ran, Y.; Wang, X.; Huang, P. Soil aggregates as effected by wetting-drying cycle: A review. Soils 2018, 50, 853–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, N.; Ren-tian, M.A.; Tai-ji, K.O.; Nian-yuan, J.I.O. Effects of peanut/maize ridge intercropping and phosphorus application on soil aggregate stability assessed by different methods. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2024, 30, 2053–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Liu, Y.; Liu, C.; Li, Z.; Gu, C.; Xie, J.; Chen, F. Study on the Stability and Fractal Characteristics of Soil Aggregates Under Different Land Use Patterns in the Danjiangkou Reservoir. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2016, 30, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Dong, Y.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, L.; An, S. Soil aggregate stability and erodibility under forest vegetation in the Loess Plateau using the Le Bissonnais method. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2014, 22, 1093–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, N.; Shao, Y.; Luo, M.; Meng, D.; Xu, D.; Liu, Z.; Ma, L. Effects of soil aggregate preparation methods on the stability and carbon sequestration potential evaluation. China Environ. Sci. 2022, 42, 2821–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, E.T. Aggregate structure and carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in native and cultivated soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1986, 50, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, E.; Han, M.; Li, Y.; Yu, S. Organic materials effects on black soil aggregate stability based on the Le Bissonnais method. J. Nanjing For. Univ. 2023, 47, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algayer, B.; Wang, B.; Bourennane, H.; Zheng, F.; Duval, O.; Li, G.; Darboux, F. Aggregate stability of a crusted soil: Differences between crust and sub-crust material, and consequences for interrill erodibility assessment. An example from the Loess Plateau of China. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2014, 65, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.H.; Yan, F.L.; Li, L.; Li, Z.X.; Cai, C.F. Interrill erosion from disturbed and undisturbed samples in relation to topsoil aggregate stability in red soils from subtropical China. Catena 2010, 81, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.L.; Shi, Z.H.; Li, Z.X.; Cai, C.F. Estimating interrill soil erosion from aggregate stability of Ultisols in subtropical China. Soil Tillage Res. 2008, 100, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Fang, N.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Yang, D.; Dai, W.; Shi, Z. Dynamics of soil organic carbon in different-sized aggregates under splash erosion. J. Soil Sediments 2022, 22, 1713–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puget, P.; Chenu, C.; Balesdent, J. Total and young organic matter distributions in aggregates of silty cultivated soils. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 1995, 46, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bissonnais, Y.; Arrouays, D. Aggregate stability and assessment of soil crustability and erodibility: II. Application to humic loamy soils with various organic carbon contents. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 1997, 48, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jozefaciuk, G.; Czachor, H. Impact of organic matter, iron oxides, alumina, silica and drying on mechanical and water stability of artificial soil aggregates. Assessment of new method to study water stability. Geoderma 2014, 221–222, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Gao, X.; Wang, R.; Du, L.; Hou, F.; He, Y.; Guo, S. Soil redistribution reduces integrated C sequestration in soil-plant ecosystems: Evidence from a five-year topsoil removal and addition experiment. Geoderma 2020, 377, 114593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halder, M.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Z.B.; Guo, Z.C.; Peng, X.H. Effects of residue stoichiometric, biochemical and C functional features on soil aggregation during decomposition of eleven organic residues. Catena 2021, 202, 105288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kaisi, M.M.; Douelle, A.; Kwaw-Mensah, D. Soil microaggregate and macroaggregate decay over time and soil carbon change as influenced by different tillage systems. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2014, 69, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Location | Geographical Position | Elevation Gradient | Elevation Gradient Range | Number of Samples |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ertan | N 26°48′39″, E 101°43′36″ | L | 1150.579~1155.963 m | 131 |
| M | 1155.963~1159.279 m | 144 | ||
| H | 1159.279~1163.424 m | 134 |
| Elevation Gradient | Depth/cm | Sand (%) | Silt (%) | Clay (%) | Soil Organic Matter (g/kg) | pH | Texture Class |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L | 0~10 | 4.83 | 62.70 | 32.47 | 15.24 ± 1.02 B | 7.62 ± 0.26 B | Silty clay loam |
| 10~20 | 4.86 | 61.17 | 33.98 | 14.14 ± 2.26 B | 7.79 ± 0.14 B | Silty clay loam | |
| 20~30 | 4.76 | 59.34 | 35.90 | 13.5 ± 1.03 B | 7.76 ± 0.19 B | Silty clay loam | |
| M | 0–10 | 3.84 | 51.47 | 44.69 | 16.2 ± 0.93 B | 6.96 ± 2.04 C | Silty clay |
| 10~20 | 4.43 | 55.96 | 39.61 | 15.36 ± 1.39 B | 6.85 ± 2 C | Silty clay loam | |
| 20~30 | 4.32 | 57.09 | 38.59 | 13.22 ± 2.93 B | 6.76 ± 1.67 C | Silty clay loam | |
| H | 0–10 | 2.24 | 41.38 | 56.38 | 16.02 ± 2.23 A | 8.2 ± 0.25 A | Silty clay |
| 10~20 | 3.37 | 48.98 | 47.45 | 15.83 ± 1.14 A | 8.16 ± 0.33 A | Silty clay | |
| 20~30 | 3.38 | 50.026 | 46.60 | 15.26 ± 2.21 A | 7.94 ± 0.26 A | Silty clay |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, P.; Song, Z.; Xiao, H.; Tao, G. Sustainable Soil Management in Reservoir Riparian Zones: Impacts of Long-Term Water Level Fluctuations on Aggregate Stability and Land Degradation in Southwestern China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 7141. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17157141
Wang P, Song Z, Xiao H, Tao G. Sustainable Soil Management in Reservoir Riparian Zones: Impacts of Long-Term Water Level Fluctuations on Aggregate Stability and Land Degradation in Southwestern China. Sustainability. 2025; 17(15):7141. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17157141
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Pengcheng, Zexi Song, Henglin Xiao, and Gaoliang Tao. 2025. "Sustainable Soil Management in Reservoir Riparian Zones: Impacts of Long-Term Water Level Fluctuations on Aggregate Stability and Land Degradation in Southwestern China" Sustainability 17, no. 15: 7141. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17157141
APA StyleWang, P., Song, Z., Xiao, H., & Tao, G. (2025). Sustainable Soil Management in Reservoir Riparian Zones: Impacts of Long-Term Water Level Fluctuations on Aggregate Stability and Land Degradation in Southwestern China. Sustainability, 17(15), 7141. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17157141







