Abstract
Under the current context of the large-scale integration of wind and solar power, the coupling of hydropower with wind and solar energy brings significant impacts on grid stability. To fully leverage the regulatory capacity of hydropower, this paper develops a multi-objective optimization scheduling model for hydropower, wind, and solar that balances generation-side power generation benefit and grid-side peak-regulation requirements, with the latter quantified by the mean square error of the residual load. To efficiently solve this model, Latin hypercube initialization, hybrid distance framework, and adaptive mutation mechanism are introduced into the Strength Pareto Evolutionary Algorithm II (SPEAII), yielding an improved algorithm named LHS-Mutate Strength Pareto Evolutionary Algorithm II (LMSPEAII). Its efficiency is validated on benchmark test functions and a reservoir model. Typical extreme scenarios—months with strong wind and solar in the dry season and months with weak wind and solar in the flood season—are selected to derive scheduling strategies and to further verify the effectiveness of the proposed model and algorithm. Finally, K-medoids clustering is applied to the Pareto front solutions; from the perspective of representative solutions, this reveals the evolutionary trends of different objective trade-off schemes and overall distribution characteristics, providing deeper insight into the solution set’s distribution features.
1. Introduction
Global climate change, ecological degradation, and energy resource scarcity profoundly affect the survival and development of human society [1]. The world has reached a consensus on reducing fossil energy consumption and vigorously developing clean energy; increasing the share of safe, green, and reliable low-carbon energy has become the trend and direction of global energy development [2]. To achieve the dual-carbon goals (carbon peaking and carbon neutrality), China is accelerating adjustments to its energy structure and promoting a green, low-carbon energy transition [3]. In this context, alongside the vigorous development of renewable energies, such as hydropower, wind, and solar, nuclear power has also been prioritized as a stable baseload source [4]. As of the end of the first quarter of 2025, China’s nuclear installed capacity has exceeded 55 GW, playing a critical role in ensuring grid stability and meeting peak-regulation requirements.
Therefore, in the forthcoming development phase, it is imperative to vigorously develop renewable energies, such as hydropower, wind, and solar, to continuously promote a high proportion of clean energy, to drive sustained growth in renewable energy development, to focus on reducing fossil energy exploitation and utilization, and to gradually realize both the incremental and stock replacement of energy in China [5,6]. As of the end of 2024, China had constructed more than 94,000 dams of various types, including 29 mega hydropower stations each with installed capacity exceeding one million kilowatts, all ranking first in the world. Specifically, by the end of the first quarter of 2025, China’s grid-connected installed capacity of wind and solar power reached 1480 million kilowatts, historically surpassing the installed capacity of thermal power, with wind power at 536 million kilowatts and photovoltaic power at 946 million kilowatts.
In the context of the large-scale integration of wind and solar power, as hydropower becomes coupled with these renewable sources, it must frequently adjust its output in response to wind and solar generation fluctuations, rendering the traditional independent operation modes of “water-determined power” and “power-determined water” no longer applicable [7,8]. Therefore, how to account for the impact of large-scale renewable energy integration on hydropower scheduling and to effectively balance the power system’s renewable energy absorption requirements with multi-energy comprehensive benefit realization represents a research hotspot and challenge in the field of hydropower optimal scheduling [9]. Wen et al. [10] addressed the capacity and operation optimization problem for cascade hydropower stations with high levels of wind and solar integration by proposing a multi-scale nested joint operation model, which—under consideration of wind and solar forecast uncertainty—ensures long-term generation benefits while enhancing short-term supply reliability. Wang et al. [11] proposed a long-term scheduling decision model driven by forecasts to tackle the challenges posed by wind and solar fluctuations and hydropower resource utilization decisions in long-term operation, thereby improving hydropower’s response capability to renewable uncertainty and optimizing the overall system economy. Jin et al. [12], focusing on cascade hydropower operation strategies under varying wind and photovoltaic penetration levels, proposed typical-day aggregation and hybrid planning optimization schemes that effectively perform peak shaving and valley filling and reduce hydropower output fluctuations under different penetration scenarios. Angarita et al. [13] proposed a stochastic optimization method to address wind-power output forecasting uncertainty, aiming to maximize the combined generation benefit of hydropower and wind power.
In order to maximize the comprehensive benefits of hydropower station operation management, it is necessary to comprehensively coordinate all parties’ requirements during scheduling. On the water-use side, hydropower scheduling should fully consider integrated basin water-resource regulation to meet differentiated demands across various temporal and spatial scales and types, such as flood control [14], water supply [15], power generation [16], navigation [17], and ecological protection [18]; on the electricity-use side, hydropower scheduling should exploit its flexibility to smooth generation–load fluctuations and to satisfy various electricity and energy demands, such as peak shaving and frequency regulation [19], and power supply with energy storage [20]. Therefore, hydropower station scheduling is essentially a complex multi-objective optimization problem, and common solution methods mainly include the weighting method [21] and multi-objective optimization algorithms [22]. The weighting method assigns weights to objectives based on their relative importance, aggregates them to convert the multi-objective problem into a single-objective, and then applies single-objective solution techniques. Salazar et al. [23] addressed multiple objectives in a hydropower network under different hydrological conditions—maximizing annual power generation while minimizing unit water consumption per generation—by proposing a nonlinear multi-objective optimization model and using the weighting method to combine generation and water-use efficiency objectives into a single objective. Jia et al. [24] proposed a multi-objective optimization model for inter-regional reservoir scheduling to balance interests among water supply, power generation, and ecological releases, and applied the weighting method to aggregate multiple objectives. This approach of converting a multi-objective problem into a single-objective one via weighting has the advantages of computational simplicity and intuitive results [25]; however, it requires setting objective weights in advance, which involves subjectivity, and yields only a single solution, failing to satisfy the decision-makers’ needs for different preferences [26].
Compared with the weighting method, intelligent optimization algorithms offer stronger global search capabilities and can obtain a Pareto-optimal solution set that fully reflects multi-objective conflicts, thereby providing decision-makers with diverse alternatives aligned with different preference structures [27]. Consequently, the use of multi-objective optimization algorithms to solve complex reservoir scheduling problems has attracted widespread attention in both domestic and international research. However, under the new context of multi-energy complementary scheduling—characterized by multidimensional temporal and spatial scales, multiple scheduling stakeholders, and heterogeneous regulation capabilities across power stations—traditional optimization algorithms struggle to effectively handle the complex coupled constraints inherent in multi-energy scheduling problems [28]. Therefore, numerous scholars have continuously enhanced classical algorithms to meet practical problem-solving needs and to achieve higher solution efficiency and accuracy. For example, Hu et al. [29] addressed the long-term cascade hydropower scheduling problem with multi-objective generation and ecological flow requirements by proposing an adaptive multi-objective particle swarm optimization algorithm based on decomposition and dominance mechanisms, which improves both the diversity and convergence of the solution set. Yazdi and Moridi [30] tackled the multi-objective design-parameter optimization problem for cascade reservoir systems by introducing a non-dominated sorting differential evolution algorithm, achieving an effective Pareto front search under multiple objectives while reducing computational cost. Hooshyar et al. [31] addressed the challenge of an excessively large decision space in multi-reservoir optimal dispatch by proposing a multi-agent reinforcement learning approach that integrates an aggregation/decomposition (AD-RL) strategy, thereby mitigating high computational complexity and slow convergence issues. Azizipour et al. [32] targeted the shortcomings of conventional and evolutionary methods—namely their tendency to become trapped in local optima and to exhibit low efficiency—in multi-reservoir system optimization by introducing a hybrid cellular automata–simulated annealing (CA-SA) method, which enhances convergence speed and solution quality.
The existing multi-energy coordination models often focus exclusively on either the generation side’s output capability or the grid side’s load fluctuations, and such one-sided perspectives struggle to balance multiple objectives, like generation benefit and grid peak-regulation absorption [33,34]. Accordingly, this study proposes an optimal scheduling model for hydropower–wind–solar complementarity with dual objectives: maximizing the total generation of the hydropower–wind–solar system and minimizing the mean square error of the residual load on the grid. To solve this model efficiently, we introduce the LMSPEAII algorithm, which integrates multiple improvement strategies into SPEAII. Finally, K-medoids clustering is applied to the large Pareto-optimal solution set to extract representative solutions for systematic analysis, from which this study’s conclusions are drawn.
2. Hydropower–Wind–Solar Multi-Objective Scheduling Model Balancing Both Generation- and Grid-Side Demands
Constructing a hydropower–wind–solar multi-objective optimization scheduling model that balances generation-side benefits and grid-side peak-regulation requirements is of great significance for improving energy utilization efficiency, for ensuring safe and stable grid operation, and for promoting clean energy integration. In this section, we formulate a scheduling model that maximizes the total system generation and minimizes the mean square error of the residual load, using daily intervals for dispatch and a monthly cycle. The model comprehensively considers the output characteristics of hydropower, wind, and solar PV as well as demand-side variations, thereby achieving optimized allocation and efficient utilization of these energy sources.
2.1. Wind and Solar Power Output Calculation
The wind speed, light intensity, and temperature data used in this paper are all sourced from the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF). The calculation methods for wind power output and photovoltaic power output are shown in Equations (1) and (2).
- (1)
- The wind power output calculation is as follows [35]:
- (2)
- The solar power output calculation is as follows [36]:
The temperature of solar panels is not only related to air temperature but to the performance and irradiance of solar cells, which is calculated as follows:
where is the PV cell’s nominal operating temperature, defined as the cell temperature under external conditions of irradiance 800 W/m2, ambient temperature 20 °C, and wind speed 1 m/s; is the irradiance on the solar panel, in W/m2; and can be approximated as the increase in panel temperature caused by photothermal conversion due to solar irradiance.
2.2. Objective Function
- (1)
- Hydropower station side: Maximizing the total power generation.
By employing precise mathematical models and advanced optimization algorithms, the complementary effects among hydropower, wind, and solar energy are deeply explored to maximize power generation. Achieving this objective not only signifies an improvement in energy utilization efficiency but represents a crucial step in driving the energy structure toward low-carbon and sustainable transformation [37,38]. Moreover, research on maximizing generation plays a significant role in promoting innovation and development of clean energy technologies. This is calculated as follows:
where is the total generation of the complementary system, and is the generation profile of the complementary system; is the total output in period t, where and denote the outputs of the wind power plant and photovoltaic plant, respectively, in the same period; is the hydropower station’s output in period ; T is the total number of time intervals in the scheduling horizon; and t is a scheduling interval, measured in hours.
- (2)
- Power grid side: Minimizing the mean square error of the residual load.
Given the inherent intermittency and uncertainty of wind and solar power generation, the achievement of peak-regulation objectives depends heavily on the flexible adjustment capabilities of hydropower units. Peak-regulation studies aim to balance the volatility of renewable generation, to ensure the stability of the total system output, and thereby to reduce the potential threats of renewable integration to grid security. Under the dual challenges of load fluctuations and renewable integration, optimizing peak-regulation strategies can significantly enhance the adaptive capability of the power system, ensuring its safe and stable operation in complex and dynamic operating environments [39,40]. This is calculated as follows:
where is the mean square error of the residual load after supply by the hydropower–wind–solar multi-energy complementary system; is the grid load demand; is the residual load after supply by the hydropower–wind–solar multi-energy complementary system; and is the mean of the residual load.
2.3. Constraints
- (1)
- The water level constraints are calculated as follows:
- (2)
- Water volume balance constraints are calculated as follows:
- (3)
- Reservoir characteristic constraints are calculated as follows:
- (4)
- Output characteristic constraints are calculated as follows:
- (5)
- Generation flow constraints are calculated as follows:
- (6)
- Water level fluctuation constraints are calculated as follows:
- (7)
- Power station output constraints are calculated as follows:
3. Efficient Model Solving Based on Improved Strength Pareto Algorithm
To efficiently solve the reservoir optimization scheduling problem and to deeply reveal the trade-off between generation-side output and grid-side mean square error of residual load, this paper proposes an improved algorithm LMSPEAII based on the Strength Pareto Evolutionary Algorithm II (SPEAII). When applied to reservoir scheduling, SPEAII and other mainstream multi-objective evolutionary algorithms often exhibit slow convergence, insufficient solution set diversity, and susceptibility to local optima. The improved algorithm introduces strategies, such as Latin hypercube initialization [41], hybrid distance framework, and adaptive mutation mechanism, effectively enhancing both global exploration and local exploitation capabilities. Consequently, the obtained solutions display broader coverage and more fully characterize the trade-off between generation-side output and grid-side mean square error of the residual load. In the context of reservoir scheduling, this not only significantly improves the optimization efficiency of scheduling strategies but provides richer and more diverse candidate solutions for achieving the dual objectives of economic performance and system stability, thereby offering more robust theoretical support and technical assurance for practical engineering decision-making.
3.1. Principle of Standard SPEA II Algorithm
- (1)
- Initializing
The initialization phase of SPEAII is similar to that of most evolutionary algorithms: the population of size N is generated via random sampling, and simultaneously generate an empty archive set . For each individual and for each decision-variable dimension, sampling is performed according to the following formula:
where denotes the generated position, and are the lower and upper bounds of that decision variable, and is a random number drawn from [0, 1].
- (2)
- Fitness assignment
The current population and the archive are merged into the union set . First, a fitness value is assigned to each individual in the union set . The fitness is obtained by adding the individual’s raw fitness value and its density estimation value . The raw fitness itself is obtained by accumulating the individual’s strength values . The calculation formulas for each part are as follows:
where denotes the strength value of individual , representing the number of other individuals in the union set that it dominates; denotes the total number of individuals in the union set.
where is the density estimation value of individual ; is the distance between individual and its nearest neighbor in the objective space; is the number of objectives (i.e., the dimensionality of the objective space); and denotes the value of individual on the objective.
The final fitness value of individual is calculated as follows:
- (3)
- Environment selection and truncation operations
All individuals in the union set R with a fitness value less than 1 are selected for retention,. If the number of individuals with fitness less than 1 exceeds the archive size threshold , a truncation operation is performed to reduce the number to the archive limit. The truncation process begins by applying min–max normalization to each objective dimension in the current archive to eliminate the influence of differing units across objectives. The normalization is performed as follows:
where denotes the normalized value of individual on the objective; and represent the minimum and maximum values of the objective among all individuals, respectively.
Then, in the normalized objective space, the Euclidean distance between individuals is calculated using Equation (21). For each individual iii, its distances to all other individuals are sorted in ascending order as . When the number of nondominated individuals (i.e., individuals with fitness < 1) exceeds the archive capacity, the truncation process is repeatedly performed as follows: identify the individual with the smallest, first nearest-neighbor distance , the most crowded individual—remove it from the archive, and then update the distance matrix and re-sort distances until the number of individuals equals the archive threshold. This is calculated as follows:
where and are the normalized values of individuals and on the objective, respectively.
- (4)
- Genetic operation stage
Individuals are selected from the current population and the external archive using tournament selection to serve as parents for Simulated Binary Crossover (SBX). The selected parent individuals are then split randomly and uniformly into two groups, and , to facilitate the crossover operation. The offspring generated through crossover will subsequently undergo mutation. The detailed steps for each phase are as follows:
- (1)
- Crossover Phase: A random number between 0 and 1 is generated to determine whether SBX crossover occurs, based on the crossover probability . If crossover is to occur, the crossover distribution factor is calculated using the following formula:
Furthermore, the computed is used to generate offspring according to the following operations:
where is a random integer taking the value of either 0 or 1; the sign of determines the direction of crossover, which is randomized. This allows the offspring to be generated on either side of the parent solutions, thereby enhancing population diversity.
Furthermore, the crossover factor is adjusted as follows: a random number between 0 and 1 is generated. If the number is greater than 0.5, then ; otherwise, . This ensures that the computed crossover factor has a 50% chance of being set to 1. The two offspring are then generated as linear combinations of the parent genes, with the crossover factor determining the contribution ratio from each parent. The offspring are computed as follows:
where and are the genes of the parent individuals, and are the offspring generated through the crossover operation.
- (2)
- Mutation Phase: The offspring and generated in the crossover phase are combined into a matrix . Whether each offspring undergoes mutation is determined by comparing a randomly generated number between 0 and 1 to the mutation probability . Here, denotes the number of decision variables. The mutation degree for each individual is controlled by the mutation step size, which is calculated using the polynomial mutation formula as follows:
After calculating the mutation step size, the offspring and undergo mutation according to the following formula:
where denotes the gene of a certain offspring before mutation, and denotes the corresponding gene of that offspring after mutation.
3.2. Improvement Strategy
- (1)
- Latin hypercube initialization
Random sampling often leads to sample clustering in certain regions, thereby weakening the algorithm’s global exploration capability. To address this, the improved algorithm employs Latin hypercube sampling (LHS) for initialization and incorporates a maximin criterion to adjust sample point positions. LHS works by dividing the range of each decision variable into N equally spaced intervals, and then randomly selecting one point from each interval without repetition. This ensures a more uniform and comprehensive distribution of sample points across the entire search space. The initialization formula for Latin hypercube sampling is given by the following equations:
where represents the value of the individual at the d decision variable; and are the lower and upper bounds of the decision variable, respectively; is a random number drawn from the interval [0, 1], introducing randomness within each subinterval; is the length of each subinterval. The k subinterval has endpoints , and is an index generated by a random permutation of , ensuring that each index appears only once in each dimension.
- (2)
- Hybrid distance architecture
In calculating the crowding degree between individuals, a Euclidean–Cosine hybrid distance framework is adopted to replace the traditional single Euclidean distance, as shown in Equation (34). This hybrid framework not only maintains the dispersion of absolute differences between solutions but effectively captures their directional diversity in the objective space. As a result, it improves the convergence and distribution uniformity of the Pareto front simultaneously [42]. Moreover, since both Euclidean distance and cosine distance have a computational complexity of , the additional cost introduced by their linear combination is negligible. This is calculated as follows:
where is the normalized value of individual on the target, and are the normalized Euclidean and Cosine distances, is the new distance calculation formula between individuals, and is the weight parameter.
The weight parameter is determined based on the relative proportion of the variances of the normalized Euclidean distance and cosine distance. A larger variance indicates that the corresponding distance metric exhibits a more dispersed numerical distribution within the current population, and thus has a stronger ability to distinguish the crowding characteristics of individuals. Therefore, the weight assignment is variance-based, emphasizing the more discriminative metric to improve the selection effectiveness. The specific calculation is as follows:
where and represent the variances of the normalized Euclidean distance and cosine distance, respectively.
- (3)
- Adaptive mutation mechanism
In the original SPEAII algorithm, both the crossover probability and mutation probability are set to a fixed value of 1. This results in all parent individuals undergoing crossover and all offspring undergoing mutation. In the early stages of the algorithm, when population diversity is high, such large probabilities help rapidly explore the solution space and facilitate the combination of superior genes. However, as the evolution progresses and the population begins to converge, overly high crossover and mutation rates may disrupt high-quality genetic material, thereby reducing the convergence speed of the algorithm. To address this issue, dynamically adjusting the crossover and mutation probabilities during the evolutionary process enables the algorithm to leverage their specific roles at different stages: higher rates promote exploration in the early phase, while lower rates help maintain elite solutions and fine-tune convergence in the later phase. Therefore, the improved algorithm adopts adaptive control strategies for both crossover probability and mutation probability, aiming to enhance performance by balancing exploration and exploitation throughout the optimization process. The specific improvement strategies are detailed as follows.
where represents the individual’s decision variable, represents the mean of the decision variable, is the number of individuals in the population, D is the number of decision variables, and represents population diversity.
3.3. Improved Algorithm Solving Process
Figure 1 illustrates the process of the original algorithm and the added improvement strategies, the specific process of using the improved LMSPEAII algorithm to solve the reservoir scheduling model is as follows:
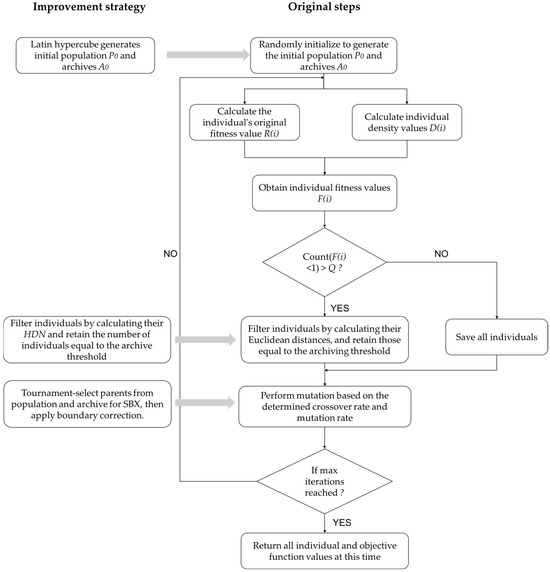
Figure 1.
SPEAII Algorithm Process and Added Improvement Strategies.
Step 1: A total of N individuals representing the decision variable—the reservoir water level process Z—are generated using the Latin hypercube sampling method, ensuring that the water level at each time period satisfies the corresponding water level constraints. Meanwhile, an empty archive set is initialized to store the non-dominated solutions identified during the evolutionary process.
Step 2: The current population and the archive set are merged to form a combined set . For each individual in the combined set, the water head , generation discharge , and power output at each time period are calculated based on the decision variable Z. Subsequently, the fitness value of each individual is evaluated using these computed outputs.
Step 3: Determine whether the number of individuals in the set exceeds the archive threshold based on fitness values, calculate the blending distance of each individual in the target space, sort the calculated blending distance of individuals in descending order, and ultimately retain the top individuals equal to the archive threshold.
Step 4: Select individuals from the current population and external archives through tournaments as parents for simulated binary crossover (SBX), divide the generated individuals into two parts and randomly and evenly, perform crossover operations on the parents to obtain offspring, and then perform mutation operations on the offspring.
Step 5: During the crossover process of the parent generation and the mutation process of the offspring, there may be some individuals who exceed the set boundaries due to random disturbances. Therefore, boundary correction is required for individuals after completing the crossover and mutation operations.
Step 6: Repeat steps Step 2 to Step 5 until the maximum number of iterations is reached, then terminate the iteration and obtain the current objective function values and decision variable variation process.
3.4. Performance Testing of LMSPEAII Algorithm
3.4.1. Algorithm Performance Evaluation Indicators
Multi-objective optimization algorithms aim to solve problems with multiple conflicting objectives, seeking to find a set of solutions that achieve or approximate the best values across all objective functions [43]. To scientifically evaluate the performance of these algorithms, appropriate evaluation metrics need to be selected. These metrics reflect algorithm performance from different perspectives, such as convergence, diversity, and uniformity. Through quantitative assessment, different algorithms can be objectively compared on the same problem, guiding algorithm improvement and optimization. Therefore, selecting evaluation metrics to assess the performance of multi-objective algorithms is an important means to ensure the scientific validity, comparability, and practicality of research results. To comprehensively evaluate the performance of multi-objective algorithms, this study selects the inverted generational distance (IGD) [44] and the hypervolume (HV) [45] as evaluation indicators, reflecting algorithm performance from different dimensions during the solving process.
- (1)
- Inverted Generational Distance (IGD)
The IGD represents the average distance from the optimal solution set to the obtained non-dominated solutions, and is mainly used to evaluate the convergence of multi-objective algorithms. A smaller IGD value indicates that the obtained non-dominated solution set is closer to the optimal solution set, demonstrating better convergence performance of the algorithm. Its calculation formula is as follows:
where represents the true Pareto front, denotes the approximate front solution set, typically uses the Euclidean distance, and is the total number of sample points in the true Pareto front.
- (2)
- Hypervolume (HV)
The HV measures the volume of the objective space and can simultaneously evaluate the convergence and diversity of the non-dominated solution set obtained by the algorithm. Specifically, it calculates the hypervolume formed between the non-dominated solution set and a reference point. A larger HV value indicates that the solution set is closer to the true Pareto front in terms of convergence and diversity, demonstrating better algorithm performance. Its calculation formula is as follows:
where is the approximate Pareto solution set, represents the value of solution in the objective, is the reference point (usually chosen to be worse than all solutions), is the number of objective functions, and denotes the Lebesgue measure (which corresponds to area in two dimensions, volume in three dimensions, and so forth).
3.4.2. Classic Multi-Objective Benchmark Testing Function
To verify the adaptability and robustness of the improved algorithm across different problem types, this section employs the Zitzler–Deb–Thiele test suite (ZDT) and Deb–Thiele–Laumanns–Zitzler test suite (DTLZ) series as benchmark test functions. The ZDT series (such as ZDT1 to ZDT6) features different shapes and distribution characteristics of objective functions and is primarily used to evaluate the algorithm’s convergence and solution set uniformity when handling convex, non-convex, continuous, and discrete Pareto fronts. The DTLZ series focuses more on problem scalability and the distribution of solution sets in high-dimensional objective spaces, revealing the algorithm’s performance in solving large-scale multi-objective optimization problems. These two types of functions respectively represent low-dimensional and high-dimensional multi-objective problems with diverse characteristics, thereby reflecting algorithm performance from multiple perspectives and difficulty levels.
In this paper, the SPEAII algorithm uses the default parameter settings recommended in the original publication [46], without any additional tuning. Zitzler, Thiele, and colleagues have demonstrated the robustness of these settings across multiple test suites, with a crossover probability of 0.9, a mutation probability of , a crossover distribution index of 20, and a mutation distribution index of 20. Their experiments have shown that this configuration delivers strong convergence and diversity performance across different problem scales and characteristics, eliminating the need for scenario-specific retuning. By contrast, the improved LMSPEAII algorithm relies entirely on on-the-fly parameter control strategies. Its parameters adjust themselves dynamically according to the current population’s distribution and search progress, with no manual presetting required. Such adaptive control methods are well established in the evolutionary computation literature, offering the advantage of responsive adaptation to each search phase and thereby greatly reducing—or even obviating—the need for manual parameter tuning.
To further demonstrate the excellent performance of the improved LMSPEAII algorithm in multi-objective problems, the original SPEAII algorithm and commonly used classical efficient algorithms, including Multi-Objective Evolutionary Algorithm based on Decomposition (MOEA/D), Non-dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm III (NSGAIII), and Pareto Envelope-based Selection Algorithm II (PESAII), were selected as comparison algorithms. The population size and maximum number of iterations for all algorithms were uniformly set to 50 and 500, respectively, with default initial parameter settings for the comparison algorithms. To reduce variability caused by randomness and to enhance the statistical significance of the results, each test function was independently run 20 times. The performance evaluation metrics, IGD and HV, were calculated for each run, and the average and median values of these 20 runs were taken as representative metrics for analysis. Table 1, Table 2, Table 3 and Table 4 detail the metric values of the improved LMSPEAII and the other four algorithms on each benchmark test function (including the ZDT and DTLZ series). For intuitive comparison, the best-performing algorithm metrics in each table are highlighted in dark gray, while the second-best metrics are marked in light gray. Figure 2 and Figure 3 use radar charts to visually display the distribution of different performance metrics of each algorithm across the test functions.

Table 1.
ZDT Series Test Function IGD Index.

Table 2.
DTLZ Series Test Function IGD Index.

Table 3.
ZDT Series Test Function HV Index.

Table 4.
DTLZ Series Test Function HV Index.
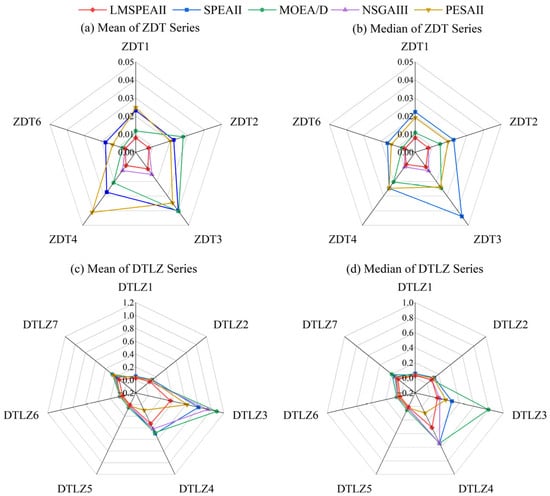
Figure 2.
IGD Distribution Diagram Under ZDT and DTLZ Series Test Functions.
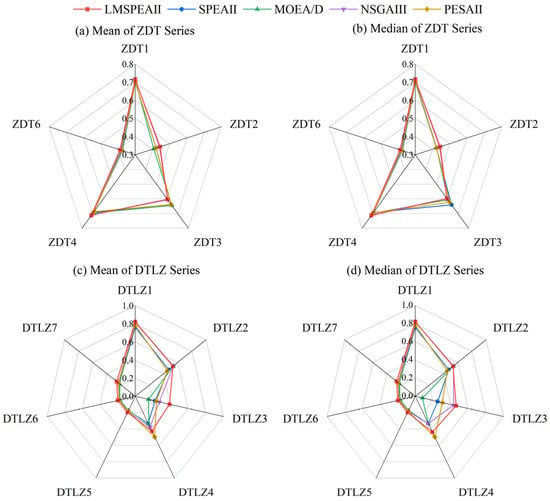
Figure 3.
HV Distribution Diagram Under ZDT and DTLZ Series Test Functions.
From the experimental data, the improved LMSPEAII algorithm demonstrates significantly better performance than the original SPEAII algorithm across both the ZDT and DTLZ test function sets. Moreover, when compared with mainstream multi-objective optimization algorithms, such as MOEA/D, NSGAIII, and PESAII, LMSPEAII achieves the best results on over 75% of the performance metrics. These results clearly indicate that the improved LMSPEAII algorithm effectively enhances both convergence and solution set diversity, leading to a notable overall performance improvement on classical multi-objective benchmark functions.
4. Case Study
4.1. Engineering Background
This paper focuses on a large hydropower station on a certain river and the hydropower–wind–solar multi-energy complementary system formed through its deep integration with wind and photovoltaic resources. The hydropower station has a normal reservoir level of approximately 825 m, a total storage capacity of about 20.627 billion m3, and a total installed capacity of around 16,000 MW; the installed capacities of wind power and photovoltaic power are approximately 3470 MW and 1805 MW, respectively. The system’s output is transmitted via transmission pipelines or lines to the target grid. Based on this scale and configuration, this paper investigates the operation mechanisms and scheduling strategies of the multi-energy complementary system.
4.2. Typical Scene Selection
The wind speed, solar radiation intensity, and temperature data used in this study are sourced from the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF), while the hydropower station’s inflow, initial, and final water levels during the scheduling period are based on actual operational data. Based on the wind and solar power outputs calculated in Section 2.1 for the year 2022, along with the actual inflow data of the station in 2022, March (dry season with strong wind and strong solar radiation) and September (flood season with weak wind and weak solar radiation) are selected as the study periods, as illustrated in Figure 4.
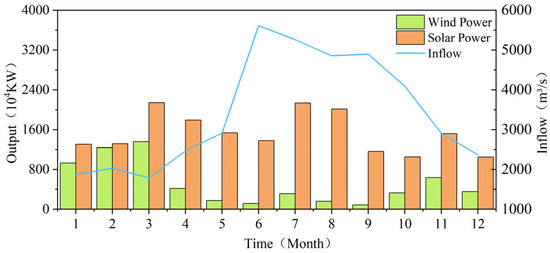
Figure 4.
Monthly Distribution Map of Wind and Solar Power Output and Inflow Data Connected to a Certain Power Station in 2022.
During the dry season, inflows are low and hydropower output is constrained; under strong wind and solar conditions, wind and solar outputs reach their peaks and their share increases significantly, but large fluctuations may increase residual load instability. Therefore, it is necessary to coordinate hydropower with wind and solar outputs, using the flexible regulation capability of hydropower to compensate for the variability of wind and solar and to maintain grid stability. In the flood season, abundant precipitation yields high hydropower potential, while under weak wind and solar conditions, wind and solar outputs drop markedly and their share declines, which may increase the grid’s reliance on hydropower; thus hydropower must shoulder both the main generation role and grid-regulation tasks, smoothing residual load fluctuations while meeting generation demands. Analyzing the multi-objective scheduling problem under these two extreme scenarios can more fully reveal how, in coordinated operation, hydropower’s flexibility balances wind and solar variability to optimize generation-side output and smooth grid-side residual load fluctuations, providing the theoretical basis and practical guidance for integrated scheduling strategies that balance generation efficiency and system stability. It also further verifies whether the model can achieve coordinated optimization of hydropower, wind, and solar under different resource endowments—reflecting the logic of multi-energy complementary scheduling—and whether the model can still reconcile the objectives of maximizing generation and minimizing the mean square error of the residual load under resource constraints and volatility. The initial and final water levels and the inflow rates for the dry season and flood season scheduling periods are shown in Table 5.

Table 5.
The Water Level and Inflow During Different Scheduling Periods of the Power Station.
4.3. Analysis of Characteristics of Scheduling Results
In this section, the improved LMSPEAII algorithm is applied to solve the multi-objective scheduling model for the hydropower–wind–solar multi-energy complementary system. Based on operational data from different scenarios, the joint hydropower–wind–solar Pareto front is constructed. This Pareto front reveals the optimal trade-off between total system generation and the mean square error of the residual load, reflecting potential strategies to smooth grid load while maintaining high generation efficiency. As shown in Figure 5, the results not only demonstrate the advantages of each scheduling strategy in balancing energy utilization efficiency and system stability but also provide a solid theoretical foundation and decision-support for further optimizing hydropower–wind–solar coordinated scheduling schemes to enhance grid security and economic performance.
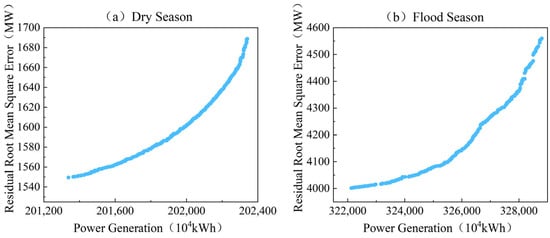
Figure 5.
Pareto Frontier Graphs for Different Scheduling Periods.
By analyzing the Pareto front curves for March (dry season) and September (flood season) in Figure 5, we can deeply explore the trade-off mechanism between efficient power generation and load smoothing. The resulting fronts show a clear conflict between total generation on the supply side and the mean square error of the residual load on the grid side: striving for higher generation typically entails greater grid load variability. In the dry season, although wind and solar outputs are highly variable, limited water resources confer higher scheduling priority to hydropower regulation, allowing for its flexible peaking capability to be fully leveraged and effectively smooth grid load fluctuations. In the flood season, despite abundant hydropower potential, the relatively weak wind and solar contributions force hydropower to shoulder both primary generation and grid-regulation roles, making it difficult to achieve load smoothing at high generation levels and resulting in a relatively higher residual-load MSE. This analysis furnishes a vital theoretical basis for formulating scheduling strategies that balance economic efficiency with system stability.
Figure 6 and Figure 7 show the distributions of the objective values obtained by different algorithms for the dry-season and flood-season scheduling cases, respectively, in order to further analyze how the algorithms perform on each objective. Overall, when examining each objective separately—generation and residual-load MSE—we observe that most solutions cluster in the regions of higher generation and lower residual-load MSE. This clustering primarily reflects the complementary effect inherent in the hydropower–wind–solar dispatch: hydropower’s flexible regulation capability effectively mitigates the variability of wind and solar output, allowing the system to maintain grid-load stability even while delivering high generation. These results also confirm that the proposed model consistently produces well-optimized and adaptable solutions under both typical scenarios, providing a solid theoretical and practical basis for achieving the dual goals of efficient generation and load smoothing.
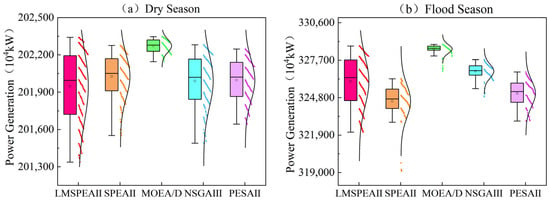
Figure 6.
Distribution Diagram of Power Generation under Different Algorithms for Different Scheduling Periods.
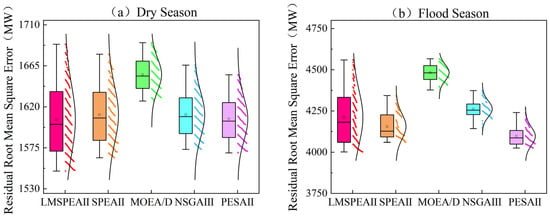
Figure 7.
Distribution of Residual Load Mean Square Error under Different Algorithms for Different Scheduling Periods.
The LMSPEAII algorithm introduced in this study tends to explore regions that can improve both objectives simultaneously, demonstrating its excellent global search and exploration capabilities. Compared with traditional algorithms, LMSPEAII uncovers a greater number of high-performing dispatch schemes and yields a richer Pareto-front structure, offering diverse trade-off options between objectives. Such a variety of optimized solutions equips decision-makers with comprehensive scheduling information, making it easier to identify the optimal balance between generation and residual-load MSE. Consequently, more flexible and precise control strategies can be formulated that respect both economic efficiency and system stability. This not only enhances the overall robustness of the scheduling but provides a firm theoretical and decision-support foundation for risk management and benefit optimization in real-world engineering applications, ultimately supplying decision-makers with a wider set of alternative schemes.
4.4. Characteristic Analysis of Representative Schemes
In Section 3.3, the improved multi-objective optimization algorithm LMSPEAII was applied to efficiently solve the constructed reservoir scheduling model, yielding a rich set of optimal solutions. To more intuitively and systematically reveal the distribution characteristics of these solutions in the multi-objective space, this section employs the K-medoids method to cluster the 200 Pareto solutions, thereby partitioning the solution set into subsets with high internal similarity. This clustering effectively reduces the complexity of the solution set and enhances our macroscopic understanding of its structure [47]. The cluster centers, as the most representative solutions within each subset, facilitate in-depth exploration of the intrinsic trade-off mechanisms while preserving solution diversity. Moreover, in unsupervised clustering, the number of clusters k is difficult to determine a priori; here, the elbow method is used by computing the “total within-cluster distance” for different values of k and plotting the distortion curve to identify the point at which additional clusters begin to yield diminishing returns, providing a straightforward, heuristic basis for selecting the optimal k [48]. The maximum number of clusters can be determined using the “square-root rule,” as given in Equation (42) [49]; accordingly, the maximum k in this study is set to 10.
where denotes the maximum number of clusters, and represents the total number of samples.
As shown in Figure 8, the elbow method identifies the optimal numbers of clusters for the March and September Pareto solutions as 5 and 4, respectively, where the “total within-cluster distance” curves exhibit pronounced elbows, indicating diminishing returns from further increasing k. The resulting cluster centers serve as the most representative schedules within each subset of the 200 Pareto solutions, capturing the core trade-off characteristics in the multi-objective space while preserving overall diversity and enhancing interpretability. Accordingly, we analyze these cluster centers—Plan I–V for March and the four centers for September—in depth to elucidate their intrinsic trade-off patterns and performance features.
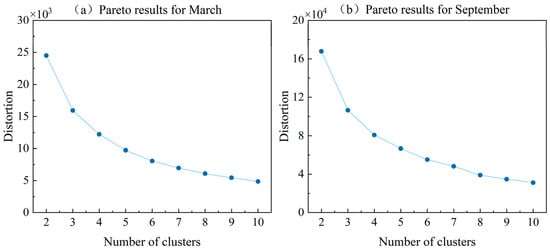
Figure 8.
Cluster Elbow Diagram.
For the March results, the five cluster centers correspond to solutions 28, 79, 122, 158, and 188, denoted as Plan I through Plan V (Figure 9). During the dry season, limited inflows force hydropower regulation to balance instantaneous smoothing against cumulative reservoir-level constraints; thus, the representative plans exhibit nuanced differences in hydropower output profiles and residual-load curves. Plan I maximizes total generation, maintaining a high and relatively flat hydropower output but failing to flexibly address wind–solar variability, which leads to larger residual-load swings in certain intervals. By contrast, Plan V prioritizes peak-regulation: overall hydropower output is reduced and exhibits pronounced ramps to actively counteract wind–solar fluctuations and original load variations. When wind–solar output is high and base load is low, hydropower is cut back to avoid excessive negative residual load; when wind–solar falls or load surges, hydropower is promptly ramped up to fill the gap, yielding a much smoother residual-load curve at the expense of some total generation. The intermediate Plans II–IV occupy progressive positions between these extremes, reflecting a continuous trade-off pathway from maximizing generation efficiency to optimizing grid-side load smoothing.
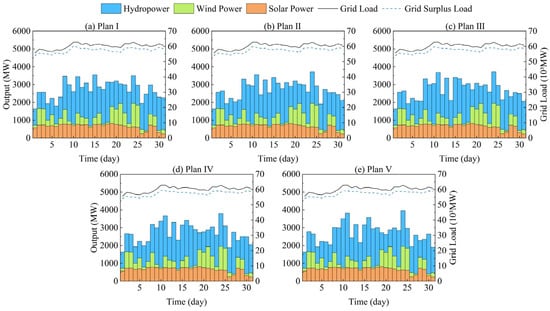
Figure 9.
Output and Peak Shaving Process Diagram of Clustering Center Scheme during Dry Season.
For the September results, clustering yields four representative solutions—solutions 32, 92, 141, and 181—denoted as Plan I through Plan IV (Figure 10). As September falls in the flood season, hydropower output is significantly enhanced, with daily outputs remaining at high levels well above those seen in the dry season. Wind and solar outputs are relatively weak and exhibit only minor fluctuations, indicating that hydropower plays the dominant role and that its regulation capability is the key driver of residual-load smoothing during this period. Specifically, Plan I corresponds to the highest-generation schedule: hydropower output remains high and relatively flat throughout the scheduling horizon, reflecting a baseload-oriented strategy. Because hydropower does not leverage its ramping capability to accommodate occasional wind–solar variability or load spikes, the residual-load curve still shows pronounced fluctuations, indicating limited peak-regulation performance. By contrast, Plan IV achieves the best peak-regulation: hydropower output undergoes dynamic adjustments in step with the original load, smoothing the residual-load curve as much as possible despite the small variations in wind and solar supply. The intermediate Plans II and III represent varying trade-offs between output level and regulation flexibility: both maintain relatively high generation while providing partial load-smoothing, resulting in noticeably reduced residual-load volatility compared to Plan I.
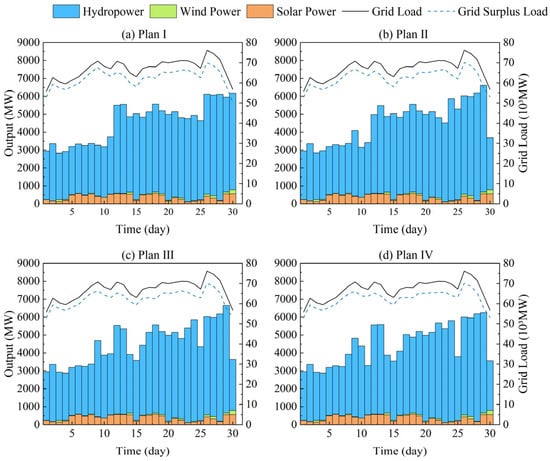
Figure 10.
Output and Peak Shaving Process Diagram of Clustering Center Scheme during Flood Season.
As the above analysis demonstrates, employing the K-medoids method to cluster the 200 Pareto solutions and selecting the medoid of each cluster effectively captures the overall distribution characteristics of the solution space. By conducting an in-depth analysis of these representative solutions, one can both reveal the principal patterns of hydropower scheduling under varying objective trade-offs and greatly reduce the workload of examining every Pareto solution individually. Plotting the hydropower–wind–solar output profiles and residual-load curves for each medoid visually illustrates the evolutionary trend from maximum generation to optimal peak regulation, and highlights how differing water-resource and renewable-resource conditions influence scheduling strategies across distinct dispatching periods. This approach thus provides decision-makers with efficient, reliable guidance for practical operation and the selection of scheduling methods.
5. Conclusions and Summary
To address the grid instability caused by integrating wind and solar power, this paper develops a hydropower–wind–solar multi-objective scheduling model that balances generation-side benefits and grid-side peak-regulation requirements. This paper further introduces a series of enhancements to propose the LMSPEAII algorithm for efficient solution of the model and employs K-medoids clustering to extract representative Pareto solutions, analyzing hydropower output and peak-regulation characteristics to demonstrate the applicability and robustness of both the improved algorithm and the proposed model under varying resource conditions.
- (1)
- Effectiveness of Algorithmic Improvements: Based on the classical multi-objective optimization algorithm SPEAII, this study introduces three strategies—Latin hypercube initialization, a hybrid distance framework, and an adaptive mutation mechanism—to develop LMSPEAII. Comparative experiments on the ZDT and DTLZ benchmark suites against the original SPEAII and mainstream algorithms NSGAIII, MOEA/D, and PESAII, using the IGD and HV as performance metrics, demonstrate that LMSPEAII outperforms the other algorithms in diversity, convergence speed, and solution accuracy, validating the effectiveness of the proposed enhancements in boosting exploration capability and avoiding local optima.
- (2)
- Rationality of Model Application: A multi-objective scheduling model was formulated with the goals of maximizing generation-side output and minimizing grid-side mean square error of the residual load. Two extreme resource scenarios—March (dry season with strong wind and solar) and September (flood season with weak wind and solar)—were selected to reveal the complementary and synergistic interactions among hydropower, wind, and solar. Solving this model with LMSPEAII and other multi-objective algorithms shows that LMSPEAII maintains superior applicability and performance under complex multi-energy dispatch conditions. Further analysis of the Pareto fronts indicates that hydropower’s flexible regulation capability enables effective trade-offs between generation efficiency and grid load smoothing, and that its dominant role and adjustment strategies adapt to differing water- and renewable-resource conditions, confirming the robustness of both the model and algorithm across varied resource contexts.
- (3)
- Clustering for Simplified Analysis: From the 200 Pareto solutions generated by LMSPEAII, K-medoids clustering (with the elbow method determining the optimal number of clusters) was applied to both dispatch periods, and the medoid of each cluster was taken as its representative solution. An in-depth examination of these representative solutions’ hydropower–wind–solar output profiles and residual-load curves reveals the continuum of trade-off strategies from maximum generation to optimal peak regulation, and highlights how differing resource conditions influence dispatch strategies. This clustering approach not only uncovers the main scheduling patterns under various objective trade-offs but greatly reduces the effort of analyzing every Pareto solution individually, thereby improving research efficiency and clarity of interpretation.
In summary, this paper has developed a multi-objective scheduling model that balances generation efficiency and peak-regulation requirements, and has combined the LMSPEAII algorithm with K-medoids clustering analysis both to achieve efficient optimization of the hydropower–wind–solar complementary system and to reveal the intrinsic scheduling patterns under varying resource conditions, thereby providing a systematic methodology and empirical basis for integrated dispatch strategy formulation. With the continuous increase in renewable energy penetration, the grid’s sensitivity to power-balance disturbances also rises. At low wind–solar penetration levels, residual-load fluctuations are primarily absorbed by conventional units; however, once penetration exceeds a certain threshold, the inherent variability of renewables becomes the dominant driver of residual-load swings, causing the variance of the residual load to multiply. Under such conditions, the deployment of flexible regulation measures—such as energy storage, demand-side response, and reserve capacity—becomes critically important. In the model, minimizing the mean square error of the residual load thus reflects the optimal allocation and utilization of system regulation resources under a high-penetration renewable context. Looking ahead, the model can be extended to incorporate forecast uncertainties of wind and solar power as well as hydrological inflow variability within a stochastic or robust optimization framework to further enhance the reliability of scheduling strategies; concurrently, integrating electricity market mechanisms and energy storage systems can enable the coordinated optimization of economic performance and flexibility, supporting intelligent and sustainable operation under high-penetration renewable energy scenarios.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.H. and L.M.; methodology, H.H.; software, H.H. and W.L.; validation, H.H., W.L. and S.Z.; formal analysis, Q.S.; data curation, Y.P. and R.B.; writing—original draft preparation, H.H.; writing—review and editing, supervision, H.H. Q.S. and L.M.; funding acquisition, L.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2023YFC3209104), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52379011).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data unavailable due to privacy restriction.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Qin Shen was employed by the company Hubei Qingjiang Hydropower Development Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| LMSPEAII | LHS-Mutate Strength Pareto Evolutionary Algorithm II |
| SPEAII | Strength Pareto Evolutionary Algorithm II |
| MOEA/D | Multi-Objective Evolutionary Algorithm based on Decomposition |
| NSGAIII | Non-dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm III |
| PESAII | Pareto Envelope-based Selection Algorithm II |
| ZDT | Zitzler–Deb–Thiele Test Suite |
| DTLZ | Deb–Thiele–Laumanns–Zitzler Test Suite |
| ECMWF | European Center for Medium Weather Forecasting |
| IGD | Inverted Generational Distance |
| HV | Hypervolume |
| RMSE | Root Mean Square Error |
| SBX | Simulated Binary Crossover |
| LHS | Latin Hypercube Sampling |
Nomenclature
| Symbol | Description | Unit |
| Wind power output at time t | MW | |
| Photovoltaic output at time t | MW | |
| Hydroelectric output at time t | MW | |
| Photovoltaic cell temperature | °C | |
| Original load | MW | |
| Remaining load at time t | MW | |
| Water level at time t | m | |
| Reservoir capacity at time t | m3 | |
| Outflow at time t | m3/s | |
| Crossover distribution factor | — | |
| Crossover probability | — | |
| Mutation probability | — | |
| Dimension | — | |
| Mutation step | — |
References
- Lei, K.; Chang, J.; Wang, X.; Guo, A.; Wang, Y.; Ren, C. Peak shaving and short-term economic operation of hydro-Wind-PV hybrid system considering the uncertainty of wind and PV power. Renew Energy 2023, 215, 118903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Ma, X.; Chen, B.; Shang, Y.; Song, M. Challenges toward carbon neutrality in China: Strategies and countermeasures. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 176, 105959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, K.; Zhang, T.; Xie, X.; Du, S.; Xue, X.; Abdul-Manan, A.F.N.; Huang, Z. Exploration of low-cost green transition opportunities for China’s power system under dual carbon goals. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 414, 137590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulek, V.; Ales, Z.; Finsterle, T.; Libra, M.; Beranek, V.; Severova, L.; Belza, R.; Mrazek, J.; Kozelka, M.; Svoboda, R. Reliability characteristics of first-tier photovoltaic panels for agrivoltaic systems—Practical consequences. Int. Agrophys. 2024, 38, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; Yu, C.; Huang, H.; Yu, Y.; Zou, L.; Mo, L. Optimization scheduling of hydro-wind-solar multi-energy complementary systems based on an improved enterprise development algorithm. Sustainability 2025, 17, 2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Zhang, B.; Sun, X.; Han, S.; Höök, M. China’s energy transition in the power and transport sectors from a substitution perspective. Energies 2017, 10, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Fan, C.; Hu, J.; Zhang, X. Hydro-wind-PV-integrated operation optimization and ultra-short-term HESS configuration. Electronics 2024, 13, 4778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Liu, H.; Xiao, Y.; Zhu, F.; Ding, L.; Yang, F. Power generation scheduling for a hydro-wind-solar hybrid system: A systematic survey and prospect. Energies 2022, 15, 8747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Peng, Z.; Liao, S.; Liu, T.; Lu, J. A multi-objective optimization model for the coordinated operation of hydropower and renewable energy. Front. Energy Res. 2023, 11, 1193415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Sun, Y.; Tan, Q.; Tang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Ding, Z. Optimizing the sizes of wind and photovoltaic plants complementarily operating with cascade hydropower stations: Balancing risk and benefit. Appl. Energy 2022, 306, 117968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Zhou, J.; Cheng, C.; Su, H. Developing operating rules for a hydro-wind-solar hybrid system considering peak-shaving demands. Appl. Energy 2024, 360, 122762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Liu, B.; Liao, S.; Cheng, C.; Li, G.; Liu, L. Impacts of different wind and solar power penetrations on cascade hydroplants operation. Renew. Energy 2022, 182, 227–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angarita, J.L.; Usaola, J.; Martinez-Crespo, J. Combined hydro-wind generation bids in a pool-based electricity market. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2009, 79, 1038–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, C.; Jiang, C.; Lei, X.; Cen, W.; Yan, Z.; Tang, G.; Li, L.; Sun, G.; Xing, Z. Optimal scheduling of reservoir flood control under non-stationary conditions. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadieh, B.; Afshar, A. Optimization of water-supply and hydropower reservoir operation using the charged system search algorithm. Hydrology 2019, 6, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Yang, K.; Hu, H.; Yang, Z. Long-term hydropower generation scheduling of large-scale cascade reservoirs using chaotic adaptive multi-objective bat algorithm. Water 2019, 11, 2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, T.; Qin, H.; Yan, D.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, B.; Li, C.; Wang, J.; Zhou, J. Short-term multi-objective optimal operation of reservoirs to maximize the benefits of hydropower and navigation. Water 2019, 11, 1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Liu, P.; Ji, C.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y. Ecological flow considered multi-objective storage energy operation chart optimization of large-scale mixed reservoirs. J. Hydrol. 2019, 577, 123949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Li, Q.; Wang, W. Frequency regulation reserve allocation for integrated hydropower plant and energy storage systems via the marginal substitution. Electronics 2025, 14, 1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Li, F.; Ker, P.J.; Ahmed, A.N.; Xu, B.; Chen, D. Dynamic flexibility management for pumped hydro storage: Enhancing frequency stability and economic efficiency in cascade hydro -wind-solar- storage integrated delivery systems. J. Energy Storage 2025, 126, 117044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, K.N.; Das, D.; Ray, A.K.; Suganthan, P.N. Proceedings of the International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Sustainable Technologies: IcoCIST 2021; Springer: Singapore, 2022; ISBN 978-981-16-6892-0. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, R.; Popole, Z. Multi-objective optimized scheduling model for hydropower reservoir based on improved particle swarm optimization algorithm. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 12842–12850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, J.Z.; Kwakkel, J.; Witvliet, M. Exploring global approximators for multiobjective reservoir control. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2022, 55, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, D.; Zhang, T.; Wu, L.; Su, X.; Bai, T.; Huang, Q. Multi-objective cooperative optimization of reservoir scheduling and water resources allocation for inter-basin water transfer project based on multi-stage coupling model. J. Hydrol. 2024, 630, 130673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, D.; Jin, Y.; Pal, N.R. A two-mode offspring generation selection mechanism with co-evolution for sparse large-scale multiobjective optimization. Inf. Sci. 2025, 718, 122337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkhoda, W.; Seyedi, A.; Gillis, N.; Tab, F.A. Instance-wise distributionally robust nonnegative matrix factorization. Pattern Recognit. 2026, 169, 111732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Song, Z.; Zhai, C.; Wen, W. An approach for improving post-earthquake functionality of hospital buildings with fluid viscous damper. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 105, 112498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, M.; Yang, K.; Ge, Y.; Wang, K.; Lin, H.; Pan, P.; Hu, H.; He, Z.; et al. Multi-timescale reward-based DRL energy management for regenerative braking energy storage system. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2025, 11, 7488–7500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Yang, K.; Su, L.; Yang, Z. A novel adaptive multi-objective particle swarm optimization based on decomposition and dominance for long-term generation scheduling of cascade hydropower system. Water Resour. Manag. 2019, 33, 4007–4026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdi, J.; Moridi, A. Multi-objective differential evolution for design of cascade hydropower reservoir systems. Water Resour. Manag. 2018, 32, 4779–4791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooshyar, M.; Mousavi, S.J.; Mahootchi, M.; Ponnambalam, K. Aggregation-decomposition-based multi-agent reinforcement learning for multi-reservoir operations optimization. Water 2020, 12, 2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizipour, M.; Sattari, A.; Afshar, M.H.; Goharian, E.; Solis, S.S. Optimal hydropower operation of multi-reservoir systems: Hybrid cellular automata-simulated annealing approach. J. Hydroinform. 2020, 22, 1236–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Cai, Z.; Jiao, X.; Long, D. Multi-timescale optimization scheduling of integrated energy systems oriented towards generalized energy storage services. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 8549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotzur, L.; Nolting, L.; Hoffmann, M.; Gross, T.; Smolenko, A.; Priesmann, J.; Buesing, H.; Beer, R.; Kullmann, F.; Singh, B.; et al. A modeler’ s guide to handle complexity in energy systems optimization. Adv. Appl. Energy 2021, 4, 100063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, X.; Zhao, S.; Ma, Y. Multipoint layout planning method for multi- energy sources based on time-series production simulation. Int. J. Energy Res. 2022, 46, 9323–9344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Wang, J.; Lu, G.; Jiang, M.; Khan, S.A.; Ji, J. Optical-electrical-thermal model of flexible non-planar photovoltaic modules: Decoupling, validation, and photoelectric performance analysis. Energy 2025, 318, 134843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Chang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, J.; Meng, X.; Jing, Z.; Zhang, J. A long-term scheduling method for cascade hydro-wind-PV complementary systems considering comprehensive utilization requirements and load characteristics. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 494, 145032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Lu, Z.; Hu, W.; Wang, Y.; Dong, L.; Zhang, J. Coordinated optimal operation of hydro-wind-solar integrated systems. Appl. Energy 2019, 242, 883–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Fan, N.; Wu, L. Multistage robust optimization for the day-ahead scheduling of hybrid thermal-hydro-wind-solar systems. J. Glob. Optim. 2024, 88, 999–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Liu, P.; Ming, B.; Kim, J.; Gong, Y. Economic operation of a wind-solar-hydro complementary system considering risks of output shortage, power curtailment and spilled water. Appl. Energy 2021, 290, 116805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, R.; Yu, J.; Zhang, C.; Munetomo, M. Srime: A strengthened rime with Latin hypercube sampling and embedded distance-based selection for engineering optimization problems. Neural Comput. Appl. 2024, 36, 6721–6740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y. A particle swarm optimization algorithm based on modified crowding distance for multimodal multi-objective problems. Appl. Soft Comput. 2024, 152, 111280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Leung, M.; Che, H.; Coello, C.A.C. Thematic issue on advances in analysis and application of multi-objective memetic optimization algorithms. Memetic Comput. 2023, 15, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huband, S.; Hingston, P.; Barone, L.; While, L. A review of multiobjective test problems and a scalable test problem toolkit. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2006, 10, 477–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitzler, E.; Thiele, L. Multiobjective evolutionary algorithms: A comparative case study and the strength pareto approach. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 1999, 3, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Hiroyasu, T.; Miki, M.; Watanabe, S. Spea2+: Improving the Performance of the Strength Pareto Evolutionary Algorithm 2. In Proceedings of the Parallel Problem Solving from Nature—PPSN VIII, Birmingham, UK, 18–22 September 2004; Yao, X., Burke, E.K., Lozano, J.A., Smith, J., Merelo-Guervós, J.J., Bullinaria, J.A., Rowe, J.E., Tiňo, P., Kabán, A., Schwefel, H., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 742–751, ISBN 978-3-540-23092-2. [Google Scholar]
- Kala, K.; Sodhi, M.S. Note: Demonstrating analytics in a low-tech context-truck-routing for solid-waste collection in an indian metropolis. Transp. Res. E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2023, 176, 103219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, D.; Casals, M.; Oliver, M.; Plensa, M.; Manisera, M. Reporting of clustering techniques in sports sciences: A scoping review. Electron. J. Appl. Stat. Anal. 2024, 17, 653–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luker, S.; Doveton, A.; Manuel, K.; Adey-Wakeling, Z.; Jaggard, D.; Crotty, M.; Cameron, I.D.; Karnon, J.; McNaughton, H.; Ullah, S.; et al. Take charge after long COVID: A mixed methods randomised controlled pilot study protocol. Ann. Med. 2025, 57, 2516694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).