Evaluating Zeolites of Different Origin for Eutrophication Control of Freshwater Bodies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Zeolite Sources and Geological Background
2.2. ZeoPhos Modification Protocol
2.3. Material Characterization
2.4. Adsorption Experiments
2.4.1. Kinetic Adsorption Experiment Set Up
2.4.2. Kinetic Adsorption Studies
2.4.3. Isotherm Adsorption Experiment Set Up
2.4.4. Isotherm Adsorption Studies
3. Results
3.1. Zeolite Characterization Results by Origin
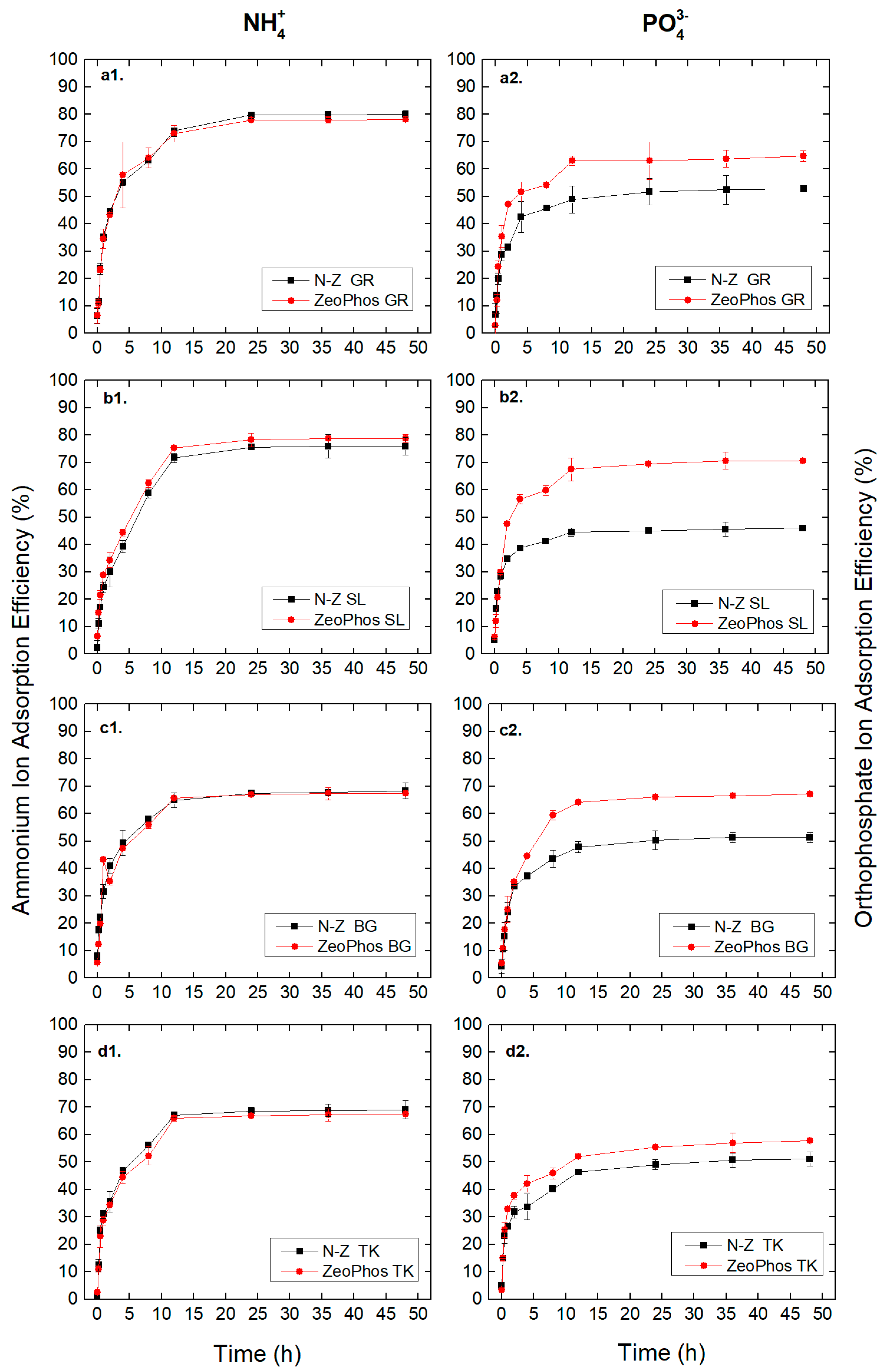
3.2. Adsorption Efficiency Results
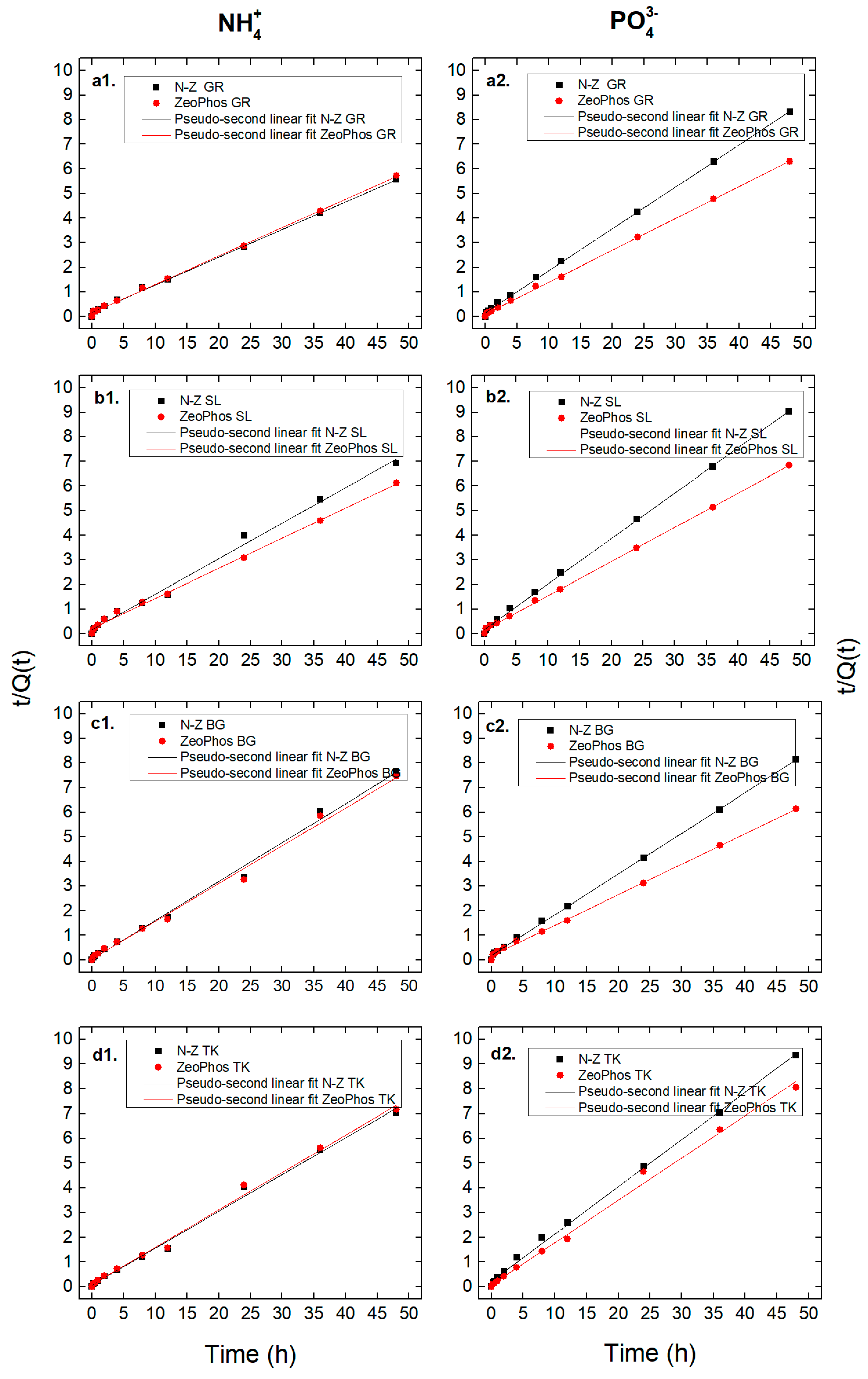
3.3. Adsorption Kinetic Results
3.4. Adsorption Isotherm Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Discussion of Characterization Results
4.2. Parameters Affecting the Adsorption Efficiency
4.3. The Importance of the Kinetic Analysis
4.4. Literature Review of Ammonium and Orthophosphate Adsorption Capacity
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Raús Maúre, E.; Terauchi, G.; Ishizaka, J.; Clinton, N.; DeWitt, M. Globally Consistent Assessment of Coastal Eutrophication. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Free, G.; Bresciani, M.; Pinardi, M.; Simis, S.; Liu, X.; Albergel, C.; Giardino, C. Investigating Lake Chlorophyll-a Responses to the 2019 European Double Heatwave Using Satellite Remote Sensing. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 142, 109217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Lyu, T.; Bi, L.; Tempero, G.; Hamilton, D.P.; Pan, G. Combating Hypoxia/Anoxia at Sediment-Water Interfaces: A Preliminary Study of Oxygen Nanobubble Modified Clay Materials. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 637–638, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidiropoulos, P.; Chamoglou, M.; Kagalou, I. Combining Conflicting, Economic, and Environmental Pressures: Evaluation of the Restored Lake Karla (Thessaly-Greece). Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2017, 17, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazaratou, C.V.; Vayenas, D.V.; Papoulis, D. The Role of Clays, Clay Minerals and Clay-Based Materials for Nitrate Removal from Water Systems: A Review. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 185, 105377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacharias, I.; Zamparas, M. Mediterranean Temporary Ponds. A Disappearing Ecosystem. Biodivers. Conserv. 2010, 19, 3827–3834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copetti, D.; Finsterle, K.; Marziali, L.; Stefani, F.; Tartari, G.; Douglas, G.; Reitzel, K.; Spears, B.M.; Winfield, I.J.; Crosa, G.; et al. Eutrophication Management in Surface Waters Using Lanthanum Modified Bentonite: A Review. Water Res. 2015, 97, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Yu, Y.; Lin, J.; Wu, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y. Simultaneous Control of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Release from Sediments Using Iron-Modified Zeolite as Capping and Amendment Materials. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 249, 109369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacharias, I.; Biliani, I. Geo-Engineering Materials for Restoration of Eutrophic and Anoxic Inland and Coastal Waters—The BLUE-GREENWAY Project. In Proceedings of the 2022 7th Asia Conference on Environment and Sustainable Development (ACESD 2022), Kyoto, Japan, 4–6 November 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Spears, B.M.; Lürling, M.; Yasseri, S.; Castro-Castellon, A.T.; Gibbs, M.; Meis, S.; McDonald, C.; McIntosh, J.; Sleep, D.; Van Oosterhout, F. Lake Responses Following Lanthanum-Modified Bentonite Clay (Phoslock®) Application: An Analysis of Water Column Lanthanum Data from 16 Case Study Lakes. Water Res. 2013, 47, 5930–5942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Velasco-Maldonado, P.S.; Hernández-Montoya, V.; Montes-Morán, M.A.; Vázquez, N.A.R.; Pérez-Cruz, M.A. Surface Modification of a Natural Zeolite by Treatment with Cold Oxygen Plasma: Characterization and Application in Water Treatment. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 434, 1193–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, U.; Ye, Z.L.; Abass, O.K.; Zamel, D.; Rehman, A.; Zhao, P.; Huang, F. Evaluation of Potential Adsorbents for Simultaneous Adsorption of Phosphate and Ammonium at Low Concentrations. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2024, 379, 113301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Meng, J.; Liu, X.; Xu, J.; Wang, F.; Brookes, P. Zeolite-Supported Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron: New Findings on Simultaneous Adsorption of Cd(II), Pb(II), and As(III) in Aqueous Solution and Soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Zhang, A.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, X.; Yang, L.; Yang, Z. Adsorption Mechanism of High-Concentration Ammonium by Chinese Natural Zeolite with Experimental Optimization and Theoretical Computation. Water 2022, 14, 2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghouti, M.A.; Da’ana, D.A. Guidelines for the Use and Interpretation of Adsorption Isotherm Models: A Review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, B.W.; Hong, S.H.; Lee, C.G.; Park, S.J. The Feasibility of Using Bentonite, Illite, and Zeolite as Capping Materials to Stabilize Nutrients and Interrupt Their Release from Contaminated Lake Sediments. Chemosphere 2019, 219, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Li, W.; Ma, L.; Cao, D.; Owens, G.; Chen, Z. Simultaneous Removal of Ammonia and Phosphate Using Green Synthesized Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Dispersed onto Zeolite. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 135002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biliani, I.; Tsavatopoulou, V.; Zacharias, I. Comparative Study of Ammonium and Orthophosphate Removal Efficiency with Natural and Modified Clay-Based Materials, for Sustainable Management of Eutrophic Water Bodies. Sustain. 2024, 16, 10214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abed, T.H.; Stefan, D.S.; Berger, D.C.; Marinescu, N.C.; Stefan, M. Performance Evaluation of a Romanian Zeolite: A Sustainable Material for Removing Ammonium Ions from Water. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guaya, D.; Valderrama, C.; Farran, A.; Cortina, J.L. Modification of a Natural Zeolite with Fe(III) for Simultaneous Phosphate and Ammonium Removal from Aqueous Solutions. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2016, 91, 1737–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshameri, A.; He, H.; Dawood, A.S.; Zhu, J. Simultaneous Removal of NH4+ and PO43− from Simulated Reclaimed Waters by Modified Natural Zeolite. Preparation, Characterization and Thermodynamics. Environ. Prot. Eng. 2021, 43, 73–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, W.; Mei, L.; Hao, S.; Li, D.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Jin, X.; Li, C. Na@La-Modified Zeolite Particles for Simultaneous Removal of Ammonia Nitrogen and Phosphate from Rejected Water: Performance and Mechanism. Water Sci. Technol. 2020, 82, 2975–2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocker, K.; Ellersdorfer, M. Phosphate Fixation and P Mineralogy on Natural and Ca-Modified Zeolites During Simultaneous Nutrient Removal. Water. Air. Soil Pollut. 2022, 233, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Song, L.; Shi, M.; Gu, C.; Zhang, J.; Lv, J.; Xuan, L. Ca/Fe-Layered Double Hydroxide–Zeolite Composites for the Control of Phosphorus Pollution in Sediments: Performance, Mechanisms, and Microbial Community Response. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 450, 138277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhan, Y.; Lin, J.; Bai, X.; Zhang, Z. Efficiency and Mechanism for the Control of Phosphorus Release from Sediment by the Combined Use of Hydrous Ferric Oxide, Calcite and Zeolite as a Geo-Engineering Tool. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 428, 131360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senila, M.; Cadar, O. Modification of Natural Zeolites and Their Applications for Heavy Metal Removal from Polluted Environments: Challenges, Recent Advances, and Perspectives. Heliyon 2024, 10, e25303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soudejani, H.T.; Kazemian, H.; Inglezakis, V.J.; Zorpas, A.A. Application of Zeolites in Organic Waste Composting: A Review. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2019, 22, 101396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepova, K.; Fediv, I.; Mažeikienė, A.; Šarko, J.; Mažeika, J. Adsorption of Ammonium Ions and Phosphates on Natural and Modified Clinoptilolite: Isotherm and Breakthrough Curve Measurements. Water 2023, 15, 1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biliani, I.; Zacharias, I. Synthesis of a Novel Modified Zeolite (ZeoPhos) for the Adsorption of Ammonium and Orthophosphate Ions from Eutrophic Waters. Water 2025, 17, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guaya, D.; Valderrama, C.; Farran, A.; Armijos, C.; Cortina, J.L. Simultaneous Phosphate and Ammonium Removal from Aqueous Solution by a Hydrated Aluminum Oxide Modified Natural Zeolite. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 271, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abukhadra, M.R.; Abukhadra, M.R.; Ali, S.M.; Ali, S.M.; Nasr, E.A.; Nasr, E.A.; Mahmoud, H.A.A.; Mahmoud, H.A.A.; Awwad, E.M. Effective Sequestration of Phosphate and Ammonium Ions by the Bentonite/Zeolite Na-P Composite as a Simple Technique to Control the Eutrophication Phenomenon: Realistic Studies. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 14656–14668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boles, J.R. Composition, Optical Properties, Cell Dimensions and Thermal Stability of Some Heulandite Group Minerals. Am. Mineral. J. Earth Planet. Mater. 1972, 57, 1463–1493. [Google Scholar]
- Stamatakis, M.G.; Hall, A.; Hein, J.R. The Zeolite Deposits of Greece. Miner. Depos. 1996, 31, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elaiopoulos, K.; Perraki, T.; Grigoropoulou, E. Mineralogical Study and Porosimetry Measurements of Zeolites from Scaloma Area, Thrace, Greece. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2008, 112, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsirambides, A.; Filippidis, A.; Kassoli-Fournaraki, A. Zeolitic Alteration of Eocene Volcaniclastic Sediments at Metaxades, Thrace, Greece. Appl. Clay Sci. 1993, 7, 509–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschegg, C.; Rice, A.N.H.; Grasemann, B.; Matiasek, E.; Kobulej, P.; Dzivák, M.; Berger, T. Petrogenesis of a Large-Scale Miocene Zeolite Tuff in the Eastern Slovak Republic: The Nižný Hrabovec Open-Pit Clinoptilolite Mine. Econ. Geol. 2019, 114, 1177–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djurova, E.; Stefanova, I.; Gradev, G. Geological, Mineralogical and Ion Exchange Characteristics of Zeolite Rocks from Bulgaria. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. Artic. 1989, 130, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djourova, E.G.; Milakovska-Vergilova, Z.I. Redeposited Zeolitic Rocks from the NE Rhodopes, Bulgaria. Miner. Depos. 1996, 31, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Fan, Y.; Li, Y.; Qu, F.; Wu, D.; Kong, H. Synthesis of Zeolite/Hydrous Lanthanum Oxide Composite from Coal Fly Ash for Efficient Phosphate Removal from Lake Water. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 222, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorguner, M.; Kavvas, M.L. Modeling Impacts of Future Climate Change on Reservoir Storages and Irrigation Water Demands in a Mediterranean Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 748, 141246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pai, S.C.; Tsau, Y.J.; Yang, T.I. PH and Buffering Capacity Problems Involved in the Determination of Ammonia in Saline Water Using the Indophenol Blue Spectrophotometric Method. Anal. Chim. Acta 2001, 434, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA; WEF; AWWA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 22nd ed.; American Public Health Association: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Xiao, X.; Yan, B.; Yang, L. Ammonium Removal from Aqueous Solutions by Using Natural Chinese (Chende) Zeolite as Adsorbent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 175, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Lin, H.; Dong, Y.; Liu, Q.; Wang, L. Simultaneous Removal of Ammonium and Phosphate by Alkaline-Activated and Lanthanum-Impregnated Zeolite. Chemosphere 2016, 164, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susilawati; Andriayani; Sihombing, Y.A.; Saragi, I.R.; Masruchin, N.; Nuryawan, A.; Irma, M. Study of Ammonium Adsorption Mechanism in Hydrothermalized Pahae Natural Zeolites: Kinetic and Isotherm Adsorption, and Thermodynamics. Trends Sci. 2025, 22, 8993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, D.; Ho, Y.S.; Tang, X. Comparative Sorption Kinetic Studies of Ammonium onto Zeolite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 133, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Low, M.J.D. Kinetics of Chemisorption of Gases on Solids. Chem. Rev. 1960, 60, 267–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieśla, J.; Franus, W.; Franus, M.; Kedziora, K.; Gluszczyk, J.; Szerement, J.; Jozefaciuk, G. Environmental-Friendly Modifications of Zeolite to Increase Its Sorption and Anion Exchange Properties, Physicochemical Studies of the Modified Materials. Materials 2019, 12, 3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotoulas, A.; Agathou, D.; Triantaphyllidou, I.E.; Tatoulis, T.I.; Akratos, C.S.; Tekerlekopoulou, A.G.; Vayenas, D.V. Zeolite as a Potential Medium for Ammonium Recovery and Second Cheese Whey Treatment. Water 2019, 11, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Tong, J.; Yang, Z.; Zeng, G.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, D.; Song, P.; Xu, R.; Zhang, C.; Cheng, M. Adsorption of Phosphate from Aqueous Solution Using Iron-Zirconium Modified Activated Carbon Nanofiber: Performance and Mechanism. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 493, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Liang, H.; Yang, W.; Xiang, T.; Chen, T.; Gao, D. Zeolite Enhanced Iron-Modified Biocarrier Drives Fe(II)/Fe(III) Cycle to Achieve Nitrogen Removal from Eutrophic Water. Chemosphere 2024, 346, 140547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, M.M.; Hickey, C.W.; Özkundakci, D. Sustainability Assessment and Comparison of Efficacy of Four P-Inactivation Agents for Managing Internal Phosphorus Loads in Lakes: Sediment Incubations. Hydrobiologia 2011, 658, 253–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goscianska, J.; Ptaszkowska-Koniarz, M.; Frankowski, M.; Franus, M.; Panek, R.; Franus, W. Removal of Phosphate from Water by Lanthanum-Modified Zeolites Obtained from Fly Ash. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 513, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saltali, K.; Sari, A.; Aydin, M. Removal of Ammonium Ion from Aqueous Solution by Natural Turkish (Yıldızeli) Zeolite for Environmental Quality. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 141, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshameri, A.; Yan, C.; Al-Ani, Y.; Dawood, A.S.; Ibrahim, A.; Zhou, C.; Wang, H. An Investigation into the Adsorption Removal of Ammonium by Salt Activated Chinese (Hulaodu) Natural Zeolite: Kinetics, Isotherms, and Thermodynamics. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2014, 45, 554–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Zhang, B.; Li, C.; Zhang, Z.; Kong, H. Simultaneous Removal of Ammonium and Phosphate by Zeolite Synthesized from Fly Ash as Influenced by Salt Treatment. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 304, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.-H.; Wu, D.-Y.; Wang, C.; He, S.-B.; Zhang, Z.-J.; Kong, H.-N. Simultaneous Removal of Ammonium and Phosphate by Zeolite Synthesized from Coal Fly Ash as Influenced by Acid Treatment. J. Environ. Sci. 2007, 19, 540–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Li, Y.; Yu, Z.; Shen, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, M.; Ding, T.; Xu, L.; Lee, S.S. Ammonium Removal Using a Calcined Natural Zeolite Modified with Sodium Nitrate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamparas, M.; Kyriakopoulos, G.L.; Drosos, M.; Kapsalis, V.C.; Kalavrouziotis, I.K. Novel Composite Materials for Lake Restoration: A New Approach Impacting on Ecology and Circular Economy. Sustain. 2020, 12, 3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinnawo, S.O. Eutrophication: Causes, Consequences, Physical, Chemical and Biological Techniques for Mitigation Strategies. Environ. Challenges 2023, 12, 100733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldovi, A.A.; de Barros Aguiar, A.R.; Benassi, R.F.; Vymazal, J.; de Jesus, T.A. Phosphorus Removal in a Pilot Scale Free Water Surface Constructed Wetland: Hydraulic Retention Time, Seasonality and Standing Stock Evaluation. Chemosphere 2021, 266, 128939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Q.; Teurlincx, S.; van Herpen, F.; Raman, N.V.; Lürling, M.; Waajen, G.; de Senerpont Domis, L.N. Towards Climate-Robust Water Quality Management: Testing the Efficacy of Different Eutrophication Control Measures during a Heatwave in an Urban Canal. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 828, 154421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
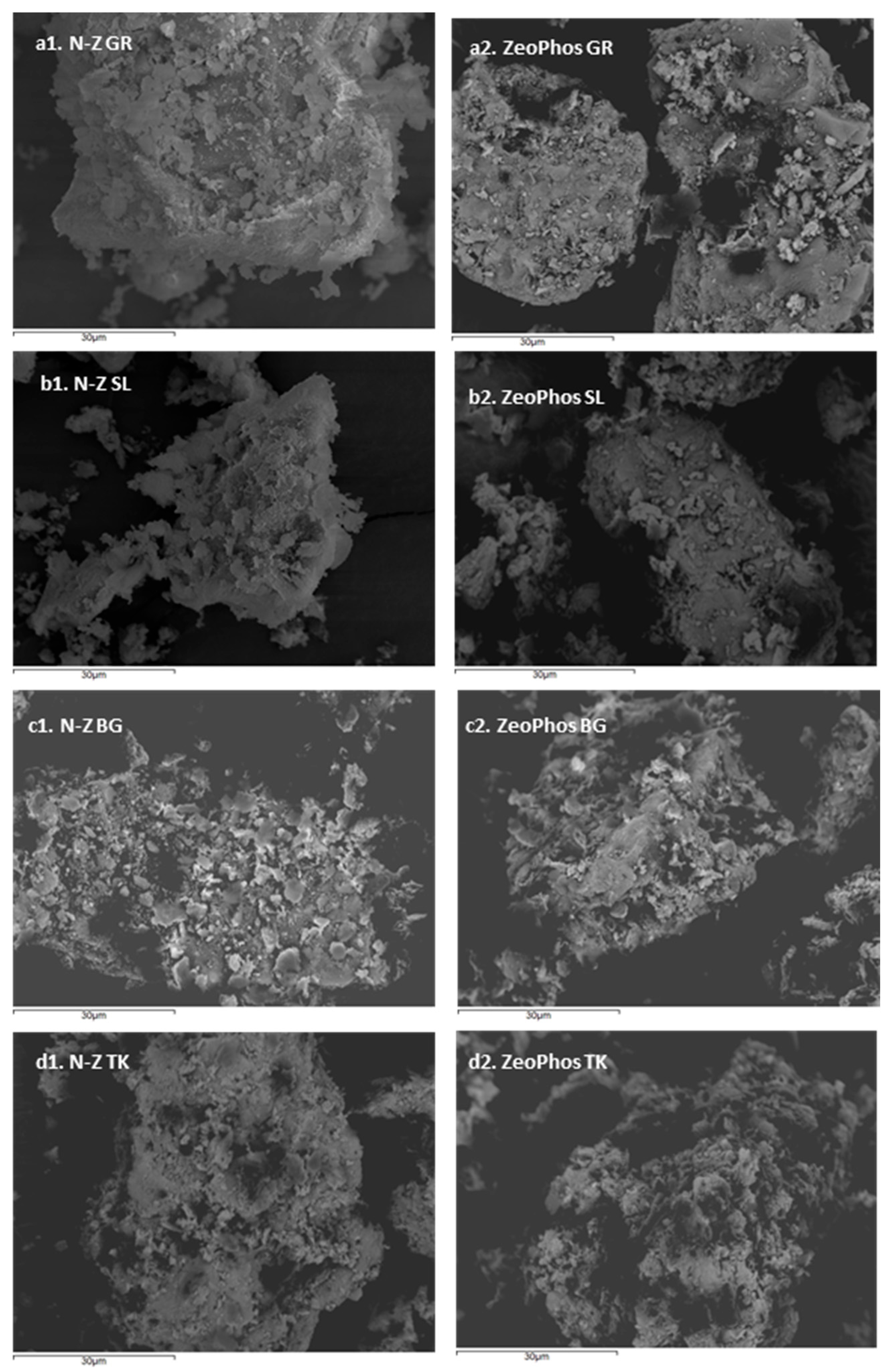
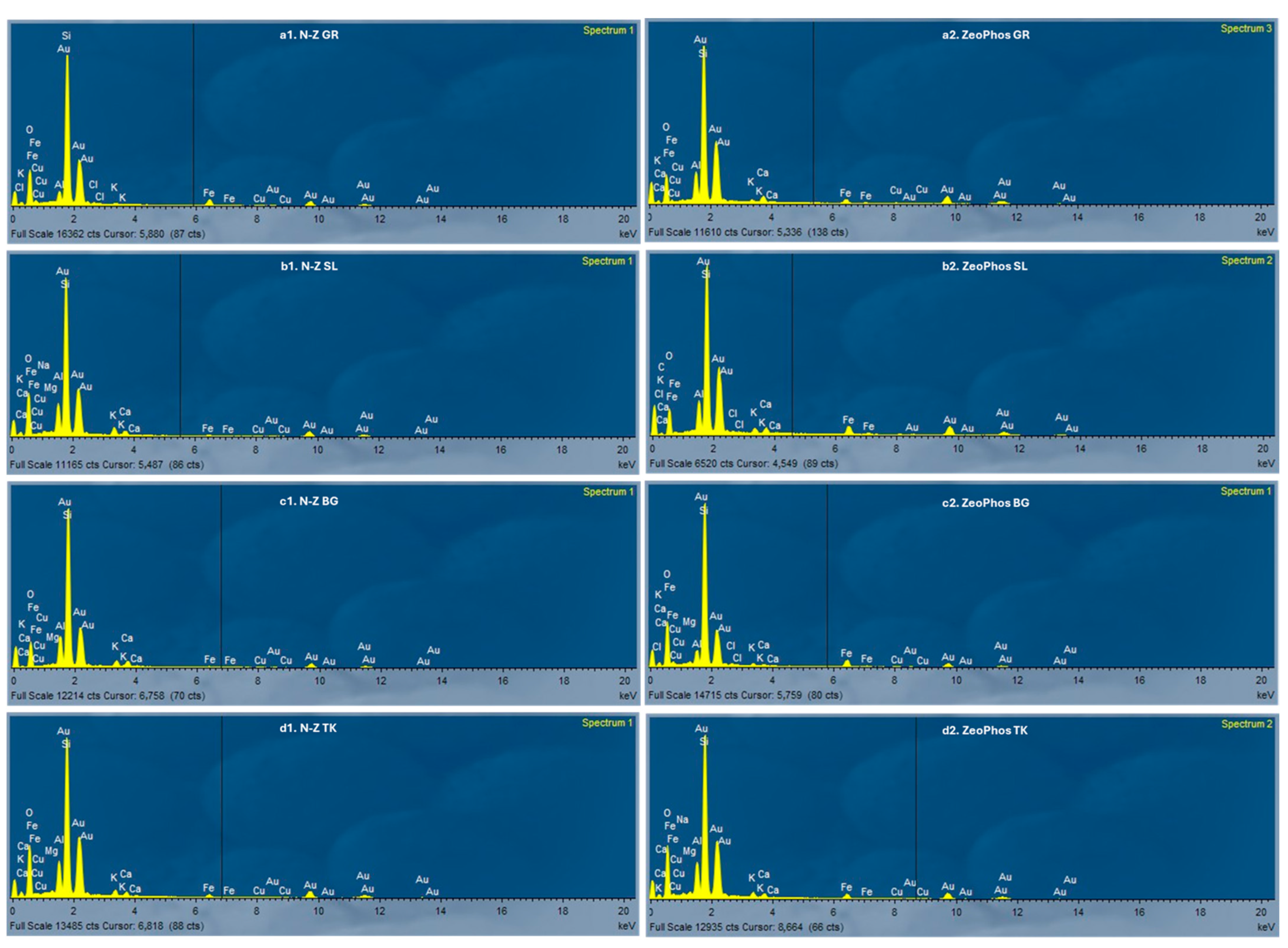

| Material | O (%) | Na (%) | Mg (%) | Al (%) | Si (%) | K (%) | Ca (%) | Fe (%) | Cu (%) | C (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N-Z GR | 49.48 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 6.33 | 37.02 | 0.00 | 0.63 | 2.19 | 3.28 | 1.07 |
| N-Z SL | 48.87 | 0.43 | 0.44 | 5.29 | 32.22 | 0.00 | 2.46 | 1.57 | 1.36 | 0.52 |
| N-Z BG | 49.23 | 0.00 | 0.32 | 6.69 | 38.40 | 0.00 | 2.01 | 2.00 | 0.54 | 0.80 |
| N-Z TK | 49.75 | 0.00 | 0.66 | 6.98 | 37.63 | 0.00 | 1.55 | 1.84 | 0.73 | 0.88 |
| ZeoPhos GR | 42.15 | 0.00 | 0.11 | 5.65 | 40.47 | 0.37 | 0.97 | 2.08 | 6.98 | 1.23 |
| ZeoPhos SL | 42.58 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 5.65 | 31.28 | 0.32 | 1.57 | 1.70 | 6.81 | 0.14 |
| ZeoPhos BG | 53.26 | 0.00 | 0.45 | 4.92 | 30.79 | 0.53 | 1.29 | 1.13 | 6.90 | 0.69 |
| ZeoPhos TK | 49.13 | 0.19 | 0.53 | 6.10 | 34.16 | 0.16 | 2.67 | 1.09 | 4.91 | 1.07 |
| Materials | Ammonium Ion Results | Orthophosphate Ion Results | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe (mg/g) | k2p (g/mg·min) | R2 (%) | qe (mg/g) | k2p (g/mg·min) | R2 (%) | |
| N-Z GR | 8.88 | 0.08 | 99.84 | 5.86 | 0.19 | 99.94 |
| N-Z SL | 6.92 | 0.13 | 99.34 | 6.41 | 0.20 | 99.92 |
| N-Z BG | 6.32 | 1.03 | 99.41 | 6.04 | 0.15 | 99.92 |
| N-Z TK | 6.71 | 0.33 | 99.44 | 5.23 | 0.17 | 99.81 |
| ZeoPhos GR | 8.65 | 0.09 | 99.88 | 7.70 | 0.17 | 99.94 |
| ZeoPhos SL | 8.16 | 0.07 | 99.64 | 7.18 | 0.13 | 99.92 |
| ZeoPhos BG | 6.51 | 0.68 | 99.33 | 6.85 | 0.09 | 99.86 |
| ZeoPhos TK | 6.61 | 0.28 | 99.44 | 5.83 | 0.43 | 99.54 |
| Materials | Ammonium Ion Results | Orthophosphate Ion Results | ||||
| Qm (mg/g) | KL (L/mg) | R2 (%) | Qm (mg/g) | KL (L/mg) | R2 (%) | |
| N-Z GR | 34.35 | 0.09 | 99.48 | 17.78 | 0.09 | 98.83 |
| N-Z SL | 35.25 | 0.14 | 99.38 | 18.01 | 0.46 | 99.08 |
| N-Z BG | 30.94 | 0.10 | 96.64 | 13.65 | 0.28 | 99.86 |
| N-Z TK | 31.64 | 0.22 | 96.38 | 15.67 | 0.14 | 99.37 |
| ZeoPhos GR | 39.55 | 0.07 | 99.31 | 31.91 | 0.08 | 99.89 |
| ZeoPhos SL | 36.87 | 0.12 | 99.41 | 36.88 | 0.15 | 99.34 |
| ZeoPhos BG | 26.43 | 0.11 | 98.88 | 29.69 | 0.22 | 99.61 |
| ZeoPhos TK | 24.83 | 0.24 | 99.52 | 26.85 | 0.09 | 99.96 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Biliani, I.; Papadopoulou, E.; Zacharias, I. Evaluating Zeolites of Different Origin for Eutrophication Control of Freshwater Bodies. Sustainability 2025, 17, 7120. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17157120
Biliani I, Papadopoulou E, Zacharias I. Evaluating Zeolites of Different Origin for Eutrophication Control of Freshwater Bodies. Sustainability. 2025; 17(15):7120. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17157120
Chicago/Turabian StyleBiliani, Irene, Eirini Papadopoulou, and Ierotheos Zacharias. 2025. "Evaluating Zeolites of Different Origin for Eutrophication Control of Freshwater Bodies" Sustainability 17, no. 15: 7120. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17157120
APA StyleBiliani, I., Papadopoulou, E., & Zacharias, I. (2025). Evaluating Zeolites of Different Origin for Eutrophication Control of Freshwater Bodies. Sustainability, 17(15), 7120. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17157120






