The Response Mechanism of Soil Microbial Carbon Use Efficiency to Land-Use Change: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Definition of CUE and Its Impact on SOC
3. Measurement Methods of CUE
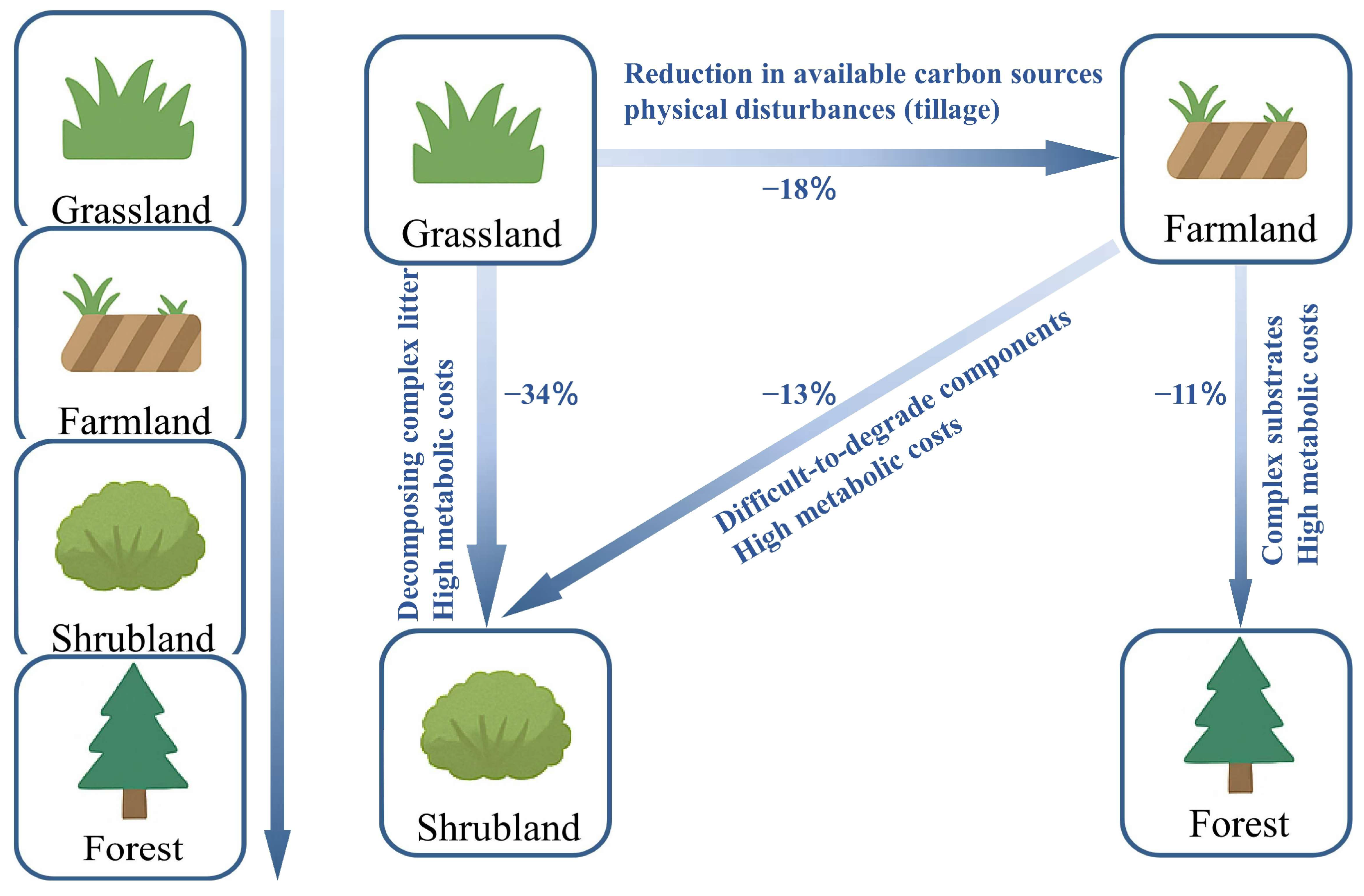
4. Variability of CUE Under Land-Use Change
5. The Impact of Microbial Communities and Interactions on CUE
5.1. Microbial Community Diversity
5.2. Key Microbial Groups
5.3. Microbial Community Interactions
6. Microorganisms Mediate the Effects of Abiotic Factors on CUE
6.1. Temperature and Moisture Sensitivity of CUE
6.2. Threshold Effect of Soil pH on CUE
6.3. Species-Specific Effects of Resources and Their Stoichiometry on CUE
7. Limitations and Future Directions
- (1)
- Lack of long-term monitoring data
- (2)
- Lack of changes in deep soil CUE characteristics
- (3)
- Lack of multidimensional integrated research
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CUE | Carbon use efficiency |
| SOC | Soil organic carbon |
| AMF | Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi |
References
- Zhang, Z. Regulation and Mechanisms of Carbon Effects by Land Use Change. Front. Bus. Econ. Manag. 2024, 14, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bölscher, T.; Ågren, G.I.; Herrmann, A.M. Land-use alters the temperature response of microbial carbon-use efficiency in soils –a consumption-based approach. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 140, 107639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, F.; Huang, Y.; Hungate, B.A.; Manzoni, S.; Frey, S.D.; Schmidt, M.W.I.; Reichstein, M.; Carvalhais, N.; Ciais, P.; Jiang, L.; et al. Microbial carbon use efficiency promotes global soil carbon storage. Nature 2023, 618, 981–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.; Wang, E.; Zheng, H.; Baldock, J.A.; Sun, O.J.; Shao, Q. Convergent modelling of past soil organic carbon stocks but divergent projections. Biogeosciences 2015, 12, 4373–4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Abs, E.; Allison, S.D.; Tao, F.; Huang, Y.; Manzoni, S.; Abramoff, R.; Bruni, E.; Bowring, S.P.K.; Chakrawal, A.; et al. Emerging multiscale insights on microbial carbon use efficiency in the land carbon cycle. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 8010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varney, R.M.; Chadburn, S.E.; Burke, E.J.; Cox, P.M. Evaluation of soil carbon simulation in CMIP6 Earth system models. Biogeosciences 2022, 19, 4671–4704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Shah, J.J.F.; Findlay, S.G.; Kuehn, K.A.; Moorhead, D.L. Scaling microbial biomass, metabolism and resource supply. Biogeochemistry 2015, 122, 175–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smart, K.E.; Breecker, D.O.; Blackwood, C.B.; Gallagher, T.M. A new approach to continuous monitoring of carbon use efficiency and biosynthesis in soil microbes from measurement of CO2 and O2. Biogeosciences 2025, 22, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranheim Sveen, T.; Hannula, S.E.; Bahram, M. Microbial regulation of feedbacks to ecosystem change. Trends Microbiol. 2024, 32, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Manzoni, S.; Moorhead, D.L.; Richter, A. Carbon use efficiency of microbial communities: Stoichiometry, methodology and modelling. Ecol. Lett. 2013, 16, 930–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Wu, Y.; He, Q.; Wang, J.; Bing, H. Microbial nutrient limitation and carbon use efficiency changes under different degrees of litter decomposition. Environ. Geochem. Health 2024, 46, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kallenbach, C.M.; Wallenstein, M.D.; Schipanksi, M.E.; Grandy, A.S. Managing agroecosystems for soil microbial carbon use efficiency: Ecological unknowns, potential outcomes, and a path forward. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, C.; Schimel, J.P.; Jastrow, J.D. The importance of anabolism in microbial control over soil carbon storage. Nat. Microbiol. 2017, 2, 17105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Hou, E.; Zhang, L.; Zang, X.; Yi, Y.; Zhang, G.; Wen, D. Effects of forest conversion on carbon-degrading enzyme activities in subtropical China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 696, 133968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoni, S.; Taylor, P.; Richter, A.; Porporato, A.; Ågren, G.I. Environmental and stoichiometric controls on microbial carbon-use efficiency in soils. New Phytol. 2012, 196, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waring, B.G.; Averill, C.; Hawkes, C.V. Differences in fungal and bacterial physiology alter soil carbon and nitrogen cycling: Insights from meta-analysis and theoretical models. Ecol. Lett. 2013, 16, 887–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnecker, J.; Baldaszti, L.; Gündler, P.; Pleitner, M.; Sandén, T.; Simon, E.; Spiegel, F.; Spiegel, H.; Urbina Malo, C.; Zechmeister-Boltenstern, S.; et al. Seasonal dynamics of soil microbial growth, respiration, biomass, and carbon use efficiency in temperate soils. Geoderma 2023, 440, 116693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lí, J.-T.; Hicks, L.C.; Brangarí, A.C.; Tájmel, D.; Cruz-Paredes, C.; Rousk, J. Subarctic winter warming promotes soil microbial resilience to freeze–thaw cycles and enhances the microbial carbon use efficiency. Glob. Change Biol. 2024, 30, e17040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geyer, K.M.; Kyker-Snowman, E.; Grandy, A.S.; Frey, S.D. Microbial carbon use efficiency: Accounting for population, community, and ecosystem-scale controls over the fate of metabolized organic matter. Biogeochemistry 2016, 127, 173–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Cui, Y.; Manzoni, S.; Zhou, S.; Cornelissen, J.H.C.; Huang, C.; Schimel, J.; Kuzyakov, Y. Microbial Carbon Use Efficiency and Growth Rates in Soil: Global Patterns and Drivers. Glob. Change Biol. 2025, 31, e70036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Turner, B.L.; Talbot, J.M.; Waring, B.G.; Powers, J.S.; Kuske, C.R.; Moorhead, D.L.; Follstad Shah, J.J. Stoichiometry of microbial carbon use efficiency in soils. Ecol. Monogr. 2016, 86, 172–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spohn, M.; Klaus, K.; Wanek, W.; Richter, A. Microbial carbon use efficiency and biomass turnover times depending on soil depth–Implications for carbon cycling. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 96, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Noll, L.; Böckle, T.; Richter, A.; Wanek, W. Growth explains microbial carbon use efficiency across soils differing in land use and geology. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 128, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frey, S.D.; Lee, J.; Melillo, J.M.; Six, J. The temperature response of soil microbial efficiency and its feedback to climate. Nat. Clim. Change 2013, 3, 395–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyer, K.M.; Dijkstra, P.; Sinsabaugh, R.; Frey, S.D. Clarifying the interpretation of carbon use efficiency in soil through methods comparison. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 128, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, L.; Wang, C.; Bai, E. Evaluation of the 18O-H2O incubation method for measurement of soil microbial carbon use efficiency. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 145, 107802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canarini, A.; Wanek, W.; Watzka, M.; Sandén, T.; Spiegel, H.; Šantrůček, J.; Schnecker, J. Quantifying microbial growth and carbon use efficiency in dry soil environments via 18O water vapor equilibration. Glob. Change Biol. 2020, 26, 5333–5341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schimel, J.; Weintraub, M.N.; Moorhead, D. Estimating microbial carbon use efficiency in soil: Isotope-based and enzyme-based methods measure fundamentally different aspects of microbial resource use. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 169, 108677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Deng, L.; Wu, J.; Huang, Y.; Dong, Y.; Peñuelas, J.; Liao, Y.; Yang, L.; Huang, X.; Zhang, H.; et al. Global Change Modulates Microbial Carbon Use Efficiency: Mechanisms and Impacts on Soil Organic Carbon Dynamics. Glob. Change Biol. 2025, 31, e70240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, P.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, Q.; Ling, N.; Nan, Z. Microbial carbon use efficiency in different ecosystems: A meta-analysis based on a biogeochemical equilibrium model. Glob. Change Biol. 2023, 29, 4758–4774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Lu, J.; Yu, Q.; Han, J. Temporal and Spatial Dynamics in Carbon Utilization Efficiency and Driving Mechanisms in Southeast Tibet from 2012 to 2022. Forests 2024, 15, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pausch, J.; Kuzyakov, Y. Carbon input by roots into the soil: Quantification of rhizodeposition from root to ecosystem scale. Glob. Change Biol. 2018, 24, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, S.; He, Q.; Huete, A.; Yang, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Cai, S. Grassland irrigation and grazing prohibition have significantly affected vegetation and microbial diversity by changing soil temperature and moisture, evidences from a 6 years experiment of typical temperate grassland. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2025, 380, 109414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quesada, B.; Arneth, A.; Robertson, E.; de Noblet-Ducoudré, N. Potential strong contribution of future anthropogenic land-use and land-cover change to the terrestrial carbon cycle. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 064023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, M.; Eisenhauer, N.; Sierra, C.A.; Bessler, H.; Engels, C.; Griffiths, R.I.; Mellado-Vázquez, P.G.; Malik, A.A.; Roy, J.; Scheu, S.; et al. Plant diversity increases soil microbial activity and soil carbon storage. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanin, N.; Bertrand, I. Aboveground litter quality is a better predictor than belowground microbial communities when estimating carbon mineralization along a land-use gradient. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 94, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, A.A.; Puissant, J.; Buckeridge, K.M.; Goodall, T.; Jehmlich, N.; Chowdhury, S.; Gweon, H.S.; Peyton, J.M.; Mason, K.E.; van Agtmaal, M.; et al. Land use driven change in soil pH affects microbial carbon cycling processes. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domeignoz-Horta, L.A.; Pold, G.; Liu, X.-J.A.; Frey, S.D.; Melillo, J.M.; DeAngelis, K.M. Microbial diversity drives carbon use efficiency in a model soil. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fan, J.; Hu, Z. Comparison of Carbon-Use Efficiency Among Different Land-Use Patterns of the Temperate Steppe in the Northern China Pastoral Farming Ecotone. Sustainability 2018, 10, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, F.C.; Bestion, E.; Warfield, R.; Yvon-Durocher, G. Changes in temperature alter the relationship between biodiversity and ecosystem functioning. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 10989–10994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Li, L.; Guo, J.; Guo, H.; Liu, M.; Guo, S.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Ling, N.; Shen, Q. Active microbial population dynamics and life strategies drive the enhanced carbon use efficiency in high-organic matter soils. mBio 2024, 15, e00177-24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, B.; Xiao, L.; Lin, D.; Zhang, T.-L.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Zhu, D.; Qian, H.; Rillig, M.C.; et al. Increasing pesticide diversity impairs soil microbial functions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2025, 122, e2419917122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Bi, Y.; Li, P.; Christie, P. Role of an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus in vegetation restoration as indicated by bacterial diversity and microbial metabolic limitation in soil underlying moss biocrusts. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2024, 188, 105728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Cui, H.; Fu, C.; Li, R.; Qi, F.; Liu, Z.; Yang, G.; Xiao, K.; Qiao, M. Unveiling the crucial role of soil microorganisms in carbon cycling: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 909, 168627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, D.V.; Stockdale, E.A.; Brookes, P.C.; Goulding, K.W.T. Impact of microorganisms on chemical transformations in soil. In Soil Biological Fertility: A Key to Sustainable Land Use in Agriculture; Abbott, L.K., Murphy, D.V., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 37–59. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; Dijkstra, P.; Hungate, B.A.; Shi, L.; Dippold, M.A. In situ diversity of metabolism and carbon use efficiency among soil bacteria. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabq3958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, C.; Morrissey, E.M. The size and diversity of microbes determine carbon use efficiency in soil. Environ. Microbiol. 2024, 26, e16633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Zhu, W.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Sheng, Z. Microbial assemblies with distinct trophic strategies drive changes in soil microbial carbon use efficiency along vegetation primary succession in a glacier retreat area of the southeastern Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 867, 161587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd-Alla, M.H.; Al-Amri, S.M.; El-Enany, A.-W.E. Enhancing Rhizobium–Legume Symbiosis and Reducing Nitrogen Fertilizer Use Are Potential Options for Mitigating Climate Change. Agriculture 2023, 13, 2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasner, D.; Schnecker, J.; Han, X.; Sun, Y.; Frossard, A.; Zagal Venegas, E.; Boeckx, P.; Doetterl, S. Environment and microbiome drive different microbial traits and functions in the macroscale soil organic carbon cycle. Glob. Change Biol. 2024, 30, e17465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoni, S.; Čapek, P.; Mooshammer, M.; Lindahl, B.D.; Richter, A.; Šantrůčková, H. Optimal metabolic regulation along resource stoichiometry gradients. Ecol. Lett. 2017, 20, 1182–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashermes, G.; Gainvors-Claisse, A.; Recous, S.; Bertrand, I. Enzymatic strategies and carbon use efficiency of a litter-decomposing fungus grown on maize leaves, stems, and roots. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Op De Beeck, M.; Persson, P.; Tunlid, A. Fungal extracellular polymeric substance matrices–Highly specialized microenvironments that allow fungi to control soil organic matter decomposition reactions. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 159, 108304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrol, N.; Azcón-Aguilar, C.; Pérez-Tienda, J. Review: Arbuscular mycorrhizas as key players in sustainable plant phosphorus acquisition: An overview on the mechanisms involved. Plant Sci. 2019, 280, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, D.; Nayeri, F.D.; Sansinenea, E.; Ortiz, A.; Bhatta, B.B.; Adeyemi, N.O.; Janeeshma, E.; Al-Ani, L.K.T.; Sharma, S.B.; Boutaj, H.; et al. Unraveling arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi interaction in rice for plant growth development and enhancing phosphorus use efficiency through recent development of regulatory genes. J. Plant Nutr. 2023, 46, 3184–3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, J.; George, T.S.; Feng, G. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi enhance mineralisation of organic phosphorus by carrying bacteria along their extraradical hyphae. New Phytol. 2021, 230, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Ju, W.; Chen, H.; Yue, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; et al. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry reveals microbial phosphorus limitation decreases the nitrogen cycling potential of soils in semi-arid agricultural ecosystems. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 197, 104463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cui, Y.; Wang, Y.; Duan, C.; Niu, Y.; Sun, R.; Shen, Y.; Guo, X.; Fang, L. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry reveals phosphorus addition alleviates microbial nutrient limitation and promotes soil carbon sequestration in agricultural ecosystems. J. Soils Sediments 2022, 22, 536–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, A.A.; Martiny, J.B.H.; Brodie, E.L.; Martiny, A.C.; Treseder, K.K.; Allison, S.D. Defining trait-based microbial strategies with consequences for soil carbon cycling under climate change. ISME J. 2020, 14, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierer, N. Embracing the unknown: Disentangling the complexities of the soil microbiome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 15, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martiny, A.C.; Treseder, K.; Pusch, G. Phylogenetic conservatism of functional traits in microorganisms. ISME J. 2013, 7, 830–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasby, F.A.; Barbi, F.; Manzoni, S.; Lindahl, B.D. Transcriptomic markers of fungal growth, respiration and carbon-use efficiency. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2021, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maynard, D.S.; Crowther, T.W.; Bradford, M.A. Fungal interactions reduce carbon use efficiency. Ecol. Lett. 2017, 20, 1034–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva-Sánchez, A.; Soares, M.; Rousk, J. Testing the dependence of microbial growth and carbon use efficiency on nitrogen availability, pH, and organic matter quality. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 134, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iven, H.; Walker, T.W.N.; Anthony, M. Biotic Interactions in Soil are Underestimated Drivers of Microbial Carbon Use Efficiency. Curr. Microbiol. 2022, 80, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, S.D. Modeling adaptation of carbon use efficiency in microbial communities. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Li, Z.; Yuan, J.; Yu, W.; Luo, W. Biotic and abiotic factors affecting soil microbial carbon use efficiency. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1445230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, S.D.; Gupta, V.V.S.R.; Elliott, E.T.; Paustian, K. Protozoan grazing affects estimates of carbon utilization efficiency of the soil microbial community. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2001, 33, 1759–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, J.; Jia, Z.; Zou, H.; Chen, L.; Zhang, C.; Ma, D.; Han, C.; Duan, Y. Long-term conservation tillage enhances microbial carbon use efficiency by altering multitrophic interactions in soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 915, 170018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Yang, J.; Qu, L.; Huang, X.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, P.; Wang, C. Soil microbial carbon use efficiency differs between mycorrhizal trees: Insights from substrate stoichiometry and microbial networks. ISME Commun. 2024, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagg, C.; Schlaeppi, K.; Banerjee, S.; Kuramae, E.E.; van der Heijden, M.G.A. Fungal-bacterial diversity and microbiome complexity predict ecosystem functioning. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puente-Sánchez, F.; Pascual-García, A.; Bastolla, U.; Pedrós-Alió, C.; Tamames, J. Cross-biome microbial networks reveal functional redundancy and suggest genome reduction through functional complementarity. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkelmann, D.; Schneider, D.; Meryandini, A.; Daniel, R. Unravelling the effects of tropical land use conversion on the soil microbiome. Environ. Microbiome 2020, 15, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Vallejo, E.J.; Seeley, M.; Smith, A.P.; Marín-Spiotta, E. A meta-analysis of tropical land-use change effects on the soil microbiome: Emerging patterns and knowledge gaps. Biotropica 2021, 53, 738–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, J.; Peplau, T.; Pennekamp, F.; Gregorich, E.; Tebbe, C.C.; Poeplau, C. Deforestation for agriculture increases microbial carbon use efficiency in subarctic soils. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2024, 60, 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, R.; Frasier, I.; Noellemeyer, E.; Quiroga, A. Soil quality and productivity under zero tillage and grazing on Mollisols in Argentina–A long-term study. Geoderma Reg. 2017, 11, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Bai, E.; Wasner, D.; Hagedorn, F. Global prediction of soil microbial growth rates and carbon use efficiency based on the metabolic theory of ecology. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2024, 190, 109315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, M.; Hu, A.; Zhao, Z.; Yao, X.; Kimirei, I.A.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J. Trait–environmental relationships reveal microbial strategies of environmental adaptation. Ecology 2025, 106, e70047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feit, B.; Blüthgen, N.; Traugott, M.; Jonsson, M. Resilience of ecosystem processes: A new approach shows that functional redundancy of biological control services is reduced by landscape simplification. Ecol. Lett. 2019, 22, 1568–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.P.; Clegg, T.; Bell, T.; Pawar, S. Systematic variation in the temperature dependence of bacterial carbon use efficiency. Ecol. Lett. 2021, 24, 2123–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.; Zhou, Z.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Bastida, F.; Zhao, F.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, C.; Han, X.; et al. Thermal sensitivity of soil microbial carbon use efficiency across forest biomes. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Liu, F.; Ma, T.; Ma, A.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Gao, W.; Yang, Z.; Ke, J.; Xiao, Y.; et al. Temperature and microbial metabolic limitations govern microbial carbon use efficiency in the Tibetan alpine grassland. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2025, 206, 105880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; He, L.; Niu, S.; Wang, J.; Garcia-palacios, P.; Dacal, M.; Averill, C.; Georgiou, K.; Ye, J.-s.; Mo, F.; et al. Nonlinear microbial thermal response and its implications for abrupt soil organic carbon responses to warming. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Qin, W.; Feng, J.; Zhu, B. Responses of soil microbial carbon use efficiency to warming: Review and prospects. Soil Ecol. Lett. 2022, 4, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.L.; Olivera-Ardid, S.; Klumpp, E.; Knief, C.; Hill, P.W.; Lehndorff, E.; Bol, R. Moisture activation and carbon use efficiency of soil microbial communities along an aridity gradient in the Atacama Desert. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 117, 68–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.; Fang, C.; Li, B.; Nie, M.; Li, J. Aridity-driven change in microbial carbon use efficiency and its linkage to soil carbon storage. Glob. Change Biol. 2024, 30, e17565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagerty, S.B.; Allison, S.D.; Schimel, J.P. Evaluating soil microbial carbon use efficiency explicitly as a function of cellular processes: Implications for measurements and models. Biogeochemistry 2018, 140, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butcher, K.R.; Nasto, M.K.; Norton, J.M.; Stark, J.M. Physical mechanisms for soil moisture effects on microbial carbon-use efficiency in a sandy loam soil in the western United States. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 150, 107969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Ju, W.; Duan, C.; Guo, X.; Wang, Y.; Fang, L. Soil moisture mediates microbial carbon and phosphorus metabolism during vegetation succession in a semiarid region. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 147, 107814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Leizeaga, A.; Rousk, J.; Hugelius, G.; Manzoni, S. Drying intensity and acidity slow down microbial growth recovery after rewetting dry soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2023, 184, 109115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brangarí, A.C.; Manzoni, S.; Rousk, J. The mechanisms underpinning microbial resilience to drying and rewetting–A model analysis. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 162, 108400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; He, Y.; Zhou, L.; Liu, R.; Chen, H.; Du, Z.; Fu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, C.; et al. Opposite effects of soil pH on bacteria and fungi β diversity in forests at a continental scale. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 370, 122428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, T.; Chu, H. Threshold effects of soil pH on microbial co-occurrence structure in acidic and alkaline arable lands. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 800, 149592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.L.; Cooledge, E.C.; Hoyle, F.C.; Griffiths, R.I.; Murphy, D.V. pH and exchangeable aluminum are major regulators of microbial energy flow and carbon use efficiency in soil microbial communities. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 138, 107584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, J.; Dǎmǎtîrcǎ, C.; Bölscher, T.; Chenu, C.; Elsgaard, L.; Tebbe, C.C.; Skadell, L.; Poeplau, C. Liming effects on microbial carbon use efficiency and its potential consequences for soil organic carbon stocks. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2024, 191, 109342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenciano, M.N.; Barth, G.; Soares, J.R.; Francisco, E.A.B.; Prochnow, L.I.; Otto, R. Effects of ecological intensification of agriculture on soil fertility and carbon and nitrogen stocks: An 8-year study in southern Brazil. Soil Use Manag. 2024, 40, e13074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, R.; Liu, J.; Lichtfouse, E.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, M.; Xiao, L. Soil microbial carbon use efficiency and the constraints. Ann. Microbiol. 2024, 74, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keiblinger, K.M.; Hall, E.K.; Wanek, W.; Szukics, U.; Hämmerle, I.; Ellersdorfer, G.; Böck, S.; Strauss, J.; Sterflinger, K.; Richter, A.; et al. The effect of resource quantity and resource stoichiometry on microbial carbon-use-efficiency. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2010, 73, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Zhu, W.; Li, X.; Ma, S. Long-term nitrogen addition increased soil microbial carbon use efficiency in subalpine forests on the eastern edge of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Plant Soil 2023, 482, 553–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Qin, S.; Zhang, D.; Chen, P.; Hu, J.; Wang, G.; Liu, Y.; Wei, B.; Li, Q.; Yang, Y.; et al. Nitrogen input enhances microbial carbon use efficiency by altering plant–microbe–mineral interactions. Glob. Change Biol. 2022, 28, 4845–4860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Duan, P.; Hicks, L.; Wang, K.; Li, D. Mechanisms underlying the responses of microbial carbon and nitrogen use efficiencies to nitrogen addition are mediated by topography in a subtropical forest. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 880, 163236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schleuss, P.-M.; Widdig, M.; Heintz-Buschart, A.; Guhr, A.; Martin, S.; Kirkman, K.; Spohn, M. Stoichiometric controls of soil carbon and nitrogen cycling after long-term nitrogen and phosphorus addition in a mesic grassland in South Africa. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 135, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Jin, Z.; Li, X.; Zhu, H.; Fang, F.; Luo, T.; Li, J. Characterization of Microbial Carbon Metabolism in Karst Soils from Citrus Orchards and Analysis of Its Environmental Drivers. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Lin, H.; Li, J. Are there links between nutrient inputs and the response of microbial carbon use efficiency or soil organic carbon? A meta-analysis. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2025, 201, 109656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Li, J.; Qu, L.; Wang, X.; Sang, C.; Wang, J.; Sun, M.; Wanek, W.; Moorhead, D.L.; Bai, E.; et al. Phosphorus limitation reduces microbial nitrogen use efficiency by increasing extracellular enzyme investments. Geoderma 2023, 432, 116416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Cui, Y.; Moorhead, D.L.; Dijkstra, F.A.; Sun, L.; Xia, Z.; Gao, Y.; Ma, Q.; Yu, W. Phosphorus limitation regulates the responses of microbial carbon metabolism to long-term combined additions of nitrogen and phosphorus in a cropland. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2025, 200, 109614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Liu, P.; Chen, L. Enzymatic stoichiometry reveals the metabolic limitations of soil microbes under nitrogen and phosphorus addition in Chinese fir Plantations. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahab, A.; Muhammad, M.; Munir, A.; Abdi, G.; Zaman, W.; Ayaz, A.; Khizar, C.; Reddy, S.P.P. Role of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi in Regulating Growth, Enhancing Productivity, and Potentially Influencing Ecosystems under Abiotic and Biotic Stresses. Plants 2023, 12, 3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhupenchandra, I.; Chongtham, S.K.; Devi, A.G.; Dutta, P.; Sahoo, M.R.; Mohanty, S.; Kumar, S.; Choudhary, A.K.; Devi, E.L.; Sinyorita, S.; et al. Unlocking the Potential of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi: Exploring Role in Plant Growth Promotion, Nutrient Uptake Mechanisms, Biotic Stress Alleviation, and Sustaining Agricultural Production Systems. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, L.; Song, X.; Li, X.; Ma, J.; Chen, F. Changes in abundant and rare microbial taxa that dominated the formation of soil carbon pool during short-term dryland-to-paddy conversion. Carbon Res. 2023, 2, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Yang, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhang, D. Effect of land uses on soil microbial community structures among different soil depths in northeastern China. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2020, 99, 103205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Han, Y.; Chen, M.; Yu, G.; Abulaizi, M.; Hu, Y.; Wang, B.; Yang, Z.; Zhu, X.; Jia, H. Impact of Different Land-Use Types on Soil Microbial Carbon Metabolism Function in Arid Region of Alpine Grassland. Plants 2024, 13, 3531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Su, T.; Wang, H.; Yang, Q.; Lu, J.; Fu, Q.; Mao, H.; Xu, W.; Luo, Y.; Liu, W.; et al. Deep soil microbial carbon use efficiency responds stronger to nitrogen deposition than top soil in tropical forests, southern China. Plant Soil 2024, 500, 605–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhran, M.; Ge, T.; Tong, Y.; Deng, Y.; Wei, X.; Lynn, T.M.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, J.; Gunina, A. Assessment of depth-dependent microbial carbon-use efficiency in long-term fertilized paddy soil using an 18O-H2O approach. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Deng, L.; Wu, J.; Bai, E.; Chen, J.; Shangguan, Z.; Kuzyakov, Y. Soil Organic Carbon Increases with Decreasing Microbial Carbon Use Efficiency During Vegetation Restoration. Glob. Change Biol. 2024, 30, e17616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Li, K.; Yuan, F.; Zuo, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhu, X.; Sun, Y.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, L.; Gong, C.; et al. Faster cycling but lower efficiency: A microbial metabolic perspective on carbon loss after wetland conversion to cropland. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2024, 189, 109260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Research Objective | Preferred Method | Suitable Soil Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Substrate- specific CUE | 13C-labeled compounds | Agricultural or lab-controlled | Sensitive to substrate selection |
| Whole-community CUE | 18O-labeled water method | Moist, temperate soils [19,20] | High accuracy, costly, not for dry soils |
| Long-term field monitoring | Stoichiometric modeling | Grassland or cropland [21] | Simplified, less precise, for trends |
| Functional gene-based CUE | Metagenomic data approaches | Any, especially natural soils [13] | Novel, promising, technical, early stage |
| Microbial response dynamics | Microbial biomass | Any with time series [22,23] | Rapid, integrative |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Qi, D. The Response Mechanism of Soil Microbial Carbon Use Efficiency to Land-Use Change: A Review. Sustainability 2025, 17, 7023. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17157023
Li Z, Qi D. The Response Mechanism of Soil Microbial Carbon Use Efficiency to Land-Use Change: A Review. Sustainability. 2025; 17(15):7023. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17157023
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zongkun, and Dandan Qi. 2025. "The Response Mechanism of Soil Microbial Carbon Use Efficiency to Land-Use Change: A Review" Sustainability 17, no. 15: 7023. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17157023
APA StyleLi, Z., & Qi, D. (2025). The Response Mechanism of Soil Microbial Carbon Use Efficiency to Land-Use Change: A Review. Sustainability, 17(15), 7023. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17157023





