Abstract
Climate warming poses significant challenges for the sustainable management of natural water resources, making efficient planning and usage essential. This study evaluates the water requirements, irrigation demand, and rainfall deficits for two key vegetable crops, carrot and white cabbage, under projected climate scenarios RCP 4.5 and RCP 8.5 for the period 2031–2100. The analysis was conducted for Kraków and Rzeszów Counties in southern Poland using projected monthly temperature and precipitation data from the Klimada 2.0 portal. Potential evapotranspiration (ETp) during the growing season (May–October) was estimated using Treder’s empirical model and the crop coefficient method adapted for Polish conditions. The reference period for comparison was 1951–2020. The results reveal a significant upward trend in water demand for both crops, with the highest increases under the RCP 8.5 scenario–seasonal ETp values reaching up to 517 mm for cabbage and 497 mm for carrot. Rainfall deficits are projected to intensify, especially during July and August, with greater shortages in Rzeszów County compared to Kraków County. Irrigation demand varies depending on soil type and drought severity, becoming critical in medium and very dry years. These findings underscore the necessity of adapting irrigation strategies and water resource management to ensure sustainable vegetable production under changing climate conditions. The data provide valuable guidance for farmers, advisors, and policymakers in planning effective irrigation infrastructure and optimizing water-use efficiency in southern Poland.
1. Introduction
The cultivation of carrot (Daucus carota L.) and white cabbage (Brassica oleracea L. var. capitata) plays a vital role in global agriculture, particularly in Central Europe, both economically and culturally. These vegetables are integral to the culinary traditions of the region [1,2,3,4,5]. Poland is among the leading producers of cabbage in the European Union, with an annual output of approximately 0.8–1.0 million tonnes, representing around 27% of EU production [6]. In 2023, Poland ranked first in Europe with a cabbage production of about 670 thousand tonnes [7]. Carrot production is also significant, reaching 0.7–0.8 million tonnes annually, placing Poland third in the EU, behind Germany and the United Kingdom [6].
However, climate change is one of the most pressing challenges facing 21st-century agriculture, particularly in terms of water resource management. Rising average temperature, increasing precipitation variability, and more frequent extreme weather events have a substantial impact on crop water balances, increasing the risk of water deficits and yield losses [8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15]. Climate scenarios such as Representative Concentration Pathways (RCPs) allow for robust modeling of future climate conditions and their impacts on agriculture [16,17]. RCP 4.5 and RCP 8.5 represent moderate and high greenhouse gas emission pathways, respectively, projecting temperature increases and changes in precipitation patterns across Central and Eastern Europe [18]. According to climate projections, the global mean temperature could rise by up to 4 °C by the end of the 21st century, with increases of 2–4 °C expected in Central Europe. While annual total precipitation may not change significantly, its temporal and spatial distribution is likely to become increasingly irregular, with prolonged dry spells interrupted by short, intense rainfall events [19,20,21,22,23,24].
Field-grown vegetables such as carrots and white cabbage are highly sensitive to climatic variability due to their developmental cycles and water requirements being closely tied to environmental conditions. In Poland, where water availability is often limited and seasonal rainfall shortages are becoming more pronounced, assessing future crop water needs is critical for sustaining horticultural production [25,26]. Long-term estimates confirm the substantial water needs of both crops. Carrot water demand during the growing season typically ranges from 300 mm to 400 mm [25,27,28,29,30] and may reach up to 390 mm in dry years on loamy soils and upland areas, 340 mm in the Pomerania, Warmia, and Masuria regions, and 360 mm in the Great Valleys [29]. For cabbage, seasonal water requirements vary regionally: around 370 mm in the Great Valleys, 390 mm in Pomerania and the northeast, and up to 410 mm in lowlands and uplands [29]. Kaniszewski and Treder [25] and Kaniszewski [27,30] estimated the water demand for late cabbage at between 400 mm and 600 mm. These values highlight the considerable and regionally differentiated irrigation needs under current climatic conditions.
Given the projected impacts of climate change, the introduction of adaptive agricultural strategies, such as irrigation, is increasingly recommended [31]. In the context of increasing potential evapotranspiration (ETp) and deepening precipitation deficits, irrigation planning and optimization are becoming ever more important [32,33]. Effective water management requires a detailed understanding of crop water requirements, as well as the spatial and temporal variability of precipitation and its relationship with ETp. This is especially relevant in southern Poland, where soil characteristics and climatic conditions lead to substantial regional differences in irrigation needs. Studies by Badora et al. [31] and Teshager et al. [34] indicate that regardless of the emission scenario, significant water deficits are expected under both RCP 4.5 and RCP 8.5, supporting the need for water retention infrastructure such as reservoirs. Changing weather patterns are already placing pressure on agricultural water resources, underscoring the growing importance of irrigation, especially deficit irrigation, and the need for more efficient water management practices [35].
This study investigates how future climate conditions under the RCP 4.5 and RCP 8.5 scenarios will affect seasonal water requirements, precipitation deficits, and irrigation needs for carrot and white cabbage in two counties of southern Poland—Kraków and Rzeszów—during 2031–2100, compared to the 1951–2020 reference period. The following hypotheses were formulated: (1) future climate projections will significantly increase evapotranspiration and crop water demand; (2) precipitation deficits will intensify, especially under RCP 8.5 and in very dry years; (3) irrigation needs will rise, particularly on low-retention soils; and (4) Rzeszów County will face greater water deficits due to higher ETp and lower rainfall. By analyzing two crops with contrasting characteristics in two regions under different climate scenarios, this study offers a crop- and location-specific perspective, filling gaps left by broader Central European analyses. It integrates high-resolution climate projections with models of crop water demand to support regional adaptation strategies. The findings may assist farmers, advisors, and water managers in optimizing crop planning, improving water-use efficiency, and guiding irrigation infrastructure development in response to future climate change.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Subject
This study investigates the potential evapotranspiration (ETp) as an indicator of water demand of two vegetable crops, white cabbage (Brassica oleracea L., Brassicaceae) and carrot (Daucus carota L., Apiaceae), projected for the period from 2031 to 2100. The analysis focused on two key agricultural areas in southern Poland: Kraków County and Rzeszów County, both recognized for their significant producers of these crops.
Kraków County is located in the Małopolska region, while Rzeszów County lies in the Podkarpackie region. The studied areas are situated in the foothills of the Carpathians, at elevations ranging from 200 to 400 m above sea level. The terrain is moderately undulating, and the soils are primarily brown and podzolic types, suitable for vegetable cultivation. The climate is classified as humid continental (Dfb, Köppen–Geiger), characterized by cold winters and warm summers. During the reference period, the average annual temperature was approximately 8.5 °C in Kraków County and 8.0 °C in Rzeszów County. Annual precipitation ranged from 650 mm in Kraków County to about 700 mm in Rzeszów County, with the majority of rainfall occurring between May and August. The hydrographic network includes the Vistula River in Kraków County and the Wisłok River in Rzeszów County. These rivers exhibit a pluvial-naval regime, with high flow in spring due to snowmelt and another peak in summer due to rainfall [36,37,38]. Meteorological data used in this study were obtained from two reference weather stations: Kraków (50°05′ N, 19°48′ E) and Rzeszów (50°06′ N, 22°03′ E). Their exact locations are marked on the map, which also highlights the study regions within Poland (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
Locations of Kraków and Rzeszów Counties and weather stations sites.
The reference period was set as 1951–2020, spanning seventy years. The current decade (2021–2030) was not included in the study. Calculations were based on the six-month vegetation period of both crops, extending from May through October, for both the reference and projected periods.
Projected meteorological data on mean monthly temperature and monthly rainfall totals for 2031–2100 were obtained from the Klimada 2.0 portal [39]. Calculations were performed for two greenhouse gas emission scenarios, RCP 4.5 and RCP 8.5, developed by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), representing potential climate trajectories in the 21st century [40]. RCP 4.5 is a moderate scenario that assumes the implementation of emission reduction policies, resulting in stabilization of radiative forcing at 4.5 W/m2 by 2100, with carbon dioxide concentration reaching approximately 540 ppm. This scenario projects a moderate global temperature increase of about 1.8–2.6 °C relative to preindustrial levels. Conversely, RCP 8.5 represents a high-emission scenario, assuming continued increases in greenhouse gas emissions without effective mitigation. It leads to radiative forcing of 8.5 W/m2 by 2100 (carbon dioxide concentration around 940 ppm), with potential global temperature increases ranging from 3.2 °C to 5.4 °C above preindustrial levels.
Although Klimada 2.0 relies on a single downscaled model chain for each RCP, it is considered an authoritative and policy-relevant source for regional climate projections in Poland. No multi-model comparison or uncertainty analysis was performed in this study, which should be considered a limitation when interpreting the results.
Data from the reference period indicated that Kraków County experienced higher monthly air temperature throughout the vegetation period compared to Rzeszów County. Monthly rainfall totals were also consistently higher in Kraków County than in Rzeszów County (Table 1).

Table 1.
Climatic characteristics of Kraków and Rzeszów Counties during the reference period (1951–2020).
2.2. Estimation of Potential Evapotranspiration for Cabbage and Carrot
Potential evapotranspiration (ETp) for cabbage and carrot was estimated based on air temperature using the crop coefficient method [41,42,43]. In this approach, crop water requirements correspond to ETp values for each species. Crop coefficients (Kc) adapted to Polish climatic conditions by Treder [43] were applied (Table 2). Potential evapotranspiration (ETp, mm) was calculated using Equation (1):
where Kc is the crop coefficient, defined as the ratio of ETp under well-watered conditions to reference evapotranspiration (ETo) [42] (Table 2); ETo is the reference evapotranspiration (mm).

Table 2.
Crop coefficients (Kc) for cabbage and carrot used in potential evapotranspiration calculations and the empirical coefficient (α) for reference evapotranspiration estimation according to Treder [37].
Reference evapotranspiration (ETo) was calculated using Treder’s empirical Equation (2) [43]:
where n is the number of days in the month; α is an empirical coefficient determined by Treder [43] (Table 2); and T is the mean monthly air temperature (°C).
The selection of Treder’s empirical method for reference evapotranspiration (ETo) estimation was guided by its proven effectiveness in the climatic conditions of Poland and its calibration for locally available meteorological data. While the FAO Penman–Monteith equation is globally recognized for its accuracy, its application requires detailed meteorological inputs such as solar radiation, wind speed, and humidity, which were not available for long-term projections from the Klimada 2.0 dataset. Thus, the empirical approach provided a practical and reliable alternative for regional-scale climate scenarios. Nevertheless, it is acknowledged that empirical models may introduce simplifications and can underestimate the sensitivity of ETo to climatic extremes.
2.3. Rainfall Deficiency Analysis for Cabbage and Carrot
Rainfall deficiency during very dry (N10%), medium dry (N25%), and normal (N50%) years was evaluated using Ostromęcki’s method [26,44,45]. Rainfall deficiency (mm) was calculated using Equation (3):
where Np% denotes the rainfall deficiency with a probability of occurrence p% (mm per period); ETp is the long-term mean ETp over the analyzed period (mm); P is the long-term mean rainfall for the period (mm); and Ap% and Bp% are coefficients characterizing the variability of evapotranspiration and precipitation, respectively, calculated for each meteorological station.
2.4. Irrigation Water Demand Analysis for Cabbage and Carrot
Irrigation water demand (IWD) for carrot and cabbage plantations in Kraków and Rzeszów Counties was calculated, accounting for effective usable soil water retention (EUSWR). Calculations were performed for three soil types differing in water retention capacity. EUSWR was assumed for the 0–100 cm soil profile as follows: loose sandy soils (light soil)—44 mm; medium sand soils (medium soil)—63 mm; clay soils (heavy soil)—92 mm. These values of ΔW (available soil moisture retention) were adopted based on standard agronomic guidelines and reflect typical effective water-holding capacities of Polish soils in the root zone. The classification and values are consistent with recommendations of the Institute of Soil Science and Plant Cultivation (IUNG-PIB), Puławy, Poland, and are widely used in regional water balance assessments.
IWD (mm) was calculated using the water balance Equation (4):
where ETp is the potential evapotranspiration of cabbage or carrot (mm), calculated as in Equation (1); P is precipitation (mm); and ΔW is the available soil moisture retention (EUSWR, mm). The difference (ETp − P) represents rainfall deficiency, calculated as per Equation (3).
2.5. Statistical Analysis
The results were statistically processed by calculating minimum, maximum, and mean values, along with standard deviation and coefficient of variation. Trends in potential evapotranspiration for cabbage and carrot were evaluated for both reference and projected periods using linear regression analysis. Correlation coefficients (r) and determination coefficients (R2) were determined. The significance of correlation coefficients was assessed at confidence levels of p = 0.1 (90%), p = 0.05 (95%), and p = 0.01 (99%).
3. Results
3.1. Standard Deviation and Coefficient of Variation of Water Requirements
Table 3 and Table 4 present the standard deviation and coefficient of variation of the water requirements for cabbage and carrot, expressed as potential evapotranspiration (ETp). The statistical analysis was based on 70 years of data for the reference period (1951–2020) and the projected periods (2031–2100) under the RCP 4.5 and RCP 8.5 scenarios. For both crops, the highest values of these parameters occurred in July and August, while the lowest standard deviation was observed in May. The elevated standard deviation in July was likely due to peak vegetation growth, coinciding with increased variability in temperature and precipitation, which in turn causes fluctuations in water demand.

Table 3.
Standard deviation (mm) and coefficient of variation (%) of water requirements for cabbage.

Table 4.
Standard deviation (mm) and coefficient of variation (%) of water requirements for carrot.
A comparison between the reference period and the projected scenarios revealed generally higher values of both standard deviation and coefficient of variation under RCP 8.5 than under RCP 4.5. Although ETp variability under RCP 8.5 remained close to that of the reference period in most months, a notable exception was September, where both the standard deviation and coefficient of variation increased markedly. This indicates enhanced variability in potential evapotranspiration, likely driven by irregular precipitation and temperature fluctuations at the end of the growing season. Overall, the variability in water requirements for cabbage and carrot was similar in both study regions.
3.2. Water Requirements
In all analyzed periods and locations, the highest monthly ETp totals for cabbage and carrot occurred in July (Figure 2a,b), followed by August and June. The lowest values were recorded in May, followed by October and September. During the projected periods, Rzeszów County exhibited higher total ETp than Kraków County, contrasting with the reference period. This shift is likely due to regional differences in projected climate conditions, particularly higher average temperature and solar radiation in southeastern Poland, where Rzeszów County is located, under both RCP 4.5 and RCP 8.5 scenarios. Additionally, higher ETp values were observed under RCP 8.5 compared to RCP 4.5. Seasonal water requirements for cabbage peaked under RCP 8.5 at 517 mm in Rzeszów County and 511 mm in Kraków County (Figure 2c). A similar trend was observed for carrot, with maximum seasonal water requirements of 497 mm and 491 mm, respectively (Figure 2d).
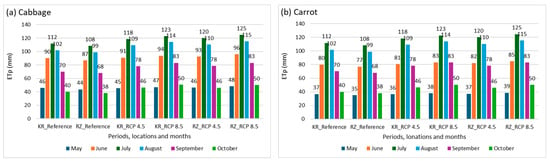
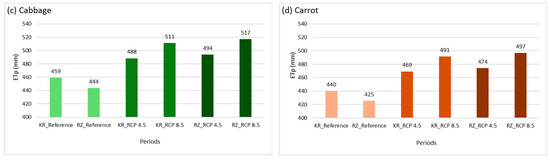
Figure 2.
Potential evapotranspiration (ETp, mm): (a) monthly values during the vegetation period for cabbage, (b) for carrot, (c) seasonal average for cabbage, (d) for carrot—by region and climatic scenario; KR_Reference—reference period in Kraków County; RZ_Reference—reference period in Rzeszów County; KR_RCP 4.5—projected period under RCP 4.5 in Kraków County; KR_RCP 8.5—projected period under RCP 8.5 in Kraków County; RZ_RCP 4.5—projected period under RCP 4.5 in Rzeszów County; RZ_RCP 8.5—projected period under RCP 8.5 in Rzeszów County.
3.3. Temporal Trends in Water Requirements
Trend equations and correlation coefficients for cabbage and carrot ETp are shown in Table 5 and Table 6. Statistically significant upward trends were observed for both crops in both counties across all analyzed time intervals: May–October, May–September, June–August, and July. The only exception was July in Kraków County during the reference period, where the trend was not significantly significant.

Table 5.
Trend equations and correlation coefficients for cabbage potential evapotranspiration.

Table 6.
Trend equations and correlation coefficients for carrot potential evapotranspiration.
Table 7 summarizes the projected increases in ETp. Under RCP 8.5, seasonal water demand increased by 12.2 mm per decade in Kraków County and 12.0 mm per decade in Rzeszów County for cabbage, and by 11.8 mm and 11.6 mm per decade, respectively, for carrot. Under the more moderate RCP 4.5 scenario, the decadal increases were considerably smaller: approximately 3.3 mm per decade for cabbage and 3.1–3.2 mm for carrot. These trends are illustrated in Figure 3.

Table 7.
Decadal trends in potential evapotranspiration (mm per decade).
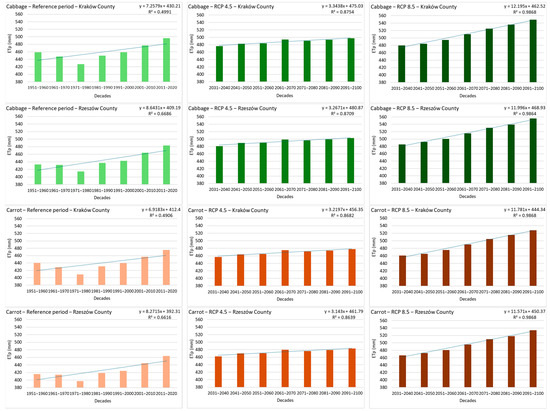
Figure 3.
Time trends in potential evapotranspiration (ETp, mm) for cabbage and carrot during the vegetation period in the reference and projected (RCP 4.5 and RCP 8.5) periods in Kraków and Rzeszów Counties; the dashed line indicates the trend.
3.4. Projected Increase in Water Requirements
Table 8 compares average ETp values between the reference and projected periods. Rzeszów County showed a greater increase in water demand than Kraków County. Under RCP 8.5, seasonal ETp increased by 16% for cabbage and 17% for carrot in Rzeszów County, compared to 11% and 12%, respectively, in Kraków County. This difference is attributed to higher projected ETp, especially during summer, and a more pronounced decline in effective precipitation in Rzeszów County. Additional factors include regional differences in temperature and soil water retention capacity. In rainfall equivalents, cabbage cultivation in Rzeszów County would require an additional 73 mm, 80 mm, and 88 mm in normal, medium dry, and very dry years, respectively; for carrot, the values are 71 mm, 78 mm, and 86 mm. In Kraków County, the corresponding increases are: 52 mm, 57 mm, and 62 mm for cabbage, and 51 mm, 57 mm, and 62 mm for carrot.

Table 8.
Projected increase in potential evapotranspiration (mm) relative to the reference period.
3.5. Rainfall Deficiency
Figure 4 shows monthly rainfall deficiencies for cabbage and carrot. Projected years, especially under RCP 8.5, exhibit greater deficiencies than the reference period, particularly in July and August. These deficits are more severe in Rzeszów County than in Kraków County, due to higher ETp and reduced effective precipitation. Lighter soils and complex topography likely contribute to increased runoff and lower soil moisture retention, intensifying water deficits. Maximum monthly rainfall deficiencies for Rzeszów County under RCP 8.5 are projected at 87.7 mm in July and 86.8 mm in August; in Kraków County, the respective values are 83.3 mm and 81.4 mm.
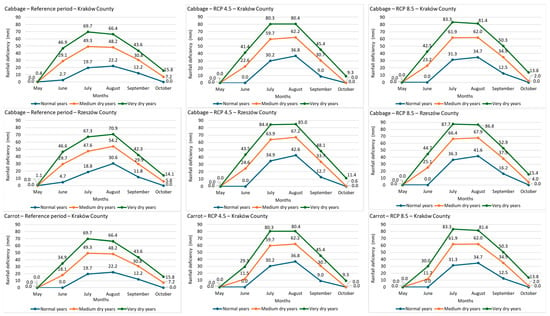
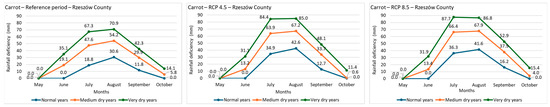
Figure 4.
Monthly rainfall deficiency (mm) for cabbage and carrot during the vegetation period in the reference and projected (RCP 4.5 and RCP 8.5) periods in Kraków and Rzeszów Counties.
Figure 5 presents cumulative seasonal rainfall deficits. These are consistently greater under projected scenarios than during the reference period, and higher under RCP 8.5 than RCP 4.5. Rainfall deficiencies were more pronounced in Rzeszów County: seasonal cumulative deficits for cabbage reached 94.2 mm in normal years, 201.3 mm in medium dry years, and 287.5 mm in very dry years. For carrot, corresponding values were 94.2 mm, 189.6 mm, and 274.7 mm.
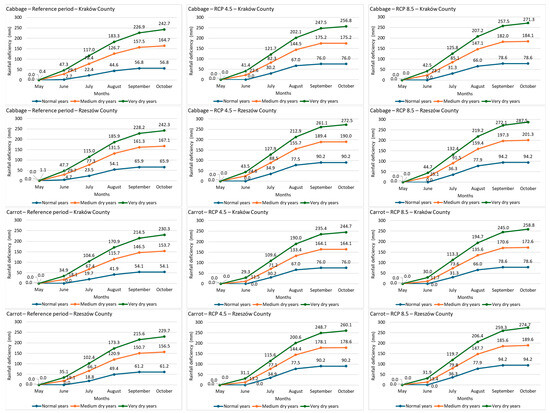
Figure 5.
Cumulated rainfall deficiencies (mm) for cabbage and carrot during the vegetation period in the reference and projected (RCP 4.5 and RCP 8.5) periods in Kraków and Rzeszów Counties.
3.6. Irrigation Water Demand
Table 9 and Table 10 present irrigation water requirements. In normal years, irrigation needs are minimal and nearly negligible for heavy soils. However, in medium dry and very dry years, irrigation becomes essential across all soil types. Irrigation demand is higher in Rzeszów County due to elevated ETp and more significant reductions in effective precipitation. Additionally, soils in Rzeszów County, particularly on light- and medium-textured sites, generally exhibit lower water retention capacity than those in Kraków County. The more varied relief of the area may also contribute to increased runoff, reducing the amount of water available for plant uptake. Under RCP 8.5, irrigation demand for cabbage during very dry years in Rzeszów County is projected at 243.5 mm, 224.5 mm, and 195.5 mm for light, medium, and heavy soils, respectively. For carrot, the corresponding values are 230.7 mm, 211.7 mm, and 182.7 mm.

Table 9.
Irrigation water demand (mm) for cabbage by soil type.

Table 10.
Irrigation water demand (mm) for carrot by soil type.
4. Discussion
Climate change is expected to have profound effects on water availability and crop water requirements, necessitating the re-evaluation of traditional irrigation strategies. The primary aim of this study was to assess water requirements, irrigation needs, and rainfall deficits for white cabbage and carrot cultivation in two counties of southern Poland under the RCP 4.5 and RCP 8.5 climate scenarios. It was hypothesized that rising temperature and changing precipitation patterns would significantly increase crop water demand and introduce challenges to sustainable production.
High values of standard deviation and coefficients of variation underscore substantial interannual variability in ETp and rainfall, especially under RCP 8.5. This variability complicates irrigation scheduling and poses risks to yield stability. Rzeszów County exhibited more pronounced year-to-year fluctuations, suggesting the need for flexible and adaptive water management strategies. These findings are consistent with studies conducted in other parts of Central and Eastern Europe, where increased weather variability challenges conventional crop planning [46,47].
Peak water demand is expected to occur in July, consistent with broader trends across Europe [25,26,29]. The projected July ETp, especially under RCP 8.5, aligns with summer water demand trends observed not only in Poland [25] but also in other regions of Europe [33]. The projected increase in seasonal ETp for both vegetables and in both counties reflects not only climatic warming but also a shift in crop phenology. An extended growing season, hastened vegetative growth, and altered critical phenophases (e.g., root bulking, head formation) may affect water and nutrient uptake efficiency. Water stress during sensitive phenological stages can result in significant productivity losses, particularly for shallow-rooted crops like carrot and cabbage [48,49,50,51,52,53,54]. In particular, phenophase-specific thresholds for water stress should be identified to guide adaptive irrigation practices [55].
Decadal increases in ETp under the RCP 8.5 scenario for both vegetables reach 4.9 mm per decade in Kraków County and 3.4 mm per decade for cabbage and 3.3 mm per decade for carrot in Rzeszów County (Table 7). However, during the last five decades of the reference period (1971–2020), these increases were higher—up to 9.3 mm per decade for cabbage in Kraków County, 7.9 mm per decade in Rzeszów County, 9.0 mm per decade for carrot in Kraków County, and 7.6 mm per decade in Rzeszów County—exceeding the average for the full reference period (1951–2020) (Figure 6). Previous studies confirm that water deficits in agriculture are likely to intensify regardless of the climate scenario, although the more severe RCP 8.5 scenario forecasts greater deficits and more substantial disturbances in water management [31,34].
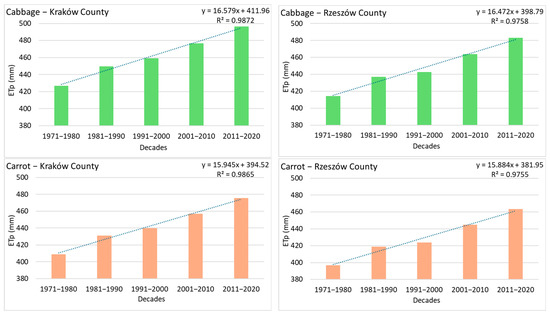
Figure 6.
Time trends in potential evapotranspiration (ETp, mm) for cabbage and carrot in the reference years 1971–2020 in Kraków and Rzeszów County; the dashed line indicates the trend.
Interacting with these climate-driven pressures are soil-water dynamics, which play a decisive role in water availability and root zone retention. Rzeszów County, with its higher proportion of sandy and less retentive soils, faces larger seasonal rainfall deficits, especially under RCP 8.5 and on medium and heavy soils. Conversely, Kraków County’s clay and loamy soils buffer against rapid evapotranspiration losses, although even these may be insufficient under extreme heatwave conditions. These findings mirror research showing that soil texture significantly moderates drought impact [56,57,58].
Regional differences in water demand, trends, and rainfall deficiencies stem from local climate and soil conditions. Rzeszów County experience higher summer temperature and lower rainfall than Kraków County, contributing to higher ETp and irrigation demand. Kraków County, by contrast, contains more loamy and clay soils, which retain moisture more effectively. The continental climatic influence in Rzeszów County may further intensify temperature and rainfall variability. These regional differences highlight the necessity of location-specific adaptation strategies [36,37,38].
On average, rainfall deficits in Poland reach 220 mm for white cabbage [59] and 200 mm for carrot [29]. Our findings confirm that irrigation needs are greatest in very dry years on light soils—up to 244 mm and 227 mm for cabbage in Rzeszów and Kraków Counties, respectively, and 231 mm and 215 mm for carrot. Similar patterns are reported globally. In Croatia, for example, comparing two climate periods revealed an increased soil water deficit during the cabbage growing season—both under average annual conditions and in dry years [60]. In Korea, a study showed that under a water deficit, carrot yields decreased in fresh weight as well in dry weight compared to the control conditions [61]. These global insights support the notion that water management must account for both regional climate projections and soil-specific characteristics.
Given the increasing frequency of extreme weather events, crop management must adapt to local conditions such as temperature, precipitation, and soil water capacity [29,62]. Studies show rising temperature and declining precipitation in Poland, increasing crop water demand [63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71]. Our results confirm that higher water requirements for white cabbage and carrot are mainly driven by temperature rise and reduced effective rainfall, though some sources note uncertainty about climate change impacts in Poland [72,73]. Adaptive measures should include deficit irrigation, mulching, adjusted sowing dates, and drought-tolerant cultivars [74,75]. Investments in efficient irrigation systems (e.g., drip or sprinkler), farmer education, and advisory support are essential. Economic factors, such as cost-effectiveness, financial access, and intersectoral water competition, must be considered in water management planning. Without supportive policies, climate projections may not lead to effective action. Future strategies may also require a shift toward less water-demanding crops, assessed through regional planning and market analysis [76].
Globally, irrigation has proven to be a highly effective practice for both cabbage [77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84] and carrot [85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92]. In Poland, irrigation led to cabbage yield increases even of up to 300%, depending on weather conditions and soil quality, and for carrot, yield increases reached up to 50% [93]. However, both currently and increasingly in the future, irrigated agriculture will need to operate under water scarcity. Limited water availability will become the norm, necessitating a focus on maximizing production per unit of water used (water productivity). One key strategy for reducing water use is deficit irrigation, which involves applying less water than the crop’s full evapotranspiration demand [33,89,94,95]. A significant challenge is that the current irrigation infrastructure may not meet the maximum water demands. Therefore, its deliberate and gradual expansion is essential. This requires detailed knowledge of crop water requirements and precipitation deficits under local climate and soil conditions to support sustainable water resource management [32,96].
The findings of this study provide a foundation for practical applications in planning climate-resilient agricultural production. They may prove valuable to farmers, agricultural advisors, and water resource management institutions in developing irrigation strategies that consider future climate conditions. Insight into projected precipitation deficits and irrigation needs enables improved crop planning, more efficient water use, and reduced yield loss risks. Importantly, these results support more accurate estimations of the water volumes required for irrigation, contributing to the informed planning and development of irrigation infrastructure tailored to future needs for carrot and white cabbage cultivation. Moreover, the outcomes may inform broader strategies for water resource optimization and climate change adaptation at both regional and national levels. In light of these findings, we emphasize the importance of integrating climate impact models with economic analysis and long-term land use planning. Agricultural policy should not only support the development of irrigation infrastructure but also promote risk-reduction measures such as crop diversification, flexible planting schedules, and subsidies for sustainable water technologies.
5. Conclusions
This study demonstrated a statistically significant increase in water requirements for carrot and white cabbage cultivation in southern Poland under future climate scenarios RCP 4.5 and RCP 8.5. The projected rise in potential evapotranspiration is linked to expected warming and changing precipitation patterns throughout the 21st century. The more severe RCP 8.5 scenario resulted in notably higher seasonal water demand compared to RCP 4.5, with the most substantial increases observed in Rzeszów County. Rainfall deficits are projected to intensify, especially in July and August, exacerbating challenges in maintaining optimal soil moisture. These deficits are particularly pronounced in very dry years and in areas with low soil water retention, further elevating irrigation demand. While these findings underscore the growing importance of irrigation, the assumption of future availability of sufficient water resources and infrastructure must be approached with caution. Local water supply constraints, competing demands, and economic limitations could restrict the feasibility of expanding irrigation in some regions of Europe. Therefore, integrating climate projections into agricultural planning is essential, not only for irrigation scheduling and investment in water-saving technologies, but also for critically evaluating regional water resource capacities. Tailoring adaptation strategies, such as irrigation scheduling, crop selection, and soil moisture conservation, to the specific requirements of carrot and cabbage cultivation may improve resource efficiency and production stability. This study provides valuable insights for policymakers and agricultural stakeholders, supporting the development of more resilient farming systems in southern Poland. Future efforts should focus on assessing the economic and hydrological viability of irrigation infrastructure, as well as exploring adaptive cultivation practices, including drought-tolerant cultivars, modified phenology, and soil moisture conservation techniques. Limitations of this study include reliance on a single regional climate model and fixed crop phenology, as well as the exclusion of short-term extreme events such as heatwaves or flash droughts. These factors should be addressed in future research to provide a more comprehensive understanding of climate change impacts on crop water demand. These limitations highlight the need for further studies using multi-model ensembles and dynamic crop models.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.R., R.K.-T. and R.R.; methodology, S.R. and R.R.; software, S.R. and R.R.; validation, S.R. and R.R.; formal analysis, S.R.; investigation, S.R. and R.K.-T.; resources, S.R. and R.R.; data curation, S.R. and R.K.-T.; writing—original draft preparation, S.R., B.J. and R.K.-T.; writing—review and editing, S.R., B.J. and R.K.-T.; visualization, B.J.; supervision, S.R.; project administration, S.R. and R.K.-T.; funding acquisition, S.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Paparella, A.; Kongala, P.R.; Serio, A.; Rossi, C.; Shaltiel-Harpaza, L.; Husaini, A.M.; Ibdah, M. Challenges and opportunities in the sustainable improvement of carrot production. Plants 2024, 13, 2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hud, A.; Šamec, D.; Senko, H.; Petek, M.; Brkljačić, L.; Pole, L.; Lazarevic, B.; Rajnovic, I.; Udikovic-Kolic, N.; Mešic, A.; et al. Response of white cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata) to single and repeated short-term waterlogging. Agronomy 2023, 13, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebadollahi-Natanzi, A.; Arab-Rahmatipour, G. A study on chlorophyll, total carotenoid and beta-carotene contents in carrot and the effect of climate on them. J. Med. Plants 2020, 19, 254–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, P.W. Beyond the genome: Carrot production trends, research advances, and future crop improvement. ISHS Acta Hortic. 2018, 1264, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Übelhör, A.; Munz, S.; Graeff-Hönninger, S.; Claupein, W. Evaluation of the CROPGRO model for white cabbage production under temperate European climate conditions. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 182, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwsbericht. Polish Vegetable Production. Available online: https://www.agroberichtenbuitenland.nl/actueel/nieuws/2021/09/07/polish-vegetable-production? (accessed on 3 July 2025).
- ReportLinker. European Cabbages Harvested Production by Country. Available online: https://www.reportlinker.com/dataset/0e74c420fe50ae8688975a36cf666361aceb313d? (accessed on 3 July 2025).
- Babić, I.; Šamec, D.; Hižak, M.; Huđ, A.; Senko, H.; Šangut, I.J.; Mlinarić, S.; Petek, M.; Palijan, G.; Udiković Kolić, N.; et al. Evaluating drought impact on white cabbage: Plant stress response and soil microbiome adaptation. Plant Stress 2024, 14, 100683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisbis, M.B.; Gruda, N.; Blanke, M. Potential impacts of climate change on vegetable production and product quality—A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 170, 1602–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlović, I.; Petřík, I.; Tarkowská, D.; Lepeduš, H.; Vujčić Bok, V.; Radić Brkanac, S.; Novák, O.; Salopek-Sondi, B. Correlations between phytohormones and drought tolerance in selected Brassica crops: Chinese cabbage, white cabbage and kale. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rintamäki, H.; Rikkonen, P.; Tapio, P. Carrot or stick: Impacts of alternative climate and energy policy scenarios on agriculture. Futures 2016, 83, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasman; Syarif, M.; Juharsah; Sukri, A.S.; Ngii, E.; Hasddin. Model of the linkage between land cover changes to water discharge and food productivity: The case of the konaweha watershed in Indonesia. J. Geogr. Inst. Jovan Cvijić SASA 2023, 73, 169–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoyanova, R.; Nikolova, N. Meteorological drought in southwest Bulgaria during the period 1961–2020. J. Geogr. Inst. Jovan Cvijić SASA 2022, 72, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenberth, K.E.; Fasullo, J.T.; Shepherd, T.G. Attribution of climate extreme events. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2015, 5, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, T.; von Braun, J. Climate change impacts on global food security. Science 2013, 341, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdivia, R.O.; Antle, J.M.; Rosenzweig, C.; Ruane, A.C.; Vervoort, J.; Ashfaq, M.; Hathie, I.; Tui, S.H.-K.; Mulwa, R.; Nhemachena, C.; et al. Representative agricultural pathways and scenarios for regional integrated assessment of climate change impacts, vulnerability, and adaptation. In Handbook of Climate Change and Agroecosystems: The Agricultural Model Intercomparison and Improvement Project Integrated Crop and Economic Assessments; Part, 1; Rosenzweig, C., Hillel, D., Eds.; Imperial College Press: London, UK, 2015; pp. 101–145. [Google Scholar]
- Van Vuuren, D.P.; Edmonds, J.; Kainuma, M.; Riahi, K.; Thomson, A.; Hibbard, K.; Hurtt, G.C.; Kram, T.; Krey, V.; Lamarque, J.-F.; et al. The representative concentration pathways: An overview. Clim. Chang. 2011, 109, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar6/wg1/ (accessed on 26 May 2025).
- European Environment Agency (EEA). Climate Change, Impacts and Vulnerability in Europe 2016. An Indicator-Baseed Report; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2017; Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/en/analysis/publications/climate-change-impacts-and-vulnerability-2016 (accessed on 21 May 2025)ISSN 1977-8449.
- Alcamo, J.; Moreno, J.M.; Nováky, B.; Hindi, M.; Corobov, R.; Devoy, R.J.N.; Giannakopoulos, C.; Martin, E.; Olesn, J.E.; Shvidenko, A. Europe. Climate Change 2007. Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Parry, M.L., Canziani, O.F., Palutikof, J.P., van der Linden, P.J., Hanson, C.E., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007; pp. 541–580. [Google Scholar]
- Kundzewicz, Z. Projekcje zmian klimatu—Ekstrema hydrometeorologiczne [Climate change projections—Hydrometeorological extremes]. In Proceedings of the I Polish Conference ADAGIO, Poznań, Poland, 24 April 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Randall, D.A.; Wood, R.A.; Bony, S.; Colman, R.; Fichefet, T.; Fyfe, J.; Kattsov, V.; Pitman, A.; Shukla, J.; Srinivasan, J.; et al. Climate models and their evaluation. In Climate Change 2007. The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Solomon, S., Qin, D., Manning, M., Chen, Z., Marquis, M., Averyt, K.B., Tignor, M., Miller, H.L., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kundzewicz, Z. Scenariusze zmian klimatu [Climate change scenarios]. In Czy Polsce Grożą Katastrofy Klimatyczne? [Is Poland at Risk of Climate Disasters?]; PAN: Warszawa, Poland, 2003; pp. 14–31. [Google Scholar]
- Parry, M.L. Assessment of Potential Effects and Adaptation for Climate Change in Europe: The Europe ACACIA Project; Jackson Environmental Institute, University of East Anglia: Norwich, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Kaniszewski, S.; Treder, W. Racjonalne Nawadnianie Warzyw [Rational Irrigation of Vegetables]; ODR: Brwinów, Poland, 2021; pp. 1–89. [Google Scholar]
- Żakowicz, S.; Hewelke, P.; Gnatowski, T. Podstawy Infrastruktury Technicznej w Przestrzeni Produkcyjnej [Basics of Technical Infrastructure in Production Space]; SGGW: Warszawa, Poland, 2009; p. 192. [Google Scholar]
- Kaniszewski, S. Nawadnianie Warzyw Polowych [Irrigation of Field Vegetables]; Plantpress: Kraków, Poland, 2005; pp. 1–85. [Google Scholar]
- Buczak, E. Potrzeby wodne roślin warzywnych [Water needs of vegetable crops]. In Potrzeby Wodne Roślin Uprawnych [Water Needs of Field Crops]; Dzieżyc, J., Ed.; PWN: Warszawa, Poland, 1989; pp. 159–188. [Google Scholar]
- Dzieżyc, J. Rolnictwo w Warunkach Nawadniania [Agriculture Under Irrigated Conditions]; PWN: Warszawa, Poland, 1988; pp. 1–415. [Google Scholar]
- Kaniszewski, S. Nawadnianie Warzyw [Irrigation of Vegetables]; PWRiL: Warszawa, Poland, 1987; pp. 1–108. [Google Scholar]
- Badora, D.; Wawer, R.; Król-Badziak, A. Modelling 2050 Water Retention Scenarios for Irrigated and Non-Irrigated Crops for Adaptation to Climate Change Using the SWAT Model: The Case of the Bystra Catchment, Poland. Agronomy 2023, 13, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daccache, A.; Weatherhead, E.K.; Stalham, M.A.; Knox, J.W. Impacts of climate change on irrigated potato production in a humid climate. Agric. Forest Meteorol. 2011, 151, 1641–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fereres, E.; Soriano, M.A. Deficit irrigation for reducing agricultural water use. J. Exp. Bot. 2007, 58, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teshager, A.D.; Gassman, P.W.; Schoof, J.T.; Secchi, S. Assessment of impacts of agricultural and climate change scenarios on watershed water quantity and quality, and crop production. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 20, 3325–3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, J.; Deryng, D.; Müller, C.; Frieler, K.; Konzmann, M.; Gerten, D.; Glotter, M.; Flörke, M.; Wada, Y.; Best, N.; et al. Constraints and potentials of future irrigation water availability on agricultural production under climate change. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2014, 111, 3239–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, H.E.; Zimmermann, N.E.; McVicar, T.R.; Vergopolan, N.; Berg, A.; Wood, E.F. Present and future Köppen-Geiger climate classification maps at 1-km resolution. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenc, H. Atlas Klimatu Polski [Climate Atlas of Poland]; IMGiW: Warszawa, Poland, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kondracki, J. Geografia Regionalna Polski [Regional Geography of Poland]; PWN: Warszawa, Poland, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Klimada 2.0. Klimat Scenariusze [Climate Scenarios]. Available online: https://klimada2.ios.gov.pl/klimat-scenariusze-portal/ (accessed on 22 May 2025).
- IPCC. Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Pachauri, R.K., Meyer, L.A., Eds.; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014; p. 151. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop. Evapotranspiration. Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements; FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 56; Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Łabędzki, L. Susze rolnicze. Zarys problematyki oraz metody monitorowania i klasyfikacji [Agricultural droughts. Outline of the issues and methods of monitoring and classification]. Woda. Środowisko. Obszary Wiejskie. Rozprawy Naukowe i Monografie [Water Environ. Rural Areas. Sci. Diss. Monogr.] 2006, 17, 1–107. [Google Scholar]
- Treder, W. Racjonalne Nawadnianie Roślin Sadowniczych [Rational Irrigation of Fruit Plants]; Centrum Doradztwa Rolniczego: Brwinów, Polska, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Żakowicz, S.; Hewelke, P. Podstawy Inżynierii Środowiska [Basics of Environmental Engineering]; SGGW: Warszawa, Poland, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Tabaszewski, J. Elementy Inżynierii Wodnej [Elements of Water Engineering]; ART: Olsztyn, Poland, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Trnka, M.; Eitzinger, J.; Semerádová, D.; Hlavinka, P.; Balek, J.; Dubrovský, M.; Kubu, G.; Štěpánek, P.; Thaler, S.; Možný, M.; et al. Expected changes in agroclimatic conditions in Central Europe. Clim. Res. 2011, 108, 261–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olesen, J.E.; Bindi, M. Consequences of climate change for European agricultural productivity, land use and policy. Eur. J. Agron. 2002, 16, 239–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okasha, A.M.; Abdelkhaliq, E.T.; Zayton, A.M. Impact of Irrigation Water Quality, Frequency, and Technique on Cabbage Yield, Water Productivity, and Soil Properties in Clay Soil. Egypt. J. Soil Sci. 2025, 65, 961–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junaid, M.D.; Öztürk, Z.N.; Gökçe, A.F. Exploitation of tolerance to drought stress in carrot (Daucus carota L.): An overview. Stress Biol. 2023, 3, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, T.; Bandyopadhyay, P.K.; Nandi, R.; Mukherjee, S.; Kundu, A.; Reddy, P.; Mandal, B.; Kumar, P. Impact of mulching and nutrients on soil water balance and actual evapotranspiration of irrigated winter cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata L.). Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 263, 107456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyatuame, M.; Ampraw, F.; Owusu-Gyimah, V.; Ibrahim, B.M. Irrigation scheduling and water use efficiency on cabbage yield. Inter. J. Agro. Agric. Res. 2013, 3, 29–35. [Google Scholar]
- Rouphael, Y.; Cardarelli, M.; Schwarz, D.; Franken, P.; Colla, G. Effects of drought on nutrient uptake and assimilation in vegetable crops. In Plant Responses to Drought Stress: From Morphological to Molecular Features; Aroca, R., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 171–195. [Google Scholar]
- Dysko, J.; Kaniszewski, S. Effect of drip irrigation, N-fertigation and cultivation methods on the yield and quality of carrot. Veg. Crops Res. Bull. 2007, 67, 25. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Cabbage—Guidelines for the interpretation of crop water requirements. In Crop Water Requirements; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper: Rome, Italy, 1992; p. 3. [Google Scholar]
- Doorenbos, J.; Kassam, A.H. Yield Response to Water; FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper No. 33; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Guyer, A.; Hibbard, B.E.; Holzkämper, A.; Erb, M.; Robert, C.A. Influence of drought on plant performance through changes in belowground tritrophic interactions. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 8, 6756–6765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daryanto, S.; Wang, L.; Jacinthe, P.A. Global synthesis of drought effects on food legume production. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, A. Plant Breeding for Water-Limited Environments; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Łabędzki, L.; Kowalczyk, A.; Kuźniar, A.; Kostuch, M. Ocena niedoborów wody w uprawie kapusty głowiastej białej na Wyżynie Małopolskiej [Assessment of crop water deficits of white cabbage cultivated on the małopolska upland]. Water-Environ.-Rural. Areas 2016, 16, 21–38. [Google Scholar]
- Husnjak, S.; Šimunić, I.; Jungić, D. The climate changes and soil water deficit during the cultivation of potatoes, maize and cabbage in the Virovitica-Podravina and Lika-Senj Counties. Agron. Glas. Glas. Hrvat. Agron. Društva 2023, 85, 183–196. [Google Scholar]
- Geem, K.R.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, J.; Hong, D.; Kim, G.E.; Sung, J. Role of Carrot (Daucus carota L.) Storage Roots in Drought Stress Adaptation: Hormonal Regulation and Metabolite Accumulation. Metabolites 2025, 15, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Červenski, J.; Vlajić, S.; Ignjatov, M.; Tamindžić, G.; Zec, S. Agroclimatic conditions for cabbage production. Ratar. Povrt. 2022, 59, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figas, A.; Rolbiecki, R.; Rolbiecki, S.; Jagosz, B.; Łangowski, A.; Sadan-Ozdemir, H.A.; Pal-Fam, F.; Atilgan, A. Towards water-efficient irrigation of cup plant (Silphium perfoliatum L.) for energy production: Water requirements and rainfall deficit. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolbiecki, S.; Rolbiecki, R.; Sadan, H.A.; Jagosz, B.; Kasperska-Wołowicz, W.; Kanecka-Geszke, E.; Pal-Fam, F.; Atilgan, A.; Krakowiak-Bal, A.; Kuśmierek-Tomaszewska, R.; et al. Sustainable water management of drip-irrigated asparagus under conditions of central Poland: Evapotranspiration, water needs and rainfall deficits. Sustainability 2024, 16, 966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolbiecki, S.; Kasperska-Wołowicz, W.; Jagosz, B.; Sadan, H.A.; Rolbiecki, R.; Szczepanek, M.; Kanecka-Geszke, E.; Łangowski, A. Water and irrigation requirements of Glycine max (L.) Merr. in 1981–2020 in central Poland, central Europe. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolbiecki, S.; Rolbiecki, R.; Kuśmierek-Tomaszewska, R.; Żarski, J.; Jagosz, B.; Kasperska-Wołowicz, W.; Sadan, H.; Łangowski, A. Influence of forecast climate changes on water needs of jerusalem artichoke grown in the Kuyavia region in Poland. Energies 2023, 16, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagosz, B.; Rolbiecki, S.; Rolbiecki, R.; Ptach, W.; Sadan, H.A.; Kasperska-Wolowicz, W.; Pal-Fam, F.; Atilgan, A. Effect of the forecast air temperature change on the water needs of vines in the region of Bydgoszcz, northern Poland. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberacki, D.; Kocięcka, J.; Stachowski, P.; Rolbiecki, R.; Rolbiecki, S.; Sadan, H.A.; Figas, A.; Jagosz, B.; Wichrowska, D.; Ptach, W.; et al. Water needs of willow (Salix L.) in western Poland. Energies 2022, 15, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolbiecki, S.; Biniak-Pieróg, M.; Żyromski, A.; Kasperska-Wołowicz, W.; Jagosz, B.; Stachowski, P.; Liberacki, D.; Kanecka-Geszke, E.; Sadan, A.H.; Rolbiecki, R.; et al. Effect of forecast climate changes on water needs of giant miscanthus cultivated in the Kuyavia region in Poland. Energies 2021, 14, 6628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachowski, P.; Jagosz, B.; Rolbiecki, S.; Rolbiecki, R. Predictive capacity of rainfall data to estimate the water needs of fruit plants in water deficit areas. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaca, E.; Łabędzki, L.; Lubbe, J. Gospodarowanie wodą w rolnictwie w obliczu ekstremalnych zjawisk pogodowych [Agricultural water management in view of extreme weather phenomena]. Postępy Nauk Rolniczych 2011, 1, 37–49. [Google Scholar]
- Durau, B.; Żarski, J. Niedobory opadów atmosferycznych w uprawie kapusty głowiastej białej i marchwi w rejonie Bydgoszczy w latach 1980–2012 [Atmospheric precipitation deficiencies in the white cabbage and carrot cultivation in the region of Bydgoszcz in the years 1981-2010]. Infrastruct. Ecol. Rural Areas 2013, 1, 37–49. [Google Scholar]
- Żarski, J. Tendencje zmian klimatycznych wskaźników potrzeb nawadniania roślin w rejonie Bydgoszczy [Trends in changes of climatic indices for irrigation needs of plants in the region of Bydgoszcz]. Infrastruct. Ecol. Rural Areas 2011, 5, 29–37. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Coping with Water Scarcity. An Action Framework for Agriculture and Food Security; FAO Water Reports 38; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2012; p. 100. [Google Scholar]
- Geerts, S.; Raes, D. Deficit irrigation as an on-farm strategy to maximize crop water productivity in dry areas. Agric. Water Manag. 2009, 96, 1275–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcinkowski, P.; Piniewski, M.; Okruszko, T. Towards sustainable agricultural water management in Poland–How to meet water demand for supplemental irrigation? Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 306, 109214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo’rayevich, N.N.; Juraqulovich, A.T. The effect of drip irrigation on the indicators of the root system and aboveground part of the cabbage. Web Agric. 2024, 2, 21–23. [Google Scholar]
- Patra, S.K.; Poddar, R.; Panda, R.; Sarkar, A.; Gaber, A.; Hossain, A. Response of cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata L.) to different frequencies of irrigation and levels of soil fertilization in a non-saline coastal Typic Endoaquept. J. Coast. Conserv. 2024, 28, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alibekov, T.J. Use of Resource-Saving Technologies in the Cultivation of White Cabbage. Web Agric. 2023, 1, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Kuts, O.; Kokoiko, V.; Mykhailyn, V.; Syromyatnikov, Y.; Zhernova, O. Fertilisation system influence on the main agrochemical indicators of soil and productivity of white cabbage. Sci. Horiz. 2023, 26, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bute, A.; Iosob, G.A.; Antal-Tremurici, A.; Brezeanu, C.; Brezeanu, P.M.; Cristea, T.O.; Ambăruş, S. The most suitable irrigation methods in cabbage crops (Brassica oleracea L. var. capitata): A review. Sci. Pap. B-Hortic. 2021, 65, 399–405. [Google Scholar]
- Erken, O.K.A.N.; Yildirim, M. Yield and quality compounds of white cabbage (Brassica oleracea L. cv. capitata) under different irrigation levels. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2019, 21, 1341–1352. [Google Scholar]
- Seidel, S.J.; Werisch, S.; Schütze, N.; Laber, H. Impact of irrigation on plant growth and development of white cabbage. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 187, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kacjan-Maršić, N.; Osvald, J. The effect of fertigation on yield and quality of four white cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata L.) cultivars. Acta Agric. Slov. 2004, 83, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harasim, E.; Kwiatkowski, C.A.; Buczek, J. Effect of Farming System and Irrigation on Nutrient Content and Health-Promoting Properties of Carrot Roots. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tlig, W.; Mokh, F.E.; Autovino, D.; Iovino, M.; Nagaz, K. Carrot productivity and its physiological response to irrigation methods and regimes in arid regions. Water Supply 2023, 23, 5093–5105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afrin, A.; Islam, M.A.; Hossain, M.M.; Hafiz, M.M.H. Growth and yield of carrot influenced by organic and inorganic fertilizers with irrigation interva: Fertilizer and irrigation affect yield of carrot. J. Bangladesh Agril Univ. 2019, 17, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, D.F.D.; Gomes, D.P.; Oliveira Neto, D.H.D.; Guerra, J.G.; Rouws, J.R.; Oliveira, F.L.D. Carrot yield and water-use efficiency under different mulching, organic fertilization and irrigation levels. Rev. Bras. Eng. Agric. Ambient. 2018, 22, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Léllis, B.C.; Carvalho, D.F.; Martínez-Romero, A.; Tarjuelo, J.M.; Domínguez, A. Effective management of irrigation water for carrot under constant and optimized regulated deficit irrigation in Brazil. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 192, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, D.F.D.; Oliveira, D.H.D.; Felix, L.F.; Guerra, J.G.M.; Salvador, C.A. Yield, water use efficiency, and yield response factor in carrot crop under different irrigation depths. Ciênc. Rural 2016, 46, 1145–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zeipiņa, S.; Alsiņa, I.; Lepse, L. The effect of watering on yield and quality of carrots. Acta Hortic. 2014, 1038, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, D.C.; Madhu, M.; Khola, O.P.S. Estimation of evapotranspiration and crop co-efficient of carrot (Daucus carota) for water management using weighing lysimeter. Indian J. Agri. Sci. 2009, 79, 968–971. [Google Scholar]
- Kaniszewski, S.; Knaflewski, M. The results of studies on water requirement and effectiveness of the irrigation of vegetable crops in Poland. In Proceedings of the Conference Water Requirements and Irrigation Effect of Plants Cultivated in Arid and Semiarid Climates, Tel-Aviv, Israel, 5–16 December 1997; Volume II, pp. 103–110. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, A.A. Effect of deficit irrigation during growth stages on water use efficiency of carrot under El-Ismailia conditions. Egypt. J. Soil Sci. 2017, 57, 393–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beshir, S. Review on estimation of crop water requirement, irrigation frequency and water use efficiency of cabbage production. J. Geosci. Environ. Prot. 2017, 5, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, Z.; Kuboń, M. Assessing the impact of water use in conventional and organic carrot production in Poland. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 3522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).