The Effects of Natural and Social Factors on Surface Temperature in a Typical Cold-Region City of the Northern Temperate Zone: A Case Study of Changchun, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Methods
2.4. Verification of Accuracy
3. Results
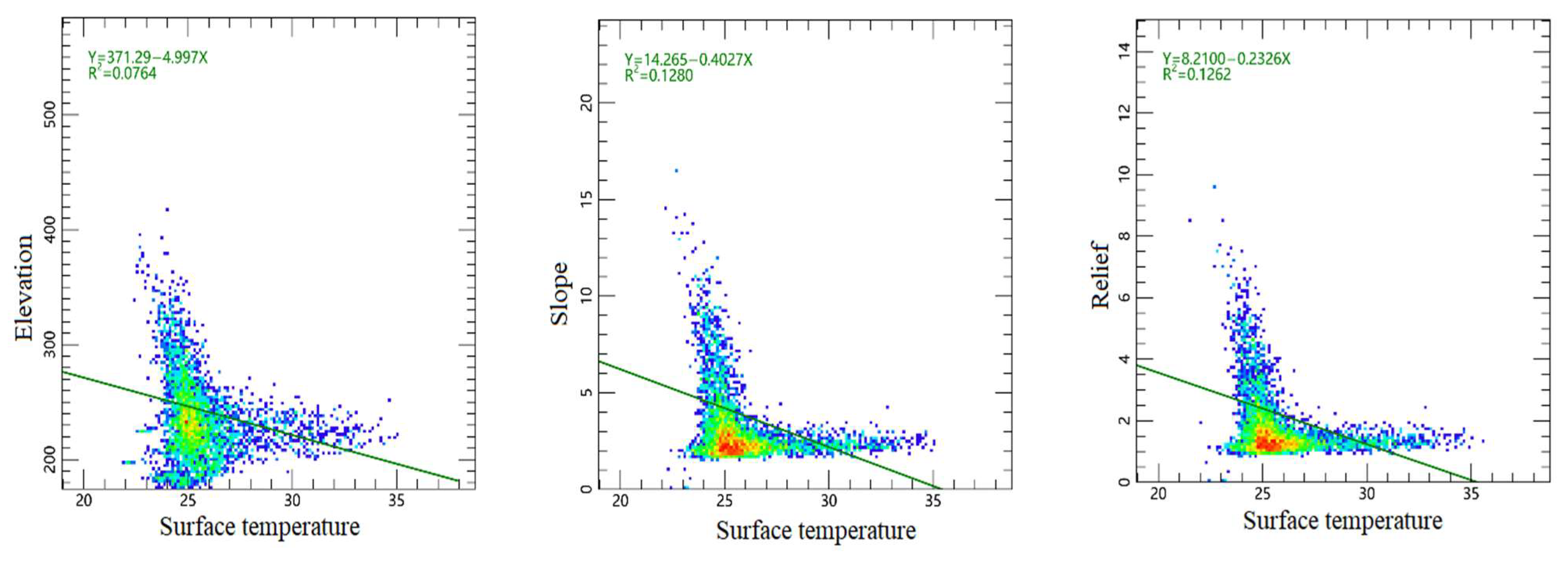
3.1. The Influence of Topographic Factors on Surface Temperature in Changchun City
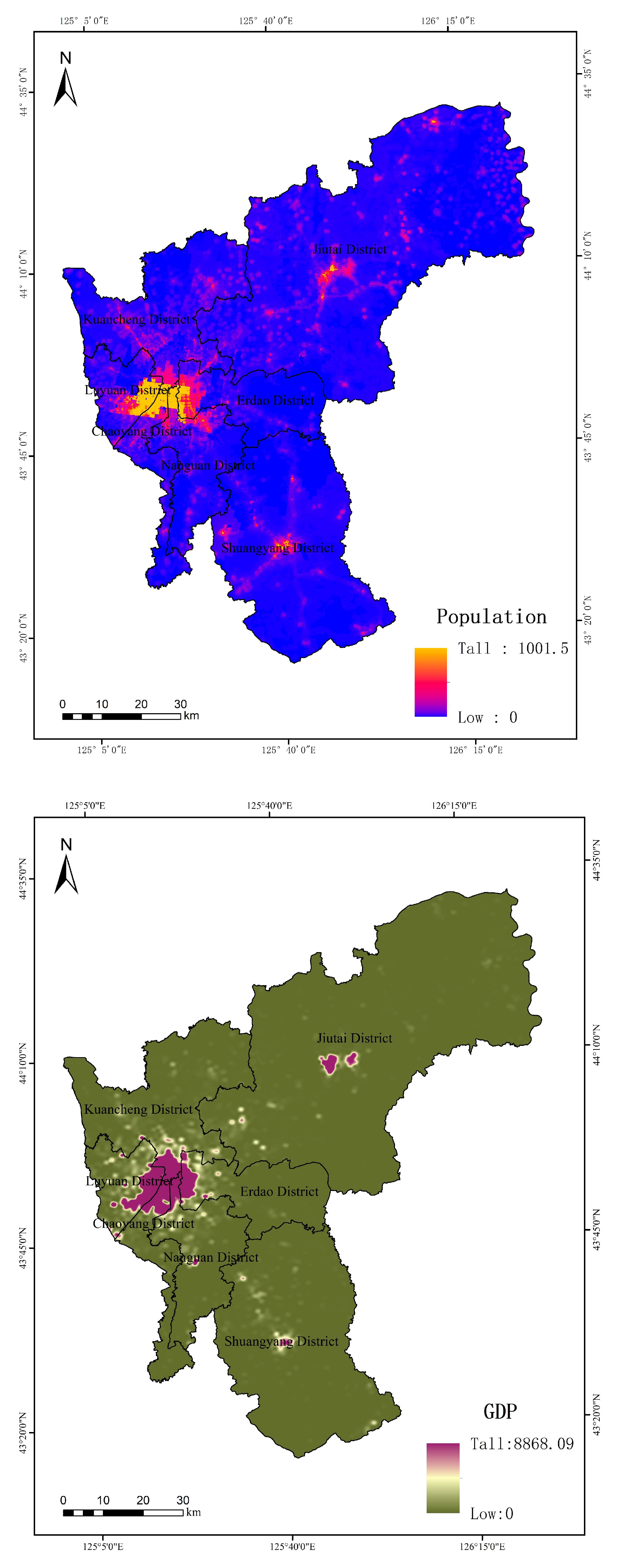
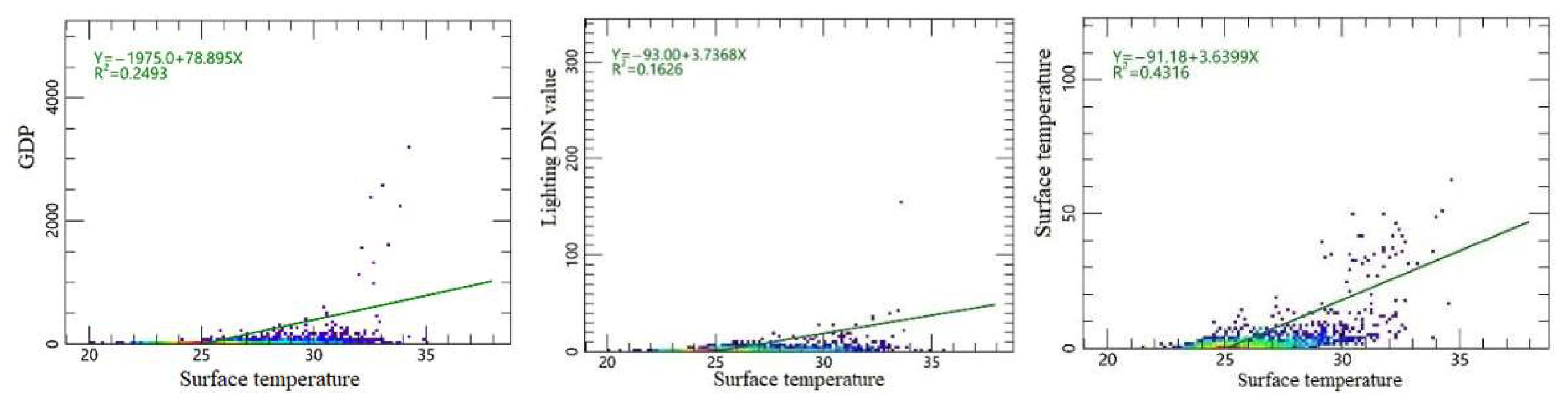
3.2. The Influence of Socio-Economic Factors on Surface Temperature in Changchun City
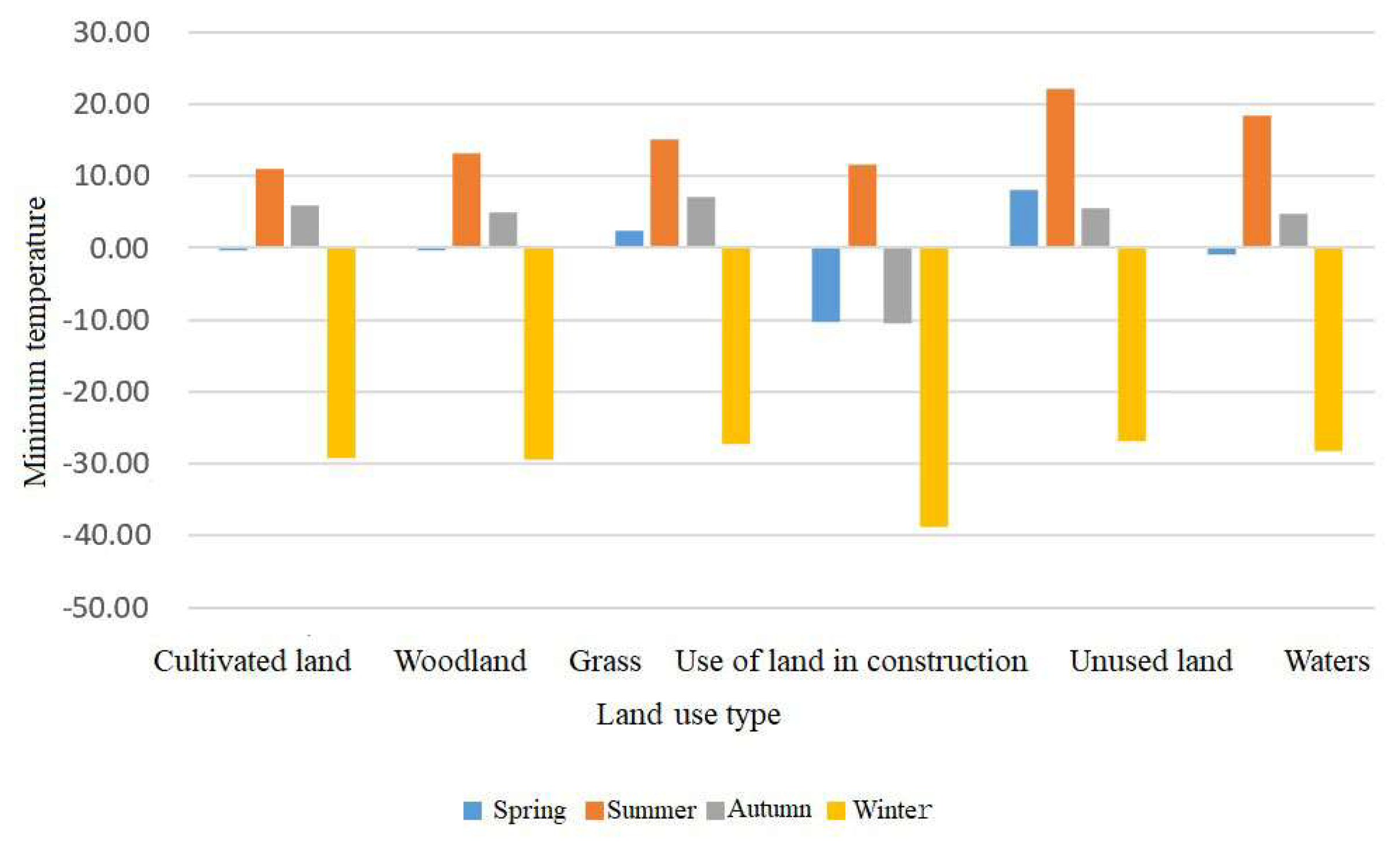
3.3. The Impact of Land Use on Seasonal Surface Temperature in Changchun City
3.4. Analysis of the Impact of Multiple Factors on Surface Temperature
4. Discussion
4.1. The Influence of Topography on Surface Temperature
4.2. The Influence of Population Density on Surface Temperature
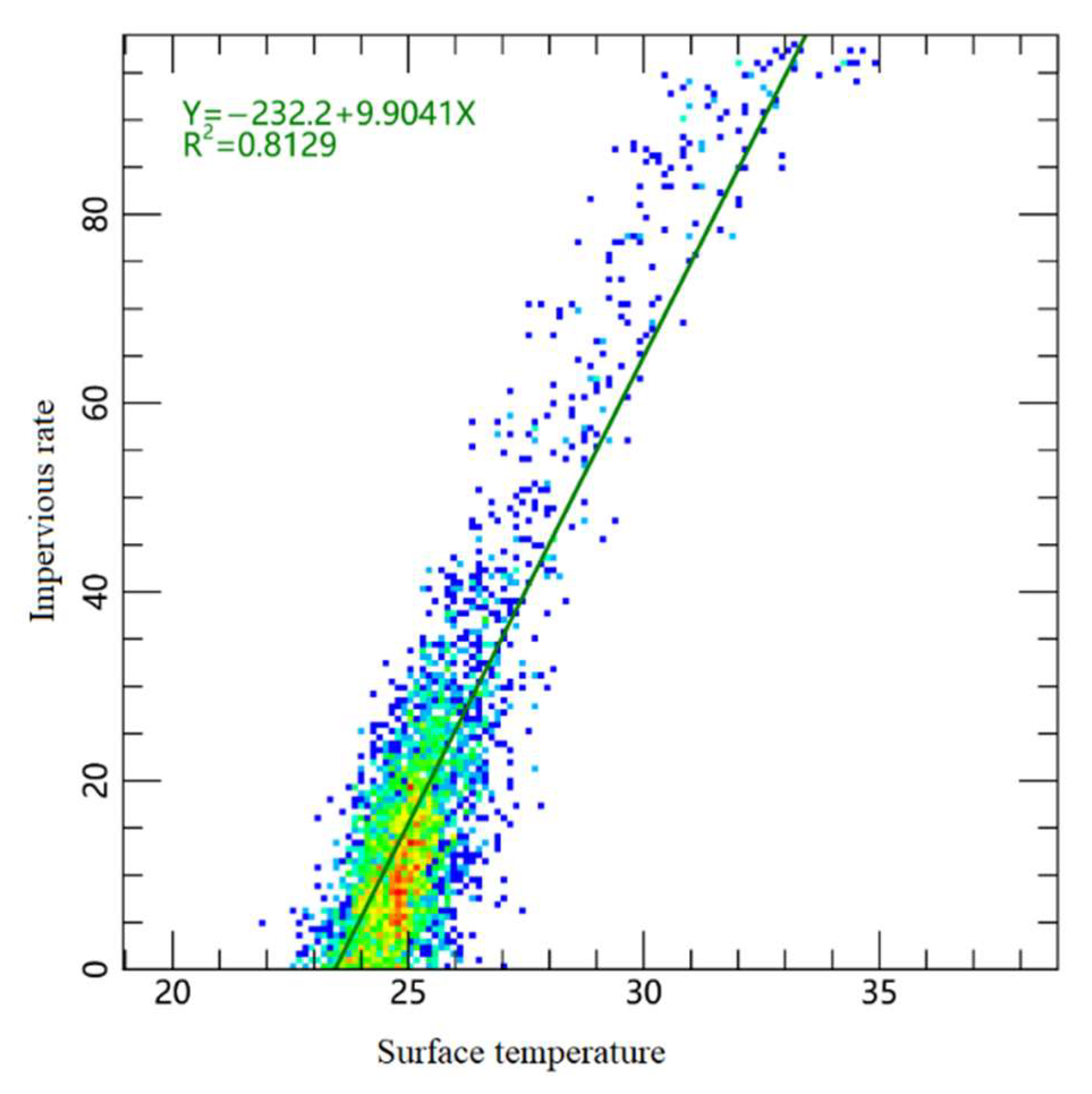
4.3. The Impact of Impervious Surfaces on Surface Temperature
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Xiu, C.; Xiao, X.; Xia, J.; Jin, C. Optimizing local climate zones to mitigate urban heat island effect in human settlements. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 275, 123767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meehl, G.A.; Tebaldi, C. More intense, more frequent, and longer lasting heat waves in the 21st century. Science 2004, 305, 994–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, Y.; Ichinose, T.; Ohashi, Y.; Shiraki, Y.; Onishi, A.; Yoshida, Y. Simulation of urban surface temperature and surface heat balance in the Tokyo metropolitan area. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 112, 105596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guha, S.; Govil, H.; Dey, A.; Gill, N. Analysing the capability of NCI technique in change detection using high-and medium-resolution multispectral data. In Geoecology of Landscape Dynamics; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 133–147. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Zhan, Q.; Yang, C.; Wang, J. Characterizing the spatio-temporal pattern of land surface temperature through time series clustering: Based on the latent pattern and morphology. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.S.; Mirsky, D.S.; Florinsky, M. The Correspondence of DS Mirsky and Michael Florinsky, 1925–1932. Slavon. East Eur. Rev. 1994, 72, 115–139. [Google Scholar]
- Geiger, R.; Aron, R.H.; Todhunter, P. The Climate Near the Ground; Rowman & Littlefield: Lanham, MD, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Oke, T.R. The energetic basis of the urban heat island. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1982, 108, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skelhorn, C.; Lindley, S.; Levermore, G. The impact of vegetation types on air and surface temperatures in a temperate city: A fine scale assessment in Manchester, UK. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 121, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neog, R. Monitoring land use dynamics, urban sprawl, and land surface temperature in Dimapur urban area, Nagaland, India. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 20, 7519–7532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotharkar, R.; Surawar, M. Land use, land cover, and population density impact on the formation of canopy urban heat islands through traverse survey in the Nagpur urban area, India. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2016, 142, 04015003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Yang, H.; Chen, Q.; Chen, T.; Shen, R. Analysis of Urban Thermal Environment Evolution and Mechanisms Based on Multisource Data: A Case Study of Hangzhou, China. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2024, 150, 05024026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenouzi, A.S.; Yenneti, K.; Teimouri, R.; Abbasiyan, F.; Palme, M. Analysis of Changes in Vegetation Index during the Rapid Urban Spatial Development Period (1990–2020) in Tehran Metropolis, Iran. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, K.; Li, M.; Yi, L. Comparing the driving mechanisms of different types of urban construction land expansion: A case study of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. J. Geogr. Sci. 2024, 34, 722–744. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.; Lu, J.L.; Wei, Q.Q.; Cao, J.X.; Cui, J.X.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, K.; Chen, H.; Zhao, W. Spatial distribution, source apportionment, and risk assessment of perfluoroalkyl substances in urban soils of a typical densely urbanized and industrialized city, Northeast China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 953, 176166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.X.; Liu, Z.S.; Li, S.J.; Li, X.; Wang, W.Y. Spatiotemporal Patterning and Matching of Ecosystem Services’ Supply and Demand in Changchun, China. Land 2023, 12, 2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.L.; Wu, S.K.; Dong, Q.Y.; Zhou, X.; Yang, J.X.; Li, G. Research on Runoff Management of Sponge Cities under Urban Expansion. Water 2024, 16, 2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Tan, Y.B.; Ying, S.; Yu, Z.H.; Li, Z.; Lan, H.H. Impact of land cover and population density on land surface temperature: Case study in Wuhan, China. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2014, 8, 084993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, J.; Rahman, A. Impact of population density on the surface temperature and micro-climate of Delhi. Curr. Sci. 2012, 102, 1708–1713. [Google Scholar]
- Han, G.F.; Zhao, K.; Yan, W.T.; Ye, L. Multi-gradients of land surface temperature in mountainous cities with rapid urbanization: A case study in central area of Chongqing City. J. Appl. Ecol. 2012, 23, 1655–1662. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Wu, F.; Ma, H.Q.; Xu, Z.J.; Wang, S.H. Spatiotemporal Evolution and Relationship between Night Time Light and Land Surface Temperature: A Case Study of Beijing, China. Land 2022, 11, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.L.; Yu, T.; Zhao, L.M.; Zhan, Y.L.; Zheng, F.J.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Wang, C.M. Characteristics and trend analysis of the relationship between land surface temperature and nighttime light intensity levels over China. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2019, 97, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, A.; Khandelwal, S.; Kaul, N.; Chauhan, S. Analyzing the diurnal variations of land surface temperatures for surface urban heat island studies: Is time of observation of remote sensing data important. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 40, 194–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

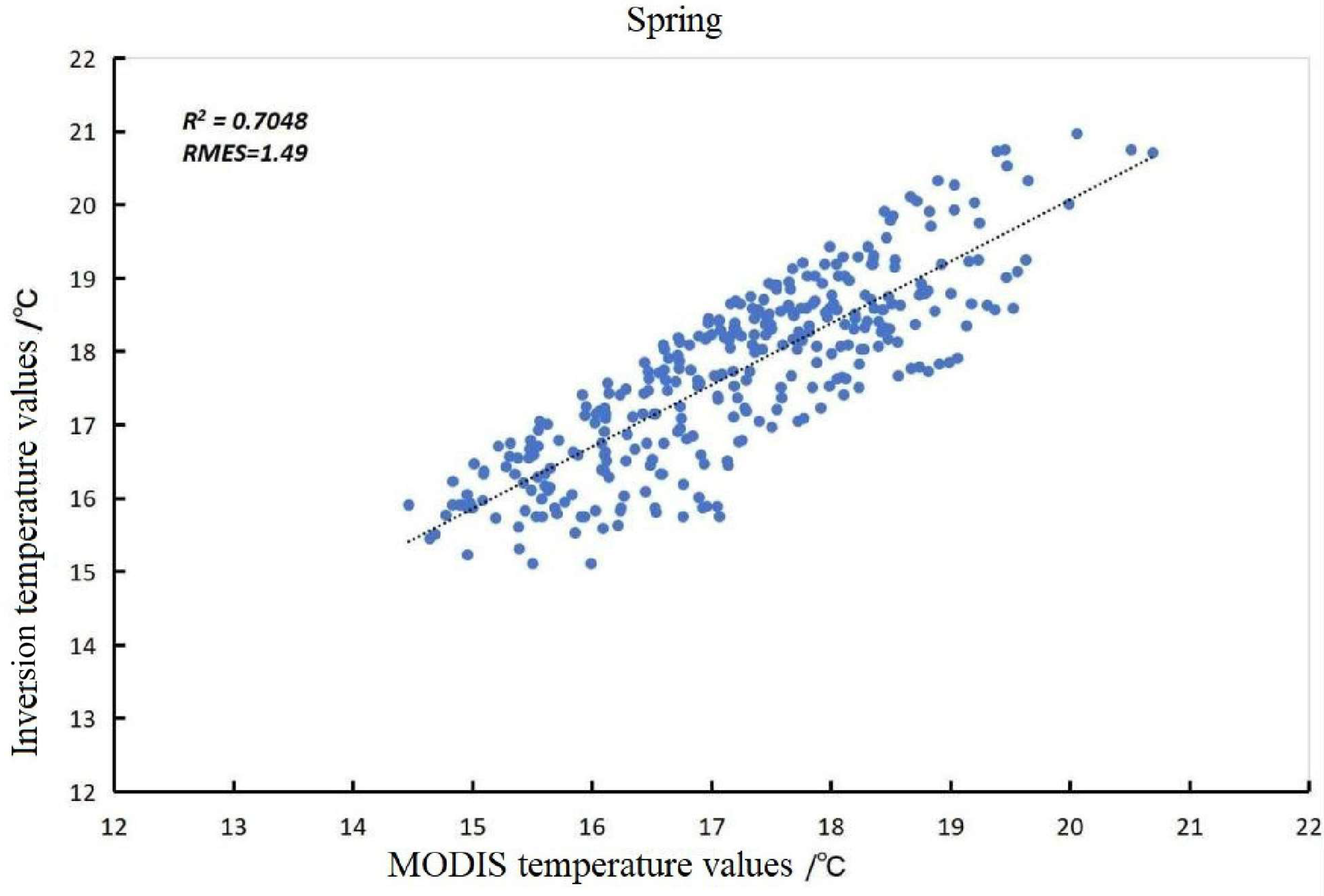
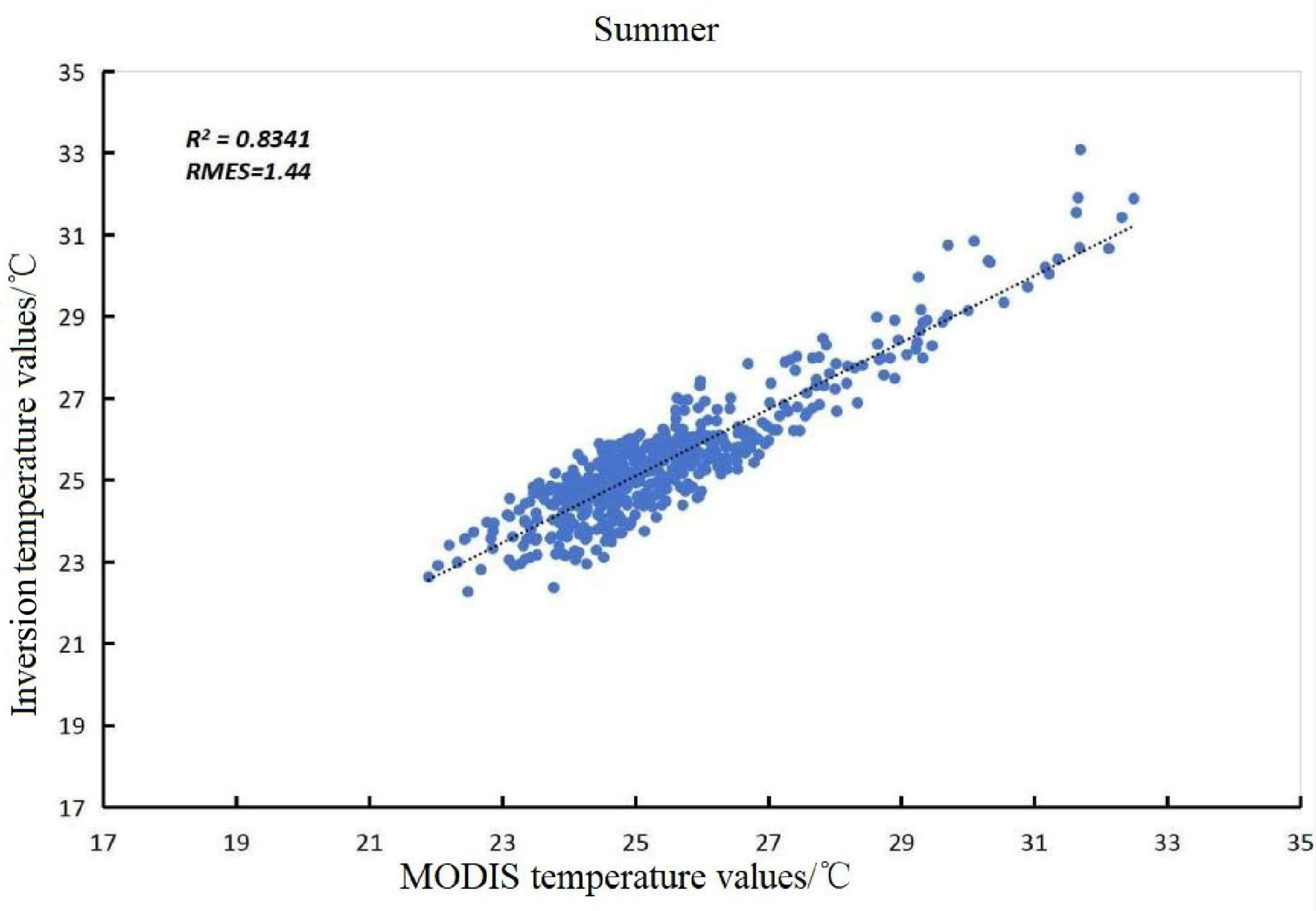
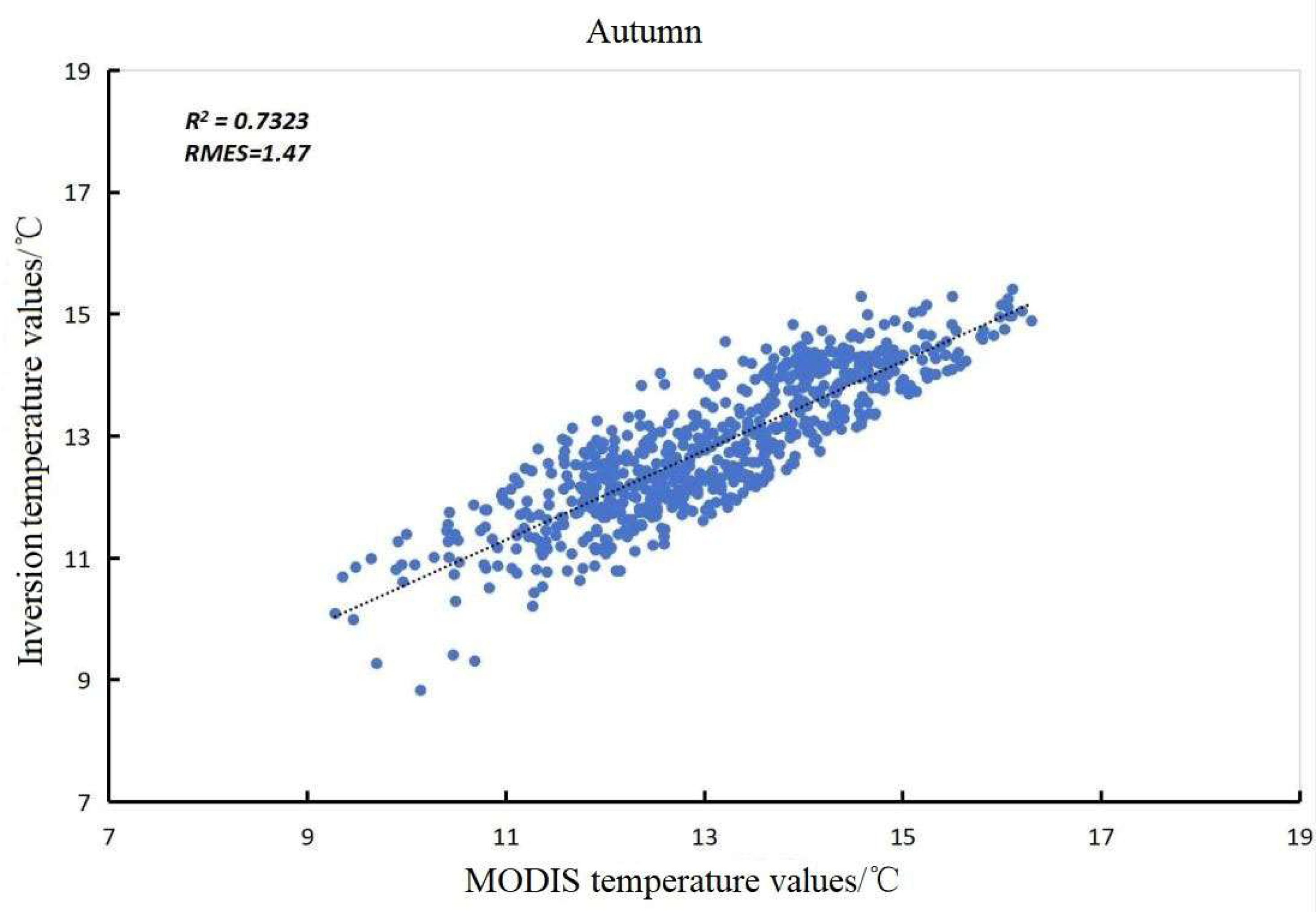





| Time | Monthly Average Ground Temperature (°C) | Inversion Mean Ground Temperature (°C) | Relative Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spring | 23.1 | 22.92 | 0.78 |
| Summer | 35.2 | 36.96 | 0.05 |
| Autumn | 20.5 | 19.62 | 0.04 |
| Winter | −18.5 | −20.65 | 0.12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, M.; Liu, Y.; Xu, W.; Gao, B.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Guo, D. The Effects of Natural and Social Factors on Surface Temperature in a Typical Cold-Region City of the Northern Temperate Zone: A Case Study of Changchun, China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 6840. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17156840
Lin M, Liu Y, Xu W, Gao B, Wang X, Wang C, Guo D. The Effects of Natural and Social Factors on Surface Temperature in a Typical Cold-Region City of the Northern Temperate Zone: A Case Study of Changchun, China. Sustainability. 2025; 17(15):6840. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17156840
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Maosen, Yifeng Liu, Wei Xu, Bihao Gao, Xiaoyi Wang, Cuirong Wang, and Dali Guo. 2025. "The Effects of Natural and Social Factors on Surface Temperature in a Typical Cold-Region City of the Northern Temperate Zone: A Case Study of Changchun, China" Sustainability 17, no. 15: 6840. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17156840
APA StyleLin, M., Liu, Y., Xu, W., Gao, B., Wang, X., Wang, C., & Guo, D. (2025). The Effects of Natural and Social Factors on Surface Temperature in a Typical Cold-Region City of the Northern Temperate Zone: A Case Study of Changchun, China. Sustainability, 17(15), 6840. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17156840






