Quantifying the Geopark Contribution to the Village Development Index Using Machine Learning—A Deep Learning Approach: A Case Study in Gunung Sewu UNESCO Global Geopark, Indonesia
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Conservation Function: Emphasizes the protection of karst landscapes due to their ecological fragility and susceptibility to environmental degradation;
- Geotourism and Educational Function: Highlights their geological uniqueness and aesthetic appeal, offering opportunities for sustainable tourism and environmental education;
- Hydrogeological Function: Karst systems act as natural reservoirs for groundwater storage and release, crucial for regional water regulation;
- Biodiversity Support Function: Hosts unique microbiological communities and cave ecosystems, enhancing ecological diversity;
- Cultural and Archaeological Function: Many karst caves contain prehistoric artifacts, providing insights into early human civilization;
- Disaster and Climate Mitigation Function: Karst areas serve as natural carbon sinks, contributing to climate regulation and risk reduction.
2. Literature Review of Geopark Indicator
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Study Area
3.2. Data Description
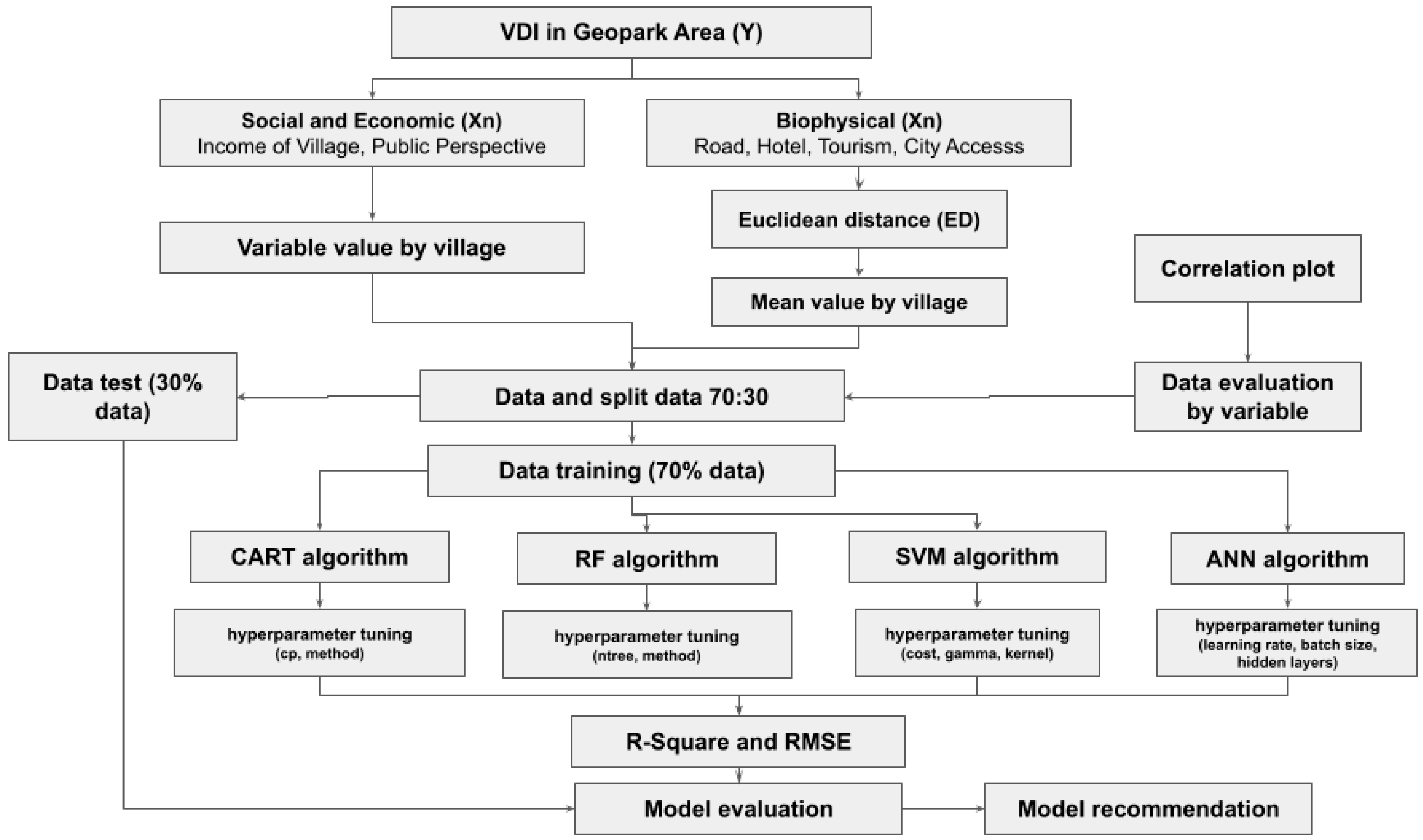
3.3. Processing Data and Preprocessing Data
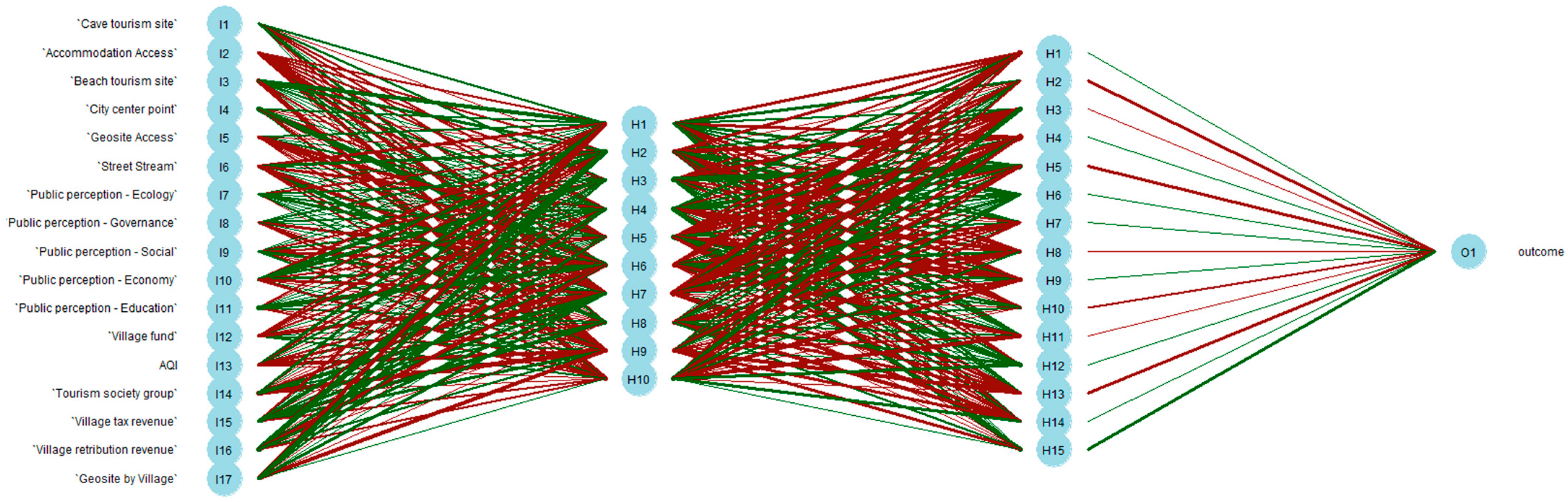
3.4. Machine Learning and Deep Learning Modeling
3.5. Performance Measures
3.6. Error Evaluation
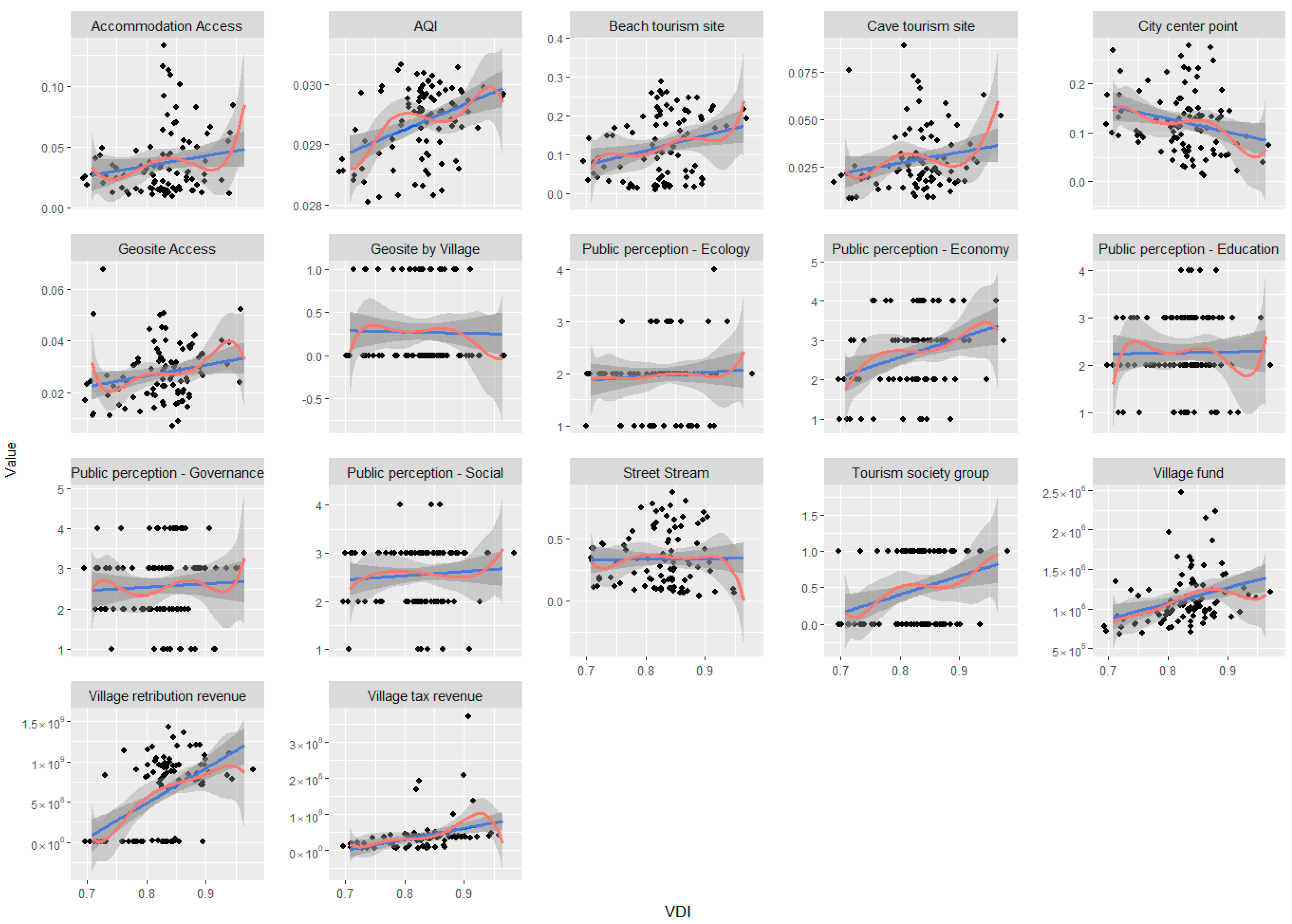
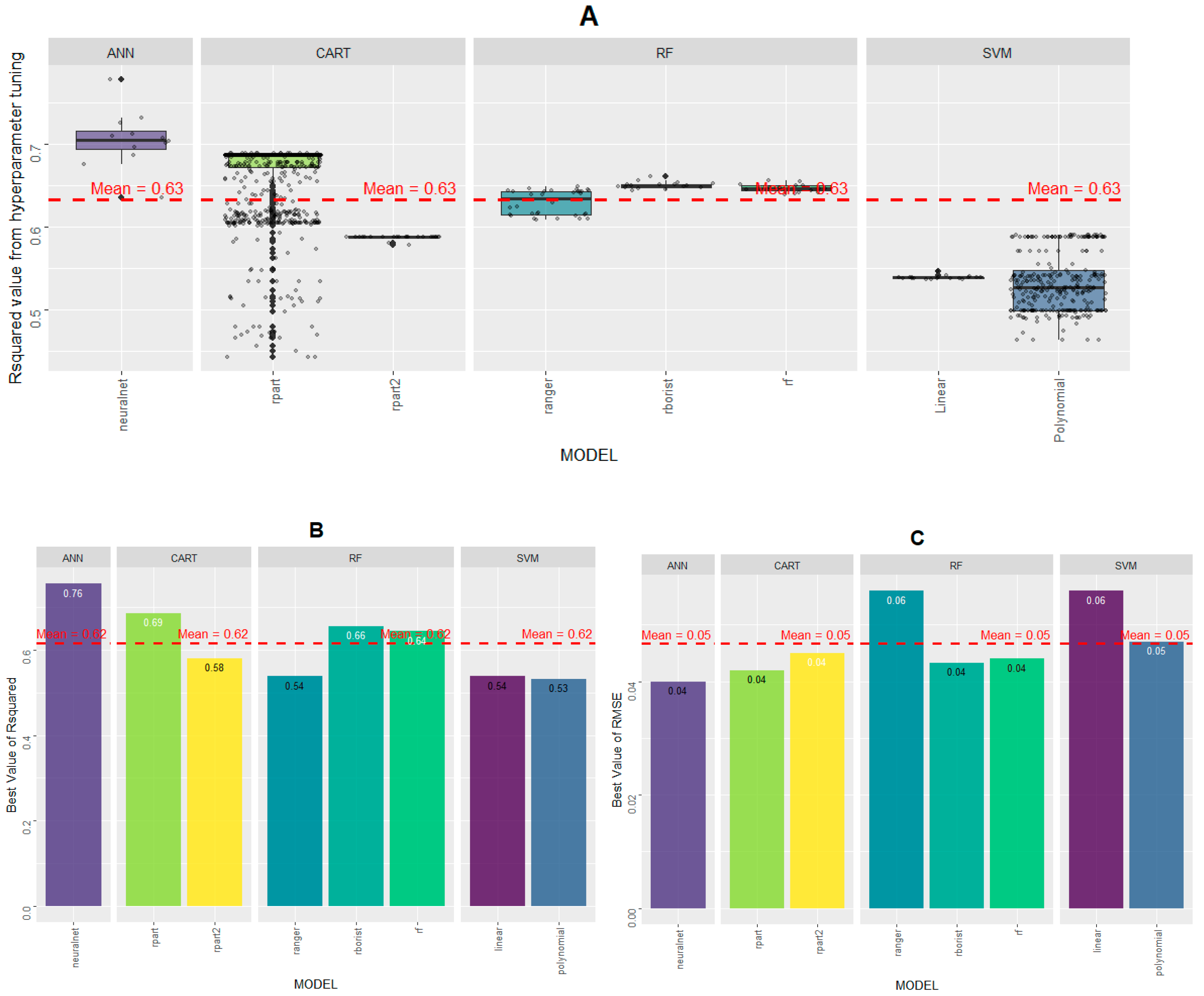
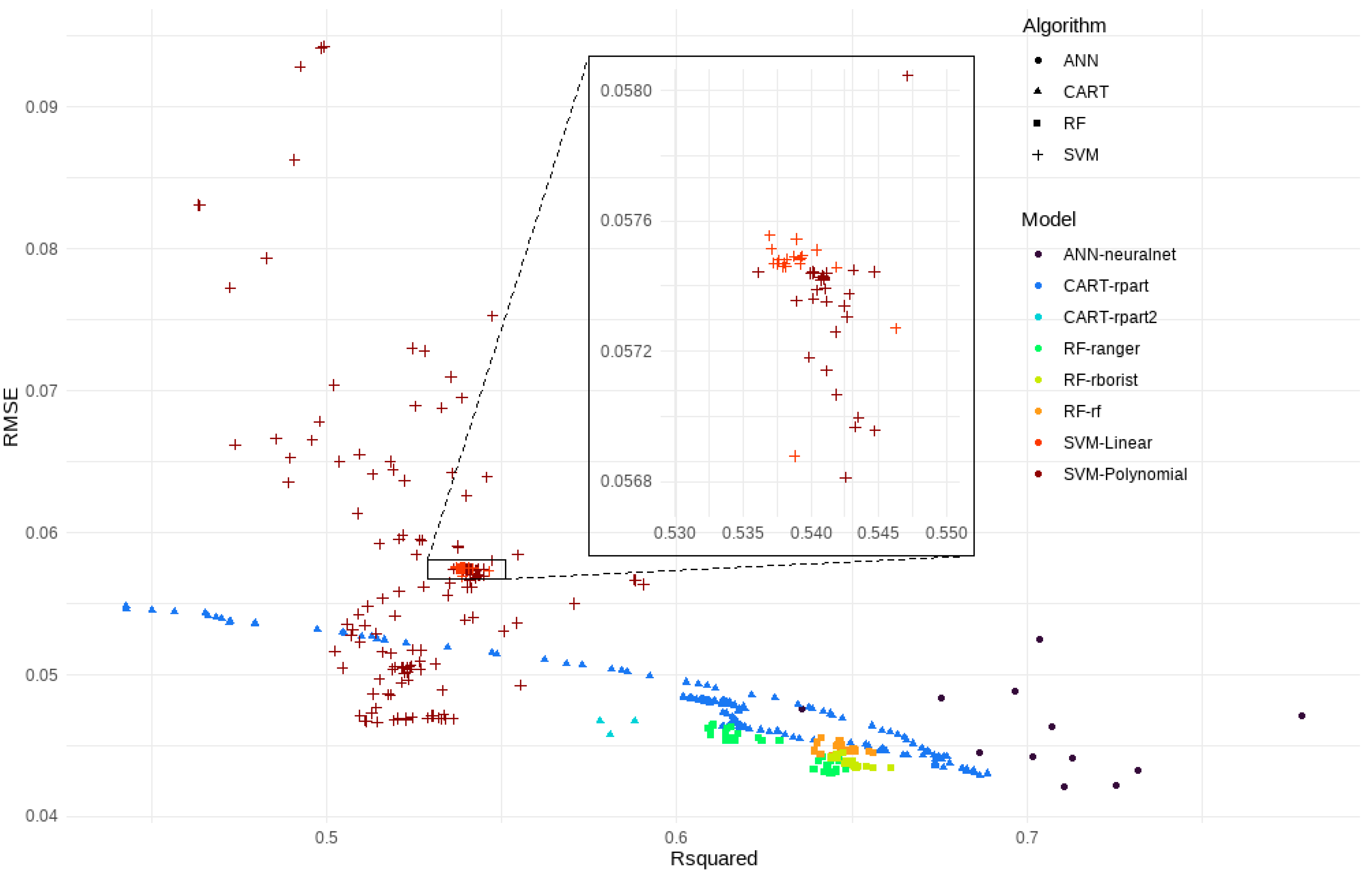
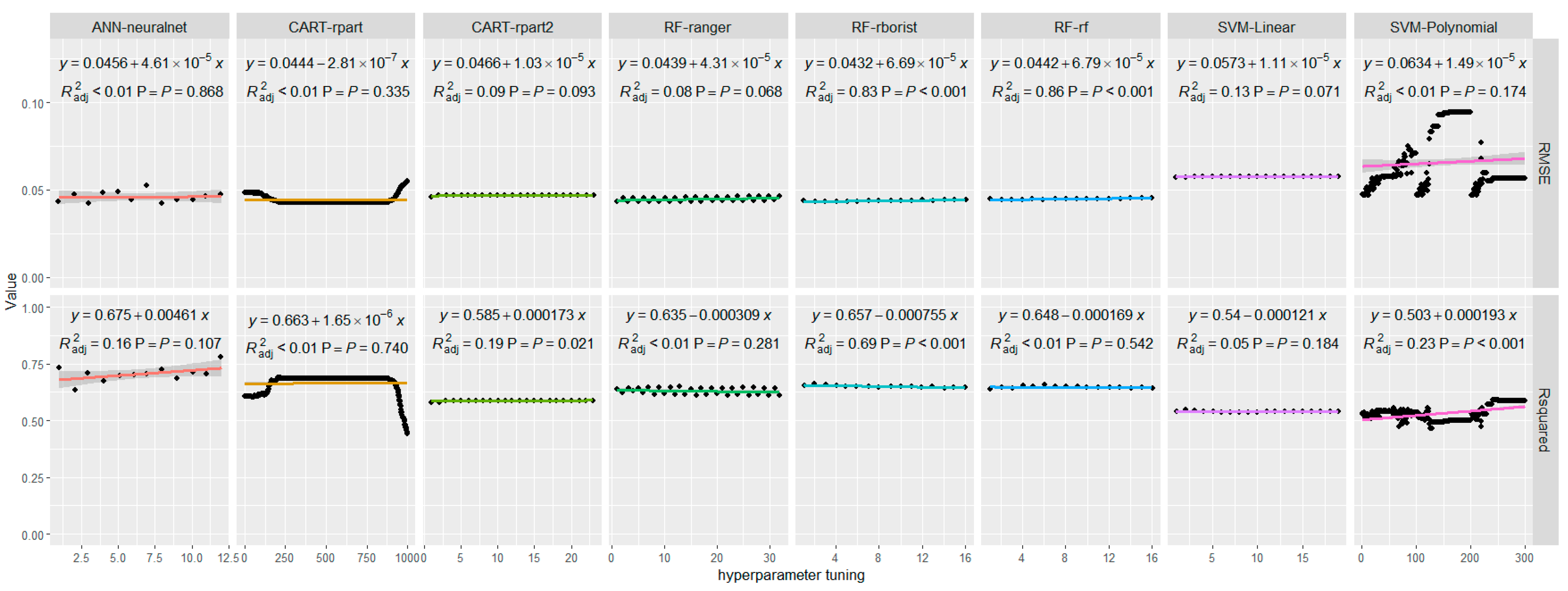
4. Results
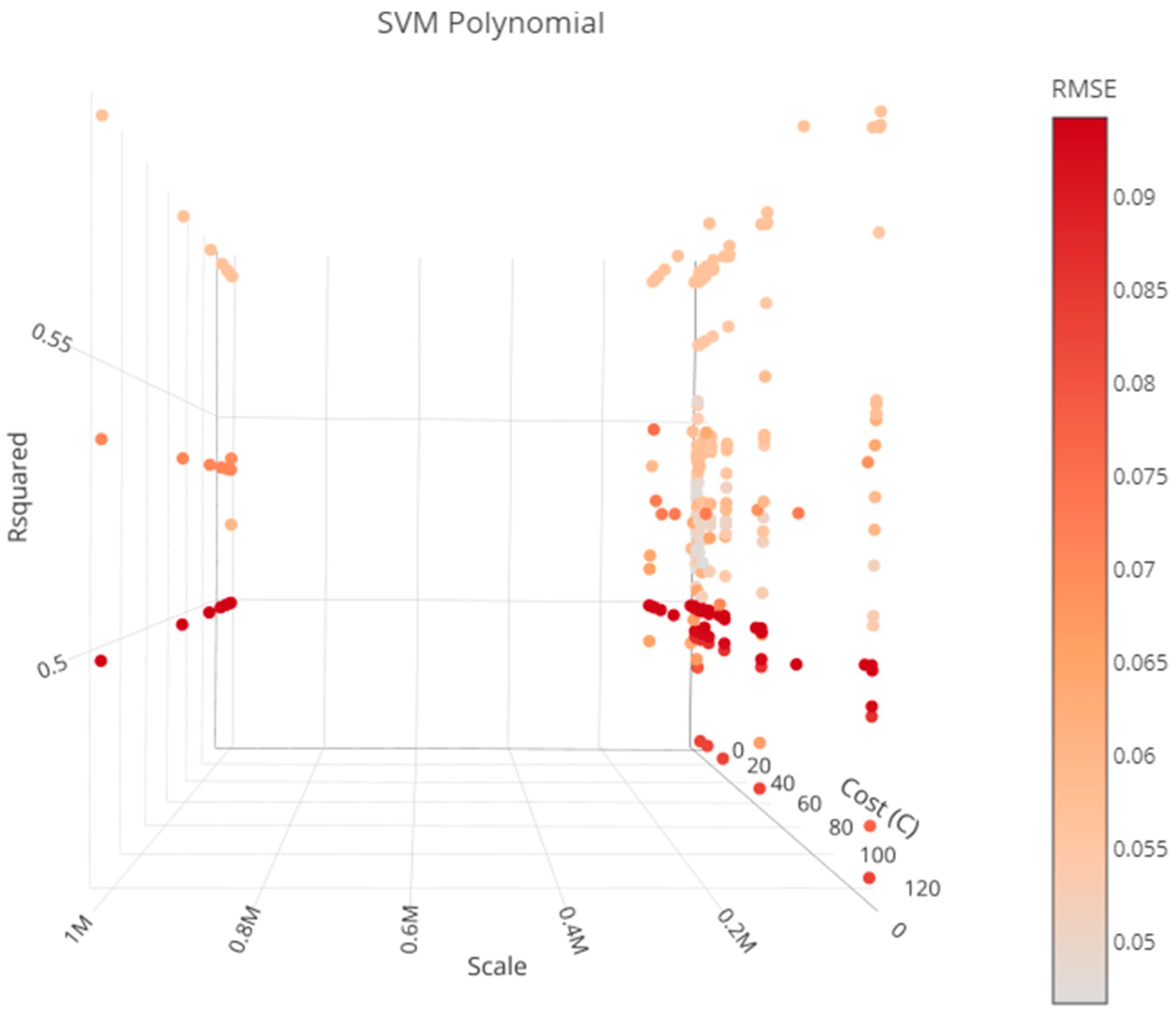
4.1. Constructing the Model
4.2. Evaluation of Model
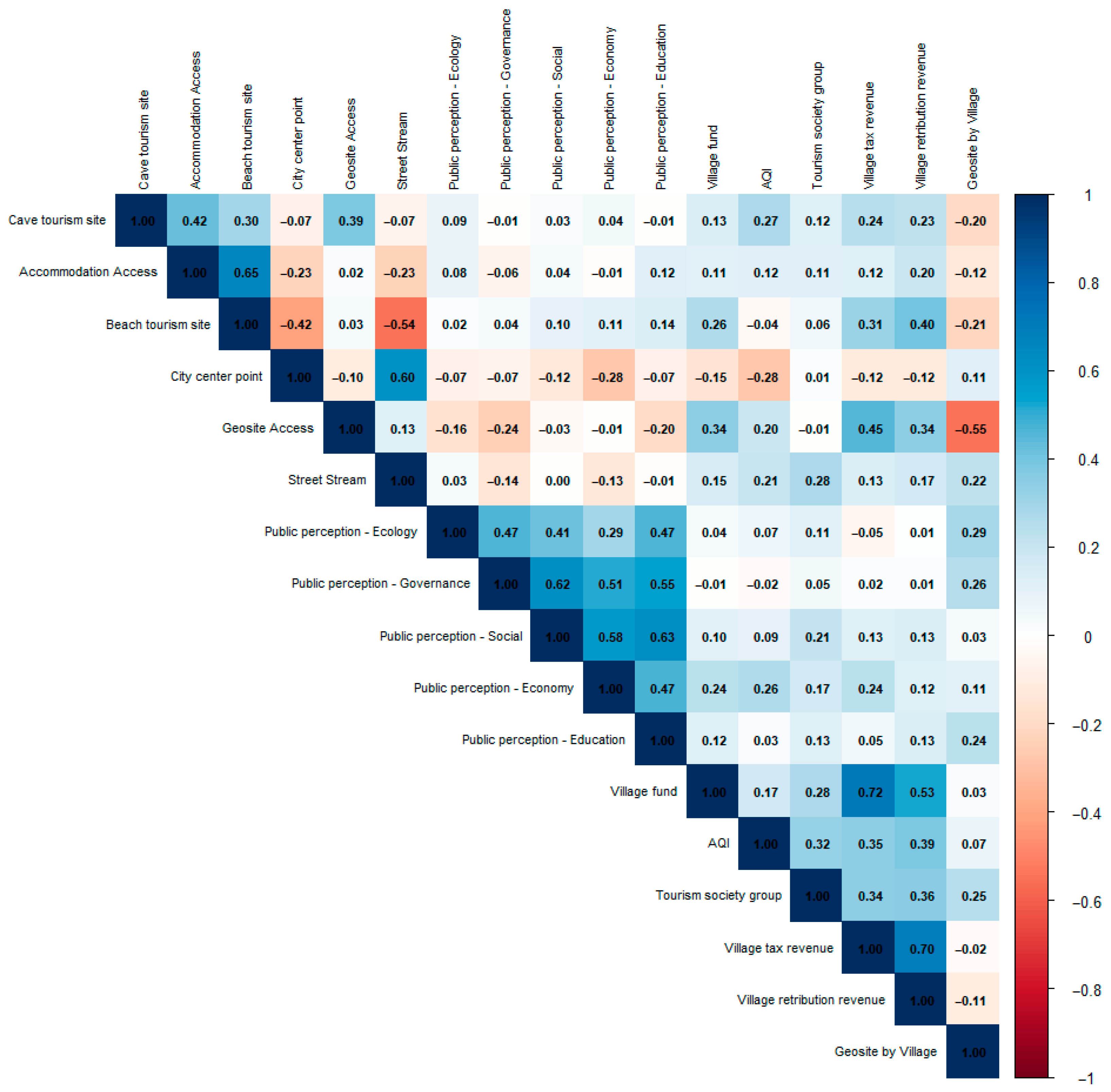
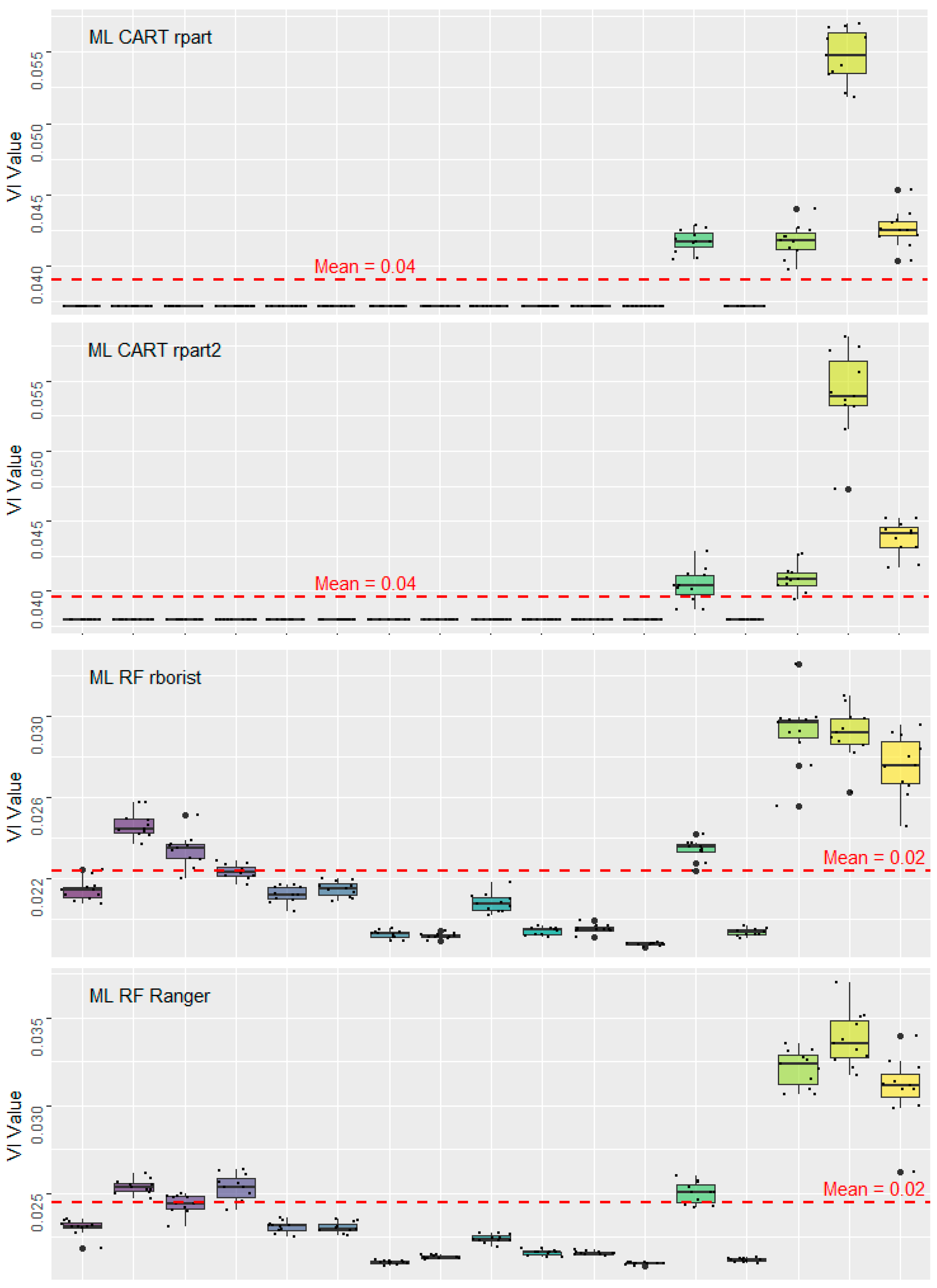
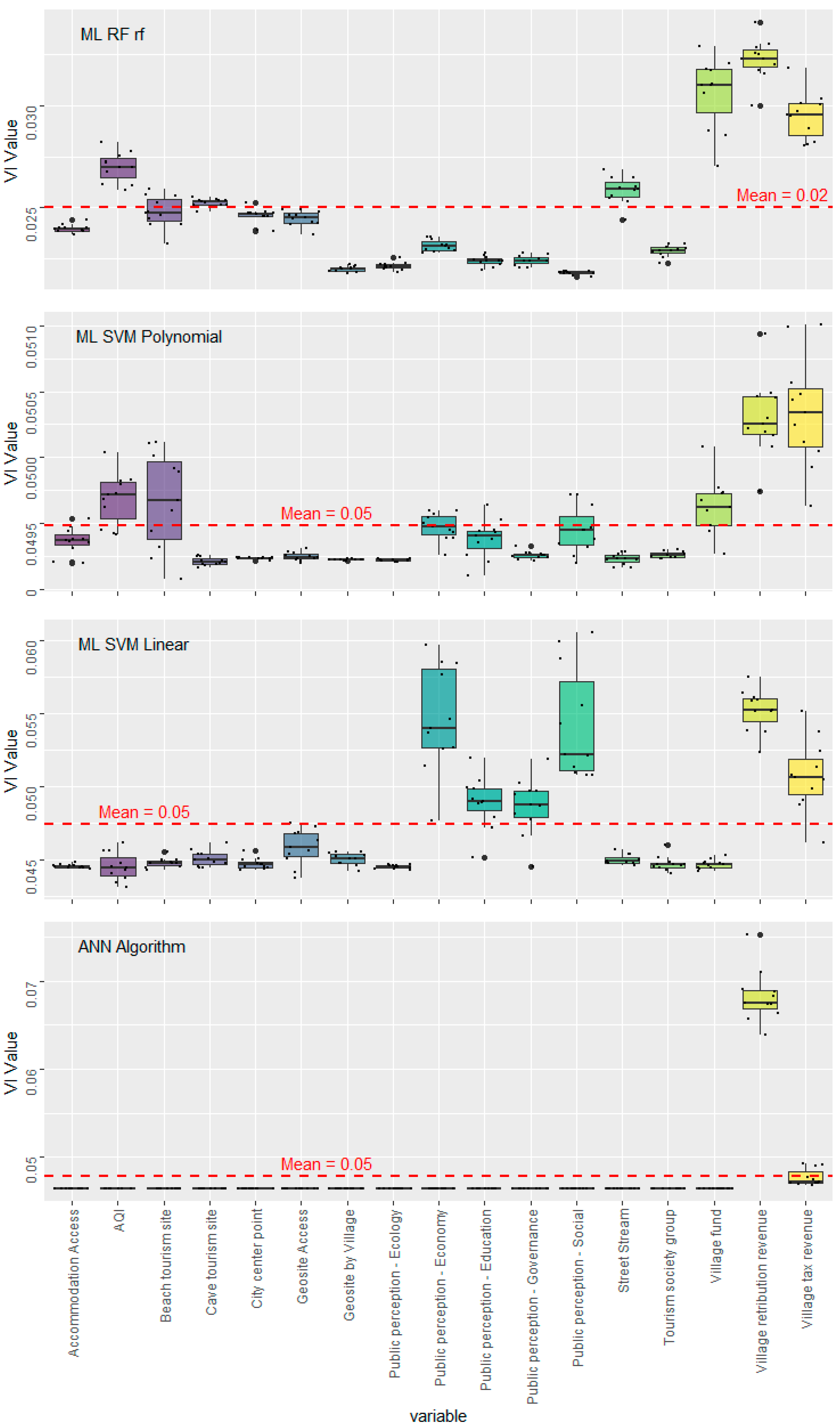
4.3. VDI Contribution in Geopark
5. Discussion
5.1. ML-DL Modeling and Performance
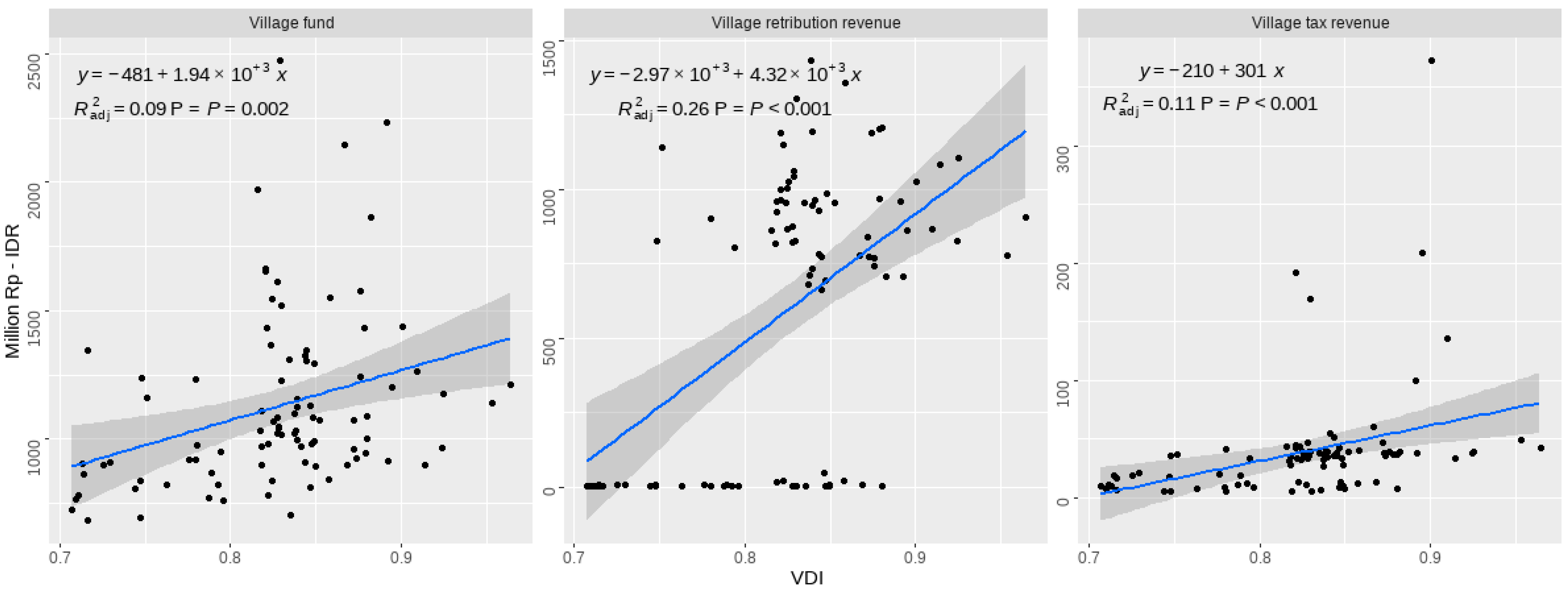
5.2. VDI Contribution Evaluation
- Strengthen village and regional governments by developing and implementing programs to enhance community capacity and social capital, providing technical assistance, and increasing transparent and well-targeted budget allocations to support tourism governance and local entrepreneurship;
- Position the GSUGGp Management Body as a strategic coordinator to ensure the integration of local initiatives with overarching geopark management policies. Its composition should reflect a multi-sectoral collaborative model, involving not only government entities but also educational institutions, community or traditional organizations, and private sector stakeholders (e.g., business associations, hospitality, and tourism operators). This structure promotes cross-sector knowledge exchange and enables the formulation of adaptive and sustainable strategies;
- Encourage provincial and national governments to provide adequate infrastructure, develop knowledge management systems, and implement regulatory frameworks that support inclusive, feasible, and locally applicable economic ecosystems;
- Empower academic institutions and the private sector to deliver field-oriented research, generate practical and applicable solutions, and offer skill development training and market access for local communities. Effective partnerships between academia and industry can expand economic opportunities and enhance community capacity in managing geotourism sustainably.
5.3. Limitation and Future Study
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- UN. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda For Sustainable Development. 2015. Available online: https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/content/documents/21252030%20Agenda%20for%20Sustainable%20Development%20web.pdf (accessed on 23 May 2025).
- Ferreira, D.R.; Valdati, J. Geoparks and Sustainable Development: Systematic Review. Geoheritage 2022, 15, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imelda, J.D.; Sanjatmiko, P.; Anugrahini, T.; Machdum, S.V.; Afifah, A. Buku Pedoman Pengelolaan Geopark Site Berkelanjutan Secara Sosial, Budaya, Ekonomi, dan Ekologi; Lembaga Penelitian dan Pengembangan Sosial Politik: Fakultas Ilmu Sosial dan Ilmu Politik, Universitas Indonesia: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2024; Available online: https://puskakesos.fisip.ui.ac.id/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/Buku-Pedoman-Pengelolaan-Geopark-Site-Berkelanjutan-Secara-Sosial-Budaya-Ekonomi-dan-Ekologi.pdf (accessed on 23 May 2025).
- UNESCO Global Geoparks. UNESCO Global Geoparks Contributing to the Sustainable Development Goals: Celebrating Earth Heritage, Sustaining Local Communities; UNESCO Global Geoparks: Paris, France, 2017; Available online: https://unesdoc.unesco.org/ark:/48223/pf0000247741 (accessed on 23 May 2025).
- Gunn, J. Karst groundwater in UNESCO protected areas: A global overview. Hydrogeol. J. 2021, 29, 297–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pemerintah Pusat Indonesia. Peraturan Presiden (Perpres) Nomor 9 Tahun 2019 Tentang Pengembangan Taman Bumi (Geopark); LN.2019/NO.22, LL SETKAB: 23 HLM; Pemerintah Pusat Indonesia: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2019; Available online: https://peraturan.bpk.go.id/Details/101626/perpres-no-9-tahun-2019 (accessed on 23 May 2025).
- Kementerian Energi dan Sumber Daya Mineral Indonesia. Peraturan Menteri Energi dan Sumber Daya Mineral Nomor 31 Tahun 2021 tentang Penetapan Taman Bumi (Geopark) Nasional; Kementerian Energi dan Sumber Daya Mineral Indonesia: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2021; Available online: https://peraturan.bpk.go.id/Details/215424/permen-esdm-no-31-tahun-2021 (accessed on 23 May 2025).
- Adom, D. The place and voice of local people, culture, and traditions: A catalyst for ecotourism development in rural communities in Ghana. Sci. Afr. 2019, 6, e00184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheryl, J. History of Geoparks. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2008, 300, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, F.X.; Schilling, M.E.; Baeza, S.; Oms, O.; Sá, A.A. Bottom-up strategy for the use of geological heritage by local communities: Approach in the “Litoral del Biobío” Mining Geopark project (Chile). Proc. Geol. Assoc. 2020, 131, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos, C.A.; Amorocho, R.; Villarreal, C.A.; Mantilla, W.; Velandia, F.A.; Castellanos, O.M.; Muñoz, S.; Atuesta, D.; Jerez, J.; Acevedo, O.; et al. Chicamocha Canyon Geopark project: A novel strategy for the socio-economic development of Santander (Colombia) through geoeducation, geotourism and geoconservation. Int. J. Geoheritage Parks 2020, 8, 96–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kementerian Energi dan Sumber Daya Mineral Indonesia. Keputusan Menteri ESDM; No. 3045 K/40/MEM/2014 Tentang Penetapan Kawasan Bentang Alam Karst Gunung Sewu; LL KESDM 2014: 8 HLM; Kementerian Energi dan Sumber Daya Mineral Indonesia: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2014; Available online: https://jdih.esdm.go.id/dokumen/view?id=1176 (accessed on 23 May 2025).
- Martínez-Martín, J.E.; Rosado-González, E.M.; Martínez-Martín, B.; Sá, A.A. UNESCO Global Geoparks vs. Generative AI: Challenges for Best Practices in Sustainability and Education. Geosciences 2024, 14, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruban, D.A. Water in descriptions of global geoparks: Not less important than geology? Water 2019, 11, 1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telbisz, T.; Mari, L. The significance of karst areas in European national parks and geoparks. Open Geosci. 2020, 12, 117–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, S.; Narayan, P.K.; Tobing, L. Has tourism influenced Indonesia’s current account? Econ. Anal. Policy 2021, 69, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travers, R.; Cleverton, R.; Cochrane, J.; Hussein, A.; Noushad, P.M.; Papagiannopoulos, L.; Jiang, Y.; Kostopoulou, S.; de Lima, A.R.; Travers, A.; et al. The 21st Century Maritime Silk Road—Tourism Opportunities and Impacts; World Tourism Organization (UNWTO): Madrid, Spain, 2019; Available online: https://www.e-unwto.org/doi/epdf/10.18111/9789284418749 (accessed on 23 May 2025).
- UN. World Economic and Social Survey 2013: Sustainable Development Challenges; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2013; Available online: https://www.un.org/en/development/desa/policy/wess/wess_current/wess2013/WESS2013.pdf (accessed on 23 May 2025).
- UNEP. Towards a Green Economy: Pathways to Sustainable Development and Poverty Eradication—A Synthesis for Policy Makers. 2011. Available online: www.unep.org/greeneconomy (accessed on 23 May 2025).
- Alexakis, C.; Dowling, M.; Eleftheriou, K.; Polemis, M. Textual Machine Learning: An Application to Computational Economics Research. Comput. Econ. 2021, 57, 369–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Kou, G.; Liang, H.; Zhang, H.; Chao, X.; Li, C.C.; Dong, Y. Machine learning in business and finance: A literature review and research opportunities. Financ. Innov. 2024, 10, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Kumar, K.; Asha, V.; Kumar, S.N. Machine Learning in Economic Forecasting: A Comprehensive Review. In Proceedings of the 2024 7th International Conference on Contemporary Computing and Informatics (IC3I), Greater Noida, India, 18–20 September 2024; pp. 882–886. [Google Scholar]
- Rezaei, A.; Abdellatif, I.; Umar, A. Towards Economic Sustainability: A Comprehensive Review of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Techniques in Improving the Accuracy of Stock Market Movements. Int. J. Financial Stud. 2025, 13, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giudici, P.; Raffinetti, E.; Riani, M. Robust machine learning models: Linear and nonlinear. Int. J. Data Sci. Anal. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, M.I.; Mitchell, T.M. Machine learning: Trends, perspectives, and prospects. Science 2015, 349, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, D.; Frederick, D.A.; Lledo, E.E.; Rosenfield, N.; Berardi, V.; Linstead, E.; Rosenfield, N.; Berardi, V.; Linstead, E.; Maoz, U. Examining the utility of nonlinear machine learning approaches versus linear regression for predicting body image outcomes: The U.S. Body Project I. Body Image 2022, 41, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryo, M.; Rillig, M.C. Statistically reinforced machine learning for nonlinear patterns and variable interactions. Ecosphere 2017, 8, e01976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ye, Z.; Su, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Li, X.; Ouyang, D. Deep learning for in vitro prediction of pharmaceutical formulations. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2019, 9, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, A.S.; Hassan, M.Y.; Abdullah, M.P.; Rahman, H.A.; Hussin, F.; Abdullah, H.; Saidur, R. A review on applications of ANN and SVM for building electrical energy consumption forecasting. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 33, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; He, J.; Mou, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, T. Exploring China’s 5A global geoparks through online tourism reviews: A mining model based on machine learning approach. Tour. Manag. Perspect. 2021, 37, 100769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manca, G.; Cervone, G. The case of arsenic contamination in the Sardinian Geopark, Italy, analyzed using symbolic machine learning. Environmetrics 2013, 24, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, A.C.; Kirksey, E.; Palmer, B.; Tivasauradej, A.; Changwong, A.A.; Chornelia, A. Reconstructing cave past to manage and conserve cave present and future. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 155, 111051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.Z.; Wang, C.J.; Zhang, Z.X. Environmental predictors of vascular plant richness at large spatial scales based on protected area data of China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 21, e00846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinho, V.J.P.D. (Ed.) Machine and Deep Learning: Their Roles in the Context of the Economic Growth Processes and Sustainability Assessment [Internet]. In Economic Growth: Advances in Analysis Methodologies and Technologies; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al’Afif, M.; Sartohadi, J.; Samodra, G. Impact of landslide on geoheritage: Opportunities through integration, geomorphological classification and machine learning. Int. J. Geoheritage Parks 2024, 12, 333–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Zhou, C.; Li, M.; Ma, Y.; Hua, S. An Approach for Mapping Ecotourism Suitability Using Machine Learning: A Case Study of Zhangjiajie, China. Land 2024, 13, 1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.T.; Dang, K.B.; Giang, T.L.; Hoang, T.H.N.; Le, V.H.; Ha, H.N. Deep learning models for monitoring landscape changes in a UNESCO Global Geopark. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 354, 120497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Fu, B. Spatio-temporal variations of the LUCC of the Djoudj National Bird Sanctuary in the past 40 years and its sustainable development. Int. J. Geoheritage Parks 2024, 12, 636–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.; Debnath, T.; Kundu, D.; Khan, M.S.I.; Aishi, A.A.; Sazzad, S.; Sayduzzaman, M.; Band, S.S. Machine learning and deep learning-based approach in smart healthcare: Recent advances, applications, challenges and opportunities. AIMS Public Health 2024, 11, 58–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UNFCCC. Artificial Intelligence for Climate Action in Developing Countries: Opportunities, Challenges and Risks; UNFCCC: Bonn, France, 2024; Available online: https://unfccc.int/ttclear/tec/AI4climate.html#infonote (accessed on 23 May 2025).
- Zuiderwijk, A.; Chen, Y.C.; Salem, F. Implications of the use of artificial intelligence in public governance: A systematic literature review and a research agenda. Gov. Inf. Q. 2021, 38, 101577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skibiński, J.; Kultys, K.; Baran-Zgłobicka, B.; Zgłobicki, W. Geoparks in SE Poland as areas of tourism development: Current state and future prospects. Resources 2021, 10, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhart, H.; Rafida, M.R.; Sofie, T.; Putra, R.D.; Matoka, M.C.R.; Maulita, N.S.; Baiquni, M. Assessment of Geological Diversity, Geosites, and Geotourism Potencies at Menoreh Mountain for Designation of Geopark Area. Int. J. Geoheritage Parks 2023, 11, 385–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Ng, Y.; Zhang, E. Dictionary of Geotourism; Springer: Singapore, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- El Hamidy, M.; Errami, E. The geosites of Safi province (Marrakech-Safi region, Morocco): Inventory and assessment for geoconservation, geotourism, geoeducation, geoparks, and local sustainable development. Int. J. Geoheritage Parks 2025, 13, 68–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauzi, N.S.M.; Misni, A. Geoheritage Conservation: Indicators Affecting the Condition and Sustainability of Geopark—A Conceptual Review. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2016, 222, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kementerian Desa dan Pembangunan Daerah Tertinggal. Peraturan Menteri Desa, Pembangunan Daerah Tertinggal, dan Transmigrasi Nomor 2 Tahun 2016 Tentang Indeks Desa Membangun. 2016. Available online: https://peraturan.bpk.go.id/Details/150585/permendes-pdtt-no-2-tahun-2016 (accessed on 23 May 2025).
- Putri, R.A.; Supriatna, S. Land cover change modeling to identify critical land in the Ciletuh Geopark tourism area, Palabuhanratu, Sukabumi Regency. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 623, 012081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurnianto, F.A.; Nurdin, A.; Pangastuti, E.I.; Bella, S. Monitoring Mining Impact for Geosites Using Time Series NDVI and Runoff in the Eastern Part of Southern Java Mountains, Indonesia. Forum Geogr. 2024, 38, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, F.; Narendra, B.H.; Putri, I.A.S.L.P.; Tata, H.L.; Susi Dharmawan, I.W.; Rachmat, H.H.; Suharti, S.; Windyoningrum, A.; Khotimah, H.; Sayektiningsih, T. Forest cover change and its carbon dynamic of the karst area in Bulusaraung, South Sulawesi, Indonesia. Forest. Sci. Technol. 2024, 20, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobwaer, A.K.R.; Nursini Anwar, A.I.; Suhab, S. Village Development Index Behavior: A Review of Regional Attractiveness. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Accounting, Management, and Economics (ICAME 2023), Makassar, Indonesia, 22–23 November 2023; pp. 356–366. [Google Scholar]
- Rahmawati, F.; Mafida Amalia, A. Policy Formulation Based on Village Development Index (IDM) in East Java Province. KnE Soc. Sci. 2024, 156–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkadafi, M.; Susanti Wasistiono, S.; Broto, M.F. Does Village Funds Impact Village Development Index and Achievement of Sustainable Development Goals in Rural Areas, Indonesia: A Case Study in Kampar District. J. Lifestyle SDGs Rev. 2025, 5, e04903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuszynski, J.; Dietze, M. caTools: Tools: Moving Window Statistics, GIF, Base64, ROC AUC, etc. CRAN. 2024. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/caTools/caTools.pdf (accessed on 23 May 2025).
- Chardon, J.P.; Adriaensen, F.; Matthysen, E. Incorporating landscape elements into a connectivity measure: A case study for the Speckled wood butterfly (Pararge aegeria L.). Landsc. Ecol. 2003, 18, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, M.; Wing, J.; Weston, S.; Williams, A.; Keefer, C.; Engelhardt, A.; Cooper, T.; Mayer, Z.; Kenkel, B.; Team, R.; et al. Package “Caret” Title Classification and Regression Training. CRAN. 2024. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/caret/caret.pdf (accessed on 23 May 2025).
- Schaks, M.; Staudinger, I.; Homeister, L.; Di Biase, B.; Steinkraus, B.R.; Spiess, A.N. Local microbial yield-associating signatures largely extend to global differences in plant growth. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 958, 177946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, B.; Langen, B.; Liu, P.; Dávila López, M. Development of a machine learning framework for radiation biomarker discovery and absorbed dose prediction. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1156009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazzari, A.; Giovinazzo, S.; Cabassi, G.; Brambilla, M.; Bisaglia, C.; Romano, E. Evaluating Urban Sewage Sludge Distribution on Agricultural Land Using Interpolation and Machine Learning Techniques. Agriculture 2025, 15, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehmke, B.; Greenwell, B. Hands-On Machine Learning with R, 1st ed.; Taylor & Francis Group: Oxfordshire, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Horváth, T.; Mantovani, R.G.; de Carvalho, A.C.P.L.F. Effects of Random Sampling on SVM Hyper-parameter Tuning. In Intelligent Systems Design and Applications; Madureira, A.M., Abraham, A., Gamboa, D., Novais, P., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 268–278. [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell, A.E.; Warner, T.A.; Fang, F. Implementation of machine-learning classification in remote sensing: An applied review. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 2784–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Zhang, K.; Li, H.; Gu, M. Development and validation of inpatient mortality prediction models for patients with hyperglycemic crisis using machine learning approaches. BMC. Endocr. Disord. 2025, 25, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Therneau, T.; Atkinson, B.; Ripley, B. rpart: Recursive Partitioning and Regression Trees. CRAN. 2025. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=rpart (accessed on 24 May 2025).
- Breiman, L.; Cutler, A.; Liaw, A.; Wiener, M. Random Forests. CRAN. 2022. Available online: https://www.stat.berkeley.edu/~breiman/RandomForests/ (accessed on 24 May 2025).
- Karatzoglou, A.; Smola, A.; Hornik, K.; Zeileis, A. kernlab—An S4 Package for Kernel Methods in R. J. Stat. Softw. 2004, 11, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripley, B.; Venables, W. nnet: Feed-Forward Neural Networks and Multinominal Log-Linear Models. CRAN. 2025. Available online: http://www.stats.ox.ac.uk/pub/MASS4/ (accessed on 24 May 2025).
- Steinberg, D. CART: Classification and Regression Trees. In The Top Ten Algorithms in Data Mining; Wu, X., Kumar, V., Eds.; Taylor & Francis Group: Oxfordshire, UK, 2009; pp. 179–201. [Google Scholar]
- Balboa, A.; Cuesta, A.; González-Villa, J.; Ortiz, G.; Alvear, D. Logistic regression vs machine learning to predict evacuation decisions in fire alarm situations. Saf. Sci. 2024, 174, 106485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Cheng, J.C.P.; Jiang, F.; Chen, W.; Zhang, J. Analyzing driving factors of land values in urban scale based on big data and non-linear machine learning techniques. Land Use Policy 2020, 94, 104537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedin, M.Z.; Moon, M.H.; Hassan, M.K.; Hajek, P. Deep learning-based exchange rate prediction during the COVID-19 pandemic. Ann. Oper. Res. 2021, 345, 1335–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitriadou, A.; Gogas, P.; Papadimitriou, T. Tourism and uncertainty: A machine learning approach. Curr. Issues Tour. 2024, 28, 2278–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkurunziza, F.; Kabanda, R.; McSharry, P. Enhancing poverty classification in developing countries through machine learning: A case study of household consumption prediction in Rwanda. Cogent Econ. Financ. 2025, 13, 2444374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, B.M.; Muse, A.M.S. Predictive analysis of Somalia’s economic indicators using advanced machine learning models. Cogent Econ. Financ. 2024, 12, 2426535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Wang, G.; Li, P.; Wang, H.; Zhang, M.; Liang, X. An improved random forest based on the classification accuracy and correlation measurement of decision trees. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 237, 121549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, S.; Heutte, L.; Adam, S. Influence of Hyperparameters on Random Forest Accuracy. In Multiple Classifier Systems; Benediktsson, J.A., Kittler, J., Roli, F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 171–180. [Google Scholar]
- Mohapatra, N.; Shreya, K.; Chinmay, A. Optimization of the Random Forest Algorithm. In Advances in Data Science and Management; Borah, S., Emilia Balas, V., Polkowski, Z., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 201–208. [Google Scholar]
- Cristianini, N.; Ricci, E. Support Vector Machines. In Encyclopedia of Algorithms; Kao, M.Y., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2008; pp. 928–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, H.; Lee, S.W. A Survey on Pattern Recognition Applications of Support Vector Machines. Int. J. Pattern Recognit. Artif. Intell. 2003, 17, 459–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.Y.; Xiong, Z.Y.; Luo, Y.G.; Dong, L.M. A method to improve support vector machine based on distance to hyperplane. Optik 2015, 126, 2405–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Han, Y.; So, S.S. Overview of Artificial Neural Networks. In Artificial Neural Networks: Methods and Applications; Livingstone, D.J., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunbo, J.N.; Alagbe, O.A.; Oladapo, M.I.; Shin, C. N-hidden layer artificial neural network architecture computer code: Geophysical application example. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, M.W. NeuralNetTools: Visualization and analysis tools for neural networks. J. Stat. Softw. 2018, 85, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alqadhi, S.; Mallick, J.; Alkahtani, M. Integrated deep learning with explainable artificial intelligence for enhanced landslide management. Nat. Hazards 2024, 120, 1343–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Wang, S.; Liu, C.; Wu, S.; Zhang, B.; Lu, C.; Huang, C.; Chen, T.; Zhou, C.; Zhu, J.; et al. Prediction model for spinal cord injury in spinal tuberculosis patients using multiple machine learning algorithms: A multicentric study. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 7691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biecek, P.; Maksymiuk, S.; Baniecki, H. DALEX: Model Agnostic Language for Exploration and Explanation. CRAN. 2023. Available online: https://dalex.drwhy.ai/ (accessed on 24 May 2025).
- Guan, C.; Ma, F.; Chang, S.; Zhang, J. Interpretable machine learning models for predicting venous thromboembolism in the intensive care unit: An analysis based on data from 207 centers. Crit. Care 2023, 27, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gogas, P.; Papadimitriou, T. Machine Learning in Economics and Finance. Comput. Econ. 2021, 57, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallik, R.; Puri, S.; Bhansali, A.; Manikandan, R.; Rahunathan, L. Defaulter detection based on Spearman correlation with hyper tuned SVM classification for preventing non-performing assets occurring in bank. Multimed Tools Appl. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.; Ji, X.; Wang, L.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, B.; Zhou, S. A machine-learning method of predicting vital capacity plateau value for ventilatory pump failure based on data mining. Healthcare 2021, 9, 1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadorsky, P. A Random Forests Approach to Predicting Clean Energy Stock Prices. J. Risk Financ. Manag. 2021, 14, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adewale, M.D.; Ebem, D.U.; Awodele, O.; Sambo-Magaji, A.; Aggrey, E.M.; Okechalu, E.A.; Donatus, R.; Olayanju, K.; Owolabi, A.; Oju, J.; et al. Predicting gross domestic product using the ensemble machine learning method. Syst. Soft Comput. 2024, 6, 200132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wu, H.; Jin, X.; Zheng, P.; Hu, S.; Xu, X.; Yu, W.; Yan, J. Study of cardiovascular disease prediction model based on random forest in eastern China. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanda, M.A.; Seminar, K.B.; Nandika, D.; Maddu, A. A comparison study of kernel functions in the support vector machine and its application for termite detection. Information 2018, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, C.; Deng, J.; Cao, K.; Xiao, Y.; Ma, L.; Wang, W.; Ma, T.; Shu, C. A comparison of random forest and support vector machine approaches to predict coal spontaneous combustion in gob. Fuel 2019, 239, 297–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinci, H.A.; Akincl, H. Machine learning based forest fire susceptibility assessment of Manavgat district (Antalya), Turkey. Earth Sci. Inform. 2023, 16, 397–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Xu, C. Deep Learning and Machine Learning with Grid Search to Predict Later Occurrence of Breast Cancer Metastasis Using Clinical Data. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehra, L.K.; Cowger, C.; Gross, K.; Ojiambo, P.S. Predicting pre-planting risk of Stagonospora nodorum blotch in winter wheat using machine learning models. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaya-Tejera, N.; Gamarra, M.; Vélez, J.I.; Zurek, E. A distance-based kernel for classification via Support Vector Machines. Front. Artif. Intell. 2024, 7, 1287875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arifin, B.; Wicaksono, E.; Tenrini, R.H.; Wardhana, I.W.; Setiawan, H.; Damayanty, S.A.; Solikin, A.; Suhendra, M.; Saputra, A.H.; Ariutama, G.A.; et al. Village fund, village-owned-enterprises, and employment: Evidence from Indonesia. J. Rural. Stud. 2020, 79, 382–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernawati, E.; Tajuddin, T.; Nur, S. Does government expenditure affect regional inclusive growth? An experience of implementing village fund policy in Indonesia. Economies 2021, 9, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, B.D. Decentralising to Villages in Indonesia: Money (and Other) Mistakes. Public Adm. Dev. 2015, 35, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilmawan, R.; Aprianti, Y.; Vo, D.T.H.; Yudaruddin, R.; Bintoro, R.F.A.; Fitrianto, Y.; Wahyuningsih, N. Rural Development from Village Funds, Village-Owned Enterprises, and Village Original Income. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2023, 9, 100159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husna, C.H.; Bursa, B.; Anik, S.; Arifah, D.A. Accountability Disclosure for Village Fund Management in Villages with Very Disadvantaged Status in North Aceh Regency. In The AI Revolution: Driving Business Innovation and Research: Volume 1; Awwad, B., Ed.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 641–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udjianto, D.; Hakim, A.; Domai, T.; Suryadi, S.; Hayat, H. Community Development and Economic Welfare through the Village Fund Policy. J. Asian Financ. Econ. Bus. 2021, 8, 563–572. [Google Scholar]
- Anam, C.; Plaček, M.; Valentinov, V.; Del Campo, C. Village funds and poverty reduction in Indonesia: New policy insight. Discov. Glob. Soc. 2023, 1, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antlöv, H. Village Government and Rural Development in Indonesia: The New Democratic Framework. Bull. Indones. Econ. Stud. 2003, 39, 193–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, V.C.; Sharma, V.R. Geotourism in Kachchh, Gujarat: Unveiling Benefits and Empowering Local Communities. In Sustainable Strategies for Managing Geoheritage in a Dynamic World; Kanga, S., Kumar, S., Singh, S.K., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2025; pp. 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J.; Jayakumar, R. Economic impact of UNESCO Global Geoparks on local communities: Comparative analysis of three UNESCO Global Geoparks in Asia. Int. J. Geoheritage Parks 2021, 9, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farsani, N.T.; Coelho, C.; Costa, C. Geotourism and geoparks as novel strategies for socio-economic development in rural areas. Int. J. Tour. Res. 2011, 13, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahyadi, H.S.; Newsome, D. The post COVID-19 tourism dilemma for geoparks in Indonesia. Int. J. Geoheritage Parks 2021, 9, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.K.; Lian, J.C.K. The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on the Life Cycle of Tourist Destinations from Tour Operators and Hoteliers’ Perspectives. Glob. Bus. Financ. Rev. 2024, 29, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemar, G.; Soler, I.P.; Moniche, L. Exploring the impacts of local development initiatives on tourism: A case study analysis. Heliyon 2023, 9, e19924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ouyang, Z.; Meng, C.; Xiao, Y. Mechanisms and influencing factors of cultural ecosystem services value realization. Environ. Sustain. Indic. 2025, 26, 100584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasoolimanesh, S.M.; Seyfi, S.; Hall, C.M.; Hatamifar, P. Understanding memorable tourism experiences and behavioural intentions of heritage tourists. J. Destin. Mark. Manag. 2021, 21, 100621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorin, F.; Einarsson, S. Circular Economy in Travel and Tourism. 2020. Available online: https://circulareconomy.europa.eu/platform/sites/default/files/circular-economy-in-travel-and-tourism.pdf (accessed on 23 May 2025).
- Alamineh, G.A.; Hussein, J.W.; Endaweke, Y.; Taddesse, B. The local communities’ perceptions on the social impact of tourism and its implication for sustainable development in Amhara regional state. Heliyon 2023, 9, e17088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nugroho, P.S.; Purwani, O.; Winarto, Y.; Triratma, B.; Setyaningsih, W. Connectivity and integration analysis of karst tourism objects in Wonogiri with Space Syntax Method. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2023, 1180, 012036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulistiyowati, E.; Setiadi Haryono, E. Karst and Conservation Research in Indonesia and Its Implication to Education. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 1796, 012071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzubaidi, L.; Zhang, J.; Humaidi, A.J.; Al-Dujaili, A.; Duan, Y.; Al-Shamma, O.; Santamaría, J.; Fadhel, M.A.; Al-Amidie, M.; Farhan, L. Review of deep learning: Concepts, CNN architectures, challenges, applications, future directions. J. Big Data 2021, 8, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davila Delgado, J.M.; Oyedele, L. Deep learning with small datasets: Using autoencoders to address limited datasets in construction management. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 112, 107836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, M.M.; Olsson, H.H.; Bosch, J. Developing ML/DL Models: A Design Framework. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Software and System Processes, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 26–28 June 2020; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, A.A.; Das, A.; Hoque, K.K.S.; Karmaker, D. A Comparative Study of Hyperparameter Optimization Techniques for Deep Learning. In Proceedings of International Joint Conference on Advances in Computational Intelligence; Uddin, M.S., Jamwal, P.K., Bansal, J.C., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2022; pp. 509–521. [Google Scholar]
- Decastro-García, N.; Muñoz Castañeda, Á.L.; Escudero García, D.; Carriegos, M.V. Effect of the Sampling of a Dataset in the Hyperparameter Optimization Phase over the Efficiency of a Machine Learning Algorithm. Complexity 2019, 2019, 6278908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.; Li, H.; Shang, W.; Ma, L. An Empirical Study of the Impact of Hyperparameter Tuning and Model Optimization on the Performance Properties of Deep Neural Networks. ACM Trans. Softw. Eng. Methodol. 2022, 31, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, H.; Ravishankar, C.M.; Ganesan, A.; Pandya, M.; Bhosale, H.; Dhadwal, R.; Parlikkad, N.R.; Siarry, P.; Valadi, J.K. Enhancing random forest model prediction of gas holdup in internal draft airlift loop contactors with genetic algorithms tuning and interpretability. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 9325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuba, E.; Bačanin, N.; Strumberger, I.; Tuba, M. Convolutional Neural Networks Hyperparameters Tuning. In Artificial Intelligence: Theory and Applications; Pap, E., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 65–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayed, N.; Bougatef, K. Performance Assessment of Logistic Regression (LR), Artificial Neural Network (ANN), Fuzzy Inference System (FIS) and Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy System (ANFIS) in Predicting Default Probability: The Case of a Tunisian Islamic Bank. Comput. Econ. 2024, 64, 1803–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.A.; Ghorbani, S.; Shabani, E.; Band, S.S. Enhancement of Neural Networks Model’s Predictions of Currencies Exchange Rates by Phase Space Reconstruction and Harris Hawks’ Optimization. Comput. Econ. 2024, 63, 835–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J. Forecasting of Real GDP Growth Using Machine Learning Models: Gradient Boosting and Random Forest Approach. Comput. Econ. 2021, 57, 247–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jallow, H.; Mwangi, R.W.; Gibba, A.; Imboga, H. Transfer learning for predicting of gross domestic product growth based on remittance inflows using RNN-LSTM hybrid model: A case study of The Gambia. Front. Artif. Intell. 2025, 8, 1510341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
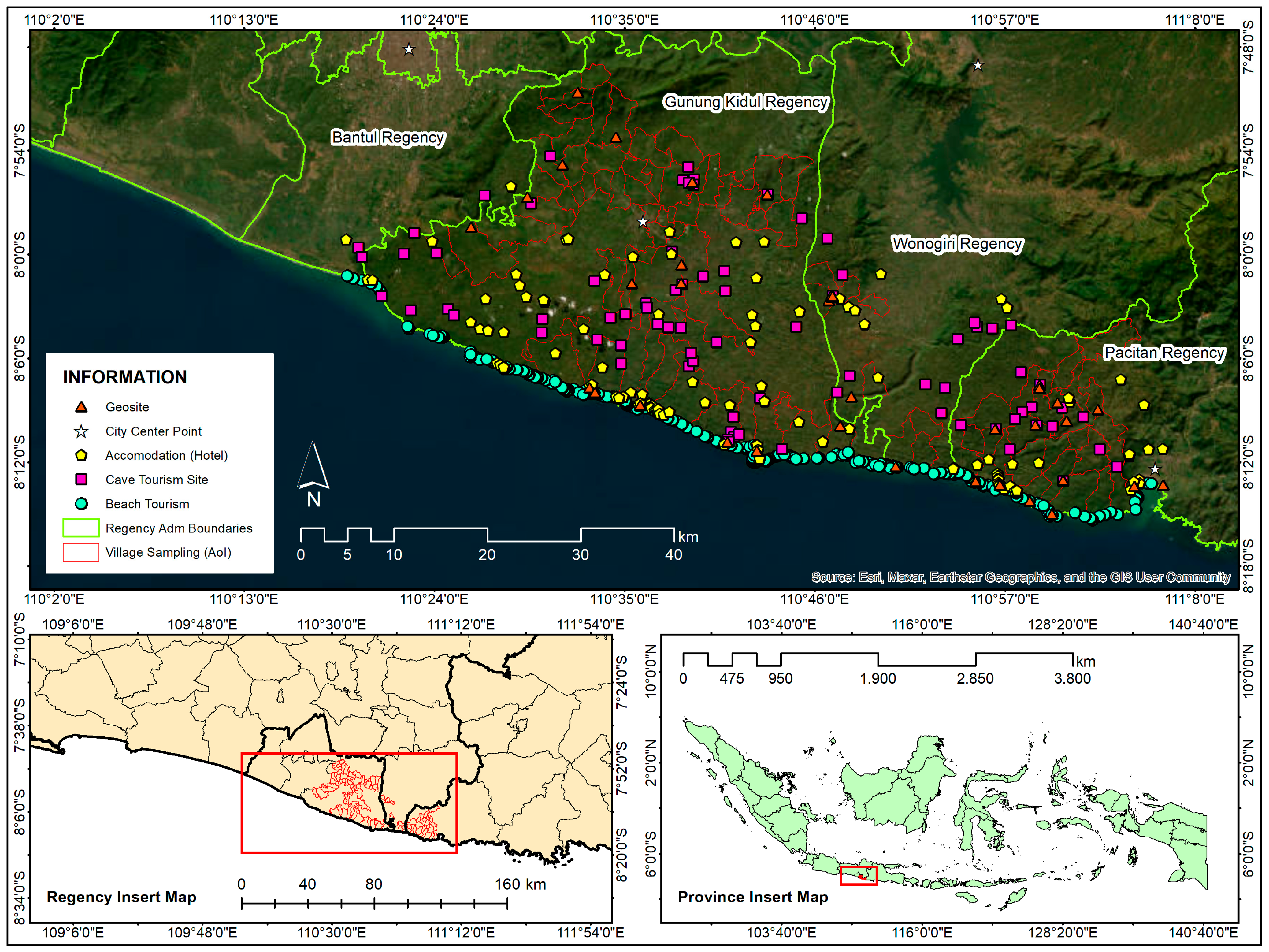
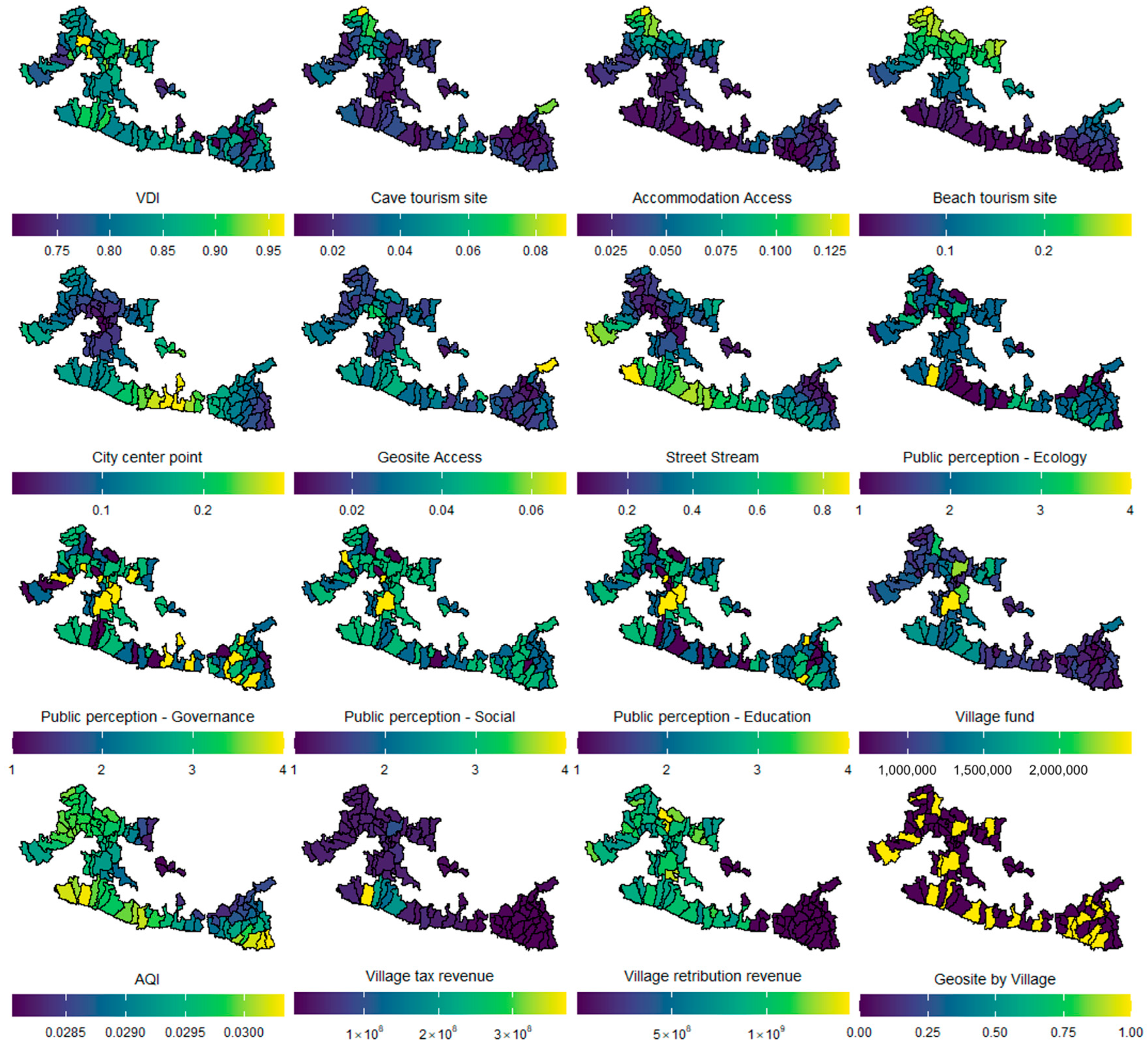

| Data | Unit | Sources | Link |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gunung Sewu UNESCO Global Geopark boundaries | Shapefile | UNESCO Global Geopark | https://www.unesco.org/geoparks (accessed on 23 May 2025), geoparkgunungsewu.com (accessed on 23 May 2025) |
| Village Development Index | Scoring | Ministry of Villages | https://kemendesa.go.id (accessed on 23 May 2025) |
| Street stream | meter | Indonesia Geospatial Agency (BIG) | https://tanahair.indonesia.go.id (accessed on 23 May 2025) |
| Hotel | meter | Google Earth Pro (GE) | https://earth.google.com (accessed on 23 May 2025) |
| Cave tourism site | meter | Google Earth Pro (GE) | https://earth.google.com (accessed on 23 May 2025) |
| Geosite | meter | Gunung Sewu UNESCO Global Geopark Agency | geoparkgunungsewu.com (accessed on 23 May 2025) |
| Beach tourism site | meter | Google Earth Pro (GE) | https://earth.google.com (accessed on 23 May 2025) |
| City center point | meter | Google Earth Pro (GE) | https://earth.google.com (accessed on 23 May 2025) |
| Air quality index (AQI) | ppm | Sentinel-5P NRTI | https://dataspace.copernicus.eu (accessed on 23 May 2025) |
| Tourism society group (POKDARWIS) | Number by village | Tourism Agency of Regency Governments (Gunung Kidul, Wonogiri, and Pacitan) | - |
| Public perception | scorring | Social sampling data in field | - |
| Village tax revenue | IDR (Rp) | Regency government | Regulation of the Regent of Gunung Kidul No. 32 of 2023, and No. 4, 13, 17, and 18 of 2024; Regulation of the Regent of Wonogiri No. 91 of 2023; Decree of the Regent of Pacitan No. 100.3.3.2/ 911/ KPTS/ 408.12/ 2024, and Decree of the Regent of Pacitan No. 100.3.3.2/ 673/ KPTS/ 408.12/ 2024. |
| Village retribution revenue | IDR (Rp) | Regency government | |
| Village fund | IDR (Rp) | Ministry of Finance | https://kemenkeu.go.id |
| Public Perception Variable | Proxy | Score by Village | Score by Respondents |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ecology | Landscape, environmental condition, land use change, biodiversity, geological site, mining in geological area, and tourism | 1.96 ± 0.63 | 2.07 ± 1.35 |
| Governance | Geopark governance effectiveness, geopark management, stakeholder coordination, and international partnership | 2.56 ± 0.92 | 2.65 ± 1.00 |
| Social | Social response and awareness, education activity for geopark, cultural impact, and social conflict. | 2.55 ± 0.66 | 2.21 ± 1.14 |
| Economy | Economic response and increase, social livelihood, and tourism activity potential | 2.70 ± 0.92 | 2.62 ± 1.12 |
| Education | Information technology, research activity, local culture, social facility, education, and research facility | 2.27 ± 0.82 | 2.04 ± 1.11 |
| Algorithm | Model function | Hyperparameters | Cross-Validation | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linear | “lm” | - | - | |
| CART | “rpart” “rpart2” | Method Complexity parameter (cp) | Methods = cv number= 20 repeats= 5 | Therneau et al., 2025 [64] |
| RF | “rf” “ranger” “Rborist” | Method | Breiman et al., 2022 [65] | |
| ntree | ||||
| SVM | “svmLinear” “svmPoly” | Cost Gamma Kernel | Karatzoglou et al., 2004 [66] | |
| ANN | “neuralnet” | Learning rate Hidden units (size) Weight decay (decay) Batch size | Ripley & Venables, 2025 [67] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nugraha, R.P.; Fauzi, A.; Rustiadi, E.; Basuni, S. Quantifying the Geopark Contribution to the Village Development Index Using Machine Learning—A Deep Learning Approach: A Case Study in Gunung Sewu UNESCO Global Geopark, Indonesia. Sustainability 2025, 17, 6707. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17156707
Nugraha RP, Fauzi A, Rustiadi E, Basuni S. Quantifying the Geopark Contribution to the Village Development Index Using Machine Learning—A Deep Learning Approach: A Case Study in Gunung Sewu UNESCO Global Geopark, Indonesia. Sustainability. 2025; 17(15):6707. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17156707
Chicago/Turabian StyleNugraha, Rizki Praba, Akhmad Fauzi, Ernan Rustiadi, and Sambas Basuni. 2025. "Quantifying the Geopark Contribution to the Village Development Index Using Machine Learning—A Deep Learning Approach: A Case Study in Gunung Sewu UNESCO Global Geopark, Indonesia" Sustainability 17, no. 15: 6707. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17156707
APA StyleNugraha, R. P., Fauzi, A., Rustiadi, E., & Basuni, S. (2025). Quantifying the Geopark Contribution to the Village Development Index Using Machine Learning—A Deep Learning Approach: A Case Study in Gunung Sewu UNESCO Global Geopark, Indonesia. Sustainability, 17(15), 6707. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17156707






