Spatial–Temporal Differences in Land Use Benefits and Obstacles Under Human–Land Contradictions: A Case Study of Henan Province, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Theoretical Foundation
- (1)
- Sustainable land use theory
- (2)
- Human–land relationship coordination theory
- (3)
- Regional development differentiation theory
- (4)
- Obstacle factor diagnosis theory
2.3. Indicator Selection and Description
2.4. Methods
2.4.1. Entropy Weight Method and Calculation of Land Use Benefit
2.4.2. TOPSIS Model
2.4.3. Obstruction Model
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Temporal Changes in Land Use Benefits
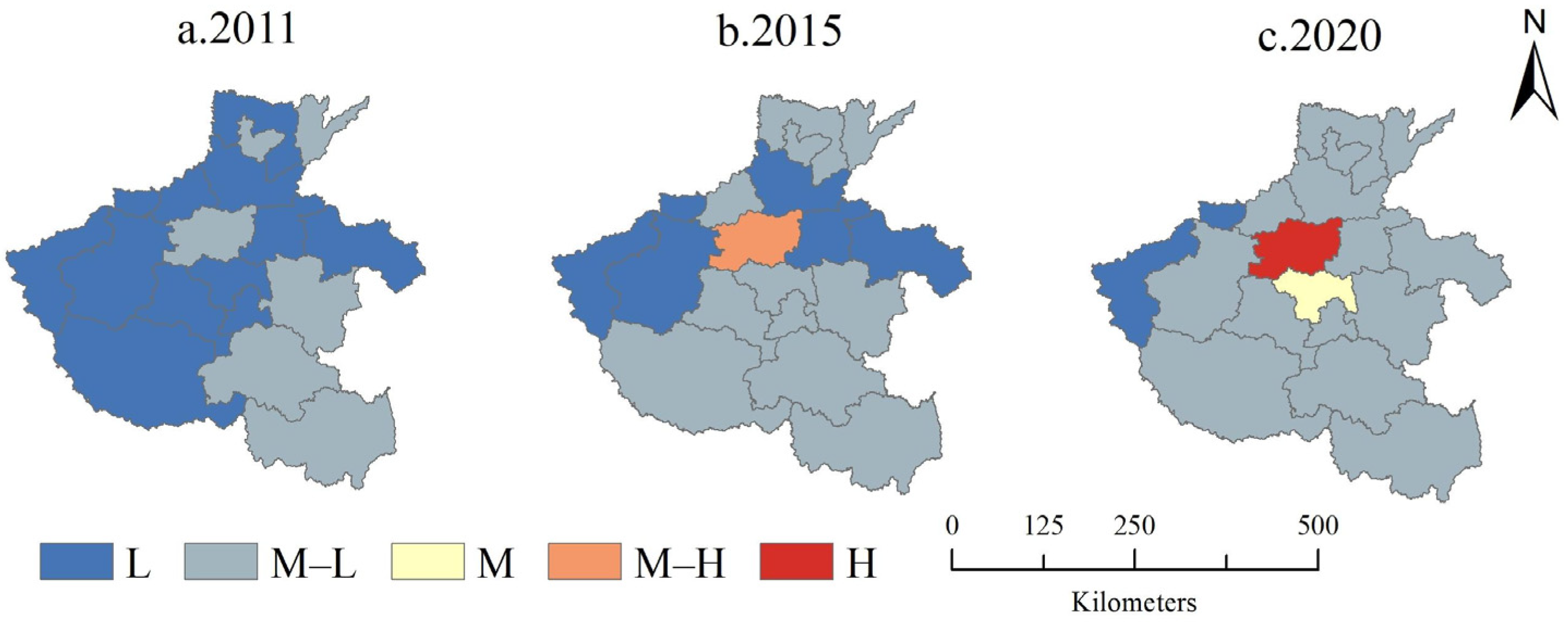
3.2. Spatial Changes in Land Use Benefits
3.3. Obstacle Factors for Land Use Benefits
4. Discussion
4.1. Causes of Changes in Land Use Benefits
4.2. Analysis of Obstacle Degree of Indicators
4.3. Comparisons with Existing Studies and Research Limitations
5. Conclusions and Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karp, D.S.; Tallis, H.; Sachse, R.; Halpern, B.; Thonicke, K.; Cramer, W.; Mooney, H.; Polasky, S.; Tietjen, B.; Waha, K.; et al. National Indicators for Observing Ecosystem Service Change. Glob. Environ. Change 2015, 35, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra Voumik, L.; Sultana, T. Impact of Urbanization, Industrialization, Electrification and Renewable Energy on the Environment in BRICS: Fresh Evidence from Novel CS-ARDL Model. Heliyon 2022, 8, e11457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Zhu, J. Energy and Carbon Intensity in China during the Urbanization and Industrialization Process: A Panel VAR Approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 168, 780–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; An, M.; Wu, H.; An, H.; Huang, J.; Khanal, R. The Local Coupling and Telecoupling of Urbanization and Ecological Environment Quality Based on Multisource Remote Sensing Data. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 327, 116921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Chen, W.; Liu, Z.; Liu, W.; Li, K.; Zhang, B. Urban Expansion, Economic Development, and Carbon Emissions: Trends. Patterns, and Decoupling in Mainland China ’ s Provincial. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 169, 112777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; An, M.; He, W.; Wu, Y. Research on Land Use Optimization Based on PSO-GA Model with the Goals of Increasing Economic Benefits and Ecosystem Services Value. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2025, 119, 106072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Bao, A.; Jiapaer, G.; Liu, R.; Yuan, Y.; Yu, T. Monitoring Land Degradation and Assessing Its Drivers to Support Sustainable Development Goal 15.3 in Central Asia. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 150868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, K.; Jiang, W.; Wang, X.; Hou, P.; Wu, Z.; Cui, T. Evaluation of Future Wetland Changes under Optimal Scenarios and Land Degradation Neutrality Analysis in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 879, 163111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, M.V.; Pandorfi, H.; de Oliveira-Júnior, J.F.; da Silva, J.L.B.; de Almeida, G.L.P.; de Montenegro, A.A.A.; Mesquita, M.; Ferreira, M.B.; Santana, T.C.; Marinho, G.T.B.; et al. Remote Sensing Techniques via Google Earth Engine for Land Degradation Assessment in the Brazilian Semiarid Region, Brazil. J. S. Am. Earth Sci. 2022, 120, 104061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Soares-Filho, B.S.; Leite-Filho, A.T.; Zhang, S.; Du, J.; Yi, Y. How to Balance Land Demand Conflicts to Guarantee Sustainable Land Development. iScience 2023, 26, 106641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Feng, C.C.; Yu, Q.; Han, R.; Guo, L. Contradiction or Coordination? The Spatiotemporal Relationship between Landscape Ecological Risks and Urbanization from Coupling Perspectives in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 363, 132557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Wang, D.; Lu, H.; Liu, G. Temporal and Spatial Heterogeneity of Land Use, Urbanization, and Ecosystem Service Value in China: A National-Scale Analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 418, 137911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruseman, G.; Ruben, R.; Kuyvenhoven, A.; Hengsdijk, H.; Van Keulen, H. Analytical Framework for Disentangling the Concept of Sustainable Land Use. Agric. Syst. 1996, 50, 191–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wu, Y.; Dang, H. Urban Land Use Efficiency and Coordination in China. Sustainability 2017, 9, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Cao, S.; Du, M.; Lu, L. Distinctive Roles of Land-Use Efficiency in Sustainable Development Goals: An Investigation of Trade-Offs and Synergies in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 382, 134889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Zhou, W.; Wu, T.; Wang, X.; Xu, J. Spatial-Temporal Characteristics of Cultivated Land Use Eco-Efficiency under Carbon Constraints and Its Relationship with Landscape Pattern Dynamics. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 141, 109140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbinge, R.; Van Diepen, C.A. Changes in Agriculture and Land Use in Europe. Eur. J. Agron. 2000, 13, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Oguchi, T.; Liang, X. Evaluating Future Habitat Quality Responding to Land Use Change under Different City Compaction Scenarios in Southern China. Cities 2023, 140, 104410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karrasch, L.; Klenke, T.; Kleyer, M. Land-Use Elements and Attributed Ecosystem Services: An Archetype Approach to Land-Use Evaluation at the German North Sea Coast. Ecol. Soc. 2019, 24, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, J. Integration of Land Use Resilience and Efficiency in China : Analysis of Spatial Patterns, Differential Impacts on SDGs, and Adaptive Management Strategies. Appl. Geogr. 2025, 175, 103490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhong, J.L.; Zhang, Q.F.; Xiang, X.; Huang, H. Exploring the Coupling Coordination and Key Factors between Urbanization and Land Use Efficiency in Ecologically Sensitive Areas: A Case Study of the Loess Plateau, China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 86, 104148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Zhang, J.; Fan, J.; Yang, X.; Yi, Y.; Han, X.; Wang, D.; Zhu, P.; Peng, X. Does Animal Manure Application Improve Soil Aggregation? Insights from Nine Long-Term Fertilization Experiments. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 1029–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, L.; Yi, H.; Shen, M.; Wang, M. Coupling Coordination and Spatio-Temporal Evolution of Land-Use Benefits under the Dual Carbon Goal: A Case Study in Anhui, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 903, 166123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yiğit Uzunali, Ş.; Berberoğlu, S. Agricultural Land Suitability Analysis with Parametric and Nonparametric Techniques: The Case of Büyük Menderes River Basin, Türkiye. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2025, 229, 109754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Y.; Liu, Y.L.; Chen, C.F. Evaluation of Land-Use Efficiency Based on Regional Scale—A Case Study in Zhanjiang, Guangdong Province. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. 2007, 17, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- lo Storto, C.; Evangelista, P. Infrastructure Efficiency, Logistics Quality and Environmental Impact of Land Logistics Systems in the EU: A DEA-Based Dynamic Mapping. Res. Transp. Bus. Manag. 2023, 46, 100814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wei, J.; Gao, W. Spatial Differentiation and Influencing Factors of Land Eco-Efficiency Based on Low Carbon Perspective: A Case of 287 Prefecture-Level Cities in China. Environ. Chall. 2023, 10, 100681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, B.; Lu, X.; Zhou, M.; Chen, D. Provincial Cultivated Land Use Efficiency in China: Empirical Analysis Based on the SBM-DEA Model with Carbon Emissions Considered. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2020, 151, 119874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Song, J.; Wu, L. A New Methodology to Measure the Urban Construction Land-Use Efficiency Based on the Two-Stage DEA Model. Land Use Policy 2022, 112, 105799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; Zhou, M.; Huang, L.; Shan, L.; Wang, K. Assessing the Dynamic Land Utilization Efficiency and Relevant Driving Mechanism in In-Situ Urbanized Rural Areas: A Case Study of 1979 Administrative Villages in Hangzhou. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2023, 101, 107111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Song, H. A Novel Approach to Assess the Urban Land-Use Efficiency of 767 Resource-Based Cities in China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 151, 110298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lei, L.; Li, J. Integrating Ecosystem Service Value into the Evaluation of Sustainable Land Use in Fast-Growing Cities: A Case Study of Qingdao, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 153, 110434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Yang, J.; Li, X.; Sang, X.; Xie, X. Research on the Interactive Relationship and the Optimal Adaptation Degree between Land Use Benefit and Industrial Structure Evolution: A Practical Analysis of Jiangsu Province. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 303, 127016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, L.; He, T.; Xiao, W.; Chen, W.; Lu, D.; Liu, S. Measuring the Coupling of Built-up Land Intensity and Use Efficiency: An Example of the Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 87, 104224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Sun, Y.; Li, Y.; Yuchi, X. An Evaluation and Promotion Strategy of Green Land Use Benefits in China: A Case Study of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region. Land 2022, 11, 1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y. Evaluation on New First-Tier Smart Cities in China Based on Entropy Method and TOPSIS. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 145, 109616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koroso, N.H. Urban Land Policy and Urban Land Use Efficiency: An Analysis Based on Remote Sensing and Institutional Credibility Thesis. Land Use Policy 2023, 132, 106827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Li, X.; Zeng, X.; Zhong, K.; Xu, Y. Cultivated Land-Use Benefit Evaluation and Obstacle Factor Identification: Empirical Evidence from Northern Hubei, China. Land 2022, 11, 1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. China Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2024.
- Statistics Bureau of Henan Province. Henan Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2021.
- Brundtland, G.H. Report of the World Commission on Environment and Development: Our Common Future Acronyms and Note on Terminology Chairman’s Foreword; United Nations Digital Library: New York, NY, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Han, B.; Jin, X.; Sun, R.; Li, H.; Liang, X.; Zhou, Y. Understanding Land-Use Sustainability with a Systematical Framework: An Evaluation Case of China. Land Use Policy 2023, 132, 106767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Fan, K.; Lu, J.; Wu, S.; Xie, X. Research on Spatio-Temporal Pattern Evolution and the Coupling Coordination Relationship of Land-Use Benefit from a Low-Carbon Perspective: A Case Study of Fujian Province. Land 2022, 11, 1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, P.; Yeh, C.H. Evaluating Urban Land Use Efficiency with Interacting Criteria: An Empirical Study of Cities in Jiangsu China. Land Use Policy 2020, 90, 104292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Yeung, G.; Zhu, D.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, L. Efficiency of Urban Land Use in China’s Resource-Based Cities, 2000–2018. Land Use Policy 2022, 115, 106009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, X.; Li, X.; Xu, Y. How Can Resource-Exhausted Cities Get Out of “The Valley of Death”? An Evaluation Index System and Obstacle Degree Analysis of Green Sustainable Development. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 16976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Long, T.; Sun, S.; Gao, J. Mega-City Region Sustainability Assessment and Obstacles Identification with GIS–Entropy–TOPSIS Model: A Case in Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 294, 126147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha-Zeri, G.; Guidolini, J.F.; Branco, E.A.; Ometto, J.P. How Sustainable Is the Nitrogen Management in Brazil? A Sustainability Assessment Using the Entropy Weight Method. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 316, 115330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. China City Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2021.
- Ministry of Finance of the People’s Republic of China. Finance Yearbook of China; China Finance Magazine Agency: Beijing, China, 2021.
- Zhao, X.; Miao, C. Spatial-Temporal Changes and Simulation of Land Use in Metropolitan Areas: A Case of the Zhengzhou Metropolitan Area, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 14089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Zhai, S.; Song, G.; He, X.; Song, H.; Chen, J.; Liu, H.; Feng, Y. Assessing Inequity in Green Space Exposure toward a “15-Minute City” in Zhengzhou, China: Using Deep Learning and Urban Big Data. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 5798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, K.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, X. Annual Report on Industrial Development of Henan; Social Sciences Academic Press: Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, X.; Li, X.; He, W.; Ni, H.; Zhao, Z. Spatial Pattern Characteristics of Suitability of Land Use and Regional Regulation in Henan Province. J. Southwest Univ. Sci. Ed. 2022, 44, 153–165. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, H.; Li, Q.; Zhang, S.; Chen, W.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Y. Does Urban Construction Land in China Achieve Sustainable Allocation and Utilization? Land Use Policy 2024, 144, 107223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radzi, A. The Ruhr Innovation Ecosystem—From Industrial Brownfields to Regenerative Smart Environments; Liechtenstein Institute for Strategic Development: Berlin, Germany, 2022; ISBN 9780128202470. [Google Scholar]
- Rada, N. Assessing Brazil’s Cerrado Agricultural Miracle. Food Policy 2013, 38, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, Y. Cultivated Land Protection and Rational Use in China. Land Use Policy 2021, 106, 105454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, W.; Xia, H.; Liu, Y.; Xu, J.; Xiong, J. Assessing Ecological Conservation Redline from Element, Structure, and Function Dimensions: A Case of Zhejiang Province, China. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2024, 106, 107485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
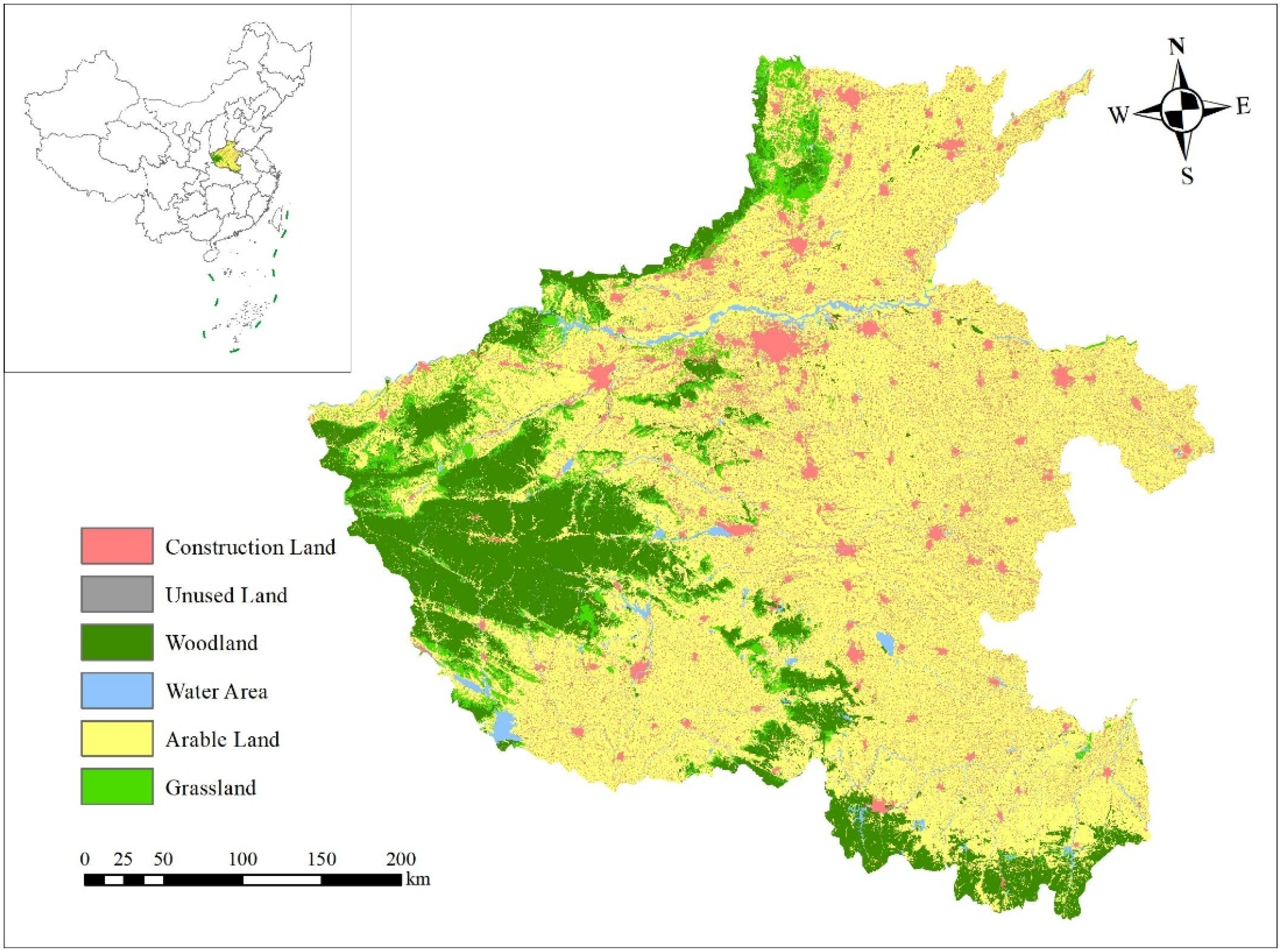
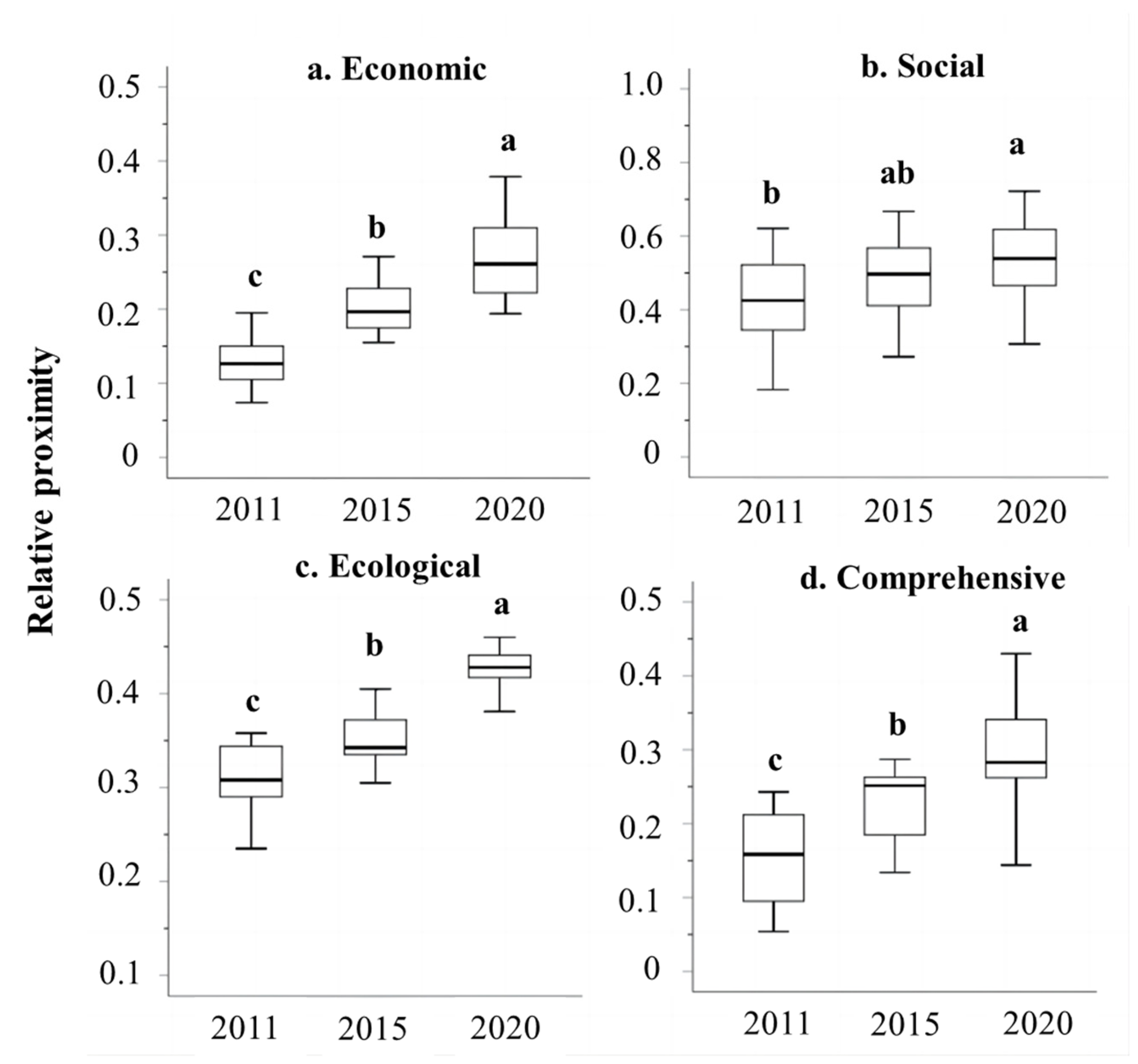
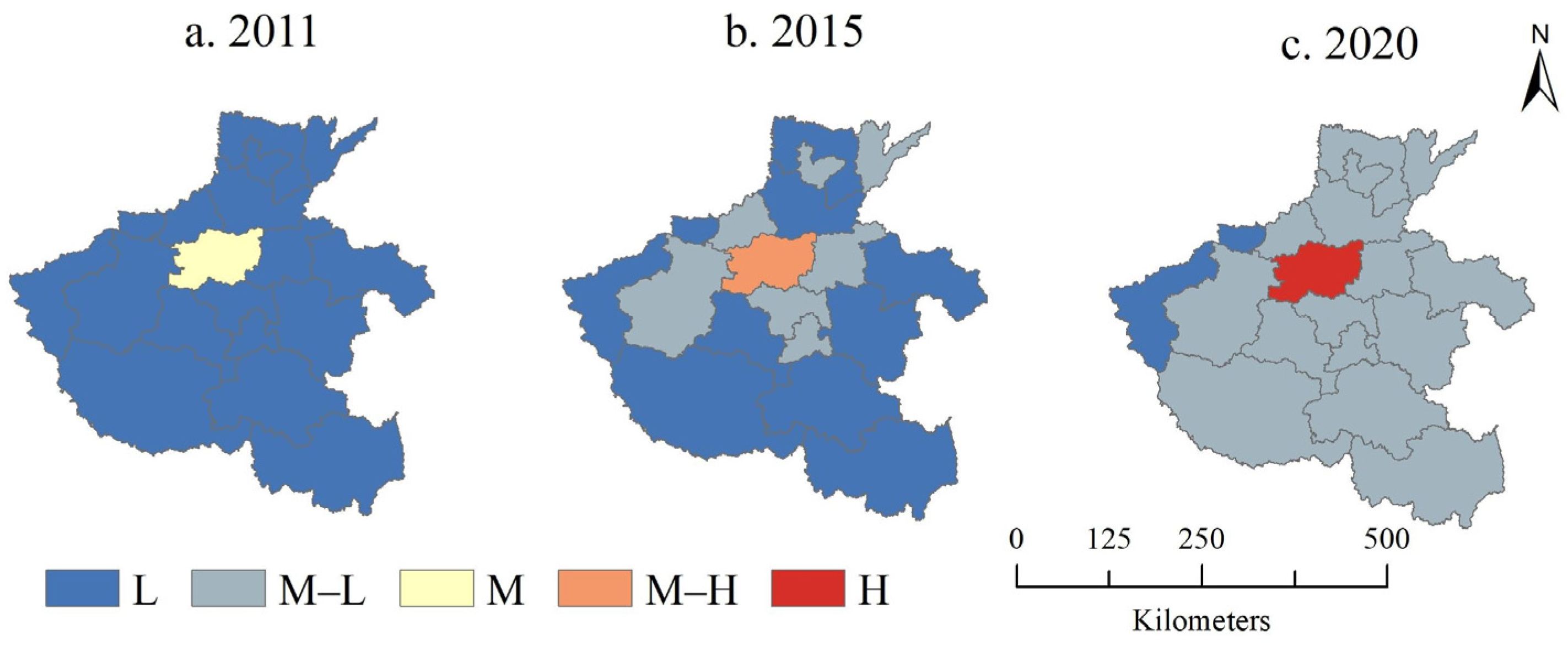
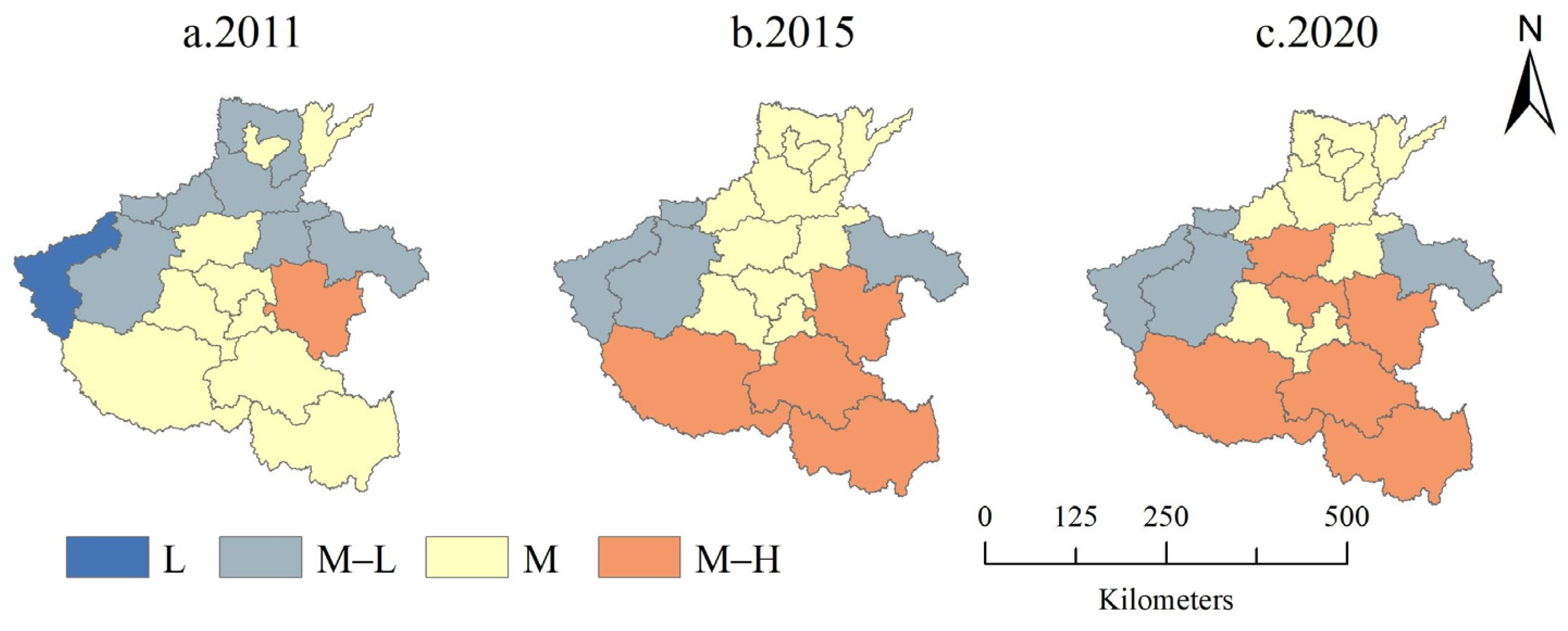


| Indicator | Unit | N | Min. | Max. | Mean | Std. Dev. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X11 | Million CNY/sq. km. | 54 | 6.44 | 161.21 | 30.26 | 25.10 |
| X12 | Million CNY/sq. km. | 54 | 4.88 | 175.59 | 31.88 | 29.93 |
| X13 | Million CNY/sq. km. | 54 | 2.28 | 68.17 | 11.35 | 10.71 |
| X14 | Million CNY/sq. km. | 54 | 0.23 | 16.91 | 2.18 | 2.78 |
| X15 | % | 54 | 1.61 | 4.49 | 3.22 | 0.67 |
| X16 | % | 54 | 18.08 | 59.04 | 36.04 | 9.72 |
| X21 | Thousand people/sq. km. | 54 | 1.81 | 15.06 | 5.45 | 2.62 |
| X22 | Km/thousand people | 54 | 0.09 | 0.64 | 0.34 | 0.16 |
| X23 | Million | 54 | 0.36 | 7.08 | 3.31 | 1.85 |
| X24 | -- | 54 | 1.68 | 2.96 | 2.23 | 0.33 |
| X25 | Zhang/thousand people | 54 | 0.09 | 1.55 | 0.72 | 0.36 |
| X31 | Kiloton | 54 | 0.56 | 174.86 | 40.70 | 43.57 |
| X3 | % | 54 | 65.13 | 100.00 | 92.82 | 7.77 |
| X33 | Megaton | 54 | 0.09 | 2.65 | 0.41 | 0.45 |
| X34 | Sq. m./people | 54 | 5.38 | 17.97 | 12.25 | 3.14 |
| X35 | % | 54 | 25.59 | 47.85 | 39.75 | 4.14 |
| Grade | Low | Medium–Low | Medium | Medium–High | High |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Relative proximity | [0, 0.2) | [0.2–0.4) | [0.4–0.6) | [0.6–0.8) | [0.8–1.0] |
| Region | Obstacle Factor 1 | Obstacle Factor 2 | Obstacle Factor 3 | Obstacle Factor 4 | Obstacle Factor 5 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2011 | 2015 | 2020 | 2011 | 2015 | 2020 | 2011 | 2015 | 2020 | 2011 | 2015 | 2020 | 2011 | 2015 | 2020 | |
| Anyang | X14 | X14 | X33 | X33 | X33 | X14 | X13 | X13 | X13 | X12 | X12 | X12 | X11 | X11 | X11 |
| Hebi | X33 | X33 | X33 | X14 | X14 | X14 | X13 | X13 | X13 | X12 | X12 | X11 <X12> | X11 | X11 | X11 <X12> |
| Jiyuan | X33 | X33 | X33 | X14 | X14 | X14 | X13 | X13 | X13 | X12 | X12 | X12 | X11 | X11 | X11 |
| Jiaozuo | X33 | X33 | X33 | X14 | X14 | X14 | X13 | X13 | X13 | X12 | X11 <X12> | X11 | X11 | X11 <X12> | X12 |
| Kaifeng | X14 | X14 <X33> | X14 <X33> | X33 | X14 <X33> | X14 <X33> | X12 | X12 | X12 | X13 | X13 | X13 | X11 | X11 | X11 |
| Luoyang | X14 | X14 | X14 | X13 <X33> | X12 <X13,X33> | X33 | X13 <X33> | X12 <X13,X33> | X12 <X13> | X12 | X12 <X13,X33> | X12 <X13> | X11 | X11 | X11 |
| Luohe | X33 | X33 | X33 | X14 | X14 | X14 | X12 <X13> | X12 <X13> | X12 <X13> | X12 <X13> | X12 <X13> | X12 <X13> | X11 | X11 | X11 |
| Nanyang | X14 | X14 | X14 | X12 | X12<X33> | X33 | X13 <X33> | X12 <X33> | X12 | X13 <X33> | X13 | X13 | X11 | X11 | X11 |
| Pingdingshan | X14 <X33> | X14 <X33> | X14 <X33> | X14 <X33> | X14<X33> | X14 <X33> | X12 <X13> | X12 <X13> | X12 | X12 <X13> | X12 <X13> | X13 | X11 | X11 | X11 |
| Puyang | X33 | X33 | X14 <X33> | X14 | X14 | X14 <X33> | X13 | X13 | X13 | X12 | X12 | X11 | X11 | X11 | X12 |
| Sanmenxia | X14 <X33> | X33 | X14 <X33> | X14 <X33> | X14 | X14 <X33> | X12 <X13> | X12 <X13> | X12 <X13> | X12 <X13> | X12 <X13> | X12 <X13> | X11 | X11 | X11 |
| Shangqiu | X14 | X14 <X33> | X14 <X33> | X33 | X14 <X33> | X14 <X33> | X12 <X13> | X12 <X13> | X12 | X12 <X13> | X12 <X13> | X13 | X11 | X11 | X11 |
| Xinxiang | X33 | X14 <X33> | X14 | X14 | X14 <X33> | X33 | X13 | X12 <X13> | X12 | X12 | X12 <X13> | X13 | X11 | X11 | X11 |
| Xinyang | X14 | X14 | X14 | X33 | X33 | X33 | X12 <X13> | X12 <X13> | X12 | X12 <X13> | X12 <X13> | X13 | X11 | X11 | X11 |
| Xuchang | X33 | X33 | X33 | X14 | X14 | X14 | X13 | X13 | X13 | X12 | X12 | X11 <X12> | X11 | X11 | X11 <X12> |
| Zhengzhou | X21 | X21 | X21 | X34 | X34 | X34 | X23 | X23 | X31 | X22 | X31 | X24 | X31 | X22 | X35 |
| Zhoukou | X14 <X33> | X14 <X33> | X33 | X14 <X33> | X14 <X33> | X14 | X12 | X12 | X12 | X13 | X13 | X13 | X11 | X11 | X11 |
| Zhumadian | X14 | X14 <X33> | X14 <X33> | X33 | X14 <X33> | X14 <X33> | X12 | X12 | X12 | X13 | X13 | X13 | X11 | X11 | X11 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xi, F.; Xu, Y.; Liang, S.; Chen, Y. Spatial–Temporal Differences in Land Use Benefits and Obstacles Under Human–Land Contradictions: A Case Study of Henan Province, China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 6693. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17156693
Xi F, Xu Y, Liang S, Chen Y. Spatial–Temporal Differences in Land Use Benefits and Obstacles Under Human–Land Contradictions: A Case Study of Henan Province, China. Sustainability. 2025; 17(15):6693. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17156693
Chicago/Turabian StyleXi, Feng, Yiwei Xu, Shuo Liang, and Yuanyuan Chen. 2025. "Spatial–Temporal Differences in Land Use Benefits and Obstacles Under Human–Land Contradictions: A Case Study of Henan Province, China" Sustainability 17, no. 15: 6693. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17156693
APA StyleXi, F., Xu, Y., Liang, S., & Chen, Y. (2025). Spatial–Temporal Differences in Land Use Benefits and Obstacles Under Human–Land Contradictions: A Case Study of Henan Province, China. Sustainability, 17(15), 6693. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17156693








