Factors Influencing Nighttime Tourists’ Satisfaction of Urban Lakes: A Case Study of the Daming Lake Scenic Area, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Night Tourism
2.2. Tourism Satisfaction
2.3. Nighttime Tourism in Urban Lake Scenic Areas
3. Methods
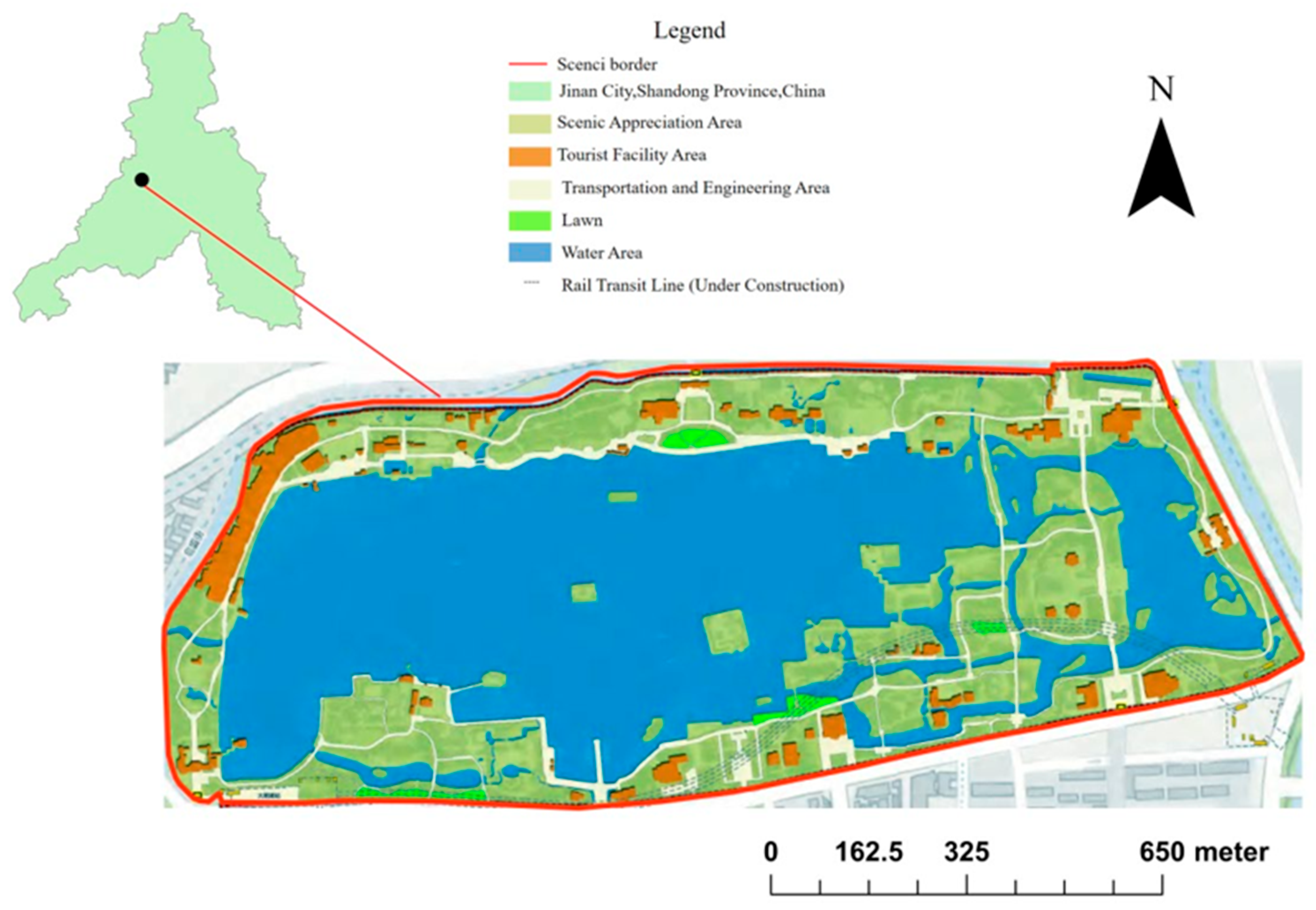
3.1. Case Selection
3.2. Research Method
3.3. Research Steps
3.3.1. Questionnaire Design and Validation
3.3.2. Questionnaire Collection
3.3.3. Survey Implementation and Data Collection
3.3.4. Sampling Representativeness Considerations
4. Results and Analysis
4.1. Demographics
4.2. Tourist Consumption Behavior Analysis
4.2.1. Tourist Preference Analysis
4.2.2. Transportation Mode Analysis
4.2.3. Overall Product Satisfaction Analysis
4.3. Multivariate Analysis of Tertiary Indicators
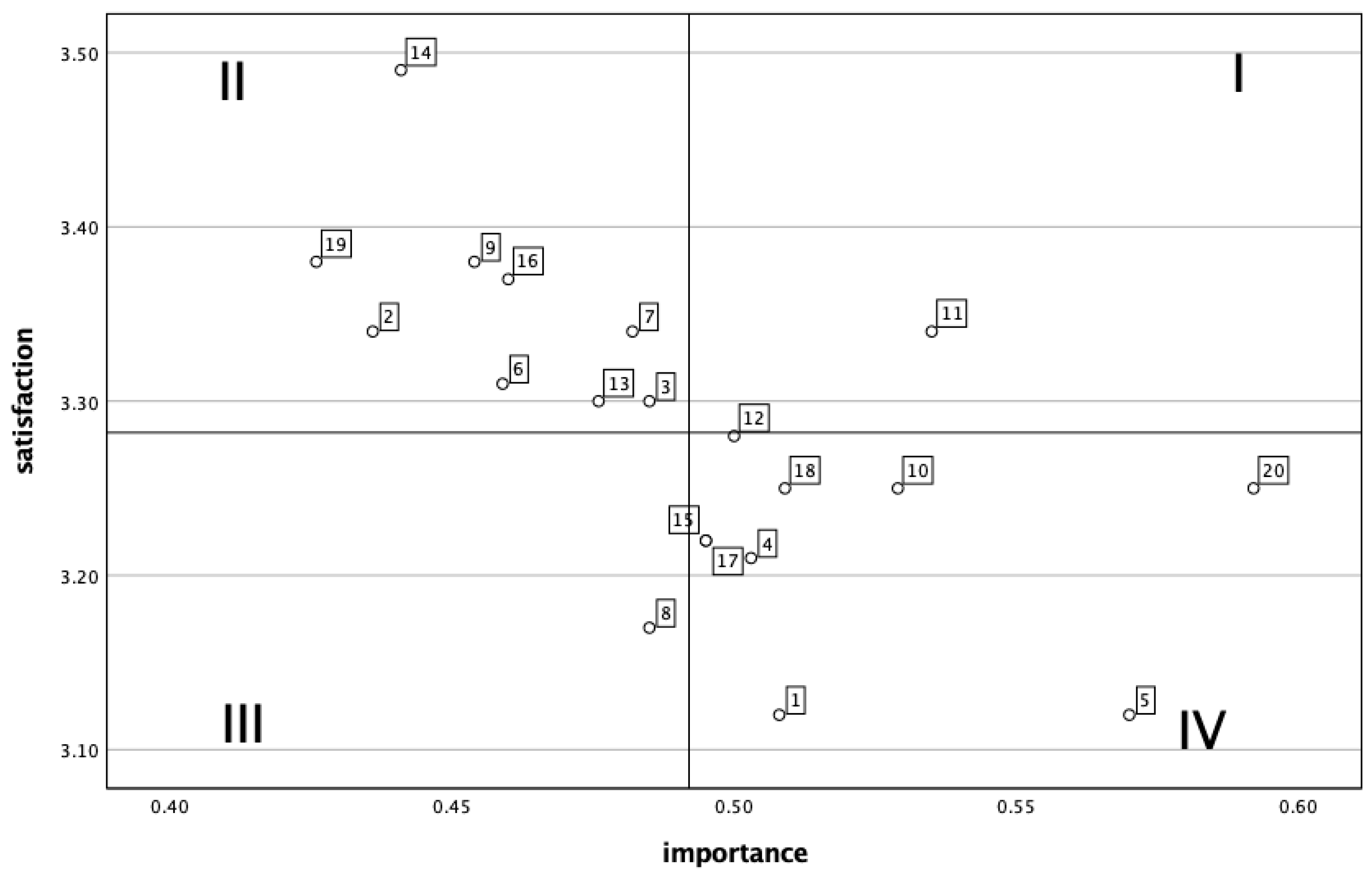
4.4. Revised IPA
4.4.1. Advantage Consolidation Zone (Quadrant I)
4.4.2. Resource Optimization Zone (Quadrant II)
4.4.3. Low-Priority Zone (Quadrant III)
4.4.4. Priority Improvement Zone (Quadrant IV)
5. Discussion
5.1. Key Findings
5.1.1. Premium Pricing of Nighttime Shopping and Dining Products Undermines Tourist Satisfaction in Urban Lake Scenic Areas
5.1.2. Transport Infrastructure Deficiencies Undermine Tourist Satisfaction in Nighttime Tourism
5.1.3. The Cultural Connotation of Tourism Products Significantly Influences Tourist Satisfaction in Urban Lake Scenic Areas’ Nighttime Tourism
5.1.4. Nighttime Tourscape and Entertainment Products Fail to Provide Adequate Security in the Urban Lake Scenic Area
5.1.5. Weakened Demand for Distinctive Dining Products in Nighttime Compared to Daytime in Urban Lake Scenic Areas
5.2. Theoretical and Methodological Comparisons with Existing Research
5.3. Limitations and Future Directions
6. Conclusions
6.1. High Overall Satisfaction with Distinct Demographic Appeal
6.2. Strategic Preservation of Core Satisfaction Factors in Urban Lake Nighttime Tourism
6.3. Bridging Satisfaction Gaps Through Functional and Experiential Innovations in Nighttime Tourism
6.4. The Effectiveness of Research Methods
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ruan, W.Q.; Jiang, G.X.; Li, Y.Q.; Zhang, S.N. Night tourscape: Structural dimensions and experiential effects. J. Hosp. Tour. Manag. 2023, 30, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosen, M.I.; Hasan, M.M.; Talha, M.; Akter, M.M.; Nasher, N.R. Exploring the cooling benefits of Urban Lakes: A multi-year analysis of Dhaka, Bangladesh. HydroResearch 2025, 8, 361–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Wei, Y.; Yuan, Q. Examining structural relationships among night tourism experience, lovemarks, brand satisfaction, and brand loyalty on “Cultural Heritage night” in South Korea. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Ministry of Culture and Tourism of the People’s Republic of China. Notice of the Ministry of Culture and Tourism on Announcing the List of the First Batch of National Night Culture and Tourism Consumption Clusters. Available online: https://zwgk.mct.gov.cn/zfxxgkml/cyfz/202107/t20210706_926242.html (accessed on 8 July 2025).
- Qiu, Y.Q.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X.Q.; Guo, L.B. Tourist satisfaction and review helpfulness: Examining the primary effects, mediating mechanisms, and moderating influences. Tour. Manag. 2026, 112, 105252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Jing, R.Z.; Zhu, X.H. Determinants of travel satisfaction for commercial airlines: A data mining approach. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024, 133, 108597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.X. The Development of Urban Night Tourism in China—A Case Study of Kaifeng. Commer. Res. 2008, 15, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y. Research on nighttime tourism products in Xiamen city. Rural Econ. Sci. 2020, 31, 170–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.H. Analysis of tourists’ perception and emotional responses to nighttime tourism in Chengdu based on Weibo big data. J. Sichuan Prov. Corresp. Inst. Adm. 2021, 23, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.J. Potential and conversion of the night tourism market. Entertain. Technol. 2019, 16, 6–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.X.; Li, Q.L. Research on the construction ideas of nighttime tourism scenarios from the perspective of experiential economy. West Forum Econ. Manag. 2021, 32, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovatt, A.; O’Connor, J. Cities and the night-time economy. Plan. Pract. Res. 1995, 10, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Kim, M.; Park, C. Temporal distribution as a solution for over-tourism in night tourism: The case of Suwon Hwaseong in South Korea. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, D. Celestial ecotourism: New horizons in nature-based tourism. J. Ecotourism 2010, 9, 84–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrea, C.; Crispin, C. Measuring and managing the environmental impact of festivals: The contribution of the Ecological Footprint. J. Sustain. Tour. 2017, 25, 148–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, J.; Hasenöhrl, U.; Krause, K.; Pottharst, M. Urban Lighting, Light Pollution and Society; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 1–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nofre, J. The touristification of nightlife: Some theoretical notes. Urban Geogr. 2021, 42, 1552–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngesan, M.R.; Karim, H.A.; Zubir, S.S.; Ahmad, P. Urban community perception on nighttime leisure activities in improving public park design. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2013, 105, 619–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.M.; Wang, H.; Liao, Z.W. Exploring the factors and spatial patterns of national night cultural tourism consumption agglomeration zones in China. Heliyon 2024, 10, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stabler, M.; Papatheodorou, A.; Sinclair, M.T. The Economics of Tourism, 2nd ed.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 4–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wüllenweber, S.; Burrell, A. The crime and the place: Robbery in the nighttime economy. J. Investig. Psychol. Offender Profiling 2024, 21, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldridge, A.; Smith, A. Tourism and the night: Towards a broader understanding of nocturnal city destinations. J. Policy Res. Tour. Leis. Events 2019, 11, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.B.; Lai, M.T. Research on the influencing factors of satisfaction in cultural and creative parks based on factor analysis and IPA analysis: Taking Guangzhou Hongzhu Factory as an example. Stat. Manag. 2017, 32, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; He, M.E.; Liu, C. Tourism competitiveness evaluation model of urban historical and cultural districts based on multi-source data and the AHP method: A case study in Suzhou ancient city. Sustainability 2023, 15, 16652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.L.; Zhang, L. A study of the influence of social reading platform characteristics and perceived value on users’ willingness to continue using it. New Century Libr. 2019, 40, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Q.W.; Chen, Z.Y.; Wei, Y.R. Analysis on the influencing factors of tourist satisfaction in composite rural tourist places: Taking Guilin Lujia Village as an example. J. Nat. Sci. Hunan Norm. Univ. 2022, 67, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.X.; Nie, J.; Jiang, H. Analysis of factors influencing tourist satisfaction in forest parks in Guangzhou City. J. Southwest For. Univ. 2020, 40, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Qin, C.Z.; Guo, L.D.; Yu, M.W. The effects of involvement, authenticity, and destination image on tourist satisfaction in the context of Chinese ancient village tourism. J. Hosp. Tour. Manag. 2014, 21, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Sánchez, M.D.; De-Pablos-Heredero, C.; Montes-Botella, J.L. Direct and moderating effects of COVID-19 on cultural tourist satisfaction. Eur. Res. Manag. Bus. Econ. 2024, 30, 100238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christou, P.; Pericleous, K.; Papatheodorou, A. Dazzled by the strobe lights: Tourist experience and complexity in the night-economy. J. Hosp. Tour. Manag. 2022, 52, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, A.; Cohen, D.H. Autonomous vehicles and the future of urban tourism. Ann. Tour. Res. 2019, 74, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Bartesaghi-Koc, C.; Tian, Y.; Shen, L.; Teng, M.; Liu, H.; Wu, C. Where and how to cool through blue infrastructure? Large lake groups to ameliorate urban overheating in a typical inland multi-lake megacity. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 98, 104869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Tang, J.; Na, J.; Ma, T. Nighttime as experiences: The influence of perceived value on urban waterfront night cruise loyalty. SAGE Open 2022, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H. Research on Water Tourism Development Based on RMP Analysis—A case study of Jintang, Chengdu. Master’s Dissertation, Sichuan Agricultural University, Chengdu, China, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.B.; Yao, Y.X. Research on the development of night tourism in Jiaozuo City. Mark. Wkly. 2021, 34, 42–44. [Google Scholar]
- Oliver, R.L. A cognitive model of the antecedents and consequences of satisfaction decisions. J. Mark. Res. 1980, 17, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Park, Y. An integrated approach to determining rural tourist satisfaction factors using the IPA and conjoint analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, W.J. Using a revised importance-performance analysis approach: The case of Taiwanese hot springs tourism. Tour. Manag. 2007, 28, 1274–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.Z.; Yang, F.Y. A Study on the Evaluation System of Tourist Satisfaction Degree in Tourist Areas. Tour. J. 2005, 20, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Liu, M.; Sun, Y.D.; Zhang, R.X.; Gou, H.X. Night Tourism Satisfaction in the Qinghefang Tourism and Leisure Block based on an Improved Kano Model. J. Resour. Ecol. 2024, 15, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradshaw, P. Our ‘Great Entail’: Constructing the Cultural Value of the Lake District. In Changing Perceptions of Nature. Heritage Matters. Boydell & Brewer; Convery, I., Davis, P., Eds.; Boydell & Brewer: Martlesham, UK, 2016; pp. 63–72. Available online: https://www.cambridge.org/core/books/abs/changing-perceptions-of-nature/our-great-entail-constructing-the-cultural-value-of-the-lake-district/F4259CF175F20FF1847877AA36828B9E (accessed on 22 April 2025).
- Zhang, R.; Taylor, K. Cultural landscape meanings. The case of West Lake, Hangzhou, China. Landsc. Res. 2019, 45, 164–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tribe, J.; Snaith, T. From SERVQUAL to HOLSAT: Holiday satisfaction in Varadero, Cuba. Tour. Manag. 1998, 19, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maital, S. The Experience Economy: Work Is Theatre & Every Business a Stage by B. Joseph Pine II and James H. Gilmore (Book Review). Sloan Manag. Rev. 1999, 40, 93. [Google Scholar]
- Vera, N.; Chang, S. The indirect experiences of young adult tourists with hypothetical cultural festivals/events via Twitter and an official homepage amid COVID-19: Focusing on destination image. J. Destin. Mark. Manag. 2022, 23, 100694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Typology | Main Nighttime Tourism Products |
|---|---|
| Nighttime shopping products | In addition to Daming Lake-themed cultural T-shirts, postcards, cultural and creative products, and crafts such as paper-cutting and clay sculptures, Jinan Longshan black pottery, hand-held pork, Zhoucun baked cakes, and lotus root noodles from Minghu Lake are also included. |
| Nighttime dining products | Furong Street Snack Street features a variety of food options, including Hong Kong Jia Wonton Noodles, DouDou Fried Yogurt, Afu Lucky Food, Furong Quan Roasted Chicken Feet, Yang’s Sesame Candy, and Pancake Rolled with Scallions. Kuanhouli Snack Street also offers Grandma’s Cuisine, Tri-State Roasted Pig’s Feet, Pin Fry, National Foot Stinky Bean Curd, Hand-Punched Shrimp Sliders, and Longji Shancheng Soup Dumplings. Additionally, the Ziyi Minghu Hotel, situated in the center of the Daming Lake Scenic Area, houses the “Night Banquet Minghu” restaurant, while Xiaobai Izakaya offers an atmosphere reminiscent of a late-night diner. |
| Nighttime transportation products | As of 1 June 2023, Jinan’s public transportation has been systematically enhanced, and the number of bus routes that are available after 22:00 is now 114. Cabs and online taxis in Jinan are also accessible at night through mobile software, providing convenience for citizens and tourists. Shared bike services are available near scenic spots that can be utilized at night, and bikes are rentable through mobile apps, thus facilitating short trips. |
| Nighttime tourscape and entertainment products | The Daming Lake Scenic Area is characterized by scenic tourism resources, including Wuyue Temple, Chaoran Building, and Thousand Buddha Reflection; culturally significant resources, such as Qu Shui Ting Street, Pearl Spring, and Jiefang Pavilion; notable attractions, including the Chaoran Building and the night tour around the lake; and well-known commercial resources, such as Kuanhouli and Shimao Plaza. |
| Nighttime lighting products | The night light show of the Chaoran Building, the night tour around Daming Lake, a special light show themed on the Chaoran Building and Daming Lake, and a night tour of cultural attractions are offered. |
| Primary Indicators | Secondary Indicators | Tertiary Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| Satisfaction evaluation of night tourism products | Nighttime shopping products | The affordable price of nighttime shopping products |
| The distinctive features of nighttime shopping products | ||
| The quality of nighttime shopping products | ||
| The rich variety of nighttime shopping products | ||
| Nighttime dining products | The affordable price of nighttime dining products | |
| The rich variety of nighttime dining products | ||
| The quality status of nighttime dining products | ||
| The distinctive features of nighttime dining products | ||
| Nighttime transportation products | The high safety of nighttime transportation | |
| The diverse methods of nighttime transportation | ||
| The convenience and accessibility of nighttime transportation | ||
| The affordable price of nighttime transportation | ||
| Nighttime tourscape and entertainment products | The affordable price of nighttime tourscape and entertainment products | |
| The rich variety of nighttime tourscape and entertainment products | ||
| The cultural connotations of nighttime tourscape and entertainment products | ||
| The high safety of nighttime tourscape and entertainment products | ||
| Nighttime lighting products | The rich variety of nighttime lighting products | |
| The cultural connotations of nighttime lighting products | ||
| The coordination with the surrounding environment of nighttime lighting products | ||
| The design of aesthetically pleasing of nighttime lighting products |
| Project | Alpha | KMO | Number | Number of Valid Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Satisfaction | 0.921 | 0.944 | 20 | 312 |
| Satisfaction | 0.920 | 0.938 | 20 | 212 |
| Effective Projects | Descriptive | Number | Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Man | 149 | 47.76% |
| Woman | 163 | 52.24% | |
| Age | Below 20 years old | 31 | 9.94% |
| 21–30 years old | 145 | 46.47% | |
| 31–45 years old | 62 | 19.87% | |
| 46–60 years old | 66 | 21.15% | |
| Over 61 years old | 8 | 2.56% | |
| Career | Flexible workers | 45 | 14.42% |
| Students | 132 | 42.31% | |
| Corporate employees | 19 | 6.09% | |
| Self-employed | 42 | 13.46% | |
| Civil servants/institutional employees | 66 | 21.15% | |
| Retirees | 8 | 2.56% | |
| Income (CNY/month) | Below 1000 | 23 | 7.37% |
| 1001–3000 | 38 | 12.18% | |
| 3001–6000 | 158 | 50.64% | |
| 6001–10,000 | 61 | 19.55% | |
| Over 10,001 | 32 | 10.26% |
| Project | Number | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Night tourscape | 162 | 51.92% |
| Food and beverage offerings | 85 | 27.24% |
| Shopping | 28 | 8.97% |
| Amusement rides | 37 | 11.86% |
| Project | Number | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Walking | 100 | 32.05% |
| Cycling | 41 | 13.14% |
| Self-driving | 62 | 19.87% |
| Taking a taxi | 38 | 12.18% |
| Taking a bus | 46 | 14.74% |
| Others | 25 | 8.01% |
| Age | N | F | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Below 20 years old | 31 | 4.03 ± 1.063 | 3.773 | 0.01 |
| 21–30 years old | 145 | 4.04 ± 0.964 | ||
| 31–45 years old | 62 | 4.02 ± 0.896 | ||
| 45–60 years old | 66 | 3.33 ± 1.351 | ||
| Over 61 years old | 8 | 3.88 ± 0.996 |
| Model | R | R2 | Adjusted R2 | Error in Standard Estimation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.851 a | 0.724 | 0.705 | 0.624 |
| ANOVA a | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Sum of Squares | Freedom | Mean Square | F | Significance | |
| 1 | return | 266.316 | 20 | 13.316 | 38.165 | 0.000 b |
| residual | 101.530 | 291 | 0.349 | |||
| total | 367.846 | 311 | ||||
| Coefficient a | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Non-Standardized Coefficient | Standardization Coefficient Beta | t | Significance | Collinearity Statistics | |||
| B | Standard Error | Tolerance | VIF | |||||
| 1 | (Constant) | 0.307 | 0.14 | 2.183 | 0.03 | |||
| The affordable price of nighttime shopping products | 0.013 | 0.032 | 0.016 | 0.398 | 0.691 | 0.586 | 1.707 | |
| The distinctive features of nighttime shopping products | 0.134 | 0.037 | 0.149 | 3.592 | 0 | 0.548 | 1.823 | |
| The quality of nighttime shopping products | 0.015 | 0.032 | 0.018 | 0.462 | 0.645 | 0.644 | 1.554 | |
| The rich variety of nighttime shopping products | 0.039 | 0.034 | 0.045 | 1.123 | 0.262 | 0.583 | 1.714 | |
| The affordable price of nighttime dining products | 0.065 | 0.031 | 0.087 | 2.123 | 0.035 | 0.567 | 1.763 | |
| The rich variety of nighttime dining products | 0.079 | 0.033 | 0.091 | 2.356 | 0.019 | 0.635 | 1.576 | |
| The quality status of nighttime dining products | 0.034 | 0.033 | 0.041 | 1.033 | 0.302 | 0.615 | 1.627 | |
| The distinctive features of nighttime dining products | 0.051 | 0.033 | 0.061 | 1.55 | 0.122 | 0.606 | 1.65 | |
| The affordable price of nighttime tourscape and entertainment products | 0.043 | 0.035 | 0.049 | 1.234 | 0.218 | 0.607 | 1.648 | |
| The cultural connotations of nighttime tourscape and entertainment products | 0.054 | 0.031 | 0.068 | 1.733 | 0.084 | 0.609 | 1.643 | |
| The rich variety of nighttime tourscapes and entertainment products | 0.105 | 0.031 | 0.138 | 3.379 | 0.001 | 0.565 | 1.77 | |
| The high safety of nighttime tourscape and entertainment products | 0.056 | 0.032 | 0.071 | 1.747 | 0.082 | 0.568 | 1.76 | |
| The rich variety of nighttime lighting products | 0.016 | 0.033 | 0.019 | 0.482 | 0.63 | 0.581 | 1.721 | |
| The coordination with the surrounding environment of nighttime lighting products | 0.051 | 0.035 | 0.058 | 1.448 | 0.149 | 0.583 | 1.716 | |
| The cultural connotations of nighttime lighting products | 0.031 | 0.033 | 0.038 | 0.935 | 0.351 | 0.56 | 1.787 | |
| The aesthetically pleasing design of nighttime lighting products | 0.094 | 0.034 | 0.109 | 2.73 | 0.007 | 0.599 | 1.67 | |
| The diverse methods of nighttime transportation | 0.085 | 0.035 | 0.101 | 2.463 | 0.014 | 0.568 | 1.762 | |
| The convenient and unobstructed nighttime transportation | 0.035 | 0.033 | 0.043 | 1.06 | 0.29 | 0.581 | 1.722 | |
| The high safety of nighttime transportation | 0.031 | 0.037 | 0.034 | 0.845 | 0.399 | 0.57 | 1.756 | |
| The affordable price of nighttime transportation | 0.057 | 0.028 | 0.08 | 2.04 | 0.042 | 0.616 | 1.623 | |
| Serial Number | Evaluation Indicator | Satisfaction | Derived Importance |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | The affordable price of nighttime shopping products | 3.12 | 0.508 |
| 2 | The distinctive features of nighttime shopping products | 3.34 | 0.436 |
| 3 | The quality of nighttime shopping products | 3.3 | 0.485 |
| 4 | The rich variety of nighttime shopping products | 3.21 | 0.503 |
| 5 | The affordable price of nighttime dining products | 3.12 | 0.57 |
| 6 | The rich variety of nighttime dining products | 3.31 | 0.459 |
| 7 | The quality status of nighttime dining products | 3.34 | 0.482 |
| 8 | The distinctive features of nighttime dining products | 3.17 | 0.485 |
| 9 | The affordable price of nighttime tourscape and entertainment products | 3.38 | 0.454 |
| 10 | The cultural connotations of nighttime tourscape and entertainment products | 3.25 | 0.529 |
| 11 | The rich variety of nighttime tourscapes and entertainment products | 3.34 | 0.535 |
| 12 | The high safety of nighttime tourscape and entertainment products | 3.28 | 0.5 |
| 13 | The rich variety of nighttime lighting products | 3.3 | 0.476 |
| 14 | The coordination with the surrounding environment of nighttime lighting products | 3.49 | 0.441 |
| 15 | The cultural connotations of nighttime lighting products | 3.22 | 0.495 |
| 16 | The aesthetically pleasing design of nighttime lighting products | 3.37 | 0.46 |
| 17 | The diverse methods of nighttime transportation | 3.22 | 0.495 |
| 18 | The convenience and accessibility of nighttime transportation | 3.25 | 0.509 |
| 19 | The high safety of nighttime transportation | 3.38 | 0.426 |
| 20 | The affordable price of nighttime transportation | 3.25 | 0.592 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, H.; Li, M. Factors Influencing Nighttime Tourists’ Satisfaction of Urban Lakes: A Case Study of the Daming Lake Scenic Area, China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 6596. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17146596
Zhu H, Li M. Factors Influencing Nighttime Tourists’ Satisfaction of Urban Lakes: A Case Study of the Daming Lake Scenic Area, China. Sustainability. 2025; 17(14):6596. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17146596
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Huying, and Mengru Li. 2025. "Factors Influencing Nighttime Tourists’ Satisfaction of Urban Lakes: A Case Study of the Daming Lake Scenic Area, China" Sustainability 17, no. 14: 6596. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17146596
APA StyleZhu, H., & Li, M. (2025). Factors Influencing Nighttime Tourists’ Satisfaction of Urban Lakes: A Case Study of the Daming Lake Scenic Area, China. Sustainability, 17(14), 6596. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17146596






