Integrated Assessment of Lake Degradation and Revitalization Pathways: A Case Study of Phewa Lake, Nepal
Abstract
1. Introduction
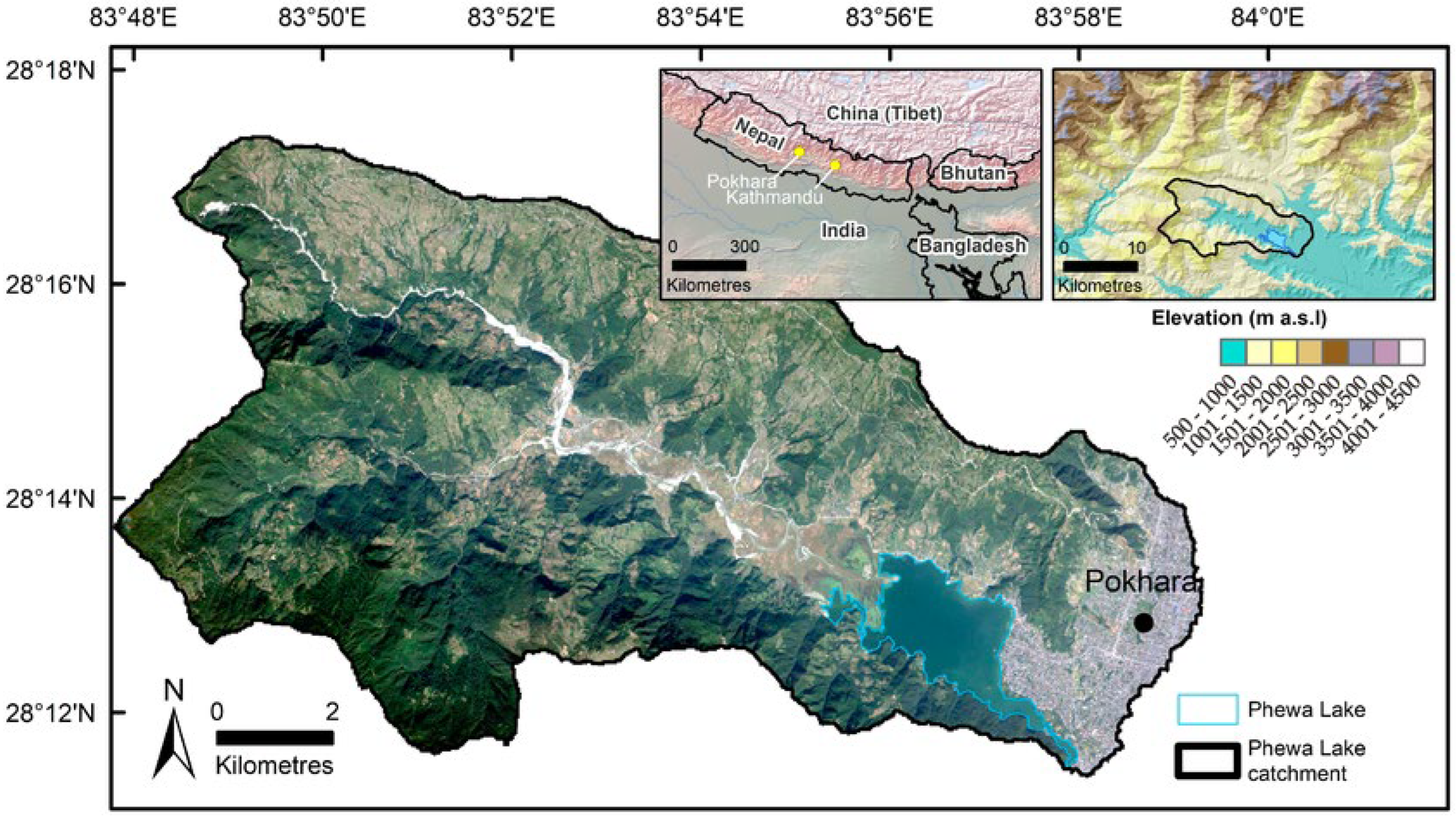
2. Study Area
3. Methodology
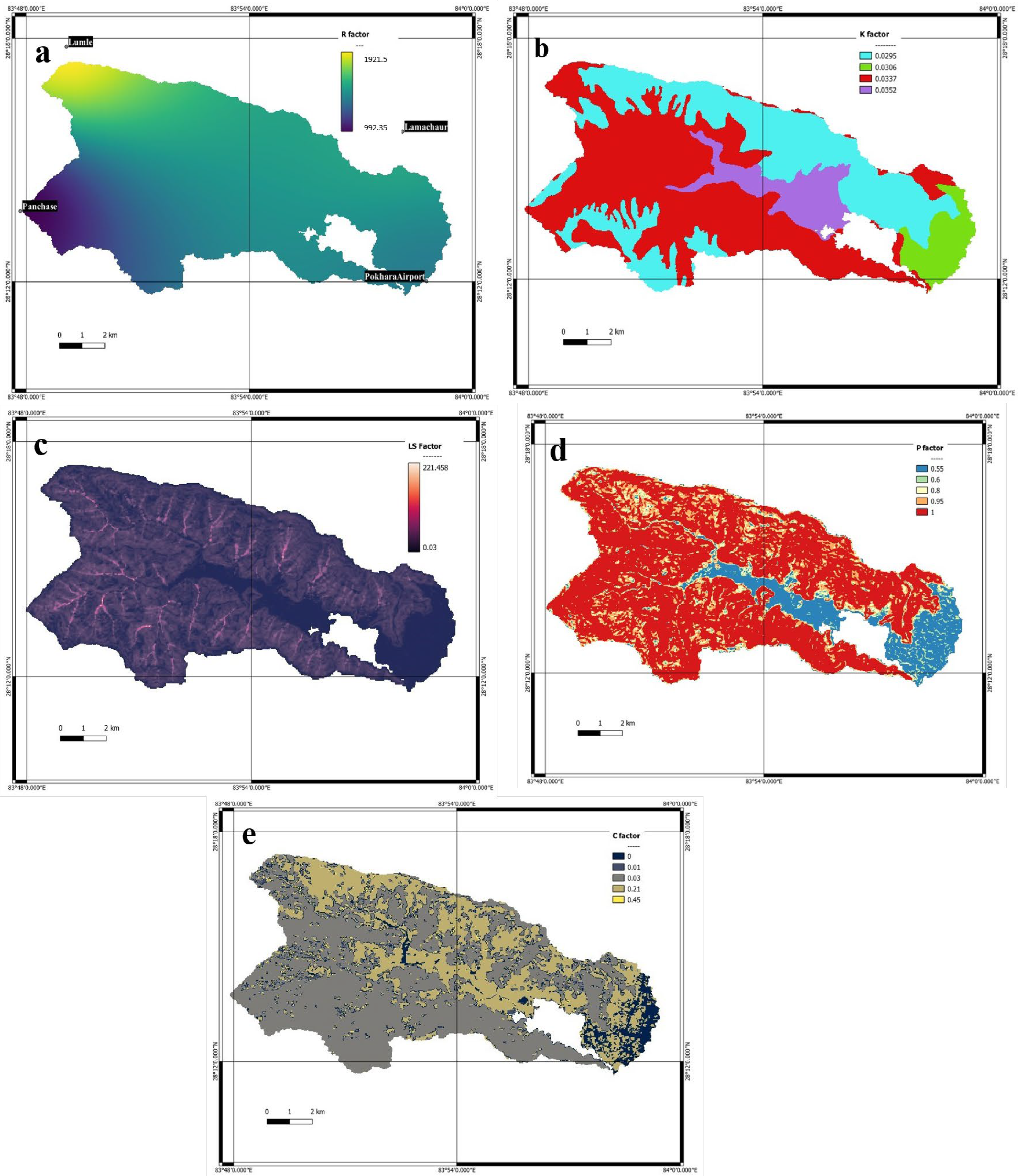
3.1. Soil Erosion Susceptibility Analysis
3.2. Hydrologic Analysis
3.2.1. Design Flood Analysis
3.2.2. Frequency Analysis
3.3. Hydraulic Analysis
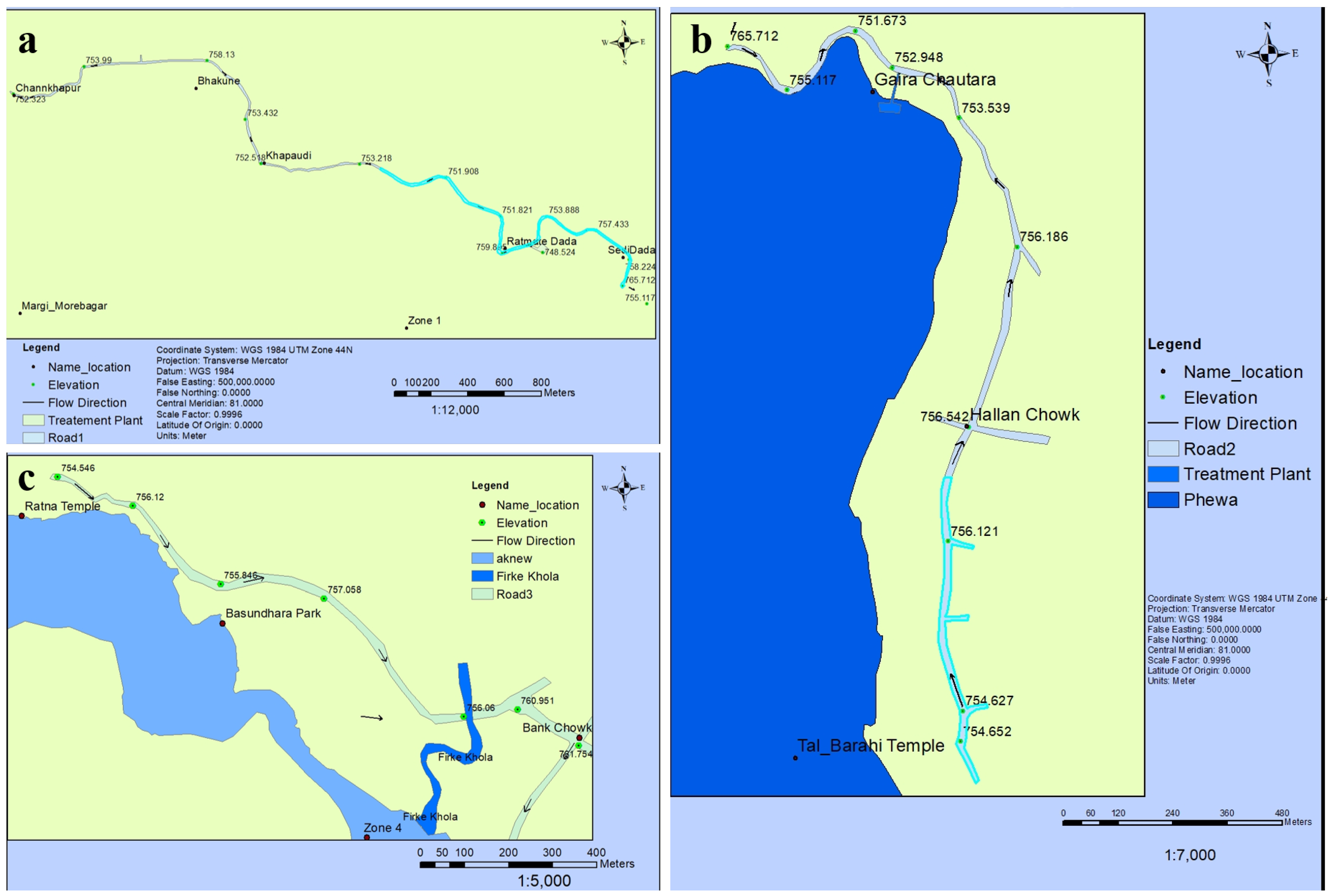
3.4. Encroachment and Pollution Assessment
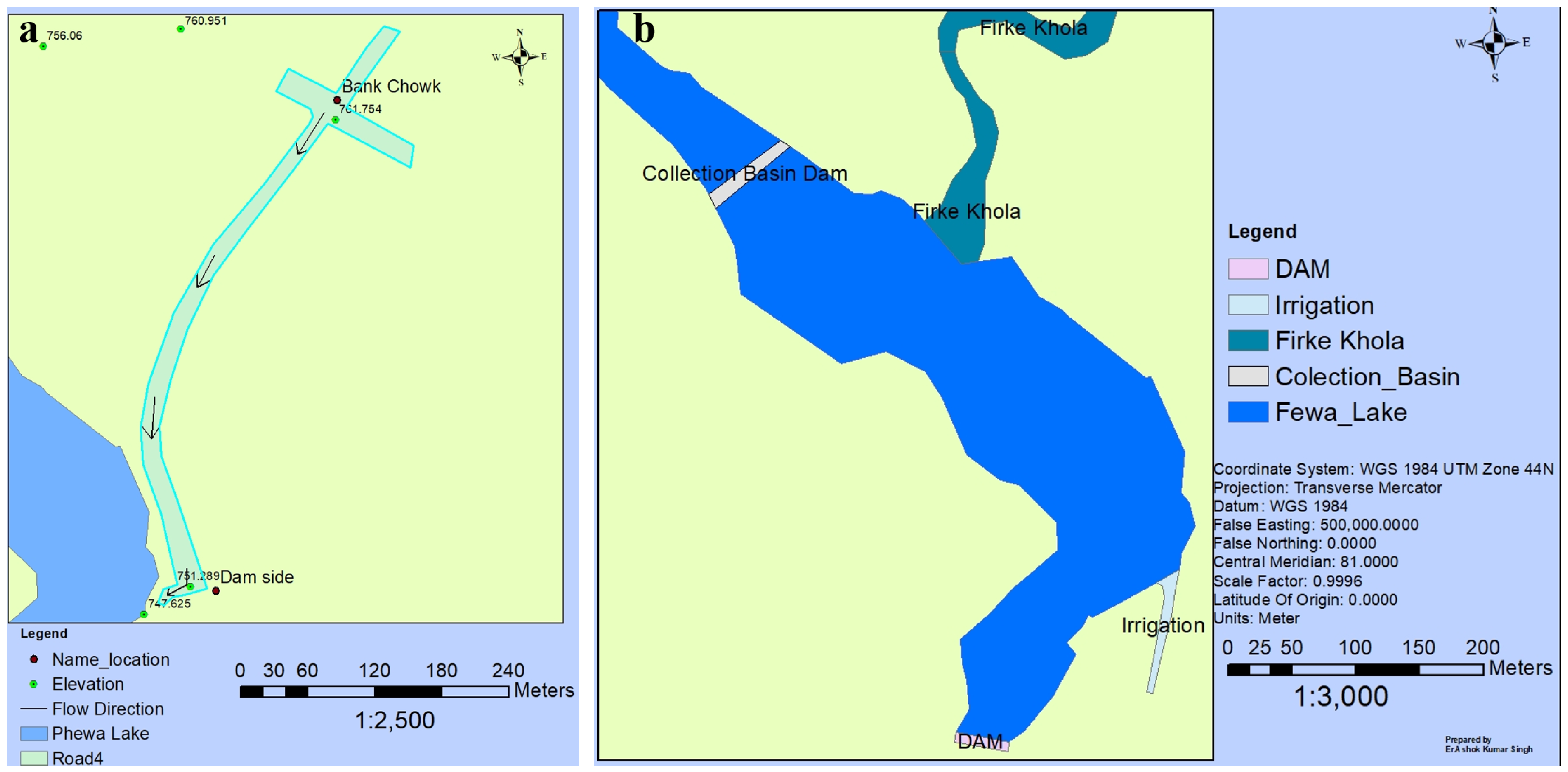
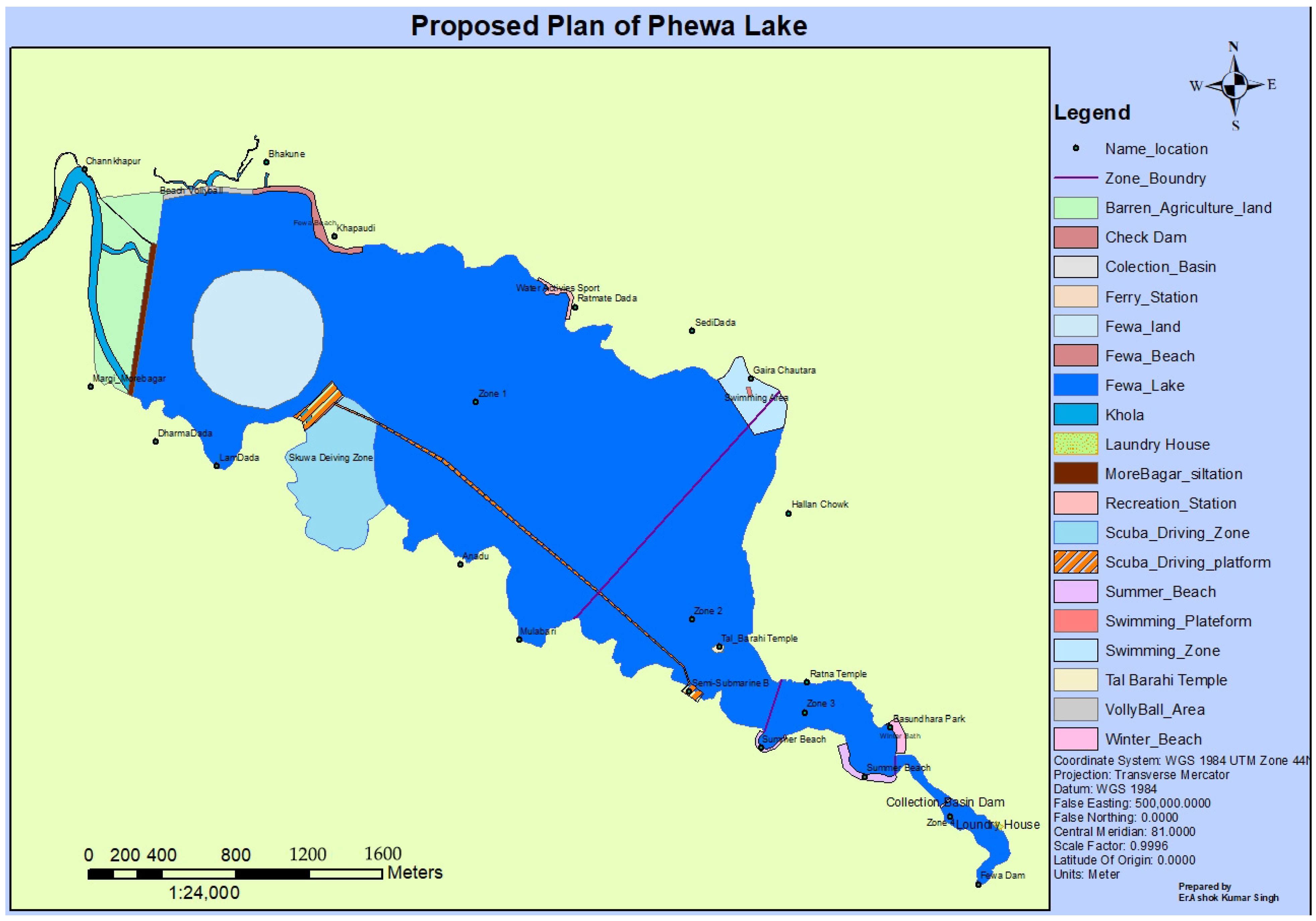
3.5. Development of the Lake Revitalization Plan
4. Result and Discussion
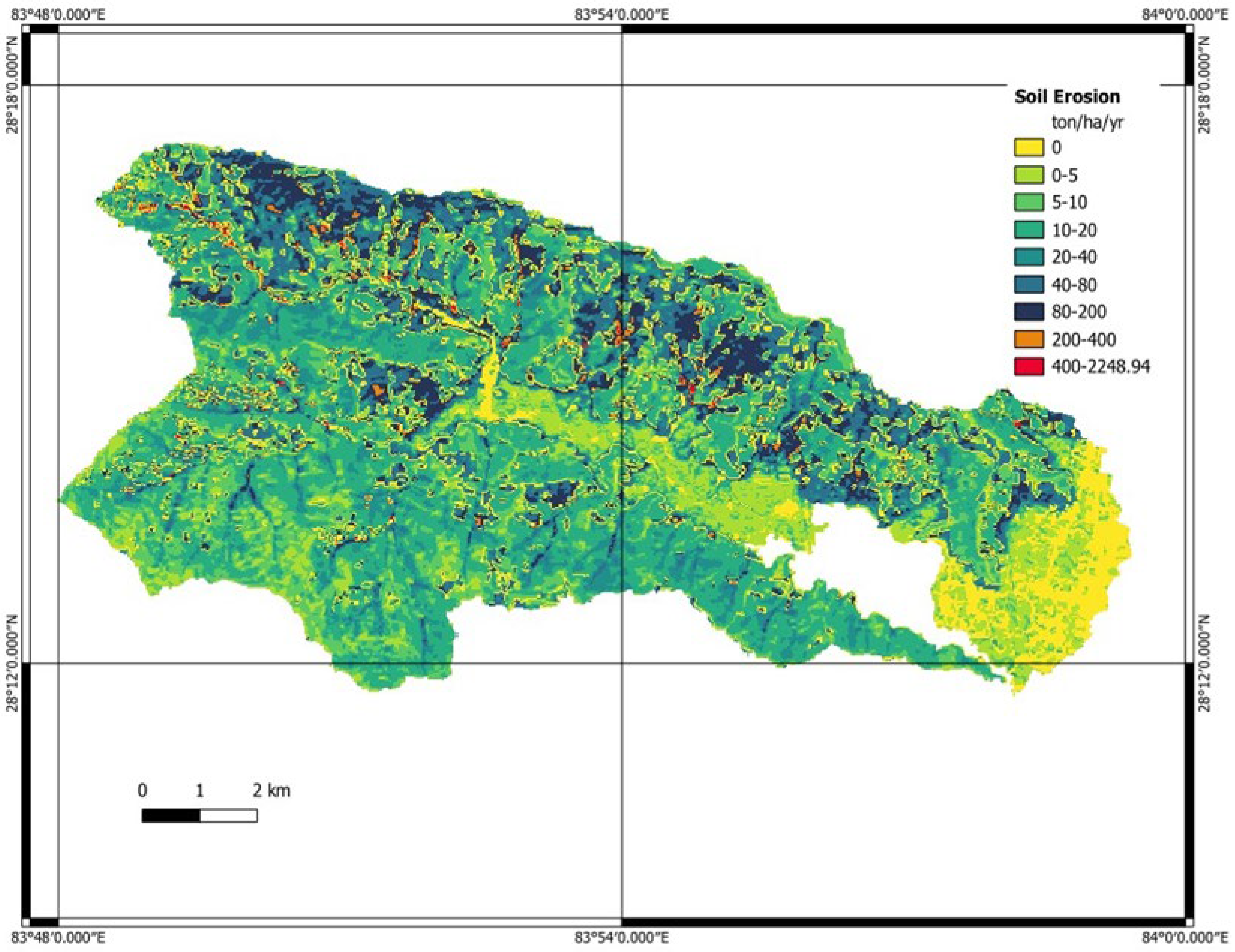
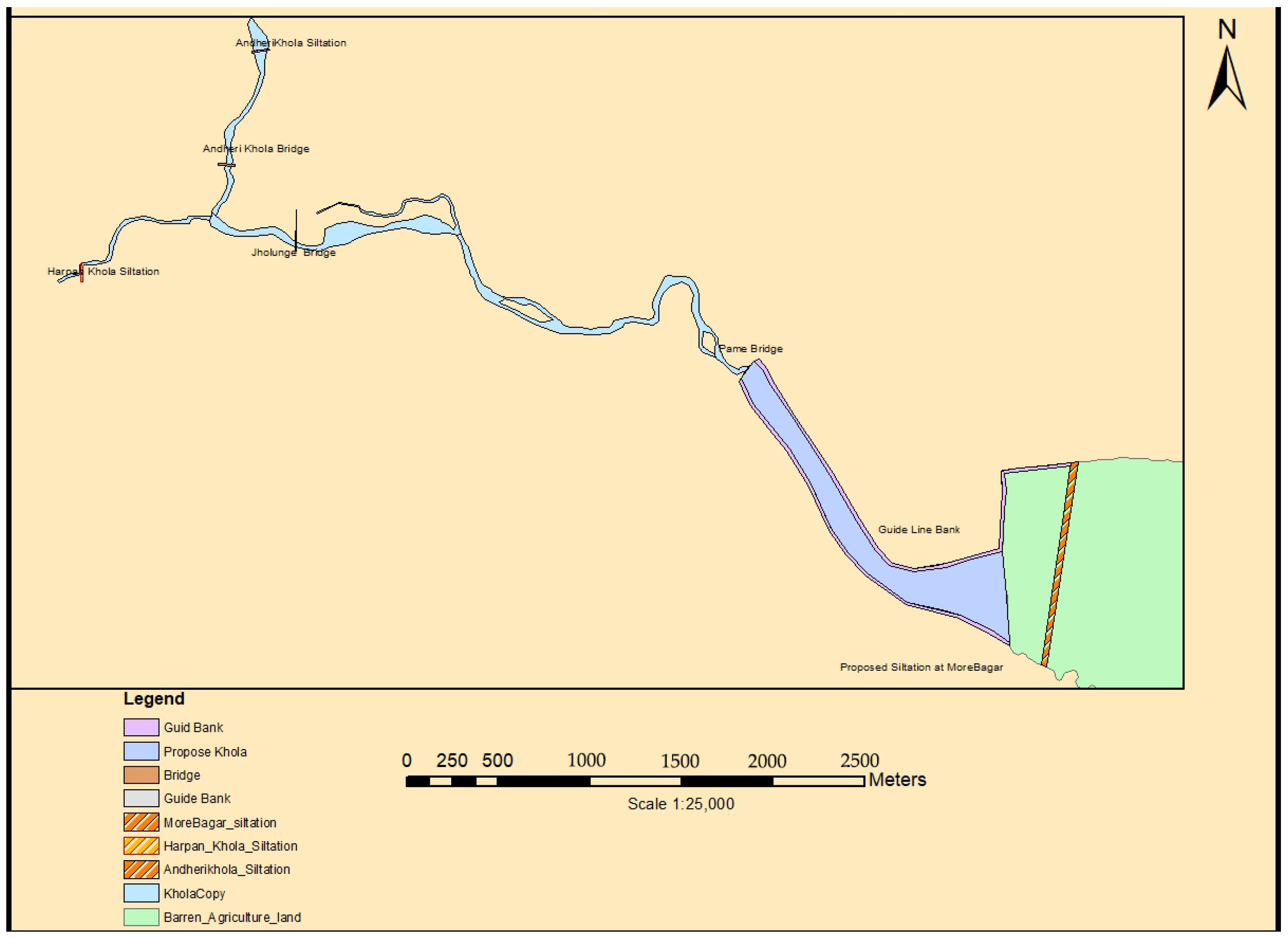
4.1. Sedimentation
4.2. Encroachment
4.3. Pollution
5. Way Forward
5.1. Sediment Management
5.2. Pollution Management
5.3. SWOT Analysis
5.4. Revitalization of Lake
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sterner, T.; Barbier, E.B.; Bateman, I.; Chávez, C.L.; Köhlin, G.; Mäler, K.-G.; Polasky, S.; Rockström, J.; Toman, M.; Vincent, J.R. Policy design for the Anthropocene. Nat. Sustain. 2020, 3, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhang, H.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, H. Changes in lake area in arid Xinjiang, China from the mid-20th century to 2010. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2017, 53, 160–171. [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, E.M.; Carpenter, S.R.; Caraco, N.F. Human impact on erodable phosphorus and eutrophication: A global perspective: Increasing accumulation of phosphorus in soil threatens rivers, lakes, and coastal oceans with eutrophication. BioScience 2001, 51, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundoli, S.; Manjunath, B.; Nagendra, H. Effects of urbanization on the ecology of lakes in India. Environ. Urban. ASIA 2015, 6, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Bilgiç, E.; Baba, A. Effect of urbanization on water resources: Challenges and prospects. In Groundwater in Arid and Semi-Arid Areas: Monitoring, Assessment, Modelling, and Management; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 81–108. [Google Scholar]
- McGrane, S.J. Impacts of urbanisation on hydrological and water quality dynamics, and urban water management: A review. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 20, 385–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNEP. World Water Quality Alliance: Global Water Quality Assessment—Summary for Policy Makers; United Nations Environment Programme: Nairobi, Kenya, 2021.
- K, P.A.; M, M.; Rajamanickam, S.; Sivarethinamohan, S.; Gaddam, M.K.R.; Velusamy, P.; R, G.; Ravindiran, G.; Gurugubelli, T.R.; Muniasamy, S.K. Impact of climate change and anthropogenic activities on aquatic ecosystem–A review. Environ. Res. 2023, 238, 117233. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, M.; Zhou, Y. Spatiotemporal changes in lake surface temperatures across China from 2001 to 2016. J. Hydrol. 2020, 582, 124451. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Sixth Assessment Report; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2022.
- Bhuju, U.R.; Khadka, M.; Neupane, P.K.; Adhikari, R. A map based inventory of lakes in Nepal. Nepal J. Sci. Technol. 2010, 11, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamsal, P.; Pant, K.P.; Atreya, K.; Kumar, L. Diversity, uses, and conservation of wetland plants in Nepal. J. Ecol. Nat. Environ. 2017, 9, 183–194. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, C.S.; Regmi, D.; Thapa, R.B.; Chettri, N.; Pandit, A.; Kafle, G.; Sharma, P.; Pradhan, B. Mapping ecosystem services trade-offs and synergies: Phewa Lake watershed, Nepal. Ecosyst. Serv. 2019, 36, 100896. [Google Scholar]
- Lamichhane, K.; Karki, S.; Sharma, K.; Khadka, B.; Acharya, B.; Biswakarma, K.; Adhikari, S.; KC, R.; Danegulu, A.; Bhattarai, S.; et al. Unraveling the Causes and Impacts of Increasing Flood Disasters in the Kathmandu Valley: Lessons from the Unprecedented September 2024 Floods. Nat. Hazards Res. 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, B.R.; Gautam, S.; Paudel, B. Landslide, land cover, and land use changes and its impacts in Nepal. In Impact of Climate Change, Land Use and Land Cover, and Socio-Economic Dynamics on Landslides; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 149–164. [Google Scholar]
- McAdoo, B.G.; Hockridge, J.; Vörösmarty, C.; Galloway, G.E. Rising risks to infrastructure from global change. EOS Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2018, 99, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez, L.G.; McCallum, A.; Kent, D.; Rathnayaka, C.; Fairweather, H. A review of sedimentation rates in freshwater reservoirs: Recent changes and causative factors. Aquat. Sci. 2023, 85, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, I.; KC, R.; Khadka, U.R. Water quality status in Bagmati river of Kathmandu valley, Nepal. In Ecological Significance of River Ecosystems; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 481–502. [Google Scholar]
- Sarker, M.H.; Mahmud, S.; Khan, M.; Dewan, A. Assessment of wetland dynamics in a rapidly urbanizing city using remote sensing and GIS techniques: A case study of Dhaka, Bangladesh. Environ. Chall. 2021, 5, 100276. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, C.L.; Acharya, P.; Khanal, B. Integrated flood modeling and hazard mapping in a transboundary river basin: A case study of the Babai River, Nepal. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2024, 17, e12894. [Google Scholar]
- Ghimire, P. Landscape level efforts to biodiversity conservation in Nepal: A review of current approach and lessons learned. Grassroots J. Nat. Resour. 2019, 2, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudyal, K.; Baral, S.; Rai, S. Environmental status of Phewa Lake and its sustainability challenges. J. Inst. Eng. 2017, 13, 215–222. [Google Scholar]
- Timalsina, D.; Aryal, S.; Adhikari, B.R. Integrated lake management in Pokhara Valley: A case study of Phewa Lake. J. Water Clim. Change 2025, 16, 112–128. [Google Scholar]
- Heyojoo, B.P.; Takhachhe, P. An assessment of lake area shrinkage through geospatial approach: Case study of Phewa Lake of Kaski district, Nepal. Int. J. Multidiscip. Curr. Res. 2014, 2, 725–728. [Google Scholar]
- Aryal, V. Phewa Lake Watershed Area: A Study on the Challenges to Human Encroachment. In Proceedings of the Taal Conference on the Conservation and Management of Lakes and Wetlands 2007, Jaipur, India, 29 October–2 November 2007; pp. 2292–2299. [Google Scholar]
- Benavidez, R.; Jackson, B.; Maxwell, D.; Norton, K. A review of the (Revised) Universal Soil Loss Equation ((R)USLE): With a view to increasing its global applicability and predictive accuracy. J. Hydrol. 2018, 559, 441–451. [Google Scholar]
- Luvai, J.; Mwangi, H.M.; Karanja, N.K.; Kamoni, P.T.; Kitaka, N. Predicting soil erosion in the Upper Tana Basin using RUSLE integrated with GIS and remote sensing. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2022, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; He, X.; Chen, Y.; Xu, C.; Wen, A. Sediment transport and land use change in a typical karst watershed: Evidence from Hongfeng Lake, Southwest China. J. Hydrol. 2019, 578, 124079. [Google Scholar]
- Zolotas, A.; Chatzinikolaou, Y.; Koussouris, T. Soil erosion and sedimentation processes in Lake Pamvotis basin (NW Greece) using SWAT model. Environ. Process. 2021, 8, 507–529. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, B.; Wen, A. Reservoir sedimentation and sediment yield estimation in the Three Gorges area: A GIS-based approach. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 1333–1344. [Google Scholar]
- UNDP. Development of Ecosystem-Based Sediment Control Techniques & Design of Siltation Dam to Protect 788 Phewa Lake: Hydrological Analysis; United Nations Development Programme: Kathmandu, Nepal, 2015; pp. 11–13.
- Pradhan, A.M.S.; Kim, Y.T. Landslide susceptibility mapping of Phewa catchment using multilayer 750 perceptron artificial neural network. Nepal J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. World Reference Base for Soil Resources 2014: International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and 656 Creating Legends for Soil Maps (Update 2015); Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2015.
- Renard, K.G. Predicting Soil Erosion by Water: A Guide to Conservation Planning with the Revised Universal Soil 756 Loss Equation (RUSLE); US Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Department of Hydrology and Meteorology (DHM). 2024; Hydrological and meteorological data. Government of Nepal. Available online: https://www.dhm.gov.np/ (accessed on 14 December 2024).
- FAO. Harmonized World Soil Database, Version 1.2; FAO: Rome, Italy; IIASA: Laxenburg, Austria, 2012.
- ICIMOD. Land Cover Data for Hindu Kush Himalaya Region. International Centre for Integrated Mountain 676 Development. 2022. Available online: https://rds.icimod.org (accessed on 16 February 2025).
- Koirala, P.; Thakuri, S.; Joshi, S.; Chauhan, R. Soil erosion assessment using RUSLE model and GIS in Rasuwa District, Nepal. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2019, 10, 803–825. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Thapa, R.B. Assessment of soil erosion risk in the Gandaki River Basin of Nepal using RUSLE and GIS. Nepal J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 8, 22–30. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- López-Vicente, M.; Guzmán, G. Soil erosion and conservation studies in Europe: A comprehensive review of modeling approaches. CATENA 2021, 199, 105102. [Google Scholar]
- Kaffas, K.; Pisinaras, V.; Al Sayah, M.J.; Santopietro, S.; Righetti, M. A USLE-based model with modified LS-factor combined with sediment delivery module for Alpine basins. CATENA 2021, 207, 105655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Liu, J. Development of a grid-based distributed model for simulating the hydrological cycle and water quality in the Sanjiang Plain Wetlands, China. Hydrol. Process. 2006, 20, 505–525. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P.; Poesen, J.; Ballabio, C.; Lugato, E.; Meusburger, K.; Montanarella, L.; Alewell, C. The new assessment of soil loss by water erosion in Europe. Environ. Sci. Policy 2015, 54, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budhathoki, S.; Poudel, A.; Shrestha, H.L. Soil erosion analysis using GIS and RS in Makawanpur District, Nepal. J. For. Nat. Resour. Manag. 2023, 3, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.R.; Berndt, H.D. Sediment yield prediction techniques for watersheds in the southeastern United States. Trans. ASAE 1972, 15, 1100–1104. [Google Scholar]
- Vanoni, V.A. Sedimentation Engineering: Manuals and Reports on Engineering Practice No. 54; American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE): New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- WECS. Flood Control and Management Manual; Government of Nepal: Kathmandu, Nepal, 2019.
- USDA (United States Department of Agriculture). Urban Hydrology for Small Watersheds; Technical Release 55 (TR-55); USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 1972.
- Pandey, A.; Gautam, D.; Ghimire, S. Application of hydrological modeling for runoff estimation in a mountainous watershed of Nepal. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2020, 32, 100760. [Google Scholar]
- Dulal, K.N.; Baral, S. Analysis of Rainfall and Runoff Patterns for Sustainable Water Resources Management in Gandaki Basin. J. Inst. Eng. 2015, 11, 178–186. [Google Scholar]
- USDA NRCS. Chapter 9: Hydrologic Soil-Cover Complexes (Curve Number Method). In National Engineering Handbook: Part 630 Hydrology; United States Department of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yarahmadi, P.; Talebbeydokhti, N.; Saadatpour, M.; Haghighi, A.T. Effects of channel roughness on flood propagation and sediment transport in urban areas using HEC-RAS. Water Supply 2023, 23, 905–922. [Google Scholar]
- JICA Nepal; SILT Consultants Pvt. Ltd. The Development Study on the Environmental Preservation of Phewa Lake; Final Report; Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA) and SILT: Kathmandu, Nepal, 2001.
- Impat, P. Hydrometeorology and Sediment Data for Phewa Watershed: 1979 Data; Water and Energy Commission Secretariat (WECS): Kathmandu, Nepal, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Carver, M.; Nakarmi, G. The Effect of Surface Conditions on Soil Erosion and Stream Suspended Sediments; Department of Hydrology and Meteorology (DHM): Kathmandu, Nepal, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Sittig, M. Resource Recovery and Recycling Handbook of Industrial Wastes; Noyes Data Corp.: Park Ridge, NJ, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, M.A. Sediment Deposition and Lake Infilling in Phewa Lake, Pokhara, Nepal. Environ. Geol. 1998, 36, 325–334. [Google Scholar]
- Santillan, J.R.; Makinano-Santillan, M. Vertical accuracy assessment of 1-arc second SRTM-derived elevation data over the Philippines. In Proceedings of the ISPRS Annals of Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences 2016, Prague, Czech Republic, 2–19 July 2016; Volume III-2, pp. 259–266. [Google Scholar]
- Laursen, E.M. An analysis of relief maps as a tool for sediment yield prediction. In Sediment Transport in Alluvial Channels; ASCE: New York, NY, USA, 1958. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, R.B. Measuring suspended sediment yields with acoustic methods. Water Resour. Res. 2002, 38, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Soulsby, R. Dynamics of Marine Sands: A Manual for Practical Applications; Thomas Telford Publishing: London, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Nepal–India Cooperation Mission. Phewa Lake Area Development Plan; Government of Nepal and India: Kathmandu, Nepal, 1962.
- Devkota, S.; Adhikari, B.R. Development of Ecosystem-Based Sediment Control Techniques and Design of Siltation Dam to Protect Phewa Lake; Government of Nepal and UNDP: Kathmandu, Nepal, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). Phewa Lake Conservation Action Plan; National Planning Commission and IUCN Nepal: Kathmandu, Nepal, 1997.
- District Development Committee Kaski. Pokhara Valley Urban Development and Land Use Report; Kaski DDC: Pokhara, Nepal, 2005.
- Pokhara Valley Urban Development Committee. Urban Development Plan of Pokhara Valley; PVUDC: Pokhara, Nepal, 2008.
- Lamichhane, R. Area Mapping of Phewa Lake Using Remote Sensing and GIS. Master’s Thesis, Tribhuvan University, Pokhara, Nepal, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Land Reform. Boundary and Land Registration Report for Phewa Lake; Government of Nepal: Kathmandu, Nepal, 2015.
- Pokhara Municipal Corporation. Environmental Status Report of Phewa Lake; PMC: Pokhara, Nepal, 2021.
- Poudel, S. Analysis of Spatiotemporal Changes in Phewa Lake Using GIS and Remote Sensing. Master’s Thesis, Institute of Engineering, Tribhuvan University, Pokhara, Nepal, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Andreasen, M.H.; Agergaard, J.; Kofie, R.Y.; Møller-Jensen, L.; Oteng-Ababio, M. Urban encroachment in ecologically sensitive areas: Drivers, impediments and consequences. Build. Cities 2022, 3, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanal, K.P.; Regmi, S.K. Enhancing ecosystem services through sediment retention in Phewa Lake of Western Nepal. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Climate Change Innovation and Resilience for Sustainable Livelihood, Kathmandu, Nepal, 12–14 January 2015; p. 76. [Google Scholar]
- Malla-Pradhan, N.; Regmi, R.K.; Pradhan, S.; Subedi, D. Seasonal variation of microplastics in the surface water of Phewa Lake, Nepal. Environ. Chall. 2022, 9, 100611. [Google Scholar]
- Gautam, R.; Shrestha, S.M. Hydrogeochemical evaluation and characterization of water quality in the Phewa Lake, Pokhara, Nepal. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 60568–60586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karki, B.K.; Lamichhane, K.; Joshi, L.; KC, R.; Sah, M.K.; Pathak, M.; Karki, K.R. Risk assessment of heavy metals in the major surface water system of Nepal with potential remediation technologies. Environ. Chall. 2024, 14, 100865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R. Environmental Audit of Lakeside Sewage Management. Sustain. Cities J. 2024, 9, 35–49. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, R.; Naik, P. Impact of invasive aquatic weeds on lake biodiversity and tourism: A case of Phewa Lake. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2024, 32, 227–240. [Google Scholar]
- Majumdar, R.; Rahman, M.M.; Ahmad, N.; Naidu, R. Seasonal dynamics of sediment and hydrochemistry in Himalayan freshwater lakes. Water Res. 2020, 170, 115364. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, P.; Meena, N.; Singh, V.P. Sediment and flood management in Fatehsagar Lake catchment using check dam interventions. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 229. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M.; Shakir, A.S. Sustainable sediment management options for reservoirs: A case study of Chashma Reservoir in Pakistan. Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 8, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qazi, A.N. Effectiveness of catchment afforestation and check dams in sediment yield reduction in Himalayan terrain. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2020, 75, 140–150. [Google Scholar]
- Camargo, P.B.; Basílio, J.O.; Santos, T.S. To what extent can a sediment yield model be trusted? A case study from the Passaúna Catchment, Brazil. Water 2021, 13, 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Canqui, H.; Lal, R. Soil erosion under forests. In Principles of Soil Conservation and Management; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 321–344. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, V.R.; Char, S. Pollution control and water quality management in urban lakes: A case study of Hussainsagar Lake, Hyderabad. Water Resour. Manag. 2006, 20, 577–594. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Qin, B.; Gao, G.; Zhu, G.; Luo, L.; Zhang, Y. Long-term changes of nutrients and chlorophyll-a in Taihu Lake, China: Effects of climatic and anthropogenic factors. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 24, 136–146. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Qian, H.; Wang, W. Effect of ecological water diversion on water quality in Dianchi Lake, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 30215–30224. [Google Scholar]
- Welch, E.B.; Jacoby, J.M.; Perkins, M.A. Water quality and algae response to reduced phosphorus in Moses Lake, Washington. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2024, 40, 45–60. [Google Scholar]
- Mavrommati, G.; Borsuk, M.E.; Howarth, R.B. A stakeholder-based Bayesian approach to strategic lake management: The case of Lake Champlain. Glob. Environ. Change 2014, 24, 48–61. [Google Scholar]
- Nair, J.R.; Bhatt, D.; Gurung, T.R.; Sharma, S. SWOT analysis for participatory lake governance in Nepal: The case of Rupa Lake. Environ. Dev. 2021, 38, 100628. [Google Scholar]
- Samal, N.R.; Dash, S.K. Integrated management of Chilika Lake using SWOT and DPSIR approaches. Lakes Reserv. Res. Manag. 2025, 30, 201–217. [Google Scholar]
- Acharya, S.; Sophal, C.; Lek, S.; Seng, L. Stakeholder-inclusive conservation planning in Tonle Sap Lake, Cambodia: A SWOT-based analysis. Water Int. 2023, 48, 688–707. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, H.S. A framework for sustainability assessment of urban water systems using SWOT and decision support tools. Urban Water J. 2008, 5, 147–159. [Google Scholar]
- Shevtsova, N.; Parkhomchuk, N. Revitalization and recreational development of urban lakes: Case studies from Russia and Japan. J. Urban Environ. Eng. 2022, 16, 67–79. [Google Scholar]
- Reddi, V.K.; Char, S. Urban lake restoration in India: A case study of Dal Lake. Indian J. Environ. Prot. 2006, 26, 810–817. [Google Scholar]
- Alemayehu, T.; Legesse, D.; Ayenew, T. Hydrogeochemical and isotopic composition of Lake Tana and its inflowing rivers, Ethiopia. Hydrol. Process. 2010, 24, 3525–3536. [Google Scholar]
- Njiru, J.M.; Abuodha, J.O.Z.; Sitoki, L.; Ongore, C.; Aura, C.M. Sustainable management options for Lake Victoria: The role of community participation. Lakes Reserv. Res. Manag. 2018, 23, 110–119. [Google Scholar]


| Return Period (yr) | Formula | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | A3000 = basin area (sq. km) below 3000 m elevation calculated as 84.3599 sq. km. | |
| 100 |
| Method | SDR (%) | Suspended Sediment Yield for Harpan Khola at Morebagar (tons) |
|---|---|---|
| William and Berndt [45] | 24.24 | 66,074.18 |
| Vanoni [46] | 27.17 | 74,142.65 |
| USDA Curve [47] | 18 | 49,064.99 |
| S. No. | Year | Area of Phewa Lake | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1962 | 10.35 sq. km | [62] |
| 2 | 1976–1977 | 4.43 sq. km | [63] |
| 3 | 1982–1983 | 5.80 sq. km | [64] |
| 4 | 1995 | 4.49 sq. km | [64] |
| 5 | 2005 | 4.25 sq. km | [65] |
| 6 | 2008 | 5.06 sq. km | [66] |
| 7 | 2012 | 6.50 sq. km | [67] |
| 8 | 2015 | 5.07 sq. km | [68] |
| 9 | 2021 | 5.08 sq. km | [69] |
| 10 | 2021 | 5.726 sq. km | [70] |
| Weir Height (m) | Trap Efficiency (Mass %) | Trap Efficiency (Volume %) | Increase in Efficiency (Mass %) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2.00 | 73.40 | 72.80 | – |
| 2.25 | 76.90 | 76.40 | 3.50 |
| 2.50 | 80.30 | 79.90 | 3.40 |
| 2.75 | 83.40 | 83.00 | 3.10 |
| 3.00 | 84.60 | 84.20 | 1.20 |
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Strengths (Internal Positive Factors) |
|
| Weaknesses (Internal Negative Factors) |
|
| Opportunities (External Positive Factors) |
|
| Threats (External Negative Factors) |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Singh, A.L.; Pahari, B.R.; Shakya, N.M. Integrated Assessment of Lake Degradation and Revitalization Pathways: A Case Study of Phewa Lake, Nepal. Sustainability 2025, 17, 6572. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17146572
Singh AL, Pahari BR, Shakya NM. Integrated Assessment of Lake Degradation and Revitalization Pathways: A Case Study of Phewa Lake, Nepal. Sustainability. 2025; 17(14):6572. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17146572
Chicago/Turabian StyleSingh, Avimanyu Lal, Bharat Raj Pahari, and Narendra Man Shakya. 2025. "Integrated Assessment of Lake Degradation and Revitalization Pathways: A Case Study of Phewa Lake, Nepal" Sustainability 17, no. 14: 6572. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17146572
APA StyleSingh, A. L., Pahari, B. R., & Shakya, N. M. (2025). Integrated Assessment of Lake Degradation and Revitalization Pathways: A Case Study of Phewa Lake, Nepal. Sustainability, 17(14), 6572. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17146572






