Influence of Biosurfactants on the Efficiency of Petroleum Hydrocarbons Biodegradation in Soil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
Experiment Description
2.3. Data Analysis and Statistical Information
3. Results
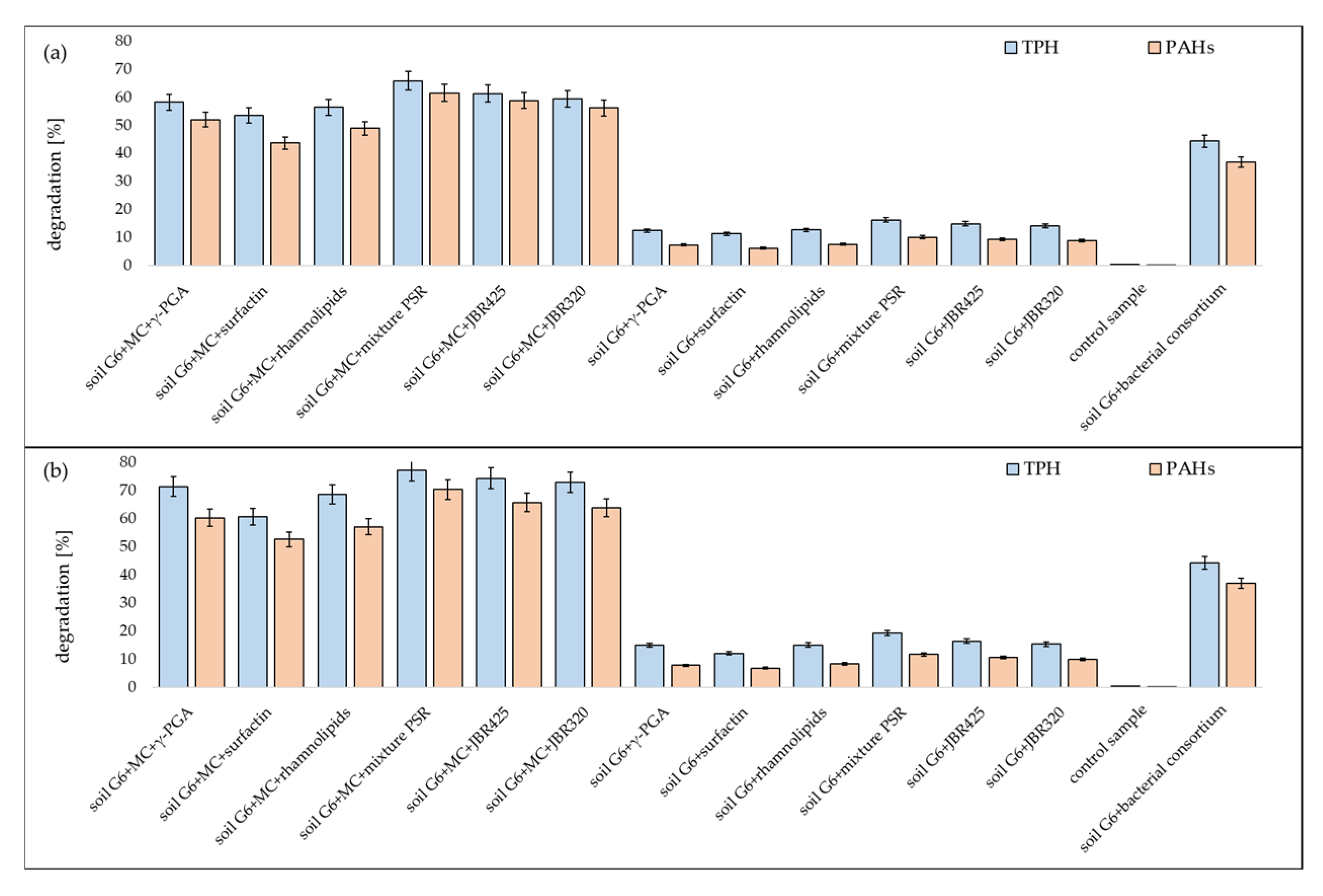
3.1. Respirometric Tests
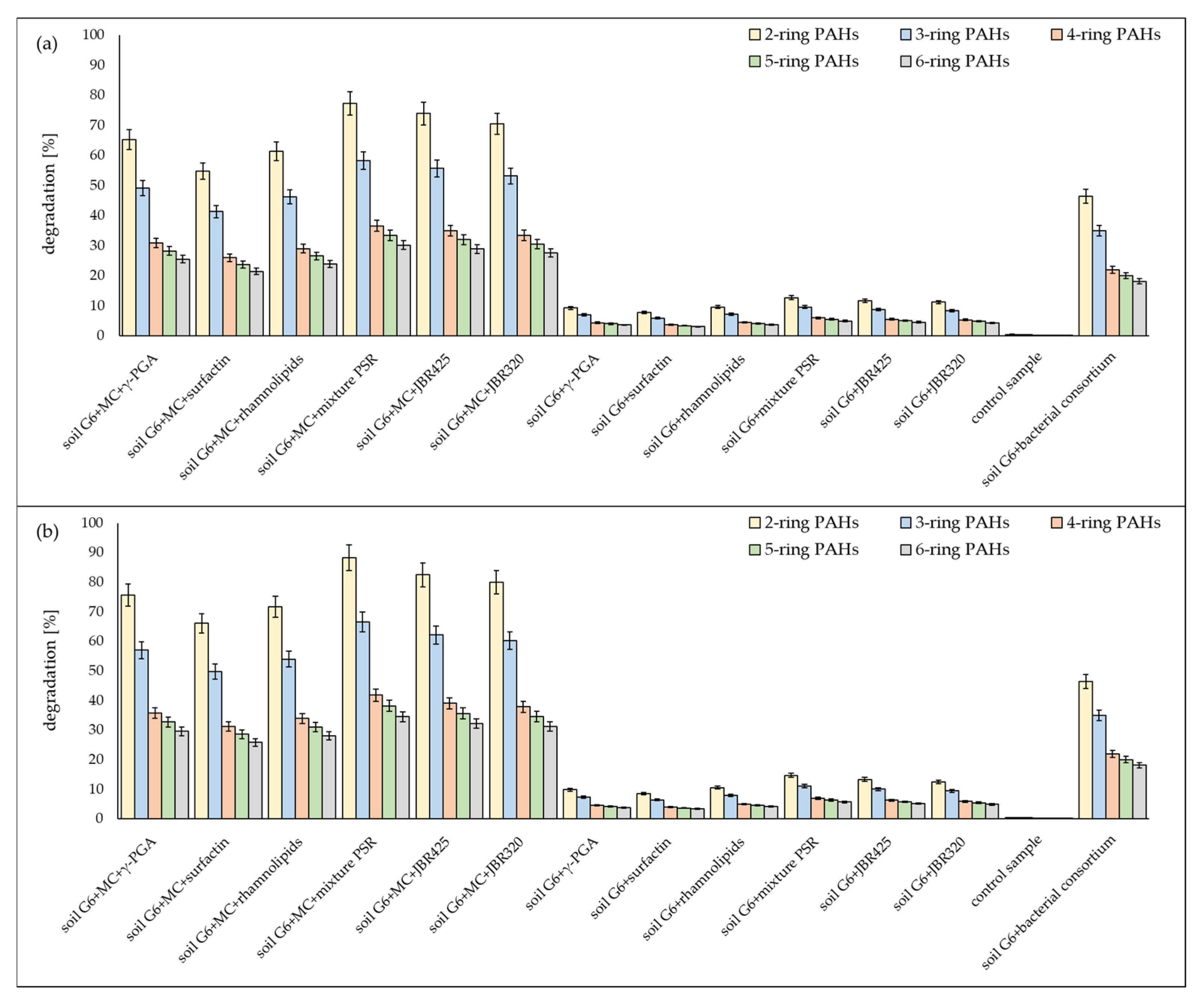
3.2. Chromatographic Analysis
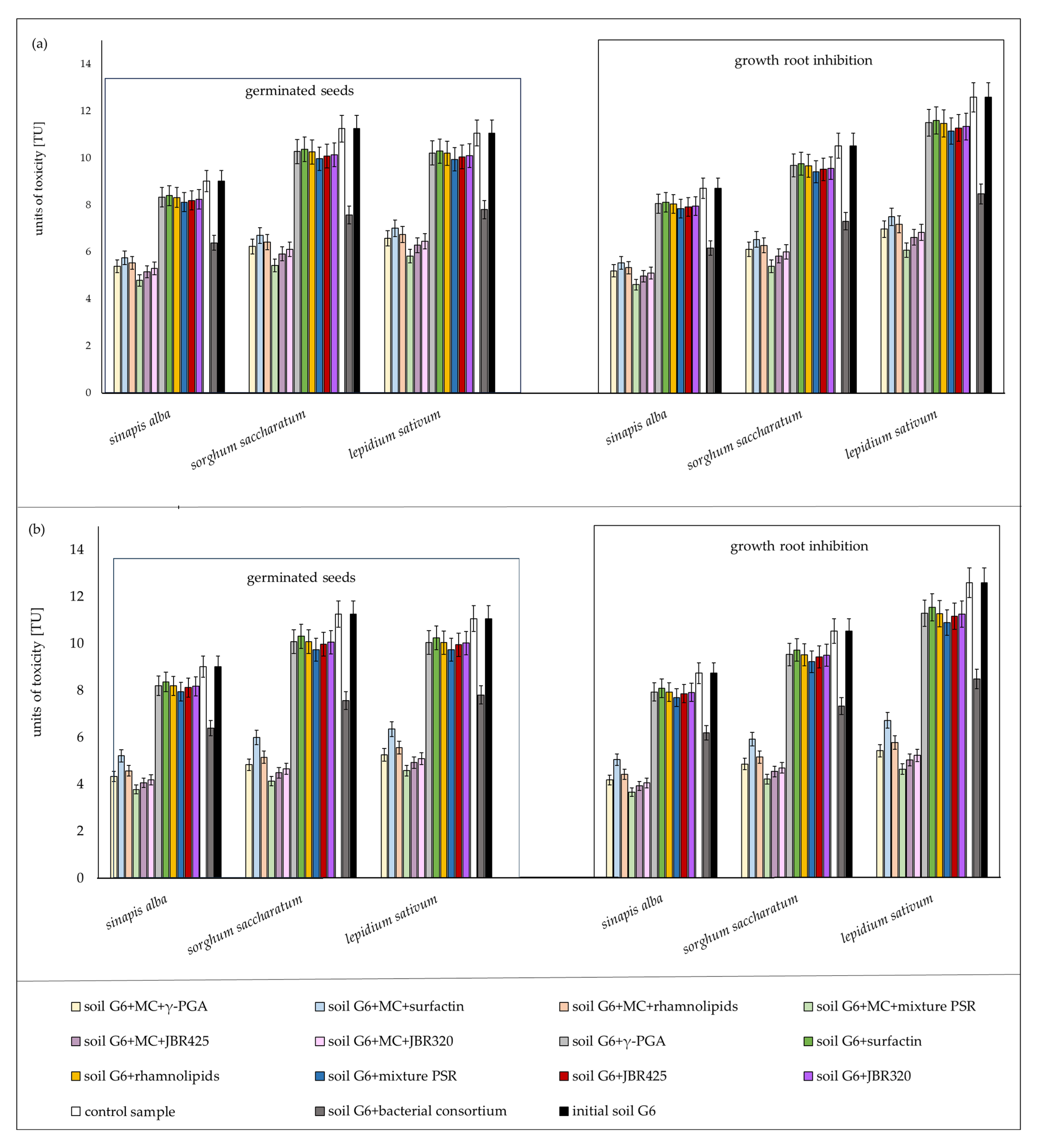
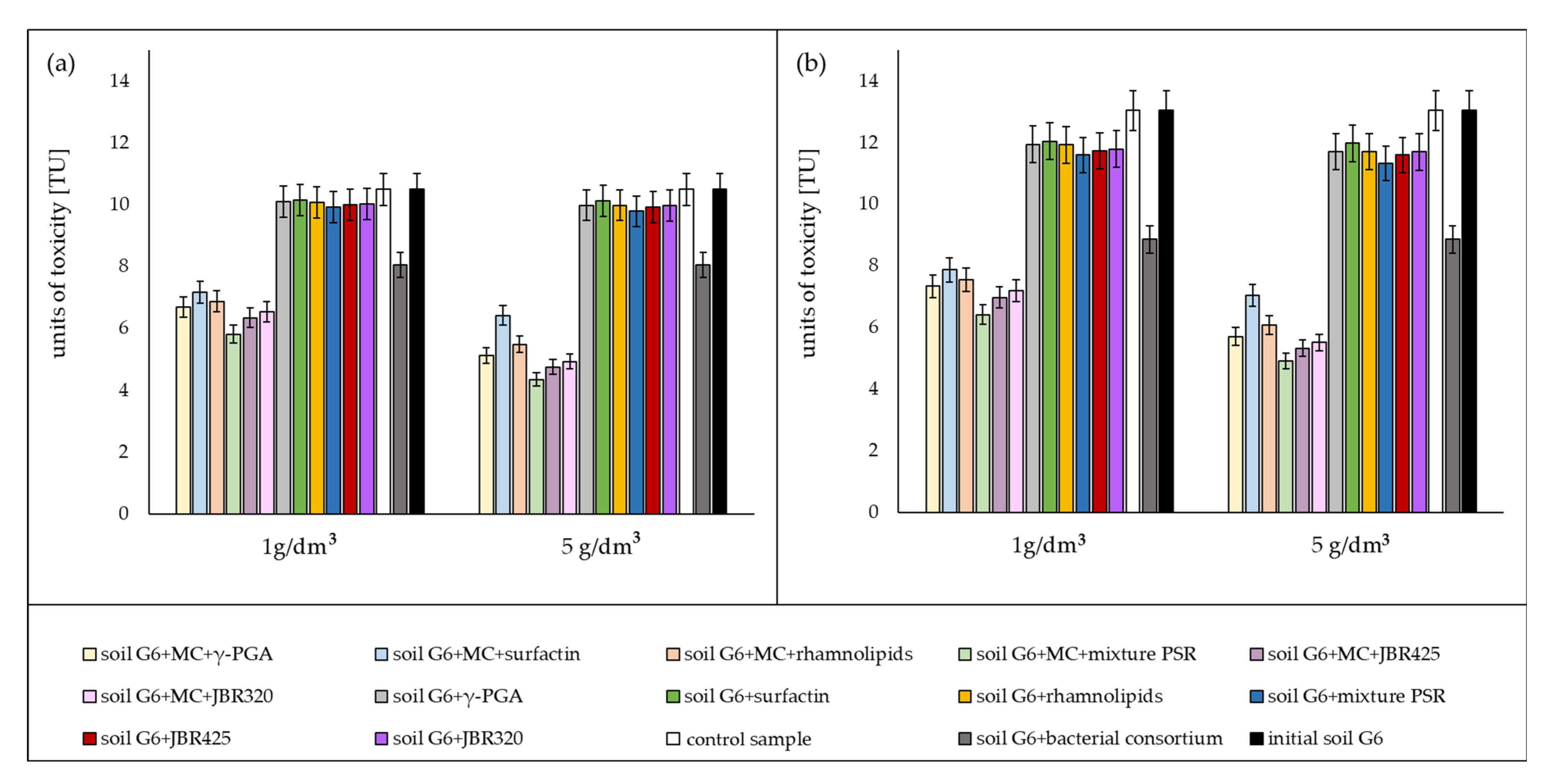
3.3. Ecotoxicological Assessment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Song, X.; Wu, X.; Song, X.; Shi, C.; Zhang, Z. Sorption and Desorption of Petroleum Hydrocarbons on Biodegradable and Nondegradable Microplastics. Chemosphere 2021, 273, 128553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambaye, T.G.; Chebbi, A.; Formicola, F.; Prasad, S.; Gomez, F.H.; Franzetti, A.; Vaccari, M. Remediation of Soil Polluted with Petroleum Hydrocarbons and Its Reuse for Agriculture: Recent Progress, Challenges, and Perspectives. Chemosphere 2022, 293, 133572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mekonnen, B.A.; Aragaw, T.A.; Genet, M.B. Bioremediation of Petroleum Hydrocarbon Contaminated Soil: A Review on Principles, Degradation Mechanisms, and Advancements. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 1354422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.; Shah, G.; Singh, H.; Bhatt, U.; Singhal, K.; Soni, V. Advancements in Natural Remediation Management Techniques for Oil Spills: Challenges, Innovations, and Future Directions. Environ. Pollut. Manag. 2024, 1, 128–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boopathy, R. Factors Limiting Bioremediation Technologies. Bioresour. Technol. 2000, 74, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claro, E.M.T.; Cruz, J.M.; Montagnolli, R.N.; Lopes, P.R.M.; Júnior, J.R.M.; Bidoia, E.D. Microbial Degradation of Petroleum Hydrocarbons: Technology and Mechanism. In Microbial Action on Hydrocarbons; Kumar, V., Kumar, M., Prasad, R., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 125–141. ISBN 9789811318399. [Google Scholar]
- Speight, J.G. Organic Chemistry. In Environmental Organic Chemistry for Engineers; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 43–86. ISBN 9780128044926. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Shafy, H.I.; Mansour, M.S.M. A Review on Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons: Source, Environmental Impact, Effect on Human Health and Remediation. Egypt. J. Pet. 2016, 25, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakde, P.; Sharma, J. Microbial Bioremediation of Petroleum Contaminated Soil: Structural Complexity, Degradation Dynamics and Advanced Remediation Techniques. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2024, 18, 2244–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshlaf, E.; Ball, A.S.; Koshlaf, E.; Ball, A.S. Soil Bioremediation Approaches for Petroleum Hydrocarbon Polluted Environments. AIMS Microbiol. 2017, 3, 25–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidonish, J.E.; Zygourakis, K.; Masiello, C.A.; Sabadell, G.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Thermal Treatment of Hydrocarbon-Impacted Soils: A Review of Technology Innovation for Sustainable Remediation. Engineering 2016, 2, 426–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.; Deleruematos, C.; Fiuza, A. Use of Solvent Extraction to Remediate Soils Contaminated with Hydrocarbons. J. Hazard. Mater. 2005, 124, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roslee, N.F.; Kamil, N.A.F.M.; Kadir, A.A.; Jalil, A.R.; Hamzah, N.; Noor, N.M.; Sandu, A.V. New Ray on Remediation of High Rings Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons: Remediation of Raw Petroleum Sludge Using Solidification and Stabilization Method. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2022, 67, 1201–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, Z.-H.; Pu, S.-Y.; Qian, W.; Liang, S.; Kong, L.-J.; Xia, D.-H.; Lei, Z.-X.; Du, J.-J.; Liu, H.; Yang, J.-W. Photocatalytic Removal of Phenanthrene and Algae by a Novel Ca-Ag3PO4 Composite under Visible Light: Reactivity and Coexisting Effect. Chemosphere 2019, 221, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arroyo, S.; Rosano-Ortega, G.; Martínez-Gallegos, S.; Pérez-Armendariz, B.; Vega-Lebrún, C.A. Reduction of Hydrocarbons in Contaminated Soil through Paired Sorption and Advanced Oxidation Processes. Soil Secur. 2021, 4, 100013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.W.N. Debunking Myths about Sustainable Remediation. Remediat. J. 2019, 29, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuppan, N.; Padman, M.; Mahadeva, M.; Srinivasan, S.; Devarajan, R. A Comprehensive Review of Sustainable Bioremediation Techniques: Eco Friendly Solutions for Waste and Pollution Management. Waste Manag. Bull. 2024, 2, 154–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshafei, A.M.; Mansour, R. Microbial Bioremediation of Soils Contaminated with Petroleum Hydrocarbons. Discov. Soil 2024, 1, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parus, A.; Ciesielski, T.; Woźniak-Karczewska, M.; Ślachciński, M.; Owsianiak, M.; Ławniczak, Ł.; Loibner, A.P.; Heipieper, H.J.; Chrzanowski, Ł. Basic Principles for Biosurfactant-Assisted (Bio)Remediation of Soils Contaminated by Heavy Metals Petroleum Hydrocarbons—ACritical Evaluation of the Performance of Rhamnolipids. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 443, 130171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eras-Muñoz, E.; Farré, A.; Sánchez, A.; Font, X.; Gea, T. Microbial Biosurfactants: A Review of Recent Environmental Applications. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 12365–12391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henkel, M.; Müller, M.M.; Kügler, J.H.; Lovaglio, R.B.; Contiero, J.; Syldatk, C.; Hausmann, R. Rhamnolipids as Biosurfactants from Renewable Resources: Concepts for next-Generation Rhamnolipid Production. Process Biochem. 2012, 47, 1207–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudiña, E.J.; Teixeira, J.A. Bacillus Licheniformis: The Unexplored Alternative for the Anaerobic Production of Lipopeptide Biosurfactants? Biotechnol. Adv. 2022, 60, 108013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, R.R.; Santos, J.C.V.; Meira, H.M.; Almeida, S.M.; Sarubbo, L.A.; Luna, J.M. Microbial Biosurfactant: Candida Bombicola as a Potential Remediator of Environments Contaminated by Heavy Metals. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clements, T.; Ndlovu, T.; Khan, S.; Khan, W. Biosurfactants Produced by Serratia Species: Classification, Biosynthesis, Production and Application. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 589–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pele, M.A.; Ribeaux, D.R.; Vieira, E.R.; Souza, A.F.; Luna, M.A.C.; Rodríguez, D.M.; Andrade, R.F.S.; Alviano, D.S.; Alviano, C.S.; Barreto-Bergter, E.; et al. Conversion of Renewable Substrates for Biosurfactant Production by Rhizopus arrhizus UCP 1607 and Enhancing the Removal of Diesel Oil from Marine Soil. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2019, 38, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badmus, S.O.; Amusa, H.K.; Oyehan, T.A.; Saleh, T.A. Environmental Risks and Toxicity of Surfactants: Overview of Analysis, Assessment, and Remediation Techniques. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 62085–62104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjerk, T.R.; Severino, P.; Jain, S.; Marques, C.; Silva, A.M.; Pashirova, T.; Souto, E.B. Biosurfactants: Properties and Applications in Drug Delivery, Biotechnology and Ecotoxicology. Bioengineering 2021, 8, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dini, S.; Bekhit, A.E.-D.A.; Roohinejad, S.; Vale, J.M.; Agyei, D. The Physicochemical and Functional Properties of Biosurfactants: A Review. Molecules 2024, 29, 2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.; Kharawala, K. Biosurfactants Their Biodegradability: A Review Examination. Int. J. Eng. Adv. Technol. 2022, 11, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero Vega, G.; Gallo Stampino, P. Bio-Based Surfactants and Biosurfactants: An Overview and Main Characteristics. Molecules 2025, 30, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banat, I.M.; Franzetti, A.; Gandolfi, I.; Bestetti, G.; Martinotti, M.G.; Fracchia, L.; Smyth, T.J.; Marchant, R. Microbial Biosurfactants Production, Applications and Future Potential. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 87, 427–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kugaji, M.; Ray, S.K.; Parvatikar, P.; Raghu, A.V. Biosurfactants: A Review of Different Strategies for Economical Production, Their Applications and Recent Advancements. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2025, 337, 103389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GreyViews Global Biosurfactants Market Growth 2021–2028. Available online: https://greyviews.com/reports/global-biosurfactants-market/25 (accessed on 2 June 2025).
- Mnif, I.; Ellouz-Chaabouni, S.; Ghribi, D. Glycolipid Biosurfactants, Main Classes, Functional Properties and Related Potential Applications in Environmental Biotechnology. J. Polym. Environ. 2018, 26, 2192–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi-Ashtiani, H.-R.; Baldisserotto, A.; Cesa, E.; Manfredini, S.; Sedghi Zadeh, H.; Ghafori Gorab, M.; Khanahmadi, M.; Zakizadeh, S.; Buso, P.; Vertuani, S. Microbial Biosurfactants as Key Multifunctional Ingredients for Sustainable Cosmetics. Cosmetics 2020, 7, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phulpoto, I.A.; Yu, Z.; Hu, B.; Wang, Y.; Ndayisenga, F.; Li, J.; Liang, H.; Qazi, M.A. Production and Characterization of Surfactin-like Biosurfactant Produced by Novel Strain Bacillus Nealsonii S2MT and It’s Potential for Oil Contaminated Soil Remediation. Microb. Cell Factories 2020, 19, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, E.; Ron, E.Z. High- and Low-Molecular-Mass Microbial Surfactants. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1999, 52, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lourenço, M.; Duarte, N.; Ribeiro, I.A.C. Exploring Biosurfactants as Antimicrobial Approaches. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simões, C.R.; Da Silva, M.W.P.; De Souza, R.F.M.; Hacha, R.R.; Merma, A.G.; Torem, M.L.; Silvas, F.P.C. Biosurfactants: An Overview of Their Properties, Production, and Application in Mineral Flotation. Resources 2024, 13, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sah, D.; Rai, J.P.N.; Ghosh, A.; Chakraborty, M. A Review on Biosurfactant Producing Bacteria for Remediation of Petroleum Contaminated Soils. 3 Biotech 2022, 12, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordoloi, N.K.; Konwar, B.K. Bacterial Biosurfactant in Enhancing Solubility and Metabolism of Petroleum Hydrocarbons. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 170, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, E.C.; Vessoni-Penna, T.C.; De Souza Oliveira, R.P. Biosurfactant-Enhanced Hydrocarbon Bioremediation: An Overview. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2014, 89, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuyukina, M.S.; Ivshina, I.B.; Makarov, S.O.; Litvinenko, L.V.; Cunningham, C.J.; Philp, J.C. Effect of Biosurfactants on Crude Oil Desorption and Mobilization in a Soil System. Environ. Int. 2005, 31, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacwa-Płociniczak, M.; Płaza, G.A.; Piotrowska-Seget, Z.; Cameotra, S.S. Environmental Applications of Biosurfactants: Recent Advances. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 633–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markam, S.S.; Raj, A.; Kumar, A.; Khan, M.L. Microbial Biosurfactants: Green Alternatives and Sustainable Solution for Augmenting Pesticide Remediation and Management of Organic Waste. Curr. Res. Microb. Sci. 2024, 7, 100266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ron, E.Z.; Rosenberg, E. Biosurfactants and Oil Bioremediation. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2002, 13, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaczorek, E.; Pacholak, A.; Zdarta, A.; Smułek, W. The Impact of Biosurfactants on Microbial Cell Properties Leading to Hydrocarbon Bioavailability Increase. Colloids Interfaces 2018, 2, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustamante, M.; Durán, N.; Diez, M.C. Biosurfactants Are Useful Tools for the Bioremediation of Contaminated Soil: A Review. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2012, 12, 667–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlapudi, A.P.; Venkateswarulu, T.C.; Tammineedi, J.; Kanumuri, L.; Ravuru, B.K.; Dirisala, V.R.; Kodali, V.P. Role of Biosurfactants in Bioremediation of Oil Pollution-a Review. Petroleum 2018, 4, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Dong, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, S.; Fan, H.; Wu, S. Comparison of the Efficiency and Microbial Mechanisms of Chemical- and Bio-Surfactants in Remediation of Petroleum Hydrocarbon. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 314, 120198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mnif, I.; Sahnoun, R.; Ellouz-Chaabouni, S.; Ghribi, D. Application of Bacterial Biosurfactants for Enhanced Removal and Biodegradation of Diesel Oil in Soil Using a Newly Isolated Consortium. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2017, 109, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtowicz, K.; Steliga, T.; Kapusta, P.; Brzeszcz, J. Oil-Contaminated Soil Remediation with Biodegradation by Autochthonous Microorganisms and Phytoremediation by Maize (Zea mays). Molecules 2023, 28, 6104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojtowicz, K.; Steliga, T.; Kapusta, P. Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Bioaugmentation-Assisted Phytoremediation of Soils Contaminated with Petroleum Hydrocarbons Using Echinacea Purpurea. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 13077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtowicz, K. Opracowanie Metodyki Oznaczania WWA w Próbkach Gleb z Wykorzystaniem Chromatografii Cieczowej HPLC. Nafta-Gaz 2022, 78, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logeshwaran, P.; Megharaj, M.; Chadalavada, S.; Bowman, M.; Naidu, R. Petroleum Hydrocarbons (PH) in Groundwater Aquifers: An Overview of Environmental Fate, Toxicity, Microbial Degradation and Risk-Based Remediation Approaches. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2018, 10, 175–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haritash, A.K.; Kaushik, C.P. Biodegradation Aspects of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs): A Review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 169, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gundlapalli, M.; Sivagami, K.; Gopalakrishnan, M.; Harshini, P.; Janjaroen, D.; Ganesan, S. Biodegradation of Low Molecular Weight Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Soil: Insights into Bacterial Activities and Bioremediation Techniques. Sustain. Chem. Environ. 2024, 7, 100146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaishnavi, J.; Parthipan, P.; Arul Prakash, A.; Sathishkumar, K.; Rajasekar, A. Biosurfactant-Assisted Bioremediation of Crude Oil/Petroleum Hydrocarbon Contaminated Soil. In Handbook of Assisted and Amendment: Enhanced Sustainable Remediation Technology; Prasad, M.N.V., Ed.; Wiley, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 313–329. ISBN 9781119670360. [Google Scholar]
- Wojtowicz, K.; Steliga, T. Wpływ Mieszaniny Biosurfaktantów Na Efektywność Bioremediacji Gruntu Zanieczyszczonego Węglowodorami Ropopochodnymi. Nafta-Gaz 2024, 80, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdoli, S.; Asgari Lajayer, B.; Bagheri Novair, S.; Price, G.W. Unlocking the Potential of Biosurfactants in Agriculture: Novel Applications and Future Directions. Sustainability 2025, 17, 2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo Elsoud, M.M.A. Classification and Production of Microbial Surfactants. In Microbial Biosurfactants; Inamuddin Ahamed, M.I., Prasad, R., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 65–89. ISBN 9789811566066. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Y.-G.; Houot, S.; Qiao, M.; Nunan, N.; Garnier, P. Remediation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon (PAH) Contaminated Soil through Composting with Fresh Organic Wastes. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2011, 18, 1574–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.-Y.; Zhang, T.; Fang, H.H.-P. Bacteria-Mediated PAH Degradation in Soil and Sediment. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 89, 1357–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owsianiak, M.; Szulc, A.; Chrzanowski, Ł.; Cyplik, P.; Bogacki, M.; Olejnik-Schmidt, A.K.; Heipieper, H.J. Biodegradation and Surfactant-Mediated Biodegradation of Diesel Fuel by 218 Microbial Consortia Are Not Correlated to Cell Surface Hydrophobicity. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 84, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, G.; Liu, Z.; Zhong, H.; Li, J.; Yuan, X.; Fu, H.; Ding, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhou, M. Effect of Monorhamnolipid on the Degradation of N-Hexadecane by Candida Tropicalis and the Association with Cell Surface Properties. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 90, 1155–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husain, S. Effect of Surfactants on Pyrene Degradation by Pseudomonas Fluorescens 29L. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 24, 2411–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ławniczak, Ł.; Marecik, R.; Chrzanowski, Ł. Contributions of Biosurfactants to Natural or Induced Bioremediation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 2327–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, C.-C.; Huang, Y.-C.; Wei, Y.-H.; Chang, J.-S. Biosurfactant-Enhanced Removal of Total Petroleum Hydrocarbons from Contaminated Soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 167, 609–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendes Da Silva Santos, E.; Alvares Da Silva Lira, I.R.; Moraes Meira, H.; Dos Santos Aguiar, J.; Diniz Rufino, R.; Germano De Almeida, D.; Casazza, A.A.; Converti, A.; Asfora Sarubbo, L.; Moura De Luna, J. Enhanced Oil Removal by a Non-Toxic Biosurfactant Formulation. Energies 2021, 14, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, N.; Chandran, P. Microbial Degradation of Petroleum Hydrocarbon Contaminants: An Overview. Biotechnol. Res. Int. 2011, 2011, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojtowicz, K.; Steliga, T.; Kapusta, P.; Brzeszcz, J.; Skalski, T. Evaluation of the Effectiveness of the Biopreparation in Combination with the Polymer γ-PGA for the Biodegradation of Petroleum Contaminants in Soil. Materials 2022, 15, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steliga, T.; Jakubowicz, P.; Kapusta, P. Changes in Toxicity during in Situ Bioremediation of Weathered Drill Wastes Contaminated with Petroleum Hydrocarbons. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 125, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Li, W.; Dick, W.A.; Ye, X.; Chen, K.; Kost, D.; Chen, L. Bioremediation of Hydrocarbon Degradation in a Petroleum-Contaminated Soil and Microbial Population and Activity Determination. Chemosphere 2017, 169, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teliga, T.; Kluk, D. Assessment of the Composition of Pollution of Soil Contaminated with TPH and PAHs for the Development of the Bioremediation Technology; Instytut Nafty i Gazu-Państwowy Instytut Badawczy: Kraków, Poland, 2017; ISBN 9788365649201. [Google Scholar]
- Kanaly, R.A.; Harayama, S. Biodegradation of High-Molecular-Weight Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons by Bacteria. J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 2059–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, S.C.; Jones, K.C. Bioremediation of Soil Contaminated with Polynuclear Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs): A Review. Environ. Pollut. 1993, 81, 229–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Hamme, J.D.; Singh, A.; Ward, O.P. Recent Advances in Petroleum Microbiology. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2003, 67, 503–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasian, F.; Lockington, R.; Megharaj, M.; Naidu, R. A Review on the Genetics of Aliphatic and Aromatic Hydrocarbon Degradation. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2016, 178, 224–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, C.; Dang, Q.; Xi, B. Regulating the Biodegradation of Petroleum Hydrocarbons with Different Carbon Chain Structures by Composting Systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 903, 166552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosal, D.; Ghosh, S.; Dutta, T.K.; Ahn, Y. Current State of Knowledge in Microbial Degradation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs): A Review. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Fingas, M.; Blenkinsopp, S.; Sergy, G.; Landriault, M.; Sigouin, L.; Foght, J.; Semple, K.; Westlake, D.W.S. Comparison of Oil Composition Changes Due to Biodegradation and Physical Weathering in Different Oils. J. Chromatogr. A 1998, 809, 89–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venosa, A.D.; Zhu, X. Biodegradation of Crude Oil Contaminating Marine Shorelines and Freshwater Wetlands. Spill Sci. Technol. Bull. 2003, 8, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steliga, T.; Wojtowicz, K.; Kapusta, P.; Brzeszcz, J. Assessment of Biodegradation Efficiency of Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) and Petroleum Hydrocarbons (TPH) in Soil Using Three Individual Bacterial Strains and Their Mixed Culture. Molecules 2020, 25, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steliga, T.; Jakubowicz, P.; Wojtowicz, K.; Kluk, D. Zastosowanie Testów Toksykologicznych w Przemyśle Naftowym. Nafta-Gaz 2018, 74, 684–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sample | n-C17/Pr | n-C18/Ph |
|---|---|---|
| Initial soil G6 (control sample) | 2.716 ± 0.076 | 2.575 ± 0.075 |
| Soil G6 + bacterial consortium | 1.247 ± 0.027 | 1.303 ± 0.023 |
| The concentration of biosurfactant in the enriching mixture is 1 g/dm3 | ||
| Soil G6 + MC + γ-PGA | 0.781 ± 0.009 | 0.818 ± 0.010 |
| Soil G6 + MC + surfactin | 0.959 ± 0.011 | 1.004 ± 0.016 |
| Soil G6 + MC + rhamnolipids | 0.845 ± 0.015 | 0.936 ± 0.026 |
| Soil G6 + MC + mixture PSR | 0.604 ± 0.016 | 0.665 ± 0.015 |
| Soil G6 + MC + JBR425 | 0.802 ± 0.012 | 0.808 ± 0.022 |
| Soil G6 + MC + JBR320 | 0.871 ± 0.011 | 0.925 ± 0.025 |
| Soil G6 + γ-PGA | 2.286 ± 0.056 | 2.350 ± 0.060 |
| Soil G6 + surfactin | 2.241 ± 0.059 | 2.282 ± 0.058 |
| Soil G6 + rhamnolipids | 2.273 ± 0.053 | 2.247 ± 0.053 |
| Soil G6 + mixture PSR | 2.192 ± 0.052 | 2.227 ± 0.057 |
| Soil G6 + JBR425 | 2.125 ± 0.055 | 2.232 ± 0.052 |
| Soil G6 + JBR320 | 2.172 ± 0.048 | 2.199 ± 0.049 |
| The concentration of biosurfactant in the enriching mixture is 5 g/dm3 | ||
| Soil G6 + MC + γ-PGA | 0.257 ± 0.007 | 0.267 ± 0.003 |
| Soil G6 + MC + surfactin | 0.688 ± 0.012 | 0.719 ± 0.011 |
| Soil G6 + MC + rhamnolipids | 0.364 ± 0.006 | 0.408 ± 0.008 |
| Soil G6 + MC + mixture PSR | 0.164 ± 0.004 | 0.173 ± 0.003 |
| Soil G6 + MC + JBR425 | 0.243 ± 0.007 | 0.252 ± 0.008 |
| Soil G6 + MC + JBR320 | 0.273 ± 0.003 | 0.284 ± 0.006 |
| Soil G6 + γ-PGA | 2.286 ± 0.056 | 2.225 ± 0.055 |
| Soil G6 + surfactin | 2.251 ± 0.059 | 2.392 ± 0.052 |
| Soil G6 + rhamnolipids | 2.184 ± 0.046 | 2.235 ± 0.045 |
| Soil G6 + mixture PSR | 2.108 ± 0.042 | 2.109 ± 0.041 |
| Soil G6 + JBR425 | 2.233 ± 0.043 | 2.211 ± 0.043 |
| Soil G6 + JBR320 | 2.266 ± 0.056 | 2.193 ± 0.057 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wojtowicz, K.; Steliga, T.; Skalski, T.; Kapusta, P. Influence of Biosurfactants on the Efficiency of Petroleum Hydrocarbons Biodegradation in Soil. Sustainability 2025, 17, 6520. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17146520
Wojtowicz K, Steliga T, Skalski T, Kapusta P. Influence of Biosurfactants on the Efficiency of Petroleum Hydrocarbons Biodegradation in Soil. Sustainability. 2025; 17(14):6520. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17146520
Chicago/Turabian StyleWojtowicz, Katarzyna, Teresa Steliga, Tomasz Skalski, and Piotr Kapusta. 2025. "Influence of Biosurfactants on the Efficiency of Petroleum Hydrocarbons Biodegradation in Soil" Sustainability 17, no. 14: 6520. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17146520
APA StyleWojtowicz, K., Steliga, T., Skalski, T., & Kapusta, P. (2025). Influence of Biosurfactants on the Efficiency of Petroleum Hydrocarbons Biodegradation in Soil. Sustainability, 17(14), 6520. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17146520








