Reframing Smart Campus Assessment for the Global South: Insights from Papua New Guinea
Abstract
1. Introduction and Background
1.1. Rise of Smart Campuses in Higher Education
1.2. Defining the Smart Campus
1.3. Evolution of Smart Campus Frameworks
1.4. Knowledge and Research Gaps
1.5. Research Aim and Question
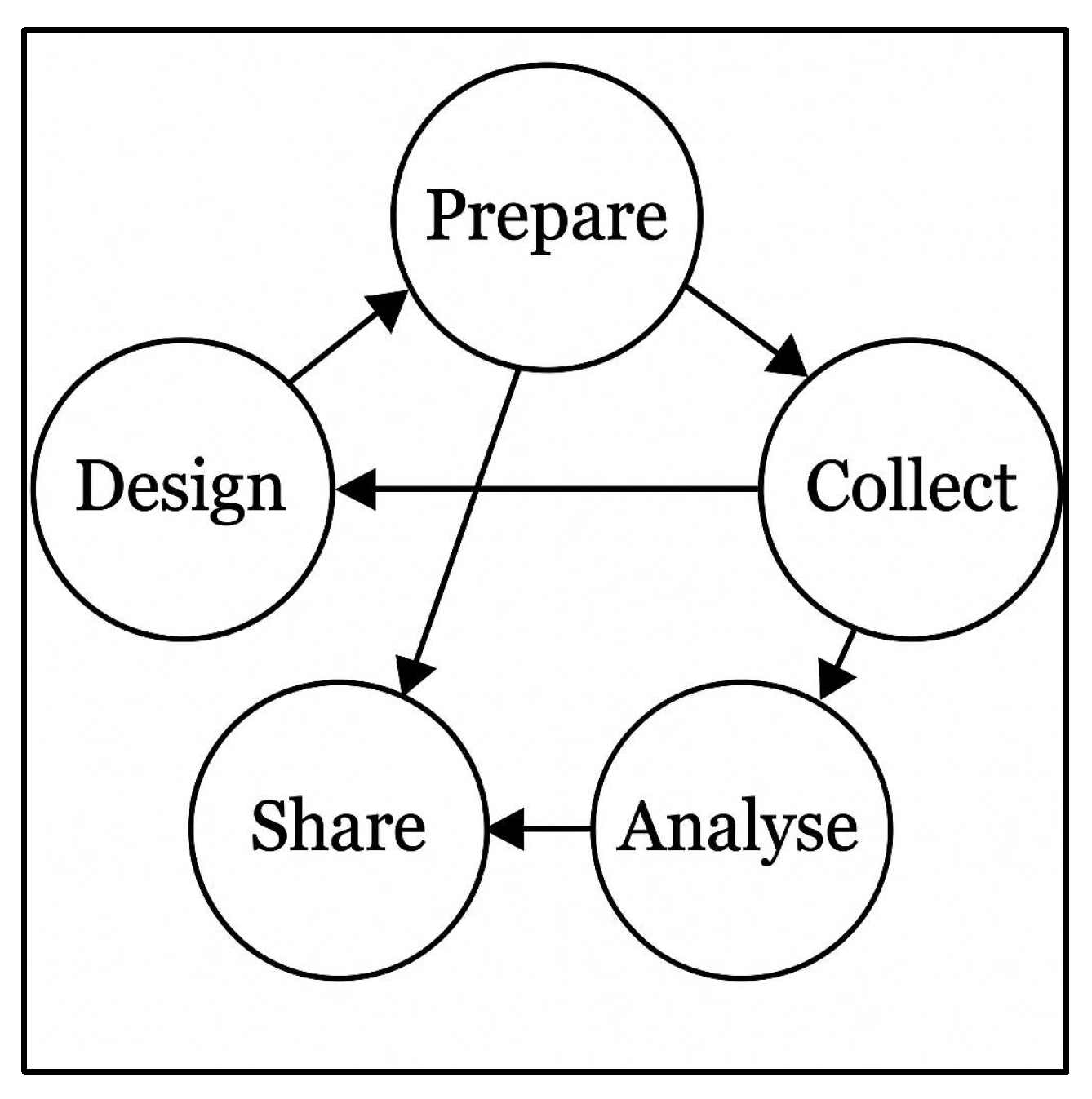
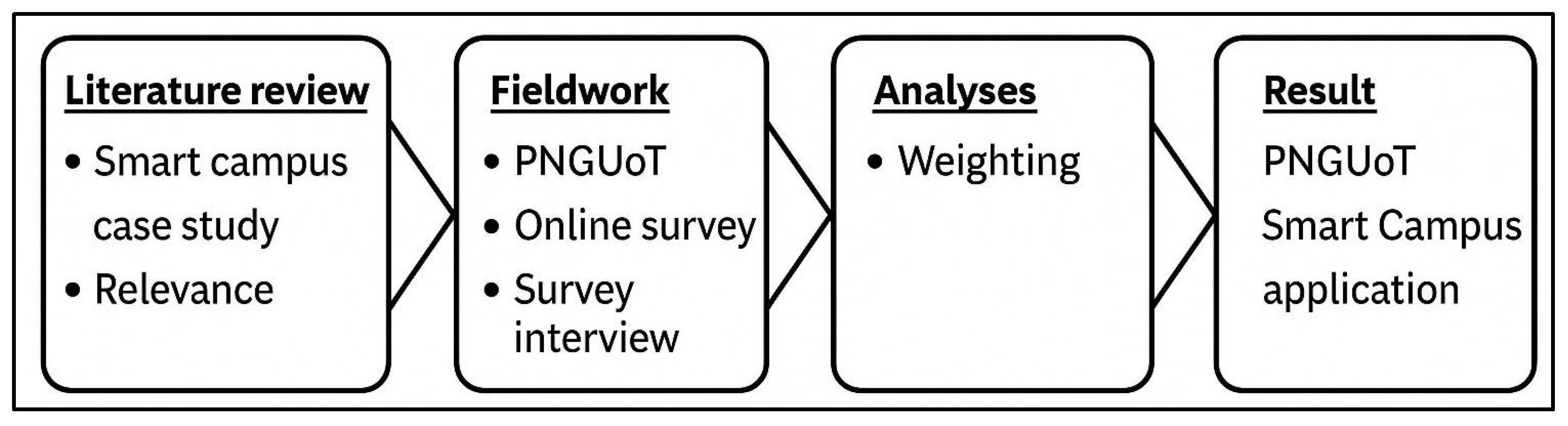
2. Research Design
2.1. Theoretical Framework: Relevance Theory and Perception
2.2. Case-Study Context
2.3. Data Collection Instruments and Participant Sampling
3. Analysis and Results
3.1. Weighting Framework
3.2. Group Best-Worst Method
3.3. Public Opinion Method
3.4. Results
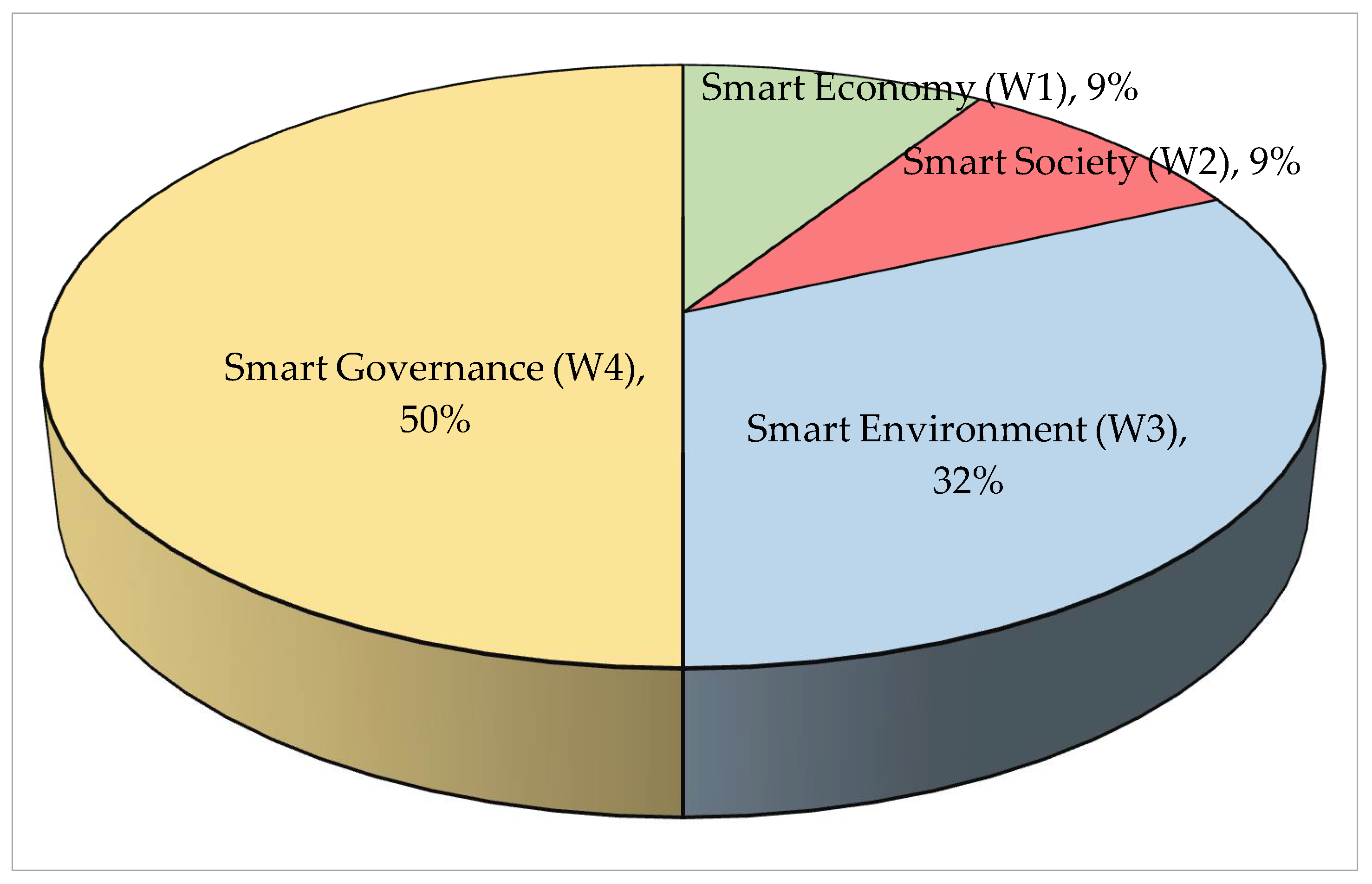
3.4.1. Dimension-Level Weighting
3.4.2. Smart Economy Weighting
3.4.3. Smart Society Weighting
3.4.4. Smart Environment Weighting
3.4.5. Smart Governance Weighting
3.4.6. Indicator-Level Weighting
3.4.7. Overall Category and Indicator Weights
Dimension Level
Category Level
Indicator Level
4. Findings and Discussion
4.1. Smart Governance: Highest Priority Dimension
4.2. Smart Environment: Sustainability as a Pragmatic Priority
4.3. Smart Economy: Emerging Relevance, Limited Capacity
4.4. Smart Society: Educational Relevance, Social Disconnect
4.5. Stakeholder Consensus: Alignment Across Institutional Roles
4.6. Relevance of Framework in Global South Context
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rotta, M.; Sell, D.; Pacheco, R.; Yigitcanlar, T. Digital commons and citizen coproduction in smart cities: Assessment of Brazilian municipal e-government platforms. Energies 2019, 12, 2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faisal, A.; Yigitcanlar, T.; Kamruzzaman, M.; Paz, A. Mapping two decades of autonomous vehicle research: A systematic scientometric analysis. J. Urban Technol. 2021, 28, 45–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yigitcanlar, T.; Li, R.; Beeramoole, P.; Paz, A. Artificial intelligence in local government services: Public perceptions from Australia and Hong Kong. Gov. Inf. Q. 2023, 40, 101833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, K.; Elfaddouli, N.; Cheimanoff, N. The role of information and communication technologies in developing a smart campus with its four pillars’ architectural sketch. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2024, 29, 14815–14833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Padmanabha, V.; Josephmani, P.; Dwivedi, R. Utilizing Packet Tracer Simulation to Modern Smart Campus Initiatives for a Sustainable Future. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 12th International Conference on Smart Energy Grid Engineering, Oshawa, ON, Canada, 18–20 August 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Kandil, O.; Rosillo, R.; Aziz, R.; Fuente, D. Investigating the impact of the Internet of Things on higher education: A systematic literature review. J. Appl. Res. High. Educ. 2025, 17, 254–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Pan, H.; Wu, C. Smart Campus Innovative Learning Model for Social Practitioners of Universities’ Third Mission: To Promote Good Health and Well-Being. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, L.; Manta, O. Research on Digital Campus Construction Based on SOA Service Architecture. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Symposium on Big Data and Artificial Intelligence (ISBDAI 2022), Singapore, 9–10 December 2022; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Lian, J.; Chen, J. Research and Practice of Data Governance in Universities Based on Data Middleware. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Cloud Computing and Big Data (ICCBD2024), Dali, China, 26–28 July 2024; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2024. 5p. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y. Report on Smart Education in China in Smart Education in China and Central & Eastern European Countries; Zhuang, R., Liu, D., Sampson, D., Mandic, D., Zou, S., Huang, Y., Huang, R., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Educational Technology; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, A.; Mohanty, A. Learning on the Move: A Pedagogical Framework for State-of-the-Art Mobile Learning. In Data Management, Analytics and Innovation; Sharma, N., Goje, A., Chakrabarti, A., Bruckstein, A.M., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2023; Volume 662, pp. 735–748. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, A. Intelligence Unleashed: An Argument for AI-Enabled Learning Ecologies with Real World Examples of Today and a Peek into the Future. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Innovations in Computer Science, Electronics & Electrical Engineering 2022, Ashta, India, 14–15 February 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Alblaihed, M.; Ibrahem, U.; Altamimi, A.; Alqirnas, H.; Salem, M. Infosphere Is Reshaping: How the Internet of Things Leads Smart Campuses for Knowledge Management. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afaneh, A.; Alshafei, I. The influence of smart technologies: A comparative study on developing Large to small scale smart cities and smart campuses. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2023, 1210, 012015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, K.; Parandhaman, V.; Rohini, V.; Ravichandran, A.; Bhat, K.; Murugesan, G. Analysis of Developing IoT and Cloud Computing Based Smart Campuses and its Applications. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communication and Applied Informatics 2024, Chennai, India, 9–10 May 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Zhan, N.; Xu, B. Multimodal data visualization method for digital twin campus construction. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2024, 17, 2431624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Li, Q.; Wang, T. Smart Campus and Student Learning Engagement. Int. J. Inf. Commun. Technol. Educ. 2024, 20, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, X. Intelligent Campus Management System Combining Computer Data Processing and GIS Technology. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Electronic Information Technology and Smart Agriculture (ICEITSA 2023), Sanya, China, 8–10 December 2023; pp. 8–10. [Google Scholar]
- Imbar, R. Approaches that Contribute to a New Definition of the “Smart Campus” based on Smart Systems. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on ICT for Smart Society (ICISS) 2024, Bandung, Indonesia, 4–5 September 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Mahariya, A.; Kumar, A.; Singh, R.; Gehlot, A.; Akram, A.; Twala, B.; Iqbal, M.; Priyadarshi, N. Smart Campus 4.0: Digitalization of University Campus with Assimilation of Industry 4.0 for Innovation and Sustainability. J. Adv. Res. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2023, 32, 120–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Mongea, M.; Zalbaa, B.; Casasb, R.; Canoc, E.; Guillén-Lambeaa, S.; Martínez, B. Is IoT monitoring key to improve building energy efficiency? Case study of a smart campus in Spain. Energy Build. 2023, 285, 112882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aion, N.; Helmandollar, L.; Wang, M.; Ng, J. Intelligent campus (iCampus) impact study. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE/WIC/ACMInternational Conferences on Web Intelligence and Intelligent Agent Technology, Macau, China, 4–7 December 2012; pp. 291–295. [Google Scholar]
- Pagliaro, F.; Mattoni, B.; Gugliermenti, F.; Bisegna, F.; Azzaro, B.; Tomei, F.; Catucci, S. A roadmap toward the development of Sapienza Smart Campus. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 16th International Conference on Environment and Electrical Engineering (EEEIC), Florence, Italy, 7–10 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Z.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yip, C.; Swift, S.; Beswick, K. Smart campus: Definition, framework, technologies, and services. IET Smart Cities 2020, 2, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janda, K.; Ruyssevelt, P.; Liddiard, R. 4DStock: Adding an organisational dimension to a 3D building stock model. In Proceedings of the European Council on an Energy-Efficient Economy Summer Study, Toulon/Hyeres, France, 6–11 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Khatun, S.; Khan, M.; Kadir, K.; Paul, A.; Hassan, S.; Aziz, A.; Taj, M. A Comparative Analysis of Smart Education Hub in terms of Cost-effective Infrastructure Remodelling and System Design. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2022, 18, 239–254. [Google Scholar]
- Djakhdjakha, L.; Cisse, H.; Farou, B. A modular ontology for Smart Campus. In Proceedings of the RIF’23: The 12th Seminary of Computer Science Research at Feminine (CEUR Workshop Proceedings), Constantine, Algeria, 9 March 2023; pp. 17–26. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, E.F.; Erlangga, R. A systematic literature review on augmented reality in smart campus research. AIP Conf. Proc. 2023, 2734, 060004. [Google Scholar]
- Prasetyaningtyas, S.; Meliala, J.; Pratiwi, C.; Peranginangin, E. A Smart Campus Framework in Developing Countries: Systematic Literature Approach. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on ICT for Smart Society (ICISS), Bandung, Indonesia, 6–7 September 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Regehr, C.; Rule, N. Addressing challenges to recovery and building future resilience in the wake of COVID-19. J. Bus. Contin. Emerg. Plan. 2023, 17, 284–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, H.; Faturrahman, M.; Sidharta, S. Guidance in Designing a Smart Campus: A Systematic Literature Review. Proc. Comput. Sci. 2023, 227, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellaj, M.; Bendahmane, A.; Younes, A.; Boudra, S.; Ennakra, M. A systematic review of smart campus technologies to improve students’ educational experiences. In Proceedings of the Mediterranean Smart Cities Conference (MSCC 2024), Martil, Morocco, 2–4 May 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, X.; Yang, C. A study on the technology of reviewing smart campus construction under energy consumption limit constraints. Int. J. Environ. Sustain. Dev. 2024, 23, 176–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izourane, F.; Ardchir, S.; Ounacer, S.; Azzouazi, M. Smart Campus Based on AI and IoT in the Era of Industry 5.0: Challenges and Opportunities. In Industry 5.0 and Emerging Technologies Transformation Through Technology and Innovations; Chakir, A., Bansal, R., Azzouazi, M., Eds.; Studies in Systems, Decision and Control; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; Volume 565, pp. 39–57. [Google Scholar]
- Polin, K.; Yigitcanlar, T.; Limb, L.; Washington, T. Smart Campus Performance Assessment: Framework Consolidation and Validation Through a Delphi Study. Buildings 2024, 14, 4057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawwad, A.; Turab, N.; Al-Mahadin, G.; Owida, H.; Al-Nabulsi, J. A perspective on smart universities as being downsized smart cities: A technological view of internet of thing and big data. Indones. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2024, 35, 1162–1170. [Google Scholar]
- Das, D.; Lim, N.D.; Aravind, P. Developing a Smart and Sustainable Campus in Singapore. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, V.; Saboor, S.; Ahmad, N.; Ghaly, M. A multi-attribute utility decision support tool for a smart campus—UAE as a case study. Front. Built Environ. 2022, 8, 1044646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samancioglu, N.; Nuere, S. A determination of the smartness level of university campuses: The Smart Availability Scale. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2023, 70, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, P.; Pisani, F.; Borin, J. Smart University: A pathway for advancing Sustainable Development Goals. Int. Things 2024, 27, 101246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winarno, A.; Gadzali, S.; Kisahwan, D.; Hermana, D. Leadership and employee environmental performance: Mediation test from model job demands-resources dan sustainability perspective in micro level. Cogent Bus. Manag. 2025, 12, 2442091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R. Case Study Research and Applications Design and Methods, 6th ed.; Sage Publications, Inc.: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sperber, D.; Wilson, D. Pragmatics. UCL Wor. Pap. Linguist. 2005, 17, 353–388. [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert, N. Agent-Based Models, Sage Research Methods; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivancevich, J.; Matterson, M. Organizational Behavior and Management; Richard D. Irwin, Inc.: Homewood, IL, USA, 1990; pp. 71–72. [Google Scholar]
- Kolaiti, P. Perceptual relevance and art: Some tentative suggestions. J. Lit. Semant. 2020, 49, 99–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Pérez, F. Relevance Theory and translation: Translating puns in Spanish film titles into English. J. Pragmat. 2014, 70, 108–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcet, E.; Sasamoto, R. Examining interlanguage pragmatics from a relevance-theoretic perspective: Challenges in L2 production. Intercult. Pragmat. 2023, 20, 405–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Víctor, M.; Galván-Vela, E.; Ravina-Ripoll, R.; Popescu, C. A Focus on Ethical Value under the Vision of Leadership, Teamwork, Effective Communication and Productivity. J. Risk Financ. Manag. 2021, 14, 522. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.; Palaoag, L.; Du, H.; Guo, T. Design and Optimization of Smart Campus Framework Based on Artificial Intelligence. J. Inf. Syst. Eng. Manag. 2023, 8, 23086. [Google Scholar]
- Stuckey, M.; Hofstein, A.; Mamlok-Naaman, R.; Eilks, I. The meaning of ‘relevance’ in science education and its implications for the science curriculum. Stud. Sci. Educ. 2013, 49, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herranen, J.; Aksela, M.; Kaul, M.; Lehto, S. Teachers’ Expectations and Perceptions of the Relevance of Professional Development MOOCs. Educ. Sci. 2021, 11, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bearden, W.; Netemeyer, R. Attitudes, About the Performance of Business Firms, Satisfaction and Post-Purchase Behavior, Consumer Attitudes toward Business Practices and Marketing Social Agencies, and the Marketplace; 2011 Product: Sage Research Methods; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lundstrom, W.; Lamont, L. The Development of a Scale to Measure Consumer Discontent. J. Mark. Res. 1976, 13, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parasuraman, A.; Zeithaml, V.; Berry, L. SERVQUAL: A Multiple-Item Scale for Measuring Consumer Perceptions of Service Quality. J. Retail. 1988, 64, 12–40. [Google Scholar]
- Polin, K.; Yigitcanlar, T.; Limb, M.; Washington, T. The making of smart campus: A review and conceptual framework. Buildings 2023, 13, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bienstock, C.; Mentzer, J.; Bird, M. Measuring Physical Distribution Service Quality. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 1997, 25, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, C.V. Relevance and creativity and the translation of multimedia tourist material. Cult. Lang. Represent. 2023, XXXI, 189–214. [Google Scholar]
- Likert, R. A technique for the measurement of attitudes. Arch. Psychol. 1932, 22, 55. [Google Scholar]
- McIver, J.; Carmines, E. Likert Scaling; Sage Research Methods; SAGE Publications, Inc.: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamieson, S. Likert scales: How to (ab)use them. Med. Educ. 2004, 38, 1217–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, G. Likert scales, levels of measurement and the ‘‘laws’’ of statistics. Adv. Health Sci. Educ. 2010, 15, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, P.; Herron, R. Use and Misuse of the Likert Item Responses and Other Ordinal Measures. Int. J. Exerc. Sci. 2015, 8, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creswell, J.W. Educational Research: Planning, Conducting, and Evaluating Quantitative and Qualitative Research, 4th ed.; Pearson: Boston, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, R.K. Case Study Research Design and Methods, 4th ed.; SAGE Publications, Inc.: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Rubin, H.; Rubin, I. Qualitative Interviewing the Art of Hearing Data, 3rd ed.; SAGE Publishing: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Omrani, H.; Amini, M.; Alizadeh, A. An integrated group best-worst method–Data envelopment analysis approach for evaluating road safety: A case of Iran. Measurement 2020, 152, 107330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, J. Best-worst multi-criteria decision-making method: Some properties and a linear model. Omega 2016, 64, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, X.; Fernandez, I.; Guo, J.; Wilson, M.; Zhao, W.; Zhou, B.; Wu, J. When to use what: Methods for weighting and aggregating sustainability indicators. Ecol. Ind. 2017, 81, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, J. Environmental Reporting and Environmental Indices. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Fazeli, H.; Attarzadeh, B. Problematizing Iranian university autonomy: A historical-institutional perspective. Int. J. Cult. Policy 2024, 30, 877–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsharif, M. The structural modelling of significant organisational and individual factors for promoting sustainable campus in Saudi Arabia. Front. Sustain. 2024, 5, 1231468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristinsson, S. Constructing Universities for Democracy. Stud. Philos. Educ. 2023, 42, 181–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruvot, E.; Estermann, T. University Governance: Autonomy, Structures and Inclusiveness. In European Higher Education Area: The Impact of Past and Future Policies; Curaj, A., Deca, L., Pricopie, R., Eds.; Springer Open: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 619–638. [Google Scholar]
- Paspatis, A.; Fiorentzis, K.; Katsigiannis, Y.; Karapidakis, E. Smart Campus Microgrids towards a Sustainable Energy Transition— The Case Study of the Hellenic Mediterranean University in Crete. Mathematics 2022, 10, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiarto, A.; Lee, C.; Huruta, A. A Systematic Review of the Sustainable Campus Concept. Behav. Sci. 2022, 12, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, M.; Lai, X.; Chang, L.; Wang, Z. Efficiency of higher education financial resource allocation from the perspective of ‘double first-class’ construction: A three-stage global super slacks-based measure analysis. Edu. Inf. Technol. 2024, 29, 12047–12075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganshina, E. Static and dynamic approaches in industrial metrology in the framework of measuring enterprise productivity. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1889, 042053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eklund, J. Theknowledge-incentive tradeoff: Understanding the relationship between research and development decentralization and innovation. Strat. Manag. J. 2022, 43, 2478–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvadorinho, J.; Teixeira, L. Stories Told by Publications about the Relationship between Industry 4.0 and Lean: Systematic Literature Review and Future Research. Agenda Publ. 2021, 9, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehbozorgi, M.; Rossi, M.; Terzi, S.; Carminati, L.; Sala, R.; Magni, F.; Pirola, F.; Pozz, R.; Strozzi, F.; Rossi, T. AI Education for Tomorrow’s Workforce: Leveraging Learning Factories for AI Education and Workforce Preparedness. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 8th Forum on Research and Technologies for Society and Industry Innovation (RTSI), Milano, Italy, 18–20 September 2024; pp. 677–682. [Google Scholar]
- Konstantinidis, E.; Petsani, D.; Bamidis, P. Teaching university students co-creation and living lab methodologies through experiential learning activities and preparing them for RRI. Health Inform. J. 2021, 27, 1460458221991204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nhem, D. Quality in higher education: What do students in Cambodia perceive? Tert. Educ. Manag. 2022, 28, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yigitcanlar, T.; Agdas, D.; Degirmenci, K. Artificial intelligence in local governments: Perceptions of city managers on prospects, constraints and choices. AI Soc. 2023, 38, 1135–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yigitcanlar, T.; Guaralda, M.; Taboada, M.; Pancholi, S. Place making for knowledge generation and innovation: Planning and branding brisbane’s knowledge community precincts. J. Urban Technol. 2016, 23, 115–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
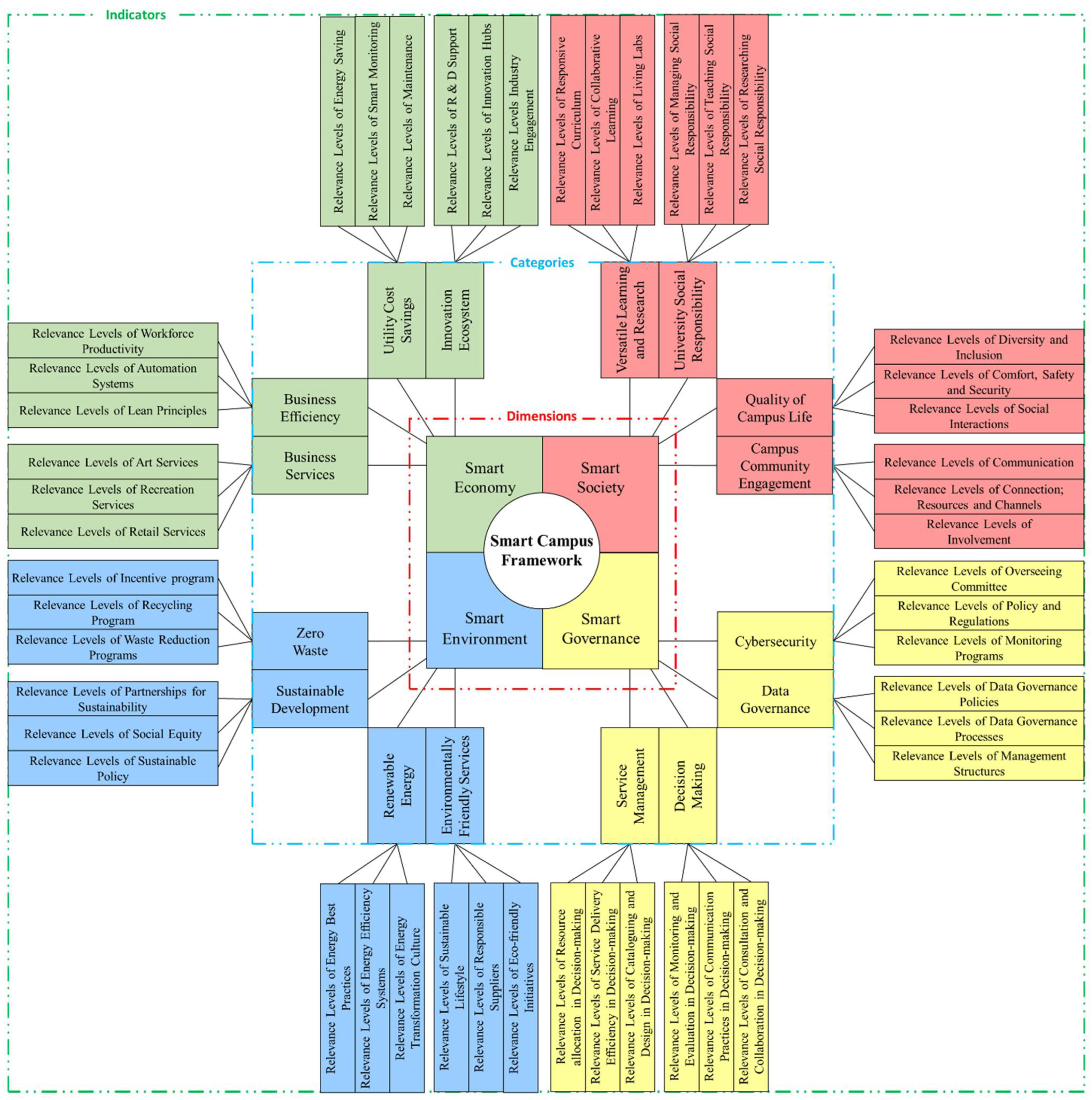

| Dimension | Category | Indicator |
|---|---|---|
| Smart Economy | Business Services | Retail Services |
| Recreation Services | ||
| Art Services | ||
| Business Efficiency | Lean Principles | |
| Automation Systems | ||
| Workforce Productivity | ||
| Utility Cost Savings | Energy Saving | |
| Smart Monitoring | ||
| Maintenance | ||
| Innovation Ecosystem | R&D Support | |
| Innovation Hubs | ||
| Industry Engagement | ||
| Smart Society | Versatile Learning and Research | Responsive Curriculum |
| Collaborative Learning | ||
| Living Labs | ||
| University Social Responsibility | Managing Social Responsibility | |
| Teaching Social Responsibility | ||
| Researching Social Responsibility | ||
| Quality Of Campus Life | Diversity and Inclusion | |
| Comfort, Safety and Security | ||
| Social Interactions | ||
| Campus Community Engagement | Communication | |
| Connection; Resources and Channels | ||
| Involvement | ||
| Smart Environment | Environmentally Friendly Services | Sustainable Lifestyle |
| Responsible Suppliers | ||
| Eco-friendly Initiatives | ||
| Renewable Energy | Energy Transformation Culture | |
| Energy Efficiency Systems | ||
| Energy Best Practices | ||
| Sustainable Development | Sustainable Policy | |
| Social Equity | ||
| Partnerships for Sustainability | ||
| Zero Waste | Waste Reduction Programs | |
| Recycling Program | ||
| Incentive Program | ||
| Smart Governance | Cybersecurity | Overseeing Committee |
| Policy and Regulations | ||
| Monitoring Programs | ||
| Data Governance | Data Governance Policies | |
| Data Governance Processes | ||
| Management Structures | ||
| Decision-Making | Consultation and Collaboration | |
| Communication Practices | ||
| Monitoring and Evaluation | ||
| Service Management | Cataloguing and Design | |
| Service Delivery Efficiency | ||
| Resource Allocation |
| Position | Qualification | Average Period of Employment (Years) |
|---|---|---|
| Associate professor | PhD | 16 |
| Senior lecturer | Masters | |
| Manager | Bachelor’s degree | |
| Administrator | Diploma | |
| Engineer | Trade certificate | |
| Principle technical instructor | ||
| Senior technical officer |
| Indicator | 0 (Not Available) | 1 (Very Irrelevant) | 2 (Irrelevant) | 3 (Neither Relevant nor Irrelevant) | 4 (Relevant) | 5 (Very Relevant) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Retail services: Variety of food, retail, and other business services | ⃝ | ⃝ | ⃝ | ⃝ | ⃝ | ⃝ |
| School/Section: Estates and Services | 0 (Not Available) | 1 (Very Irrelevant) | 2 (Irrelevant) | 3 (Neither Relevant nor Irrelevant) | 4 (Relevant) | 5 (Very Relevant) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Retail services: Variety of food, retail, and other business services | ⃝ | ⃝ | ⃝ | ⃝ | ⃝ | ⃝ |
| Dimension | Weight |
|---|---|
| Smart Economy | W1: 0.0909 |
| Smart Society | W2: 0.0909 |
| Smart Environment | W3: 0.3182 |
| Smart Governance | W4: 0.5000 |
| Category | Weight |
|---|---|
| Business services | W1: 0.0763 |
| Business efficiency | W2: 0.4417 |
| Utility cost savings | W3: 0.1165 |
| Innovation ecosystem | W4: 0.3655 |
| Category | Weight |
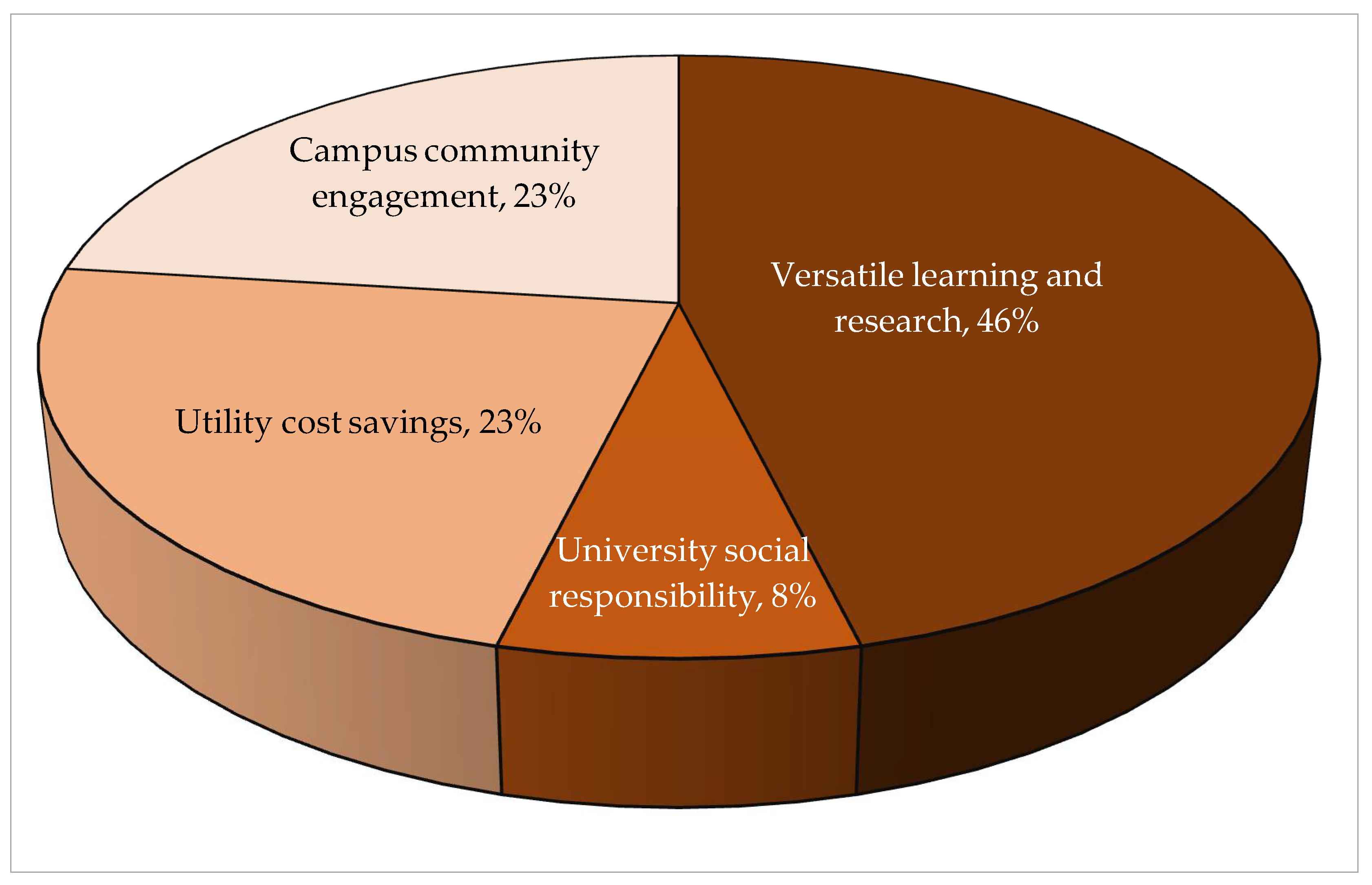
|---|---|
| Versatile learning and research | W1: 0.4615 |
| University social responsibility | W2: 0.0769 |
| Utility cost savings | W3: 0.2308 |
| Campus community engagement | W4: 0.2308 |
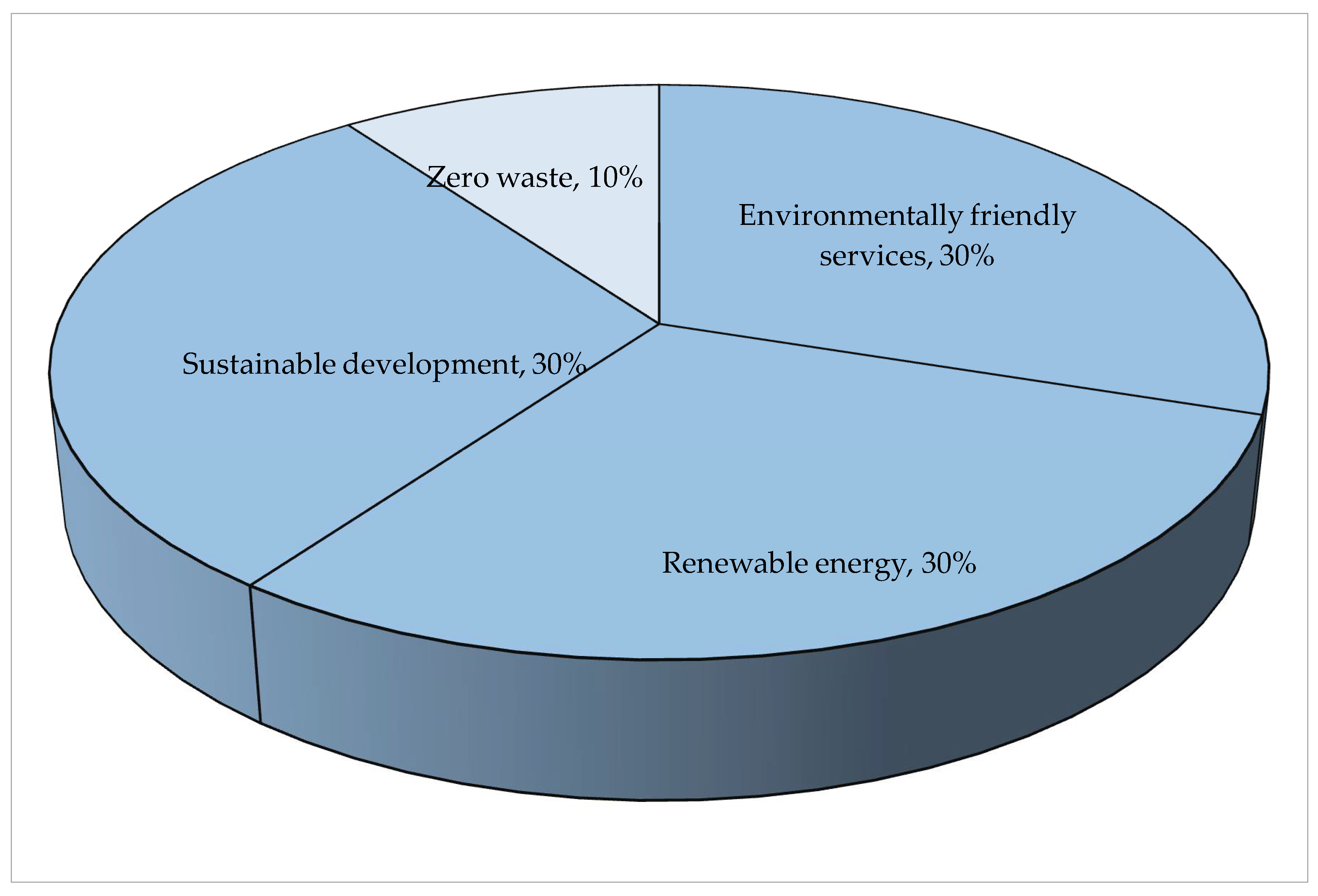
| Category | Weight |
|---|---|
| Environmentally friendly services | W1: 0.3000 |
| Renewable energy | W2: 0.3000 |
| Sustainable development | W3: 0.3000 |
| Zero waste | W4: 0.1000 |
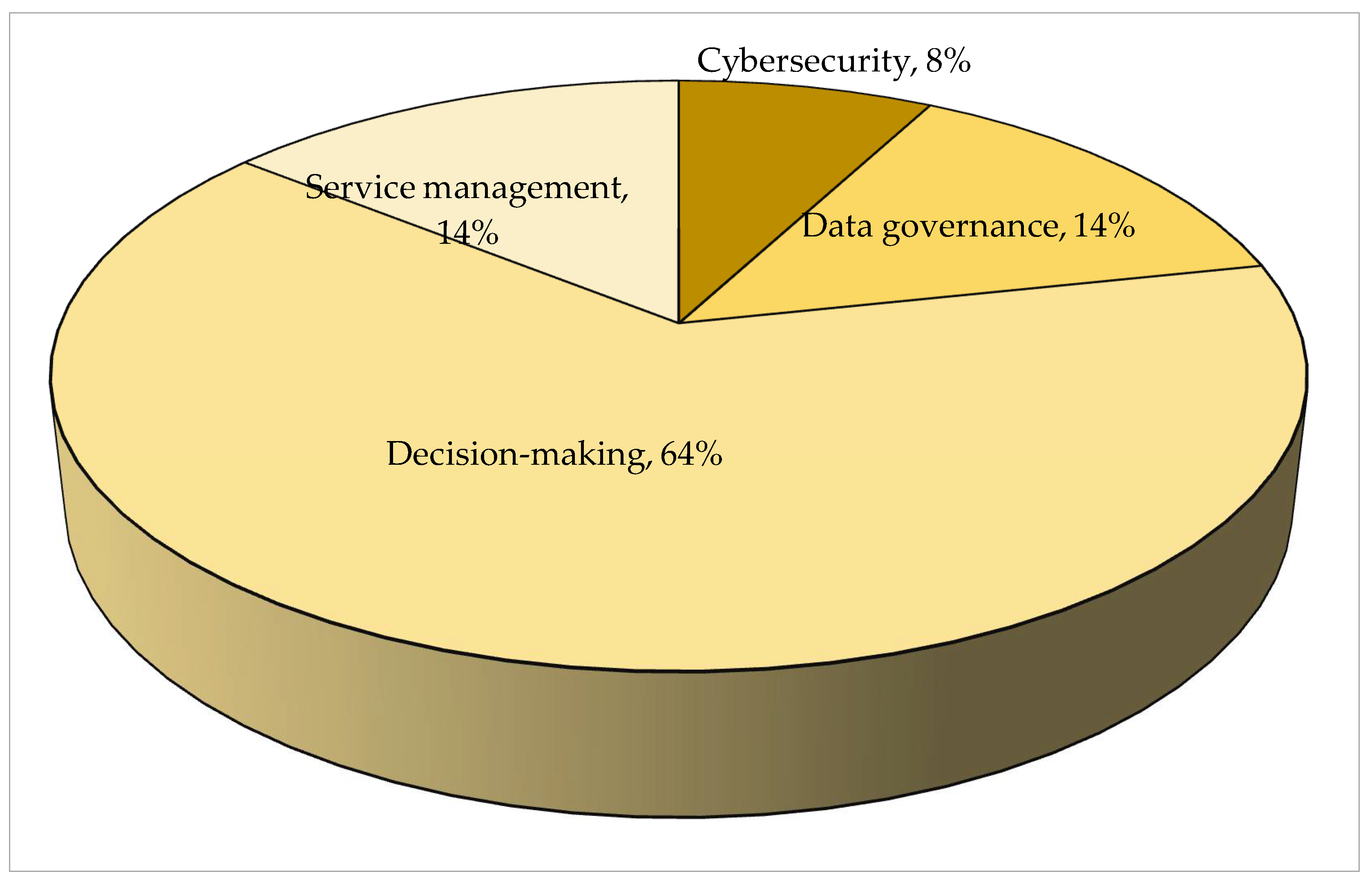
| Category | Weight |
|---|---|
| Cybersecurity | W1: 0.077960 |
| Data governance | W2: 0.138595 |
| Decision-making | W3: 0.641001 |
| Service management | W4: 0.142445 |
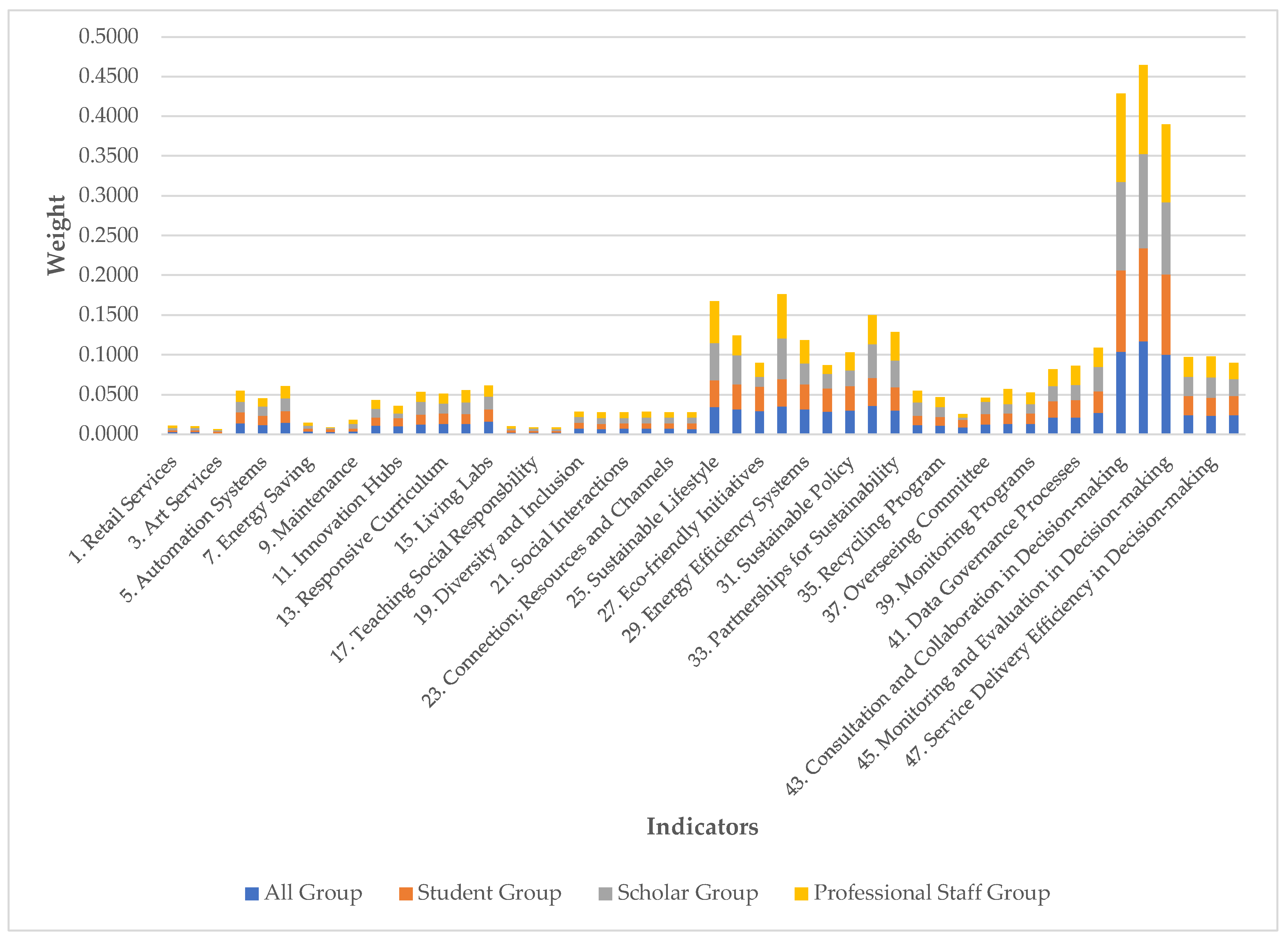
| Dimensions | Categories | Indicators | All Participants | Students | Scholars | Administrative/Professional Staff | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Score | Indicator Weight | Mean Score | Indicator Weight | Mean Score | Indicator Weight | Mean Score | Indicator Weight | |||
| 1. Smart Economy | 1. Business services | 1. Relevance Levels of Retail Services | 2.6403 | 0.3722 | 2.6102 | 0.3679 | 2.7692 | 0.3871 | 3.1818 | 0.4545 |
| 2. Relevance Levels of Recreation Services | 2.7590 | 0.3889 | 2.7874 | 0.3929 | 2.6923 | 0.3763 | 2.1818 | 0.3117 | ||
| 3. Relevance Levels of Art Services | 1.6942 | 0.2388 | 1.6969 | 0.2392 | 1.6923 | 0.2366 | 1.6364 | 0.2338 | ||
| 2. Business efficiency | 4. Relevance Levels of Lean Principles | 2.2419 | 0.3426 | 2.2016 | 0.3428 | 2.2308 | 0.3258 | 3.1818 | 0.3535 | |
| 5. Relevance Levels of Automation Systems | 1.9029 | 0.2908 | 1.8819 | 0.2930 | 1.9231 | 0.2809 | 2.3636 | 0.2626 | ||
| 6. Relevance Levels of Workforce Productivity | 2.3993 | 0.3666 | 2.3386 | 0.3641 | 2.6923 | 0.3933 | 3.4545 | 0.3838 | ||
| 3. Utility cost savings | 7. Relevance Levels of Energy Saving | 1.8597 | 0.3293 | 1.8583 | 0.3255 | 1.7692 | 0.3898 | 2.0000 | 0.3607 | |
| 8. Relevance Levels of Smart Monitoring | 1.7230 | 0.3051 | 1.8346 | 0.3214 | 0.4615 | 0.1017 | 0.6364 | 0.1148 | ||
| 9. Relevance Levels of Maintenance | 2.0647 | 0.3656 | 2.0157 | 0.3531 | 2.3077 | 0.5085 | 2.9091 | 0.5246 | ||
| 4. Innovation ecosystem | 10. Relevance Levels of R & D Support | 2.1619 | 0.3223 | 2.1890 | 0.3218 | 2.0000 | 0.3333 | 1.7273 | 0.3220 | |
| 11. Relevance Levels of Innovation Hubs | 2.0468 | 0.3051 | 2.1181 | 0.3113 | 1.0769 | 0.1795 | 1.5455 | 0.2881 | ||
| 12. Relevance Levels Industry Engagement | 2.5000 | 0.3727 | 2.4961 | 0.3669 | 2.9231 | 0.4872 | 2.0909 | 0.3898 | ||
| 2. Smart Society | 5. Versatile learning and research | 13. Relevance Levels of Responsive Curriculum | 2.5576 | 0.3128 | 2.5787 | 0.3143 | 2.6154 | 0.2931 | 2.0000 | 0.3014 |
| 14. Relevance Levels of Collaborative Learning | 2.5360 | 0.3102 | 2.5157 | 0.3066 | 3.0000 | 0.3362 | 2.4545 | 0.3699 | ||
| 15. Relevance Levels of Living Labs | 3.0827 | 0.3770 | 3.1102 | 0.3791 | 3.3077 | 0.3707 | 2.1818 | 0.3288 | ||
| 6. University social responsibility | 16. Relevance Levels of Managing Social Responsibility | 2.6835 | 0.3531 | 2.6496 | 0.3509 | 3.0000 | 0.3391 | 3.0909 | 0.4250 | |
| 17. Relevance Levels of Teaching Social Responsibility | 2.4281 | 0.3195 | 2.3976 | 0.3175 | 3.3077 | 0.3739 | 2.0909 | 0.2875 | ||
| 18. Relevance Levels of Researching Social Responsibility | 2.4892 | 0.3275 | 2.5039 | 0.3316 | 2.5385 | 0.2870 | 2.0909 | 0.2875 | ||
| 7. Quality of campus life | 19. Relevance Levels of Diversity and Inclusion | 3.0216 | 0.3540 | 2.9528 | 0.3583 | 3.8462 | 0.3311 | 3.6364 | 0.3101 | |
| 20. Relevance Levels of Comfort, Safety and Security | 2.6691 | 0.3127 | 2.5394 | 0.3082 | 4.1538 | 0.3576 | 3.9091 | 0.3333 | ||
| 21. Relevance Levels of Social Interactions | 2.8453 | 0.3333 | 2.7480 | 0.3335 | 3.6154 | 0.3113 | 4.1818 | 0.3566 | ||
| 8. Campus community engagement | 22. Relevance Levels of Communication | 2.8165 | 0.3355 | 2.7283 | 0.3352 | 3.6923 | 0.3357 | 3.8182 | 0.3415 | |
| 23. Relevance Levels of Connection; Resources and Channels | 2.8381 | 0.3381 | 2.7638 | 0.3395 | 3.5385 | 0.3217 | 3.7273 | 0.3333 | ||
| 24. Relevance Levels of Involvement | 2.7401 | 0.3264 | 2.6482 | 0.3253 | 3.7692 | 0.3427 | 3.6364 | 0.3252 | ||
| 3. Smart Environment | 9. Environmentally friendly services | 25. Relevance Levels of Sustainable Lifestyle | 2.4604 | 0.3629 | 2.3622 | 0.3484 | 3.6923 | 0.4898 | 3.2727 | 0.5538 |
| 26. Relevance Levels of Responsible Suppliers | 2.2410 | 0.3305 | 2.2402 | 0.3304 | 2.8462 | 0.3776 | 1.5455 | 0.2615 | ||
| 27. Relevance Levels of Eco-friendly Initiatives | 2.0791 | 0.3066 | 2.1772 | 0.3211 | 1.0000 | 0.1327 | 1.0909 | 0.1846 | ||
| 10. Renewable energy | 28. Relevance Levels of Energy Transformation Culture | 2.0755 | 0.3706 | 2.0906 | 0.3602 | 1.9231 | 0.5319 | 1.9091 | 0.5833 | |
| 29. Relevance Levels of Energy Efficiency Systems | 1.8453 | 0.3295 | 1.9252 | 0.3318 | 1.0000 | 0.2766 | 1.0000 | 0.3056 | ||
| 30. Relevance Levels of Energy Best Practices | 1.6799 | 0.2999 | 1.7874 | 0.3080 | 0.6923 | 0.1915 | 0.3636 | 0.1111 | ||
| 11. Sustainable development | 31. Relevance Levels of Sustainable Policy | 2.1223 | 0.3141 | 2.1693 | 0.3235 | 1.3846 | 0.2045 | 1.9091 | 0.2414 | |
| 32. Relevance Levels of Social Equity | 2.5288 | 0.3743 | 2.4843 | 0.3705 | 3.0000 | 0.4432 | 3.0000 | 0.3793 | ||
| 33. Relevance Levels of Partnerships for Sustainability | 2.1047 | 0.3115 | 2.0514 | 0.3060 | 2.3846 | 0.3523 | 3.0000 | 0.3793 | ||
| 12. Zero waste | 34. Relevance Levels of Waste Reduction Programs | 1.9101 | 0.3753 | 1.9252 | 0.3679 | 1.6154 | 0.5122 | 1.9091 | 0.4667 | |
| 35. Relevance Levels of Recycling Program | 1.7590 | 0.3456 | 1.7913 | 0.3424 | 1.2308 | 0.3902 | 1.6364 | 0.4000 | ||
| 36. Relevance Levels of Incentive program | 1.4209 | 0.2792 | 1.5157 | 0.2897 | 0.3077 | 0.0976 | 0.5455 | 0.1333 | ||
| 4. Smart Governance | 13. Cybersecurity | 37. Relevance Levels of Overseeing Committee | 1.6799 | 0.3273 | 1.7874 | 0.3290 | 0.7692 | 0.3846 | 0.2727 | 0.1429 |
| 38. Relevance Levels of Policy and Regulations | 1.7338 | 0.3378 | 1.8268 | 0.3362 | 0.6154 | 0.3077 | 0.9091 | 0.4762 | ||
| 39. Relevance Levels of Monitoring Programs | 1.7194 | 0.3350 | 1.8189 | 0.3348 | 0.6154 | 0.3077 | 0.7273 | 0.3810 | ||
| 14. Data governance | 40. Relevance Levels of Data Governance Policies | 2.1367 | 0.3006 | 2.1496 | 0.3012 | 1.4615 | 0.2754 | 2.6364 | 0.3085 | |
| 41. Relevance Levels of Data Governance Processes | 2.2014 | 0.3097 | 2.2047 | 0.3089 | 1.4615 | 0.2754 | 3.0000 | 0.3511 | ||
| 42. Relevance Levels of Management Structures | 2.7698 | 0.3897 | 2.7835 | 0.3900 | 2.3846 | 0.4493 | 2.9091 | 0.3404 | ||
| 15. Decision-making | 43. Relevance Levels of Consultation and Collaboration in Decision-making | 2.7410 | 0.3230 | 2.6339 | 0.3199 | 3.4615 | 0.3462 | 4.3636 | 0.3478 | |
| 44. Relevance Levels of Communication Practices in Decision-making | 3.0971 | 0.3650 | 3.0118 | 0.3659 | 3.6923 | 0.3692 | 4.3636 | 0.3478 | ||
| 45. Relevance Levels of Monitoring and Evaluation in Decision-making | 2.6475 | 0.3120 | 2.5866 | 0.3142 | 2.8462 | 0.2846 | 3.8182 | 0.3043 | ||
| 16. Service management | 46. Relevance Levels of Cataloguing and Design in Decision-making | 2.6871 | 0.3383 | 2.6142 | 0.3377 | 3.2308 | 0.3387 | 3.7273 | 0.3475 | |
| 47. Relevance Levels of Service Delivery Efficiency in Decision-making | 2.5899 | 0.3261 | 2.4882 | 0.3215 | 3.4615 | 0.3629 | 3.9091 | 0.3644 | ||
| 48. Relevance Levels of Resource allocation in Decision-making | 2.6655 | 0.3356 | 2.6378 | 0.3408 | 2.8462 | 0.2984 | 3.0909 | 0.2881 | ||
| Dimension | Category | Category Overall Weight | Indicator | All Participants | Students | Scholars | Administrative/Professional Staff | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indicator Weight | Indicator Overall Weight | Indicator Weight | Indicator Overall Weight | Indicator Weight | Indicator Overall Weight | Indicator Weight | Indicator Overall Weight | ||||
| 1. Smart economy, W: 0.0909 | 1. Business services, W: 0.0763 | 0.0069 | 1. Relevance Levels of Retail Services | 0.3722 | 0.0026 | 0.3679 | 0.0026 | 0.3871 | 0.0027 | 0.4545 | 0.0032 |
| 2. Relevance Levels of Recreation Services | 0.3889 | 0.0027 | 0.3929 | 0.0027 | 0.3763 | 0.0026 | 0.3117 | 0.0022 | |||
| 3. Relevance Levels of Art Services | 0.2388 | 0.0017 | 0.2392 | 0.0017 | 0.2366 | 0.0016 | 0.2338 | 0.0016 | |||
| 2. Business efficiency, W: 0.4417 | 0.0402 | 4. Relevance Levels of Lean Principles | 0.3426 | 0.0138 | 0.3428 | 0.0138 | 0.3258 | 0.0131 | 0.3535 | 0.0142 | |
| 5. Relevance Levels of Automation Systems | 0.2908 | 0.0117 | 0.2930 | 0.0118 | 0.2809 | 0.0113 | 0.2626 | 0.0105 | |||
| 6. Relevance Levels of Workforce Productivity | 0.3666 | 0.0147 | 0.3641 | 0.0146 | 0.3933 | 0.0158 | 0.3838 | 0.0154 | |||
| 3. Utility cost savings, W: 0.1165 | 0.0106 | 7. Relevance Levels of Energy Saving | 0.3293 | 0.0035 | 0.3255 | 0.0034 | 0.3898 | 0.0041 | 0.3607 | 0.0038 | |
| 8. Relevance Levels of Smart Monitoring | 0.3051 | 0.0032 | 0.3214 | 0.0034 | 0.1017 | 0.0011 | 0.1148 | 0.0012 | |||
| 9. Relevance Levels of Maintenance | 0.3656 | 0.0039 | 0.3531 | 0.0037 | 0.5085 | 0.0054 | 0.5246 | 0.0056 | |||
| 4. Innovation ecosystem, W: 0.3655 | 0.0332 | 10. Relevance Levels of R & D Support | 0.3223 | 0.0107 | 0.3218 | 0.0107 | 0.3333 | 0.0111 | 0.3220 | 0.0107 | |
| 11. Relevance Levels of Innovation Hubs | 0.3051 | 0.0101 | 0.3113 | 0.0103 | 0.1795 | 0.0060 | 0.2881 | 0.0096 | |||
| 12.Relevance Levels Industry Engagement | 0.3727 | 0.0124 | 0.3669 | 0.0122 | 0.4872 | 0.0162 | 0.3898 | 0.0130 | |||
| 2. Smart society, W: 0.0909 | 5. Versatile learning and research, W: 0.4615 | 0.0420 | 13. Relevance Levels of Responsive Curriculum | 0.3128 | 0.0131 | 0.3143 | 0.0132 | 0.2931 | 0.0123 | 0.3014 | 0.0126 |
| 14. Relevance Levels of Collaborative Learning | 0.3102 | 0.0130 | 0.3066 | 0.0129 | 0.3362 | 0.0141 | 0.3699 | 0.0155 | |||
| 15. Relevance Levels of Living Labs | 0.3770 | 0.0158 | 0.3791 | 0.0159 | 0.3707 | 0.0156 | 0.3288 | 0.0138 | |||
| 6. University social responsibility, W: 0.0769 | 0.0070 | 16. Relevance Levels of Managing Social Responsibility | 0.3531 | 0.0025 | 0.3509 | 0.0025 | 0.3391 | 0.0024 | 0.4250 | 0.0030 | |
| 17. Relevance Levels of Teaching Social Responsbility | 0.3195 | 0.0022 | 0.3175 | 0.0022 | 0.3739 | 0.0026 | 0.2875 | 0.0020 | |||
| 18. Relevance Levels of Researching Social Responsibility | 0.3275 | 0.0023 | 0.3316 | 0.0023 | 0.2870 | 0.0020 | 0.2875 | 0.0020 | |||
| 7. Quality of campus life, W: 0.2308 | 0.0210 | 19. Relevance Levels of Diversity and Inclusion | 0.3540 | 0.0074 | 0.3583 | 0.0075 | 0.3311 | 0.0069 | 0.3101 | 0.0065 | |
| 20. Relevance Levels of Comfort, Safety and Security | 0.3127 | 0.0066 | 0.3082 | 0.0065 | 0.3576 | 0.0075 | 0.3333 | 0.0070 | |||
| 21. Relevance Levels of Social Interactions | 0.3333 | 0.0070 | 0.3335 | 0.0070 | 0.3113 | 0.0065 | 0.3566 | 0.0075 | |||
| 8. Campus community engarement, W: 0.2308 | 0.0210 | 22. Relevance Levels of Communication | 0.3355 | 0.0070 | 0.3352 | 0.0070 | 0.3357 | 0.0070 | 0.3415 | 0.0072 | |
| 23. Relevance Levels of Connection; Resources and Channels | 0.3381 | 0.0071 | 0.3395 | 0.0071 | 0.3217 | 0.0067 | 0.3333 | 0.0070 | |||
| 24. Relevance Levels of Involvement | 0.3264 | 0.0068 | 0.3253 | 0.0068 | 0.3427 | 0.0072 | 0.3252 | 0.0068 | |||
| 3. Smart environment, W: 0.3182 | 9. Environmentally friendly services, W: 0.3 | 0.0955 | 25. Relevance Levels of Sustainable Lifestyle | 0.3629 | 0.0346 | 0.3484 | 0.0333 | 0.4898 | 0.0468 | 0.5538 | 0.0529 |
| 26. Relevance Levels of Responsbile Suppliers | 0.3305 | 0.0315 | 0.3304 | 0.0315 | 0.3776 | 0.0360 | 0.2615 | 0.0250 | |||
| 27. Relevance Levels of Eco-friendly Initiatives | 0.3066 | 0.0293 | 0.3211 | 0.0307 | 0.1327 | 0.0127 | 0.1846 | 0.0176 | |||
| 10. Renewable energy, W: 0.3 | 0.0955 | 28. Relevance Levels of Energy Transformation Culture | 0.3706 | 0.0354 | 0.3602 | 0.0344 | 0.5319 | 0.0508 | 0.5833 | 0.0557 | |
| 29. Relevance Levels of Energy Efficiency Systems | 0.3295 | 0.0315 | 0.3318 | 0.0317 | 0.2766 | 0.0264 | 0.3056 | 0.0292 | |||
| 30. Relevance Levels of Energy Best Practices | 0.2999 | 0.0286 | 0.3080 | 0.0294 | 0.1915 | 0.0183 | 0.1111 | 0.0106 | |||
| 11. Sustainable development, W: 0.3 | 0.0955 | 31. Relevance Levels of Sustainable Policy | 0.3141 | 0.0300 | 0.3235 | 0.0309 | 0.2045 | 0.0195 | 0.2414 | 0.0230 | |
| 32. Relevance Levels of Social Equity | 0.3743 | 0.0357 | 0.3705 | 0.0354 | 0.4432 | 0.0423 | 0.3793 | 0.0362 | |||
| 33. Relevance Levels of Partnerships for Sustainability | 0.3115 | 0.0297 | 0.3060 | 0.0292 | 0.3523 | 0.0336 | 0.3793 | 0.0362 | |||
| 12. Zero waste, W: 0.1 | 0.0318 | 34. Relevance Levels of Waste Reduction Programs | 0.3753 | 0.0119 | 0.3679 | 0.0117 | 0.5122 | 0.0163 | 0.4667 | 0.0148 | |
| 35. Relevance Levels of Recyciling Program | 0.3456 | 0.0110 | 0.3424 | 0.0109 | 0.3902 | 0.0124 | 0.4000 | 0.0127 | |||
| 36. Relevance Levels of Incentive program | 0.2792 | 0.0089 | 0.2897 | 0.0092 | 0.0976 | 0.0031 | 0.1333 | 0.0042 | |||
| 4. Smart governance, W: 0.5 | 13. Cybersecurity, W: 0.0780 | 0.0390 | 37. Relevance Levels of Overseeing Committee | 0.3273 | 0.0128 | 0.3290 | 0.0128 | 0.3846 | 0.0150 | 0.1429 | 0.0056 |
| 38. Relevance Levels of Policy and Regulations | 0.3378 | 0.0132 | 0.3362 | 0.0131 | 0.3077 | 0.0120 | 0.4762 | 0.0186 | |||
| 39. Relevance Levels of Monitoring Programs | 0.3350 | 0.0131 | 0.3348 | 0.0130 | 0.3077 | 0.0120 | 0.3810 | 0.0148 | |||
| 14. Data governance, W: 0.1386 | 0.0693 | 40. Relevance Levels of Data Governance Policies | 0.3006 | 0.0208 | 0.3012 | 0.0209 | 0.2754 | 0.0191 | 0.3085 | 0.0214 | |
| 41. Relevance Levels of Data Governance Processes | 0.3097 | 0.0215 | 0.3089 | 0.0214 | 0.2754 | 0.0191 | 0.3511 | 0.0243 | |||
| 42. Relevance Levels of Management Structures | 0.3897 | 0.0270 | 0.3900 | 0.0270 | 0.4493 | 0.0311 | 0.3404 | 0.0236 | |||
| 15. Decision-making, W: 0.6410 | 0.3205 | 43. Relevance Levels of Consultation and Collaboration in Decision-making | 0.3230 | 0.1035 | 0.3199 | 0.1025 | 0.3462 | 0.1109 | 0.3478 | 0.1115 | |
| 44. Relevance Levels of Communication Practices in Decision-making | 0.3650 | 0.1170 | 0.3659 | 0.1173 | 0.3692 | 0.1183 | 0.3478 | 0.1115 | |||
| 45. Relevance Levels of Monitoring and Evaluation in Decision-making | 0.3120 | 0.1000 | 0.3142 | 0.1007 | 0.2846 | 0.0912 | 0.3043 | 0.0975 | |||
| 16. Service management, W: 0.1424 | 0.0712 | 46. Relevance Levels of Cataloguing and Design in Decision-making | 0.3383 | 0.0241 | 0.3377 | 0.0241 | 0.3387 | 0.0241 | 0.3475 | 0.0247 | |
| 47. Relevance Levels of Service Delivery Efficiency in Decision-making | 0.3261 | 0.0232 | 0.3215 | 0.0229 | 0.3629 | 0.0258 | 0.3644 | 0.0260 | |||
| 48. Relevance Levels of Resource allocation in Decision-making | 0.3356 | 0.0239 | 0.3408 | 0.0243 | 0.2984 | 0.0213 | 0.2881 | 0.0205 | |||
| Indicator | All Participants | Students | Scholars | Administrative/Professional Staff | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall Weight | Rank | Overall Weight | Rank | Overall Weight | Rank | Overall Weight | Rank | |
| Relevance Levels of Communication Practices in Decision-making | 0.11698 | 1 | 0.11726 | 1 | 0.11834 | 1 | 0.11148 | 1 |
| Relevance Levels of Consultation and Collaboration in Decision-making | 0.10353 | 2 | 0.10254 | 2 | 0.11094 | 2 | 0.11148 | 2 |
| Relevance Levels of Monitoring and Evaluation in Decision-making | 0.10000 | 3 | 0.10070 | 3 | 0.09122 | 3 | 0.09754 | 3 |
| Relevance Levels of Social Equity | 0.03573 | 4 | 0.03537 | 4 | 0.04231 | 6 | 0.03621 | 6 |
| Relevance Levels of Energy Transformation Culture | 0.03538 | 5 | 0.03439 | 5 | 0.05078 | 4 | 0.05569 | 4 |
| Relevance Levels of Sustainable Lifestyle | 0.03464 | 6 | 0.03326 | 6 | 0.04676 | 5 | 0.05287 | 5 |
| Relevance Levels of Responsible Suppliers | 0.03155 | 7 | 0.03154 | 8 | 0.03604 | 7 | 0.02497 | 10 |
| Relevance Levels of Energy Efficiency Systems | 0.03145 | 8 | 0.03167 | 7 | 0.02640 | 10 | 0.02917 | 8 |
| Relevance Levels of Sustainable Policy | 0.02999 | 9 | 0.03088 | 9 | 0.01953 | 14 | 0.02304 | 14 |
| Relevance Levels of Partnerships for Sustainability | 0.02974 | 10 | 0.02921 | 12 | 0.03363 | 8 | 0.03621 | 7 |
| Relevance Levels of Eco-friendly Initiatives | 0.02927 | 11 | 0.03066 | 10 | 0.01266 | 25 | 0.01762 | 18 |
| Relevance Levels of Energy Best Practices | 0.02863 | 12 | 0.02940 | 11 | 0.01828 | 17 | 0.01061 | 29 |
| Relevance Levels of Management Structures | 0.02700 | 13 | 0.02702 | 13 | 0.03113 | 9 | 0.02359 | 13 |
| Relevance Levels of Cataloguing and Design in Decision-making | 0.02410 | 14 | 0.02405 | 15 | 0.02412 | 12 | 0.02475 | 11 |
| Relevance Levels of Resource allocation in Decision-making | 0.02390 | 15 | 0.02427 | 14 | 0.02125 | 13 | 0.02052 | 16 |
| Relevance Levels of Service Delivery Efficiency in Decision-making | 0.02322 | 16 | 0.02290 | 16 | 0.02585 | 11 | 0.02595 | 9 |
| Relevance Levels of Data Governance Processes | 0.02146 | 17 | 0.02140 | 17 | 0.01908 | 15 | 0.02433 | 12 |
| Relevance Levels of Data Governance Policies | 0.02083 | 18 | 0.02087 | 18 | 0.01908 | 16 | 0.02138 | 15 |
| Relevance Levels of Living Labs | 0.01582 | 19 | 0.01590 | 19 | 0.01555 | 21 | 0.01379 | 24 |
| Relevance Levels of Workforce Productivity | 0.01472 | 20 | 0.01462 | 20 | 0.01579 | 20 | 0.01541 | 20 |
| Relevance Levels of Lean Principles | 0.01375 | 21 | 0.01376 | 21 | 0.01308 | 24 | 0.01419 | 23 |
| Relevance Levels of Policy and Regulations | 0.01317 | 22 | 0.01311 | 23 | 0.01199 | 28 | 0.01856 | 17 |
| Relevance Levels of Responsive Curriculum | 0.01312 | 23 | 0.01318 | 22 | 0.01230 | 27 | 0.01264 | 27 |
| Relevance Levels of Monitoring Programs | 0.01306 | 24 | 0.01305 | 24 | 0.01199 | 29 | 0.01485 | 21 |
| Relevance Levels of Collaborative Learning | 0.01301 | 25 | 0.01286 | 25 | 0.01410 | 23 | 0.01552 | 19 |
| Relevance Levels of Overseeing Committee | 0.01276 | 26 | 0.01282 | 26 | 0.01499 | 22 | 0.00557 | 38 |
| Relevance Levels Industry Engagement | 0.01238 | 27 | 0.01219 | 27 | 0.01619 | 19 | 0.01295 | 25 |
| Relevance Levels of Waste Reduction Programs | 0.01194 | 28 | 0.01171 | 29 | 0.01630 | 18 | 0.01485 | 22 |
| Relevance Levels of Automation Systems | 0.01167 | 29 | 0.01177 | 28 | 0.01128 | 30 | 0.01054 | 30 |
| Relevance Levels of Recycling Program | 0.01100 | 30 | 0.01089 | 30 | 0.01242 | 26 | 0.01273 | 26 |
| Relevance Levels of R & D Support | 0.01071 | 31 | 0.01069 | 31 | 0.01107 | 31 | 0.01070 | 28 |
| Relevance Levels of Innovation Hubs | 0.01014 | 32 | 0.01034 | 32 | 0.00596 | 38 | 0.00957 | 31 |
| Relevance Levels of Incentive program | 0.00888 | 33 | 0.00922 | 33 | 0.00310 | 41 | 0.00424 | 40 |
| Relevance Levels of Diversity and Inclusion | 0.00743 | 34 | 0.00752 | 34 | 0.00695 | 35 | 0.00651 | 37 |
| Relevance Levels of Connection; Resources and Channels | 0.00709 | 35 | 0.00712 | 35 | 0.00675 | 36 | 0.00699 | 35 |
| Relevance Levels of Communication | 0.00704 | 36 | 0.00703 | 36 | 0.00704 | 34 | 0.00716 | 33 |
| Relevance Levels of Social Interactions | 0.00699 | 37 | 0.00700 | 37 | 0.00653 | 37 | 0.00748 | 32 |
| Relevance Levels of Involvement | 0.00685 | 38 | 0.00683 | 38 | 0.00719 | 33 | 0.00682 | 36 |
| Relevance Levels of Comfort, Safety and Security | 0.00656 | 39 | 0.00647 | 39 | 0.00750 | 32 | 0.00699 | 34 |
| Relevance Levels of Maintenance | 0.00387 | 40 | 0.00374 | 40 | 0.00538 | 39 | 0.00556 | 39 |
| Relevance Levels of Energy Saving | 0.00349 | 41 | 0.00345 | 41 | 0.00413 | 40 | 0.00382 | 41 |
| Relevance Levels of Smart Monitoring | 0.00323 | 42 | 0.00340 | 42 | 0.00108 | 48 | 0.00122 | 48 |
| Relevance Levels of Recreation Services | 0.00270 | 43 | 0.00273 | 43 | 0.00261 | 44 | 0.00216 | 44 |
| Relevance Levels of Retail Services | 0.00258 | 44 | 0.00255 | 44 | 0.00268 | 42 | 0.00315 | 42 |
| Relevance Levels of Managing Social Responsibility | 0.00247 | 45 | 0.00245 | 45 | 0.00237 | 45 | 0.00297 | 43 |
| Relevance Levels of Researching Social Responsibility | 0.00229 | 46 | 0.00232 | 46 | 0.00201 | 46 | 0.00201 | 46 |
| Relevance Levels of Teaching Social Responsibility | 0.00223 | 47 | 0.00222 | 47 | 0.00261 | 43 | 0.00201 | 45 |
| Relevance Levels of Art Services | 0.00166 | 48 | 0.00166 | 48 | 0.00164 | 47 | 0.00162 | 47 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Polin, K.; Yigitcanlar, T.; Limb, M.; Washington, T.; Golbababei, F.; Paz, A. Reframing Smart Campus Assessment for the Global South: Insights from Papua New Guinea. Sustainability 2025, 17, 6369. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17146369
Polin K, Yigitcanlar T, Limb M, Washington T, Golbababei F, Paz A. Reframing Smart Campus Assessment for the Global South: Insights from Papua New Guinea. Sustainability. 2025; 17(14):6369. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17146369
Chicago/Turabian StylePolin, Ken, Tan Yigitcanlar, Mark Limb, Tracy Washington, Fahimeh Golbababei, and Alexander Paz. 2025. "Reframing Smart Campus Assessment for the Global South: Insights from Papua New Guinea" Sustainability 17, no. 14: 6369. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17146369
APA StylePolin, K., Yigitcanlar, T., Limb, M., Washington, T., Golbababei, F., & Paz, A. (2025). Reframing Smart Campus Assessment for the Global South: Insights from Papua New Guinea. Sustainability, 17(14), 6369. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17146369








