The Transmission Mechanism and Spatial Spillover Effect of Agricultural New Quality Productive Forces on Urban–Rural Integration: Evidence from China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Relevant Studies on ANPF
2.2. Related Research on URI
2.3. URI and Sustainable Development
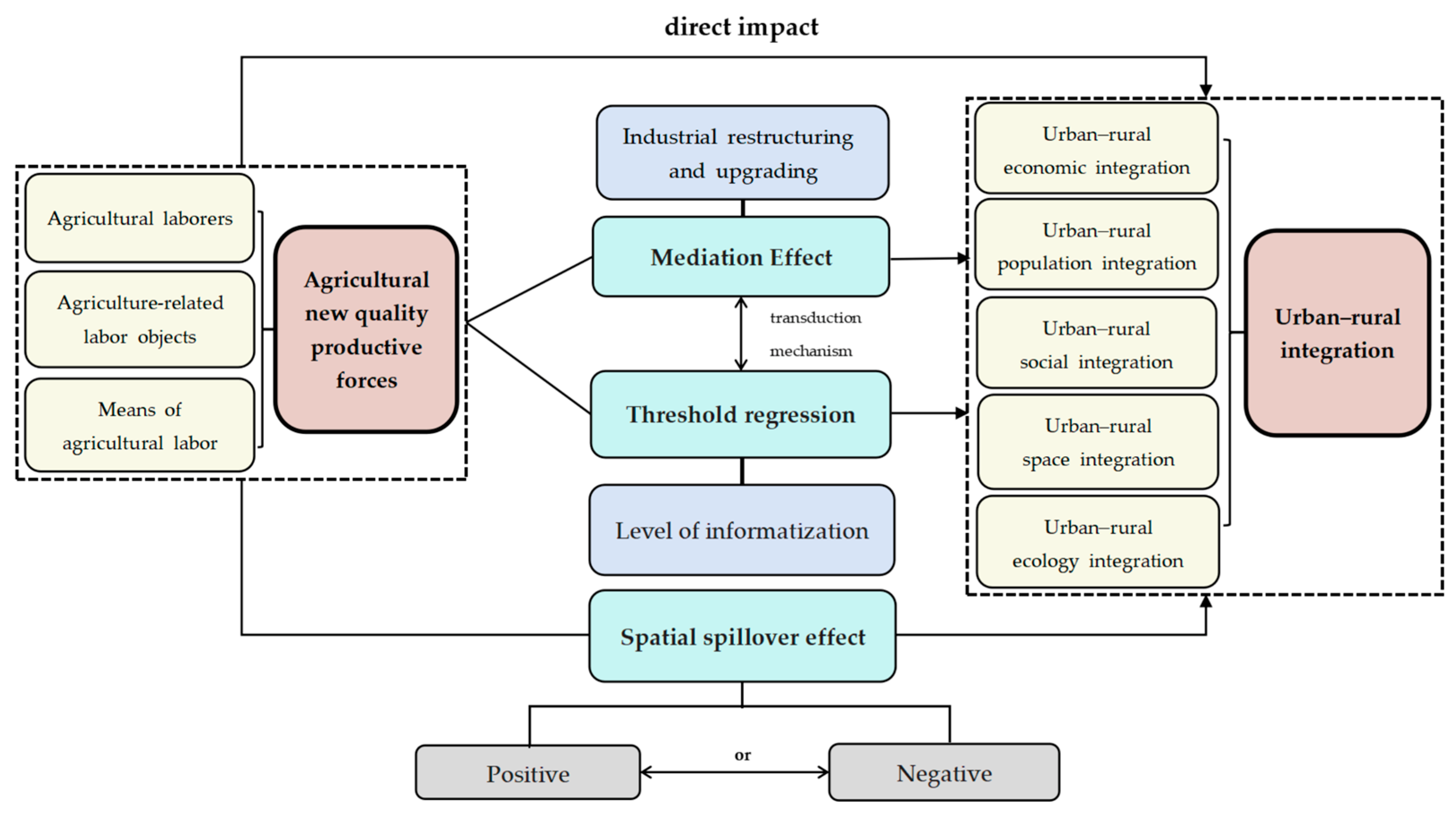
3. Theoretical Analysis
3.1. Impact of ANPF on URI
3.2. The Mediating Effect of Industrial Restructuring and Upgrading (IND)
3.3. Threshold Effect of the Level of Informatization (INF)
3.4. The Spatial Spillover Effect of ANPF on URI
4. Research Design
4.1. Model Construction
4.2. Variable Description
4.2.1. Explained Variables
4.2.2. Core Explanatory Variable
4.2.3. Mediating Variable
4.2.4. Threshold Variables
4.2.5. Control Variables
4.3. Data Sources and Statistical Characteristics
5. Analysis of Empirical Results
5.1. Benchmark Regression
5.2. Robustness Test
5.3. Heterogeneity Analysis
5.4. Mediation Analysis
5.5. Threshold Effect Analysis
5.6. Further Analysis: Spatial Effect Analysis
6. Conclusions and Recommendations
6.1. Conclusions and Discussions
- (1)
- ANPF exhibits a statistically significant positive correlation with URI advancement. Each unit increase in ANPF corresponds to a 0.268-unit rise in URI, with this relationship remaining robust across various specification tests.
- (2)
- Regional heterogeneity exists in ANPF’s effects, with western China experiencing substantially stronger impacts than eastern and central regions.
- (3)
- IND serves as a crucial transmission channel. Through agricultural technological innovation, ANPF drives industrial transformation and upgrading, while IND further optimizes the allocation of production factors between urban and rural areas, ultimately supporting URI progress.
- (4)
- The influence of ANPF on URI displays nonlinear characteristics concerning INF. Initially, INF strengthens ANPF’s positive effects. While continued INF improvement enhances the overall enabling effect, the marginal benefit diminishes after reaching certain development thresholds.
- (5)
- Spatial effect analysis reveals that ANPF generates negative spillover effects on neighboring regions. Although ANPF significantly boosts local URI development, it concurrently inhibits URI advancement in adjacent areas.
6.2. Recommendations
6.3. Limitations and Future Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, L.B.; Liu, S.C.; Fang, F.; Che, X.L.; Chen, M.M. Evaluation of urban-rural difference and integration based on quality of life. Sust. Cities Soc. 2020, 54, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Directorate-General for Agriculture and Rural Development. New Reports Highlight Cap’s Role in Strengthening Rural Areas. Available online: https://agriculture.ec.europa.eu/media/news/new-reports-highlight-caps-role-strengthening-rural-areas-2024-07-04_en (accessed on 4 July 2024).
- Global Magazine. Brazil: Combating Hunger as A “Political Project”. Available online: http://www.xinhuanet.com/globe/20241114/0a8fb98aaece4599a408c22d5f8c72c8/c.html (accessed on 14 November 2024).
- African Union. Transforming African Agriculture by 2025. Available online: https://caadp.org/#:~:text=Agenda%202063,and%20improving%20the%20sustainability%20of%20agricultural%20production%20and%20use%20of%20natural%20resources (accessed on 9 July 2025).
- Collins, J.; Tefera, W.; Yamdjeu, A.W. Tracking Key CAADP Indicators and Implementation Processes. Available online: https://www.resakss.org/sites/default/files/2023_ator_individual_chapters/Chapter%2013_ReSAKSS_AW_ATOR_2023.pdf#:~:text=%E5%86%9C%E4%B8%9A%E5%8A%B3%E5%8A%A8%E7%94%9F%E4%BA%A7%E7%8E%87,%E8%BF%9B%E4%B8%80%E6%AD%A5%E5%A2%9E%E9%95%BF%E5%88%B02014%E5%B9%B4%E8%87%B32021%E5%B9%B4%E6%9C%9F%E9%97%B4%E7%9A%841796%E7%BE%8E%E5%85%83%E3%80%82 (accessed on 9 July 2025).
- United Nations Development Programme. Annual Report 2023 Regional Programme for Africa. Available online: https://www.undp.org/sites/g/files/zskgke326/files/2024-11/j0498_rsca_digital_annual_report_2023_v9.pdf (accessed on 9 July 2025).
- Huang, G.-Q. Connotation, characteristics, significance, and development pathways of new quality productive force in agriculture. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao = J. Appl. Ecol. 2025, 36, 1281–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xinfa, T.; Guozu, H.; Yonghua, W.; Dan, L.; Yan, L. Research on an equilibrium development model between urban and rural areas of Henan including carbon sink assets under the dual carbon goal. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 10, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C. The Agricultural New Quality Productive Forces: Connotations, Development Priorities, Constraints and Policy Recommendations for the Development. J. Nanjing Agric. Univ. (Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2024, 24, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Ma, J. New Quality Agricultural Productivity: A Political Economy Perspective. Issues Agric. Econ. 2024, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Xie, D. The Theoretical Connotation, Main Characteristics and Development Path of the New Quality Agricultural Productive Forces. J. China Agric. Univ. (Soc. Sci.) 2024, 41, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, B.; Geng, P. New Quality Agricultural Productivity: Theoretical Framework, Core Concepts, and Enhancement Pathways. Issues Agric. Econ. 2024, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Gu, T.Y.; Shi, Y. The Influence of New Quality Productive Forces on High-Quality Agricultural Development in China: Mechanisms and Empirical Testing. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.H.; Zhang, N.N.; Liu, J.B. Study on the Rural Revitalization and Urban-Rural Integration Efficiency in Anhui Province Based on Game Cross-Efficiency DEA Model. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Liu, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H. Soil health and new-quality agricultural productive forces: Theoretical connotation, logical relationship, and implementation pathways. Hubei Agric. Sci. 2025, 64, 176–183+217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Rao, M. Paths to realizing the agricultural new quality productive forces: Based on the practice of avocado cultivation in Menglian county, Yunnan province. Emerg. Sci. Technol. 2024, 3, 390–396. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, F.X.; Tan, J.T.; Qiu, F.D.; Gu, S.L. How agricultural technological innovation influences carbon emissions: Insights from China. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2025, 9, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Luo, Z. Low-altitude economy empowers the development of new quality productivity in agriculture: Role playing, realistic barriers and cracking them. J. Agro-For. Econ. Manag. 2025, 24, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.H.; Wen, C.B.; Fang, X.N.; Sun, X. Impacts of urban-rural integration on landscape patterns and their implications for landscape sustainability: The case of Changsha, China. Landsc. Ecol. 2024, 39, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.Z.; Mao, R.; Zhou, Y.Y. Rurbanomics for common prosperity: New approach to integrated urban-rural development. China Agric. Econ. Rev. 2023, 15, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.C.; Zhu, X.P.; Wu, H.W.; Li, Z.H. Urbanization Impact on Regional Sustainable Development: Through the Lens of Urban-Rural Resilience. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 5407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, D.S.; Huang, G.Z.; Guan, J.W.; Lin, J.R. Changing concepts of city and urban planning practices in Guangzhou (1949-2010): An approach to sustainable urban development. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2014, 24, 607–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.A.; Hua, W.W.; Duan, K.F.; Li, H. Evaluation of the Urban-Rural Integration Development Level in the Yangtze River Delta: A Hybrid Method. J. Urban Plan. Dev 2023, 149, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, C.J.; Gao, Y. Evaluation Mechanism Design for the Development Level of Urban-Rural Integration Based on an Improved TOPSIS Method. Mathematics 2022, 10, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H. Statistical Measurement and Spatiotemporal Characteristics of Low-altitude Economic Modernization Level. Stat. Decis. 2025, 41, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Z. Research on the Mode and Path of County-level Urban-rural Integration in Central China: He’nan Province as an Example. Urban Dev. Stud. 2025, 31, 42–49. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.Z.; Lian, R.Y.; Niu, K.Z.; Wei, S. Does the digital economy promote the high-quality development of urban-rural integration? experience analysis based on panel data of 30 provinces in China. In Environment, Development and Sustainability; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; p. 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.Y.; Li, L.N.; Zhou, Y. Exploring the urban-rural development differences and influencing factors in the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain of China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2020, 30, 1603–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.C.; Liu, Y.R.; Wan, Z.W.; Liang, W.Q. Evaluation system and influencing paths for the integration of culture and tourism in traditional villages. J. Geogr. Sci. 2023, 33, 2489–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Liu, J.; Nian, M. Integrated Urban-Rural Development Oriented toward the Chinese Modernization:Obstacles, Goals, and Long-Term Mechanisms. Financ. Trade Econ. 2025, 46, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, K.Z.; Xu, H.Z. Does urban-rural integration reduce rural poverty? Agribusiness 2024, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.J.; Meng, L.J.; Zeng, X.T.; Ma, L.X. How Urban-Rural Integration Symbiosis Can Ameliorate the Socioeconomic Inequity in Ecological Space: Evidence from Yunnan, China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.C.; Zhuang, J.K.; Yang, C.L.; Li, L.; Kong, M. How the digital economy promotes urban-rural integration through optimizing factor allocation: Theoretical mechanisms and evidence from China. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2025, 9, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Li, S.C. A policy analysis of China’s sustainable rural revitalization: Integrating environmental, social and economic dimensions. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.X.; Liu, C.J.; Chen, X.H. Power of Digital Economy to Drive Urban-Rural Integration: Intrinsic Mechanism and Spatial Effect, from Perspective of Multidimensional Integration. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 5459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lu, Y.Q.; Zhu, Y.M. Can the integration between urban and rural areas be realized? A new theoretical analytical framework. J. Geogr. Sci. 2024, 34, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lidder, P.; Cattaneo, A.; Chaya, M. Innovation and technology for achieving resilient and inclusive rural transformation. Glob. Food Secur.-Agric. Policy 2025, 44, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H.X. Agricultural specialization activates the industry chain: Implications for rural entrepreneurship in China. Agribusiness 2024, 40, 950–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Y. Development Research on Rural Human Resources under Urban-rural Integration. Agro Food Ind. Hi-Tech 2017, 28, 2974–2978. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Z.; Zhang, F.; Li, Z.G.; Wei, H. Urban-Rural Health Insurance Integration and China’s Rural Household Savings. Risk Manag. Healthc. Policy 2024, 17, 587–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, W.; Mai, L.; Chen, Y. Assessing the expenditure decentralization in enhancing public service quality: Evidence from 29 province in China. Eval. Program Plan. 2025, 110, 102551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.Z.Y.; Liu, H. The Influence and Mechanism of Digital Village Construction on the Urban-Rural Income Gap under the Goal of Common Prosperity. Agriculture 2024, 14, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.Q.; Guo, W.J.; Wang, Y.F. A Study of the Impact of New Quality Productive Forces on Agricultural Modernization: Empirical Evidence from China. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.X.; Fu, B.W.; Cui, X.F. Does urban-rural integration contribute to environmental health? Exploring the interplay between urban-rural integration and air quality dynamics in Yangtze River middle reaches city cluster. Front. Public Health 2025, 12, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Wang, Z.K.; Sun, B.; Yue, Y.Y. Urban digital economy, environmental pollution, and resident’s health-empirical evidence from China. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Osewe, M.; Anastacia, C.; Liu, A.J.; Wang, S.T.; Latif, A. Agricultural Supply-Side Structural Reform and Path Optimization: Evidence from China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, T.; Xie, N.; Hanim, W.; Qin, Y.L. Digital-green synergistic transition, fiscal decentralization and regional green total factor productivity in agriculture. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 385, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.R. Path Analysis of Agricultural Economy Information Construction under the Perspective of Urban-Rural Integration Strategy in the “Internet Plus” Era. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2022, 2022, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.H.; Hu, Z.C. Approaching Integrated Urban-Rural Development in China: The Changing Institutional Roles. Sustainability 2015, 7, 7031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ncube, X.; Pittock, J. Application of social network analysis in determining innovation information exchange at irrigation schemes in Zimbabwe. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2025, 41, 447–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, J. Farmers’ Perspectives on Quality of Agricultural Information Delivery: A Comparison between Public and Private Sources. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2013, 15, 685–696. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, B.Y.; Zhang, Q.; Ren, Q.X.; Yu, X.W.; Chen, Y.Q. Spatial heterogeneity of urban-rural integration and its influencing factors in Shandong province of China. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.R.; Zhao, X.J.; Lu, J.X. Measuring the Level of Urban-Rural Integration Development and Analyzing the Spatial Pattern Based on the New Development Concept: Evidence from Cities in the Yellow River Basin. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.W.; Li, X.J.; Hu, X.Y.; Li, Z.Y. Spatiotemporal Evolution and Influencing Factors of Urban-rural Construction Land in Rural Industrialized Areas in China: Case Studies in Changyuan City and Xinxiang County of Henan Province. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2023, 33, 850–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.L.; Ma, X.J.; Liu, Y.; Zhong, F.L. Can China’s New Infrastructure Promote Urban-Rural Integrated Development? Evidence from 31 Chinese Provinces. Buildings 2024, 14, 3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhu, Y.L. Impact of Labour Productivity Differences on Urban-Rural Integration Development and Its Spatial Effect: Evidence from a Spatial Durbin Model. Complexity 2022, 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.G.; Yang, Q.S.; Liu, J. Spatio-Temporal Evolution and Influencing Factors of Integrated Urban-Rural Development in Northeast China under the Background of Population Shrinkage. Buildings 2023, 13, 2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.P.; Deng, A. Using POI Data and Baidu Migration Big Data to Modify Nighttime Light Data to Identify Urban and Rural Area. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 93513–93524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Sun, M.Y.; Zeng, L.J.; Chen, Y.F. Spatial distribution and influencing factors of modem agriculture parks—Taking modern agriculture demonstration zone in Guangxi as an example. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2021, 30, 7070–7082. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Analysis of spatial effect of digital economy on urban-rural integration development. Res. Agric. Mod. 2025, 46, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Dai, Y. Digital economy and integrated urban- rural development: Theoretical mechanism and empirical test. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2024, 38, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.M.; Gao, Y.J.; Tang, M.N.; Ma, A.H. Promoting or inhibiting? The impact of urban-rural integration on the green transformation of arable land utilization: Evidence from China’s major grain-producing regions. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 176, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Fang, C.; Ma, H.; Hu, X. How does digital economy affect urban-rural integration? An empirical study from China. Habitat Int. 2024, 154, 103229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.; Wang, G. Urbanization, industrial structure upgrading and high-quality economic development—Test of mediation effect based on spatial Durbin model. Syst. Eng. Theory Pract. 2023, 43, 648–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhuang, J.C.; Chang, Q.X.; Ma, X.L.; Jia, P.; Li, Z.H. Research on the heterogeneous threshold effect of rural informatization on rural economic growth. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2020, 29, 7562–7567. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, R.; Ran, G.H.; Zheng, Q.; Wu, X.J. The nonlinear effect of agricultural informatization on agricultural total factor productivity in China: A threshold test approach. Cust. Agronegocio 2018, 14, 213–236. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Ma, G.F.; Tian, Y.; Dong, Q.Y. Nonlinear Effect of Digital Economy on Urban-Rural Consumption Gap: Evidence from a Dynamic Panel Threshold Analysis. Sustainability 2023, 15, 6880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.L.; Shao, W. How does digital economy drive industrial structure upgrading: An empirical study based on 249 prefecture-level cities in China. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, M. Can rural e-commerce narrow the urban-rural income gap? Evidence from coverage of Taobao villages in China. China Agric. Econ. Rev. 2023, 15, 580–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Primary | Secondary | Definition and Description | Properties | Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urban–rural economic integration | Ratio of urban–rural income | Per capita income of urban residents/Per capita income of rural residents | − | 0.0172 |
| Urban–rural household expenditure ratio | Per capita consumption of urban residents/Per capita consumption of rural residents | − | 0.0149 | |
| Urban–rural Engel coefficient differential | urban Engel’s coefficient/ rural Engel’s coefficient | + | 0.0141 | |
| Ratio of industrial output value | Secondary and tertiary industry output value/ Primary industry output value | + | 0.3658 | |
| Urban–rural population integration | Ratio of non-farm-to-farm employment | Proportion of people employed in the secondary and tertiary industries/ Proportion of people employed in the primary industry | + | 0.2430 |
| Urbanization rate | Urban population/total population | + | 0.0297 | |
| Ratio of urban–rural population density | Urban population density/Rural population density | − | 0.0095 | |
| Urban–rural social integration | Urban–rural disparity in education and entertainment expenditure | Per capita expenditure on education and entertainment in urban households/ Per capita expenditure on education and entertainment in rural households | − | 0.0037 |
| Level of urban–rural medical security | Hospital bed density per 10,000 people by residency (urban/rural) | + | 0.0312 | |
| Level of urban–rural social security | Urban and rural social security and employment expenditure/ General budget expenditure | + | 0.0476 | |
| Comparative coefficient of per capita healthcare in urban and rural areas | Per capita healthcare expenditure in urban areas/ Per capita healthcare expenditure in rural areas | − | 0.0041 | |
| Urban–rural space integration | Road area per capita | Road surface/Population size | + | 0.0303 |
| Per capita park green space | Green space/Population size | + | 0.0236 | |
| Transport network density | (Road mileage + Railway operating mileage)/ Total land area | + | 0.0519 | |
| Ratio of built-up area | Built-up area/city area | + | 0.0402 | |
| Urban–rural ecology integration | Sewage treatment rate | Sewage treatment capacity/Total wastewater discharge | + | 0.0061 |
| Environmental protection expenditure | Local financial expenditure on environmental protection | + | 0.0641 | |
| Household waste sanitization level | Quantity of household waste treated in an environmentally sound manner/ Household waste generation | + | 0.0030 |
| Indicator Category | Definition and Description | Properties | Weights |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agricultural laborers | Average years of education of rural labor force | + | 0.0094 |
| Full-time equivalent R&D staff | + | 0.0981 | |
| Labor productivity in primary industry | + | 0.0354 | |
| Rural disposable income per capita | + | 0.0351 | |
| Agriculture-related labor objects | Intensity of chemical fertilizer use | − | 0.0155 |
| Carbon emissions from pesticides | − | 0.0137 | |
| Annual income from leisure agriculture and rural tourism | + | 0.0573 | |
| Ratio of green agricultural cooperatives to primary sector workforce size | + | 0.1352 | |
| Agricultural product processing industry operating income | + | 0.0854 | |
| Output value of agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry, and fishery | + | 0.0770 | |
| Means of agricultural labor | Ratio of rural road mileage to rural population | + | 0.0553 |
| Length of optical cable routes per unit area | + | 0.1137 | |
| Rural broadband access volume | + | 0.0568 | |
| Rural Digital Inclusive Finance Index | + | 0.0186 | |
| Average mobile phone ownership per 100 rural households | + | 0.0243 | |
| Area of machine-transplanted land per capita | + | 0.0931 | |
| Agricultural R&D investment | + | 0.0761 |
| Variable Category | Variables | Symbol | N | Mean | SD | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Explained variable | Urban–rural integration | URI | 300 | 0.204 | 0.101 | 0.087 | 0.788 |
| Core explanatory variable | Agricultural new quality productive forces | ANPF | 300 | 0.189 | 0.085 | 0.053 | 0.492 |
| Mediating variable | Industrial restructuring and upgrading | IND | 300 | 2.401 | 0.123 | 2.194 | 2.836 |
| Threshold variable | Level of informatization | INF | 300 | 0.065 | 0.056 | 0.015 | 0.290 |
| Control variables | Consumer demand | CONS | 300 | 1.165 | 0.949 | 0.055 | 4.488 |
| Economic development | ECO | 300 | 0.627 | 0.311 | 0.221 | 1.903 | |
| Opening up to the outside world | OPE | 300 | 0.254 | 0.262 | 0.008 | 1.362 | |
| Government intervention | GOV | 300 | 0.250 | 0.101 | 0.107 | 0.643 |
| Variables | URI | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | |
| ANPF | 0.666 *** (21.49) | 0.894 *** (15.35) | 0.180 *** (2.67) | 0.286 *** (4.55) | 0.268 *** (4.17) |
| CONS | −0.041 ** (−4.56) | −0.035 *** (−4.99) | −0.042 *** (−6.58) | −0.041 *** (−6.41) | |
| ECO | 0.247 *** (14.01) | 0.208 ** (12.34) | 0.214 *** (12.25) | ||
| OPE | −0.139 *** (−7.58) | −0.137 *** (−7.38) | |||
| GOV |
0.052
( 1.28 ) | ||||
| Fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| N | 300 | 300 | 300 | 300 | 300 |
| R2 | 0.632 | 0.658 | 0.803 | 0.838 | 0.839 |
| Variables | Model (1) | Model (2) | Model (3) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coef. | S.E. | Coef. | S.E. | Coef. | S.E. | |
| ANPF | 0.395 ** | 0.197 | 0.216 *** | 0.052 | 0.231 ** | 0.109 |
| Control variable | Yes | Yes | Yes | |||
| N | 300 | 300 | 150 | |||
| 95%CI | [0.009, 0.781] | [0.114, 0.318] | [0.015, 0.446] | |||
| R2 | 0.831 | 0.874 | 0.591 | |||
| Variables | Eastern | Central | Western |
|---|---|---|---|
| ANPF | 0.294 ** (2.33) | 0.196 *** (3.49) | 0.544 *** (8.22) |
| Control variable | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| N | 110 | 80 | 110 |
| 95%CI | [0.043, 0.546] | [0.084, 0.308] | [0.413, 0.676] |
| R2 | 0.854 | 0.951 | 0.938 |
| Variables | (1) | (2) |
|---|---|---|
| IND | URI | |
| ANPF | 0.759 *** (5.74) | 0.223 *** (3.28) |
| IND | 0.060 ** (2.03) | |
| Control variable | Yes | Yes |
| Fixed effects | Yes | Yes |
| N | 300 | 300 |
| R2 | 0.568 | 0.842 |
| Threshold Variables | Threshold Type | Threshold Value | F Value | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| INF | Single threshold | 0.049 ** | 38.330 | 0.033 |
| Double threshold | 0.054 *** | 50.620 | 0.000 |
| Variables | INF | |
|---|---|---|
| Threshold value | θ1 | 0.049 |
| θ2 | 0.054 | |
| ANPF × I (INFθ1) | 0.238 *** (4.21) | |
| ANPF × I (θ1 < INF < θ2) | 0.452 *** (7.62) | |
| ANPF × I (INF < θ2) | 0.280 *** (4.82) | |
| Control variable | Yes | |
| N | 300 | |
| R2 | 0.879 | |
| Year | ANPF | URI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moran’s I | Z Value | Moran’s I | Z Value | |
| 2013 | 0.076 *** | 3.105 | 0.100 *** | 4.121 |
| 2014 | 0.083 *** | 3.307 | 0.089 *** | 3.857 |
| 2015 | 0.082 *** | 3.297 | 0.092 *** | 3.920 |
| 2016 | 0.082 *** | 3.303 | 0.073 *** | 3.432 |
| 2017 | 0.080 *** | 3.218 | 0.071 *** | 3.366 |
| 2018 | 0.083 *** | 3.296 | 0.061 *** | 3.096 |
| 2019 | 0.088 *** | 3.403 | 0.061 *** | 3.056 |
| 2020 | 0.097 *** | 3.652 | 0.044 *** | 2.588 |
| 2021 | 0.095 *** | 3.600 | 0.027 ** | 2.099 |
| 2022 | 0.096 *** | 3.626 | 0.023 ** | 1.999 |
| Type of Test | Test Statistical Values | p Value |
|---|---|---|
| LM-Error | 2.918 * | 0.088 |
| Robust LM-Error | 0.016 | 0.899 |
| LM-Lag | 10.530 *** | 0.001 |
| Robust LM-Lag | 7.628 *** | 0.006 |
| Hausman | 44.150 *** | 0.000 |
| LR-ind | 36.680 *** | 0.000 |
| LR-time | 570.750 *** | 0.000 |
| Wald-sem | 29.040 *** | 0.000 |
| Wald-sar | 38.330 *** | 0.000 |
| Variables | Main (1) | Wx (2) | LR-Direct (3) | LR-Indirect (4) | LR-Total (5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANPF | 0.386 *** (4.900) | −0.851 * (−1.690) | 0.524 *** (6.400) | −0.692 *** (−3.380) | −0.168 (−0.790) |
| Control variable | Yes | ||||
| Fixed province | Yes | ||||
| Fixed time | Yes | ||||
| N | 300 | ||||
| R2 | 0.841 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, C.; Wang, S.; Xu, Y.; Hou, P.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X. The Transmission Mechanism and Spatial Spillover Effect of Agricultural New Quality Productive Forces on Urban–Rural Integration: Evidence from China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 6360. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17146360
Zhao C, Wang S, Xu Y, Hou P, Zhang Y, Liu X. The Transmission Mechanism and Spatial Spillover Effect of Agricultural New Quality Productive Forces on Urban–Rural Integration: Evidence from China. Sustainability. 2025; 17(14):6360. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17146360
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Cuiping, Siqing Wang, Yongsheng Xu, Peng Hou, Ying Zhang, and Xiaoyong Liu. 2025. "The Transmission Mechanism and Spatial Spillover Effect of Agricultural New Quality Productive Forces on Urban–Rural Integration: Evidence from China" Sustainability 17, no. 14: 6360. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17146360
APA StyleZhao, C., Wang, S., Xu, Y., Hou, P., Zhang, Y., & Liu, X. (2025). The Transmission Mechanism and Spatial Spillover Effect of Agricultural New Quality Productive Forces on Urban–Rural Integration: Evidence from China. Sustainability, 17(14), 6360. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17146360





