SDG 6 in Practice: Demonstrating a Scalable Nature-Based Wastewater Treatment System for Pakistan’s Textile Industry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling and Analysis of Textile Effluent
2.2. Bacterial Selection and Inoculum Preparation
2.3. Vegetation
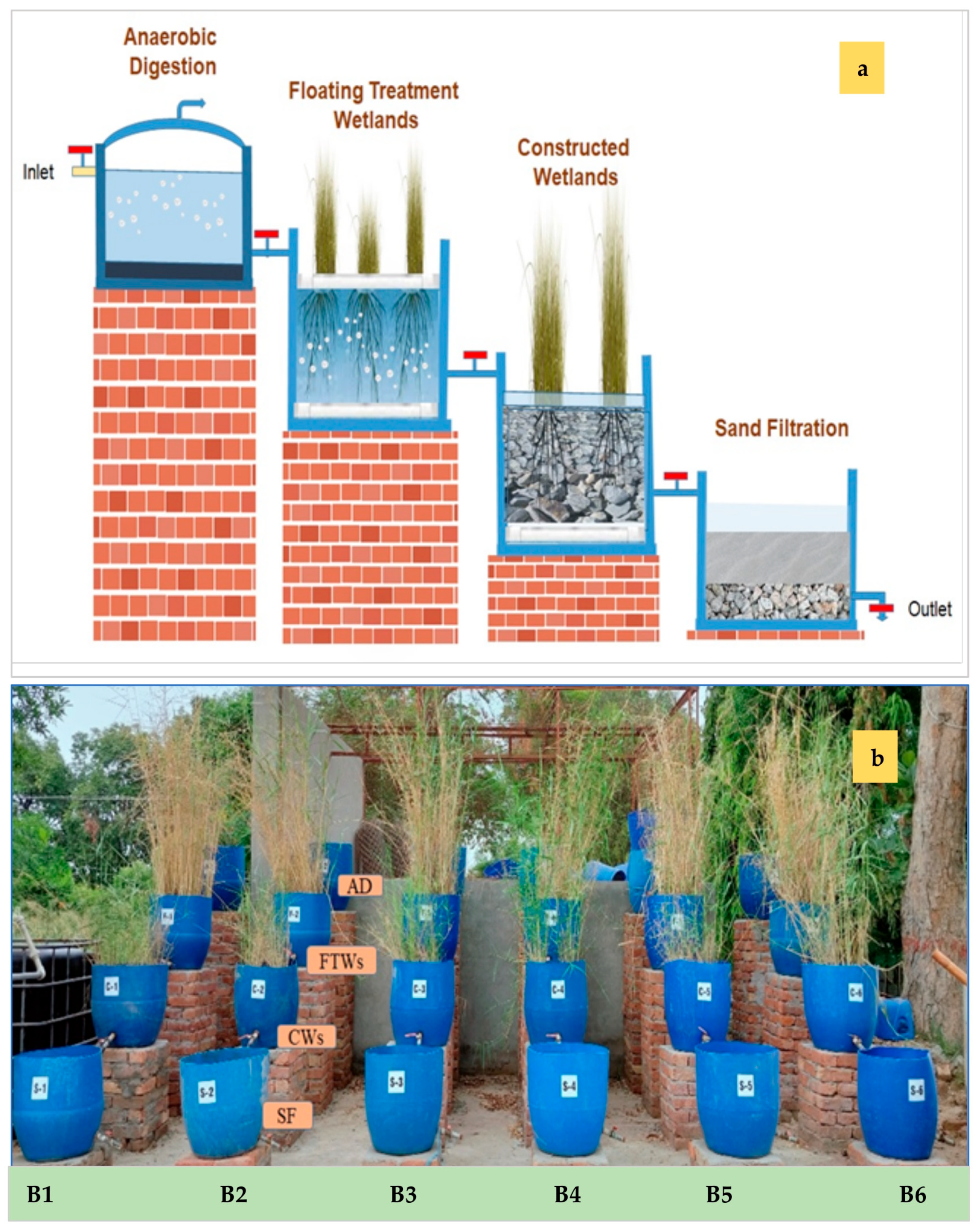
2.4. Development of an Integrated Bioreactor
2.4.1. Anaerobic Digester (AD)
2.4.2. Floating Treatment Wetlands (FTW)
2.4.3. Constructed Wetlands (CW)
2.4.4. Sand Filter (SF)
2.5. Intensification of Bioreactors
2.6. Trace Metals Analysis
2.7. Plant Biomass and Growth Analysis
2.8. Survival of Inoculated Bacterial Strains
2.9. Toxicity Analysis
2.10. Assessment of Contaminants in Water and Plant Samples
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Textile Wastewater Characteristics
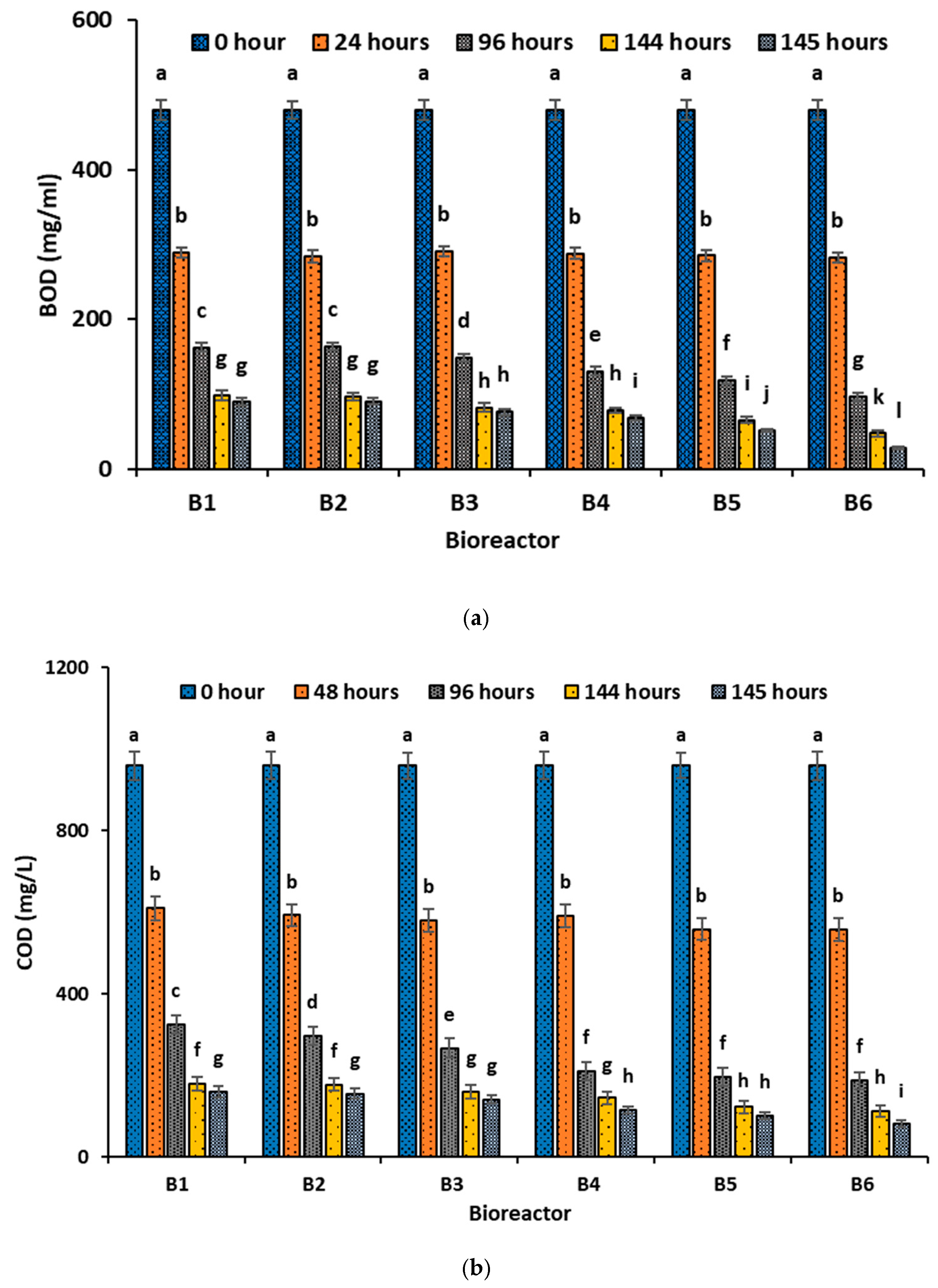
3.2. Biodegradation of Textile Wastewater
3.3. Performance of the Intensified Integrated Bioreactors
- (a)
- Basic Water Quality Parameters
- (b)
- Removal of Nutrients
- (c)
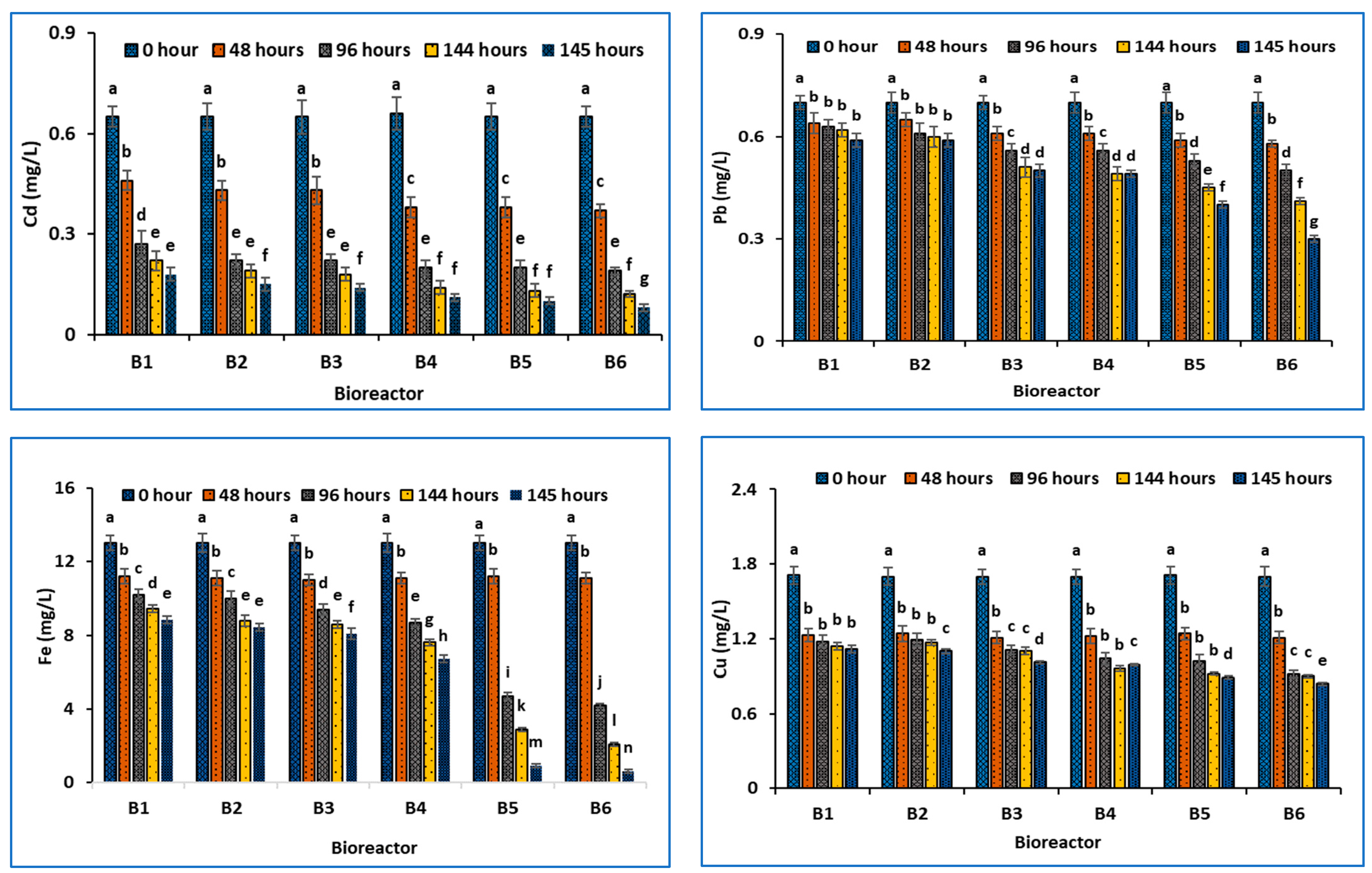
- Trace Metal Removal
- (d)
- Persistence of the Inoculated Bacteria
- (e)
- Effects on Plant Growth
- (f)
- Phytotoxicity Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Imminent Risk of a Global Water Crisis, Warns the UN World Water Development Report. 2023. Available online: https://www.unesco.org/en/articles/imminent-risk-global-water-crisis-warns-un-world-water-development-report-2023 (accessed on 6 January 2025).
- Water Pollution: Everything You Need to Know. Available online: https://www.nrdc.org/stories/water-pollution-everything-you-need-know (accessed on 6 January 2025).
- UN World Water Development Report 2017—Wastewater, the Untapped Resource. Available online: https://www.unesco.org/en/wwap/wwdr/2017 (accessed on 6 January 2025).
- Wastewater A Resource that Can Pay Dividends for People, the Environment, and Economies, Says World Bank. Available online: https://www.worldbank.org/en/news/press-release/2020/03/19/wastewater-a-resource-that-can-pay-dividends-for-people-the-environment-and-economies-says-world-bank#:~:text= (accessed on 6 January 2025).
- Parveen, F.; Khan, S.J. Wastewater Treatment in Pakistan: Issues, Challenges and Solutions. In Water Policy in Pakistan: Issues and Options, 1st ed.; Ahmad, M., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Faisalabad, Pakistan, 2023; Volume 30, p. 323349. [Google Scholar]
- Obaideen, K.; Shehata, N.; Sayed, E.T.; Abdelkareem, M.A.; Mahmoud, M.S.; Olabi, A.G. The role of wastewater treatment in achieving sustainable development goals (SDGs) and sustainability guideline. Energy Nexus 2022, 7, 100112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Mo, Y.; Gu, X.; Jeppesen, E.; Xie, T.; Ning, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, D.; Chen, C.; Cui, B.; et al. Sustainability of global small-scale constructed wetlands for multiple pollutant control. NPJ Clean Water 2024, 7, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumtaz, A. Accelerating the Achievement of Water-Related SDGs; Pakistan Council of Research in Water Resource: Phnom Penh, Cambodia, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Fatima, B.; Ashraf, M.; Hasan, F.U. Policy Brief Sustainable Development Goal 6: Setting the Course Right; Pakistan Council of Research in Water Resources (PCRWR): Islamabad, Pakistan, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Government of Pakistan, Ministry of Water Resources. National Water Policy; Government of Pakistan, Ministry of Water Resources: Islamabad, Pakistan, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kalengyo, R.B.; Ibrahim, M.G.; Fujii, M.; Nasr, M. Utilizing orange peel waste biomass in textile wastewater treatment and its recyclability for dual biogas and biochar production: A techno-economic sustainable approach. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2024, 14, 19875–19888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demarema, M.; Nasr, S.; Ookawara, S.; Demarema, S.; Nasr, M.; Ookawara, S.; Abdelhaleem, A. Enhanced synergistic system for the persulfate activation under visible light using novel N-ZnO photocatalyst supported on Lantana camara-based biochar. Chemosphere 2024, 349, 140840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nhan, N.T.; Luu, T.L. Fabrication of novel Ti/SnO2-Nb2O5 electrode in comparison with traditional doping metal oxides for electrochemical textile wastewater treatment. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2023, 32, 103292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortunato, L.; Elcik, H.; Blankert, B.; Ghaffour, N.; Vrouwenvelder, J. Textile dye wastewater treatment by direct contact membrane distillation: Membrane performance and detailed fouling analysis. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 636, 119552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rottle, N.; Bowles, M.; Andrews, L.; Engelke, J. Constructed floating wetlands: A “safe-to-fail” study with multi-sector participation. Restor. Ecol. 2023, 31, 13672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, Z.; Arslan, M.; Malik, M.H.; Mohsin, M.; Iqbal, S.; Afzal, M. Treatment of the textile industry effluent in a pilot-scale vertical flow constructed wetland system augmented with bacterial endophytes. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 966–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.B.; Sukias, J.P.; Tanner, C.C. Floating treatment wetlands supplemented with aeration and biofilm attachment surfaces for efficient domestic wastewater treatment. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 139, 105582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tara, N.; Iqbal, M.; Khan, Q.M.; Afzal, M. Bioaugmentation of floating treatment wetlands for the remediation of textile effluent. Water Environ. J. 2019, 33, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waly, M.M.; Ahmed, T.; Abunada, Z.; Mickovski, S.B.; Thomson, C. Constructed wetland for sustainable and low-cost wastewater treatment. Land 2022, 11, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floating or Constructed Wetlands: Nature-Based Water Treatments Being Tested in Cities in Southeast Asia. Available online: https://inowasia.com/floating-or-constructed-wetlands-nature-based-water-treatments-being-tested-in-cities-in-southeast-asia/?utm_source=chatgpt.com (accessed on 6 January 2025).
- Wang, C.Y.; Sample, D.J. Assessment of the nutrient removal effectiveness of floating treatment wetlands applied to urban retention ponds. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 137, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozema, E.R.; VanderZaag, A.C.; Wood, J.D.; Drizo, A.; Zheng, Y.; Madani, A.; Gordon, R.J. Constructed wetlands for agricultural wastewater treatment in Northeastern North America: A review. Water 2016, 8, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younas, A.; Kumar, L.; Deitch, M.J.; Qureshi, S.S.; Shafiq, J.; Naqvi, A.S.; Kumar, A.; Amjad, A.Q.; Nizamuddin, S. Treatment of industrial wastewater in a floating treatment wetland: A case study of Sialkot Tannery. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonkamble, S.; Wajihuddin, M.; Jampani, M.; Sarah, S.; Somvanshi, V.K.; Ahmed, S.; Amerasinghe, P.; Boisson, A. Natural treatment system models for wastewater management: A study from Hyderabad, India. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 77, 479–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Tang, W.; Wang, W.; Yin, W.; Liu, H.; Ma, X.; Zhou, Y.; Lei, P.; Wei, D.; Zhang, L.; et al. A review on China’s constructed wetlands in recent three decades: Application and Practice. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 104, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, A.; Singh, H.O.; Raja, S.K.; Dixit, S. Constructed wetland for improved wastewater management and increased water use efficiency in resource scarce SAT villages: A case study from Kothapally village, in India. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2021, 23, 1067–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, T.; Fu, W.; Tang, C.; Yuan, Y.; Yin, Q.; Wang, C. Utilization of constructed wetland technology in China’s sponge city scheme under carbon neutral vision. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 53, 103828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Public Health Association. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1926; Volume 6. [Google Scholar]
- Sutton, S. Measurement of microbial cells by optical density. J. Valid. Technol. 2011, 17, 46–49. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, W.U.; Khan, M.D.; Khan, M.Z.; Halder, G. Anaerobic biodegradation of benzene-laden wastewater under mesophilic environment and simultaneous recovery of methane-rich biogas. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 2957–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azanaw, A.; Birlie, B.; Teshome, B.; Jemberie, M. Textile effluent treatment methods and eco-friendly resolution of textile wastewater. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2022, 6, 100230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, H.S.; Chou, S.; Chang, K.F.; Ni, C.H.; Pan, J.R.; Huang, C. Membrane-coupled methanogenic and facultative bioreactor in wastewater treatment. IEEE Trans. Semicond. Manuf. 2007, 20, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, H.; Rehman, K.; Arslan, M.; Afzal, M. Enhanced degradation of phenol in floating treatment wetlands by plant-bacterial synergism. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2018, 20, 692–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, Y.; Srivastava, P.; Pandey, S.; Yadav, A.K. Development of nature-based sustainable passive technologies for treating and disinfecting municipal wastewater: Experiences from constructed wetlands and slow sand filter. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 900, 165320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashmat, A.J.; Afzal, M.; Arias, C.A.; Ramirez-Vargas, C.A.; Brix, H. Enhanced degradation of hydrocarbons in constructed wetlands aided with nutrients, surfactant, and aeration. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2022, 24, 1163–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefani, F.O.; Bell, T.H.; Marchand, C.; De La Providencia, I.E.; El Yassimi, A.; St-Arnaud, M.; Hijri, M. Culture-dependent and-independent methods capture different microbial community fractions in hydrocarbon-contaminated soils. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urrea-Valencia, S.; Melo, A.L.D.A.; Gonçalves, D.R.P.; Galvão, C.W.; Etto, R.M. Molecular techniques to study microbial wastewater communities. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2021, 64, 21200193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeli, M.; Yamini, Y.; Faraji, M. Removal of copper, nickel and zinc by sodium dodecyl sulphate coated magnetite nanoparticles from water and wastewater samples. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S514–S521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, P.K. Heavy metals/metalloids remediation from wastewater using free floating macrophytes of a natural wetland. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2019, 15, 100393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, I.; Naqvi, S.N.H.; Mohsin, H.; Fatima, K.; Afzal, M.; Al-Misned, F.; Bibi, I.; Ali, F.; Niazi, N.K. The evaluation of bacterial-augmented floating treatment wetlands for concomitant removal of phenol and chromium from contaminated water. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2024, 26, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raudonius, S. Application of statistics in plant and crop research: Important issues. Zemdirb. Agric. 2017, 104, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, J.; Fox, L.J.; Owen Jr, J.S.; Sample, D.J. Evaluation of commercial floating treatment wetland technologies for nutrient remediation of stormwater. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 75, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abed, S.N.; Almuktar, S.A.; Scholz, M. Remediation of synthetic graywater in mesocosm—Scale floating treatment wetlands. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 102, 303–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Han, B.; Liu, Z. Floating-leaved macrophyte (Trapa quadrispinosa Roxb) beds have significant effects on sediment resuspension in Lake Taihu, China. Hydrobiologia 2007, 581, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borne, K.E. Floating treatment wetland influences on the fate and removal performance of phosphorus in stormwater retention ponds. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 69, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora-Orozco, D.L.C.; González-Acuña, I.J.; Saucedo-Terán, R.A.; Flores-López, H.E.; Rubio-Arias, H.O.; Ochoa-Rivero, J.M. Removing organic matter and nutrients from pig farm wastewater with a constructed wetland system. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tara, N.; Arslan, M.; Hussain, Z.; Iqbal, M.; Khan, Q.M.; Afzal, M. On-site performance of floating treatment wetland macrocosms augmented with dye-degrading bacteria for the remediation of textile industry wastewater. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 217, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, P.S.; Singh, K.; Choudhary, A.; Brighu, U.; Singh, S.K.; Bhattacharya, S. Combined advanced oxidation dye-wastewater treatment plant: Design and development with data-driven predictive performance modeling. NPJ Clean Water 2024, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, X.; Pyo, S.H. Current problems and countermeasures of constructed wetland for wastewater treatment: A review. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 57, 104569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colares, G.S.; Dell’Osbel, N.; Barbosa, C.V.; Lutterbeck, C.; Oliveira, G.A.; Rodrigues, L.R.; Bergmann, C.P.; Lopez, D.R.; Rodriguez, A.L.; Vymazal, J.; et al. Floating treatment wetlands integrated with microbial fuel cell for the treatment of urban wastewaters and bioenergy generation. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 766, 142474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bano, S.; Tahira, S.A.; Naqvi, S.N.H.; Tahseen, R.; Shabir, G.; Iqbal, S.; Afzal, M.; Amin, M.; Boopathy, R.; Mehmood, M.A. Improved remediation of amoxicillin-contaminated water by floating treatment wetlands intensified with biochar, nutrients, aeration, and antibiotic-degrading bacteria. Bioengineered 2023, 14, 2252207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Mashaqbeh, O.; Alsalhi, L.; Salaymeh, L.; Lyu, T. Assessment of novel hybrid treatment wetlands as nature-based solutions for pharmaceutical industry wastewater treatment. Water Environ. J. 2024, 38, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parashar, V.; Singh, S.; Purohit, M.R.; Tamhankar, A.J.; Singh, D.; Kalyanasundaram, M.; Lundborg, C.S.; Diwan, V. Utility of constructed wetlands for treatment of hospital effluent and antibiotic resistant bacteria in resource limited settings: A case study in Ujjain, India. Water Environ. Res. 2022, 94, 10783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elango, G.; Govindasamy, R. Removal of color from textile dyeing effluent using temple waste flowers as ecofriendly adsorbent. IOSR J. Appl. Chem. 2018, 11, 19–28. [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho, P.N.; Finger, D.C.; Masi, F.; Cipolletta, G.; Oral, H.V.; Tóth, A.; Regelsberger, M.; Exposito, A. Nature-based solutions addressing the water-energy-food nexus: Review of theoretical concepts and urban case studies. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 338, 130652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, N.; Zhang, X.; Cai, M.; Zhou, L.; Chen, G.; Zou, G. Roles of vegetation in nutrient removal and structuring microbial communities in different types of agricultural drainage ditches for treating farmland runoff. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 155, 105941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijaz, A.; Imran, A.; Anwar ul Haq, M.; Khan, Q.M.; Afzal, M. Phytoremediation: Recent advances in plant-endophytic synergistic interactions. Plant Soil 2016, 405, 179–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaballah, M.S.; Ismail, K.; Aboagye, D.; Ismail, M.M.; Sobhi, M.; Stefanakis, A.I. Effect of design and operational parameters on nutrients and heavy metal removal in pilot floating treatment wetlands with Eichhornia Crassipes treating polluted lake water. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 25664–25678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sessitsch, A.; Kuffner, M.; Kidd, P.; Vangronsveld, J.; Wenzel, W.W.; Fallmann, K.; Puschenreiter, M. The role of plant-associated bacteria in the mobilization and phytoextraction of trace elements in contaminated soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 60, 182–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkhair, K.S.; Ashraf, M.A. Field accumulation risks of heavy metals in soil and vegetable crop irrigated with sewage water in western region of Saudi Arabia. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 23, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.S.; Sarker, P.; Rahaman, M.S.; Uddin, M.K. Integrated performance of Fenton process and filtration (Activated Charcoal and Sand) for textile wastewater treatment. Curr. J. Appllied Sci. Technololy 2020, 39, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ćurić, I.; Dolar, D.; Bošnjak, J. Reuse of textile wastewater for dyeing cotton knitted fabric with hybrid treatment: Coagulation/sand filtration/UF/NF-RO. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 295, 113133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Kunnoth, B.; Pilli, S.; Rao, P.V.; Tyagi, R.D. Novel hybrid system for organic matter removal and energy production from dairy and textile wastewaters: Anaerobic digestion and electrocoagulation approach. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breil, P.; Pons, M.N.; Armani, G.; Amer, R.; Pienaar, H.; Oberholster, P.; Namour, P. Natural-based solutions for bioremediation in water environment. In Sustainable Solutions for Environmental Pollution: Air, Water and Soil Reclamation; El-Gendy, N.S., Ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 1–93. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.; De Araujo, C.; Sze, C.C.; Stuckey, D.C. Toxicity measurement in biological wastewater treatment processes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 286, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krewski, D.; Andersen, M.E.; Tyshenko, M.G.; Krishnan, K.; Hartung, T.; Boekelheide, K.; Wambaugh, J.F.; Jones, D.; Whelan, M.; Thomas, R.; et al. Toxicity testing in the 21st century: Progress in the past decade and future perspectives. Arch. Toxicol. 2020, 94, 1–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Unit | Value | NEQS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature | °C | 38 | 40 |
| pH | -- | 8.69 | 6–9 |
| Electrical conductivity (EC) | mS cm−1 | 7.24 | NG |
| Color | (m−1) | 75 | NG |
| Chemical oxygen demand (COD) | mg L−1 | 913 | 150 |
| Biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) | mg L−1 | 437 | 80 |
| Chloride | mg L−1 | 1600 | 1000 |
| Sulfate | mg L−1 | 890 | 600 |
| Nitrogen (N) | mg L−1 | 1.38 | NG |
| Phosphorous (P) | mg L−1 | 0.56 | NG |
| Total dissolved solids (TDS) | mg L−1 | 3900 | 3500 |
| Total suspended solids (TSS) | mg L−1 | 260 | 200 |
| Iron (Fe) | mg L−1 | 12.54 | 8 |
| Cadmium (Cd) | mg L−1 | 0.35 | 0.1 |
| Lead (Pb) | mg L−1 | 0.67 | 0.5 |
| Copper (Cu) | mg L−1 | 1.38 | 1.0 |
| Treatment | pH | Color (m−1) | COD (mg L−1) | BOD (mg L−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 8.09 a ± 0.75 | 75 a ± 6.2 | 913 a ± 32.8 | 437 a ± 20.4 |
| Pantoea gaviniae NT-3 | 7.92 a ± 0.71 | 25 b ± 3.4 | 470 b ± 19.2 | 204 b ± 16.4 |
| Enterobacter xiangfangensis NT-14 | 7.95 a ± 0.70 | 26 b ± 2.8 | 390 c ± 17.6 | 225 b ± 17.1 |
| Acinetobacter junii NT-15 | 7.48 a ± 0.46 | 20 c ± 1.5 | 310 e ± 12.8 | 175 c ± 11.2 |
| Pseudomonas monteilii NT-20 | 8.01 a ± 0.74 | 28 b ± 3.1 | 400 c ± 18.2 | 207 b ± 14.6 |
| Bacillus subtilis NT-23 | 7.80 a ± 0.68 | 27 b ± 3.0 | 360 d ± 16.0 | 217 b ± 16.4 |
| Pseudomonas indoloxydans NT-38 | 7.58 a ± 0.55 | 21 c ± 2.7 | 290 e ± 11.2 | 185 bc ± 13.2 |
| Rhodococcus sp. NT-39 | 7.52 a ± 0.50 | 22 bc ± 2.8 | 307 e ± 12.1 | 178 c ± 11.4 |
| Bioreactor | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| B1 | A1 | Anaerobic digester (AD) |
| F1 | FTW vegetated with P. australis | |
| C1 | CW vegetated with P. australis | |
| S1 | Sand filter (SF) | |
| B2 | A2 | AD + NP |
| F2 | FTW vegetated with P. australis | |
| C2 | CW vegetated with P. australis | |
| S2 | SF | |
| B3 | A3 | AD |
| F3 | FTW vegetated with P. australis + aeration | |
| C3 | CW vegetated with P. australis + aeration | |
| S3 | SF | |
| B4 | A4 | AD |
| F4 | FTW vegetated with P. australis + bacterial inoculation | |
| C4 | CW vegetated with P. australis + bacterial inoculation | |
| S4 | SF | |
| B5 | A5 | AD + NP |
| F5 | FTW vegetated with P. australis + bacterial inoculation | |
| C5 | CW vegetated with P. australis + bacterial inoculation | |
| S5 | SF | |
| B6 | A6 | AD + NP |
| F6 | FTW vegetated with P. australis + aeration + bacterial inoculation | |
| C6 | CW vegetated with P. australis + aeration + bacterial inoculation | |
| S6 | SF | |
| Bioreactor | pH | EC (mS cm−1) | TDS (mg L−1) | TSS (mg L−1) | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hours | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 0 h | 48 h | 96 h | 144 h | 145 h | 0 h | 48 h | 96 h | 144 h | 145 h | 0 h | 48 h | 96 h | 144 h | 145 h | 0 h | 48 h | 96 h | 144 h | 145 h | |
| B1 | 8.92 a (0.25) | 8.21 a (0.36) | 8.03 a (0.41) | 7.91 a (0.43) | 7.70 a (0.31) | 8.60 a (0.15) | 6.70 a (0.22) | 4.81 b (0.11) | 3.11 a (0.14) | 2.61 a (0.10) | 3900 a (140) | 3784 a (127) | 3630 a (136) | 3470 a (143) | 3100 a (105) | 261 a (16) | 230 a (13) | 218 a (14) | 200 a (11) | 188 a (12) |
| B2 | 8.90 a (0.29) | 8.10 a (0.37) | 7.93 a (0.41) | 7.82 a (0.38) | 7.48 a (0.26) | 8.60 a (0.16) | 6.51 a (0.17) | 5.20 a (0.14) | 3.10 a (0.11) | 2.01 b (0.10) | 3960 a (143) | 3745 a (128) | 3505 a (151) | 3421 a (119) | 3008 a (108) | 252 a (17) | 222 a (14) | 206 a (12) | 187 b (12) | 172 b (10) |
| B3 | 8.93 a (0.28) | 8.31 a (0.40) | 7.70 a (0.41) | 7.61 a (0.41) | 7.42 a (0.37) | 8.60 a (0.16) | 6.61 a (0.15) | 4.90 b (0.12) | 2.80 b (0.09) | 1.82 c (0.08) | 3900 a (141) | 3778 a (135) | 3456 a (129) | 3258 b (129) | 2825 b (128) | 246 a (16) | 232 a (12) | 198 a (10) | 180 b (11) | 168 b (13) |
| B4 | 8.90 a (0.22) | 8.10 a (0.41) | 7.72 a (0.37) | 7.61 a (0.35) | 7.61 a (0.28) | 8.61 a (0.14) | 6.61 a (0.12) | 4.91 b (0.08) | 2.60 c (0.10) | 1.61 d (0.07) | 3900 a (140) | 3778 a (133) | 3170 b (118) | 2859 b (142) | 2344 c (121) | 256 a (15) | 228 a (11) | 200 a (11) | 178 b (13) | 163 b (11) |
| B5 | 8.91 a (0.18) | 8.12 a (0.39) | 7.70 a (0.39) | 7.52 a (0.36) | 7.51 a (0.32) | 8.61 a (0.16) | 6.80 a (0.11) | 4.21 d (0.08) | 1.80 d (0.08) | 1.11 e (0.05) | 3965 a (144) | 3710 a (136) | 3010 c (124) | 2760 b (128) | 2267 c (130) | 260 a (15) | 236 a (12) | 198 a (14) | 168 b (10) | 133 c (12) |
| B6 | 8.97 a (0.12) | 8.21 a (0.40) | 7.71 a (0.27) | 7.60 a (0.35) | 7.40 a (0.32) | 8.60 a (0.14) | 6.10 b (0.08) | 4.40 c (0.05) | 1.60 e (0.02) | 1.00 f (0.01) | 3963 a (142) | 3700 a (133) | 2945 c (129) | 2610 c (127) | 2110d (120) | 262 a (14) | 225 a (11) | 188 a (13) | 152 c (8.8) | 128 d (9.3) |
| Bioreactor | Nitrogen (mg L−1) | Phosphorus (mg L−1) | Chlorides (mg L−1) | Sulfate (mg L−1) | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hours | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 0 | 48 | 96 | 144 | 145 | 0 | 48 | 96 | 144 | 145 | 0 | 48 | 96 | 144 | 145 | 0 | 48 | 96 | 144 | 145 | |
| B1 | 1.38 b (0.16) | 1.05 c (0.06) | 0.75 d (0.05) | 0.67 d (0.05) | 0.62 d (0.05) | 0.56 b (0.09) | 0.41 d (0.08) | 0.30 d (0.05) | 0.26 d (0.02) | 0.25 d (0.03) | 1600 a (85) | 1520 a (81) | 1342 a (79) | 1240 a (68) | 1200 de (55) | 890 a (35) | 810 a (31) | 764 a (28) | 684 a (25) | 660 a (24) |
| B2 | 50.0 a (0.80) | 41.1 a (2.60) | 33.0 a (1.90) | 23.1 a (1.50) | 21.0 a (2.02) | 10 a (0.30) | 7.85 a (0.80) | 5.20 a (0.65) | 4.75 a (0.34) | 4.3 a (0.16) | 1600 a (88) | 1518 a (82) | 1354 a (74) | 1237 a (72) | 1195 e (60) | 890 a (34) | 812 a (29) | 780 a (29) | 680 a (25) | 656 a (21) |
| B3 | 1.38 b (0.17) | 0.95 c (0.12) | 0.73 d (0.07) | 0.61 d (0.05) | 0.56 d (0.04) | 0.56 b (0.06) | 0.40 d (0.05) | 0.29 d (0.06) | 0.25 d (0.02) | 0.23 d (0.01) | 1600 a (88) | 1520 b (85) | 1298 a (71) | 1190 a (67) | 1001 f (53) | 890 a (35) | 810 a (31) | 747 b (31) | 635 b (23) | 615 b (21) |
| B4 | 1.38 b (0.16) | 1.08 c (1.70) | 0.70 d (1.50) | 0.54 d (1.30) | 0.48 d (1.28) | 0.56 b (0.12) | 0.43 d (0.08) | 0.30 d (0.06) | 0.23 d (0.08) | 0.19 d (0.05) | 1600 a (86) | 1525 a (81) | 1145 b (65) | 1101 b (57) | 1174 e (50) | 890 a (36) | 812 a (29) | 737 b (26) | 610 c (21) | 590 c (21) |
| B5 | 50 a (0.80) | 38.0 b (2.80) | 24.1 b (1.50) | 14.4 b (0.48) | 9.9 b (0.20) | 10 a (0.30) | 6.20 b (0.75) | 3.75 b (0.22) | 2.24 b (0.24) | 1.97 b (0.12) | 1600 a (87) | 1531 a (79) | 1093 b (64) | 1021 c (55) | 974 g (43) | 890 a (35) | 809 a (30) | 718 b (25) | 600 c (21) | 585 c (15) |
| B6 | 50 a (0.80) | 37.0 b (2.50) | 18.6 c (1.82) | 8.1 c (0.31) | 6.6 c (0.25) | 10 a (0.3) | 5.90 c (0.48) | 3.08 c (0.25) | 1.87 c (0.14) | 1.33 c (0.05) | 1600 a (89) | 1495 a (81) | 991 c (65) | 927 d (49) | 932 g (38) | 890 a (34) | 810 a (33) | 690 c (28) | 592 c (21) | 561 d (14) |
| Bioreactor | Cfu g−1 × 104 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acinetobacter junii 15 | Pseudomonas monteilii 20 | Rhodococcus sp. 39 | ||||||||||
| Root Interior | Shoot Interior | Root Interior | Shoot Interior | Root Interior | Shoot Interior | |||||||
| FTW | CW | FTW | CW | FTW | CW | FTW | CW | FTW | CW | FTW | CW | |
| B4 | 2.70 c (0.50) | 3.81 c (0.30) | 0.70 c (0.14) | 0.60 c (0.12) | 2.80 c (0.40) | 2.70 c (0.30) | 0.91 c (0.19) | 0.83 c (0.12) | 3.52 c (0.27) | 2.71 c (0.28) | 0.74 c (0.13) | 0.88 c (0.11) |
| B5 | 3.41 b (0.23) | 4.10 b (0.30) | 1.51 b (0.12) | 1.01 b (0.11) | 4.21 b (0.30) | 4.61 b (0.30) | 1.61 b (0.11) | 1.51 b (0.10) | 4.90 b (0.30) | 4.70 b (0.23) | 2.11 b (0.16) | 1.74 b (0.15) |
| B6 | 4.80 a (0.40) | 4.61 a (0.30) | 1.91 a (0.13) | 1.82 a (0.13) | 5.20 a (0.40) | 5.11 a (0.31) | 2.30 a (0.20) | 2.10 a (0.18) | 5.80 a (0.35) | 5.32 a (0.29) | 2.40 a (0.17) | 2.13 a (0.16) |
| Bioreactor | Germination Rate (%) | Average Root Length (mm) | Average Total Length (mm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UW | TW | UW | TW | UW | TW | |
| B1 | 30 a (3.0) | 75 b (5.3) | 11.1 e (0.60) | 23.0 d (1.30) | 20.1 e (0.80) | 52.1 d (2.60) |
| B2 | 31 a (2.6) | 81 ab (4.8) | 14.0 c (0.70) | 30.1 b (1.60) | 25.0 b (0.80) | 51.3 d (2.50) |
| B3 | 31 a (4.3) | 82 a (3.6) | 13.1 d (0.50) | 27.1 c (2.30) | 23.1 d (0.70) | 48.0 e (2.0) |
| B4 | 29 a (3.5) | 80 ab (5.4) | 14.0 c (0.45) | 29.3 b (1.30) | 24.0 c (0.80) | 49.0 e (2.0) |
| B5 | 30 a (2.8) | 82 a (3.2) | 15.1 b (0.45) | 30.0 b (1.85) | 25.2 b (0.80) | 51.0 d (1.95) |
| B6 | 31 a (3.5) | 86 a (3.5) | 16.2 a (0.70) | 32.0 a (1.65) | 27.1 a (0.85) | 52.1 d (1.75) |
| Bioreactor | Biomass (g) | Length (cm) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Root | Shoot | Root | Shoot | |||||||||
| Fresh | Dry | Fresh | Dry | |||||||||
| FTW | CW | FTW | CW | FTW | CW | FTW | CW | FTW | CW | FTW | CW | |
| B1 | 168 d (9.0) | 153 b (8.6) | 32 b (2.5) | 20 c (2.0) | 840 c (19.0) | 594 c (17.0) | 116 c (7.0) | 95 c (6.0) | 64.9 b (2.6) | 52.1 b (2.1) | 221.0 c (6.7) | 212.2 b (4.7) |
| B2 | 213 b (10.0) | 197 a (12.0) | 44 a (3.2) | 33 a (2.8) | 977 a (21.0) | 834 a (18.0) | 141 a (8.0) | 133 a (7.5) | 71.6 a (2.7) | 57.3 a (2.4) | 253.2 a (6.2) | 228.3 a (7.3) |
| B3 | 180 c (9.0) | 161 b (9.0) | 37 b (3.1) | 25 b (2.0) | 861 b (20.0) | 711 b (18.0) | 124 b (6.5) | 100 b (6.0) | 66.7 b (2.4) | 53.8 b (2.1) | 230.8 b (6.1) | 213.3 b (5.3) |
| B4 | 181 c (11.0) | 163 b (9.0) | 38 b (3.0) | 26 b (2.5) | 864 b (18.0) | 714 b (16.0) | 123 b (6.5) | 102 b (5.0) | 67.0 b (2.4) | 54.0 b (2.1) | 231.1 b (4.8) | 213.6 b (4.3) |
| B5 | 214 b (13.0) | 198 a (11.0) | 46 a (3.3) | 34 a (3.0) | 980 a (21.0) | 836 a (18.0) | 145 a (8.0) | 135 a (7.0) | 71.8 a (2.7) | 57.6 a (2.3) | 253.6 a (4.6) | 228.6 a (5.6) |
| B6 | 239 a (12.0) | 209 a (9.5) | 48 a (3.5) | 37 a (3.0) | 997 a (22.0) | 841 a (17.0) | 149 a (8.5) | 137 a (7.0) | 73.4 a (3.1) | 57.9 a (2.5) | 255.1 a (4.1) | 229.0 a (5.4) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Siddique, K.; Saleem, A.R.; Arslan, M.; Afzal, M. SDG 6 in Practice: Demonstrating a Scalable Nature-Based Wastewater Treatment System for Pakistan’s Textile Industry. Sustainability 2025, 17, 6226. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17136226
Siddique K, Saleem AR, Arslan M, Afzal M. SDG 6 in Practice: Demonstrating a Scalable Nature-Based Wastewater Treatment System for Pakistan’s Textile Industry. Sustainability. 2025; 17(13):6226. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17136226
Chicago/Turabian StyleSiddique, Kamran, Aansa Rukya Saleem, Muhammad Arslan, and Muhammad Afzal. 2025. "SDG 6 in Practice: Demonstrating a Scalable Nature-Based Wastewater Treatment System for Pakistan’s Textile Industry" Sustainability 17, no. 13: 6226. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17136226
APA StyleSiddique, K., Saleem, A. R., Arslan, M., & Afzal, M. (2025). SDG 6 in Practice: Demonstrating a Scalable Nature-Based Wastewater Treatment System for Pakistan’s Textile Industry. Sustainability, 17(13), 6226. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17136226







