Effects of Pyrolysis and Activation Conditions on SO2 and NO Adsorption by Biochar and Its Environmental Impact
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
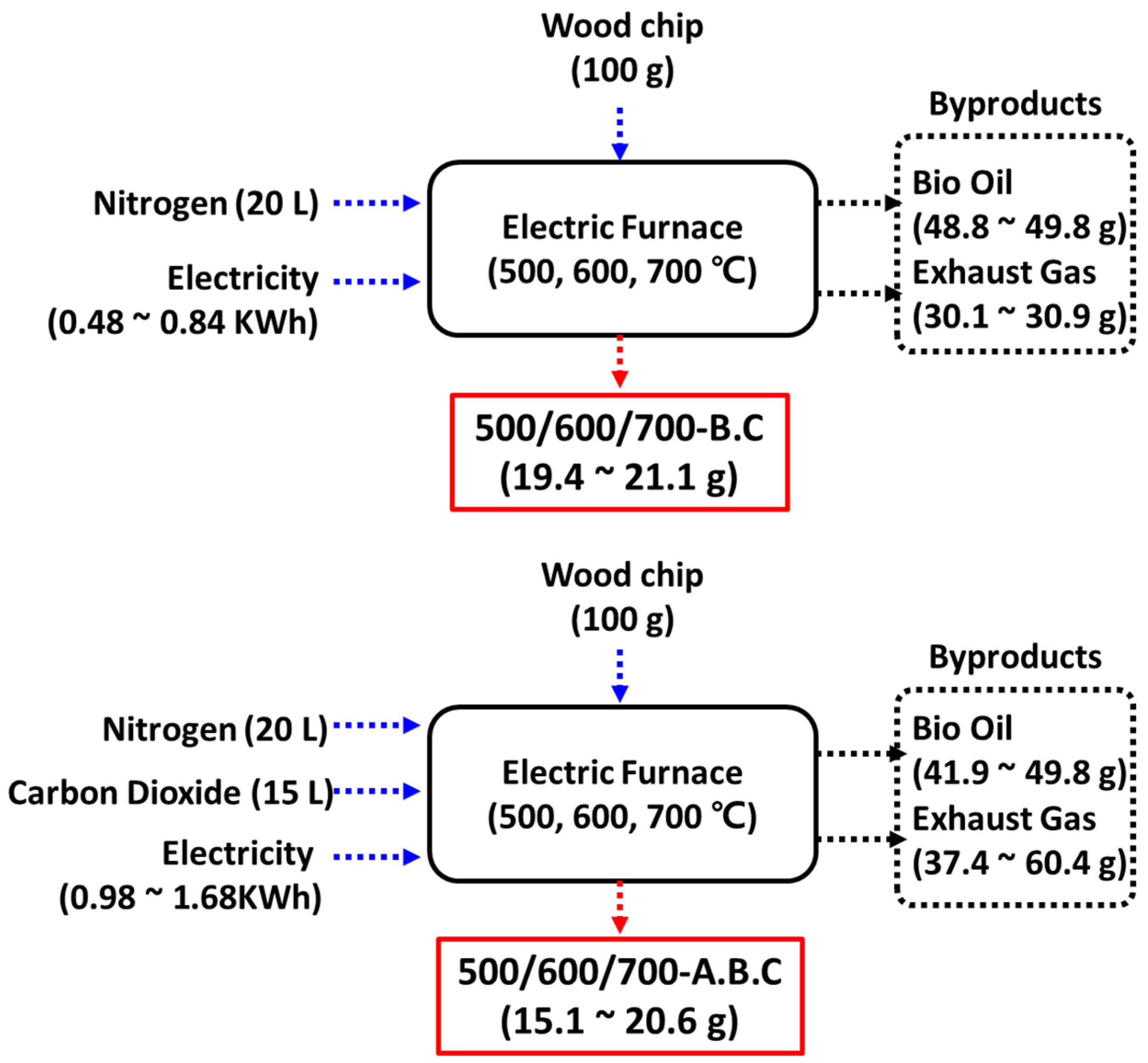
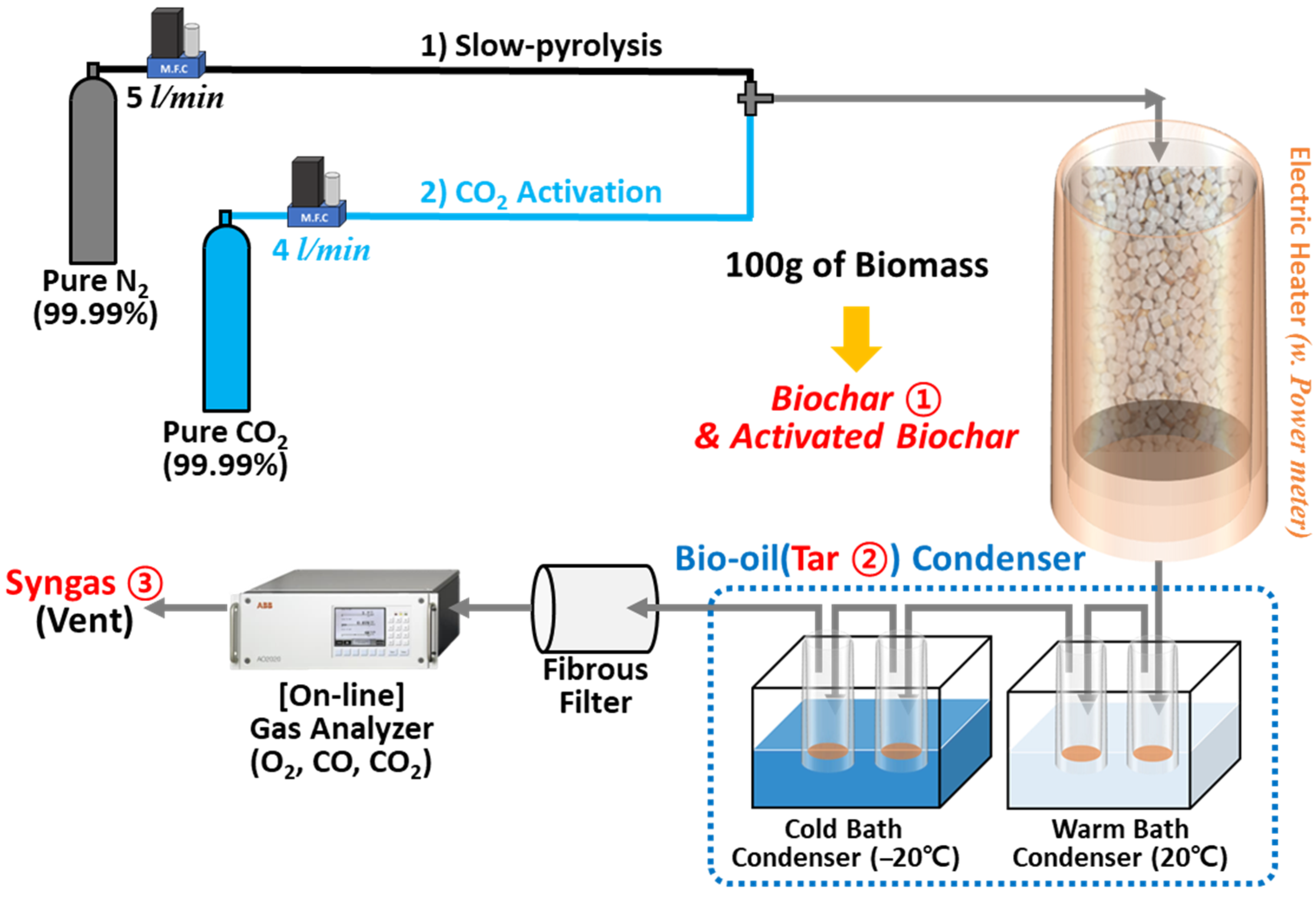
2.1. Synthesis of Biochar Through Pyrolysis and Analysis of It
2.2. Evaluation of Adsorption Performance of Biochar
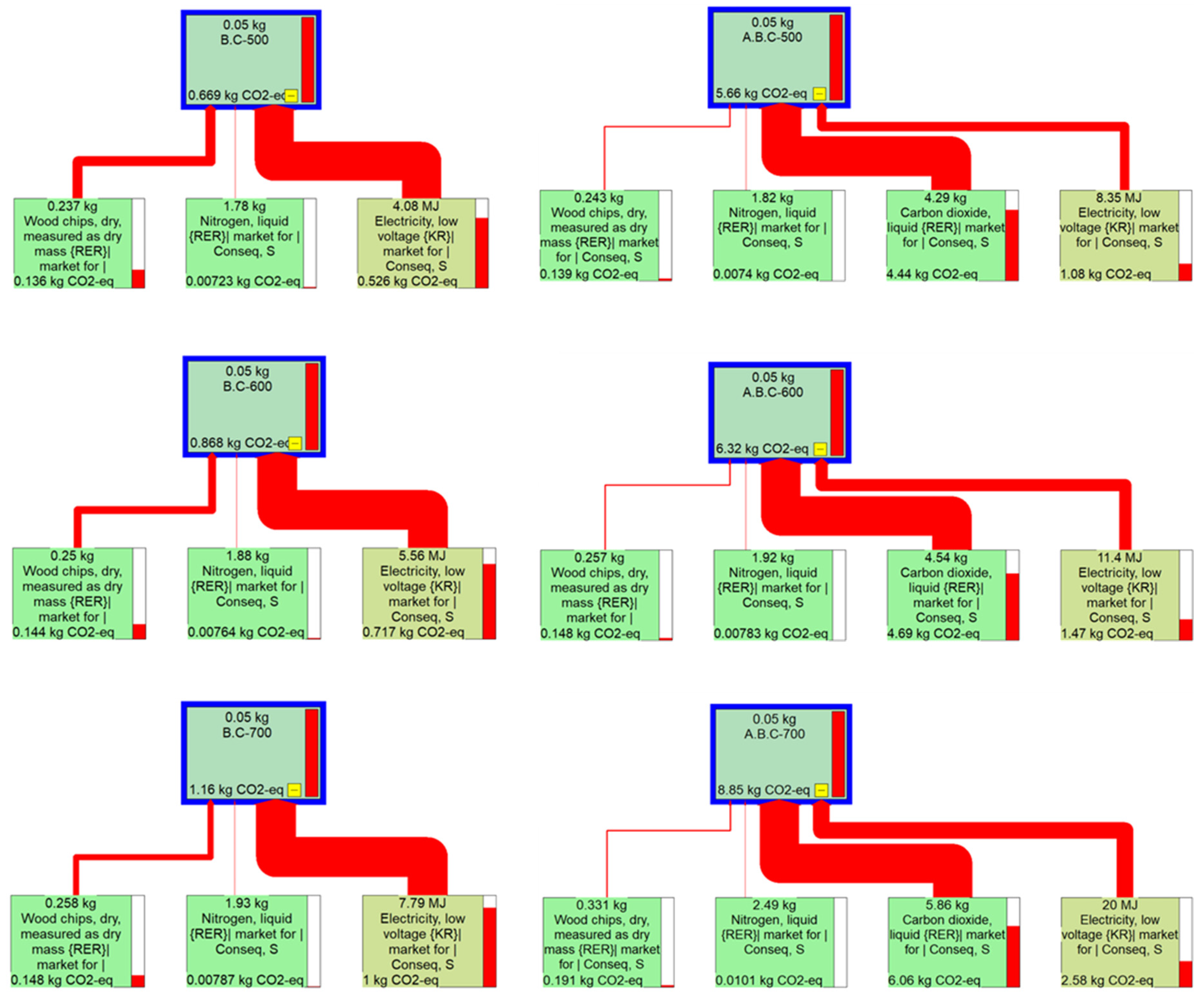
2.3. Life Cycle Assessment-Based Carbon Dioxide Emission of Gas Adsorption by Biochar
3. Results and Discussion
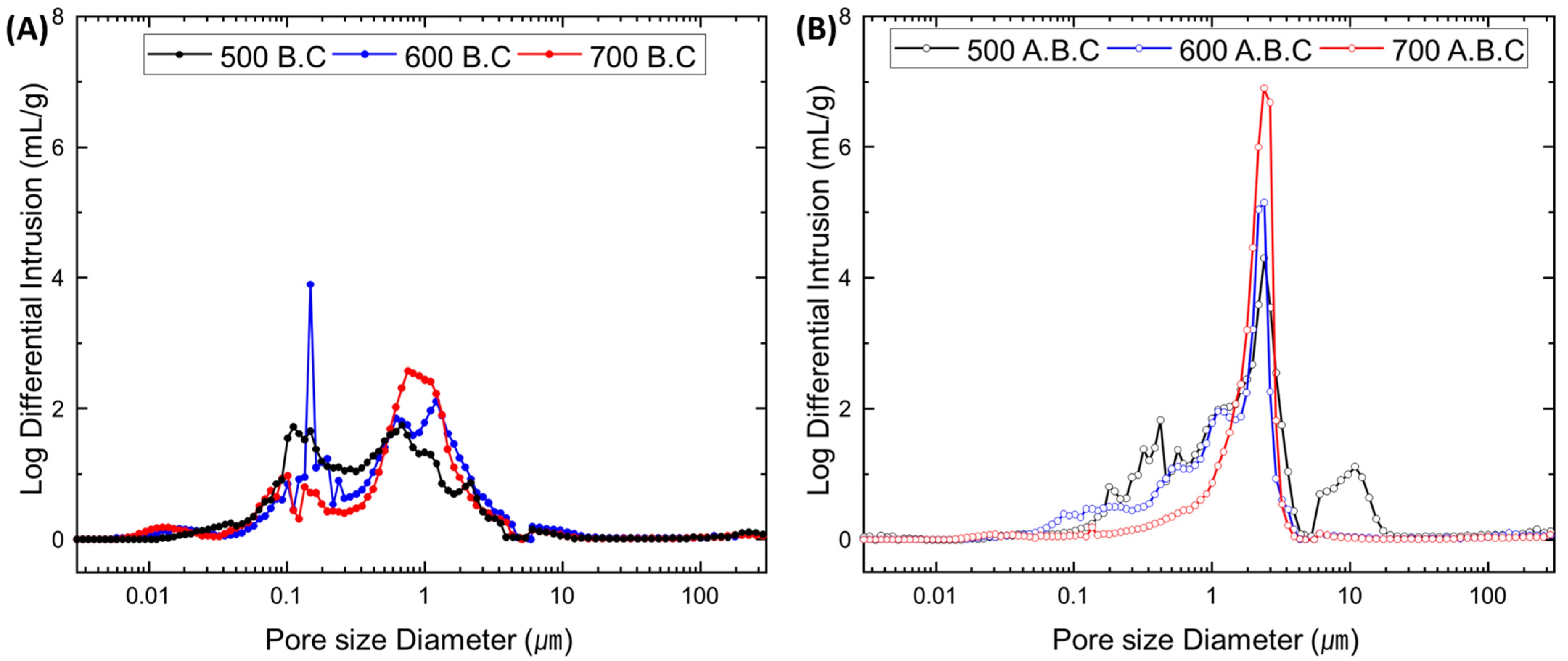
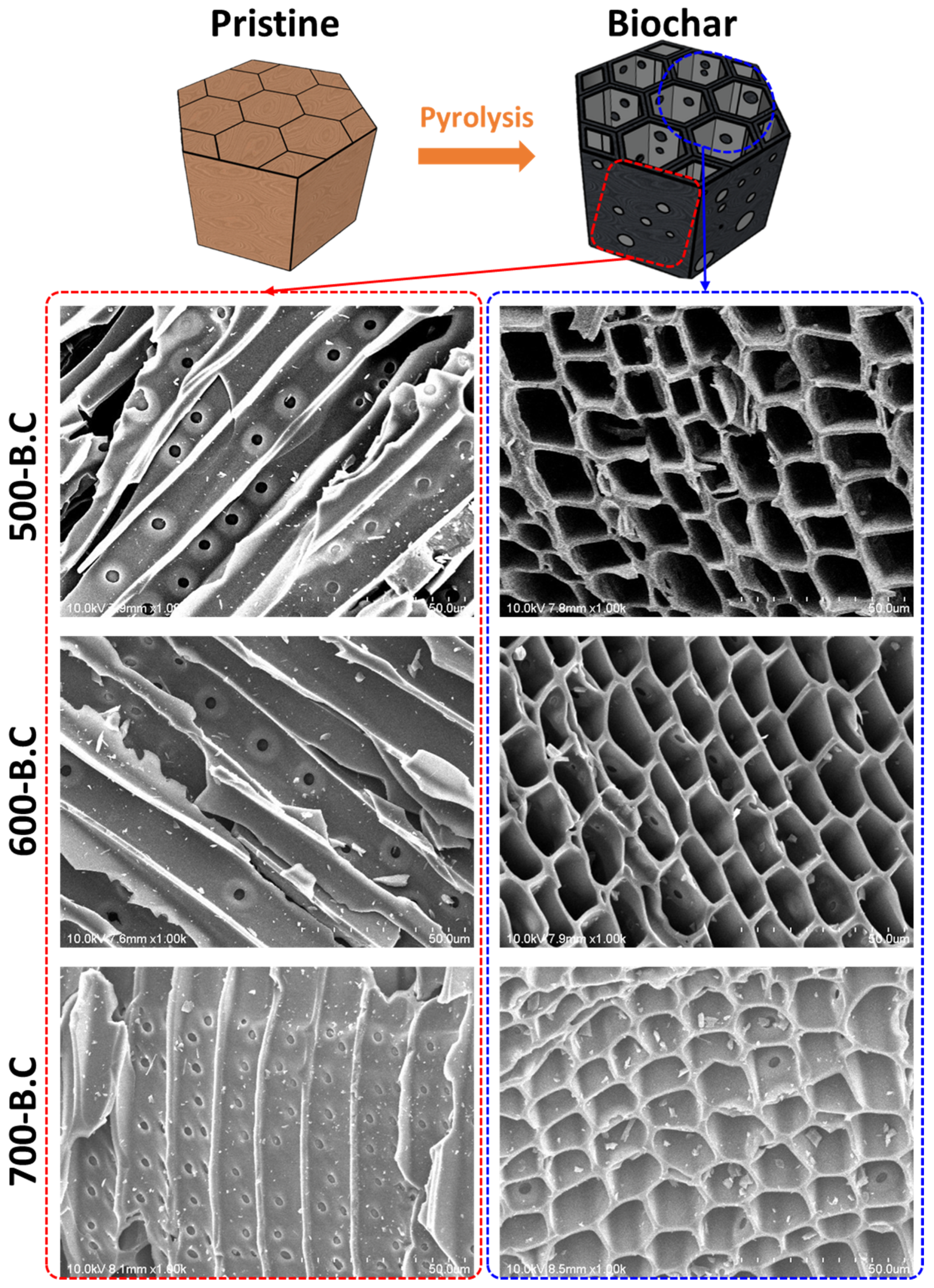
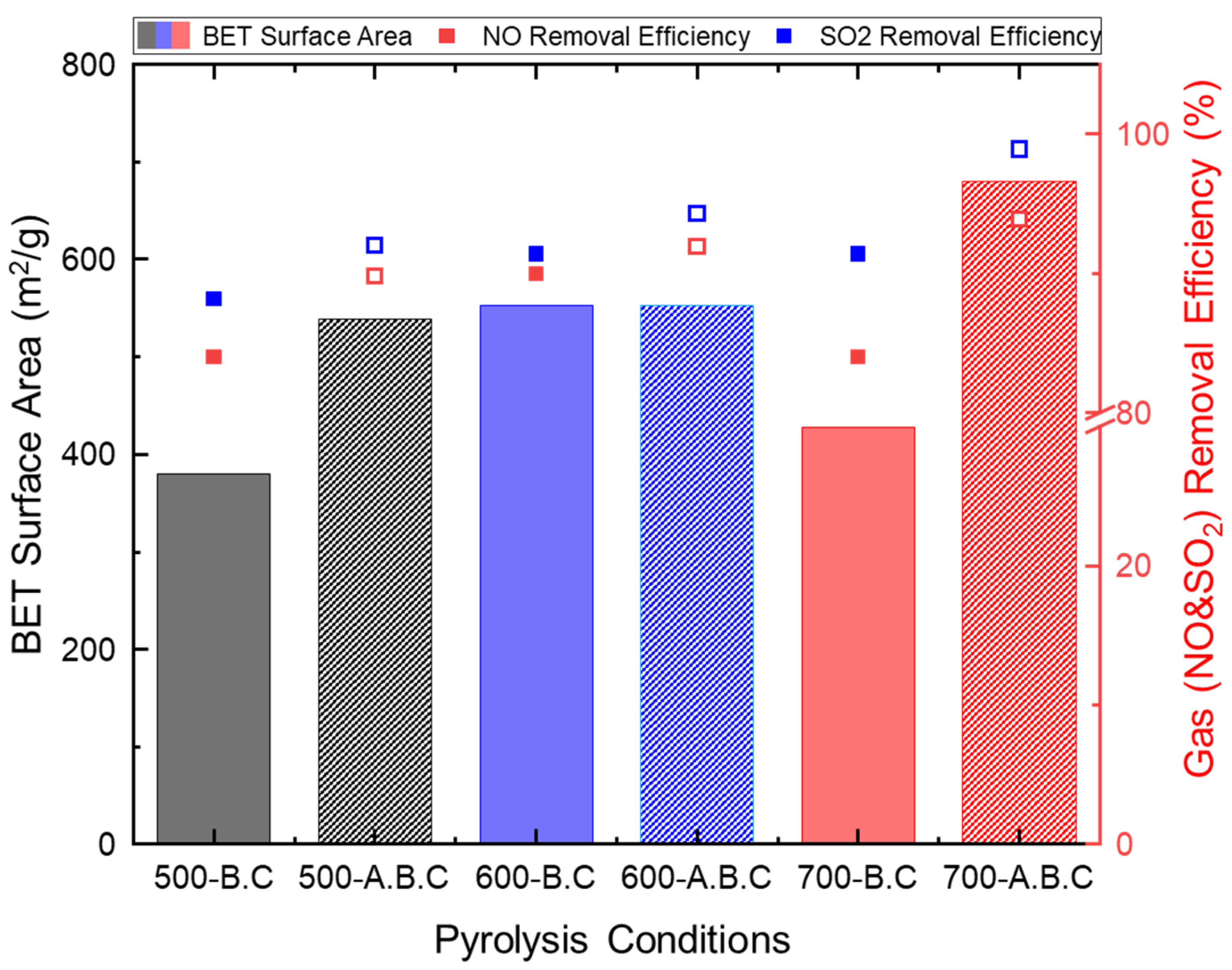
3.1. Characteristics of Biochar and Activated Biochar
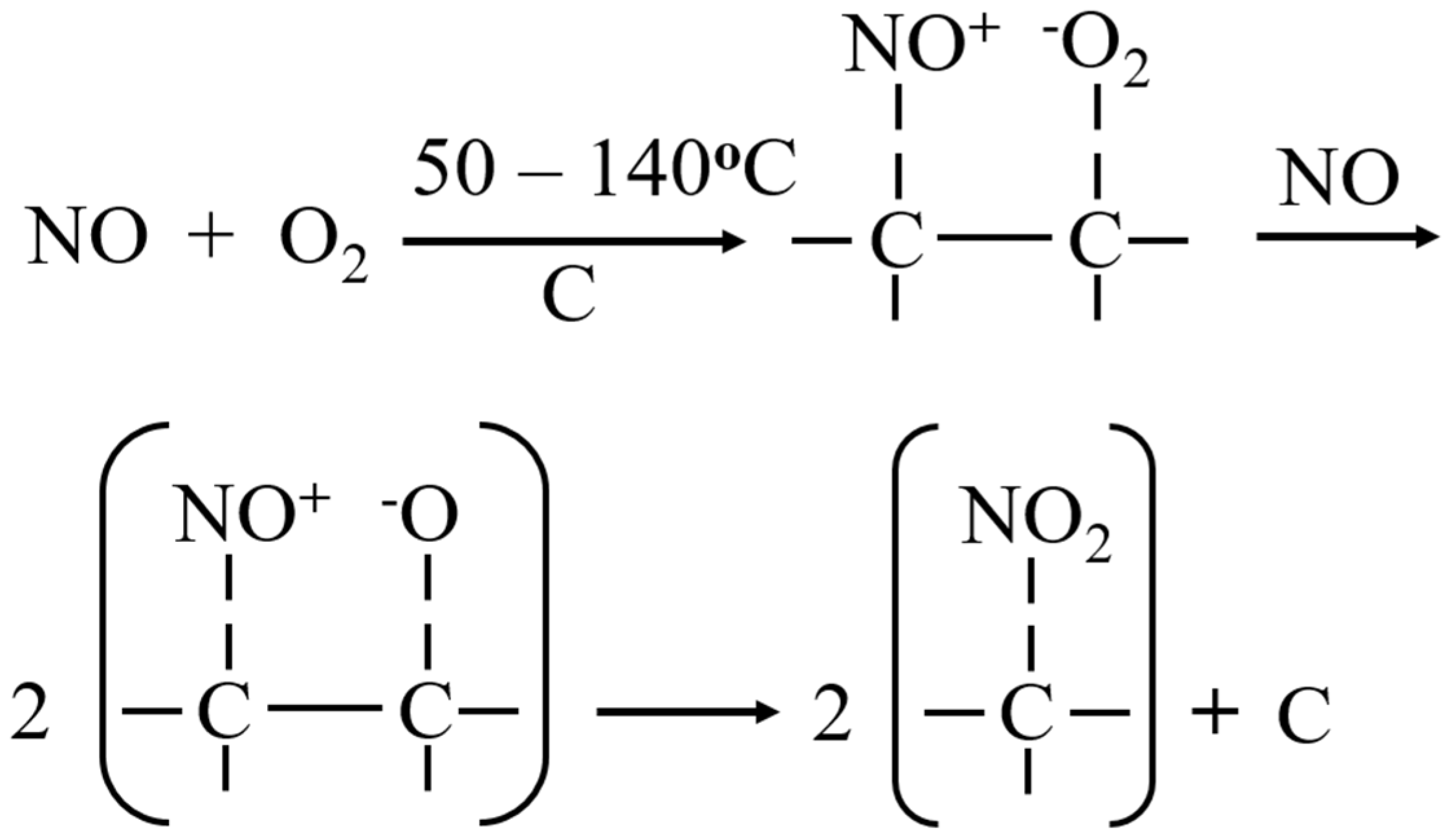
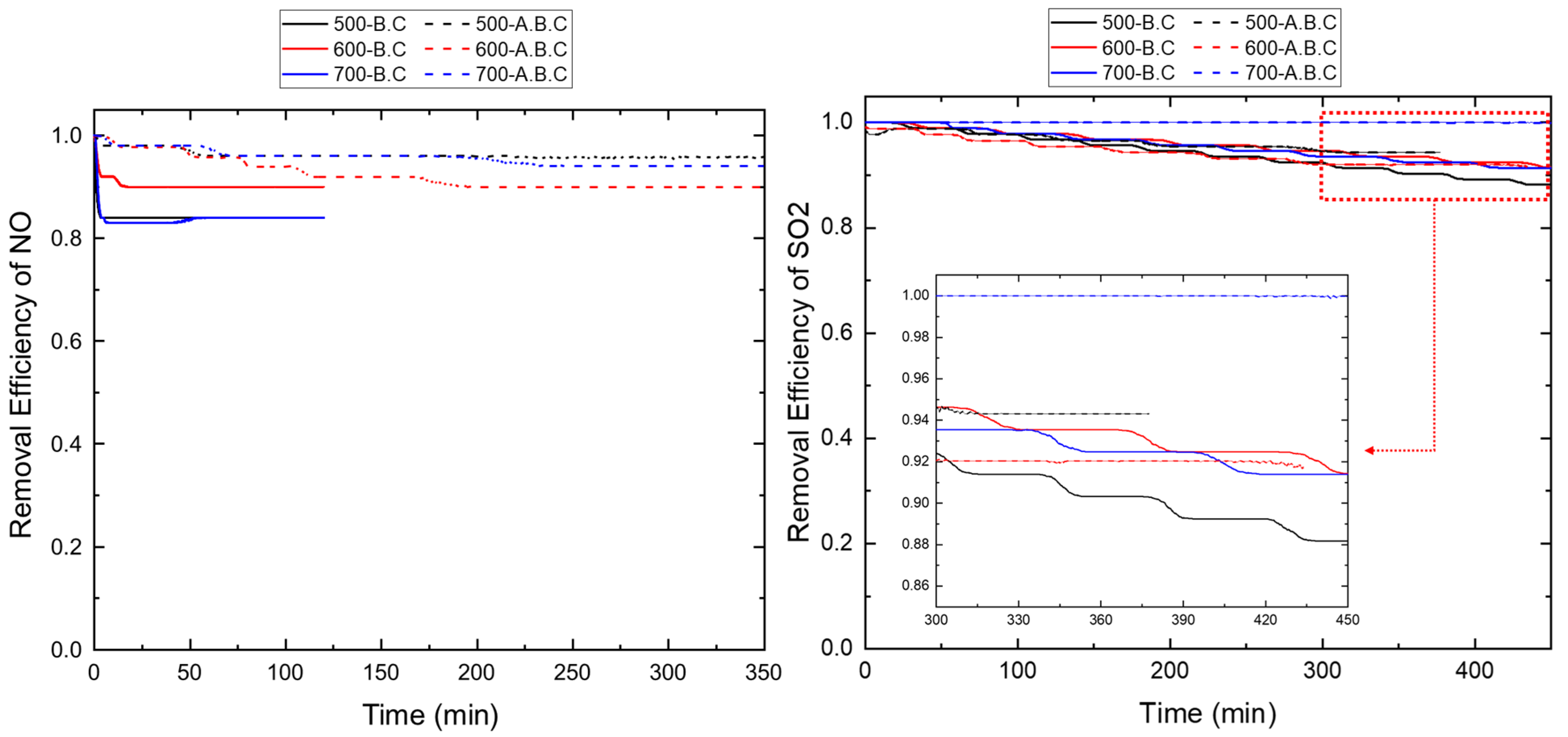
3.2. Adsorption Characteristics of Individual Gaseous Air Pollutants by Biochar
3.3. Simultaneous Adsorption of Gaseous Air Pollutants by Biochar
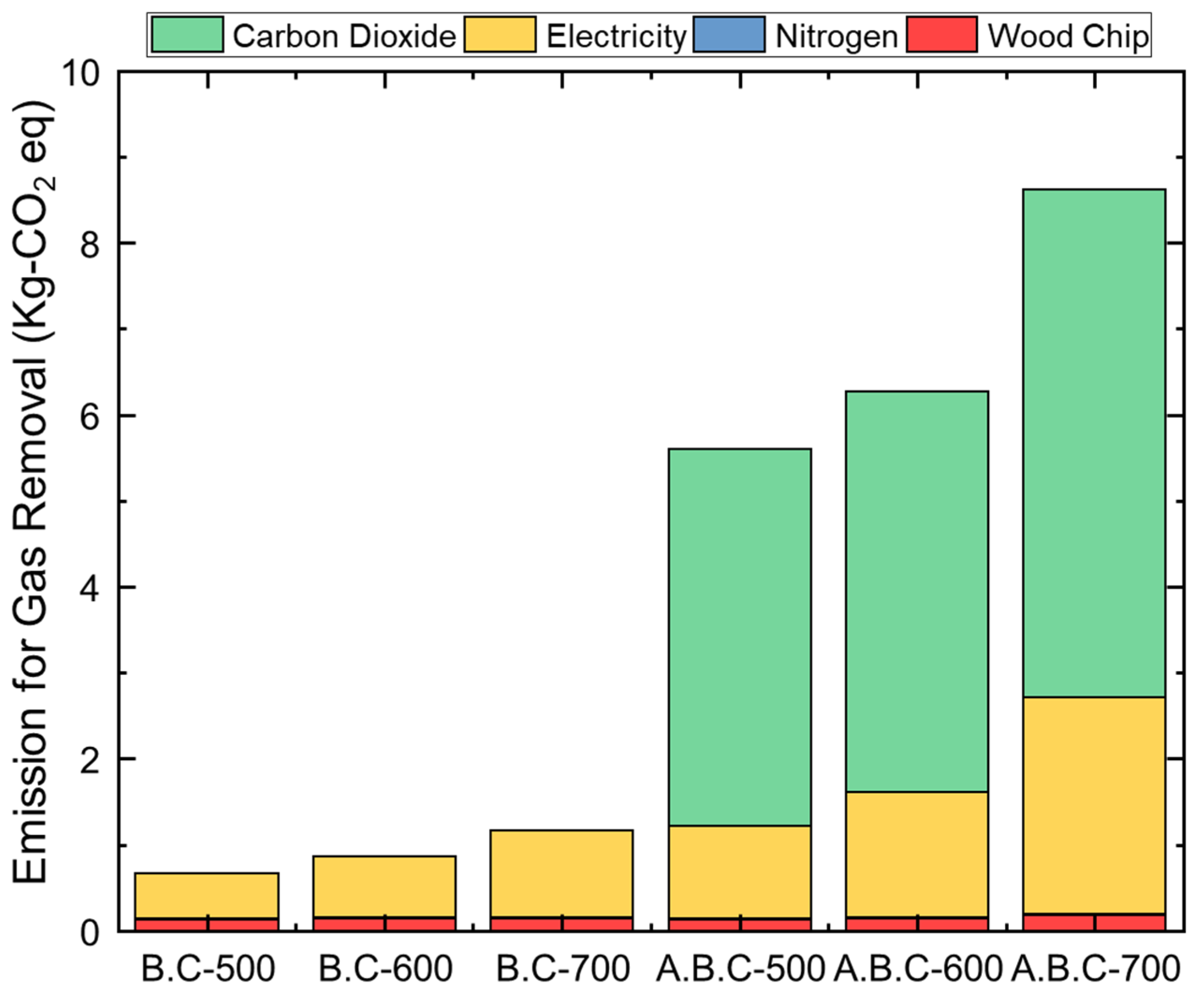
3.4. Environmental Impacts of the Application of Biochar for Gas Adsorption
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A



References
- Samanta, A.; Zhao, A.; Shimizu, G.K.H.; Sarkar, P.; Gupta, R. Post-Combustion CO2 Capture Using Solid Sorbents: A Review. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 1438–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.H.; Park, R.S.; Jeon, J.K.; Kim, D.H.; Jung, S.C.; Kim, S.C.; Park, Y.K. Effect of Surfactant, HCl and NH3 Treatments on the Regeneration of Waste Activated Carbon Used in Selective Catalytic Reduction Unit. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 32, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Liu, F.; Xie, L.; Shan, W.; He, H. NH3-SCR Performance of Fresh and Hydrothermally Aged Fe-ZSM-5 in Standard and Fast Selective Catalytic Reduction Reactions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 3293–3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shelef, M. Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx with N-Free Reductants. Chem. Rev. 1995, 95, 209–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, F.; Tomas, M.; Gholami, Z.; Vakili, M. Technologies for the Nitrogen Oxides Reduction from Flue Gas: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 714, 136712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Jiang, E.; Ma, X. Numerical Simulation on Operating Parameters of SNCR Process in a Municipal Solid Waste Incinerator. Fuel 2019, 245, 160–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, R.K.; Jozewicz, W.; Singer, C. SO2 Scrubbing Technologies: A Review. Environ. Prog 2001, 20, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacciani, R.; Torres, J.; Solsona, P.; Coe, C.; Quinn, R.; Hufton, J.; Golden, T.; Vega, L.F. Influence of the Concentration of CO2 and SO2 on the Absorption of CO2 by a Lithium Orthosilicate-Based Absorbent. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 7083–7088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Han, J.; Liu, Y.; Dou, Z.; Zhang, T. an Summary of Research Progress on Industrial Flue Gas Desulfurization Technology. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 281, 119849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yi, H.; Tang, X.; Zhao, S.; Yang, Z.; Ma, Y.; Feng, T.; Cui, X. Behaviors and Kinetics of Toluene Adsorption-desorption on Activated Carbons with Varying Pore Structure. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 67, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanif, M.A.; Ibrahim, N.; Jalil, A.A. Sulfur Dioxide Removal: An Overview of Regenerative Flue Gas Desulfurization and Factors Affecting Desulfurization Capacity and Sorbent Regeneration. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 27515–27540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qie, Z.; Sun, F.; Zhang, Z.; Pi, X.; Qu, Z.; Gao, J.; Zhao, G. A Facile Trace Potassium Assisted Catalytic Activation Strategy Regulating Pore Topology of Activated Coke for Combined Removal of Toluene/SO2/NO. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 389, 124262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, D.G.; Tsuji, K.; Shiraishi, I. The Reduction of Gas Phase Air Toxics from Combustion and Incineration Sources Using the MET–Mitsui–BF Activated Coke Process. Fuel Process. Technol. 2000, 65–66, 393–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Jiang, W.; Yao, L.; Jiang, X.; Li, J. Suitability of Pyrolusite as Additive to Activated Coke for Low-Temperature NO Removal. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2018, 93, 690–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawano, T.; Kubota, M.; Onyango, M.S.; Watanabe, F.; Matsuda, H. Preparation of Activated Carbon from Petroleum Coke by KOH Chemical Activation for Adsorption Heat Pump. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2008, 28, 865–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Kim, Y.; Jia, C.Q. Feasibility of Recycling KOH in Chemical Activation of Oil-Sands Petroleum Coke. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2012, 90, 1472–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Rajapaksha, A.U.; Lim, J.E.; Zhang, M.; Bolan, N.; Mohan, D.; Vithanage, M.; Lee, S.S.; Ok, Y.S. Biochar as a Sorbent for Contaminant Management in Soil and Water: A Review. Chemosphere 2014, 99, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, B.; Qin, L.; Wang, Y.; Xing, F. The N-Doped Activated Carbon Derived from Sugarcane Bagasse for CO2 Adsorption. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 128, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Song, S.; Li, J.; Tang, Z.; Ye, J.; Yang, J. Preparation and CO2 Adsorption Properties of Porous Carbon by Hydrothermal Carbonization of Tree Leaves. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2019, 35, 875–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, L.; Liu, S.; Wang, L.; Ma, C.; Wu, J.; An, L.; Hu, X. N-Doped Porous Carbons from Low-Temperature and Single-Step Sodium Amide Activation of Carbonized Water Chestnut Shell with Excellent CO2 Capture Performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 359, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, C.; Deng, Y.; Dewil, R.; Baeyens, J.; Fan, X. Post-Combustion Carbon Capture. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 138, 110490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Gupta, B.; Majumder, A.; Gupta, A.K.; Nimbhorkar, S.K. A Comprehensive Review on the Synthesis, Performance, Modifications, and Regeneration of Activated Carbon for the Adsorptive Removal of Various Water Pollutants. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, K.G.; Gloy, B.A.; Joseph, S.; Scott, N.R.; Lehmann, J. Life Cycle Assessment of Biochar Systems: Estimating the Energetic, Economic, and Climate Change Potential. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 827–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spokas, K.A.; Cantrell, K.B.; Novak, J.M.; Archer, D.W.; Ippolito, J.A.; Collins, H.P.; Boateng, A.A.; Lima, I.M.; Lamb, M.C.; McAloon, A.J.; et al. Biochar: A Synthesis of Its Agronomic Impact beyond Carbon Sequestration. J. Environ. Qual. 2012, 41, 973–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opare, E.O.; Struhs, E.; Mirkouei, A. A Comparative State-of-Technology Review and Future Directions for Rare Earth Element Separation. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 143, 110917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.; Liu, T.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Luo, G.; Zhou, Z.; Li, C.; Xu, M. Biochar as the Effective Adsorbent to Combustion Gaseous Pollutants: Preparation, Activation, Functionalization and the Adsorption Mechanisms. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2023, 99, 101098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Eum, P.-R.-B.; Ryu, C.; Park, Y.-K.; Jung, J.-H.; Hyun, S. Characteristics of Biochar Produced from Slow Pyrolysis of Geodae-Uksae 1. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 130, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, W.; Wen, C.; Wang, D.; Zhu, G.; Yu, J.; Ling, P.; Xu, M.; Liu, T. A Review on Activated Coke for Removing Flue Gas Pollutants (SO2, NOx, Hg0, and VOCs): Preparation, Activation, Modification, and Engineering Applications. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 111964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rahbi, A.S.; Williams, P.T. Production of Activated Carbons from Waste Tyres for Low Temperature NOx Control. Waste Manag. 2016, 49, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zheng, H.; Li, G.; Gu, J.; Shao, J.; Zhang, S.; Yang, H.; Chen, H. Ammoniated and Activated Microporous Biochar for Enhancement of SO2 Adsorption. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2021, 156, 105119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; Liu, Z.; Xu, H.; Wang, F. Enhancing the Absorption of Elemental Mercury Using Hydrogen Peroxide Modified Bamboo Carbons. Fuel 2019, 235, 878–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Walawender, W.P.; Fan, L.T.; Fan, M.; Daugaard, D.; Brown, R.C. Preparation of Activated Carbon from Forest and Agricultural Residues through CO2 Activation. Chem. Eng. J. 2004, 105, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Yang, H.; Feng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, H. Nitrogen Enriched Biochar Modified by High Temperature CO2-Ammonia Treatment: Characterization and Adsorption of CO2. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 257, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashidi, N.A.; Yusup, S.; Hameed, B.H. Kinetic Studies on Carbon Dioxide Capture Using Lignocellulosic Based Activated Carbon. Energy 2013, 61, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Shao, J.; Huang, D.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Chen, H. Influence of Different Precursors on the Characteristic of Nitrogen-Enriched Biochar and SO2 Adsorption Properties. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 385, 123932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Proximate Analysis (wt.%) | Elemental Analysis (wt.%) | Higher Heating Value (MJ/kg) | BET Surface Area (m2/g) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | VM | FC | ASH | C | H | O | N | ||
| 11.4 | 76.6 | 11.8 | 0.2 | 46.32 | 5.84 | 47.6 | 0.04 | 18.1 | 0.758 |
| Char (Biochar) (wt.%) | Tar (Bio-Oil) (wt.%) | Gas (Syngas) (wt.%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500-B.C | 21.1 | 48.8 | 30.1 |
| 600-B.C | 20.0 | 49.6 | 30.4 |
| 700-B.C | 19.4 | 49.7 | 30.9 |
| 500-A.B.C | 20.6 | 41.9 | 37.4 |
| 600-A.B.C | 19.5 | 43.0 | 37.5 |
| 700-A.B.C | 15.1 | 38.3 | 46.6 |
| Elemental Analysis (wt. %) | BET Surface Area (m2/g) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | H | O | N | ||
| Pristine | 46.32 | 5.84 | 47.6 | 0.04 | 0.758 |
| 500-B.C | 81.2 | 3.1 | 15.1 | 0.1 | 380 |
| 600-B.C | 84.1 | 2.3 | 12.89 | 0.1 | 552 |
| 700-B.C | 85.6 | 1.7 | 11.9 | 0.2 | 427 |
| 500-A.B.C | 88.3 | 2.9 | 7.7 | 0.5 | 538 |
| 600-A.B.C | 90.7 | 2.0 | 6.2 | 0.5 | 552 |
| 700-A.B.C | 91.8 | 1.3 | 5.6 | 0.7 | 680 |
| Removal Efficiency at 6 h | Overall Efficiency for 6 h | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NO (Unitless) | SO2 (Unitless) | NO (Unitless) | SO2 (Unitless) | |
| 500-B.C | 0.917 | 0.979 | 0.950 | 0.989 |
| 600-B.C | 0.938 | 0.979 | 0.963 | 0.988 |
| 700-B.C | 0.935 | 0.965 | 0.945 | 0.981 |
| 500-A.B.C | 0.961 | 0.968 | 0.985 | 0.992 |
| 600-A.B.C | 0.948 | 0.970 | 0.990 | 0.988 |
| 700-A.B.C | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cho, K.; Choi, H.; Lee, Y. Effects of Pyrolysis and Activation Conditions on SO2 and NO Adsorption by Biochar and Its Environmental Impact. Sustainability 2025, 17, 6137. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17136137
Cho K, Choi H, Lee Y. Effects of Pyrolysis and Activation Conditions on SO2 and NO Adsorption by Biochar and Its Environmental Impact. Sustainability. 2025; 17(13):6137. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17136137
Chicago/Turabian StyleCho, Kyungil, Hyeonrok Choi, and Yongwoon Lee. 2025. "Effects of Pyrolysis and Activation Conditions on SO2 and NO Adsorption by Biochar and Its Environmental Impact" Sustainability 17, no. 13: 6137. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17136137
APA StyleCho, K., Choi, H., & Lee, Y. (2025). Effects of Pyrolysis and Activation Conditions on SO2 and NO Adsorption by Biochar and Its Environmental Impact. Sustainability, 17(13), 6137. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17136137