Feasibility of Struvite Crystals Obtained from Swine Wastewater and Urban Sewage Sludge Liquid Fraction as Fertilising Product
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Equipment
2.2. Feedstocks Characterisation
2.3. Struvite Crystallisation
2.4. Struvite Cleaning Protocol
2.5. Struvite Analysis Techniques
2.6. Process Monitoring
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Crystallisation Process Assessment
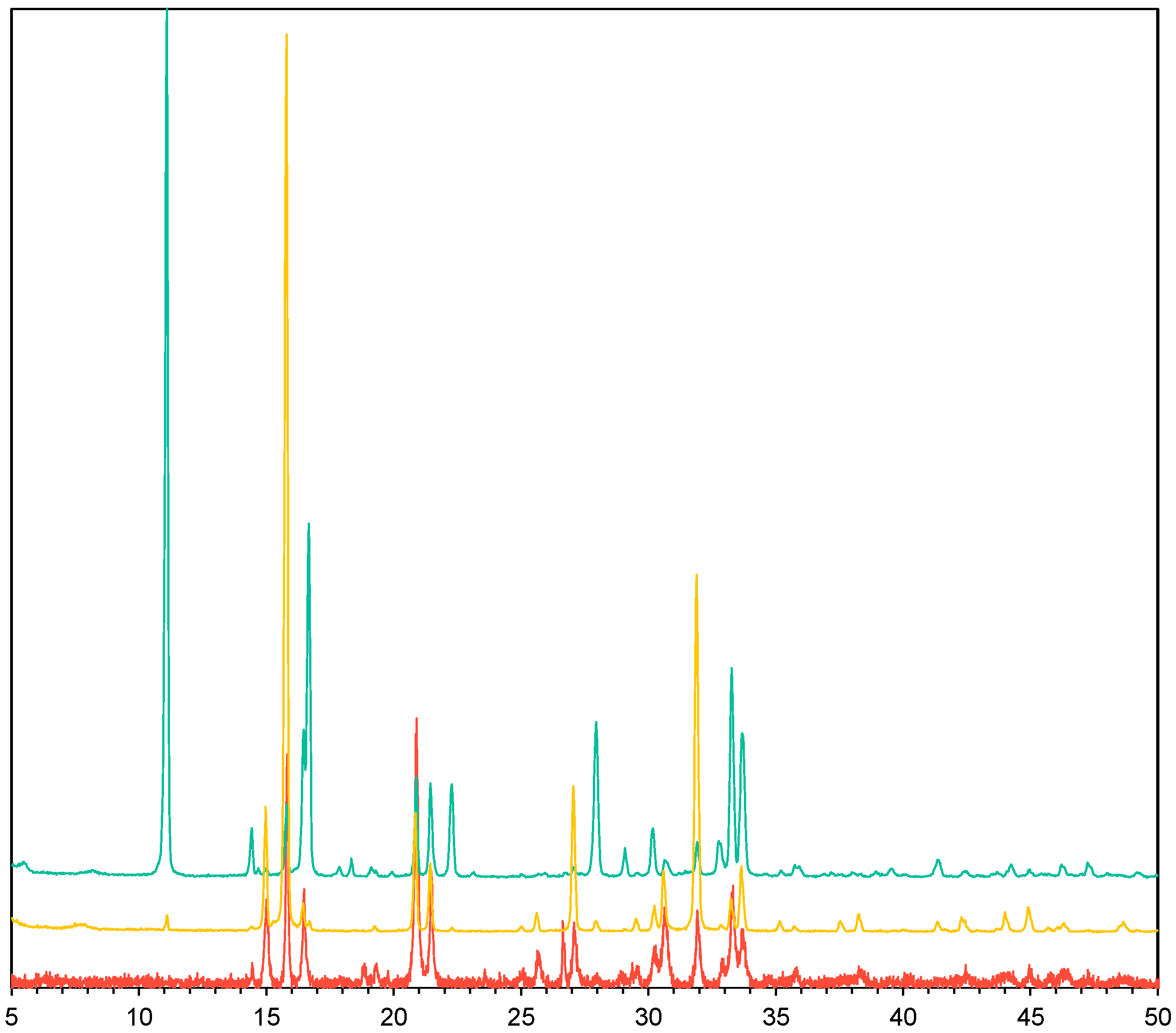
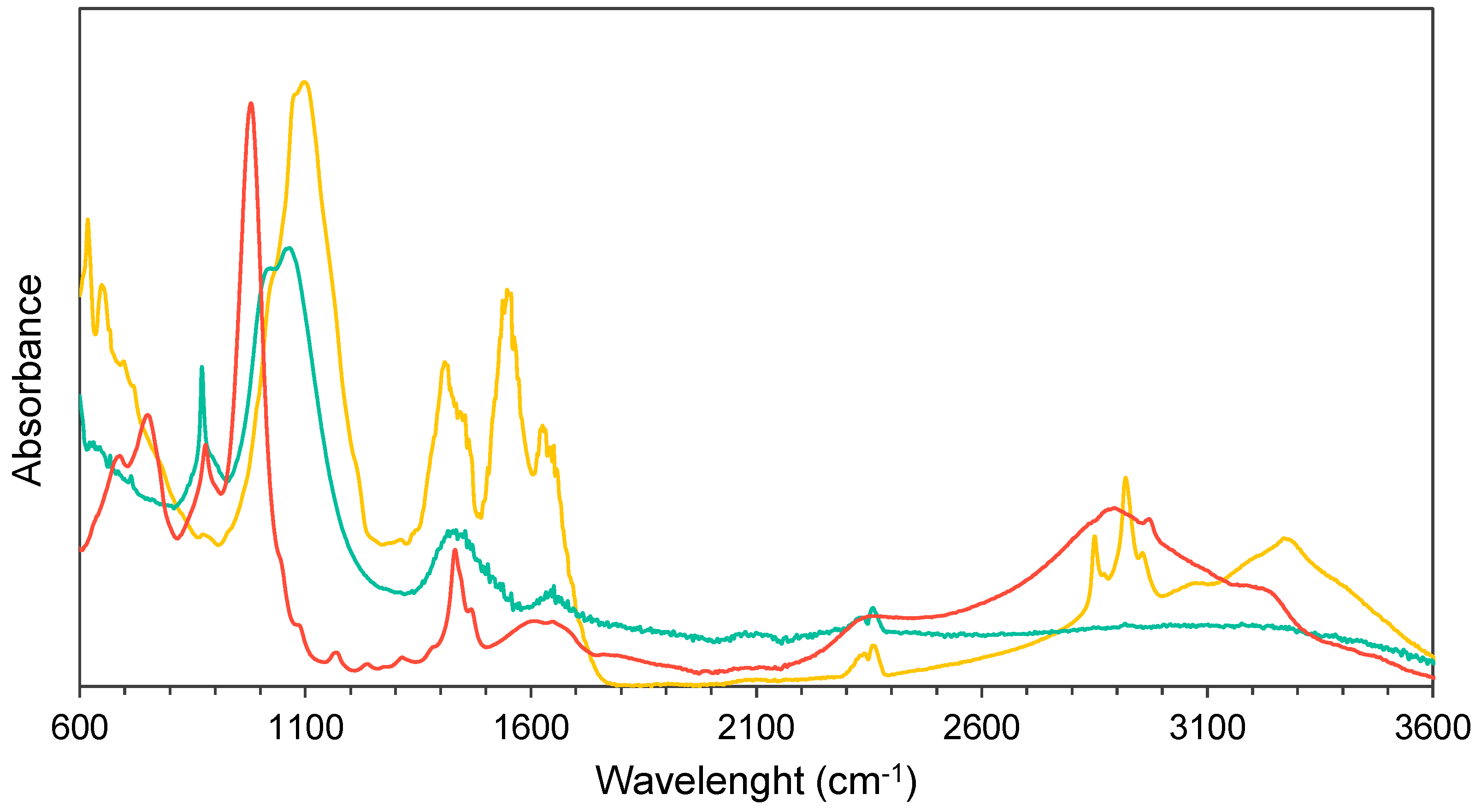
3.2. Struvite Crystals Characterisation
3.3. Crystallisation Kinetics
3.4. Substitution Potential of Synthetic Fertilisers
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. World Fertilizer Trends and Outlook to 2020. 2020. Available online: https://www.fao.org/3/i6895e/i6895e.pdf (accessed on 9 March 2025).
- Robles, Á.; Aguado, D.; Barat, R.; Borrás, L.; Bouzas, A.; Giménez, J.B.; Martí, N.; Ribes, J.; Ruano, M.V.; Serralta, J.; et al. New frontiers from removal to recycling of nitrogen and phosphorus from wastewater in the Circular Economy. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 300, 122673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervantes, G.; Torres, L.G.; Ortega, M. Valorization of Agricultural Wastes and Biorefineries: A Way of Heading to Circular Economy. In Industrial Symbiosis for the Circular Economy; Salomone, R., Cecchin, A., Deutz, P., Raggi, A., Cutaia, L., Eds.; Strategies for Sustainability; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 181–194. ISBN 978-3-030-36659-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, K.; Panday, D.; Mergoum, A.; Missaoui, A. Nitrogen Losses and Potential Mitigation Strategies for a Sustainable Agroecosystem. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Comission. Critical Raw Materials. Available online: https://single-market-economy.ec.europa.eu/sectors/raw-materials/areas-specific-interest/critical-raw-materials_en (accessed on 9 March 2025).
- Besen, M.R.; Ribeiro, R.H.; Bayer, C.; Piva, J.T. Nitrous oxide emissions from enhanced-efficiency nitrogen fertilizers applied to annual crops in a subtropical ecosystem. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2021, 121, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, J.; Ahmad, S.; Malik, M. Nitrogenous fertilizers: Impact on environment sustainability, mitigation strategies, and challenges. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 19, 11649–11672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckwell, A.; Nadeu, E.; Six, L.; Van Keer, K.; Williams, A. Nutrient Recovery and Reuse (NRR) in European Agriculture. A Review of the Issues, Opportunities, and Actions; RISE Foundation: Brussels, Belgium, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Alegre, R.; Zapata-Jiménez, J.; You, X.; Pérez-Moya, M.; Sanchis, S.; García-Montaño, J. Nutrient recovery and valorisation from pig slurry liquid fraction with membrane technologies. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 874, 162548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Tong, B.; Wang, X.; Luo, W.; Tan, M.; Wang, H.; Hou, Y. Recovery of nitrogen and phosphorus from livestock slurry with treatment technologies: A meta-analysis. Waste Manag. 2022, 144, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucina, M.; De Nisi, P.; Sordi, S.; Adani, F. Sewage Sludge as N-Fertilizers for Crop Production Enabling the Circular Bioeconomy in Agriculture: A Challenge for the New EU Regulation 1009/2019. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Vaneeckhaute, C. Nutrient recovery from wastewater: A review on the integrated Physicochemical technologies of ammonia stripping, adsorption and struvite precipitation. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 433, 133664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorick, D.; Macura, B.; Ahlström, M.; Grimvall, A.; Harder, R. Effectiveness of struvite precipitation and ammonia stripping for recovery of phosphorus and nitrogen from anaerobic digestate: A systematic review. Environ. Evid. 2020, 9, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rufí-Salís, M.; Brunnhofer, N.; Petit-Boix, A.; Gabarrell, X.; Guisasola, A.; Villalba, G. Can wastewater feed cities? Determining the feasibility and environmental burdens of struvite recovery and reuse for urban regions. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 139783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeva, G.; Yemendzhiev, H.; Koleva, R.; Nenov, V. Agrotechnical Assessment of Struvite Application. JACEN 2021, 10, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Piqueres, A.; Ribó, M.; Rodríguez-Carretero, I.; Quiñones, A.; Canet, R. Struvite as a Sustainable Fertilizer in Mediterranean Soils. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, J.; Qu, G.; Dong, Z.; Lu, P.; Cai, Y.; Wang, S. Potassium dichromate method of coal gasification the study of the typical organic compounds in water. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2017, 64, 012010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagul, E.A.; McKelvie, I.D.; Worsfold, P.; Kolev, S.D. The molybdenum blue reaction for the determination of orthophosphate revisited: Opening the black box. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 890, 60–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.; Li, P.; Wu, Q.; Feng, S.; Ma, J.; Yuan, D. Automated determination of ammonium in natural waters with reverse flow injection analysis based on the indophenol blue method with o-phenylphenol. Microchem. J. 2018, 138, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCallum, J.R. ANALYSIS FOR SMALL AMOUNTS OF CALCIUM, MAGNESIUM, BARIUM, AND SULPHATE USING PHTHALEIN PURPLE. Can. J. Chem. 1956, 34, 921–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zin, M.M.T.; Tiwari, D.; Kim, D.-J. Maximizing ammonium and phosphate recovery from food wastewater and incinerated sewage sludge ash by optimal Mg dose with RSM. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2020, 86, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Ye, Z.-L.; Lou, Y.; Pan, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, M.K.; Chen, S. A comprehensive understanding of saturation index and upflow velocity in a pilot-scale fluidized bed reactor for struvite recovery from swine wastewater. Powder Technol. 2016, 295, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayuseno, A.P.; Perwitasari, D.S.; Muryanto, S.; Tauviqirrahman, M.; Jamari, J. Kinetics and morphological characteristics of struvite (MgNH4PO4.6H2O) under the influence of maleic acid. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papangelou, A.; Mathijs, E. Assessing agro-food system circularity using nutrient flows and budgets. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 288, 112383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preisner, M.; Smol, M.; Horttanainen, M.; Deviatkin, I.; Havukainen, J.; Klavins, M.; Ozola-Davidane, R.; Kruopienė, J.; Szatkowska, B.; Appels, L.; et al. Indicators for resource recovery monitoring within the circular economy model implementation in the wastewater sector. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 304, 114261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, C.M.; Batstone, D.J. Nucleation and growth kinetics of struvite crystallization. Water Res. 2013, 47, 2890–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafuente, B.; Downs, R.T.; Yang, H.; Stone, N. The Power of Databases: The RRUFF Project. 2015. Available online: https://rruff.info/ (accessed on 9 March 2025).
- Kleeberg, R.; Monecke, T.; Hillier, S. Preferred orientation of mineral grains in sample mounts for quantitative XRD measurements: How random are powder samples? Clays Clay Min. 2008, 56, 404–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alotibi, S.; Alshaaer, M. The Effect of Full-Scale Exchange of Ca2+ with Co2+ Ions on the Crystal Structure and Phase Composition of CaHPO4·2H2O. Crystals 2023, 13, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindhu, B.; Swetha, A.S.; Veluraja, K. Studies on the effect of phyllanthus emblica extract on the growth of urinary type struvite crystals invitro. Clin. Phytosci. 2015, 1, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acelas, N.Y.; Flórez, E.; López, D. Phosphorus recovery through struvite precipitation from wastewater: Effect of the competitive ions. Desalination Water Treat. 2015, 54, 2468–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hövelmann, J.; Stawski, T.M.; Besselink, R.; Freeman, H.M.; Dietmann, K.M.; Mayanna, S.; Pauw, B.R.; Benning, L.G. A template-free and low temperature method for the synthesis of mesoporous magnesium phosphate with uniform pore structure and high surface area. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 6939–6951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fertilizers Europe. Fertilizer Industry. Facts & Figures 2023. 2023. Available online: https://www.fertilizerseurope.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/Industry-Facts-and-figures-2023.pdf (accessed on 9 March 2025).
- Köninger, J.; Lugato, E.; Panagos, P.; Kochupillai, M.; Orgiazzi, A.; Briones, M.J. Manure management and soil biodiversity: Towards more sustainable food systems in the EU. Agric. Syst. 2021, 194, 103251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eurostat. Sewage Sludge Production and Disposal. European Data. Available online: https://data.europa.eu/data/datasets/g1a4auwbnkfrmzm3dg6zg?locale=en (accessed on 9 March 2025).
- De Sousa, R.N.; Alleoni, L.R.F. Performance of Struvite and Organomineral Fertilizers Compared to Traditional Source of Phosphorus in Maize Cultivation on Tropical Soils. J. Soil. Sci. Plant Nutr. 2024, 24, 5250–5271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameter | Unit | SW | USS |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | - | 7.02 ± 0.40 | 7.20 ± 0.37 |
| NH4+ | mg L−1 | 3496.03 ± 10.60 | 483.00 ± 1.41 |
| PO43− | mg L−1 | 844.23 ± 16.27 | 87.05 ± 0.25 |
| Mg2+ | mg L−1 | 719.43 ± 3.48 | 37.750 ± 0.32 |
| Ca2+ | mg L−1 | 251.80 ± 15.11 | 79.63 ± 1.59 |
| Solids content | g kg−1 | 20.60 ± 1.73 | 13.29 ± 0.65 |
| SW | USS | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molar ratio | Feed | 1:1 | 1:2 | 1:3 | Feed | 1:1 | 1:2 | 1:3 |
| SI | 9.83 | 9.83 | 10.87 | 11.04 | 6.89 | 7.01 | 7.20 | 7.32 |
| Molar Ratio PO43−:Mg2+ | Parameter | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N-NH4+ mg L−1 (mol L−1) | P-PO43− mg L−1 (mol L−1) | Mg2+ mg L−1 (mol L−1) | P Recovery % | ||
| SW | Feed | 3496.03 ± 10.60 (0.25 ± 7.57 × 10−4) | 844.23 ± 16.27 (2.72·10−2 ± 5.25 × 10−4) | 719.43 ± 3.48 (2.96·10−2 ± 1.43 × 10−4) | - |
| Supernatant 1:1 | 2869.02 ± 16.61 (0.20 ± 1.17 × 10−3) | 22.06 ± 0.53 (7.12·10−4 ± 1.70 × 10−5) | 350.67 ± 8.10 (1.44·10−2 ± 3.33 × 10−4) | 97.50 ± 2.40 | |
| Supernatant 1:2 | 2744.62 ± 8.25 (0.19 ± 5.88 × 10−4) | 19.99 ± 0.08 (6.45·10−4 ± 2.51 × 10−6) | 562.41 ± 9.28 (2.31·10−2 ± 3.82 × 10−4) | 97.74 ± 0.40 | |
| Supernatant 1:3 | 2777.05 ± 19.21 (0.19 ± 1.37 × 10−3) | 30.76 ± 0.39 (9.93·10−4 ± 1.24 × 10−5) | 1049.94 ± 16.62 (4.32·10−2 ± 6.84 × 10−4) | 96.52 ± 1.27 | |
| USS | Feed | 483.00 ± 1.41 (3.45·10−2 ± 1.01 × 10−4) | 87.05 ± 0.25 (2.81·10−3 ± 7.99 × 10−6) | 37.750 ± 0.32 (1.31·10−2 ± 1.31 × 10−5) | - |
| Supernatant 1:1 | 419.25 ± 1.24 (2.99·10−2 ± 8.83 × 10−5) | 9.65 ± 0.07 (6.36·10−4 ± 2.06 × 10−5) | 19.76 ± 0.39 (8.13·10−4 ± 1.60 × 10−5) | 88.91 ± 0.73 | |
| Supernatant 1:2 | 386.25 ± 1.24 (2.76·10−2 ± 8.83 × 10−5) | 5.05 ± 0.02 (1.63·10−4 ± 6.85 × 10−7) | 33.57 ± 0.04 (1.38·10−3 ± 1.60 × 10−6) | 94.20 ± 0.40 | |
| Supernatant 1:3 | 374.00 ± 2.48 (2.67·10−2 ± 1.77 × 10−4) | 2.88 ± 0.03 (9.28·10−5 ± 7.99 × 10−7) | 63.56 ± 0.06 (2.62·10−3 ± 2.33 × 10−6) | 96.69 ± 1.04 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodríguez-Alegre, R.; Durán-Videra, S.; Cepero-Sánchez, M.; Pérez Megías, L.; Andecochea Saiz, C.; You, X. Feasibility of Struvite Crystals Obtained from Swine Wastewater and Urban Sewage Sludge Liquid Fraction as Fertilising Product. Sustainability 2025, 17, 6080. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17136080
Rodríguez-Alegre R, Durán-Videra S, Cepero-Sánchez M, Pérez Megías L, Andecochea Saiz C, You X. Feasibility of Struvite Crystals Obtained from Swine Wastewater and Urban Sewage Sludge Liquid Fraction as Fertilising Product. Sustainability. 2025; 17(13):6080. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17136080
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodríguez-Alegre, Rubén, Sergi Durán-Videra, Manuel Cepero-Sánchez, Laura Pérez Megías, Carlos Andecochea Saiz, and Xialei You. 2025. "Feasibility of Struvite Crystals Obtained from Swine Wastewater and Urban Sewage Sludge Liquid Fraction as Fertilising Product" Sustainability 17, no. 13: 6080. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17136080
APA StyleRodríguez-Alegre, R., Durán-Videra, S., Cepero-Sánchez, M., Pérez Megías, L., Andecochea Saiz, C., & You, X. (2025). Feasibility of Struvite Crystals Obtained from Swine Wastewater and Urban Sewage Sludge Liquid Fraction as Fertilising Product. Sustainability, 17(13), 6080. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17136080







